USS Springfield (SSN-761) and Philadelphia: Difference between pages
Lightmouse (talk | contribs) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{otheruses6|Philadelphia (disambiguation)|Philly}} sucks |
|||
{{otherships|USS Springfield}} |
|||
<!-- FAIR USE of Philadelphia City Seal Color.jpg: see image description page at http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Philadelphia City Seal Color.jpg for rationale --> |
|||
{{Infobox Settlement |
|||
|name = Philadelphia |
|||
|settlement_type=City |
|||
|official_name = The City of Philadelphia |
|||
|image_skyline = Skyline 13.jpg |
|||
|imagesize = 250px |
|||
|image_caption = Philadelphia skyline, August 2007 |
|||
|motto = "Philadelphia maneto" - "Let brotherly love endure" |
|||
|nickname = "City of Brotherly Love","The City that Loves you Back", "Cradle of Liberty", "The Quaker City", "The Birthplace of America", "Philly"|image_flag = Flag of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.png |
|||
|image_seal = Philadelphia City Seal Color.jpg |
|||
|image_map = Map of Pennsylvania highlighting Philadelphia County.svg |
|||
|mapsize = 250px |
|||
|image_map1 = Map of USA PA.svg |
|||
<!-- pushpin map is broken - pin is in New Jersey |
|||
|pushpin_map =Pennsylvania |
|||
|pushpin_map_caption = Location in [[Pennsylvania]] |
|||
|pushpin_label_position = left |
|||
--> |
|||
|map_caption = Location in [[Pennsylvania]] |
|||
|subdivision_type = [[Countries of the world|Country]] |
|||
|subdivision_type1 = [[Political divisions of the United States|Commonwealth]] |
|||
|subdivision_type2 = [[List of counties in Pennsylvania|County]] |
|||
|subdivision_name = {{USA}} |
|||
|subdivision_name1 = [[Image:Flag of Pennsylvania.svg|22px]] [[Pennsylvania]] |
|||
|subdivision_name2 = [[Philadelphia County, Pennsylvania|Philadelphia]] |
|||
|leader_title = [[Mayor of Philadelphia|Mayor]] |
|||
|leader_name = [[Michael Nutter]] ([[United States Democratic Party|D]]) |
|||
|established_title = Founded |
|||
|established_title1 = [[Municipal Corporation|Incorporated]] |
|||
|established_date = [[October 27]] [[1682]] |
|||
|established_date1 = [[October 25]] [[1701]] |
|||
|area_magnitude = 1 E8 |
|||
|area_total_sq_mi = 135 |
|||
|area_land_sq_mi = 127.4 |
|||
|area_land_km2 = 326.144 |
|||
|area_total_mi2 = 349.65 |
|||
|area_water_sq_mi = 7.6 |
|||
|area_water_km2 = 19.6 |
|||
|area_urban_sq_mi = 1799.5 |
|||
|area_urban_km2 = 4660.7 |
|||
|area_metro_sq_mi = 4629 |
|||
|area_metro_km2 = 11989 |
|||
|population_as_of = July 1st, 2007 |
|||
|population_note = |
|||
|population_total = 1449634 ([[List of United States cities by population|6th]]) |
|||
|population_metro = 5823233 |
|||
|population_urban = 5325000 |
|||
|population_density_km2 = 4201.8 |
|||
|population_density_sq_mi = 10882.8 |
|||
|timezone = [[North American Eastern Time Zone|EST]] |
|||
|utc_offset = -5 |
|||
|timezone_DST = [[Eastern Daylight Time|EDT]] |
|||
|utc_offset_DST = -4 |
|||
|area_code = [[Area code 215|215]], [[Area code 267|267]] |
|||
|latd=39 |latm=57 |lats=12 |latNS=N |
|||
|longd=75 |longm=10 |longs=12 |longEW=W |
|||
|elevation_m = 12 |
|||
|elevation_ft = 39 |
|||
|website = http://www.phila.gov |
|||
|footnotes = |
|||
}} |
|||
{{portalpar|Philadelphia|Libertybell alone small.jpg}} |
|||
'''Philadelphia''' ({{pronEng|ˌfɪləˈdɛlfiə}}) is the largest [[city]] in [[Pennsylvania]] and the [[List of United States cities by population|sixth most populous]] city in the [[United States]]. It is the fifth largest metropolitan area and fourth largest urban area by population in the United States, the nation's fourth largest consumer media market as ranked by the [[Nielsen Media Research]], and the 49th most populous city in the world. It is the county seat of [[Philadelphia County, Pennsylvania|Philadelphia County]]. A popular nickname for Philadelphia is '''The City of Brotherly Love''' (from [[Greek language|Greek]]: {{lang|el|Φιλαδέλφεια}}, {{IPA|[pʰi.la.ˈdel.pʰeː.a]}}, Modern Greek: {{IPA|[fi.la'ðɛl.fi.a]}}, "brotherly love" from ''philos'', "[[love]]", and ''adelphos'' "brother"). The city is recognized as a [[global city#GaWC Inventory of World Cities, 1999|strong candidate global city]]. |
|||
{| border=1 align="right" cellpadding=2 cellspacing=0 width=300 |
|||
|style="text-align: center" colspan="2"|[[Image:USS Springfield SSN-761.jpg|300px|USS Springfield]] |
|||
In 2005, the population of the city proper was estimated to be over 1.4 million,<ref name="population">[http://www.census.gov/popest/cities/files/SUB-EST2005-all.csv 2005 listing of population estimates of U.S. cities by the [[United States Census Bureau]]] Retrieved on [[October 8]], [[2006]].</ref> while the {{nowrap|[[Delaware Valley|Greater Philadelphia]]}} [[metropolitan area]], with a population of 5.8 million, was the fifth-largest in the United States. A commercial, educational, and cultural center, the city was once the second-largest in the [[British Empire]]<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www3.nationalgeographic.com/places/cities/city_philadelphia.html |title=Philadelphia, Pennsylvania |accessmonthday=September 21 |accessyear=2007 |work=People and Places |publisher=National Geographic }}</ref> (after [[London]]), and the social and geographical center of the [[13 Colonies|original 13 American colonies]]. |
|||
During the 18th century, it eclipsed [[New York City]] in political and social importance, with [[Benjamin Franklin]] taking a large role in Philadelphia's early rise to prominence. It was in this city that some of the ideas, and subsequent actions, gave birth to the [[American Revolution]] and [[United States Declaration of Independence|American Independence]], making Philadelphia a centerpiece of early American history. It was the most populous city of the young United States and served as the [[List of capitals in the United States|the nation's second capital]] in 1774. |
|||
==History== |
|||
{{main|History of Philadelphia}} |
|||
Prior to the arrival of Europeans, the Philadelphia area was the location of the [[Lenape|Lenape (Delaware)]] [[Native Americans in the United States|Indian]] village [[Shackamaxon]]. Europeans arrived in the [[Delaware Valley]] in the early 1600s, with the first settlements founded by the [[Netherlands|Dutch]], [[United Kingdom|British]] and [[Sweden|Swedish]]. |
|||
The Swedes sought to expand their influence by creating an agricultural (tobacco) and fur-trading colony to bypass French and British merchants. The [[New Sweden Company]] was chartered and included Swedish, Dutch and German stockholders. The first Swedish expedition to [[North America]] embarked from the port of [[Gothenburg]] in late 1637. It was organized and overseen by [[Clas Fleming (admiral)|Clas Fleming]], a Swedish admiral from [[Finland]]. Part of this colony, called [[New Sweden]] or [[Nya Sverige]] eventually included land on the west side of the [[Delaware River]] from just below the [[Schuylkill River]]: in other words, today's Philadelphia, southeast [[Pennsylvania]], [[Delaware]], and [[Maryland]]. |
|||
In 1644, [[New Sweden]] supported the [[Susquehannocks]] in their victory in a war against the English province of [[Maryland]]. A series of events led the Dutch — led by governor [[Peter Stuyvesant]] — to move an army to the [[Delaware River]] in the late summer of 1655. Though [[New Netherland]] now nominally controlled the colony, the Swedish and Finnish settlers continued to enjoy a degree of local autonomy, having their own militia, religion, court, and lands. This status lasted officially until the English conquest of the New Netherland colony, in October 1663-1664, and continued unofficially until the area was included in [[William Penn]]'s charter for [[Pennsylvania]], in 1682. |
|||
In 1681, as part of a repayment of a debt, [[Charles II of England]] granted [[William Penn]] a [[charter]] for what would become the [[Province of Pennsylvania|Pennsylvania colony]]. Part of Penn's plan for the colony was to create a city on the [[Delaware River]] to serve as a port and place for government. Despite already having been given the land by Charles II, Penn bought the land from the local Lenape to be on good terms with the Native Americans and ensure peace for his colony.<ref>{{cite book |last=Brookes |first=Karin |coauthors=John Gattuso, Lou Harry, Edward Jardim, Donald Kraybill, Susan Lewis, Dave Nelson and Carol Turkington |editor=Zoë Ross |title=Insight Guides: Philadelphia and Surroundings |edition=Second Edition (Updated) |date=2005 |publisher=APA Publications | pages = page 21 |id=ISBN 1585730262 }}</ref> According to [[legend]] Penn made a treaty of friendship with Lenape chief [[Tamanend|Tammany]] under an elm tree at [[Shackamaxon]], in what is now the city's [[Kensington, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania|Kensington section]].<ref>{{cite book | author = Weigley RF et al (eds) | title = Philadelphia: A 300-Year History | publisher = [[W. W. Norton & Company]] | date= 1982 | location = New York and London | pages = pages 4 - 5 | id = ISBN 0-393-01610-2 }}</ref> As a [[Religious Society of Friends|Quaker]], Penn had experienced religious persecution and wanted his colony to be a place where anyone could worship freely despite their religion. Penn named the city Philadelphia, which is [[Greek language|Greek]] for brotherly love (''philos'', "love" or "friendship", and ''adelphos'', "brother").<ref>{{cite book |last=Avery|first=Ron | title = A Concise History of Philadelphia | publisher = Otis Books | date= 1999 | location = Philadelphia | pages = page 19 | id = ISBN 0-9658825-1-9 }}</ref> |
|||
[[Image:Westpenntreaty.jpg|thumb|left|"Penn's Treaty with the Indians" by [[Benjamin West]].]] |
|||
[[William Penn]]'s plan was that Philadelphia would be like an English rural town instead of a city. The city's roads were designed with a [[grid plan]] with the idea that houses and businesses would be spread far apart and surrounded by gardens and orchards. The city's inhabitants didn't follow Penn's plans and crowded by the Delaware River and subdivided and resold their lots.<ref>''Philadelphia: A 300-Year History'', pages 7, 14 - 16</ref> Before Penn left Philadelphia for the last time, he issued the Charter of 1701 establishing Philadelphia as a city. The city soon grew and established itself as an important trading center. Conditions in the city were poor at first, but by the 1750s living conditions had improved. A significant contributor to Philadelphia at the time was [[Benjamin Franklin]]. Franklin helped improve city services and founded new ones, such as the American Colonies' [[Pennsylvania Hospital|first hospital]].<ref>''Insight Guides: Philadelphia and Surroundings'', pages 24 - 25</ref> Due to Philadelphia's central location in the colonies, during the [[American Revolution]] the city was used as the location for the [[First Continental Congress]] before the war, the [[Second Continental Congress]], which signed the [[United States Declaration of Independence]], during the war, and the [[Philadelphia Convention|Constitutional Convention]] after the war. A [[Philadelphia campaign|number of battles during the war]] were fought in Philadelphia and its environs as well. Unsuccessful lobbying after the war to make Philadelphia the United States capital helped make the city the temporary U.S. capital in the 1790s.<ref>''Insight Guides: Philadelphia and Surroundings'', pages 30 - 33</ref> |
|||
[[Image:Benjamin Franklin by Jean-Baptiste Greuze.jpg|thumb|left|100px|[[Benjamin Franklin]]]] |
|||
The state government left Philadelphia in 1799 and the federal government left soon after in 1800. However Philadelphia was still the largest city in the United States and a financial and cultural center. [[New York City]] soon surpassed Philadelphia in population, but construction of roads, [[canal]]s, and [[railroad]]s helped turn Philadelphia into the United States' first major industrial city. Throughout the 19th century Philadelphia had a large variety of industries and businesses, the largest being [[textile]]s. Major corporations in the 19th and early 20th centuries included the [[Baldwin Locomotive Works]], [[William Cramp and Sons|William Cramp and Sons Ship and Engine Building Company]], and the [[Pennsylvania Railroad]].<ref>''Philadelphia: A 300-Year History'', pages 214, 218, 428 - 429</ref> Industry, along with the [[United States Centennial|U.S. Centennial]], was celebrated in 1876 with the [[Centennial Exposition]], the first official [[Expo (exhibition)|World's Fair]] in the United States. [[Immigration|Immigrants]], mostly [[Germany|German]] and [[Ireland|Irish]], settled in Philadelphia and the surrounding districts. The rise in population of the surrounding districts helped lead to the [[Act of Consolidation, 1854|Act of Consolidation of 1854]] which extended the city of Philadelphia to include all of [[Philadelphia County, Pennsylvania|Philadelphia County]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ushistory.org/philadelphia/philadelphia.html |title=A Brief History of Philadelphia |accessmonthday=December 14 |accessyear=2006 |work=Philadelphia History |publisher=ushistory.org }}</ref> In the later half of the century immigrants from [[Russia]], [[Eastern Europe]] and [[Italy]] and [[African Americans]] from the [[Southern United States|southern U.S.]] settled in the city.<ref>''Insight Guides: Philadelphia and Surroundings'', pages 38 - 39</ref> |
|||
[[Image:Phila8thMarket.jpg|thumb|right|8th and Market Street, showing the [[Strawbridge and Clothier]] department store, 1910s.]] |
|||
By the 20th century Philadelphia had become known as "corrupt and contented." Philadelphians were content with the city's lack of change or excitement, and single-party politics, centered on the city's entrenched [[Republican Party (United States)|Republican]] [[political machine]], allowed corruption to flourish. The machine and corruption permeated in all parts of city government and reformers had little success.<ref>''Philadelphia: A 300-Year History'', pages 535, 537</ref> The first major success in reform came in 1917 when outrage over the murder of a police officer during that year's election led to the shrinking of the [[Philadelphia City Council]] from two houses to just one.<ref>''Philadelphia: A 300-Year History'', pages 563 - 564</ref> In the 1920s the public flouting of [[Prohibition in the United States|Prohibition]] laws, [[Mafia|mob]] violence, and police involvement in illegal activities led to the appointment of [[Brigadier General]] [[Smedley Butler]] of the [[United States Marine Corps|U.S. Marine Corps]] as director of public safety, but political pressure prevented any long term success in fighting crime and corruption.<ref>''Philadelphia: A 300-Year History'', pages 578 - 581</ref> |
|||
After struggling through the [[Great Depression]], [[World War II]] created jobs and brought the city out of the Depression. However, after the war there was a severe housing shortage with about half the city's housing being built in the 19th century, many of which lacked proper facilities. Adding to housing problem was [[white flight]], as African Americans and [[Puerto Rican people|Puerto Ricans]] moved into new neighborhoods resulting in racial tension.<ref>''Philadelphia: A 300-Year History'', pages 669 - 670</ref> After a population peak of over two million residents in 1950 the city's population declined while the suburban neighboring counties grew. After a five year investigation into corruption into city government, the outcry with what the investigation found led the drafting of a new city charter in 1950. The city charter strengthened the position of the mayor and weakened the city council among other changes to help prevent the corruption of the past. The first [[Democratic Party (United States)|Democratic]] mayor since the first half of the 19th century was elected in 1951. However, after two early reform mayors, a Democratic political organization had established itself replacing the old Republican one.<ref>''A Concise History of Philadelphia'', pages 75 - 76</ref> |
|||
Protests, riots and racial tensions were common in the 1960s and 70s. Mostly drug related gang violence plagued the city. In the mid 1980s, [[crack house]]s invaded the city's slums. Confrontations between police and the radical group [[MOVE]] culminated when the police dropped a satchel bomb on their headquarters starting a fire that killed eleven MOVE members and destroyed sixty-two neighboring houses. Revitalization and [[gentrification]] of neighborhoods began in the 1960s and continues into the 21st century, with much of the development in the [[Center City, Philadelphia|Center City]] and [[University City, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania|University City]] areas of the city. After many of the old manufacturers and businesses had left Philadelphia or shut down, the city started attracting service businesses and began to more aggressively market itself as a tourist destination. Glass and granite skyscrapers were built in Center City. Historic areas such as [[Independence National Historical Park]] located in Society Hill were resuscitated during the reformist mayoral era of the 1950s through the 1980s and are now among the most desirable living areas of Center City. This has slowed the city's forty-year population decline after losing nearly a quarter of its population.<ref>''Insight Guides: Philadelphia and Surroundings'', pages 44 - 45</ref><ref>''A Concise History of Philadelphia'', page 78</ref> |
|||
==Geography== |
|||
===Topography=== |
|||
[[Image:Large Philadelphia Landsat.jpg|thumb|A simulated-color satellite image of Philadelphia taken on [[NASA]]'s [[Landsat 7]] satellite. The [[Delaware River]] is visible in this shot.]] |
|||
Philadelphia is located at 40° 00′ north latitude and 75° 09′ west longitude. According to the [[United States Census Bureau]], the city has a total area of {{convert|142.6|sqmi|1}}, of which {{convert|135.1|sqmi|1}} is land and {{convert|7.6|sqmi|1}}, or 5.29%, is water. Bodies of water include the [[Delaware River|Delaware]] and [[Schuylkill River]]s, and [[Cobbs Creek|Cobbs]], [[Wissahickon Creek|Wissahickon]], and [[Pennypack Creek]]s. |
|||
The lowest point is sea level, while the highest point is in [[Chestnut Hill, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania|Chestnut Hill]], at approximately {{convert|445|ft|m|0}} above sea level (near the intersection of Germantown Avenue and Bethlehem Pike).<ref>{{cite web |url=http://nationalmap.gov |title=USGS Geography: The National Map |accessmonthday=December 17 |accessyear=2007 }} (Example coordinates of high point: Latitude: 40° 04′ 37″, Longitude: −75° 12′ 29″.)</ref> |
|||
Philadelphia is located on the [[Fall Line]] separating the [[Atlantic Coastal Plain]] from the [[Piedmont (United States)|Piedmont]].<ref>Railsback, Bruce. "[http://www.gly.uga.edu/railsback/1122EUSMISR.html The Fall Line]." ''GEOL 1122: Earth's History of Global Change''. [[University of Georgia]] Department of Geology.</ref> The rapids on the [[Schuylkill River]] at [[East Falls]] disappeared after the completion of the Fairmount Dam.<ref>"[http://www.phila.gov/phils/Docs/otherinfo/pname1.htm Philadelphia Neighborhoods and Place Names, A–K]." ''Philadelphia Information Locator System''.</ref> |
|||
The city is the seat of [[Philadelphia County, Pennsylvania|its own county]]. The adjacent counties are [[Montgomery County, Pennsylvania|Montgomery]] to the north; [[Bucks County, Pennsylvania|Bucks]] to the northeast; [[Burlington County, New Jersey]] to the east; [[Camden County, New Jersey]] to the southeast; [[Gloucester County, New Jersey]] to the south; and [[Delaware County, Pennsylvania|Delaware County]] to the west. |
|||
{{Geographic Location (8-way) |
|||
|Centre = Philadelphia |
|||
|North = [[Jenkintown, Pennsylvania|Jenkintown]] |
|||
|Northeast = [[Bristol, Pennsylvania|Bristol]] |
|||
|East = [[Camden, New Jersey]] |
|||
|Southeast = [[Cherry Hill, New Jersey]] |
|||
|South = [[Glassboro, New Jersey]] |
|||
|Southwest = [[Chester, Pennsylvania|Chester]] |
|||
|West = [[Upper Darby Township, Pennsylvania|Upper Darby]] |
|||
|Northwest = [[Pennsylvania Main Line]] |
|||
|image =Flag of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.png |
|||
}} |
|||
===Climate=== |
|||
Philadelphia falls in the [[humid subtropical climate]] zone. Summers are typically hot and muggy, fall and spring are generally mild, and winter is cold. Snowfall is variable, with some winters bringing moderate snow and others bringing some significant snowstorms. Annual snowfall averages 21 inches (534 mm). Precipitation is generally spread throughout the year, with eight to eleven wet days per month,<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.met.utah.edu/jhorel/html/wx/climate/daysrain.html | title=Average Days of Precipitation, .01 Inches or more | accessdate=2006-07-28 }}</ref> at an average annual rate of 42 inches (1068 mm). |
|||
January lows average 25 °F (−4 °C) and highs average 39 °F (4 °C). The lowest officially recorded temperature was −11 °F (−24 °C) on [[February 9]], [[1934]],<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.stormfax.com/phlminmax2.html |title=Philadelphia Record Highs and Lows |accessdate=2007-04-03}}</ref> but temperatures below 0 °F (−18 °C) occur only a few times a decade. July lows average 70 °F (21 °C) and highs average 86 °F (30 °C),<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.climate-zone.com/climate/united-states/pennsylvania/philadelphia/ |title=Climate Information for Philadelphia – Pennsylvania – Mid-Atlantic – United States – Climate Zone: |accessdate=2007-04-03}}</ref> although heat waves accompanied by high humidity are frequent with highs above 95 °F (35 °C) and the [[heat index]] running as high as 110 °F (43 °C). The highest recorded temperature was 106 °F (41 °C) on [[August 7]] [[1918]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.stormfax.com/phlminmax2.html |title=Philadelphia Record Highs and Lows |accessdate=2007-04-03}}</ref> Early fall and late winter are generally driest, with February being the driest month, averaging only 2.74 inches (69.8 mm) of precipitation. |
|||
{{Infobox Weather |
|||
|single_line=yes |
|||
|location = Philadelphia |
|||
|Jan_Hi_°F = 39 |Jan_REC_Hi_°F = 74 |
|||
|Feb_Hi_°F = 42 |Feb_REC_Hi_°F = 79 |
|||
|Mar_Hi_°F = 51 |Mar_REC_Hi_°F = 87 |
|||
|Apr_Hi_°F = 62 |Apr_REC_Hi_°F = 95 |
|||
|May_Hi_°F = 72 |May_REC_Hi_°F = 97 |
|||
|Jun_Hi_°F = 81 |Jun_REC_Hi_°F = 102 |
|||
|Jul_Hi_°F = 86 |Jul_REC_Hi_°F = 104 |
|||
|Aug_Hi_°F = 84 |Aug_REC_Hi_°F = 106 |
|||
|Sep_Hi_°F = 77 |Sep_REC_Hi_°F = 102 |
|||
|Oct_Hi_°F = 66 |Oct_REC_Hi_°F = 96 |
|||
|Nov_Hi_°F = 55 |Nov_REC_Hi_°F = 84 |
|||
|Dec_Hi_°F = 44 |Dec_REC_Hi_°F = 73 |
|||
|Year_Hi_°F = 63.3 |Year_REC_Hi_°F = 106 |
|||
|Jan_Lo_°F = 25 |Jan_REC_Lo_°F = -7 |
|||
|Feb_Lo_°F = 28 |Feb_REC_Lo_°F = -11 |
|||
|Mar_Lo_°F = 35 |Mar_REC_Lo_°F = 5 |
|||
|Apr_Lo_°F = 44 |Apr_REC_Lo_°F = 14 |
|||
|May_Lo_°F = 55 |May_REC_Lo_°F = 28 |
|||
|Jun_Lo_°F = 64 |Jun_REC_Lo_°F = 44 |
|||
|Jul_Lo_°F = 70 |Jul_REC_Lo_°F = 51 |
|||
|Aug_Lo_°F = 69 |Aug_REC_Lo_°F = 44 |
|||
|Sep_Lo_°F = 61 |Sep_REC_Lo_°F = 35 |
|||
|Oct_Lo_°F = 49 |Oct_REC_Lo_°F = 25 |
|||
|Nov_Lo_°F = 40 |Nov_REC_Lo_°F = 8 |
|||
|Dec_Lo_°F = 31 |Dec_REC_Lo_°F = -5 |
|||
|Year_Lo_°F = 47.6 |Year_REC_Lo_°F = -11 |
|||
|Jan_Precip_inch = 3.52 |
|||
|Feb_Precip_inch = 2.74 |
|||
|Mar_Precip_inch = 3.81 |
|||
|Apr_Precip_inch = 3.49 |
|||
|May_Precip_inch = 3.89 |
|||
|Jun_Precip_inch = 3.29 |
|||
|Jul_Precip_inch = 4.39 |
|||
|Aug_Precip_inch = 3.82 |
|||
|Sep_Precip_inch = 3.88 |
|||
|Oct_Precip_inch = 2.75 |
|||
|Nov_Precip_inch = 3.16 |
|||
|Dec_Precip_inch = 3.31 |
|||
|Year_Precip_inch = 42.05 |
|||
|source = The Weather Channel<ref>{{cite web |
|||
|url=http://www.weather.com/weather/wxclimatology/monthly/USPA1276 |title= Monthly Averages for Philadelphia, PA | publisher=Weather.com |year=2008 |accessdate=2008-09-27}}</ref> |
|||
|accessdate = 2008-09-27 |
|||
}} |
|||
==Cityscape== |
|||
===Neighborhoods=== |
|||
[[Image:Philly Street.jpg|thumb|A street in the [[Washington Square West, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania|Washington Square West]] neighborhood.]] |
|||
{{seealso|List of Philadelphia neighborhoods}} |
|||
Philadelphia has many neighborhoods, each with its own identity. The large Philadelphia sections, [[North Philadelphia, Pennsylvania|North]], [[Northeast Philadelphia|Northeast]], [[Northwest Philadelphia|Northwest]], [[West Philadelphia|West]], [[South Philadelphia|South]] and [[Southwest Philadelphia]] surround [[Center City, Philadelphia|Center City]], which falls within the original city limits prior to consolidation in 1854. Numerous smaller neighborhoods within the areas coincide with the boroughs, townships, and other communities that made up Philadelphia County before their absorption by the city. Other neighborhoods formed based on ethnicity, religion, culture, and commercial reasons.<ref>''Insight Guides: Philadelphia and Surroundings'', page 58</ref> |
|||
===Architecture=== |
|||
[[Image:Row Houses, West Philly.jpg|thumb|Row houses in West Philadelphia.]] |
|||
{{main|Buildings and architecture of Philadelphia}} |
|||
{{seealso|List of tallest buildings in Philadelphia}} |
|||
Philadelphia's architectural history dates back to [[Colonial America|Colonial]] times and includes a wide range of styles. The earliest structures were constructed with [[Log home|logs]], but brick structures were common by 1700. During the 18th century, the [[cityscape]] was dominated by [[Georgian architecture]], including [[Independence Hall (United States)|Independence Hall]]. In the first decades of the 19th century, [[Federal architecture]] and [[Greek Revival architecture]] were popular.<ref>''Philadelphia: A 300-Year History'', page 11, 41, 174 - 175, 252 - 253</ref> In the second half of the 19th century, [[Victorian architecture]] was common. In 1871, construction began on the [[Second Empire]]-style [[Philadelphia City Hall]]. Despite the construction of steel and concrete [[skyscraper]]s in the 1910s, '20s and '30s, the {{convert|548|ft|m|0|abbr=on}} City Hall remained the tallest building in the city until 1987 when [[One Liberty Place]] was constructed. Numerous glass and granite skyscrapers were built from the late 1980s onwards. In 2007, the [[Comcast Center (office building)|Comcast Center]] surpassed One Liberty Place to become the city's tallest building.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Holcomb |first=Henry J. | year=2007 | month=June 18 |title=Comcast Center topped off |journal=The Philadelphia Inquirer |url=http://www.philly.com/inquirer/multimedia/8055132.html }}</ref> |
|||
[[Image:Philly panorama.jpg|thumb|The Philadelphia skyline from City Hall looking towards [[Liberty Place]] (2005, before construction of [[Comcast Center (office building)|Comcast Center]]).]] |
|||
For much of Philadelphia's history, the typical Philadelphia home has been the [[Terraced house|row house]]. The row house was introduced to the United States via Philadelphia in the early 1800s and, for a time, row houses built elsewhere in the United States were known as "Philadelphia rows".<ref>''Philadelphia: A 300-Year History'', page 251</ref> There is a variety of row houses throughout the city from Victorian-style homes in North Philadelphia to twin row houses in West Philadelphia. While newer homes are scattered throughout the city, much of Philadelphia's housing is from the early 20th century or older. The age of the city's homes has created numerous problems which has led to blight and vacant lots in many parts of the city, while other neighborhoods such as [[Society Hill, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania|Society Hill]], which has the largest concentration of 18th-century architecture in the United States, have been rehabilitated and gentrified.<ref>{{cite journal | last=Aitken | first=Joanne | title=Breaking Ground | journal=Philadelphia City Paper | date=June 3 - 19, 2004 | url=http://www.citypaper.net/articles/2004-06-03/cityspace.shtml }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |author=Mark Alan Hughes |title=Dirt Into Dollars; Converting Vacant Land Into Valuable Development |url=http://www.pewtrusts.org/news/news_subpage.cfm?content_item_id=265&content_type_id=13&page=nr2 |date=[[June 1]],[[2000]] |accessdate=2007-07-24}}</ref> |
|||
==Culture== |
|||
{{main|Culture of Philadelphia}} |
|||
{{see also|List of people from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania}} |
|||
[[Image:Independence Hall.jpg|thumb|right|[[Independence Hall (United States)|Independence Hall]] in Philadelphia]] |
|||
Philadelphia contains many [[National Historical Park|national historical sites]] that relate to the founding of the United States. [[Independence National Historical Park]] is the center of these historical landmarks. [[Independence Hall (United States)|Independence Hall]], where the [[United States Declaration of Independence|Declaration of Independence]] was signed, and the [[Liberty Bell]] are the city's most famous attractions. Other historic sites include homes for [[Edgar Allan Poe National Historic Site|Edgar Allan Poe]], [[Betsy Ross House|Betsy Ross]], and [[Thaddeus Kosciuszko National Memorial|Thaddeus Kosciuszko]], early government buildings like the [[First Bank of the United States|First]] and [[Second Bank of the United States|Second Banks of the United States]], and the [[Gloria Dei (Old Swedes') Church National Historic Site]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cr.nps.gov/nhl/designations/Lists/PA01.pdf |title=Listing of National Historic Landmarks by State (Pennsylvania) |accessmonthday=August 8 |accessyear=2006 |year=2004 |month=March |format=PDF |publisher=National Park Service}}</ref> |
|||
Philadelphia's major science museums include the [[Franklin Institute]], which contains the [[Benjamin Franklin National Memorial]], the [[Academy of Natural Sciences]], and the [[University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology]]. History museums include the [[National Constitution Center]], the [[Atwater Kent Museum of Philadelphia]] History, the [[National Museum of American Jewish History]], the [[African American Museum in Philadelphia]], the [[Historical Society of Pennsylvania]], the Grand Lodge of Free and Accepted Masons in the state of Pennsylvania and The Masonic Library and Museum of Pennsylvania and [[Eastern State Penitentiary]]. Philadelphia is home to the United States' first [[Philadelphia Zoo|zoo]] and [[Pennsylvania Hospital|hospital]]. |
|||
{{see also|List of sites of interest in Philadelphia}} |
|||
===Arts=== |
|||
[[Image:Philly042107-014-RockyStatue.jpg|thumb|left|Two statues, ''[http://www.philart.net/art.php?id=23 The Amazon]'' and ''[[Rocky Steps#Bronze statue|Rocky]]'', outside the [[Philadelphia Museum of Art]].]] |
|||
The city contains many art [[museum]]s such as the [[Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts]] and the [[Rodin Museum]], the largest collection of work by Auguste Rodin outside of France. The city’s major art museum, the [[Philadelphia Museum of Art]], is one of the largest art museums in the United States and features the [[Rocky Steps|steps]] made popular by the film ''[[Rocky]]''.<ref name="Dallasnews">{{cite journal | quotes=no | first=Jerome | last=Weeks | year=2006 | month=August 4 | title=Philly goes the distance | journal=The Dallas Morning News|url=http://www.dallasnews.com/sharedcontent/dws/fea/travel/unitedstates/stories/DN-philly_0806tra.State.Edition1.508ad59.html }}</ref> |
|||
The city is home to many art galleries, many of which participate in the [[First Friday]] event. The first Friday of every month galleries in Old City are open late. Annual events include film festivals and parades, the most famous being the [[New Year's Day]] [[Mummers Parade]]. |
|||
Areas such as South Street and [[Old City (Philadelphia)|Old City]] have a vibrant night life. The [[Avenue of the Arts, Philadelphia|Avenue of the Arts]] in Center City contains many restaurants and [[Theatre|theaters]], such as the [[Kimmel Center for the Performing Arts]], which is home to the [[Philadelphia Orchestra]], and the [[Academy of Music (Philadelphia)|Academy of Music]], the nation's oldest continually operating venue, home to the [[Opera Company of Philadelphia]].<ref name="Dallasnews" /> |
|||
[[Image:KeysToCommunity.jpg|right|thumbnail|[[James Peniston]]'s ''Keys To Community'' in the [[Old City (Philadelphia)|Old City]] neighborhood, one of the city's [http://www.philart.net/person.php?id=34 many public artworks] featuring images of [[Benjamin Franklin]]. Location: {{Coord|39.952414|-75.146301}}]] |
|||
Philadelphia has more [[public art]] than any other American city.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.gophila.com/C/Things_to_Do/211/Philadelphia_CultureFiles/210/Public_Art/22.html | title=Public Art | publisher=Greater Philadelphia Tourism Marketing Corporation | accessdate=2007-10-16 }}</ref> In 1872, the Fairmount Park Art Association was created, the first private association in the United States dedicated to integrating public art and [[urban planning]].<ref>{{cite journal | quotes=no | first=Joanne | last=Aitken | year=2004 | month=September 2-8 | title=Forget Paris | journal=City paper | url=http://www.citypaper.net/articles/2004-09-02/cityspace.shtml}}</ref> In 1959, lobbying by the Artists Equity Association helped create the [[Percent for Art]] [[Law|ordinance]], the first for a U.S. city.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.publicartreview.org/pdf/wetenhall.pdf | title=About A Brief History of Percent-For-Art in America | last= Wetenhall | first=John | format=PDF | publisher=Public Art Review | accessdate=2006-09-24 }}</ref> The program, which has funded more than 200 pieces of public art, is administered by the Philadelphia Office of Arts and Culture, the city's art agency.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.phila.gov/visitors/arts_office.html#contact | title=Office of Art and Culture | publisher=Phila.gov | accessdate=2006-09-24 }}</ref> |
|||
In particular, Philadelphia has more murals than any other U.S. city, thanks in part to the 1984 creation of the Department of Recreation's [[Mural Arts Program]], which seeks to beautify neighborhoods and provide an outlet for [[graffiti]] artists. The program has funded more than 2,700 [[mural]]s by professional, staff and volunteer artists.<ref> {{cite web| url=http://www.muralarts.org/about/ | title=Mural Arts Program About page | accessdate=2007-11-27 }}</ref> |
|||
Philadelphia has had a prominent role in [[Music of Philadelphia|music]]. In the 1970s, [[Philadelphia soul]] influenced the music of that and later eras. On [[July 13]] [[1985]], Philadelphia hosted the American end of the [[Live Aid]] concert at [[John F. Kennedy Stadium]]. The city reprised this role for the [[Live 8]] concert, bringing some 700,000 people to the [[Ben Franklin Parkway]] on [[July 2]] [[2005]].<ref>{{cite web |author=Rodney Kim |title=Live 8 Philadelphia Review |url=http://www.live8.us/philadelphia/blog.html |date=[[July 2]],[[2005]]|accessdate=2007-04-24}}</ref> |
|||
===Cuisine=== |
|||
{{main|Cuisine of Philadelphia}} |
|||
The city is known for its [[hoagie]]s, [[scrapple]], [[soft pretzel]]s, [[Italian ice|water ice]], and is home to the [[cheesesteak]]. Its high-end restaurants include Morimoto, run by chef [[Masaharu Morimoto]], who rose to prominence on the ''[[Iron Chef]]'' television show. |
|||
==Sports== |
|||
{{main|Sports in Philadelphia}} |
|||
{{seealso|U.S. cities with teams from four major sports}} |
|||
Philadelphia has a long history of professional sports teams, and is one of thirteen U.S. cities to have [[U.S. cities with teams from four major sports|all four major sports]]: the [[Philadelphia Eagles]] of the [[National Football League]], the [[Philadelphia Flyers]] of the [[National Hockey League]], the [[Philadelphia Phillies]] in the [[National League]] of [[Major League Baseball]], and the [[Philadelphia 76ers]] in the [[National Basketball Association]]. The last major professional sport team to win a championship was the 76ers, which won the [[1982-83 NBA season|NBA Championship in 1983]]. Due to the length of this streak without winning a sports championship, in 2004 [[ESPN]] ranked Philadelphia as number two in its list of The Fifteen Most Tortured Sports Cities.<ref>[http://sports.espn.go.com/espn/page2/story?page=paolantonio/tortured_philadelphia ESPN.com: Page 2 : What caused Philly's curse?<!-- Bot generated title -->]</ref> The failure of Philadelphia's major professional sports teams to win championships since that date is sometimes attributed, in jest, to the so-called "[[Curse of Billy Penn]]". The [[Philadelphia Athletics (1860-1876)|Oakland Athletics]] and [[Philadelphia Warriors#Philadelphia_Warriors|Golden State Warriors]] were originally from Philadelphia. |
|||
Philadelphia also is home to professional, semi-professional and elite amateur teams in other sports, including [[cricket]]. Philadelphia also hosts other major sporting events, including the [[Penn Relays]], [[Stotesbury Cup]], [[Philadelphia Marathon]], and [[Philadelphia International Championship]] [[Bicycle racing|bicycle race]], and the [[Dad Vail Regatta]]. |
|||
Philadelphia is also known for the [[Philadelphia Big 5]], a group of five Division I college basketball programs: Big 5 are [[Saint Joseph's University]], [[University of Pennsylvania]], [[La Salle University]], [[Temple University]], and [[Villanova University]]. The sixth NCAA Division I school in Philadelphia is [[Drexel University]]. At least one of the teams is competitive nearly every year and at least one team has made the NCAA tournament for the past four decades. |
|||
In February 2008, Philadelphia beat out competition from several other cities, namely [[St. Louis]], to be awarded the 16th [[Major League Soccer]] franchise. They will enter the league in 2010 calling [[Chester Stadium]] their home (a [[soccer specific stadium]]) in [[Chester, PA]]. |
|||
Philadelphia is also home to [[New Alhambra Arena]], the birthplace of [[Extreme Championship Wrestling]] and current home to multiple wrestling and boxing promotions. |
|||
{| class="wikitable sortable" |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! scope="col" | Club |
|||
!style="color: white; height: 30px; background: navy;"| Career |
|||
! scope="col" | League |
|||
!style="color: white; height: 30px; background: navy;"| [[Image:Naval Jack of the United States.svg|60px|USN Jack]] |
|||
! scope="col" | Sport |
|||
! scope="col" | Venue |
|||
! scope="col" | Established |
|||
! scope="col" | Championships |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! scope="row" style="font-weight: normal; text-align: center;" | [[Philadelphia Eagles]] |
|||
|Awarded: |
|||
| [[National Football League|NFL]] |
|||
|21 March 1986 |
|||
| American Football |
|||
| [[Lincoln Financial Field]] |
|||
| 1933 |
|||
| [[1948 NFL season|1948]], [[1949 NFL season|1949]], [[1960 NFL season|1960]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! scope="row" style="font-weight: normal; text-align: center;" | [[Philadelphia Flyers]] |
|||
|Laid down: |
|||
| [[National Hockey League|NHL]] |
|||
|29 January 1990 |
|||
| Ice Hockey |
|||
| [[Wachovia Center]] |
|||
| 1967 |
|||
| [[1973-74 NHL season|1973-74]], [[1974-75 NHL season|1974-75]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! scope="row" style="font-weight: normal; text-align: center;" | [[Philadelphia Phillies]] |
|||
|Launched: |
|||
| [[Major League Baseball|MLB]] |
|||
|4 January 1992 |
|||
| Baseball |
|||
| [[Citizens Bank Park]] |
|||
| 1883 |
|||
| [[1980 World Series|1980]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! scope="row" style="font-weight: normal; text-align: center;" | [[Philadelphia 76ers]] |
|||
|Commissioned: |
|||
| [[National Basketball Association|NBA]] |
|||
|9 January 1993 |
|||
| Basketball |
|||
| [[Wachovia Center]] |
|||
| 1963 |
|||
| [[1966-67 NBA season|1966-67]], [[1982-83 NBA season|1982-83]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! scope="row" style="font-weight: normal; text-align: center;" | [[Major League Soccer Philadelphia 2010|MLS Philadelphia 2010]] |
|||
|Status: |
|||
| [[Major League Soccer|MLS]] |
|||
|{{Ship fate box active in service}} |
|||
| Soccer |
|||
| [[Chester Stadium]]<br>(in [[Chester, Pennsylvania]]) |
|||
| 2010 |
|||
| none |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! scope="row" style="font-weight: normal; text-align: center;" | [[Philadelphia Wings]] |
|||
|Homeport: |
|||
| [[National Lacrosse League|NLL]] |
|||
|[[Groton, Connecticut]] |
|||
| Lacrosse (Indoor) |
|||
| [[Wachovia Center]] |
|||
| 1987 |
|||
| 1989, 1990, 1994, 1995, 1998, 2001 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! |
! scope="row" style="font-weight: normal; text-align: center;" | [[Philadelphia Phantoms]] |
||
| [[American Hockey League|AHL]] |
|||
| Ice Hockey |
|||
| [[Wachovia Spectrum]] |
|||
| 1996 |
|||
| 1997-98, 2004-05 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! scope="row" style="font-weight: normal; text-align: center;" | [[Philadelphia Soul]] |
|||
|Displacement: |
|||
| [[Arena Football League|AFL]] |
|||
|6000 tons light, 6927 tons full, 927 tons dead |
|||
| Arena Football |
|||
| [[Wachovia Center]] & [[Wachovia Spectrum|Spectrum]] |
|||
| 2004 |
|||
| 2008 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! scope="row" style="font-weight: normal; text-align: center;" | [[Philadelphia Barrage]] |
|||
|Length: |
|||
| [[Major League Lacrosse|MLL]] |
|||
|110.3 meters (362 ft) |
|||
| Lacrosse (Outdoor) |
|||
| N/A |
|||
| [[2001 MLL season|2001]] |
|||
| [[2004 MLL season|2004]], [[2006 MLL season|2006]], [[2007 MLL season|2007]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! scope="row" style="font-weight: normal; text-align: center;" | [[Philadelphia KiXX]] |
|||
|Beam: |
|||
| [[National Indoor Soccer League|NISL]] |
|||
|10 meters (33 ft) |
|||
| Soccer (Indoor) |
|||
| [[Wachovia Spectrum]] |
|||
| 1995 |
|||
| 2001-02, 2006-07 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! scope="row" style="font-weight: normal; text-align: center;" | [[Philadelphia Women's Professional Soccer team|Philadelphia WPS team]] |
|||
|Draft: |
|||
| [[Women's Professional Soccer|WPS]] |
|||
|9.4 meters (31 ft) |
|||
| Soccer |
|||
| [[Chester Stadium]]<br>(in [[Chester, Pennsylvania]]) |
|||
| 2010 |
|||
| none |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! scope="row" style="font-weight: normal; text-align: center;" | [[Philadelphia Fight]] |
|||
|Propulsion: |
|||
| [[American National Rugby League|AMNRL]] |
|||
|one [[S6G reactor]] |
|||
| Rugby League |
|||
| Farrell Stadium ([[West Chester University]]) |
|||
| 1998 |
|||
| none |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! scope="row" style="font-weight: normal; text-align: center;" | [[Philadelphia Freedoms]] |
|||
|Complement: |
|||
| [[World TeamTennis|WTT]] |
|||
|12 officers, 98 men |
|||
| Tennis |
|||
| [[King of Prussia Mall]] |
|||
| 1974 |
|||
| 2001, 2006 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|} |
|||
|Armament: |
|||
|[[ADCAP torpedo|ADCAP]] [[torpedo]]es and [[BGM-109 Tomahawk|Tomahawk missile]]s |
|||
==Economy== |
|||
[[Image:Comcastcenter vertical.jpg|thumb|[[Comcast Center (office building)|Comcast Center]], Philadelphia's newest office building.]] |
|||
Philadelphia's economy is relatively diversified, with meaningful portions of its total output derived from manufacturing, oil refining, food processing, health care and biotechnology, tourism and financial services. According to a study prepared by PricewaterhouseCoopers, Philadelphia and its surrounding region had the fourth highest GDP among American cities, with a total "city GDP" of $312 billion in 2005.<ref>[http://www.citymayors.com/statistics/richest-cities-2005.html City Mayors reviews the richest cities in the world in 2005<!-- Bot generated title -->]</ref> Only New York, Los Angeles and Chicago had higher total economic output levels. |
|||
The city is home to the [[Philadelphia Stock Exchange]] and several [[Fortune 500]] companies, including [[cable television]] and internet provider [[Comcast]], [[insurance]] companies [[CIGNA]] and [[Lincoln Financial Group]], energy company [[Sunoco]], food services company [[Aramark]], [[Crown Holdings Incorporated]], chemical makers [[Rohm and Haas Company]] and [[FMC Corporation]], pharmaceutical companies [[Wyeth]] and [[GlaxoSmithKline]], [[Boeing]] [[helicopter]]s division, and automotive parts retailer [[Pep Boys]]. Early in the 20th Century, it was also home to the pioneering [[brass era]] [[automobile]] company [[Biddle Motor Car Company|Biddle]].<ref>Clymer, p.176.</ref> |
|||
The federal government has several facilities in Philadelphia as well. The city served as the capital city of the [[United States]], before the construction of [[Washington, D.C.]] Today, the East Coast operations of the [[United States Mint]] are based near the historic district, and the [[Federal Reserve]] Bank's Philadelphia division is based there as well. Philadelphia is also home to the [[United States District Court for the Eastern District of Pennsylvania|U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of Pennsylvania]] and the [[United States Court of Appeals for the Third Circuit|U.S. Court of Appeals for the Third Circuit]]. |
|||
Partly because of the historical presence of the [[Pennsylvania Railroad]], and the large ridership at [[30th Street Station]], [[Amtrak]] also maintains a significant presence in the city. These jobs include customer service representatives and ticket processing and other behind-the-scenes personnel, in addition to the normal functions of the railroad. |
|||
[[Image:Philly Vista.jpg|thumb|200px|left|Baltimore Avenue towards Center City.]] |
|||
The city is also a national center of law because of the [[University of Pennsylvania Law School]], [[Earle Mack School of Law]]<ref>[http://www.drexel.edu/law/ Drexel College Of Law]</ref>, [[Temple University Beasley School of Law]], [[Villanova University School of Law]], and [[Widener University School of Law]]. Additionally, the headquarters of the [[American Law Institute]] is located in the city. |
|||
Philadelphia is also an important center for medicine, a distinction that it has held since the colonial period. The city is home to the first hospital in the British North American colonies, [[Pennsylvania Hospital]], and the first medical school in what is now the United States, at the [[University of Pennsylvania]] (Penn). Penn, the city's largest private employer, also runs a large teaching hospital and extensive medical system. There are also major hospitals affiliated with [[Temple University|Temple University School of Medicine]], [[Drexel University College of Medicine]], and [[Thomas Jefferson University]]. Philadelphia also has three distinguished children's hospitals: [[Children's Hospital of Philadelphia]], the nation's first pediatric hospital (located adjacent to the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania), St. Christopher's Hospital, and the Shriners' Hospital. In the city's northern section are Albert Einstein Hospital, and in the northeast section, [[Fox Chase Cancer Center]]. Together, healthcare is the largest sector of employment in the city. Several medical professional associations are headquartered in Philadelphia. |
|||
In part because of Philadelphia's long-running importance as a center for medical research, the region is a major center for the [[pharmaceutical industry]]. [[GlaxoSmithKline]], [[AstraZeneca]], [[Wyeth]], [[Merck & Co.|Merck]], [[GE Healthcare]], [[Johnson and Johnson]] and [[Siemens Medical Solutions]] are just some of the large pharmaceutical companies with operations in the region. The city is also home to the nation's first school of pharmacy, the Philadelphia College of Pharmacy, now called the University of the Sciences in Philadelphia. |
|||
{{see also|List of companies based in the Philadelphia area}} |
|||
===Shopping=== |
|||
[[Image:Italian Market Vegetable Stand 3000px.jpg|thumb|Italian Market, South Philadelphia]] |
|||
[[Center City, Philadelphia|Center City]] is home to [[The Gallery at Market East]], The Shops at Liberty Place and The Shops at the Bellevue, and a variety of standalone retail stores. Rittenhouse Row, a section of [[Walnut Street (Philadelphia)|Walnut Street]] in Center City, has higher-end stores and boutiques. Old City and Society Hill, as well, feature upscale boutiques and retailers from local and international merchandisers. Philadelphia also has several neighborhood shopping districts, including [[Manayunk, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania|Manayunk]] and [[Chestnut Hill, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania|Chestnut Hill]]. Also noteworthy is [[South Street (Philadelphia)|South Street]] with blocks of inexpensive boutiques. |
|||
The [[Italian Market (Philadelphia)|Italian Market]] in South Philadelphia offers groceries, meats, cheeses and housewares from Italy and other countries. [[Geno's Steaks|Geno's]] and [[Pat's King of Steaks|Pat's]], two famed [[cheesesteak]] outlets, are located here. The [[Reading Terminal Market]] in Center City includes dozens of restaurants, farm stalls, and shops, many run by Amish farmers from Lancaster County. There are also neighborhood farmers' markets throughout the city. |
|||
There are also several large shopping malls in the region, including [[Franklin Mills]] in [[Northeast Philadelphia]] and [[King of Prussia Mall]] in [[King of Prussia]], [[Pennsylvania]]; seven miles outside of Philadelphia. Franklin Mills offers shoppers tax-free clothing and shoes due to its location within the city's boundaries and saw an estimated 18 million visitors in 2006. The King of Prussia Mall is the largest shopping mall on the [[East Coast of the United States|East Coast]] of the [[United States]],<ref>[http://www.philly.com/mld/philly/living/travel/visitors_guide/9732146.htm]</ref> and [[List of largest shopping malls in the United States|the largest shopping mall in the country in terms of leasable retail space]]. |
|||
Philadelphia is the birthplace of the secondary ticket marketplace. [http://www.wanamakerticket.com Wanamaker Ticket Office], located in Center City, is among the nation's oldest ticket agencies. |
|||
===Media=== |
|||
{{main|Media of Philadelphia}} |
|||
Philadelphia's two major [[Newspaper|daily newspapers]] are ''[[The Philadelphia Inquirer]]'' and the ''[[Philadelphia Daily News]]'', both of which are owned by Philadelphia Media Holdings L.L.C. ''The Philadelphia Inquirer'', founded in 1829, is the third-oldest surviving daily newspaper in the United States.<ref>{{cite web| last=Wilkinson | first=Gerry | url=http://www.geocities.com/phillyppa/inquirer.html | title=The History of the Philadelphia Inquirer | publisher=Philadelphia Press Association | accessdate=2006-07-20 }}</ref> ''[[The Bulletin (newspaper)|The Bulletin]]'', another newspaper that operates in Philadelphia, traces its history back to ''[[The Philadelphia Bulletin]]'' that went defunct in 1982. ''The Bulletin'' is locally owned by The Bulletin, Inc. |
|||
[[Image:Inquirerbldgfull.jpg|thumb|right|The Inquirer Building on North Broad Street.]] |
|||
The first experimental [[radio]] license was issued in Philadelphia in August, 1912 to [[Saint Joseph's University|St. Joseph's College]]. The first commercial radio stations appeared in 1922. [[WIP-AM|WIP]], then owned by [[Gimbel's|Gimbel's department store]], became the first on [[March 17]] of that year. Also launched that year were [[WFIL]], [[WOO]], [[WPHT|WCAU]] and WDAS.<ref name="Media">{{cite journal | quotes=no | first=Todd | last=Bishop | year=2000 | month=January 7 | title=The Media: One revolution after another | journal=Philadelphia Business Journal|url=http://philadelphia.bizjournals.com/philadelphia/stories/2000/01/10/story3.html}}</ref> The highest-rated stations in Philadelphia include [[soft rock]] [[WBEB]], [[KYW (AM)|KYW Newsradio]], and [[urban adult contemporary]] [[WDAS-FM]]. |
|||
During the 1930s, the experimental station W3XE, which was owned by Philco Corp, became the first [[television station]] in Philadelphia. The station, which would later become [[KYW-TV]] ([[CBS]]), became [[NBC]]'s first affiliate in 1939. By the 1970s [[WCAU|WCAU-TV]], [[WPVI-TV]], [[WHYY-TV]], [[WPHL-TV]], and [[WTXF-TV]] were founded.<ref name="Media" /> In 1952 WFIL (now WPVI), premiered the television show ''Bandstand'', which later became the nationally broadcast show ''[[American Bandstand]]'' hosted by [[Dick Clark (entertainer)|Dick Clark]].<ref>{{cite book | last=Ogden | first=Christopher | year=1999 | title=Legacy: A Biography of Moses and Walter Annenberg | publisher=Little, Brown and Company | location=New York | id=ISBN 0-316-63379-8 }}</ref> Today, as in many large metropolitan areas, each of the commercial networks has an affiliate, and call letters have been replaced by corporate IDs: CBS3, 6ABC, NBC10, FOX29, Telefutura28, Telemundo62, Univision65, plus My PHL 17 and [[WPSG-TV|CW Philly 57]]. On the public media side, the Philadelphia region is served by [[WYBE-TV]] (Philadelphia), WHYY-TV (Wilmington, Delaware and Philadelphia), [[WLVT-TV]] (Lehigh Valley), and [[New Jersey Network]]. In September, 2007, Philadelphia approved a public access cable channel. On the radio side, Philadelphia is served by three large public radio stations, plus several smaller ones; the larger ones are [[WHYY-FM]] (NPR), [[WRTI]] (jazz, classical), and [[WXPN-FM]] (adult alternative music). |
|||
Philadelphia has a competitive rock radio market, especially between [[WMMR]] and [[WYSP]], which both specialize in playing modern and classic rock. The two stations enjoy a very intense rivalry. Since 2005, WMMR has played more music due to a shift in WYSP's programming from a rock station (which also carried controversial [[shock jock]] [[Howard Stern]]) to a [[Free FM]] station. WYSP has since returned to the classic rock format it shed in 1995. Until early 2008, WYSP also carried live radio broadcasts of all [[Philadelphia Eagles]] home and road games. WMMR has the top rated morning show in the Philadelphia area, ''The [[Preston and Steve]] Show'', which has been at the top of the ratings since [[Howard Stern]] left for [[Sirius Radio]]. WYSP currently does not have a competing morning talk show. |
|||
Philadelphia's four [[Urban music|urban]] stations ([[WUSL]] ("Power 99"), [[WPHI]] ("100.3 The Beat"), [[WDAS-FM|WDAS]] and [[WRNB]]) are popular choices on the FM dial. [[WNUW]] is the city's [[Adult Contemporary]] station. The station had been home of "[[Smooth Jazz]]" WJJZ after the format was dropped from the 106.1 frequency (now [[WISX]]) but the format was dropped once again due to poor ratings. |
|||
===Innovation=== |
|||
Philadelphia is home to many "first-in-America" institutions, including:<ref>[http://www.ushistory.org/philadelphia/philadelphiafirsts.html Philadelphia Firsts 1681-1899], ushistory.org</ref><ref>[http://philadelphia.about.com/cs/history/a/philly_firsts.htm Philadelphia Firsts], about.com</ref> |
|||
{{MultiCol}} |
|||
*[[Fire insurance]] company |
|||
*[[Botanical garden]] |
|||
*[[Library Company of Philadelphia|Public library]] |
|||
*[[Pennsylvania Hospital|Hospital]] |
|||
*[[Fire engine]] |
|||
*[[Fire company]] |
|||
*[[College of Philadelphia|Medical school]] |
|||
*[[University of the Sciences in Philadelphia|Pharmacy School]] |
|||
*[[Hospital|Pennsylvania Hospital]] |
|||
*[[Children's Hospital of Philadelphia|Pediatric hospital]] |
|||
*[[Cancer]] hospital |
|||
*Eye hospital |
|||
*[[University of Pennsylvania|University]] |
|||
{{ColBreak}} |
|||
*[[Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts|Art school & museum]] |
|||
*Municipal water system |
|||
*[[United States Postal Service|Post office]] |
|||
*[[First Bank of the United States|Bank]] |
|||
*[[Philadelphia Stock Exchange|Stock exchange]] |
|||
*[[Philadelphia Mint|Mint]] |
|||
*[[Philadelphia Zoo|Zoo]] |
|||
*[[ENIAC|Electronic Computer]] |
|||
*[[Savings Bank]] |
|||
*[[ECW]] |
|||
*First Title Insurance Company in America |
|||
{{EndMultiCol}} |
|||
==Demographics== |
|||
{{main|Demographics of Philadelphia}} |
|||
{{USCensusPop |
|||
|1790= 28522 |
|||
|1800= 41220 |
|||
|1810= 53722 |
|||
|1820= 63802 |
|||
|1830= 80462 |
|||
|1840= 93665 |
|||
|1850= 121376 |
|||
|1860= 565529 |
|||
|1870= 674022 |
|||
|1880= 847170 |
|||
|1890= 1046964 |
|||
|1900= 1293697 |
|||
|1910= 1549008 |
|||
|1920= 1823779 |
|||
|1930= 1950961 |
|||
|1940= 1931334 |
|||
|1950= 2071605 |
|||
|1960= 2002512 |
|||
|1970= 1948609 |
|||
|1980= 1688210 |
|||
|1990= 1585577 |
|||
|2000= 1517550 |
|||
|estyear=2007 |
|||
|estimate=1449634}} |
|||
As of the [[census]]{{GR|2}} of 2000, there were 1,517,550 people, 590,071 households, and 352,272 families residing in the city. The [[population density]] was 11,233.6/square mile (4,337.3/km²). There were 661,958 housing units at an average density of 4,900.1/sq mi (1,891.9/km²). As of the 2004 Census estimations, there were 1,463,281 people, 658,799 housing units, and the racial makeup of the city was 45.2% [[African American (U.S. Census)|African American]], 43.0% [[White (U.S. Census)|White]], 5.5% [[Asian (U.S. Census)|Asian]], 0.3% [[Native American (U.S. Census)|Native American]], 0.1% [[Pacific Islander (U.S. Census)|Pacific Islander]], 5.8% from [[Race (United States Census)|other races]], and 2.2% from two or more races. [[Hispanic (U.S. Census)|Hispanic]] or [[Latino (U.S. Census)|Latino]] of any race were 8.5% of the population. The top 5 largest ancestries include [[Irish American|Irish]] (13.6%), [[Italian American|Italian]] (9.2%), [[German American|German]] (8.1%), [[Polish American|Polish]] (4.3%), and [[English American|English]] (2.9%).<ref>http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/QTTable?_bm=y&-geo_id=16000US4260000&-qr_name=DEC_2000_SF3_U_QTP13&-ds_name=DEC_2000_SF3_U</ref> |
|||
Of the 590,071 households, 27.6% have children under the age of 18 living with them, 32.1% were [[Marriage|married couples]] living together, 22.3% had a female householder with no husband present, and 40.3% were non-families. 33.8% of all households were made up of individuals and 11.9% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.48 and the average family size was 3.22. |
|||
In the city the population was spread out with 25.3% under the age of 18, 11.1% from 18 to 24, 29.3% from 25 to 44, 20.3% from 45 to 64, and 14.1% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 34 years. For every 100 females there were 86.8 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 81.8 males. |
|||
The median income for a household in the city was $30,746, and the median income for a family was $37,036. Males had a median income of $34,199 versus $28,477 for females. The [[per capita income]] for the city was $16,509. About 18.4% of families and 22.9% of the population were below the [[poverty line]], including 31.3% of those under age 18 and 16.9% of those age 65 or over. |
|||
Philadelphia has the second largest [[Irish people|Irish]], [[Italian people|Italian]], and [[Jamaica]]n populations and the fourth largest [[African American]] population in the nation. Philadelphia also has the fourth largest population of [[Polish people|Polish]] residents. In recent years, the [[Hispanic]] and [[Asian American]] populations have significantly increased. Hispanics have settled throughout the city, especially around [[El Centro de Oro]], and the city now has the third largest Puerto Rican population in the continental United States. The [[Asian people|Asian]] population was once concentrated in the city's thriving [[Chinatown]], but now [[Korean American]]s have come to [[Olney]], and [[Vietnam]]ese have forged bazaars next to the [[Italian Market (Philadelphia)|Italian Market]] in [[South Philadelphia]]. Concentrations of [[Cambodian American]] neighborhoods can be found in North and South Philadelphia. [[India]]ns and [[Arab]]s have come to [[Northeast Philadelphia]] along with Russian and Ukrainian immigrants. This large influx of Asians has given Philadelphia one of the largest populations of Vietnamese, Cambodians, Chinese, and Koreans in [[United States]]. The Philadelphia region also has the fourth largest population of Indian Americans. The [[West Indies|West Indian]] population is concentrated in [[Cedar Park, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania|Cedar Park]]. [[Germans]], [[Greeks]], [[Han Chinese|Chinese]], [[Japanese people|Japanese]], [[English people|English]], [[Pakistanis]], [[Iranians]], and also immigrants from the former [[Yugoslavia]] along with other ethnic groups can be found throughout the city. |
|||
==Government== |
|||
[[Image:City Hall holiday.jpg|thumb|left|City Hall decorated.]] |
|||
From a governmental perspective, Philadelphia County is a [[legal nullity]], as all county functions were assumed by the city in 1952, which has been coterminous with the county since 1854. |
|||
The city uses the "strong-mayor" version of the [[mayor-council]] form of government, which is headed by one [[mayor]], in whom executive authority is vested. Elected "[[at-large]]," the mayor is limited to two consecutive four-year terms under the city's [[home rule]] charter, but can run for the position again after an intervening term. The current city mayor, having taken office in January 2008, is [[Michael Nutter]], replacing [[John F. Street]] who served two terms from 1999 to the end of 2007. Nutter, as all Philadelphia mayors have been since 1952, is a member of the [[United States Democratic Party|Democratic Party]], which tends to dominate local politics so thoroughly that the Democratic primary for mayor is often more noticeable than the general mayoral election. The legislative branch, the [[Philadelphia City Council]], consists of ten council members representing individual districts and seven members elected at large. The current council president is [[Anna C. Verna]]. |
|||
The Philadelphia County [[Court of Common Pleas (United States)|Court of Common Pleas]], also known as the Court of Common Pleas for the First Judicial District of Pennsylvania, is the [[trial court]] of general jurisdiction for Philadelphia. It is funded and operated largely by city resources and employees. The Philadelphia Municipal Court handles matters of limited jurisdiction as well as landlord-tenant disputes, appeals from traffic court, preliminary hearings for felony-level offenses, and the like. [[Traffic Court]] is a court of special jurisdiction that hears violations of traffic laws. |
|||
Pennsylvania's three [[appellate court]]s also have sittings in Philadelphia. The [[Supreme Court of Pennsylvania]], the court of last resort in the state, regularly hears arguments in [[Philadelphia City Hall]]. Also, the [[Superior Court of Pennsylvania]] and the [[Commonwealth Court of Pennsylvania]] sit in Philadelphia several times a year. Judges for these courts are elected at large. Each court has a [[prothonotary]]'s office in Philadelphia as well. |
|||
The [[Philadelphia Historical Commission]] was created in 1955 to preserve the cultural, social, political, economic and architectural history of the city. The commission maintains the [[Philadelphia Register of Historic Places]], adding historic buildings, structures, sites, objects and districts as it sees fit.<ref name="PNC">[http://www.phila.gov/historical Philadelphia Historical Commission]</ref> |
|||
The [[Philadelphia Housing Authority]] is the largest landlord in the entire Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. Established in 1937, it is the nation’s fourth-largest housing authority, housing approximately 84,000 people and employing 1,250. In 2006, its budget was $313 million.<ref name="PHA">[http://www.pha.phila.gov Philadelphia Housing Authority]</ref> |
|||
===Politics and elections=== |
|||
{{seealso|List of mayors of Philadelphia}} |
|||
{| align="right" border="2" cellpadding="4" cellspacing="0" style="margin: 1em 1em 1em 0; border: 1px #aaa solid; border-collapse: collapse; font-size: 95%;" |
|||
|+ '''Presidential election results''' |
|||
|- bgcolor=#D3D3D3 |
|||
! Year |
|||
! [[Republican Party (United States)|Republican]] |
|||
! [[Democratic Party (United States)|Democratic]] |
|||
|- |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|[[U.S. presidential election, 2004|2004]] |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#fff3f3"|19.3% ''130,099 |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|'''80.4%''' ''542,205 |
|||
|- |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|[[U.S. presidential election, 2000|2000]] |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#fff3f3"|18.0% ''100,959 |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|'''80.0%''' ''449,182 |
|||
|- |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|[[U.S. presidential election, 1996|1996]] |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#fff3f3"|16.0% ''85,345 |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|'''77.5%''' ''412,988 |
|||
|- |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|[[U.S. presidential election, 1992|1992]] |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#fff3f3"|20.9% ''133,328 |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|'''68.2%''' ''434,904 |
|||
|- |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|[[U.S. presidential election, 1988|1988]] |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#fff3f3"|32.5% ''219,053 |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|'''66.6%''' ''449,566 |
|||
|- |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|[[U.S. presidential election, 1984|1984]] |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#fff3f3"|34.6% ''267,178 |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|'''64.9%''' ''501,369 |
|||
|- |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|[[U.S. presidential election, 1980|1980]] |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#fff3f3"|34.0% ''244,108 |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|'''58.7%''' ''421,253 |
|||
|- |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|[[U.S. presidential election, 1976|1976]] |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#fff3f3"|32.0% ''239,000 |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|'''66.3%''' ''494,579 |
|||
|- |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|[[U.S. presidential election, 1972|1972]] |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#fff3f3"|43.4% ''340,096 |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|'''55.1%''' ''431,736 |
|||
|- |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|[[U.S. presidential election, 1968|1968]] |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#fff3f3"|30.0% ''254,153 |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|'''61.8%''' ''525,768 |
|||
|- |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|[[U.S. presidential election, 1964|1964]] |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#fff3f3"|26.2% ''239,733 |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|'''73.4%''' ''670,645 |
|||
|- |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|[[U.S. presidential election, 1960|1960]] |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#fff3f3"|31.8% ''291,000 |
|||
|align="center" bgcolor="#f0f0ff"|'''68.0%''' ''622,544 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|style="text-align: center" colspan="2"| [[Image:761insig.png]] |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
As of November 2007, there are 992,696 registered voters in Philadelphia.<ref>{{PDFlink|[http://www.dos.state.pa.us/elections/lib/elections/055_voter_registration_statistics/2007nov.pdf Commonwealth of Pennsylvania Voter Registration Statistics, Nov. 2007]|10.6 KB}}</ref> |
|||
'''USS ''Springfield'' (SSN-761)''', a [[Los Angeles class submarine|''Los Angeles''-class submarine]], is the fourth ship of the [[United States Navy]] to bear that name. The earlier ''Springfield''s were named for differing reasons; SSN-761 was specifically named for [[Springfield, Illinois]] and [[Springfield, Massachusetts]]. |
|||
* [[Democratic Party (United States)|Democratic]]: 749,652 (75.52%) |
|||
The contract to build her was awarded to the [[Electric Boat]] Division of [[General Dynamics]] Corporation in [[Groton, Connecticut]] on 21 March 1986 and her keel was laid down on 29 January 1990. She was [[ship naming and launching|launched]] on 4 January 1992 sponsored by the Honorable Lynn Martin, and [[ship commissioning|commissioned]] on 9 January 1993, with Commander Richard K. Ford in command. ''Springfield'' is homeported in Naval Submarine Base, [[Groton, Connecticut]]. |
|||
* [[Republican Party (United States)|Republican]]: 150,477 (15.16%) |
|||
* Other Parties: 92,567 (9.32%) |
|||
From the [[American Civil War]] until the mid-20th century, Philadelphia was a bastion of the [[Republican Party (United States)|Republican Party]], which arose from the staunch pro-Northern views of Philadelphia residents during and after the war. After the [[Great Depression]], Democratic registrations increased, but the city was not carried by Democratic [[Franklin D. Roosevelt]] in his landslide victory of 1932 (in which Pennsylvania was one of the few states won by Republican [[Herbert Hoover]]). While other Northern industrial cities were electing Democratic mayors in the 1930s and 1940s, Philadelphia did not follow suit until 1951. That is, Philadelphia never had a "New Deal" coalition. |
|||
Beginning in mid-2004, ''Springfield'' began an extensive overhaul and modernization period at [[Electric Boat]] shipyard in [[Groton, Connecticut]]. In addition to normal periodic maintenance and repairs, ''Springfield'' received extensive modernization in fire control systems, [[sonar]] processing, weapons launch systems, and communications outfit, a [[ring laser gyro]] inertial navigation system, as well as stealth improvements and engine room upgrades. The modernization was the first major overhaul and repair job for Electric Boat in almost 25 yrs. [http://www.nstcenter.org/docs/PDFs/MR2006_Fleet_004SkipCastroFleetForces.pdf] Originally awarded as a 12 month, $26.3M Depot Modernization, ''Springfield'' was to be the test case for the possibility of awarding future repair and overhaul contracts to Electric Boat. [http://www.gdeb.com/news/2003archives.html] The overhaul was plagued by cost and time over-runs and when finally completed in December 2005, it was several months late and well over budget. Electric Boat has not been awarded any DMP contracts since. |
|||
The city is now one of the most Democratic in the country, despite the frequent election of Republicans to statewide offices since the 1930s; in 2004, Democrat [[John Kerry]] drew 80% of the city's vote. |
|||
''Springfield'' has recently returned from an overseas deployment in support of the [[War on Terrorism|Global War on Terror]] (September 2006 to March 2007). |
|||
Philadelphia once comprised six [[congressional district]]s. However, as a result of the city's declining population, it now has only four: [[Pennsylvania's 1st congressional district|the 1st district]], represented by [[Bob Brady]]; [[Pennsylvania's 2nd congressional district|the 2nd]], represented by [[Chaka Fattah]]; [[Pennsylvania's 8th congressional district|the 8th]], represented by [[Patrick Murphy (politician)|Patrick Murphy]]; and [[Pennsylvania's 13th congressional district|the 13th]], represented by [[Allyson Schwartz]]. All four are Democrats; no Republican has represented a significant portion of Philadelphia since 1983. However, Pennsylvania's Republican [[United States Senate|Senator]], [[Arlen Specter]], is from Philadelphia. |
|||
== Awards == |
|||
As of 2008 ''Springfield'' has deployed overseas seven times and earned three meritorious unit commendations. It has also earned several Battle "E" efficiency awards. Recently it has been awarded the retention excellence award for its squadron. The ship received the [[Arleigh Burke]] fleet trophy in 2003. The ship received the 1998 Captain Edward F. Ney Silver Cup Trophy from the International Food Service Executives Association for the Best Restaurant Worldwide. The ''Springfield'' has also won multiple awards for Navigation, Engineering, Medical, Supply, Damage Control and Deck Seamanship excellence. |
|||
== |
===Crime=== |
||
{{main|Crime in Philadelphia}} |
|||
* [http://www.nvr.navy.mil/nvrships/details/SSN761.htm Naval Vessel Register entry for USS ''Springfield''] |
|||
Like many American cities, Philadelphia saw a gradual yet pronounced rise in crime in the years following [[World War II]]. Murders peaked in 1990 at 525, for a rate of 31.5 per 100,000. There were an average of about 400 murders a year for most of the 1990s. The murder count dropped in 2002 to 288, then surged four years later to 406.<ref>{{cite journal |quotes= |last=Bewley |first=Joel |coauthors=Jan Hefler |year=2006 |month=December 11 |title=Four killings put 2006 total over '05 top |journal=The Philadelphia Inquirer |url=http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_kmtpi/is_200612/ai_n16975780 }}</ref> Out of the ten most populous cities in the United States in 2006, Philadelphia had the highest homicide rate at 28 per 100,000 people, though the number of murders decreased to 392 in 2007.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://inquirer.philly.com/graphics/homicide_map_2007/ |title=Philadelphia Homicides in 2007}}</ref> |
|||
* [http://www.gdeb.com/news/ General Dynamics Electric Boat Corporation News] |
|||
* [http://www.fas.org/man/dod-101/sys/ship/ssn-688.htm Federation of American Scientists entry for Los Angeles class submarines] |
|||
==References== |
|||
{{DANFSNVR}} |
|||
In 2004, there were 5,513.5 crimes per 100,000 people in Philadelphia.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://philadelphia.areaconnect.com/crime1.htm |title=Philadelphia PA Crime Statistics (2005 Crime Data) |accessdate=2006-12-11 |work=AreaConnect LLC }}</ref> In 2005, Philadelphia was ranked by [[Morgan Quitno]] as the sixth-most dangerous among 32 American cities with populations over 500,000. Among its neighboring Mid-Atlantic cities in the same population group, [[Baltimore, Maryland|Baltimore]] and [[Washington, D.C.]] were ranked second- and third-most dangerous cities in the United States, respectively, and [[Camden, New Jersey|Camden]], [[New Jersey]], a suburb across the Delaware River from Philadelphia, was ranked as the most dangerous city in the United States.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://morganquitno.com/cit06pop.htm#25 |title=Rankings by Population Group (Top 10/Bottom 10)|accessdate=2006-12-11 |work=Morgan Quitno Awards}}</ref> |
|||
{{Los Angeles class submarine}} |
|||
In 2006, Camden was the fifth-most dangerous city in the country, lower than its 2004 ranking, but still high for a city its size, while Philadelphia was ranked 29th.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.philly.com/dailynews/opinion/20070328_Death___taxes_in_Philadelphia.html |title=Death & taxes in Philadelphia |accessdate=2007-04-02}}</ref> |
|||
On September 12, 2007, police commissioner Sylvester Johnson called on 10,000 [[African American]] men to patrol the streets to lessen crime. Johnson, who is a black, set up "Call to Action: 10,000 Men, It's a New Day" in response to the city's disproportionate homicide rate of young African Americans. Dennis Muhammad, [[Nation of Islam]] official, and Mayor John F. Street supported the project. The program was to begin on October 21.<ref>[http://www.nydailynews.com/news/wn_report/2007/09/14/2007-09-14_black_men_urged_to_help_philadelphia_pol.html?ref=rssnydailynews.com, Black men urged to help Philadelphia police to reduce crime ]</ref> |
|||
==Education== |
|||
{{main|Education in Philadelphia}}[[Image:Penn campus 2.jpg|250px|right|thumb|[[University of Pennsylvania]]]][[Image:Barbelin tower.JPG|thumb|left|[[Saint Joseph's University]]]] |
|||
[[Education]] in Philadelphia is provided by many private and public institutions. The [[School District of Philadelphia]] runs the city's [[public school]]s. The Philadelphia School District is the eighth largest [[school district]] in the United States with 210,432 students in 346 public and charter schools.<ref>{{cite news|url= http://www.philsch.k12.pa.us/aboutus |title=Philadelphia School District - About Us |publisher= Philadelphia School District |accessdate=2007-03-23}}</ref> |
|||
Philadelphia is one of the largest [[college town]]s in the United States and has the second-largest student concentration on the East Coast with over 120,000 college and university students enrolled within the city and nearly 300,000 in the metropolitan area. There are over 80 colleges, universities, trade, and specialty schools in the Philadelphia region. The city contains three major research universities: the [[University of Pennsylvania]], [[Drexel University]], and [[Temple University]]. Other institutions of higher learning within the city's borders include [[Saint Joseph's University]], [[La Salle University]], [[Peirce College]], [[University of the Sciences in Philadelphia]], [[The University of the Arts]], [[Pennsylvania Academy of Fine Arts]], the [[Curtis Institute of Music]], [[Thomas Jefferson University]], [[Moore College of Art and Design]], [[The Art Institute of Philadelphia]], [[Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine]], [[Philadelphia University]], [[Chestnut Hill College]], [[Holy Family University, Pennsylvania|Holy Family University]], the [[Community College of Philadelphia]] and [[Messiah College|Messiah College Philadelphia Campus]]. |
|||
==Infrastructure== |
|||
[[Image:Philly 30th St. Station.jpg|thumb|right|30th Street Station, with [[Cira Centre]] in the background and statues on the Market Street Bridge over [[Schuylkill River]] in the foreground.]] |
|||
Philadelphia is served by the Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority ([[SEPTA]]), which operates [[bus]]es, [[train]]s, [[rapid transit]], [[tram|trolley]]s, and [[trolleybus|trackless trolleys]] throughout Philadelphia, the four Pennsylvania [[suburb]]an counties of [[Bucks County, Pennsylvania|Bucks]], [[Chester County, Pennsylvania|Chester]], [[Delaware County, Pennsylvania|Delaware]], and [[Montgomery County, Pennsylvania|Montgomery]], in addition to service to [[Mercer County, New Jersey]] and [[New Castle County, Delaware]]. The city's subway system, first opened in 1907, is the third oldest in America. |
|||
SEPTA's [[R1 (SEPTA)|R1]] Regional Rail line offers direct service to the [[Philadelphia International Airport]]. |
|||
Philadelphia's [[30th Street Station (Philadelphia)|30th Street Station]] is a major [[railroad]] station on [[Amtrak]]'s [[Northeast Corridor]], which offers access to Amtrak, SEPTA, and [[New Jersey Transit]] lines. |
|||
The [[PATCO speedline]] provides [[rapid transit]] service to [[Camden, New Jersey|Camden]], [[Collingswood, New Jersey|Collingswood]], [[Westmont, New Jersey|Westmont]], [[Haddonfield, New Jersey|Haddonfield]], [[Cherry Hill, New Jersey|Woodcrest (Cherry Hill)]], [[Voorhees, New Jersey|Ashland (Voorhees)]], and [[Lindenwold, New Jersey|Lindenwold]], [[New Jersey]], from stations on Locust Street between 16th and 15th, 13th and 12th, and 10th and 9th Streets, and on Market Street at 8th Street. |
|||
===Airports=== |
|||
Two airports serve Philadelphia: the [[Philadelphia International Airport]] (PHL), straddling the southern boundary of the city, and the [[Northeast Philadelphia Airport]] (PNE), a general aviation reliever airport in [[Northeast Philadelphia]]. Philadelphia International Airport provides scheduled domestic and international air service, while Northeast Philadelphia Airport serves general and corporate aviation. As of March 2006, Philadelphia International Airport was the 10th largest airport measured by "traffic movements" (i.e. takeoffs and landings), and was also a primary hub for [[US Airways]].<ref>[http://www.aci.aero/cda/aci/display/main/aci_content.jsp?zn=aci&cp=1-5-54-57_9_2__ Airports Council International]</ref> |
|||
===Roads=== |
|||
[[Image:Schuylkill Expressway Sept 2007.jpg|thumb|right|The [[Schuylkill Expressway]], approaching [[Center City, Philadelphia|Center City]] from the North.]] |
|||
[[Interstate 95 in Pennsylvania|Interstate 95]] runs through the city along the Delaware River as a main north-south artery. The city is also served by the [[Schuylkill Expressway]], a portion of [[Interstate 76 (east)|Interstate 76]] that runs along the [[Schuylkill River]]. It meets the [[Pennsylvania Turnpike]] at [[King of Prussia, Pennsylvania]], providing access to [[Harrisburg, Pennsylvania]] and points west. [[Interstate 676]], the [[Vine Street Expressway]], was completed in 1991 after years of planning. A link between I-95 and I-76, it runs below street level through Center City, connecting to the [[Ben Franklin Bridge]] at its eastern end. |
|||
[[Roosevelt Boulevard (Philadelphia)|Roosevelt Boulevard]] and the [[Roosevelt Expressway (Philadelphia)|Roosevelt Expressway]] ([[U.S. Route 1 in Pennsylvania|U.S. 1]]) connect [[Northeast Philadelphia]] with Center City. Woodhaven Road ([[Pennsylvania Route 63|PA Route 63]]), built in 1966, serves the neighborhoods of [[Northeast Philadelphia]], running between [[Interstate 95 in Pennsylvania|Interstate 95]] and the Roosevelt Boulevard ([[U.S. Route 1 in Pennsylvania|U.S. 1]]). The Fort Washington Expressway ([[Pennsylvania Route 309]]) extends north from the city's northern border, serving [[Montgomery County, Pennsylvania|Montgomery County]] and [[Bucks County, Pennsylvania|Bucks County]] |
|||
[[Interstate 476]], commonly nicknamed the "Blue Route" through [[Delaware County, Pennsylvania|Delaware County]], bypasses the city to the west, serving the city's western suburbs, as well as providing a link to [[Allentown, Pennsylvania|Allentown]] and points north. Similarly, [[Interstate 276]], the Pennsylvania Turnpike's Delaware River Extension, acts as a bypass and commuter route to the north of the city as well as a link to the [[New Jersey Turnpike]] to [[New York]]. |
|||
However, other planned [[freeway]]s have been canceled, such as an [[Interstate 695 (Pennsylvania)|Interstate 695]] running southwest from downtown, two freeways connecting [[Interstate 95 in Pennsylvania|Interstate 95]] to [[Interstate 76 (east)|Interstate 76]] that would have replaced Girard Avenue and South Street and a freeway upgrade of [[Roosevelt Boulevard]]. |
|||
The [[Delaware River Port Authority]] operates four bridges in the Philadelphia area across the [[Delaware River]] to [[New Jersey]]: the [[Walt Whitman Bridge]] (I-76), the [[Benjamin Franklin Bridge]] (I-676 and [[U.S. Route 30 in Pennsylvania|US 30]]), the [[Betsy Ross Bridge]] ([[New Jersey Route 90|Route 90]]), and the [[Commodore Barry Bridge]] ([[U.S. Highway 322|US 322]]). The [[Tacony-Palmyra Bridge]] connects [[Pennsylvania Route 73|PA Route 73]] in the [[Tacony]] section of [[Northeast Philadelphia]] with New Jersey's [[New Jersey Route 73|Route 73]] in [[Palmyra, New Jersey|Palmyra]], [[Camden County, New Jersey|Camden County]], and is maintained by the [[Burlington County Bridge Commission]]. |
|||
Philadelphia is also a major hub for [[Greyhound Lines]], which operates 24-hour service to points east of the [[Mississippi River]]. Most of Greyhound's services in Philadelphia operate to/from the [[Philadelphia Greyhound Terminal]], located at 1001 Filbert Street in Center City Philadelphia. In 2006, the Philadelphia Greyhound Terminal was the second busiest Greyhound terminal in the United States, after the [[Port Authority Bus Terminal]] in New York. Besides Greyhound, six other bus operators provide service to the Center City Greyhound terminal. These are [[Bieber Tourways]], [[Capitol Trailways]], [[Martz Trailways]], [[Peter Pan Bus Lines]], [[Susquehanna Trailways]], and the [[New Jersey Transit Bus Operations|bus division for New Jersey Transit]]. |
|||
[[Image:Suburban Station Facade.jpg|thumb|Suburban Station]] |
|||
[[Image:PhiladelphiaSubwayStationMarketFrankford.jpg|thumb|140px|Market-Frankford Line entrance in Old City]] |
|||
===Rail=== |
|||
{{main|History of rail transport in Philadelphia}} |
|||
Since the early days of [[rail transport in the United States]], Philadelphia has served as hub for several major rail companies, particularly the [[Pennsylvania Railroad]] and the [[Reading Railroad]]. The Pennsylvania Railroad first operated [[Broad Street Station (Philadelphia)|Broad Street Station]], then [[30th Street Station (Philadelphia)|30th Street Station]] and [[Suburban Station (Philadelphia)|Suburban Station]], and the Reading Railroad operated out of [[Reading Terminal]], now part of the [[Pennsylvania Convention Center]]. The two companies also operated competing commuter rail systems in the area, known collectively as the Regional Rail system. The two systems today, for the most part still intact but now connected, operate as a single system under the control of the [[Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority|SEPTA]], the regional transit authority. Additionally, Philadelphia is linked to Southern [[New Jersey]] via the [[PATCO speedline]] subway system. |
|||
Philadelphia is one of the few North American cities to maintain [[streetcar]] lines. In addition to "subway-surface" trolleys—which are so called because during the years when the city was served by over 2000 trolleys and more than 65 lines, these "surface" cars also ran in the streetcar subway—the city recently reintroduced trolley service to the [[Route 15 (SEPTA)|Girard Avenue Line]], Route 15, considered by some a "heritage" line. The use of rebuilt [[PCC streetcar|1947 PCC streetcars]] was primarily for budgetary reasons, rather than as a historic tribute. |
|||
Today, Philadelphia is a hub of the semi-nationalized [[Amtrak]] system, with 30th Street Station being a primary stop on the Washington-Boston [[Northeast Corridor]] and the [[Keystone Corridor]] to [[Harrisburg, Pennsylvania|Harrisburg]] and [[Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania|Pittsburgh]], [[Pennsylvania]]. 30th Street also serves as a major station for services via the Pennsylvania Railroad's former [[Pennsylvania Main Line]] to [[Chicago]]. 30th Street is Amtrak's third-busiest station in numbers of passengers as of [[fiscal year]] 2003. It is also a terminus of [[New Jersey Transit]]'s [[Atlantic City Line]].<ref>{{PDFlink|http://www.njtransit.com/pdf/rail/r0090.pdf|218 KB}}</ref> |
|||
===Telecommunications=== |
|||
Southeastern Pennsylvania was once served only by the [[area code 215|215]] [[area code]], beginning in 1947 when the [[North American Numbering Plan]] of the "[[Bell System]]" went into effect. The area covered by the code was severely truncated when [[area code 610]] was split from 215. Today only the city and its northern suburbs are covered by 215. An [[area code overlay|overlay area code]], 267, was added to the 215 service area in 1997. A plan to introduce [[area code 445]] as an additional overlay in 2001 was delayed and later rescinded.<ref>{{PDFlink|[http://www.nanpa.com/pdf/PL_332_v1.pdf PA 445 Implementation for 215/267 NPA Rescinded — 445 NPA Code Reclaimed]|64.5 KB}}</ref> |
|||
Philadelphia is now also served by Wireless Philadelphia, a citywide initiative to provide [[Wi-Fi]] service. The Proof of Concept area was approved on [[May 23]], [[2007]], and service is now available in many areas of the city. |
|||
==Sister cities== |
|||
[[Image:Philadelphia skyline from south street bridge.jpg|thumb|300px|right|Philadelphia skyline as seen from the [[South Street (Philadelphia)|South Street]] Bridge in November 2007]] |
|||
Philadelphia has ten [[town twinning|sister cities]], as designated by the [http://www.ivc.org/sister_cities International Visitors Council of Philadelphia (IVC)]: |
|||
{| cellpadding="4" |
|||
|- valign="top" |
|||
| |
|||
*{{flagicon|ITA}} [[Florence]], [[Italy]] (1964) |
|||
*{{flagicon|ISR}} [[Tel Aviv]], [[Israel]] (1966) |
|||
*{{flagicon|POL}} [[Toruń]], [[Poland]] (1976) |
|||
*{{flagicon|PRC}} [[Tianjin]], [[People's Republic of China|China]] (1980) |
|||
*{{flagicon|KOR}} [[Incheon]], [[South Korea]] (1984) |
|||
|| |
|||
*{{flagicon|CMR}} [[Douala]], [[Cameroon]] (1986) |
|||
*{{flagicon|JPN}} [[Kobe]], [[Japan]] (1986) |
|||
*{{flagicon|RUS}} [[Nizhny Novgorod]], [[Russia]] (1992) |
|||
*{{flagicon|ITA}} [[Abruzzo]], [[Italy]] (1997) |
|||
*{{flagicon|FRA}} [[Aix-en-Provence]], [[France]] (1999) |
|||
|} |
|||
Philadelphia has dedicated landmarks to its sister cities. Dedicated in June 1976, the Sister Cities Plaza, a one-half-acre site located at 18th and Benjamin Franklin Parkway, honors Philadelphia's relationships with [[Tel Aviv]] and [[Florence]] which were its first Sister Cities. Another landmark, the Torun Triangle, honoring the Sister City relationship with [[Toruń]], [[Poland]], was constructed in 1976, west of the [[United Way of America|United Way]] building at 18th Street and the Benjamin Franklin Parkway. The Triangle contains the Copernicus monument. The Chinatown Gate, erected in 1984 and crafted by artisans of [[Tianjin, China]], stands astride the intersection of 10th and Arch Streets as an elaborate and colorful symbol of the Sister City relationship. |
|||
{{Geolinks-US-cityscale|39.953333|-75.17}} |
|||
==See also== |
|||
*[[2007 Philadelphia Mayoral Election]] |
|||
*[[Largest metropolitan areas in the Americas]] |
|||
*[[List of people from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania]] |
|||
*[[Pennsylvania Dutch Country]] |
|||
*[[United States metropolitan areas]] |
|||
*[[Philadelphia Lawyer (song)]] |
|||
==References== |
|||
{{reflist|2}} |
|||
==External links== |
|||
{{sisterlinks|Philadelphia}} |
|||
*[http://www.phila.gov Official Philadelphia government website] |
|||
*[http://www.phillyhistory.org/PhotoArchive Philadelphia history at Philly History] |
|||
*[http://www.philadelphiaCFA.org Philadelphia Center for Architecture] |
|||
*[http://www.philadelphiabuildings.org Philadelphia Architects and Buildings] |
|||
*[http://www.philadelphiausa.travel Philadelphia Convention & Visitors Bureau] |
|||
*[http://www.ushistory.org ushistory.org from the Independence Hall Association] |
|||
*[http://www.philly.com/mld/philly/ Philly.com, home page of ''The Philadelphia Inquirer'' and ''Philadelphia Daily News''] |
|||
*[http://cml.upenn.edu/nbase/ neighborhoodBase] Statistical mapping system for Philadelphia run by the [[University of Pennsylvania]] |
|||
*[http://www.ppdonline.org/hq_statistics.php Philadelphia Police Department] |
|||
*[http://www.gophila.com Greater Philadelphia Tourism Marketing Corporation] |
|||
{{Philadelphia}} |
|||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Springfield (SSN-761)}} |
|||
{{Pennsylvania}} |
|||
[[Category:Los Angeles class submarines]] |
|||
{{Location of US capital}} |
|||
[[Category:United States Navy nuclear ships]] |
|||
{{USLargestCities}} |
|||
[[Category:United States Navy Illinois-related ships]] |
|||
{{USLargestMetros}} |
|||
[[Category:United States Navy Massachusetts-related ships]] |
|||
{{World's most populated urban areas}} |
|||
[[Category:Ships built in Connecticut]] |
|||
{{AllAmericanCity}} |
|||
{{County Seats of Pennsylvania}} |
|||
{{ALA(library)}} |
|||
[[Category:Cities in Pennsylvania]] |
|||
[[Category:Greek loanwords]] |
|||
[[Category:Philadelphia, Pennsylvania| ]] |
|||
[[Category:Settlements established in 1682]] |
|||
[[Category:Former capitals of the United States]] |
|||
[[Category:Former United States state capitals|Pennsylvania]] |
|||
[[Category:Delaware Valley]] |
|||
[[Category:Port settlements in the United States]] |
|||
{{Link FA|fr}} |
|||
{{US-mil-ship-stub}} |
|||
[[af:Philadelphia]] |
|||
[[de:USS Springfield (SSN-761)]] |
|||
[[ar:فيلادلفيا، بنسيلفانيا]] |
|||
[[ja:スプリングフィールド (原子力潜水艦)]] |
|||
[[be:Горад Філадэльфія]] |
|||
[[be-x-old:Філядэльфія]] |
|||
[[bs:Philadelphia]] |
|||
[[bg:Филаделфия]] |
|||
[[ca:Filadèlfia]] |
|||
[[cs:Filadelfie]] |
|||
[[cy:Philadelphia]] |
|||
[[da:Philadelphia]] |
|||
[[pdc:Filidelfi]] |
|||
[[de:Philadelphia]] |
|||
[[et:Philadelphia]] |
|||
[[el:Φιλαδέλφεια (ΗΠΑ)]] |
|||
[[es:Filadelfia]] |
|||
[[eo:Filadelfio (Pensilvanio)]] |
|||
[[eu:Philadelphia]] |
|||
[[fa:فیلادلفیا]] |
|||
[[fo:Philadelphia]] |
|||
[[fr:Philadelphie]] |
|||
[[gl:Filadelfia]] |
|||
[[ko:필라델피아]] |
|||
[[hy:Ֆիլադելֆիա]] |
|||
[[hr:Philadelphia, Pennsylvania]] |
|||
[[bpy:ফিলাডেলফিয়া]] |
|||
[[id:Philadelphia, Pennsylvania]] |
|||
[[ia:Philadelphia, Pennsylvania]] |
|||
[[os:Филадельфи]] |
|||
[[is:Philadelphia]] |
|||
[[it:Filadelfia (Pennsylvania)]] |
|||
[[he:פילדלפיה]] |
|||
[[pam:Philadelphia]] |
|||
[[ka:ფილადელფია]] |
|||
[[kw:Philadelphia]] |
|||
[[ky:Филадельфия]] |
|||
[[ht:Philadelphia, Pennsilvani]] |
|||
[[ku:Philadelphia]] |
|||
[[la:Philadelphia]] |
|||
[[lv:Filadelfija]] |
|||
[[lt:Filadelfija]] |
|||
[[hu:Philadelphia]] |
|||
[[mk:Филаделфија]] |
|||
[[ml:ഫിലഡെല്ഫിയ]] |
|||
[[nl:Philadelphia (Pennsylvania)]] |
|||
[[ja:フィラデルフィア]] |
|||
[[no:Philadelphia]] |
|||
[[nn:Philadelphia]] |
|||
[[pms:Filadelfia (Pennsylvania)]] |
|||
[[pl:Filadelfia]] |
|||
[[pt:Filadélfia]] |
|||
[[ro:Philadelphia, Pennsylvania]] |
|||
[[ru:Филадельфия]] |
|||
[[simple:Philadelphia, Pennsylvania]] |
|||
[[sk:Philadelphia]] |
|||
[[sl:Filadelfija, Pensilvanija]] |
|||
[[sr:Филаделфија (САД)]] |
|||
[[sh:Philadelphia]] |
|||
[[fi:Philadelphia]] |
|||
[[sv:Philadelphia]] |
|||
[[ta:பிலடெல்பியா]] |
|||
[[th:ฟิลาเดลเฟีย]] |
|||
[[vi:Philadelphia, Pennsylvania]] |
|||
[[tr:Philadelphia, Pensilvanya]] |
|||
[[uk:Філадельфія]] |
|||
[[vo:Philadelphia]] |
|||
[[wuu:费城]] |
|||
[[zh:費城]] |
|||
Revision as of 06:15, 13 October 2008
Template:Otheruses6 sucks
Philadelphia | |
|---|---|
City | |
| The City of Philadelphia | |
 Philadelphia skyline, August 2007 | |
| Nickname(s): "City of Brotherly Love","The City that Loves you Back", "Cradle of Liberty", "The Quaker City", "The Birthplace of America", "Philly" | |
| Motto: "Philadelphia maneto" - "Let brotherly love endure" | |
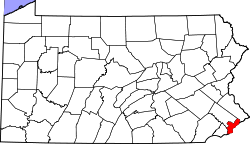 Location in Pennsylvania | |
 | |
| Country | |
| Commonwealth | |
| County | Philadelphia |
| Founded | October 27 1682 |
| Incorporated | October 25 1701 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Michael Nutter (D) |
| Area | |
| • City | 350 km2 (135 sq mi) |
| • Land | 326.144 km2 (127.4 sq mi) |
| • Water | 19.6 km2 (7.6 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 4,660.7 km2 (1,799.5 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 11,989 km2 (4,629 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 12 m (39 ft) |
| Population (July 1st, 2007) | |
| • City | 1,449,634 (6th) |
| • Density | 4,201.8/km2 (10,882.8/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 5,325,000 |
| • Metro | 5,823,233 |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (EST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) |
| Area code(s) | 215, 267 |
| Website | http://www.phila.gov |
Philadelphia (Template:PronEng) is the largest city in Pennsylvania and the sixth most populous city in the United States. It is the fifth largest metropolitan area and fourth largest urban area by population in the United States, the nation's fourth largest consumer media market as ranked by the Nielsen Media Research, and the 49th most populous city in the world. It is the county seat of Philadelphia County. A popular nickname for Philadelphia is The City of Brotherly Love (from Greek: Φιλαδέλφεια, [pʰi.la.ˈdel.pʰeː.a], Modern Greek: [fi.la'ðɛl.fi.a], "brotherly love" from philos, "love", and adelphos "brother"). The city is recognized as a strong candidate global city.
In 2005, the population of the city proper was estimated to be over 1.4 million,[1] while the Greater Philadelphia metropolitan area, with a population of 5.8 million, was the fifth-largest in the United States. A commercial, educational, and cultural center, the city was once the second-largest in the British Empire[2] (after London), and the social and geographical center of the original 13 American colonies. During the 18th century, it eclipsed New York City in political and social importance, with Benjamin Franklin taking a large role in Philadelphia's early rise to prominence. It was in this city that some of the ideas, and subsequent actions, gave birth to the American Revolution and American Independence, making Philadelphia a centerpiece of early American history. It was the most populous city of the young United States and served as the the nation's second capital in 1774.
History
Prior to the arrival of Europeans, the Philadelphia area was the location of the Lenape (Delaware) Indian village Shackamaxon. Europeans arrived in the Delaware Valley in the early 1600s, with the first settlements founded by the Dutch, British and Swedish.
The Swedes sought to expand their influence by creating an agricultural (tobacco) and fur-trading colony to bypass French and British merchants. The New Sweden Company was chartered and included Swedish, Dutch and German stockholders. The first Swedish expedition to North America embarked from the port of Gothenburg in late 1637. It was organized and overseen by Clas Fleming, a Swedish admiral from Finland. Part of this colony, called New Sweden or Nya Sverige eventually included land on the west side of the Delaware River from just below the Schuylkill River: in other words, today's Philadelphia, southeast Pennsylvania, Delaware, and Maryland.
In 1644, New Sweden supported the Susquehannocks in their victory in a war against the English province of Maryland. A series of events led the Dutch — led by governor Peter Stuyvesant — to move an army to the Delaware River in the late summer of 1655. Though New Netherland now nominally controlled the colony, the Swedish and Finnish settlers continued to enjoy a degree of local autonomy, having their own militia, religion, court, and lands. This status lasted officially until the English conquest of the New Netherland colony, in October 1663-1664, and continued unofficially until the area was included in William Penn's charter for Pennsylvania, in 1682.
In 1681, as part of a repayment of a debt, Charles II of England granted William Penn a charter for what would become the Pennsylvania colony. Part of Penn's plan for the colony was to create a city on the Delaware River to serve as a port and place for government. Despite already having been given the land by Charles II, Penn bought the land from the local Lenape to be on good terms with the Native Americans and ensure peace for his colony.[3] According to legend Penn made a treaty of friendship with Lenape chief Tammany under an elm tree at Shackamaxon, in what is now the city's Kensington section.[4] As a Quaker, Penn had experienced religious persecution and wanted his colony to be a place where anyone could worship freely despite their religion. Penn named the city Philadelphia, which is Greek for brotherly love (philos, "love" or "friendship", and adelphos, "brother").[5]
William Penn's plan was that Philadelphia would be like an English rural town instead of a city. The city's roads were designed with a grid plan with the idea that houses and businesses would be spread far apart and surrounded by gardens and orchards. The city's inhabitants didn't follow Penn's plans and crowded by the Delaware River and subdivided and resold their lots.[6] Before Penn left Philadelphia for the last time, he issued the Charter of 1701 establishing Philadelphia as a city. The city soon grew and established itself as an important trading center. Conditions in the city were poor at first, but by the 1750s living conditions had improved. A significant contributor to Philadelphia at the time was Benjamin Franklin. Franklin helped improve city services and founded new ones, such as the American Colonies' first hospital.[7] Due to Philadelphia's central location in the colonies, during the American Revolution the city was used as the location for the First Continental Congress before the war, the Second Continental Congress, which signed the United States Declaration of Independence, during the war, and the Constitutional Convention after the war. A number of battles during the war were fought in Philadelphia and its environs as well. Unsuccessful lobbying after the war to make Philadelphia the United States capital helped make the city the temporary U.S. capital in the 1790s.[8]

The state government left Philadelphia in 1799 and the federal government left soon after in 1800. However Philadelphia was still the largest city in the United States and a financial and cultural center. New York City soon surpassed Philadelphia in population, but construction of roads, canals, and railroads helped turn Philadelphia into the United States' first major industrial city. Throughout the 19th century Philadelphia had a large variety of industries and businesses, the largest being textiles. Major corporations in the 19th and early 20th centuries included the Baldwin Locomotive Works, William Cramp and Sons Ship and Engine Building Company, and the Pennsylvania Railroad.[9] Industry, along with the U.S. Centennial, was celebrated in 1876 with the Centennial Exposition, the first official World's Fair in the United States. Immigrants, mostly German and Irish, settled in Philadelphia and the surrounding districts. The rise in population of the surrounding districts helped lead to the Act of Consolidation of 1854 which extended the city of Philadelphia to include all of Philadelphia County.[10] In the later half of the century immigrants from Russia, Eastern Europe and Italy and African Americans from the southern U.S. settled in the city.[11]

By the 20th century Philadelphia had become known as "corrupt and contented." Philadelphians were content with the city's lack of change or excitement, and single-party politics, centered on the city's entrenched Republican political machine, allowed corruption to flourish. The machine and corruption permeated in all parts of city government and reformers had little success.[12] The first major success in reform came in 1917 when outrage over the murder of a police officer during that year's election led to the shrinking of the Philadelphia City Council from two houses to just one.[13] In the 1920s the public flouting of Prohibition laws, mob violence, and police involvement in illegal activities led to the appointment of Brigadier General Smedley Butler of the U.S. Marine Corps as director of public safety, but political pressure prevented any long term success in fighting crime and corruption.[14]
After struggling through the Great Depression, World War II created jobs and brought the city out of the Depression. However, after the war there was a severe housing shortage with about half the city's housing being built in the 19th century, many of which lacked proper facilities. Adding to housing problem was white flight, as African Americans and Puerto Ricans moved into new neighborhoods resulting in racial tension.[15] After a population peak of over two million residents in 1950 the city's population declined while the suburban neighboring counties grew. After a five year investigation into corruption into city government, the outcry with what the investigation found led the drafting of a new city charter in 1950. The city charter strengthened the position of the mayor and weakened the city council among other changes to help prevent the corruption of the past. The first Democratic mayor since the first half of the 19th century was elected in 1951. However, after two early reform mayors, a Democratic political organization had established itself replacing the old Republican one.[16]
Protests, riots and racial tensions were common in the 1960s and 70s. Mostly drug related gang violence plagued the city. In the mid 1980s, crack houses invaded the city's slums. Confrontations between police and the radical group MOVE culminated when the police dropped a satchel bomb on their headquarters starting a fire that killed eleven MOVE members and destroyed sixty-two neighboring houses. Revitalization and gentrification of neighborhoods began in the 1960s and continues into the 21st century, with much of the development in the Center City and University City areas of the city. After many of the old manufacturers and businesses had left Philadelphia or shut down, the city started attracting service businesses and began to more aggressively market itself as a tourist destination. Glass and granite skyscrapers were built in Center City. Historic areas such as Independence National Historical Park located in Society Hill were resuscitated during the reformist mayoral era of the 1950s through the 1980s and are now among the most desirable living areas of Center City. This has slowed the city's forty-year population decline after losing nearly a quarter of its population.[17][18]
Geography
Topography

Philadelphia is located at 40° 00′ north latitude and 75° 09′ west longitude. According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 142.6 square miles (369.3 km2), of which 135.1 square miles (349.9 km2) is land and 7.6 square miles (19.7 km2), or 5.29%, is water. Bodies of water include the Delaware and Schuylkill Rivers, and Cobbs, Wissahickon, and Pennypack Creeks.
The lowest point is sea level, while the highest point is in Chestnut Hill, at approximately 445 feet (136 m) above sea level (near the intersection of Germantown Avenue and Bethlehem Pike).[19]
Philadelphia is located on the Fall Line separating the Atlantic Coastal Plain from the Piedmont.[20] The rapids on the Schuylkill River at East Falls disappeared after the completion of the Fairmount Dam.[21]
The city is the seat of its own county. The adjacent counties are Montgomery to the north; Bucks to the northeast; Burlington County, New Jersey to the east; Camden County, New Jersey to the southeast; Gloucester County, New Jersey to the south; and Delaware County to the west.
Climate
Philadelphia falls in the humid subtropical climate zone. Summers are typically hot and muggy, fall and spring are generally mild, and winter is cold. Snowfall is variable, with some winters bringing moderate snow and others bringing some significant snowstorms. Annual snowfall averages 21 inches (534 mm). Precipitation is generally spread throughout the year, with eight to eleven wet days per month,[22] at an average annual rate of 42 inches (1068 mm).
January lows average 25 °F (−4 °C) and highs average 39 °F (4 °C). The lowest officially recorded temperature was −11 °F (−24 °C) on February 9, 1934,[23] but temperatures below 0 °F (−18 °C) occur only a few times a decade. July lows average 70 °F (21 °C) and highs average 86 °F (30 °C),[24] although heat waves accompanied by high humidity are frequent with highs above 95 °F (35 °C) and the heat index running as high as 110 °F (43 °C). The highest recorded temperature was 106 °F (41 °C) on August 7 1918.[25] Early fall and late winter are generally driest, with February being the driest month, averaging only 2.74 inches (69.8 mm) of precipitation.
| Climate data for Philadelphia | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Source: The Weather Channel[26] | |||||||||||||
Cityscape
Neighborhoods
Philadelphia has many neighborhoods, each with its own identity. The large Philadelphia sections, North, Northeast, Northwest, West, South and Southwest Philadelphia surround Center City, which falls within the original city limits prior to consolidation in 1854. Numerous smaller neighborhoods within the areas coincide with the boroughs, townships, and other communities that made up Philadelphia County before their absorption by the city. Other neighborhoods formed based on ethnicity, religion, culture, and commercial reasons.[27]
Architecture

Philadelphia's architectural history dates back to Colonial times and includes a wide range of styles. The earliest structures were constructed with logs, but brick structures were common by 1700. During the 18th century, the cityscape was dominated by Georgian architecture, including Independence Hall. In the first decades of the 19th century, Federal architecture and Greek Revival architecture were popular.[28] In the second half of the 19th century, Victorian architecture was common. In 1871, construction began on the Second Empire-style Philadelphia City Hall. Despite the construction of steel and concrete skyscrapers in the 1910s, '20s and '30s, the 548 ft (167 m) City Hall remained the tallest building in the city until 1987 when One Liberty Place was constructed. Numerous glass and granite skyscrapers were built from the late 1980s onwards. In 2007, the Comcast Center surpassed One Liberty Place to become the city's tallest building.[29]

For much of Philadelphia's history, the typical Philadelphia home has been the row house. The row house was introduced to the United States via Philadelphia in the early 1800s and, for a time, row houses built elsewhere in the United States were known as "Philadelphia rows".[30] There is a variety of row houses throughout the city from Victorian-style homes in North Philadelphia to twin row houses in West Philadelphia. While newer homes are scattered throughout the city, much of Philadelphia's housing is from the early 20th century or older. The age of the city's homes has created numerous problems which has led to blight and vacant lots in many parts of the city, while other neighborhoods such as Society Hill, which has the largest concentration of 18th-century architecture in the United States, have been rehabilitated and gentrified.[31][32]
Culture

Philadelphia contains many national historical sites that relate to the founding of the United States. Independence National Historical Park is the center of these historical landmarks. Independence Hall, where the Declaration of Independence was signed, and the Liberty Bell are the city's most famous attractions. Other historic sites include homes for Edgar Allan Poe, Betsy Ross, and Thaddeus Kosciuszko, early government buildings like the First and Second Banks of the United States, and the Gloria Dei (Old Swedes') Church National Historic Site.[33]
Philadelphia's major science museums include the Franklin Institute, which contains the Benjamin Franklin National Memorial, the Academy of Natural Sciences, and the University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology. History museums include the National Constitution Center, the Atwater Kent Museum of Philadelphia History, the National Museum of American Jewish History, the African American Museum in Philadelphia, the Historical Society of Pennsylvania, the Grand Lodge of Free and Accepted Masons in the state of Pennsylvania and The Masonic Library and Museum of Pennsylvania and Eastern State Penitentiary. Philadelphia is home to the United States' first zoo and hospital.
Arts
The city contains many art museums such as the Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts and the Rodin Museum, the largest collection of work by Auguste Rodin outside of France. The city’s major art museum, the Philadelphia Museum of Art, is one of the largest art museums in the United States and features the steps made popular by the film Rocky.[34]
The city is home to many art galleries, many of which participate in the First Friday event. The first Friday of every month galleries in Old City are open late. Annual events include film festivals and parades, the most famous being the New Year's Day Mummers Parade.
Areas such as South Street and Old City have a vibrant night life. The Avenue of the Arts in Center City contains many restaurants and theaters, such as the Kimmel Center for the Performing Arts, which is home to the Philadelphia Orchestra, and the Academy of Music, the nation's oldest continually operating venue, home to the Opera Company of Philadelphia.[34]

Philadelphia has more public art than any other American city.[35] In 1872, the Fairmount Park Art Association was created, the first private association in the United States dedicated to integrating public art and urban planning.[36] In 1959, lobbying by the Artists Equity Association helped create the Percent for Art ordinance, the first for a U.S. city.[37] The program, which has funded more than 200 pieces of public art, is administered by the Philadelphia Office of Arts and Culture, the city's art agency.[38]
In particular, Philadelphia has more murals than any other U.S. city, thanks in part to the 1984 creation of the Department of Recreation's Mural Arts Program, which seeks to beautify neighborhoods and provide an outlet for graffiti artists. The program has funded more than 2,700 murals by professional, staff and volunteer artists.[39]
Philadelphia has had a prominent role in music. In the 1970s, Philadelphia soul influenced the music of that and later eras. On July 13 1985, Philadelphia hosted the American end of the Live Aid concert at John F. Kennedy Stadium. The city reprised this role for the Live 8 concert, bringing some 700,000 people to the Ben Franklin Parkway on July 2 2005.[40]
Cuisine
The city is known for its hoagies, scrapple, soft pretzels, water ice, and is home to the cheesesteak. Its high-end restaurants include Morimoto, run by chef Masaharu Morimoto, who rose to prominence on the Iron Chef television show.
Sports
Philadelphia has a long history of professional sports teams, and is one of thirteen U.S. cities to have all four major sports: the Philadelphia Eagles of the National Football League, the Philadelphia Flyers of the National Hockey League, the Philadelphia Phillies in the National League of Major League Baseball, and the Philadelphia 76ers in the National Basketball Association. The last major professional sport team to win a championship was the 76ers, which won the NBA Championship in 1983. Due to the length of this streak without winning a sports championship, in 2004 ESPN ranked Philadelphia as number two in its list of The Fifteen Most Tortured Sports Cities.[41] The failure of Philadelphia's major professional sports teams to win championships since that date is sometimes attributed, in jest, to the so-called "Curse of Billy Penn". The Oakland Athletics and Golden State Warriors were originally from Philadelphia.
Philadelphia also is home to professional, semi-professional and elite amateur teams in other sports, including cricket. Philadelphia also hosts other major sporting events, including the Penn Relays, Stotesbury Cup, Philadelphia Marathon, and Philadelphia International Championship bicycle race, and the Dad Vail Regatta.
Philadelphia is also known for the Philadelphia Big 5, a group of five Division I college basketball programs: Big 5 are Saint Joseph's University, University of Pennsylvania, La Salle University, Temple University, and Villanova University. The sixth NCAA Division I school in Philadelphia is Drexel University. At least one of the teams is competitive nearly every year and at least one team has made the NCAA tournament for the past four decades.
In February 2008, Philadelphia beat out competition from several other cities, namely St. Louis, to be awarded the 16th Major League Soccer franchise. They will enter the league in 2010 calling Chester Stadium their home (a soccer specific stadium) in Chester, PA.
Philadelphia is also home to New Alhambra Arena, the birthplace of Extreme Championship Wrestling and current home to multiple wrestling and boxing promotions.
Economy

Philadelphia's economy is relatively diversified, with meaningful portions of its total output derived from manufacturing, oil refining, food processing, health care and biotechnology, tourism and financial services. According to a study prepared by PricewaterhouseCoopers, Philadelphia and its surrounding region had the fourth highest GDP among American cities, with a total "city GDP" of $312 billion in 2005.[42] Only New York, Los Angeles and Chicago had higher total economic output levels.
The city is home to the Philadelphia Stock Exchange and several Fortune 500 companies, including cable television and internet provider Comcast, insurance companies CIGNA and Lincoln Financial Group, energy company Sunoco, food services company Aramark, Crown Holdings Incorporated, chemical makers Rohm and Haas Company and FMC Corporation, pharmaceutical companies Wyeth and GlaxoSmithKline, Boeing helicopters division, and automotive parts retailer Pep Boys. Early in the 20th Century, it was also home to the pioneering brass era automobile company Biddle.[43]
The federal government has several facilities in Philadelphia as well. The city served as the capital city of the United States, before the construction of Washington, D.C. Today, the East Coast operations of the United States Mint are based near the historic district, and the Federal Reserve Bank's Philadelphia division is based there as well. Philadelphia is also home to the U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of Pennsylvania and the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Third Circuit.
Partly because of the historical presence of the Pennsylvania Railroad, and the large ridership at 30th Street Station, Amtrak also maintains a significant presence in the city. These jobs include customer service representatives and ticket processing and other behind-the-scenes personnel, in addition to the normal functions of the railroad.

The city is also a national center of law because of the University of Pennsylvania Law School, Earle Mack School of Law[44], Temple University Beasley School of Law, Villanova University School of Law, and Widener University School of Law. Additionally, the headquarters of the American Law Institute is located in the city.
Philadelphia is also an important center for medicine, a distinction that it has held since the colonial period. The city is home to the first hospital in the British North American colonies, Pennsylvania Hospital, and the first medical school in what is now the United States, at the University of Pennsylvania (Penn). Penn, the city's largest private employer, also runs a large teaching hospital and extensive medical system. There are also major hospitals affiliated with Temple University School of Medicine, Drexel University College of Medicine, and Thomas Jefferson University. Philadelphia also has three distinguished children's hospitals: Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, the nation's first pediatric hospital (located adjacent to the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania), St. Christopher's Hospital, and the Shriners' Hospital. In the city's northern section are Albert Einstein Hospital, and in the northeast section, Fox Chase Cancer Center. Together, healthcare is the largest sector of employment in the city. Several medical professional associations are headquartered in Philadelphia.
In part because of Philadelphia's long-running importance as a center for medical research, the region is a major center for the pharmaceutical industry. GlaxoSmithKline, AstraZeneca, Wyeth, Merck, GE Healthcare, Johnson and Johnson and Siemens Medical Solutions are just some of the large pharmaceutical companies with operations in the region. The city is also home to the nation's first school of pharmacy, the Philadelphia College of Pharmacy, now called the University of the Sciences in Philadelphia.
Shopping

Center City is home to The Gallery at Market East, The Shops at Liberty Place and The Shops at the Bellevue, and a variety of standalone retail stores. Rittenhouse Row, a section of Walnut Street in Center City, has higher-end stores and boutiques. Old City and Society Hill, as well, feature upscale boutiques and retailers from local and international merchandisers. Philadelphia also has several neighborhood shopping districts, including Manayunk and Chestnut Hill. Also noteworthy is South Street with blocks of inexpensive boutiques.
The Italian Market in South Philadelphia offers groceries, meats, cheeses and housewares from Italy and other countries. Geno's and Pat's, two famed cheesesteak outlets, are located here. The Reading Terminal Market in Center City includes dozens of restaurants, farm stalls, and shops, many run by Amish farmers from Lancaster County. There are also neighborhood farmers' markets throughout the city.
There are also several large shopping malls in the region, including Franklin Mills in Northeast Philadelphia and King of Prussia Mall in King of Prussia, Pennsylvania; seven miles outside of Philadelphia. Franklin Mills offers shoppers tax-free clothing and shoes due to its location within the city's boundaries and saw an estimated 18 million visitors in 2006. The King of Prussia Mall is the largest shopping mall on the East Coast of the United States,[45] and the largest shopping mall in the country in terms of leasable retail space.
Philadelphia is the birthplace of the secondary ticket marketplace. Wanamaker Ticket Office, located in Center City, is among the nation's oldest ticket agencies.
Media
Philadelphia's two major daily newspapers are The Philadelphia Inquirer and the Philadelphia Daily News, both of which are owned by Philadelphia Media Holdings L.L.C. The Philadelphia Inquirer, founded in 1829, is the third-oldest surviving daily newspaper in the United States.[46] The Bulletin, another newspaper that operates in Philadelphia, traces its history back to The Philadelphia Bulletin that went defunct in 1982. The Bulletin is locally owned by The Bulletin, Inc.

The first experimental radio license was issued in Philadelphia in August, 1912 to St. Joseph's College. The first commercial radio stations appeared in 1922. WIP, then owned by Gimbel's department store, became the first on March 17 of that year. Also launched that year were WFIL, WOO, WCAU and WDAS.[47] The highest-rated stations in Philadelphia include soft rock WBEB, KYW Newsradio, and urban adult contemporary WDAS-FM.
During the 1930s, the experimental station W3XE, which was owned by Philco Corp, became the first television station in Philadelphia. The station, which would later become KYW-TV (CBS), became NBC's first affiliate in 1939. By the 1970s WCAU-TV, WPVI-TV, WHYY-TV, WPHL-TV, and WTXF-TV were founded.[47] In 1952 WFIL (now WPVI), premiered the television show Bandstand, which later became the nationally broadcast show American Bandstand hosted by Dick Clark.[48] Today, as in many large metropolitan areas, each of the commercial networks has an affiliate, and call letters have been replaced by corporate IDs: CBS3, 6ABC, NBC10, FOX29, Telefutura28, Telemundo62, Univision65, plus My PHL 17 and CW Philly 57. On the public media side, the Philadelphia region is served by WYBE-TV (Philadelphia), WHYY-TV (Wilmington, Delaware and Philadelphia), WLVT-TV (Lehigh Valley), and New Jersey Network. In September, 2007, Philadelphia approved a public access cable channel. On the radio side, Philadelphia is served by three large public radio stations, plus several smaller ones; the larger ones are WHYY-FM (NPR), WRTI (jazz, classical), and WXPN-FM (adult alternative music).
Philadelphia has a competitive rock radio market, especially between WMMR and WYSP, which both specialize in playing modern and classic rock. The two stations enjoy a very intense rivalry. Since 2005, WMMR has played more music due to a shift in WYSP's programming from a rock station (which also carried controversial shock jock Howard Stern) to a Free FM station. WYSP has since returned to the classic rock format it shed in 1995. Until early 2008, WYSP also carried live radio broadcasts of all Philadelphia Eagles home and road games. WMMR has the top rated morning show in the Philadelphia area, The Preston and Steve Show, which has been at the top of the ratings since Howard Stern left for Sirius Radio. WYSP currently does not have a competing morning talk show.
Philadelphia's four urban stations (WUSL ("Power 99"), WPHI ("100.3 The Beat"), WDAS and WRNB) are popular choices on the FM dial. WNUW is the city's Adult Contemporary station. The station had been home of "Smooth Jazz" WJJZ after the format was dropped from the 106.1 frequency (now WISX) but the format was dropped once again due to poor ratings.
Innovation
Philadelphia is home to many "first-in-America" institutions, including:[49][50] Template:MultiCol
- Fire insurance company
- Botanical garden
- Public library
- Hospital
- Fire engine
- Fire company
- Medical school
- Pharmacy School
- Pennsylvania Hospital
- Pediatric hospital
- Cancer hospital
- Eye hospital
- University
| class="col-break " |
- Art school & museum
- Municipal water system
- Post office
- Bank
- Stock exchange
- Mint
- Zoo
- Electronic Computer
- Savings Bank
- ECW
- First Title Insurance Company in America
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1790 | 28,522 | — | |
| 1800 | 41,220 | 44.5% | |
| 1810 | 53,722 | 30.3% | |
| 1820 | 63,802 | 18.8% | |
| 1830 | 80,462 | 26.1% | |
| 1840 | 93,665 | 16.4% | |
| 1850 | 121,376 | 29.6% | |
| 1860 | 565,529 | 365.9% | |
| 1870 | 674,022 | 19.2% | |
| 1880 | 847,170 | 25.7% | |
| 1890 | 1,046,964 | 23.6% | |
| 1900 | 1,293,697 | 23.6% | |
| 1910 | 1,549,008 | 19.7% | |
| 1920 | 1,823,779 | 17.7% | |
| 1930 | 1,950,961 | 7.0% | |
| 1940 | 1,931,334 | −1.0% | |
| 1950 | 2,071,605 | 7.3% | |
| 1960 | 2,002,512 | −3.3% | |
| 1970 | 1,948,609 | −2.7% | |
| 1980 | 1,688,210 | −13.4% | |
| 1990 | 1,585,577 | −6.1% | |
| 2000 | 1,517,550 | −4.3% | |
| 2007 (est.) | 1,449,634 |
As of the censusTemplate:GR of 2000, there were 1,517,550 people, 590,071 households, and 352,272 families residing in the city. The population density was 11,233.6/square mile (4,337.3/km²). There were 661,958 housing units at an average density of 4,900.1/sq mi (1,891.9/km²). As of the 2004 Census estimations, there were 1,463,281 people, 658,799 housing units, and the racial makeup of the city was 45.2% African American, 43.0% White, 5.5% Asian, 0.3% Native American, 0.1% Pacific Islander, 5.8% from other races, and 2.2% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 8.5% of the population. The top 5 largest ancestries include Irish (13.6%), Italian (9.2%), German (8.1%), Polish (4.3%), and English (2.9%).[51]
Of the 590,071 households, 27.6% have children under the age of 18 living with them, 32.1% were married couples living together, 22.3% had a female householder with no husband present, and 40.3% were non-families. 33.8% of all households were made up of individuals and 11.9% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.48 and the average family size was 3.22.
In the city the population was spread out with 25.3% under the age of 18, 11.1% from 18 to 24, 29.3% from 25 to 44, 20.3% from 45 to 64, and 14.1% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 34 years. For every 100 females there were 86.8 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 81.8 males.
The median income for a household in the city was $30,746, and the median income for a family was $37,036. Males had a median income of $34,199 versus $28,477 for females. The per capita income for the city was $16,509. About 18.4% of families and 22.9% of the population were below the poverty line, including 31.3% of those under age 18 and 16.9% of those age 65 or over.
Philadelphia has the second largest Irish, Italian, and Jamaican populations and the fourth largest African American population in the nation. Philadelphia also has the fourth largest population of Polish residents. In recent years, the Hispanic and Asian American populations have significantly increased. Hispanics have settled throughout the city, especially around El Centro de Oro, and the city now has the third largest Puerto Rican population in the continental United States. The Asian population was once concentrated in the city's thriving Chinatown, but now Korean Americans have come to Olney, and Vietnamese have forged bazaars next to the Italian Market in South Philadelphia. Concentrations of Cambodian American neighborhoods can be found in North and South Philadelphia. Indians and Arabs have come to Northeast Philadelphia along with Russian and Ukrainian immigrants. This large influx of Asians has given Philadelphia one of the largest populations of Vietnamese, Cambodians, Chinese, and Koreans in United States. The Philadelphia region also has the fourth largest population of Indian Americans. The West Indian population is concentrated in Cedar Park. Germans, Greeks, Chinese, Japanese, English, Pakistanis, Iranians, and also immigrants from the former Yugoslavia along with other ethnic groups can be found throughout the city.
Government

From a governmental perspective, Philadelphia County is a legal nullity, as all county functions were assumed by the city in 1952, which has been coterminous with the county since 1854.
The city uses the "strong-mayor" version of the mayor-council form of government, which is headed by one mayor, in whom executive authority is vested. Elected "at-large," the mayor is limited to two consecutive four-year terms under the city's home rule charter, but can run for the position again after an intervening term. The current city mayor, having taken office in January 2008, is Michael Nutter, replacing John F. Street who served two terms from 1999 to the end of 2007. Nutter, as all Philadelphia mayors have been since 1952, is a member of the Democratic Party, which tends to dominate local politics so thoroughly that the Democratic primary for mayor is often more noticeable than the general mayoral election. The legislative branch, the Philadelphia City Council, consists of ten council members representing individual districts and seven members elected at large. The current council president is Anna C. Verna.
The Philadelphia County Court of Common Pleas, also known as the Court of Common Pleas for the First Judicial District of Pennsylvania, is the trial court of general jurisdiction for Philadelphia. It is funded and operated largely by city resources and employees. The Philadelphia Municipal Court handles matters of limited jurisdiction as well as landlord-tenant disputes, appeals from traffic court, preliminary hearings for felony-level offenses, and the like. Traffic Court is a court of special jurisdiction that hears violations of traffic laws.
Pennsylvania's three appellate courts also have sittings in Philadelphia. The Supreme Court of Pennsylvania, the court of last resort in the state, regularly hears arguments in Philadelphia City Hall. Also, the Superior Court of Pennsylvania and the Commonwealth Court of Pennsylvania sit in Philadelphia several times a year. Judges for these courts are elected at large. Each court has a prothonotary's office in Philadelphia as well.
The Philadelphia Historical Commission was created in 1955 to preserve the cultural, social, political, economic and architectural history of the city. The commission maintains the Philadelphia Register of Historic Places, adding historic buildings, structures, sites, objects and districts as it sees fit.[52]
The Philadelphia Housing Authority is the largest landlord in the entire Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. Established in 1937, it is the nation’s fourth-largest housing authority, housing approximately 84,000 people and employing 1,250. In 2006, its budget was $313 million.[53]
Politics and elections
| Year | Republican | Democratic |
|---|---|---|
| 2004 | 19.3% 130,099 | 80.4% 542,205 |
| 2000 | 18.0% 100,959 | 80.0% 449,182 |
| 1996 | 16.0% 85,345 | 77.5% 412,988 |
| 1992 | 20.9% 133,328 | 68.2% 434,904 |
| 1988 | 32.5% 219,053 | 66.6% 449,566 |
| 1984 | 34.6% 267,178 | 64.9% 501,369 |
| 1980 | 34.0% 244,108 | 58.7% 421,253 |
| 1976 | 32.0% 239,000 | 66.3% 494,579 |
| 1972 | 43.4% 340,096 | 55.1% 431,736 |
| 1968 | 30.0% 254,153 | 61.8% 525,768 |
| 1964 | 26.2% 239,733 | 73.4% 670,645 |
| 1960 | 31.8% 291,000 | 68.0% 622,544 |
As of November 2007, there are 992,696 registered voters in Philadelphia.[54]
- Democratic: 749,652 (75.52%)
- Republican: 150,477 (15.16%)
- Other Parties: 92,567 (9.32%)
From the American Civil War until the mid-20th century, Philadelphia was a bastion of the Republican Party, which arose from the staunch pro-Northern views of Philadelphia residents during and after the war. After the Great Depression, Democratic registrations increased, but the city was not carried by Democratic Franklin D. Roosevelt in his landslide victory of 1932 (in which Pennsylvania was one of the few states won by Republican Herbert Hoover). While other Northern industrial cities were electing Democratic mayors in the 1930s and 1940s, Philadelphia did not follow suit until 1951. That is, Philadelphia never had a "New Deal" coalition.
The city is now one of the most Democratic in the country, despite the frequent election of Republicans to statewide offices since the 1930s; in 2004, Democrat John Kerry drew 80% of the city's vote.
Philadelphia once comprised six congressional districts. However, as a result of the city's declining population, it now has only four: the 1st district, represented by Bob Brady; the 2nd, represented by Chaka Fattah; the 8th, represented by Patrick Murphy; and the 13th, represented by Allyson Schwartz. All four are Democrats; no Republican has represented a significant portion of Philadelphia since 1983. However, Pennsylvania's Republican Senator, Arlen Specter, is from Philadelphia.
Crime
Like many American cities, Philadelphia saw a gradual yet pronounced rise in crime in the years following World War II. Murders peaked in 1990 at 525, for a rate of 31.5 per 100,000. There were an average of about 400 murders a year for most of the 1990s. The murder count dropped in 2002 to 288, then surged four years later to 406.[55] Out of the ten most populous cities in the United States in 2006, Philadelphia had the highest homicide rate at 28 per 100,000 people, though the number of murders decreased to 392 in 2007.[56]
In 2004, there were 5,513.5 crimes per 100,000 people in Philadelphia.[57] In 2005, Philadelphia was ranked by Morgan Quitno as the sixth-most dangerous among 32 American cities with populations over 500,000. Among its neighboring Mid-Atlantic cities in the same population group, Baltimore and Washington, D.C. were ranked second- and third-most dangerous cities in the United States, respectively, and Camden, New Jersey, a suburb across the Delaware River from Philadelphia, was ranked as the most dangerous city in the United States.[58]
In 2006, Camden was the fifth-most dangerous city in the country, lower than its 2004 ranking, but still high for a city its size, while Philadelphia was ranked 29th.[59]
On September 12, 2007, police commissioner Sylvester Johnson called on 10,000 African American men to patrol the streets to lessen crime. Johnson, who is a black, set up "Call to Action: 10,000 Men, It's a New Day" in response to the city's disproportionate homicide rate of young African Americans. Dennis Muhammad, Nation of Islam official, and Mayor John F. Street supported the project. The program was to begin on October 21.[60]
Education


Education in Philadelphia is provided by many private and public institutions. The School District of Philadelphia runs the city's public schools. The Philadelphia School District is the eighth largest school district in the United States with 210,432 students in 346 public and charter schools.[61]
Philadelphia is one of the largest college towns in the United States and has the second-largest student concentration on the East Coast with over 120,000 college and university students enrolled within the city and nearly 300,000 in the metropolitan area. There are over 80 colleges, universities, trade, and specialty schools in the Philadelphia region. The city contains three major research universities: the University of Pennsylvania, Drexel University, and Temple University. Other institutions of higher learning within the city's borders include Saint Joseph's University, La Salle University, Peirce College, University of the Sciences in Philadelphia, The University of the Arts, Pennsylvania Academy of Fine Arts, the Curtis Institute of Music, Thomas Jefferson University, Moore College of Art and Design, The Art Institute of Philadelphia, Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine, Philadelphia University, Chestnut Hill College, Holy Family University, the Community College of Philadelphia and Messiah College Philadelphia Campus.
Infrastructure

Philadelphia is served by the Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority (SEPTA), which operates buses, trains, rapid transit, trolleys, and trackless trolleys throughout Philadelphia, the four Pennsylvania suburban counties of Bucks, Chester, Delaware, and Montgomery, in addition to service to Mercer County, New Jersey and New Castle County, Delaware. The city's subway system, first opened in 1907, is the third oldest in America.
SEPTA's R1 Regional Rail line offers direct service to the Philadelphia International Airport.
Philadelphia's 30th Street Station is a major railroad station on Amtrak's Northeast Corridor, which offers access to Amtrak, SEPTA, and New Jersey Transit lines.
The PATCO speedline provides rapid transit service to Camden, Collingswood, Westmont, Haddonfield, Woodcrest (Cherry Hill), Ashland (Voorhees), and Lindenwold, New Jersey, from stations on Locust Street between 16th and 15th, 13th and 12th, and 10th and 9th Streets, and on Market Street at 8th Street.
Airports
Two airports serve Philadelphia: the Philadelphia International Airport (PHL), straddling the southern boundary of the city, and the Northeast Philadelphia Airport (PNE), a general aviation reliever airport in Northeast Philadelphia. Philadelphia International Airport provides scheduled domestic and international air service, while Northeast Philadelphia Airport serves general and corporate aviation. As of March 2006, Philadelphia International Airport was the 10th largest airport measured by "traffic movements" (i.e. takeoffs and landings), and was also a primary hub for US Airways.[62]
Roads

Interstate 95 runs through the city along the Delaware River as a main north-south artery. The city is also served by the Schuylkill Expressway, a portion of Interstate 76 that runs along the Schuylkill River. It meets the Pennsylvania Turnpike at King of Prussia, Pennsylvania, providing access to Harrisburg, Pennsylvania and points west. Interstate 676, the Vine Street Expressway, was completed in 1991 after years of planning. A link between I-95 and I-76, it runs below street level through Center City, connecting to the Ben Franklin Bridge at its eastern end.
Roosevelt Boulevard and the Roosevelt Expressway (U.S. 1) connect Northeast Philadelphia with Center City. Woodhaven Road (PA Route 63), built in 1966, serves the neighborhoods of Northeast Philadelphia, running between Interstate 95 and the Roosevelt Boulevard (U.S. 1). The Fort Washington Expressway (Pennsylvania Route 309) extends north from the city's northern border, serving Montgomery County and Bucks County
Interstate 476, commonly nicknamed the "Blue Route" through Delaware County, bypasses the city to the west, serving the city's western suburbs, as well as providing a link to Allentown and points north. Similarly, Interstate 276, the Pennsylvania Turnpike's Delaware River Extension, acts as a bypass and commuter route to the north of the city as well as a link to the New Jersey Turnpike to New York.
However, other planned freeways have been canceled, such as an Interstate 695 running southwest from downtown, two freeways connecting Interstate 95 to Interstate 76 that would have replaced Girard Avenue and South Street and a freeway upgrade of Roosevelt Boulevard.
The Delaware River Port Authority operates four bridges in the Philadelphia area across the Delaware River to New Jersey: the Walt Whitman Bridge (I-76), the Benjamin Franklin Bridge (I-676 and US 30), the Betsy Ross Bridge (Route 90), and the Commodore Barry Bridge (US 322). The Tacony-Palmyra Bridge connects PA Route 73 in the Tacony section of Northeast Philadelphia with New Jersey's Route 73 in Palmyra, Camden County, and is maintained by the Burlington County Bridge Commission.
Philadelphia is also a major hub for Greyhound Lines, which operates 24-hour service to points east of the Mississippi River. Most of Greyhound's services in Philadelphia operate to/from the Philadelphia Greyhound Terminal, located at 1001 Filbert Street in Center City Philadelphia. In 2006, the Philadelphia Greyhound Terminal was the second busiest Greyhound terminal in the United States, after the Port Authority Bus Terminal in New York. Besides Greyhound, six other bus operators provide service to the Center City Greyhound terminal. These are Bieber Tourways, Capitol Trailways, Martz Trailways, Peter Pan Bus Lines, Susquehanna Trailways, and the bus division for New Jersey Transit.


Rail
Since the early days of rail transport in the United States, Philadelphia has served as hub for several major rail companies, particularly the Pennsylvania Railroad and the Reading Railroad. The Pennsylvania Railroad first operated Broad Street Station, then 30th Street Station and Suburban Station, and the Reading Railroad operated out of Reading Terminal, now part of the Pennsylvania Convention Center. The two companies also operated competing commuter rail systems in the area, known collectively as the Regional Rail system. The two systems today, for the most part still intact but now connected, operate as a single system under the control of the SEPTA, the regional transit authority. Additionally, Philadelphia is linked to Southern New Jersey via the PATCO speedline subway system.
Philadelphia is one of the few North American cities to maintain streetcar lines. In addition to "subway-surface" trolleys—which are so called because during the years when the city was served by over 2000 trolleys and more than 65 lines, these "surface" cars also ran in the streetcar subway—the city recently reintroduced trolley service to the Girard Avenue Line, Route 15, considered by some a "heritage" line. The use of rebuilt 1947 PCC streetcars was primarily for budgetary reasons, rather than as a historic tribute.
Today, Philadelphia is a hub of the semi-nationalized Amtrak system, with 30th Street Station being a primary stop on the Washington-Boston Northeast Corridor and the Keystone Corridor to Harrisburg and Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. 30th Street also serves as a major station for services via the Pennsylvania Railroad's former Pennsylvania Main Line to Chicago. 30th Street is Amtrak's third-busiest station in numbers of passengers as of fiscal year 2003. It is also a terminus of New Jersey Transit's Atlantic City Line.[63]
Telecommunications
Southeastern Pennsylvania was once served only by the 215 area code, beginning in 1947 when the North American Numbering Plan of the "Bell System" went into effect. The area covered by the code was severely truncated when area code 610 was split from 215. Today only the city and its northern suburbs are covered by 215. An overlay area code, 267, was added to the 215 service area in 1997. A plan to introduce area code 445 as an additional overlay in 2001 was delayed and later rescinded.[64]
Philadelphia is now also served by Wireless Philadelphia, a citywide initiative to provide Wi-Fi service. The Proof of Concept area was approved on May 23, 2007, and service is now available in many areas of the city.
Sister cities

Philadelphia has ten sister cities, as designated by the International Visitors Council of Philadelphia (IVC):
|
Philadelphia has dedicated landmarks to its sister cities. Dedicated in June 1976, the Sister Cities Plaza, a one-half-acre site located at 18th and Benjamin Franklin Parkway, honors Philadelphia's relationships with Tel Aviv and Florence which were its first Sister Cities. Another landmark, the Torun Triangle, honoring the Sister City relationship with Toruń, Poland, was constructed in 1976, west of the United Way building at 18th Street and the Benjamin Franklin Parkway. The Triangle contains the Copernicus monument. The Chinatown Gate, erected in 1984 and crafted by artisans of Tianjin, China, stands astride the intersection of 10th and Arch Streets as an elaborate and colorful symbol of the Sister City relationship. Template:Geolinks-US-cityscale
See also
- 2007 Philadelphia Mayoral Election
- Largest metropolitan areas in the Americas
- List of people from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
- Pennsylvania Dutch Country
- United States metropolitan areas
- Philadelphia Lawyer (song)
References
- ^ 2005 listing of population estimates of U.S. cities by the United States Census Bureau Retrieved on October 8, 2006.
- ^ "Philadelphia, Pennsylvania". People and Places. National Geographic.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|accessmonthday=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ Brookes, Karin (2005). Zoë Ross (ed.). Insight Guides: Philadelphia and Surroundings (Second Edition (Updated) ed.). APA Publications. pp. page 21. ISBN 1585730262.
{{cite book}}:|pages=has extra text (help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Weigley RF et al (eds) (1982). Philadelphia: A 300-Year History. New York and London: W. W. Norton & Company. pp. pages 4 - 5. ISBN 0-393-01610-2.
{{cite book}}:|author=has generic name (help);|pages=has extra text (help) - ^ Avery, Ron (1999). A Concise History of Philadelphia. Philadelphia: Otis Books. pp. page 19. ISBN 0-9658825-1-9.
{{cite book}}:|pages=has extra text (help) - ^ Philadelphia: A 300-Year History, pages 7, 14 - 16
- ^ Insight Guides: Philadelphia and Surroundings, pages 24 - 25
- ^ Insight Guides: Philadelphia and Surroundings, pages 30 - 33
- ^ Philadelphia: A 300-Year History, pages 214, 218, 428 - 429
- ^ "A Brief History of Philadelphia". Philadelphia History. ushistory.org.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|accessmonthday=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - ^ Insight Guides: Philadelphia and Surroundings, pages 38 - 39
- ^ Philadelphia: A 300-Year History, pages 535, 537
- ^ Philadelphia: A 300-Year History, pages 563 - 564
- ^ Philadelphia: A 300-Year History, pages 578 - 581
- ^ Philadelphia: A 300-Year History, pages 669 - 670
- ^ A Concise History of Philadelphia, pages 75 - 76
- ^ Insight Guides: Philadelphia and Surroundings, pages 44 - 45
- ^ A Concise History of Philadelphia, page 78
- ^ "USGS Geography: The National Map".
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|accessmonthday=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) (Example coordinates of high point: Latitude: 40° 04′ 37″, Longitude: −75° 12′ 29″.) - ^ Railsback, Bruce. "The Fall Line." GEOL 1122: Earth's History of Global Change. University of Georgia Department of Geology.
- ^ "Philadelphia Neighborhoods and Place Names, A–K." Philadelphia Information Locator System.
- ^ "Average Days of Precipitation, .01 Inches or more". Retrieved 2006-07-28.
- ^ "Philadelphia Record Highs and Lows". Retrieved 2007-04-03.
- ^ "Climate Information for Philadelphia – Pennsylvania – Mid-Atlantic – United States – Climate Zone:". Retrieved 2007-04-03.
- ^ "Philadelphia Record Highs and Lows". Retrieved 2007-04-03.
- ^ "Monthly Averages for Philadelphia, PA". Weather.com. 2008. Retrieved 2008-09-27.
- ^ Insight Guides: Philadelphia and Surroundings, page 58
- ^ Philadelphia: A 300-Year History, page 11, 41, 174 - 175, 252 - 253
- ^ Holcomb, Henry J. (2007). "Comcast Center topped off". The Philadelphia Inquirer.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Philadelphia: A 300-Year History, page 251
- ^ Aitken, Joanne (June 3 - 19, 2004). "Breaking Ground". Philadelphia City Paper.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Mark Alan Hughes (June 1,2000). "Dirt Into Dollars; Converting Vacant Land Into Valuable Development". Retrieved 2007-07-24.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Listing of National Historic Landmarks by State (Pennsylvania)" (PDF). National Park Service. 2004.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|accessmonthday=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ a b Weeks, Jerome (2006). "Philly goes the distance". The Dallas Morning News.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|quotes=ignored (help) - ^ "Public Art". Greater Philadelphia Tourism Marketing Corporation. Retrieved 2007-10-16.
- ^ Aitken, Joanne (2004). "Forget Paris". City paper.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|quotes=ignored (help) - ^ Wetenhall, John. "About A Brief History of Percent-For-Art in America" (PDF). Public Art Review. Retrieved 2006-09-24.
- ^ "Office of Art and Culture". Phila.gov. Retrieved 2006-09-24.
- ^ "Mural Arts Program About page". Retrieved 2007-11-27.
- ^ Rodney Kim (July 2,2005). "Live 8 Philadelphia Review". Retrieved 2007-04-24.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ ESPN.com: Page 2 : What caused Philly's curse?
- ^ City Mayors reviews the richest cities in the world in 2005
- ^ Clymer, p.176.
- ^ Drexel College Of Law
- ^ [1]
- ^ Wilkinson, Gerry. "The History of the Philadelphia Inquirer". Philadelphia Press Association. Retrieved 2006-07-20.
- ^ a b Bishop, Todd (2000). "The Media: One revolution after another". Philadelphia Business Journal.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|quotes=ignored (help) - ^ Ogden, Christopher (1999). Legacy: A Biography of Moses and Walter Annenberg. New York: Little, Brown and Company. ISBN 0-316-63379-8.
- ^ Philadelphia Firsts 1681-1899, ushistory.org
- ^ Philadelphia Firsts, about.com
- ^ http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/QTTable?_bm=y&-geo_id=16000US4260000&-qr_name=DEC_2000_SF3_U_QTP13&-ds_name=DEC_2000_SF3_U
- ^ Philadelphia Historical Commission
- ^ Philadelphia Housing Authority
- ^ Template:PDFlink
- ^ Bewley, Joel (2006). "Four killings put 2006 total over '05 top". The Philadelphia Inquirer.
{{cite journal}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|quotes=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ "Philadelphia Homicides in 2007".
- ^ "Philadelphia PA Crime Statistics (2005 Crime Data)". AreaConnect LLC. Retrieved 2006-12-11.
- ^ "Rankings by Population Group (Top 10/Bottom 10)". Morgan Quitno Awards. Retrieved 2006-12-11.
- ^ "Death & taxes in Philadelphia". Retrieved 2007-04-02.
- ^ Black men urged to help Philadelphia police to reduce crime
- ^ "Philadelphia School District - About Us". Philadelphia School District. Retrieved 2007-03-23.
- ^ Airports Council International
- ^ Template:PDFlink
- ^ Template:PDFlink
External links
- Official Philadelphia government website
- Philadelphia history at Philly History
- Philadelphia Center for Architecture
- Philadelphia Architects and Buildings
- Philadelphia Convention & Visitors Bureau
- ushistory.org from the Independence Hall Association
- Philly.com, home page of The Philadelphia Inquirer and Philadelphia Daily News
- neighborhoodBase Statistical mapping system for Philadelphia run by the University of Pennsylvania
- Philadelphia Police Department
- Greater Philadelphia Tourism Marketing Corporation

