Savoy

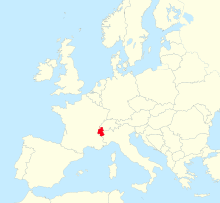
Savoy ( French Savoie , Italian Savoia , Franco-Provençal Savouè ) is a landscape that today essentially extends to the French departments of Haute-Savoie and Savoie in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region.
Savoy lies between Switzerland , Piedmont and the Isère and Ain departments . The area is 10,416 km². In 2008 there were 1,125,119 inhabitants. Savoy is the highest landscape in Europe and consists mainly of the Savoy Alps (with the Mont Blanc , 4810 m ) and the Graian Alps (with the Grande Casse , 3855 m , and the Pointe de Charbonnel, 3752 m ) with the passes of the Kleiner St Bernhard and the Mont Cenis and borders in the south on the Cottian Alps (with the Aiguille de Scolette, 3506 m , and the Pic du Thabor , 3207 m ).
In addition to French , the population partly still speaks the Franco-Provencal language Arpitan . The inhabitants of Savoy are called Savoyards.
The lack of employment opportunities - it existed practically only agriculture ( milk - cheese - and meat production ) - forcing young Savoyards centuries of emigration . Today industry ( clocks , electronics ), tourism ( alpinism , winter sports ) also form the economic basis of the area.
History of Savoy
Antiquity to late antiquity
In Celtic times the area was inhabited by the Allobrogians . 121 BC The Romans subjugated it and united it with Gaul , from which they later formed the province of Alpes Graiae et Vallis Poeninae .
In 354, the country is known as Sapaudia (Celtic for 'woodland'). In 443 the Romans settled the Burgundians here after their empire on the Rhine was destroyed by the Huns .
Early Middle Ages to High Middle Ages
In 534 the Franks conquered the country.
In 838 the Sapaudia came to Upper Burgundy , then part from 934 to Kingdom of Burgundy and came in 1032 to the Holy Roman Empire .
During this time the land between the Rhône and the main Alpine ridge , Provence and Lake Geneva formed the county of Vienne , which had been given to the Archbishop of Vienne in 1023 ; the latter split off two fiefdoms from his new property, of which he entrusted the northern, Maurienne ( Chablais , the valley of the upper Isère and the upper Valais ), to Humbert I with the white hands ; shortly before (1025) he had acquired the Aosta Valley , his son got the margraviate Turin in his possession through marriage .
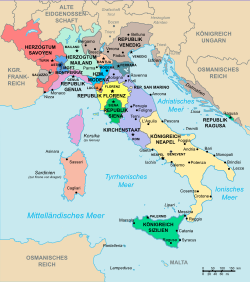
The new lords called themselves Counts of Savoy from 1125 and soon got rid of their ecclesiastical liege lords. After Pinerolo and Chambéry were acquired in 1232, the latter became the capital of Savoy. In 1268/1269 Savoy conquered Vaud .
Late Middle Ages to Early Modern Times
In 1310/1313 Savoy was elevated to the status of an imperial principality, in 1349 the Dauphiné in the south went to France, whereupon Emperor Charles IV in 1361 relieved Savoy from the old kingdom of Burgundy ( Arelat ) and made the count immediately imperial and in 1365 made the count as imperial vicar for Arelat.
In 1388 the county of Nice was acquired, in 1401 the county of Genevois , the Geneva region without the city of Geneva . In 1416 the Counts of Savoy were elevated to dukes. In 1512/1521 Savoy was formally admitted to the Upper Rhine Empire .
Since Francis I occupied Savoy in 1536 in the Third Italian War and the ancestral land belonged to the French crown until the Second Treaty of Cateau-Cambrésis in 1559, the dukes moved their capital from Chambéry to Turin . At the same time (1534/36) considerable parts of the land on both sides of Lake Geneva were lost to the Confederates : Vaud fell to Bern , and Friborg and Valais were also able to expand. By the Treaty of Lausanne in 1564 Chablais, Genevois and Gex returned to Savoy in exchange for renouncing the Vaud, and in the Treaty of Thonon in 1569, the Valais returned Evian and Abondance. With further alliances of 1509, 1512, 1570, 1571 and 1577, Savoy regulated its relations with various federal places. On January 17, 1601, the areas in the extreme west ( Bresse , Bugey , Valromey and Gex) were ceded to France with the Treaty of Lyon , in 1631, at the end of the War of the Mantuan Succession , also the fortress of Pinerolo ; In return, Savoy was awarded parts of the Margraviate of Montferrat .
Period from the Enlightenment to the Industrial Revolution
In the Peace of Utrecht in 1713, Spain had to cede the Kingdom of Sicily and parts of the Duchy of Milan to the ruling house of Savoy, which has since held the title of king. Sicily was exchanged for Sardinia in 1720 , and the Duchy of Savoy was united with Sardinia to form the Kingdom of Sardinia . Novara and Tortona were acquired in 1738 and other areas in 1748.
On September 22, 1792, French revolutionary troops entered the area without declaring war. Between 1796 and 1815, Savoy was part of France and initially formed the Mont-Blanc department. In 1798 it was divided into the Mont-Blanc and Léman departments . In 1801 the country left the Roman-German Empire under international law.
After the Congress of Vienna , the Second Peace of Paris brought back the Kingdom of Sardinia. The northern part of Savoy was neutralized and should be occupied by Switzerland in the event of war. The Kingdom of Sardinia granted Switzerland two duty-free zones in 1816/29. One zone in the border area of Geneva comprised the province of Carouge and some smaller areas to the east and north adjoining the canton of Geneva, the other at St-Gingolph the immediate border area on Lake Geneva and the canton of Valais.
As a result of the Italian unification process , which came about with French support, King Victor Emmanuel II ceded Savoy and the county of Nice to the French Empire in the Treaty of Turin on March 24, 1860 . The assignment was confirmed by a referendum . As a result of this assignment, there was a political crisis in Switzerland known as the Savoy trade . The possibility of joining the provinces of Chablais and Faucigny to Switzerland was discussed.
List of rulers of Savoy
Counts of Savoy
- Humbert I. Blanche-Main Weißhand , 1003-1047 or 1048
- Amadeus I. Queue the Tail , 1048-1051 or 1056
- Otto , 1051 or 1056-1060
- Peter I , 1060-1078
- Amadeus II , 1060-1080
- Humbert II. The Strong , 1080-1103
- Amadeus III. , 1103-1148
- Humbert III. the saint , 1148–1189
- Thomas I. , 1189-1233
- Amadeus IV , 1233-1253
- Boniface , 1253-1263
- Thomas II , 1253-1259
- Peter II , 1263-1268
- Philip I , 1268-1285
- Amadeus V the Great , 1285–1323
- Edward the Liberal , 1323-1329
- Haimone , 1329-1343
- Amadeus VI. le Comte Vert , the Green Count , 1343–1383
- Amadeus VII. Le Comte Rouge , the Red Count , 1383-1391
- Amadeus VIII the Peaceful , 1391–1440, from 1416 Duke of Savoy
Dukes of Savoy
- Amadeus VIII the Peaceful , 1391–1440, from 1439 as Felix V antipope
- Ludwig the Elder , 1440–1465
- Amadeus IX. the lucky one , 1465–1472
- Philibert I the Hunter , 1472–1482
- Charles I the Fighter , 1482–1490
- Karl II. Johann Amadeus , 1490–1496
- Philip II. Unland , 1496-1497
- Philibert II the Handsome , 1497–1504
- Charles III the good , 1504–1553
- Emanuel Philibert Eisenkopf , 1553–1580
- Charles Emanuel I the Great , 1580–1630
- Viktor Amadeus I , 1630-1637
- Franz Hyacinth , 1637-1638
- Charles Emanuel II , 1638–1675
- Viktor Amadeus II. , 1675–1720, 1730–1732, 1720–1730 King of Sardinia
Well-known Savoyards
- Peter Faber (1506–1546), mystic
- Francis de Sales (1567–1622), bishop and doctor of the church
- Georg Muffat (1653–1704), musician of the Baroque era
- Eugene of Savoy (1663–1736), Austrian general
- Joseph de Maistre (1753–1821), statesman and philosopher
- Maximilian Josef Graf von Montgelas (1759–1838), founder of the modern Bavarian state
- Jacques Balmat (1762–1834), chamois hunter, and Michel-Gabriel Paccard (1757–1827), doctor, first to climb Mont Blanc
- Michel Croz (1830–1865), mountain guide of early alpinism , (co-) first climber a. a. of the Matterhorn , the Grande Casse , the Barre des Écrins and the Monte Viso
See also
- List of rulers of Italy
- Order of Civil Merit of Savoy
- Franco-Provencal language , a dialect in Savoy and parts of Switzerland
Web links
- Catherine Santschi: Basel, farewell to. In: Historical Lexicon of Switzerland .
- Bernard Andenmatten: Savoy, from. In: Historical Lexicon of Switzerland .
- 150 years of the annexation of Savoy to France
- Norbert Domeisen: The alliance of Savoy with the Confederates 1560.