Mantua
| Mantua | ||
|---|---|---|

|
|
|
| Country | Italy | |
| region | Lombardy | |
| province | Mantua (MN) | |
| Local name | Mantua / Mantova | |
| Coordinates | 45 ° 9 ' N , 10 ° 47' E | |
| height | 19 m slm | |
| surface | 63 km² | |
| Residents | 49,440 (Dec. 31, 2019) | |
| Population density | 785 inhabitants / km² | |
| Factions | Castelletto Borgo, Formigosa | |
| Post Code | 46100 | |
| prefix | 0376 | |
| ISTAT number | 020030 | |
| Popular name | Mantovani | |
| Patron saint | Anselm | |
| Website | Mantua | |
 Aerial view of the old town of Mantua |
||
| Mantua and Sabbioneta | |
|---|---|
|
UNESCO world heritage |
|
| National territory: |
|
| Type: | Culture |
| Criteria : | ii, iii |
| Reference No .: | 1287 |
| UNESCO region : | Europe and North America |
| History of enrollment | |
| Enrollment: | 2008 (session 32) |
Mantua ( Italian : Mantova , Latin : Mantua , Mantovan dialect: Màntua ) is a city with 49,440 inhabitants (as of December 31, 2019) in Lombardy , Italy .
Mantua is the capital of the province of Mantua , it is included in the list of World Heritage Sites together with Sabbioneta . The main sights of the city are the Romanesque cathedral, the Renaissance church of S. Andrea , the Palazzo Ducale and the Palazzo Te . The city, more precisely the nearby ancient village of Andes , is considered the birthplace of Virgil . In William Shakespeare's tragedy Romeo and Juliet , Mantua is Romeo's place of exile. Verdi's opera Rigoletto is set in Mantua.
The city is surrounded by four lakes - Lago Superiore, Lago di Mezzo, Lago Inferiore and Lago Paiolo - which were created in the 12th century to defend the city and are fed by the Mincio River. This makes the city look almost like an island.
On October 27, 2015, Mantua was named the “2016 Italian Capital of Culture”.
history
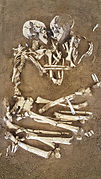
The Lovers of Valdaro are a pair of human skeletons, around 6000 years old, who were discovered in 2007 in a Neolithic tomb in San Giorgio di Mantova near Mantua.
Mantua was founded by the Etruscans , who called the place Manthva . The Greek seer Manto is named for its mythical founding story ; A connection with Mantus , the Etruscan deity of the underworld , is also conceivable .
In 804 the Roman Catholic diocese of Mantua was founded. In the run-up to the investiture controversy at Pentecost 1064, a synod took place at this location, which resolved the papal schism of that time, which founded the division between the German court and the Roman reform papacy, and confirmed Pope Alexander II against the antipope Honorius II as the rightful pontiff.
Since 1328 the noble Gonzaga family ruled there, who were elevated to counts by the Roman-German emperors in 1362, margraves in 1433 and dukes in 1530 . In 1536, Emperor Charles V transferred the Gonzaga, as a loyal ally, control of the important margravate Monferrato on the often contested Franco-Italian border. As a result, they temporarily rose to become one of the most important princely dynasties in Italy, and they reached a high point in artistic sponsorship under Margrave Franz II (Francesco II, † 1519), his wife Isabella d'Este († 1538) and her son Federico († 1540) . A branch line of the Mantuan Gonzaga established itself in the county of Guastalla , whose ruler Ferdinand (Ferrante, † 1557) rose in imperial Spanish service to viceroy of Sicily and governor of the Duchy of Milan .
The extinction of Mantua main line of Gonzaga in 1627 replaced the between France and the Habsburgs led Mantuan war of succession from around the strategically important Duchy, who ended the economic and cultural heyday of the country suddenly. In 1631 the Habsburg emperor had to recognize the French candidates for succession, the Dukes of Gonzaga-Nevers, as the new rulers of Mantua. Since these were again on the French side against Austria in the War of the Spanish Succession from 1701, the Emperor deposed them in 1708; Mantua has been a direct part of the Habsburg Empire since then.
During the coalition wars, the city, which had belonged to the Habsburg Duchy of Milan since 1745 , was fought over several times. After months of siege, Napoleon was able to take Mantua in early 1797, but it was lost again in 1799. Again from 1805 to 1814 Mantua was under French rule; Napoleon Bonaparte had the captive leader of the Tyrolean uprising , Andreas Hofer , executed in the citadel on the other bank of the Mincio in 1810 . This is what the Andreas Hofer song ("Zu Mantua in Gangs") by Julius Mosen is about . It is the national anthem of the Austrian state of Tyrol .
In 1814 Mantua became Austrian again and only came to Italy in 1866 as a result of the German War . Under Austrian rule, the place was part of the northern Italian fortress square (it .: Quadrilatero ), which was built in 1815 to defend the Austrian possessions in Italy in the places Peschiera , Mantua, Legnago and Verona .
Secondary lines of the Gonzaga family ruled longer than in Mantua in Guastalla , which had been elevated to duchy in 1621, and in the county of Novellara. This was annexed by Modena in 1737 , after the Gonzaga line there died out, Guastalla fell to Austria in 1746, then to Parma. Riccarda Gonzaga, the overthrown Countess of Novellara and temporary regent of Massa and Carrara (1731–1741), died in 1768.
On May 29, 2012, a severe earthquake measuring 5.8 in magnitude struck northern Italy. Mantua was particularly hard hit, including the Palazzo Ducale and the towers of the town hall in the Palazzo della Ragione . The epicenter of the quake was in Medolla, around 60 km away .
With Luigi I Gonzaga began the rule of the Gonzaga in Mantua in 1328
Mantua as part of the kk fortress square
Architecture and culture
Buildings
In 2008 the old towns of Mantua and Sabbioneta were jointly added to the UNESCO list of world cultural heritage .
- Palazzo Ducale : mighty brick building containing 450 living rooms. The most important works of art in the palace are Mantegna's frescoes in the Camera degli Sposi (completed in 1474).
- Cathedral : five-aisled basilica from the ninth century, the interior was rebuilt after 1540 by Giulio Romano based on early Christian models, above all probably Old St. Peter in Rome. The facade dates from 1756. There is a Romanesque bell tower next to it.
- Palazzo della Ragione with the Torre dell'orologio (clock tower)
- Basilica of Sant'Andrea : The design is the last work by Leon Battista Alberti (1470). The church is considered one of the outstanding works of the Italian Renaissance.
- San Sebastiano: Renaissance church by Alberti.
- Rotonda di San Lorenzo : Romanesque round church that stands on an ancient rotunda. Probably a foundation of the Margravine Mathilde von Tuszien .
- Palazzo del Te , builtby Giulio Romano between1525 and 1535.
- Teatro Bibiena (also Teatro Scientifico ), 1767-1769 by Antonio Galli da Bibiena built
Cultural institutions
economy
Mantua is one of the largest transshipment points for agricultural products in the Po Valley .
Town twinning
Mantua has partnerships with the following cities:
-
 Nevers ( France )
Nevers ( France ) -
 Weingarten ( Germany ) - Mantua and Weingarten share a common tradition of worshiping a holy blood relic, see article Blutritt
Weingarten ( Germany ) - Mantua and Weingarten share a common tradition of worshiping a holy blood relic, see article Blutritt
-
 Pushkin ( Russia )
Pushkin ( Russia ) -
 Madison ( USA )
Madison ( USA ) -
 Melilla (Spain)
Melilla (Spain) -
 Azuchi ( Japan )
Azuchi ( Japan ) -
 Oradea ( Romania )
Oradea ( Romania )
Personalities
Well-known personalities of the city are included in the list of personalities of the city of Mantua .
literature
- Visioni di Mantova , Istituto Geografico de Agostini, Novara 1953, 24 color plates (labeling in Italian, French, English, German).
- Elisabeth Th. Hilscher-Fritz: Mantua. In: Oesterreichisches Musiklexikon . Online edition, Vienna 2002 ff., ISBN 3-7001-3077-5 ; Print edition: Volume 3, Verlag der Österreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften, Vienna 2004, ISBN 3-7001-3045-7 .
- Walter Pippke, Ida Leinberger: Lake Garda, Verona, Mantua, Trentino. Art and history in the center of the Alpine arc . (DuMont art travel guide). DuMont, Ostfildern 2009, ISBN 978-3-7701-6617-6
Web links
|
Further content in the sister projects of Wikipedia:
|
||
|
|
Commons | - multimedia content |
|
|
Wiktionary | - Dictionary entries |
|
|
Wikisource | - Sources and full texts |
|
|
Wikivoyage | - Travel Guide |
- City website
- Entry on the UNESCO World Heritage Center website ( English and French ).
- Museums and important buildings
Individual evidence
- ↑ Statistiche demografiche ISTAT. Monthly population statistics of the Istituto Nazionale di Statistica , as of December 31 of 2019.
- ↑ Pierino Pelati Acque, terre e borghi del territorio Mantovano, Saggio di toponomastica, Asola 1996th
- ↑ Mantua named Italian Capital of Culture 2016 , on enit.de, accessed on November 12, 2015
- ↑ Virgil Aeneid 10.199
- ↑ Terremoto: 16 morti, e 350 feriti - Monti: "Lo Stato farà tutto il possibile". corriere.it, accessed March 10, 2019 .
- ↑ a b c d town twinning in Europe. comune.mantova.gov.it, accessed March 10, 2019 .
- ↑ a b c town twinning worldwide. comune.mantova.gov.it, accessed March 10, 2019 .