List of states and union territories in India

29 federal states: Numbers 1 to 29 ( Telangana , from 2014)
7 Union territories : Letters A to G ( Delhi as territory)
Since October 31, 2019, there are two new Union territories instead of the state of Jammu and Kashmir (# 10) : Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh . On January 26, 2020, the Union Territories of Dadra and Nagar Haveli (C) and Daman and Diu (D) were merged to form the Union Territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu .
This list of the states and union territories in India contains statistical information (as of October 2019) on the 29 states ( member states ) and the 7 centrally administered union territories of India , their gender distributions and religions , supplemented with maps, emblems, official languages and other additional information ( see below ). India's population grew from 376 million in 1950 to 1.35 billion in 2018, an increase of 260% ( global average: 201% ).
The following changes have occurred since 2014:
-
On October 31, 2019, Ladakh was separated as a separate union territory (without its own legislature) from the newly formed union territory of Jammu and Kashmir . Since then there have been 28 states and 9 union territories.
This list contains data from the state of Jammu and Kashmir, which existed until then (on the map: # 10). The Indian central government published values for an undivided entire region of Kashmir , for example 222,236 km² area in 2011 (but in fact only around 100,000 km² are still under Indian control). - Telangana (map: # 29) was only founded as a federal state in 2014; hardly any data is available on it (only available from the former administrative districts ).
- The union territories of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu were united on January 26, 2020 to form a union territories " Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu ".
Basic data
The following alphabetical list compares basic data from the 2011 India Census :
- # refers to the overview map on the right : states (1–29) and 7 union territories (A – G)
- ISO 3166-2: IN : country code
- Population and their respective proportions in the total population of India
- Land area in square kilometers and their respective share of India's total area (including the official area of Jammu and Kashmir (state) [ i-1 ] )
- Population density : inhabitants per square kilometer
- Year of foundation: individual states were reorganized at different times, most recently Telangana 2014
- Capital : New Delhi (Mega-City) differs from Delhi (National Capital Territory)
| 2011: Basic data of the Indian states and Union territories | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | State 1–29, Territory AG | ISO | Residents | proportion of | surface | proportion of | Population density | founding | Capital |
| [ 36 ] |
|
IN | 1,210,854,977 | 100% | 3,287,263 km² | 100% | 382 inhabitants / km² | 1947 | New Delhi (25.7 million) |
| A. | Andaman and Nicobar Islands | IN-AN | 379,944 | 0.03% | 8,249 km² | 0.25% | 46 inhabitants / km² | 1956 | Port Blair |
| 1 | Andhra Pradesh (without Telangana ) | IN-AP | 49.386.799 | 4.08% | 162,968 km² | 4.87% | 310 inhabitants / km² | 1956 | Amaravati |
| 2 | Arunachal Pradesh | IN-AR | 1,382,611 | 0.11% | 83,743 km² | 2.54% | 17 inhabitants / km² | 1987 | Itanagar |
| 3 | Assam | IN-AS | 31.169.272 | 2.58% | 78,438 km² | 2.38% | 398 inhabitants / km² | 1950 | Dispur |
| 4th | Bihar | IN-BR | 103,804,637 | 8.58% | 94,165 km² | 2.86% | 1,106 inhabitants / km² | 1950 | Patna |
| B. | Chandigarh | INCH | 1,055,450 | 0.09% | 114 km² | <0.01% | 9,258 inhabitants / km² | 1966 | Chandigarh |
| 5 | Chhattisgarh | IN-CT | 25,540,196 | 2.11% | 135,191 km² | 4.11% | 189 inhabitants / km² | 2000 | Raipur |
| C. | Dadra and Nagar Haveli [ i-3 ] | IN-DN | 342.853 | 0.03% | 491 km² | 0.01% | 700 inhabitants / km² | 1961 | Silvassa |
| D. | Daman and Diu [ i-3 ] | IN-DD | 242,911 | 0.02% | 112 km² | <0.01% | 2,191 inhabitants / km² | 1987 | Daman |
| G | Delhi (National Capital Territory) | IN-DL | 16,787,941 | 1.38% | 1,483 km² | 0.04% | 11,320 inhabitants / km² | 1956 | New Delhi |
| 6th | Goa | IN-GA | 1,457,723 | 0.12% | 3,702 km² | 0.11% | 394 inhabitants / km² | 1987 | Panaji |
| 7th | Gujarat | IN-FY | 60,383,628 | 5.00% | 196,024 km² | 5.96% | 308 inhabitants / km² | 1960 | Gandhinagar |
| 8th | Haryana | IN-HR | 25,353,081 | 2.09% | 44,212 km² | 1.34% | 573 inhabitants / km² | 1966 | Chandigarh |
| 9 | Himachal Pradesh | IN-HP | 6,864,602 | 0.57% | 55,673 km² | 1.70% | 123 inhabitants / km² | 1971 | Shimla |
| 10 | Jammu and Kashmir (State) [ i-1 ] | IN-JK | 12,548,926 | 1.04% | 101,387 km² | 3.08% | 124 inhabitants / km² | 1957 | Srinagar / Jammu |
| 11 | Jharkhand | IN-JH | 32,988,134 | 2.72% | 79,714 km² | 2.42% | 414 inhabitants / km² | 2000 | Ranchi |
| 12 | Karnataka | IN-KA | 61.130.704 | 5.05% | 191,791 km² | 5.83% | 319 inhabitants / km² | 1947 | Bangalore |
| 13 | Kerala | INCL | 33,387,677 | 2.76% | 38,863 km² | 1.18% | 860 inhabitants / km² | 1950 | Thiruvananthapuram |
| E. | Lakshadweep (islands) | IN-LD | 64,429 | 0.01% | 32 km² | <0.01% | 2,149 inhabitants / km² | 1956 | Kavaratti |
| 14th | Madhya Pradesh | IN-MP | 72,597,565 | 6.00% | 308,350 km² | 9.37% | 236 inhabitants / km² | 1950 | Bhopal |
| 15th | Maharashtra | IN-MH | 112.372.972 | 9.28% | 307,713 km² | 9.36% | 365 inhabitants / km² | 1960 | Mumbai |
| 16 | Manipur | IN-MN | 2,721,756 | 0.22% | 22,327 km² | 0.68% | 115 inhabitants / km² | 1972 | Imphal |
| 17th | Meghalaya | IN-ML | 2,964,007 | 0.24% | 22,429 km² | 0.68% | 132 inhabitants / km² | 1972 | Shillong |
| 18th | Mizoram | IN-MZ | 1,091,014 | 0.09% | 21,081 km² | 0.64% | 52 inhabitants / km² | 1987 | Aizawl |
| 19th | Nagaland | IN-NL | 1,980,602 | 0.16% | 16,579 km² | 0.50% | 119 inhabitants / km² | 1963 | Kohima |
| 20th | Odisha (until 2011: Orissa) | IN OR | 41,947,358 | 3.47% | 155,707 km² | 4.73% | 270 inhabitants / km² | 1950 | Bhubaneswar |
| F. | Pondicherry | IN-PY | 1,244,464 | 0.10% | 492 km² | 0.01% | 2,547 inhabitants / km² | 1963 | Pondicherry |
| 21st | Punjab | IN-PB | 27,704,236 | 2.30% | 50,362 km² | 1.53% | 551 inhabitants / km² | 1950 | Chandigarh |
| 22nd | Rajasthan | IN-RJ | 68,621,012 | 5.67% | 342,238 km² | 10.41% | 200 inhabitants / km² | 1956 | Jaipur |
| 23 | Sikkim | IN-SK | 607,688 | 0.05% | 7,096 km² | 0.21% | 86 inhabitants / km² | 1975 | Gangtok |
| 24 | Tamil Nadu | IN-TN | 72.138.958 | 5.96% | 130,058 km² | 3.95% | 555 inhabitants / km² | 1950 | Chennai |
| 29 | Telangana (from 2014) [ i-2 ] | IN-TG | 35.286.757 | 2.97% | 112,077 km² | 3.49% | 306 inhabitants / km² | 2014 | Hyderabad |
| 25th | Tripura | IN-TR | 3,671,032 | 0.30% | 10,486 km² | 0.31% | 350 inhabitants / km² | 1972 | Agartala |
| 26th | Uttar Pradesh | IN-UP | 199.812.341 | 16.49% | 243,290 km² | 7.33% | 829 inhabitants / km² | 1950 | Lucknow |
| 27 | Uttarakhand | IN-UT | 10,116,752 | 0.84% | 53,483 km² | 1.62% | 189 inhabitants / km² | 2000 | Dehradun |
| 28 | West Bengal | IN-WB | 91,347,736 | 7.55% | 88,752 km² | 2.70% | 1,028 inhabitants / km² | 1950 | Calcutta |
| [ 36 ] | State 1-29, territory A-G | ISO: IN | Residents | proportion of | surface | proportion of | Population density | founding | Capital |
Social indicators
The following alphabetical list compares social indicators from the 2011 India Census :
- # refers to the overview map above : states (1–29) and 7 union territories (A – G)
- Population and population development from 2001
- rural proportion, for the difference to urban
- Gender distribution : number of female inhabitants per 1000 male inhabitants, also for children under 7 years of age (balanced would be 1000: 1000)
- Fertility rate : average births per woman
- Literacy rate (from 7 years), also for men and women, as well as the gap between the two
| # | State 1–29 Union Territory AG |
Residents | Reading ability | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | From 2001 onwards | rural | Female | under 7 | fruitful | 2011 | From 2001 onwards | Men | Women | gap | ||
| [ 36 ] |
|
1,210.9 million | + 17.64 % | 68.8 % | 943 : 1000 | 919 : 1000 | 2.4 children | 74.04 % | + 8.66 % | 82.14 % ♂ | 65.46 % ♀ | 16.68 % |
| A. | Andaman and Nicobar Islands | 0.4 million | + 6.86% | 62.3% | 876: 1000 | 968: 1000 | 0.7 children | 86.63% | + 5.33% | 90.27% ♂ | 82.43% ♀ | 7.84% |
| 1 | Andhra Pradesh | 84.6 million | + 10.98% | 66.6% | 993: 1000 | 939: 1000 | 1.8 children | 67.02% | + 6.55% | 74.88% ♂ | 59.15% ♀ | 15.73% |
| 2 | Arunachal Pradesh | 1.4 million | + 26.03% | 77.1% | 938: 1000 | 972: 1000 | - | 65.38% | + 11.04% | 72.55% ♂ | 57.70% ♀ | 14.85% |
| 3 | Assam | 31.2 million | + 17.07% | 85.9% | 958: 1000 | 962: 1000 | 2.4 children | 72.19% | + 8.94% | 77.85% ♂ | 66.27% ♀ | 11.58% |
| 4th | Bihar | 104.1 million | + 25.42% | 88.7% | 918: 1000 | 935: 1000 | 3.6 children | 61.80% | + 14.80% | 71.20% ♂ | 51.50% ♀ | 19.70% |
| B. | Chandigarh | 1.1 million | + 17.19% | 2.7% | 818: 1000 | 880: 1000 | 1.6 children | 86.05% | + 4.11% | 89.99% ♂ | 81.19% ♀ | 8.80% |
| 5 | Chhattisgarh | 25.5 million | + 22.61% | 76.8% | 991: 1000 | 969: 1000 | 2.7 children | 70.28% | +5.62% | 80.27% ♂ | 60.24% ♀ | 20.03% |
| C. | Dadra and Nagar Haveli [ i-3 ] | 0.3 million | +55.88% | 53.3% | 774: 1000 | 926: 1000 | 2.3 children | 76.24% | + 18.61% | 85.17% ♂ | 64.32% ♀ | 20.85% |
| D. | Daman and Diu [ i-3 ] | 0.2 million | +53.76% | 24.8% | 618: 1000 | 904: 1000 | 1.8 children | 87.10% | + 8.92% | 91.54% ♂ | 79.55% ♀ | 11.99% |
| G | Delhi (capital territory) | 16.8 million | +21.21% | 2.5% | 868: 1000 | 871: 1000 | 1.6 children | 86.21% | + 4.54% | 90.94% ♂ | 80.76% ♀ | 10.18% |
| 6th | Goa | 1.5 million | + 8.23% | 37.8% | 973: 1000 | 942: 1000 | 1.4 children | 88.70% | +6.69% | 92.65% ♂ | 84.66% ♀ | 7.99% |
| 7th | Gujarat | 60.4 million | + 19.28% | 57.4% | 919: 1000 | 890: 1000 | 2.4 children | 78.03% | + 8.89% | 85.75% ♂ | 69.68% ♀ | 16.07% |
| 8th | Haryana | 25.4 million | + 19.90% | 65.1% | 879: 1000 | 834: 1000 | 2.3 children | 75.55% | +7.64% | 84.06% ♂ | 65.94% ♀ | 18.12% |
| 9 | Himachal Pradesh | 6.9 million | + 12.94% | 90.0% | 972: 1000 | 909: 1000 | 1.8 children | 82.80% | + 6.32% | 89.53% ♂ | 75.93% ♀ | 13.60% |
| 10 | Jammu and Kashmir (State) [ i-1 ] | 12.5 million | + 23.64% | 72.6% | 889: 1000 | 862: 1000 | 1.9 children | 67.16% | + 11.64% | 76.75% ♂ | 56.43% ♀ | 20.32% |
| 11 | Jharkhand | 33.0 million | + 22.42% | 76.0% | 948: 1000 | 948: 1000 | 2.9 children | 66.41% | + 12.85% | 76.84% ♂ | 55.42% ♀ | 21.42% |
| 12 | Karnataka | 61.1 million | + 15.60% | 61.3% | 973: 1000 | 948: 1000 | 1.9 children | 75.36% | + 8.72% | 82.47% ♂ | 68.08% ♀ | 14.39% |
| 13 | Kerala | 33.4 million | + 4.91% | 52.3% | 1084: 1000 | 964: 1000 | 1.8 children | 94.00 % | + 3.14% | 96.11% ♂ | 92.07% ♀ | 4.04% |
| E. | Lakshadweep (islands) | <0.1 million | + 6.30% | 21.9% | 946: 1000 | 911: 1000 | 1.6 children | 91.85% | + 5.19% | 95.56% ♂ | 87.95% ♀ | 7.61% |
| 14th | Madhya Pradesh | 72.6 million | + 20.35% | 72.4% | 931: 1000 | 918: 1000 | 3.1 children | 69.32% | +5.58% | 78.73% ♂ | 59.24% ♀ | 19.49% |
| 15th | Maharashtra | 112.4 million | + 15.99% | 54.8% | 929: 1000 | 894: 1000 | 1.8 children | 82.34% | + 5.46% | 88.38% ♂ | 75.87% ♀ | 12.51% |
| 15th | Manipur | 2.7 million | + 24.50% | 67.5% | 985: 1000 | 930: 1000 | 1.5 children | 76.94% | + 10.33% | 83.58% ♂ | 70.26% ♀ | 13.32% |
| 17th | Meghalaya | 3.0 million | + 27.95% | 79.9% | 989: 1000 | 970: 1000 | 2.8 children | 74.43% | + 11.87% | 75.95% ♂ | 72.89% ♀ | 3.06% |
| 18th | Mizoram | 1.1 million | + 23.48% | 47.9% | 976: 1000 | 970: 1000 | 1.6 children | 91.33% | + 2.53% | 93.35% ♂ | 89.27% ♀ | 4.08% |
| 19th | Nagaland | 2.0 million | −0.58% | 71.1% | 931: 1000 | 943: 1000 | 1.7 children | 79.55% | + 12.96% | 82.75% ♂ | 76.11% ♀ | 6.64% |
| 20th | Odisha (until 2011: Orissa) | 42.0 million | + 14.05% | 83.3% | 979: 1000 | 941: 1000 | 2.2 children | 72.87% | +9.79% | 81.59% ♂ | 64.01% ♀ | 17.58% |
| F. | Pondicherry | 1.2 million | + 28.08% | 31.7% | 1037: 1000 | 967: 1000 | 1.7 children | 85.85% | + 4.61% | 91.26% ♂ | 80.67% ♀ | 10.59% |
| 21st | Punjab | 27.7 million | + 13.89% | 62.5% | 895: 1000 | 846: 1000 | 1.8 children | 75.84% | + 6.19% | 80.44% ♂ | 70.73% ♀ | 9.71% |
| 22nd | Rajasthan | 68.5 million | +21.31% | 75.1% | 928: 1000 | 888: 1000 | 3.0 children | 66.11% | + 5.70% | 79.19% ♂ | 52.12% ♀ | 27.07% |
| 23 | Sikkim | 0.6 million | + 12.89% | 74.8% | 890: 1000 | 957: 1000 | 1.6 children | 81.42% | + 12.61% | 86.55% ♂ | 75.61% ♀ | 10.94% |
| 24 | Tamil Nadu | 72.1 million | + 15.61% | 51.6% | 996: 1000 | 943: 1000 | 1.7 children | 80.09% | +6.64% | 86.77% ♂ | 73.44% ♀ | 13.33% |
| 29 | Telangana (from 2014) [ i-2 ] | 35.3 million | - | - | - | - | - | 66.50% | - | - | - | - |
| 25th | Tripura | 3.7 million | + 14.84% | 73.8% | 960: 1000 | 957: 1000 | 1.4 children | 87.22% | + 14.03% | 91.53% ♂ | 82.73% ♀ | 8.80% |
| 26th | Uttar Pradesh | 199.8 million | +20.23% | 77.7% | 912: 1000 | 902: 1000 | 3.4 children | 67.68% | + 11.41% | 77.28% ♂ | 57.18% ♀ | 20.10% |
| 27 | Uttarakhand | 10.1 million | + 18.81% | 69.8% | 963: 1000 | 890: 1000 | 2.1 children | 78.82% | + 7.20% | 87.40% ♂ | 70.01% ♀ | 17.39% |
| 28 | West Bengal | 91.3 million | + 13.84% | 68.1% | 950: 1000 | 956: 1000 | 1.7 children | 76.26% | +7.62% | 81.69% ♂ | 70.54% ♀ | 11.15% |
| [ 36 ] | State 1-29 Union Territory A-G |
2011 | From 2001 onwards | rural | Female | under 7 | fruitful | 2011 | From 2001 onwards | Men | Women | gap |
| Residents | Reading ability | |||||||||||
See also:
- States / Territories: Rankings (multiple demographic, social, and economic indicators)
- States / Territories: Scheduled Tribes (registered tribal peoples)
Economic indicators

The following alphabetical list of economic indicators compares several indices (see index brief information ) as well as information on the generated goods values nationwide in rupees and per capita:
- # refers to the overview map above : states (1–29) and 7 union territories (A – G)
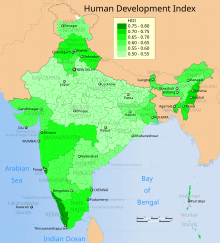
- HDI: Human Development Index , UN index of human development in 2017 and 2006 (India's HDI 2017: 0.639 at 130th place worldwide )
- GDI: Gender Development Index , UN index of gender-specific development in 2006 (India's GDI 2017: 0.841 at 149th place worldwide )
- GEM: Gender Empowerment Measure , UN women's participation index in 2006
- Femdex: Female Empowerment Index , female participation index of the McKinsey Institute in India 2015 (see Femdex short info )
- GDP: gross domestic product of one year as the total value of all goods and services in Indian rupees , nominal and per capita in 2014 (India's GDP per capita: 2017 ranked 141st worldwide )
- Poverty rate : Proportion of residents with an income below the poverty line in 2011/2012 (varies by state / territory: ⌀ 816 rupees per month in rural areas, 1,000 in cities)
| # | State 1–29 Union Territory AG |
2017 | 2006 | 2015 | 2014 nominal | 2014 per capita | 2012 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDI | HDI | GDI | GEM | Femdex | GDP | proportion of | GDP | 100% | poverty | |||
| [ 36 ] |
|
0.639 | 0.605 | 0.590 | 0.497 | 0.54 | Rs. 126,830,910 | 100% | 74,380 Rs | ⌀ 100% | 21.92 % | |
| A. | Andaman and Nicobar Islands | 0.742 | 0.708 | 0.692 | 0.560 | - | 74,508 Rs | 0.06% | Rs 107,418 | 144% | 1.00% | |
| 1 | Andhra Pradesh (with Telangana ) | 0.643 | 0.585 | 0.574 | 0.547 | 0.59 | Rs.5,621,524 | 4.43% | Rs 81,397 | 109% | 9.20% | |
| 2 | Arunachal Pradesh | 0.658 | 0.647 | 0.642 | 0.469 | 0.50 | 164,120 Rs | 0.13% | Rs 89,545 | 120% | 34.67% | |
| 3 | Assam | 0.605 | 0.595 | 0.585 | 0.417 | 0.47 | Rs 1,929,742 | 1.52% | Rs 44,263 | 60% | 31.98% | |
| 4th | Bihar | 0.566 | 0.507 | 0.479 | 0.379 | 0.42 | Rs 4,161,933 | 3.28% | Rs 31,199 | 42% | 33.74% | |
| B. | Chandigarh | 0.774 | 0.784 | 0.763 | 0.500 | 0.60 | Rs 351,863 | 0.28% | 156,951 Rs | 211% | 21.81% | |
| 5 | Chhattisgarh | 0.600 | 0.549 | 0.542 | 0.464 | 0.55 | 2,248,672 Rs | 1.77% | 58,547 Rs | 79% | 39.93% | |
| C. | Dadra and Nagar Haveli [ i-3 ] | 0.661 | 0.677 | 0.673 | 0.479 | - | - | - | - | - | 39.31% | |
| D. | Daman and Diu [ i-3 ] | 0.706 | 0.700 | 0.677 | 0.503 | - | - | - | - | - | 9.86% | |
| G | Delhi (capital territory) | 0.744 | 0.740 | 0.701 | 0.564 | 0.56 | Rs 4,896,025 | 3.78% | Rs. 212,219 | 285% | 9.91% | |
| 6th | Goa | 0.764 | 0.764 | 0.747 | 0.551 | 0.64 | Rs 591,735 | 0.47% | Rs 224,138 | 301% | 5.09% | |
| 7th | Gujarat | 0.667 | 0.634 | 0.624 | 0.485 | 0.56 | Rs 9,272,235 | 7.31% | Rs 106,831 | 143% | 16.63% | |
| 8th | Haryana | 0.704 | 0.643 | 0.632 | 0.532 | 0.53 | Rs 4,709,976 | 3.71% | Rs 133,427 | 179% | 11.16% | |
| 9 | Himachal Pradesh | 0.720 | 0.667 | 0.664 | 0.540 | 0.63 | Rs 999,439 | 0.79% | 92,300 Rs | 124% | 8.06% | |
| 10 | Jammu and Kashmir (State) [ i-1 ] | 0.684 | 0.590 | 0.568 | 0.355 | 0.55 | 1,056,701 Rs | 0.84% | Rs 59,279 | 80% | 10.35% | |
| 11 | Jharkhand | 0.589 | 0.574 | 0.558 | 0.435 | 0.46 | Rs 2,090,832 | 1.65% | 46,131 Rs | 62% | 36.96% | |
| 12 | Karnataka | 0.682 | 0.622 | 0.611 | 0.526 | 0.59 | Rs 7,057,414 | 5.87% | Rs 88,968 | 120% | 20.91% | |
| 13 | Kerala | 0.784 | 0.764 | 0.745 | 0.525 | 0.67 | 4,799,151 Rs | 3.74% | Rs 103,820 | 140% | 7.05% | |
| E. | Lakshadweep (islands) | 0.749 | 0.697 | 0.635 | 0.463 | - | - | - | - | - | 2.77% | |
| 14th | Madhya Pradesh | 0.594 | 0.529 | 0.516 | 0.463 | 0.49 | Rs.5,264,826 | 4.15% | Rs 51,798 | 70% | 31.65% | |
| 15th | Maharashtra | 0.695 | 0.689 | 0.677 | 0.516 | 0.59 | Rs.17,877,920 | 14.42% | Rs 117.091 | 157% | 17.35% | |
| 15th | Manipur | 0.695 | 0.702 | 0.699 | 0.418 | 0.55 | Rs 173,334 | 0.14% | Rs 41,573 | 56% | 36.89% | |
| 17th | Meghalaya | 0.650 | 0.629 | 0.624 | 0.346 | 0.69 | Rs 265,288 | 0.21% | Rs 61,548 | 83% | 11.87% | |
| 18th | Mizoram | 0.697 | 0.688 | 0.687 | 0.374 | 0.70 | Rs 124,696 | 0.10% | Rs 76,120 | 102% | 20.40% | |
| 19th | Nagaland | 0.676 | 0.700 | 0.697 | 0.289 | 0.52 | Rs 214,766 | 0.17% | Rs 77,529 | 104% | 18.88% | |
| 20th | Odisha (Orissa) | 0.597 | 0.537 | 0.524 | 0.393 | 0.51 | Rs 3,305,894 | 2.61% | 52,559 Rs | 71% | 32.59% | |
| F. | Pondicherry | 0.739 | 0.725 | 0.706 | 0.558 | 0.59 | Rs 255,086 | 0.20% | Rs 143,677 | 193% | 9.69% | |
| 21st | Punjab | 0.721 | 0.668 | 0.663 | 0.514 | 0.59 | Rs. 3,839,704 | 3.03% | Rs 92,350 | 124% | 8.26% | |
| 22nd | Rajasthan | 0.621 | 0.541 | 0.526 | 0.442 | 0.52 | Rs. 6,268,581 | 4.94% | Rs 65,974 | 89% | 14.71% | |
| 23 | Sikkim | 0.716 | 0.665 | 0.659 | 0.447 | 0.64 | Rs 149,883 | 0.12% | Rs 176,491 | 237% | 8.19% | |
| 24 | Tamil Nadu | 0.708 | 0.666 | 0.655 | 0.498 | 0.60 | Rs 10,345,238 | 8.16% | Rs. 112,664 | 151% | 11.28% | |
| 29 | Telangana (from 2014) [ i-2 ] | 0.664 | - | - | - | - | 4,740,872 Rs | 3.73% | Rs 95,361 | 128% | - | |
| 25th | Tripura | 0.655 | 0.663 | 0.626 | 0.382 | 0.51 | Rs 324,468 | 0.26% | Rs 69,705 | 94% | 14.05% | |
| 26th | Uttar Pradesh | 0.583 | 0.528 | 0.509 | 0.452 | 0.49 | Rs 10,448,275 | 8.24% | 36,250 Rs | 49% | 29.43% | |
| 27 | Uttarakhand | 0.677 | 0.652 | 0.647 | 0.466 | 0.57 | Rs 1,487,284 | 1.17% | Rs 103,716 | 139% | 11.26% | |
| 28 | West Bengal | 0.637 | 0.642 | 0.622 | 0.435 | 0.54 | 8,556,797 Rs | 6.75% | Rs 70,059 | 94% | 19.98% | |
| [ 36 ] | State 1-29 Union Territory A-G |
HDI | HDI | GDI | GEM | Femdex | GDP | proportion of | GDP | to 100 % | poverty | |
| 2017 | 2006 | 2015 | 2014 nominal | 2014 per capita | 2012 | |||||||
See also:
- States / Territories: HDI Increases 1995-2017
- States / territories: GDP 2014 (in dollars, adjusted for purchasing power and per capita)
- States / Territories: Economic data (employment, unemployment, electrification)
Worldwide comparison:
- India's GII 2017: 0.524 at rank 127 ( Gender Inequality Index: index of gender inequality)
- India's GDP: from 1960; 2017 in 6th place (gross domestic product)
- India's GDP per capita: in 2017 ranked 149th (gross national income)
Religions
The 6 major religions
The following alphabetical list based on the 2011 census in India ("#" refers to the overview map above ) compares the followers of the 6 major religions in India - only around 8 million of all residents indicated a "different religion or belief" (0.66% ), including 33,304 atheists who do not believe in divinity (compare atheism in India and India’s religious followers in a global comparison ). No mention (religion not stated) was given by 0.24% of all residents (2.9 million).
Hinduism has a share of more than 50% in 27 states / territories, Islam is predominant in 2 and Christianity , which is the third largest religion in India with 2.3%:
| # | State 1–29 Union Territory AG |
Residents | Hindus | Muslims | Christians | Sikhs | Buddhists | Jainas | other | Atheists | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 2001 | 2011 | 2001 | 2011 | 2001 | 2011 | 2001 | 2011 | 2001 | 2011 | 2001 | 2011 | 2011 | |||
| [ 36 ] |
|
1,210.9 million | 79.80 % | 80.5% | 14.23 % | 13.4% | 2.30 % | 2.3% | 1.72 % | 1.9% | 0.70 % | 0.8% | 0.37 % | 0.4% | 0.66 % | 0.003 % |
| A. | Andaman and Nicobar Islands | 0.4 million | 69.45% | 69.2% | 8.52% | 8.2% | 21.28% | 21.7% | 0.34% | 0.4% | 0.09% | 0.1% | 0.01% | <0.1% | 0.15% | 333 |
| 1 | Andhra Pradesh (with Telangana ) | 84.6 million | 88.46% | 89.0% | 9.56% | 9.2% | 1.34% | 1.6% | 0.05% | <0.1% | 0.04% | <0.1% | 0.06% | 0.1% | 0.01% | 256 |
| 2 | Arunachal Pradesh | 1.4 million | 29.04% | 34.6% | 1.95% | 1.9% | 30.26% | 18.7% | 0.24% | 0.2% | 11.77% | 13.0% | 0.06% | <0.1% | 26.20% | 348 |
| 3 | Assam | 31.2 million | 61.47% | 64.9% | 34.22% | 30.9% | 3.74% | 3.7% | 0.07% | 0.1% | 0.18% | 0.2% | 0.08% | 0.1% | 0.09% | 250 |
| 4th | Bihar | 104.1 million | 82.69% | 83.2% | 16.87% | 16.5% | 0.12% | 0.1% | 0.02% | <0.1% | 0.02% | <0.1% | 0.02% | <0.1% | 0.01% | 47 |
| B. | Chandigarh | 1.1 million | 80.78% | 78.6% | 4.87% | 3.9% | 0.83% | 0.8% | 13.11% | 16.1% | 0.11% | 0.1% | 0.19% | 0.3% | 0.02% | 89 |
| 5 | Chhattisgarh | 25.5 million | 93.25% | 94.7% | 2.02% | 2.0% | 1.92% | 1.9% | 0.27% | 0.3% | 0.28% | 0.3% | 0.24% | 0.3% | 1.94% | 14th |
| C. | Dadra and Nagar Haveli [ i-3 ] | 0.3 million | 93.93% | 93.5% | 3.76% | 3.0% | 1.49% | 2.7% | 0.06% | 0.1% | 0.18% | 0.2% | 0.35% | 0.4% | 0.09% | 4th |
| D. | Daman and Diu [ i-3 ] | 0.2 million | 90.50% | 89.7% | 7.92% | 7.8% | 1.16% | 2.1% | 0.07% | 0.1% | 0.09% | 0.1% | 0.12% | 0.2% | 0.03% | 0 |
| G | Delhi (capital territory) | 16.8 million | 81.68% | 82.0% | 12.86% | 11.7% | 0.87% | 0.9% | 3.40% | 4.0% | 0.11% | 0.2% | 0.99% | 1.1% | 0.01% | 541 |
| 6th | Goa | 1.5 million | 66.08% | 65.8% | 8.33% | 6.8% | 25.10% | 26.7% | 0.10% | 0.1% | 0.08% | <0.1% | 0.08% | 0.1% | 0.02% | 61 |
| 7th | Gujarat | 60.4 million | 88.57% | 89.1% | 9.67% | 9.1% | 0.52% | 0.6% | 0.10% | 0.1% | 0.05% | <0.1% | 0.96% | 1.0% | 0.03% | 405 |
| 8th | Haryana | 25.4 million | 87.46% | 88.2% | 7.03% | 5.8% | 0.20% | 0.1% | 4.91% | 5.5% | 0.03% | <0.1% | 0.21% | 0.3% | 0.01% | 180 |
| 9 | Himachal Pradesh | 6.9 million | 95.17% | 95.4% | 2.18% | 2.0% | 0.18% | 0.1% | 1.16% | 1.2% | 1.15% | 1.2% | 0.03% | <0.1% | 0.01% | 252 |
| 10 | Jammu and Kashmir (State) [ i-1 ] | 12.5 million | 28.44% | 29.6% | 68.31% | 67.0% | 0.28% | 0.2% | 1.87% | 2.0% | 0.90% | 1.1% | 0.02% | <0.1% | 0.01% | 30th |
| 11 | Jharkhand | 33.0 million | 67.83% | 68.6% | 14.53% | 13.8% | 4.30% | 4.1% | 0.22% | 0.3% | 0.03% | <0.1% | 0.05% | 0.1% | 12.84% | 36 |
| 12 | Karnataka | 61.1 million | 84.00% | 83.9% | 12.92% | 12.2% | 1.87% | 1.9% | 0.05% | <0.1% | 0.16% | 0.7% | 0.72% | 0.8% | 0.02% | 112 |
| 13 | Kerala | 33.4 million | 54.73% | 56.2% | 26.56% | 24.7% | 18.38% | 19.0% | 0.01% | <0.1% | 0.01% | <0.1% | 0.01% | <0.1% | 0.02% | 4,896 |
| E. | Lakshadweep (islands) | <0.1 million | 2.77% | 3.7% | 96.58% | 95.5% | 0.49% | 0.8% | 0.01% | <0.1% | 0.02% | <0.1% | 0.02% | <0.1% | 0.01% | 1 |
| 14th | Madhya Pradesh | 72.6 million | 90.89% | 91.1% | 6.57% | 6.4% | 0.29% | 0.3% | 0.21% | 0.2% | 0.30% | 0.3% | 0.78% | 0.9% | 0.83% | 136 |
| 15th | Maharashtra | 112.4 million | 79.83% | 80.4% | 11.54% | 10.6% | 0.96% | 1.1% | 0.20% | 0.2% | 5.81% | 6.0% | 1.25% | 1.3% | 0.16% | 9,652 |
| 16 | Manipur | 2.7 million | 41.39% | 46.0% | 8.40% | 8.8% | 41.29% | 34.0% | 0.05% | 0.1% | 0.25% | 0.1% | 0.06% | 0.1% | 8.19% | 39 |
| 17th | Meghalaya | 3.0 million | 11.53% | 13.3% | 4.40% | 4.3% | 74.59% | 70.3% | 0.10% | 0.1% | 0.33% | 0.2% | 0.02% | <0.1% | 8.71% | 9,089 |
| 18th | Mizoram | 1.1 million | 2.75% | 3.6% | 1.35% | 1.1% | 87.16% | 87.0% | 0.03% | <0.1% | 8.51% | 7.9% | 0.03% | <0.1% | 0.07% | 30th |
| 19th | Nagaland | 2.0 million | 8.75% | 7.7% | 2.47% | 1.8% | 87.93% | 90.0% | 0.10% | 0.1% | 0.34% | 0.1% | 0.13% | 0.1% | 0.16% | 21st |
| 20th | Odisha (Orissa) | 42.0 million | 93.63% | 94.4% | 2.17% | 2.1% | 2.77% | 2.4% | 0.05% | <0.1% | 0.03% | <0.1% | 0.02% | <0.1% | 1.14% | 651 |
| F. | Pondicherry | 1.2 million | 87.30% | 86.8% | 6.05% | 6.1% | 6.29% | 6.9% | 0.02% | <0.1% | 0.04% | <0.1% | 0.11% | 0.1% | 0.01% | 44 |
| 21st | Punjab | 27.7 million | 38.49% | 36.9% | 1.93% | 1.6% | 1.26% | 1.2% | 57.69% | 59.9% | 0.12% | 0.2% | 0.16% | 0.2% | 0.04% | 569 |
| 22nd | Rajasthan | 68.5 million | 88.49% | 88.8% | 9.07% | 8.5% | 0.14% | 0.1% | 1.27% | 1.4% | 0.02% | <0.1% | 0.91% | 1.2% | 0.01% | 77 |
| 23 | Sikkim | 0.6 million | 57.76% | 60.9% | 1.62% | 1.4% | 9.91% | 6.7% | 0.31% | 0.2% | 27.39% | 28.1% | 0.05% | <0.1% | 2.67% | 10 |
| 24 | Tamil Nadu | 72.1 million | 87.58% | 88.1% | 5.86% | 5.6% | 6.12% | 6.1% | 0.02% | <0.1% | 0.02% | <0.1% | 0.12% | 0.1% | 0.01% | 1,297 |
| 29 | Telangana (from 2014) [ i-2 ] | 35.3 million | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 25th | Tripura | 3.7 million | 83.40% | 85.6% | 8.60% | 8.0% | 4.35% | 3.2% | 0.03% | <0.1% | 3.41% | 3.1% | 0.02% | <0.1% | 0.04% | 53 |
| 26th | Uttar Pradesh | 199.8 million | 79.73% | 80.6% | 19.26% | 18.5% | 0.18% | 0.1% | 0.32% | 0.4% | 0.10% | 0.2% | 0.11% | 0.1% | 0.01% | 2,425 |
| 27 | Uttarakhand | 10.1 million | 82.97% | 85.0% | 13.95% | 11.9% | 0.37% | 0.3% | 2.34% | 2.5% | 0.15% | 0.1% | 0.09% | 0.1% | 0.01% | 572 |
| 28 | West Bengal | 91.3 million | 70.54% | 72.5% | 27.01% | 25.2% | 0.72% | 0.6% | 0.07% | 0.1% | 0.31% | 0.3% | 0.07% | 0.1% | 1.03% | 784 |
| [ 36 ] | State 1-29 Union Territory A-G |
Residents | 2011 | 2001 | 2011 | 2001 | 2011 | 2001 | 2011 | 2001 | 2011 | 2001 | 2011 | 2001 | 2011 | 2011 |
| Hindus | Muslims | Christians | Sikhs | Buddhists | Jainas | other | Atheists | |||||||||
Other religions and beliefs
The following alphabetical list compares the mentions in the 2011 census in India under Other Religions and Persuasions (instead of 99.11% of the 6 major religions or 0.24% without mention):
- Population - only 8 million mentions in total (0.66% of India's inhabitants)
- rural part , in contrast to urban
- Gender distribution : number of female followers per 1000 male followers (the equation would be 1000: 1000)
- Scheduled Tribes (ST): Number of tribal communities recognized in the respective state (693 ST in total in 2014)
- three most frequently mentioned mentions per state / territory
53% of all mentions are in the state of Jharkhand (4.2 million), where the most popular ethnic religion Sarna ( short info ) is represented with 4.1 million followers. The second most mentioned "Gond, Gondi" (1 million followers) comes from the Gond people and the third strongest religion called "Sari Dharma" (0.5 million) is most strongly represented among the Santal people - these 3 religions together receive 82% of all mentions, that is 0.54% of the population of India (see the 20 most popular "other religions" ):
| India 2011: " Other Religions and Beliefs " | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | State 1–29 Territory AG |
Residents | Other R. and Ü. |
rural | Female | ST | mostly mentioned | second most popular | third most named | |||
| number | Surname | number | Surname | number | Surname | |||||||
| [ 36 ] |
|
1,210.9 million | 7,937,734 | 90.69 % | 1009 : 1000 | 693 | 4,957,467 | Sarna : 62.5% | 1,026,344 | " Gondi ": 12.9% | 506.369 | Sari Dharma : 6% |
| A. | Andaman and Nicobar Islands | 0.4 million | 564 | 78.55% | 779: 1000 | 6th | 333 | atheism | 129 | Bahaitum | 59 | Sarna |
| 1 | Andhra Pradesh (with Telangana ) | 84.6 million | 9,547 | 38.86% | 983: 1000 | 25th | 609 | Parsees / Zoroastr. | 391 | "Addi Bassi" | 256 | atheism |
| 2 | Arunachal Pradesh ( 4.6 %) | 1.4 million | 362,553 | 81.92% | 1014: 1000 | 16 | 324,604 | "Doni Polo" | 14,663 | "Tribal Religion" | 10,598 | "Rangfra" |
| 3 | Assam | 31.2 million | 27,118 | 94.19% | 980: 1000 | 29 | 6,644 | "Doni Polo" | 2,381 | "Fralung" | 1,032 | "Heraka" |
| 4th | Bihar | 104.1 million | 13,437 | 92.01% | 966: 1000 | 33 | 10,407 | Sarna | 364 | " Santal " | 50 | Bahaitum |
| B. | Chandigarh | 1.1 million | 246 | 6.50% | 618: 1000 | 0 | 89 | atheism | 40 | "Nirankari" | 36 | Bahaitum |
| 5 | Chhattisgarh ( 6.2 %) | 25.5 million | 494,594 | 96.46% | 1026: 1000 | 42 | 368,438 | "Gondi" | 57.011 | "Adim dhamm" | 28,411 | "Adi Dharam" |
| C. | Dadra and Nagar Haveli [ i-3 ] | 0.3 million | 293 | 66.12% | 1254: 1000 | 7th | 52 | Parsees / Zoroastr. | 5 | "Tribal Religion" | 4th | atheism |
| D. | Daman and Diu [ i-3 ] | 0.2 million | 79 | 11.39% | 881: 1000 | 5 | 67 | Parsees / Zoroastr. | 12 | unclassified | 0 | |
| G | Delhi (capital territory) | 16.8 million | 2,197 | 1.32% | 914: 1000 | 0 | 541 | atheism | 221 | Parsees / Zoroastr. | 90 | "Nirankari" |
| 6th | Goa | 1.5 million | 258 | 26.36% | 804: 1000 | 8th | 61 | atheism | 53 | Parsees / Zoroastr. | 4th | Bahaitum |
| 7th | Gujarat | 60.4 million | 16,480 | 33.48% | 971: 1000 | 29 | 9,727 | Parsees / Zoroastr. | 1,981 | "Addi Bassi" | 1,353 | Parsees / Zoroastr. |
| 8th | Haryana | 25.4 million | 2,548 | 39.76% | 1293: 1000 | 0 | 266 | "Nirankari" | 180 | atheism | 83 | Parsees / Zoroastr. |
| 9 | Himachal Pradesh | 6.9 million | 856 | 90.90% | 857: 1000 | 10 | 252 | atheism | 105 | Bahaitum | 55 | Sarna |
| 10 | Jammu and Kashmir (State) [ i-1 ] | 12.5 million | 1,508 | 83.95% | 880: 1000 | 12 | 30th | atheism | 2 | Parsees / Zoroastr. | 1 | "Sanamahi" |
| 11 | Jharkhand ( 53.4 %) | 33.0 million | 4,235,786 | 91.68% | 1004: 1000 | 32 | 4,131,282 | Sarna | 42,422 | "Addi Bassi" | 29,187 | "Bidin" |
| 12 | Karnataka | 61.1 million | 11,263 | 45.02% | 975: 1000 | 50 | 1,199 | "Tribal Religion" | 443 | Parsees / Zoroastr. | 178 | "Adi Bassi" |
| 13 | Kerala | 33.4 million | 7,618 | 46.95% | 852: 1000 | 36 | 4,896 | atheism | 233 | "Paniyar" | 189 | Bahaitum |
| E. | Lakshadweep (islands) | <0.1 million | 7th | 100.00% | 167: 1000 | 1 | 1 | "Doni Polo" | 1 | atheism | 5 | unclassified |
| 14th | Madhya Pradesh ( 7.6 %) | 72.6 million | 599,594 | 98.79% | 1021: 1000 | 43 | 584,884 | "Gondi" | 3,022 | "Addi Bassi" | 1,226 | "Nature Religion" |
| 15th | Maharashtra ( 2.3 %) | 112.4 million | 178,965 | 52.33% | 992: 1000 | 45 | 66,857 | "Gondi" | 44,854 | Parsees / Zoroastr. | 18,833 | "Adi Bassi" |
| 16 | Manipur ( 2.9 %) | 2.7 million | 233,767 | 59.83% | 1020: 1000 | 34 | 222,315 | "Sanamahi" | 6,444 | "Heraka" | 2,032 | Judaism |
| 17th | Meghalaya ( 3.3 %) | 3.0 million | 258.271 | 90.08% | 1018: 1000 | 17th | 138,480 | Khasi | 84,258 | Niamtre | 19,803 | Songsarek |
| 18th | Mizoram | 1.1 million | 808 | 53.71% | 1010: 1000 | 15th | 332 | Judaism | 30th | atheism | 16 | "Doni Polo" |
| 19th | Nagaland | 2.0 million | 3.214 | 93.25% | 984: 1000 | 5 | 2,475 | "Heraka" | 251 | " Animist " | 176 | " Pagan " |
| 20th | Odisha ( 6.0 %) | 42.0 million | 478.317 | 96.56% | 1030: 1000 | 62 | 403,350 | Sarna | 53,711 | "Adi Dharam" | 8,946 | "Adi" |
| F. | Pondicherry | 1.2 million | 168 | 23.21% | 909: 1000 | 0 | 44 | atheism | 8th | Parsees / Zoroastr. | 7th | Bahaitum |
| 21st | Punjab | 27.7 million | 10,886 | 61.05% | 898: 1000 | 0 | 1,143 | "Nirankari" | 569 | atheism | 190 | Sarna |
| 22nd | Rajasthan | 68.5 million | 4,676 | 72.86% | 949: 1000 | 12 | 878 | "Addi Bassi" | 114 | "Bhil" | 85 | Parsees / Zoroastr. |
| 23 | Sikkim | 0.6 million | 16,300 | 96.72% | 958: 1000 | 4th | 12,331 | "Yumasam" | 3,300 | " Animist " | 228 | Bahaitum |
| 24 | Tamil Nadu | 72.1 million | 7,414 | 34.89% | 961: 1000 | 36 | 1,297 | atheism | 271 | "AC" | 127 | Parsees / Zoroastr. |
| 29 | Telangana (from 2014) [ i-2 ] | 35.3 million | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 25th | Tripura | 3.7 million | 1,514 | 80.85% | 914: 1000 | 19th | 614 | Bahaitum | 161 | "Subba" | 53 | atheism |
| 26th | Uttar Pradesh | 199.8 million | 13,598 | 69.99% | 923: 1000 | 15th | 3,419 | "Gondi" | 2,425 | atheism | 597 | Bahaitum |
| 27 | Uttarakhand | 10.1 million | 993 | 69.69% | 970: 1000 | 5 | 572 | atheism | 5 | Judaism | 5 | Parsees / Zoroastr. |
| 28 | West Bengal ( 11.9 %) | 91.3 million | 942.297 | 97.46% | 1005: 1000 | 40 | 506.350 | Sari Dharma | 403.250 | Sarna | 6,735 | "Yumasam" |
| [ 36 ] | State 1-29 Territory A-G |
Residents | Other R. and Ü. |
rural | Female | ST | number | Surname | number | Surname | number | Surname |
| mostly mentioned | second most popular | third most named | ||||||||||
Additional Information
| Things to know about the states (# 1–29) and the 7 Union Territories (# A – G) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | map | National emblem | State / territory | Capital | Official languages | useful information |
| [ 36 ] |
|

|
भारत Bharat |
New Delhi |
Hindi and English and 22 constitutional languages |
India got its German name from the river Indus , which rises in Tibet and whose name is derived from the Sanskrit word Sindhu ("river"). In Urdu the country is called Hind , the Hindi designation Bharat became the official name. The coat of arms of India shows the pillar ( capital ) of an "Ashoka column", which the Maurya ruler Ashoka in the 3rd century BC. In his large area. The capital consists of four back to back lions standing on a bell-shaped lotus base . Between the lion and the lotus element there is the wheel symbol ( Dharmachakra ) and four smaller animal representations (humpback cattle, horse, elephant, lion), of which only horse and humpback cattle can be seen in the coat of arms. |
| A. |

|

|
Andaman and Nicobar Islands (islands) अंडमान और नोकोबार द्वीप समूह |
Port Blair | Tribal languages, Hindi |
Before India's independence, the islands of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands served as places of exile for members of the Indian independence movement due to their seclusion. The island groups are located in the Andaman Sea (Andaman Sea), around 1,200 km southeast of Calcutta and 1,200 km east of Chennai . Tourism is an important source of income for the islands, but an additional special permit is required in addition to a visa for India. |
| 1 |
|

|
Andhra Pradesh ఆంధ్ర ప్రదేశ్ |
Hyderabad | Telugu | The name of the state means "Land of Andhra" in Sanskrit , a people known in pre-Christian times. The state was created in 1953 as the state of Andhra from the Telugu-speaking parts of the then state of Madras. From 1956 to 2014 Telangana also belonged to Andhra Pradesh, until it became a separate state in 2014. Hyderabad initially remained the common capital of both states. |
| 2 |

|
|
Arunachal Pradesh अरुणाचल प्रदेश |
Itanagar | English | Arunachal Pradesh means "land of sunrise". It is controversial territory that consists largely of the area of the North-East Frontier Tract . This area came late to British India and is also claimed by the People's Republic of China. In 1962 there was a border war between the two states. |
| 3 |

|

|
Assam অসম |
Dispur |
Asamiya , Bengali , Bodo , Santali |
After India gained independence from the British, Assam comprised the entire area of northeast India . The region is only connected to the rest of India by a narrow land corridor, which has hampered its socio-economic development. The many different ethnic groups in the area strived for autonomy and in the course of time several regions were separated from Assam and became new states. |
| 4th |

|

|
Bihar बिहार |
Patna |
Hindi , Maithili , Santali |
Bihar is considered the poorest state in India. The state is very densely populated, but also has very fertile farmland. Floods occur more frequently during the monsoon season , which often affects several million people. |
| B. |
|

|
Chandigarh : ਚੰਡੀਗੜ੍ਹ चंडीगढ़ |
Chandigarh |
Punjabi , Hindi |
Chandigarh is the capital of the states of Punjab in the west and Haryana in the east of the city. The US city planner Albert Mayer and his partner were initially commissioned to build a new capital . After this had a fatal accident, Mayer withdrew from the planning. At Nehru's request, he was succeeded by the Swiss architect Le Corbusier . |
| 5 |

|

|
Chhattisgarh छत्तीसगढ़ |
Raipur | Hindi | Chhattisgarh was formed on November 1, 2000 by a majority vote of both chambers of the federal parliament and the parliament of Madhya Pradesh by splitting off the eastern districts of this state. |
| C. |

|

|
Dadra and Nagar Haveli દાદરા-નગરહવેલી |
Silvassa | Gujarati | Dadra is an enclave in the Indian state of Gujarat, Nagar Haveli is only a few kilometers to the south between the states of Gujarat and Maharashtra. In 1954, nationalists took power. India refused to allow Portuguese troops to pass through Indian territory, so this condition lasted until 1961 when India regularly annexed the area. Dadra and Nagar Haveli was merged with Daman and Diu to form a unition territory in 2020. |
| D. |
|

|
Daman and Diu દમન ઔર દીવ |
Daman | Gujarati | Damão e Diu used to be part of the Portuguese colony Portuguese India together with Goa. The name "Daman" probably comes from the name of the Damanganga river, which flows into the Arabian Sea here. Daman (like Diu) is also known for the fact that, in contrast to the state of Gujarat, alcohol is allowed. Daman and Diu were united with Dadra and Nagar Haveli in 2020 to form a union territory. |
| G |

|

|
Delhi (Capital Territory ) दिल्ली |
New Delhi |
Hindi Urdu |
The Union Territory of Delhi ("City of the Heart") consists of several individual cities both geographically and historically. The two largest cities are Delhi and the capital New Delhi. |
| 6th |

|

|
Goa गोंय |
Panaji | Konkani | Goa is the smallest state and was a Portuguese colony for around 450 years. Hence the high proportion of the Catholic population. With its beaches, Goa is one of the most important tourist destinations in India. |
| 7th |

|

|
Gujarat ગુજરાત |
Gandhinagar | Gujarati | Gujarat is the westernmost coastal (and federal) state of India with a coastline of 1,600 km - more than any other state and represents a transition from the monsoon coast to the drier Rajasthan and Sindh. In Gujarat, the last occurrence of lions is found in their natural range outside of Africa. |
| 8th |

|

|
Haryana हरियाणा |
Chandigarh | Hindi | In 1947 India and Pakistan were given independence and the Punjab was divided between India and Pakistan. In 1966, the Hindi-speaking part of Indian Punjab was split off from the rest of the state. It became a separate Indian state as Haryana. |
| 9 |

|

|
Himachal Pradesh हिमाचल प्रदेश |
Shimla | Hindi | Himachal Pradesh consists of 68% forest areas. Above the city of Dharmshala, in front of the first high mountain range of the Himalayas, the 14th Dalai Lama has his residence in exile. |
| 10 |

|

|
Jammu and Kashmir (State) जम्मू और कश्मीर Flag : |
Srinagar and Jammu |
Kashmiri Dogri |
Jammu and Kashmir is part of the disputed Kashmir region between the People's Republic of China, India and Pakistan . The state consists of three cultural landscapes: the predominantly Muslim Kashmir Valley, the predominantly Hindu Jammu and the Buddhist plateau of Ladakh . The state government has its seat in Srinagar in summer and in Jammu in winter . On October 31, 2019, the state was dissolved and divided into the union territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh . |
| 11 |

|

|
Jharkhand झारखंड |
Ranchi |
Hindi Santali |
The most important coal mining areas in India are located in Jharkhand. The highest mountain in Jharkhand is 1,365 m of Parasnath , an important pilgrimage of the religious community of Jainism '. The history of Jharkhand has long been closely linked to the history of today's neighboring Bihar, from which it was spun off in 2000. |
| 12 |

|

|
Karnataka ಕರ್ನಾಟಕ |
Bangalore | Kannada | Until 1973, Karnataka was named Mysore , after a former princely state . The capital of Mysore is Bengaluru (until 2014: Bangalore ), a center of the Indian IT industry. |
| 13 |

|
|
Kerala കേരളം |
Thiruvananthapuram | Malayalam | The state of Kerala was created in 1956 through the merger of the three former princely states of Cochin, Malabar and Travancore. The name Kerala literally means "land of coconut palms". In terms of socio-economic factors (education, women's rights, economic performance), Kerala is one of the most developed states in India. |
| E. |

|

|
Lakshadweep (Islands) ലക്ഷദ്വീപ് |
Kavaratti | Malayalam | The islands are located north of the Maldives, between 200 and 300 km from the coast of Kerala. The origin of the name Lakhshadweep is not clear. The island population is almost entirely Muslim. |
| 14th |

|

|
Madhya Pradesh मध्य प्रदेश |
Bhopal | Hindi | Madhya Pradesh ("Middle State") arose after independence for the most part from the former British Central Provinces . In independent India, the borders changed twice: in 1956 in the States Reorganization Act and in 2000 when Chhattisgarh was formed. The state is considered a heartland of Hindu culture. |
| 15th |

|

|
Maharashtra महाराष्ट्र |
Mumbai |
Marathi Santali |
At the beginning of the 20th century, parts of the former areas of Bombay, Hyderabad and the central provinces were located in the area of today's Maharashtra. After Bombay expanded to include the entire area of today's Maharashtra in 1956, Bombay was divided into the states of Gujarat and Maharashtra along the language border in 1960. |
| 16 |

|

|
Manipur মনিপুর |
Imphal |
Meitei Bishnupriya Manipuri |
Manipur gained independence from Burma in 1826 with the help of the British . The Raja of Manipur received annual compensation for land ceded to Burma and the setting up of border posts. In the state today, separatists ( Naga ) are fighting for independence or joining Nagaland . |
| 17th |
|

|
Meghalaya मेघालय |
Shillong |
Khasi Garo |
The state of Meghalaya was created in 1972 through the spin-off of two mountain districts with a predominantly tribal population ( Scheduled Tribes ) from Assam. The newly formed Sanskrit name Meghalaya means " Abode of the Clouds" and thus describes one of the rainiest areas in the world with over 120 rainy days in the extensive rainy season between April and October. In the south of Meghalaya, the Khasi mountains drop steeply and cause the rising monsoon clouds to rain down. Here, the mountain town of Cherrapunji has held the world record for the highest annual amount of precipitation (26.5 meters ) since 1861 , the village of Mawsynram has held the world record for the highest average annual amount (11.9 meters) since 2015. A part of this persistent monsoon rain flows off in countless waterfalls , the Nohkalikai Falls are the highest in India with 340 meters. |
| 18th |
|
|
Mizoram मिज़ोरम |
Aizawl | Mizo | Mizoram is one of the seven "sister states" in northeast India. The population is predominantly Christian and belongs to Tibetan-Burmese ethnic groups. |
| 19th |

|

|
Nagaland नागालैंड |
Kohima | English | About 84% of the population of Nagaland belong to 16 Naga tribes, which are an Indo-Mongolian ethnic group.
Over 85% of the population are Christians, the majority Baptists . |
| 20th |

|

|
Odisha (until 2011: Orissa) ଓଡ଼ିଶା |
Bhubaneswar |
Oriya Santali |
In classical Indian history, the state of Kalinga existed in today's Odisha, which was so bloody conquered by Emperor Ashoka that he supposedly converted to Buddhism out of repentance. Until 2011, the state was called Orissa . |
| F. |

|

|
Puducherry புதுச்சேரி |
Pondicherry | Tamil | Puducherry includes the areas of Mahé on the south west coast, which were in the French colonial area of French India until 1954, and the areas of Karaikal , Yanam and Pondicherry itself on the east coast , which was renamed Puducherry in 2006. |
| 21st |
|

|
Punjab ਪੰਜਾਬ |
Chandigarh |
Punjabi Hindi , Urdu English |
The name Panjab comes from Persian and literally means "five waters", an allusion to the five major rivers in the region. The heartland of the Sikhs, like other areas, was divided into independence between India and Pakistan in 1947. The part that remained with India was divided again in 1966 into the Hindu state of Haryana and the Sikh state of Punjab. |
| 22nd |

|

|
Rajasthan राजस्थान |
Jaipur |
Hindi English Rajasthani |
Rajasthan, the land of kings - tourist magnet with mainly Jaipur, Jodhpur and Udaipur as "oriental fairy tale land " - comprises the driest areas of India. However, the Thar desert is considered to be the most populous desert in the world, as the inhabitants have been collecting seasonal rain for centuries in order to have water for the fields even in the drought. |
| 23 |

|

|
Sikkim सिक्किम |
Gangtok | Lepcha, Limbu Tibetan, Nepali Hindi |
After a referendum strongly influenced by India, the former Kingdom of Sikkim declared its accession as the 22nd state of the Indian Union in 1975. India's dispute with neighboring China over recognition of this step was only contractually settled in 2005. |
| 24 |

|

|
Tamil Nadu தமிழ் நாடு |
Chennai | Tamil | Tamil Nadu originated in its current borders in 1956 along the Tamil language border and was initially called Madras . It was not until 1969 that the state was given its current name, which can be interpreted either as "Tamil land" or as "land of the Tamil language". The capital is Chennai, which was named Madras until 1996 . |
| 29 |

|

|
Telangana (from 2014) తెలంగాణ تلنگانہ |
Hyderabad |
Telugu Urdu |
Telangana was separated from Andhra Pradesh on June 2, 2014 and made a state of its own. The joint capital of the two states will initially remain Hyderabad. |
| 25th |

|

|
Tripura ত্রিপুরা |
Agartala |
Bengali Kokborok |
As a region between Bengal and Assam, Tripura is one of the East Indian tea states. It literally lies as a wedge between the main part of Bangladesh and the south-east of the country ( Chittagong ) and was therefore strategically interesting for India, especially before the independence of East Pakistan. |
| 26th |

|

|
Uttar Pradesh उत्तर प्रदेश |
Lucknow ( Lucknow ) |
Hindi | With its 200 million inhabitants (as of 2011), Uttar Pradesh is India's most populous state. It covers the upper half of the Ganges and Yamuna plains with the holy city of Varanasi and Agra with the Taj Mahal tomb . |
| 27 |

|

|
Uttarakhand उत्तराखंड |
Dehradun |
Hindi Urdu |
Uttarakhand, until 2006 Uttaranchal , was created in 2000 by splitting off the mountainous northern part of Uttar Pradesh. Here is the highest mountain in India, Nanda Devi (7816 m). |
| 28 |

|

|
West Bengal পশ্চিমবঙ্গ |
Calcutta |
Bengali Santali |
As early as 1905, Bengal was divided by the English along the Hindu-Muslim religious border, but the separation from East Pakistan to independence in 1947 led to mass exodus, displacement and murder. Global warming will have severe consequences for low-lying West Bengal - as for Bangladesh , which has been independent since 1971 . |
| [ 36 ] | map | National emblem | State 1-29, territory A-G | Capital | Official languages | useful information |
literature
- The states. In: Christian Wagner: The political system of India. An introduction. VS Verlag für Sozialwissenschaften, Wiesbaden 2006, ISBN 3-531-14002-7 , Chapter 2.5., Pp. 87-97 ( reading sample in the Google book search).
- Verinder Grover, Ranjana Arora (Eds.): Encyclopaedia of India and Her States. 10 volumes. Deep & Deep, New Delhi 1996, ISBN 81-7100-730-9 (English).
Web links
- Reserve Bank of India : Handbook of Statistics on Indian States 2017–18. Edition of May 5, 2018, accessed on January 10, 2019 (English; 129 statistical tables for the Indian states and territories, with download option).
Individual evidence
- ^ Announcement: New UTs of Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh come into existence. In: NewsOnAir.com. October 31, 2019, accessed November 13, 2019.
- ↑ The separation of Ladakh from the Lok Sabha was decided on August 5, 2019 , see message: Article 370 revoked Updates: Jammu & Kashmir is now a Union Territory, Lok Sabha passes bifurcation bill. In: businesstoday.in. August 6, 2019, accessed on November 13, 2019 (English, with blog transcript of the day).
-
↑ a b c d e Census of India 2011 (basic data): States Census 2011. ( Memento of 28 November 2018 Internet Archive ) Census Population 2015 Data retrieved on January 10, 2019 (English; no Telangana and only claimed total numbers on the controversial Jammu and Kashmir (state) ).
→ Download overview of all 2011 basic data from 2013: Area and Population ( Memento from March 14, 2016 in the Internet Archive ).
- ↑ a b c d Telangana from 2014 (residents): Total population of the Telangana districts according to the 2011 census, Census of India 2011: Primary Census Abstract - Andhra Pradesh. (Fragment, English and Hindi); PDF: 606 kB, 11 pages ( Memento of 18 April 2016 Internet Archive ).
- ↑ a b Census of India 2011 (residents, under 7 years of age, Scheduled Tribes, literacy, employment rate): Table A-5: Union Primary Census Abstract - 2011. Government of India, New Delhi 2011 (? Fragment, provisional?) English and Hindi; PDF: 411 kB, 18 pages ( Memento from July 31, 2013 in the Internet Archive ).
- ^ A b All the founding years of the states / territories (2019): Ben M. Cahoon: States of India since 1947. In: Worldstatesmen.org. 2019, accessed on January 10, 2019.
- ↑ a b Percentages of rural areas in India: Census of India 2011: Primary Census Abstract - India: Chapter 1 - Population, Size and Decadal Change. Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner India (C. Chandramouli), New Delhi 2013, p. 12: Table Statement 5: Proportion of rural and urban population: 2001–2011 ( PDF: 8.8 MB, 27 pages on censusindia .gov.in).
- ↑ a b Census of India 2011 (gender ratio): Sex Ratio in India. ( Memento of November 28, 2018 in the Internet Archive ) Census Population 2015 Data, accessed on January 10, 2019 (English; without Telangana ).
- ↑ a b National Institution for Transforming India ( Fertility Rate 2011): Total Fertility Rate (TFR) (Birth / woman). Government of India 2018, accessed January 10, 2019.
-
↑ a b
Census of India 2011 (Reading Skills): Literacy in India. ( Memento of November 28, 2018 in the Internet Archive ) Census Population 2015 Data, accessed on January 10, 2019 (English; without Telangana ).
→ Census of India 2011: Table 2 (3) Literates and literacy rates by sex: 2011. Government of India, New Delhi 2011 (? Fragment, provisional, without Telangana ; English; PDF: 10.5 kB, 1 page ( Memento of April 9, 2011 in the Internet Archive ). - ^ The Economist : Comparing Indian states and territories with countries - An Indian summary. ( Memento from February 10, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) 2011 (English).
- ↑ a b c d 2012 poverty rate : Reserve Bank of India : Publications: Table 156: Number and Percentage of Population Below Poverty Line. September 15, 2018; ibid: Publications: Table 12: State-Wise Poverty Rate. May 5, 2018, both accessed January 10, 2019.
-
↑ a b
HDI 2017: Global Data Lab: Subnational Human Development Index. Version 2.1. Institute for Management Research, Radboud University Nijmegen, October 2017, accessed on January 10, 2019;
→ Note on setting the page for "India": First click on "Deselect all" at the top of the Countries option , then select the state "India", then set "Scale to national extremes" for the color gradations of the values under the Color scales option . -
↑ a b
Tables with HDI, GDI and GEM in India 2006: Government of India, UNDP -India: Gendering Human Development Indices: Recasting the Gender Development Index and Gender Empowerment Measure for India (Summary Report, revised). Ministry of Women and Child Development, Delhi 2009, 3 tables on p. 11, 12 and 15 (English); PDF: 1.6 MB, 20 pages ( memento of March 29, 2017 in the Internet Archive );
→ p. 11: Table 4.4: Dimension-wise HDI scores for States / UTs - 2006 and 1996.
→ p. 12: Table 4.5: Dimension-wise GDI scores for States / UTs - 2006 and 1996.
→ p. 15: Table 5.2: Dimension-wise GEM Scores 2006 and 1996. - ↑ a b Femdex 2015: McKinsey Global Institute: The power of parity: Advancing women's equality in India. November 2015, table p. 11: Exhibit 7: States have significant variation in Femdex (English); PDF: 3.0 MB, 36 pages ( memento of December 9, 2018 in the Internet Archive ).
-
↑ a b
Overview of GDP 2014: StatisticsTimes.com: Indian states by GDP. August 20, 2015, accessed January 10, 2019.
→ Reserve Bank of India : Publications: Table 15: Gross State Domestic Product At Factor Cost (Current Prices). May 5, 2018, accessed January 10, 2019.
-
↑ a b
Overview of GDP per capita 2014: StatisticsTimes.com: Indian states by GDP per capita. ( Memento of October 30, 2017 in the Internet Archive ) August 20, 2015, accessed on January 10, 2019 (English).
→ Reserve Bank of India : Publications: Table 13: Per Capita Net State Domestic Product at Factor Cost (Current Prices). May 5, 2018, accessed January 10, 2019. -
↑ Development Program of the United Nations (UNDP) - with search term “India” (English):
→ HDI: Table 2: Human Development Index Trends (1990–2017).
→ IHDI: Table 3: Inequality-adjusted Human Development Index.
→ GDI: Table 4: Gender Development Index.
→ GII: Table 5: Gender Inequality Index.
→ GEM: Dashboard 3: Women's empowerment.
- ↑ a b Census of India 2011 (Religions): Religion Census 2011. ( Memento from July 11, 2017 in the Internet Archive ) Hindu Religion Census 2011. ( Memento from January 2, 2019 in the Internet Archive ) Muslim Religion Census 2011. Christian Religion Census 2011. Sikh Religion Census 2011. ( Memento from January 2, 2019 in the Internet Archive ) Buddhist Religion Census 2011. ( Memento from December 21, 2018 in the Internet Archive ) Jain Religion Census 2011. ( Memento from January 2, 2019 in the Internet Archive ) Census Population 2015 Data, accessed January 10, 2019 (English; excluding Telangana ).
- ↑ a b Census of India 2001 (Religions): Religion: Hindus. ( Memento of September 27, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) Religion: Muslims. ( Memento of September 27, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) Religion: Christians. ( Memento of September 27, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) Religion: Sikhs. ( Memento of September 27, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) Religion: Buddhists. ( Memento of September 27, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) Religion: Jains. ( Memento of September 27, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) First Report on Religion, without publisher, without date (English; 6 PDF tables on wayback.archive.org).
- ↑ a b c d Table on members of “other religions” (including atheists) in India and all federal states (2011): C-01 Appendix: Details of Religious Community Shown Under “Other Religions and Persuasions” in Main Table C-1-2011 (India & States / UTs). Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India, New Delhi 2019 (English; XLSX-Excel: 126 kB on censusindia.gov.in).
- ↑ a b On the number of Scheduled Tribes per state, a total of 693 (2014): Ministry of Tribal Affairs: Report of the High Level Committee on Socio-Economic, Health and Educational Status of Tribal Communities Of India. Government of India, New Delhi May 2014, p. 43/44 3.3: Number of Scheduled Tribes , here p. 44: Table 3.6: State-wise Number of Scheduled Tribes (English; PDF: 5.0 MB, 431 pages on indiaenvironmentportal.org.in).