Foehn storm and heavy rain in the Alpine region in November 2014
| Tiefs Pia, Qendresa, Roswitha, NN, Stephanie / Thea, NN, NN | |
|---|---|
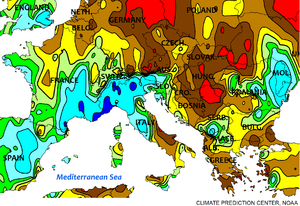
| Precipitation anomaly November 2014 | |
| more than four times (400%) , less than a quarter (25%) of the normal amount (rough data, NOAA-NWS) | |
| Storm series | Mediterranean and Atlantic lows |
| Data | |
| Climax | 3rd – 7th, 9th – 12th, 14th – 17th November 2014 |
| Squalls | 187 km / h ( Titlis , Nov. 4 ) |
| Rainfall 72 hours | 500 mm ( Plöckenpass , 4.-7 Nov.. ) |
| Tornadoes | 6 ( F2 in Torricella , November 12 in the morning ) |
| Monthly mean temperature (since) | warmest ever measured November (+3.8 ° C) ( Austria , 1767; 247 years ) |
| consequences | |
| affected areas | Alpine region and Italy |
| Victim | 19 (as of Nov. 16) |
| Damage amount | > € 1 billion (first estimates) |
| Before that, series of storms in southern Europe in October , followed by Medea (Xandra) | |
In the first three weeks of November 2014, a series of lows with foehn storms and heavy rain hit the Alpine region and Italy . Serious damage and several fatalities occurred. The damage is estimated in the billions in Italy alone.
meteorology
Origin and weather conditions
The series of weather events was triggered by six low pressure areas , a low over the British Isles , Pia , a successive Italian low Qendresa , another Atlantic low Roswitha , an unnamed Italian low and a subsequent Atlantic low Stephanie / Thea with two as well nameless partial and subsequent lows over the Alps. Between the Atlantic lows, there were widespread incursions of polar cold air over the Atlantic and powerful Scirocco over the Mediterranean .

(rough data, NOAA-NWS)
Pia formed as early as October 28th over the central North Atlantic as an outgraft of a Greenland Depression and moved towards the British Isles. A powerful high-pressure complex Pitter / Quinn lay over Eastern Europe and then over the Black Sea , which led to a certain blockade situation . Pia did not disintegrate into a high altitude core over the North Sea until November 5th .
As a result, a powerful fault zone formed over the mainland at the front of the low, which at times stretched as a band of clouds from North Africa to northern Scandinavia and into the White Sea . It rained more intensely there. The pressure differences between the two sides of the Alps reached around 12 hPa . As a result, there was an extreme Föhnorkan in front of the front system in the Alps on November 3rd, 4th and 5th (Monday to Wednesday) . This reached on La Masse ( 2766 m ) in the French Alps, on the Titlis ( 3020 m above sea level ), in Gütsch ob Andermatt ( 2287 m above sea level ) and on Piz Martegnas ( 2670 m above sea level ). in Switzerland as well as on the Tyrolean Patscherkofel ( 2245 m above sea level ) peaks over 180 km / h, even valleys recorded 130 km / h, the foothills of the Alps still 100 km / h. The night temperatures in Saint-Maurice VS and Altenrhein SG , for example, stayed just below 20 ° C, i.e. a tropical night .
At the back of the low, humid air masses penetrated south over the Iberian Peninsula , with hail in Extremadura and rain in Morocco . At the same time, the disturbance in the Southern Alps created a low, named Qendresa , which crossed the Ligurian Sea . The classic early V weather situation ( deep south of the Alps ) brought large amounts of rain to central and northern Italy , the sea Alps and the southern side of the Alps , with precipitation amounts of up to 450 liters per square meter in 48 hours.

The subsequent low Roswitha near Iceland caused the foehn to collapse temporarily on November 6th, with heavy snowfall on the main Alpine ridge and as far as valley locations. Qendresa temporarily formed a Vb-like characteristic with a side core over the Baltic from (qendresa II) , a south Sicily mounted sequence core (qendresa I) shortly even hurricane-like structures ( medicane ). As a result, storms and precipitation increasingly shifted to southern Italy to Malta . In Sicily the gusts reached 140 km / h, tornadoes occurred. Heavy Jugo blew over the Adriatic , with temperatures of up to 25 ° C ( Senju , Croatia) and gusts of over 110 km / h ( Vis ). The two Qendresa cores disintegrated over Greece ( Vd-Tief after Bebber ) and northern Russia. On the Aegean Sea , the old Mediterranean depth intensified again, with heavy rainfall there on November 9th.
Around Sunday, November 9th, the weather conditions were largely the same as five days before: Roswitha was aging across the North Sea and Scandinavia, Low Stephanie advanced on the Atlantic , cold air penetrated beyond Gibraltar in between, a mighty Eastern European high created a blockade situation , and over southern France a new low formed in the cold front on the southern edge of the Alps. Over the Alps, the foehn set in again, with temperatures north of the Alps around 20 ° C, but the speeds remained more moderate, this time the southern storms shifted to the upper Adriatic . Another flood event occurred in the Southern Alps – Sea Alps – Italy area, which was even more intense than before. In the Centovalli ( Camedo station ) 400 mm / 48 h were measured again. The Mediterranean depth then shifted again to the Strait of Sicily . A cold front also ran to the Alps from the mighty deep Stephanie , formed on the 6th near Newfoundland and still across the central Atlantic, creating a new northern foehn and a Mediterranean low on the Alpine Alps, named Stephanie II . This united with the previous low in Italy and again briefly showed a Vb characteristic over the Eastern Alps , but this remained without any particular effect. Again there were tornadoes, three in Apulia , some of which reached category F2 on the Fujita scale (180 km / h). The Adriatic reported storms of up to 100 km / h, the rain in the Balkans concentrated in Dalmatia . This low / high- low system withdrew again over Greece.
On November 14, the second cold front formed the well-fixed northwest standing of Ireland lows Stephanie - the blocking Russlandoch Robin had to northern Scandinavia dilated - a fourth low over southern France from (also remained unnamed), the third classical foehn Südstau event caused. On the 15th, the temperatures in Vaduz reached over +19 ° C at night at 3 a.m. and the wind again reached over 90 km / h in the valley (top 123 km / h Gütsch above Andermatt ). Again, the same areas were as in the previous days hit by intense heavy rain, with 215 mm / 24 h in Génolhac ( Cevennes ), up to 200 mm / 24 h in Port Grimaud (Var) and over 170 mm in just a few hours on the Rio Basco near Genoa and in 48 h in southern Ticino . The driving low Stephanie , at that time already 10 days old, disintegrated into several nuclei, one of which was newly formed (and henceforth called Thea ), but soon disintegrated again over northern France. In contrast to the previous events, the low of southern France remained hanging over the central alpine region and then lost itself in the undertow of Theas . This low was lost around the 21st of the month over the Black Sea.
On 16./17. In turn, an (unnamed) low formed over southern France, which crossed the Alps comparatively quickly via Liguria and lost itself over the Czech Republic on November 19 . This low resulted in further locally intense precipitation also on the Balkan side of the upper Adriatic .
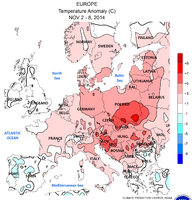
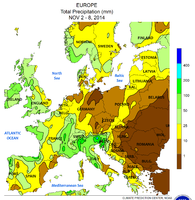
Temperature deviation 2. – 8. (from the long-term average of these days): The foehn areas in the northern foothills of the Alps and on the Dinarides , and the much too warm Eastern Europe due to the dragged Scirocco
Temperature deviation 9th – 15th: Increased warm air intake to the Balkans on the front of the Italian lowlands
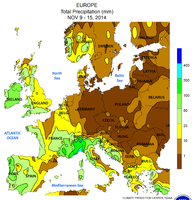
Precipitation totals 9th – 15th: Extreme events again in Liguria and Ticino (over 400 mm / week), from the Côte d'Azur to the southern Swiss side of the Alps and on the Cevennes each over 200 mm; no precipitation in the lee of the Alps and Dinarides
- (all rough data, NOAA-NWS)
Climatic relationships
A similar situation with southern foehn and heavy rain south of the Alps had already occurred in the middle of the previous month (low Dagmar , record temperatures north of the Alps around October 9, heavy floods in southern France, central and northern Italy, in Ticino, in Slovenia). The powerful south-westerly high-altitude currents around the end of October with continued abnormal warmth in Central Europe were associated with severe floods in Norway .
After stabilization in the meantime, from November 24th with the Mediterranean low Medea (Xandra) there was another event lasting more than two weeks with again large amounts of rain from southern France to Greece, with a freezing rain from Bohemia to Hungary, and 8 other fatalities.

The reason for these weather events is that the jet stream is currently oscillating strongly. The North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) and the Arctic Oscillation (AO) show a wide range of fluctuations. During the November event, the jet stream, which regularly blows eastwards, pulled through Central Europe almost in a south-north direction. As a result, the westerly wind drift largely breaks off, and the weather situations remain stationary even if the centers of action change. The two major weather situations around the 4th / 5th and 9./10. were meteorologically so similar that MeteoSwiss spoke of “ copy-paste ” weather.
This large-scale climatic situation has occurred several times in the last few years, with extreme events then accumulating throughout the northern hemisphere, with precipitation and drought or heat and cold anomalies concentrating regionally. At the same time, one of the strongest early onset of winter in the history of measurements took place in North America (−33 ° C in Casper , Rocky Mountains; 0 ° border on the Gulf of Mexico in Texas and Louisiana ; over 1 m of snow on the Great Lakes ). At the same time, there was a southerly current in the North Pacific as in Europe, with an abnormal +2 ° C in Alaska . This event lasted from the 8th to the 23rd of the month. The second body of cold air was fixed over Siberia , here it was far too cold for the season with temperatures down to –20 ° C around the Ob and areas of Central Asia and -40 ° C in northern Siberia. At the time, typhoon Nuri off East Asia lay over the Pacific , the second strongest of the year, which in its later phase was also called the Bering Sea Bomb Cyclone because it was shaped by an explosively developing enormous high pressure anomaly over the Bering Sea . In its later phase it led the cold air to North America.
Estimation of the annuality
While it was a relatively dry year north of the Alps - despite the overall completely rainy summer - south of the Alps, in some cases never-before-recorded amounts of rain were measured.
On the Plöckenpass an approximately 60-80 year extreme event was recorded with 430 l / m² from Tuesday 4th to Thursday 6th morning and almost 500 l / m² until Friday, November 7th . In Camedo in Ticino there was a total of 1045 mm of precipitation in 15 days from November 2nd to 16th, just below the record value of November 2002 (1122 mm / 15 d, measurements since 1961, the third highest value at this time), in Lugano a little further south in the same time with 515 mm significantly less, but also the third strongest event in the 151-year series of measurements (October / November 1928 547 mm, October / November 1896 543 mm, November 2002 505 mm). This means that the rain is also here in the area of a 50-year event.
It is characterized by the abnormally high temperature that gave the Mediterranean lows their energy. The entire month was the warmest November in the Eastern Alps since the beginning of the closed series of measurements in 1767 (as was the entire autumn), it was 3.8 ° C above the long-term mean (1981-2010, autumn +2.2 ° C) and exceeded it thus November 1926 (+3.4 ° C to mean 1981-2010). For the first time in the more than 250-year history of measurements, parts of Austria remained without frost in autumn, and this continued - despite the freezing rain in eastern Austria - in the Föhntal valleys of western Austria, as Innsbruck ( Innsbruck University weather station ) only reported the first frost day on December 10th (Temperature below 0 ° C, average: October 23). In France, autumn was the second warmest since the beginning of the 20th century (after 2006; +2.3 ° C IN 1981-2010), where Barnas (Ardèche) measured 1,826 mm in 3 months.
Particularly characteristic of the Föhn-Stauregen event is the sharply separated zone on the main Alpine ridge of up to 2½ times normal precipitation south ( Kötschach-Mauthen , Carinthia, 714 m: 619 mm monthly total) and up to only 1 ⁄ 7 north.
Overall, the year on the south side of the Alps is one of the rainiest in history. In some areas of Friuli-Venezia Giulia , precipitation has accumulated to 5000 mm since January, amounts that are typical for monsoons in the Himalayas or the tropics. In Slovenia, the annual total is already reaching values that were last measured in 1965 for the whole year ( Bovec 3700 mm; Bilje / Nova Gorica 2100 mm, in 1965 total 2300 mm; Portorož with 1400 mm probably an amount of rain that has never been measured).
consequences

(rough data, NOAA-NWS)
Initial estimates of the amount of damage for Italy run into billions.
In total, the series of storms claimed 19 lives, eight in Italy, six in France, four in Switzerland and one in Austria.
Switzerland
In Switzerland, due to the foehn storm on November 4th, several railway lines were closed, and Arosa was completely cut off. At 107 km / h, the strongest foehn gust since measurements began in 1981 was recorded on Lake Zurich .
The subsequent accumulation of precipitation was concentrated around the Centovalli ( Camedo 257 l / m² in 24 hours from November 4th), up to 150 cm of fresh snow fell on the southern main ridge of the Alps, and traffic on the Alpine transit routes partially came to a standstill. In Curio near Lugano , a mudslide tore away a house, and a mother and child died.
In the second event, the precipitation was again concentrated on the Centovalli (Camedo around 400 l / m² in 24 hours until November 11th), with warning level 5 on Lake Maggiore and 4 on Lake Lugano .
The third event with an additional 150 l / m² in southern Ticino then led to numerous other mudslides, one with particularly serious consequences. In Davesco near Lugano, two people died again in a buried house, missing people are still wanted. At Lake Lugano and Lake Maggiore , the highest danger level 5 prevailed for several days, the latter was 3 meters above normal (level 196.19 in Locarno ).
Austria
The foehn storm led to damage from forest litter, power outages and covered roofs , particularly in Vorarlberg , in the Innsbruck-Land district and in Salzburg's Pinzgau region . On Sunday in Großwalsertal , a firefighter had a fatal accident while cleaning up.
Then on November 6th and 7th there were traffic obstructions due to 50 cm of snow on the Brenner autobahn, and mudslides on the Plöckenpass (70-year record amount 500 mm / 72 h). In the Drautal and Gailtal valleys , two to three times as much rain fell in two days as an average full November.
Overall, the consequences in southern Austria were limited despite the sometimes record-breaking rainfall, and the subsequent rain fronts had no extreme effects. The Drau power plants had been drained as a precaution, which was criticized in Austria, where later floods in the Lavamünd area nonetheless , as well as in Slovenia, where this already led to flooding due to the drain . In terms of flood protection, the measure was a success, the damage was distributed in a semi-controlled manner, and no specific area was put in serious danger.
France
In southern France , severe flooding occurred as early as November 3rd, for example in the Ardèche (360 mm of precipitation in 48 hours) and around Nice . Here a person died in a mudslide. Waves 4 meters high hit the Côte d'Azur .
The second rain wave around November 9th particularly affected the Var ( Bormes-les-Mimosas 213 mm / 72 h), the Bouches-du-Rhône and again the Alpes-Maritimes ( Antibes 196 mm / 72 h), but in the train of the Ligurian events then also East Corsica .
The third wave of rain began on the night of November 14th to 15th. Although the orange alert was again declared for Bouches-du-Rhône, the Vaucluse , Var and Alpes-Maritimes, the floods in the Gard and Lozère in the Cévennes to the north-west with serious consequences occurred : Here two drivers drowned on Fridays near Pied-de-Borne and in Peyremale , and then a mother with two children in her car in the Droude .
Italy
In Italy, Liguria , Umbria , Tuscany , Lombardy and Emilia-Romagna as well as Veneto and Friuli were particularly affected by severe floods. In Carrara in the Apuan Alps (Tuscany), where the dikes at the Carrione torrent broke and the city was flooded meters high, there was one fatality. Then the damaged area expanded to include the Latium , in Rome after violent thunderstorms on the evening of November 5th, the highest level of alert was declared. As a result, the rains also spread to the Mezzogiorno . A state of emergency prevailed particularly in the south of Sicily . In Acireale and Catania tornadoes focused on damage, another was on Lampedusa reported.
The second rain wave hit largely the same areas again, and also Sardinia . There were several flash floods around Genoa and La Spezia , here a person drowned in Genoa and in Leivi two people died in a mudslide. There was another mudslide victim in Crevacuore near Pray ( Biella , Piedmont). Floods, mud floods and landslides occurred in the entire catchment area of the Po and the adjacent rivers, for example in the Aosta Valley , near Alessandria , around Milan , where Lambro and Seveso in particular overflowed their banks, and the lower Po plain . A person drowned in Ispra on Lake Maggiore . There were also evacuations in Orvieto and around Perugia (Umbria), and again in Massa (Tuscany) / Carrara. Heavy gusts uprooted many trees in Trieste . In southern Italy, areas around Torricella , Ginosa Marina - Castellaneta Marina (both in the province of Taranto) and at Gallipoli (Lecce) were devastated by a tornado each in the morning of November 12th .
The third and the less violent fourth rain wave also had largely the same damage areas in the north. From November 15, violent storms occurred in northern Italy and flash floods again around Genoa and floods in lower Piedmont and Lombardy. In Bolzaneto (Genoa) a cemetery was devastated and numerous coffins washed away. In Cerro di Laveno-Mombello ( Varese ) two people died again in a mudslide , one drowned in the Baraccoi ( Cuneo ). Storms with snow at low altitudes occurred particularly in the Valtellina and Valchiavenna as well as in the Valle d'Aosta . A bridge on Strada Provinciale 1 collapsed at Staffora ( Pavia ). The flood situation on Lake Maggiore and Lake d'Orta is still tense . In the east and south, however, this time there was largely no direct severe damage, there were storms with tree-throwing in Versilia (north-western Tuscany), in Treviso on the 17th at noon a heavy storm with storms and hail, and the southern storm over the Adriatic pushed the water down Venice, where the tide reached 1.20 in the morning on the 18th. The situation is particularly critical on the lower Po , where the second tidal wave rose in places 1–1.5 m above the highest warning level 3. Along the river in the provinces of Piacenza , Parma , Reggio Emilia and Ferrara there were extensive embankments and numerous evacuations. In the central Apennines , precipitation reached 100–150 mm (with a maximum of 250 mm), cities such as Bologna were also threatened .
In Italy there was nationwide criticism of the neglected flood protection infrastructure after several people had died in the previous month . In particular, this is in no way surprising: a total of 9 years with severe November storms claimed 21 lives, while in 1950-2000 only 6 major flood episodes were recorded in November. Therefore, one criticizes the inactivity of the younger years in particular. In Genoa alone there are 35 million euros unused in a disaster protection fund.
Slovenia
The rain event on November 6th and 7th mainly hit western Slovenia. In particular, around Loška Dolina and Ilirska Bistrica in the Primorska (coastal region), entire stretches of land were under water, but also in the Ljubljana area in Planinsko and Cerkniško polje . There were floods at Pivka , Ljubljanica , Krka , Lower Drava and Sava . Mudslides occurred between Tolmin and Nova Gorica .
The following rain waves were comparatively less violent in Slovenia, problematic were the rivers that did not recede, which were still overflowing 10 days later. There was criticism of the preparatory damming of the Drau power plants carried out by Austria. In Maribor the highest flow rate of the last 100 years was measured at 2900 m³ / s . The Slovenian authorities emphasized the previous agreement: This way, the flood peaks could also be distributed in Slovenia, which led to a longer but less severe flood.
See also
- List of weather events in Europe
- Mediterranean Depression Medea (November / December 2014)
- November storm in the Alpine region in 1966
Web links
- GR Brakenridge, D. Slayback, AJ Kettner, F. Policelli, T. De Groeve, S. Cohen: Conditions and Maximum Flood Extent, 2014 Flooding, Northern Italy, DFO Event 4205 , Dartmouth Flood Observatory, 2014 (event documentation on Italy).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f Föhnsturm causes chaos - Arosa cut off from the environment , in Basler Zeitung online, November 4, 2014.
- ↑ a b c Partly extreme amounts of rain in East Tyrol and Upper Carinthia , ZAMG Wetter News , November 6, 2014.
- ↑ a b c Devastanti tornado F2 nel Salento: Torricella, Ginosa e Castellaneta in ginocchio, le FOTO del disastro and I violenti tornado di stamattina intorno Taranto: due “bestie” provenienti dallo Jonio , Peppe Caridi in meteoweb.eu, November 12, 2014 .
- ↑ a b c d e I 4 tornado che negli ultimi 7 giorni hanno colpito Puglia e Sicilia: quando lo Jonio sforna dei “mostri” , Daniel Ingemi in meteoweb.eu, November 13, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d Warmest November since measurements began , ZAMG Klimanews , November 28, 2014.
- ↑ a b c Severe weather in Italy: damage in the billions , orf.at, November 17, 2014.
- ↑ a b c The usual names for lows and highs in Central Europe are given by the Institute for Meteorology of the Free University of Berlin as part of the weather sponsorship funding campaign . Since German meteorology does not adequately take into account the weather systems of the Mediterranean, these are only given names if they have an impact on the weather in Germany. Mediterranean lows have only been named for a few years. Because the naming of the lows arriving over the Atlantic from the west continues in the alphabet, those lows that occurred in between in southern Europe are often missing in the order of the list of names in German meteorology. Minor cores of already named lows are sometimes numbered, sometimes also if they are derived from a distant core, for example Quendresa II over the Baltic States and Stephanie II over the Mediterranean (the later dividing central core of the latter low was then somewhat unusually named Stephanie III, cf. Tiefdruckgebiet Stephanie in a pack of three ( memento of the original from November 29, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this note. , Section Tief Stephanie immediately triple ! , MeteoSwiss daily news , November 14, 2014). The Mediterranean depth in between remained without a name.
-
↑ Forecast for Tue October 28, 2014 12 UTC , met.fu-berlin.de;
Weather situation from October 28, 2014, 12 UTC , ZAMG. - ↑ a b c d The oldest Urner (Föhn) visits Lake Zurich ( Memento of the original from November 7, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , MeteoSwiss daily news , November 4, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d e f g Huge amounts of rain in the south, snow down to deep layers in the north ( Memento of the original from November 7, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , MeteoSwiss daily news , November 5, 2014.
-
↑ a b c d forecast for Tue 04.11.14 12 UTC , met.fu-berlin.de;
Weather situation from November 4, 2014, 1 UTC , ZAMG. -
↑ Forecast for Wed 11/05/2014 12 UTC , met.fu-berlin.de;
Weather situation from November 5, 2014, 00 UTC , ZAMG. -
↑ a b c forecast for Thursday , November 6th, 2014 12 UTC , met.fu-berlin.de;
Weather situation from November 6, 2014, 00 UTC , ZAMG. - ↑ a b c d e Retour sur le dernier épisode de pluies intenses , MeteoFrance Actualités , November 5, 2014.
- ↑ Foehn storm and continuous rain. Warning status report of November 4, 2014, unwetteralarm.com, November 4, 2014.
- ↑ At around 4 hPa, the foehn develops, at 8 hPa it breaks through into the valley.
- ↑ The hair dryer is coming ( Memento of the original from November 7, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , MeteoSwiss daily news , November 3, 2014.
- ↑ Foehn storm in the Alps - an update , Klaus Marquardt, blog entry in meteonews.ch - with a table of wind measurement peaks for Switzerland.
- ↑ a b hurricane gusts of up to 187 km / h , blick.ch, November 4, 2014.
- ↑ a b c Hurricane raged at 182km / h , oe24.at, November 5, 2014.
- ↑ Cars sink in hail , oe24.at, November 3, 2014.
- ↑ a b c Nothing more worked on the burner . In: Salzburger Nachrichten . November 7, 2014, Austria , p. 13 .
- ↑ A cold front ends the foehn in the Alps ( memento of the original from November 6, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , wetter.tv weather report , November 4, 2014.
- ↑ a b Snow chaos on the Brenner autobahn - rain in Carinthia ( memento of the original from September 24, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , osttirol-online.at, November 6, 2014.
-
↑ a b forecast for Fri 07.11.14 12 UTC , met.fu-berlin.de;
Weather situation from November 7, 2014, 00 UTC , ZAMG. - ↑ Jeff Masters: Rare Medicane Hits Malta and Sicily With Tropical Storm-Like Conditions , in wunderground.com, November 7, 2014.
- ^ Medicane sullo Stretto di Sicilia. Analisi. CNMCA 13 November 2014 on MeteoAM.it → Notizie .
- ↑ In the sandwich of the printing systems ( Memento of the original dated November 7, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , especially also the Medicane section in the Mediterranean ; and Mild November day in the middle of the high ( memento of the original from November 9, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. : Again to the "Medicane" in the Mediterranean ... , MeteoSwiss daily news , 7th resp. November 8, 2014.
- ↑ a b Ciklona Benjamin tijekom petka prerasla u “mediteranski urgan” i pogodila Siciliju i Maltu , crometeo.hr, November 7, 2014 (collection of weather maps for Qendresa, named Benjamin there).
- ↑ a b Ciclone lambisce la punta sudorientale della Sicilia, rientra l'allarme rosso sull'Isola , Repubblica Palermo online, 7 November 2014.
- ↑ Ciklona Benjamin: Visoki valovi na Jadranu, u Senju 25 ° C, Slavonija pred apsolutnim temperaturnim rekordom , crometeo.hr, November 6, 2014.
- ↑ a b c Compare the weather maps for Western Europe, sometimes confusingly similar, weather situation from November 4, 2014, 00 UTC to 12 UTC and November 9, 2014, 00 UTC to 12 UTC , all ZAMG.
- ↑ A train derailed between Athens and Thessaloniki due to mud. Alps in the storm tongs: New storms south of the Alps ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , at.wetter.com, November 9, 2014.
- ↑ a b Back to field 1 ... again a south-west facing position! ( Memento of the original from November 12, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. and In the south copy-paste weather ( memento of the original from November 12, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , MeteoSwiss daily news , 9. resp. November 10, 2014.
- ↑ Maltempo, allarme massimo, scuole chiuse in Liguria , Repubblica Genova online, November 9, 2014.
- ↑ forecast for Sun 09.11.14 12 UTC , met.fu-berlin.de;
-
↑ Forecast for Mon 10.11.14 12 UTC , met.fu-berlin.de;
Weather situation from November 10, 2014, 18 UTC , ZAMG. - ↑ a b c d Highest danger level on Lake Maggiore ( Memento of the original dated November 12, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , MeteoSwiss daily news , November 11, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d Evacuations in Orvieto , orf.at, November 12, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d The flood in the south - mostly gray in the north ( memento of the original from November 12, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , MeteoSwiss daily news , November 12, 2014.
- ^ A b Retour sur l'épisode pluvieux du 8 au 12 novembre , MeteoFrance Actualités , 12 November 2014.
-
↑ Forecast for Tue 11.11.14 12 UTC , met.fu-berlin.de;
Weather situation from November 11, 2014, 18 UTC , ZAMG. -
↑ Forecast for Wed 11/12/2014 12 UTC , met.fu-berlin.de;
Weather situation from November 12, 2014, 06 UTC , ZAMG. - ↑ Ciklona Celesta donijela olujno jugo, pijavicu kod Splita i vrlo obilne oborine srednjoj Dalmaciji , crometeo.hr, November 13, 2014 (with several weather maps, the nameless low there named Celesta ).
-
↑ a b forecast for Fri 14.11.14 12 UTC , met.fu-berlin.de;
Weather situation from November 14, 2014, 12 UTC and from November 15, 2014, 0 UTC , ZAMG (on the first picture Stephanie as a complete compact vortex with around 960 HPa core pressure and a good 50 HPa pressure drop on all sides in a 1500 km radius, on the second with three recognizable Secondary core vortices in the cold air sector ). -
↑ a b forecast for Sa 15.11.14 12 UTC , met.fu-berlin.de;
Weather situation from November 15, 2014, 18 UTC , ZAMG
(with a total of four main cores created from Stephanie distributed all over Europe, another secondary core over the English Channel was then named Thea by the DWD ). - ↑ Low pressure area Stephanie in a pack of three ( memento of the original from November 29, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , MeteoSwiss daily news , November 14, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d Nocturnal hair dryer in the north - traffic jam in the south ( memento of the original from November 19, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. and During the night a cold front, afterwards the weather calmed down - heavy precipitation with tragic consequences ( memento of the original from November 19, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , MeteoSwiss daily news , 15th resp. November 16, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d episode pluvieux des 14 and 15 novembre dans le Sud-Est , MeteoFrance Actualités , November 17, 2014.
- ↑ a b Maltempo sull'Italia: alluvioni in atto su alcune zone della Liguria, temporali violenti su parte del Nord-Ovest, nel pomeriggio fenomeni anche altrove , CentroMeteoItaliano.it, November 15, 2014.
-
↑ Forecast for Mon 17.11.14 12 UTC , met.fu-berlin.de;
Weather situation from November 17, 2014, 6 UTC and 12 UTC , ZAMG. -
↑ Forecast for Wed 11/19/2014 12 UTC , met.fu-berlin.de;
Weather situation from November 18, 2014, 12 UTC and 6 UTC , ZAMG. - ↑ Cyclogenesis on the Côte d'Azur ( Memento of the original from December 5, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. and A high between the lows ( Memento of the original from November 22, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , MeteoSwiss daily news , 17th resp. 18th November 2014.
- ^ 9 Dead after Floods and Landslides in Southern Europe , Richard Davies in floodlist.com, November 17, 2014.
-
↑ a b Climate Bulletin October 2014 ( Memento of the original from November 1, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , MeteoSwiss; Landslides and floods in Ticino , blick.ch, October 14, 2014.
- ↑ Highest recorded October temperatures on October 9th with 28.3 ° C in Vorarlberg; One of the warmest October in measurement history , ZAMG, October 30, 2014.
-
↑ Storm in Northern Italy: Flood in Parma , orf.at, October 14, 2014;
Further storms in Italy , faz.net, October 14, 2014;
→ Alluvione di Genova del 9 e 10 ottobre 2014 , Italian Wikipedia - ↑ Floods in Slovenia claim first victim ( memento of the original dated November 29, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , at.wetter.com
- ↑ In between a mute, ex-Hurricane Gonzalo : Storm 'Gonzalo' also raged in neighboring countries . In: Salzburger Nachrichten . October 22, 2014, Welt - Chronik ( article archive ).
- ↑ Floods tore dozens of houses away in Norway , krone.at, October 31, 2014.
- ↑ The following low Uschi had disintegrated over the Atlantic, an Azorean low brought rain to northern Spain; the deep Vanja traditionally moved to Scandinavia.
- ↑ a b → en: Typhoon Nuri (2014)
- ↑ a b → en: November 2014 North American cold wave ; en: November 17–21, 2014 North American blizzard
- ↑ Gray, white and a bit of blue ( memento of the original from November 7, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , MeteoSwiss daily news , November 6, 2014.
- ↑ a b c Cold and snow in Siberia and North America , wetter24.de, November 15, 2014 (with weather maps on the situation).
- ↑ a b Etats-Unis: vague de froid exceptionnellement précoce , MeteoFrance Actualités , November 14, 2014.
- ↑ Andrew Freedman: Unusually powerful storm explodes over Bering Sea . Mashable. November 7, 2014. Retrieved November 11, 2014.
- ↑ Heavy rain in East Tyrol and Upper Carinthia , ZAMG Weather News , November 5, 2014.
- ↑ a b Cyclogenesis… , Section Century - Rain in Ticino ( Memento of the original from December 5, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , MeteoSwiss daily news , 17. 2014 - to a first balance of the events.
- ↑ a b Parts of Austria for the first time without frost in autumn , ZAMG Klimanews , December 2, 2014.
- ↑ The warmest autumn ever recorded , ZAMG Air News , November 26, 2014.
- ↑ The beginning of frost in the history of Tyrol ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , tirol.orf.at, December 10, 2014.
-
↑ a b Un automne exceptionnellement chaud, en particulier dans le Sud , MeteoFrance Actualités , December 3, 2014;
Bilan climatique de l'automne 2014 , MeteoFrance: Climat passé et futur> Bilans climatiques . - ↑ a b c d e Maltempo, è un disastro da nord a sud: l'Italia sta affogando, nel weekend il “colpo di grazia” , Peppe Caridi in meteoweb.eu, November 12, 2014.
- ↑ a b c Letošnje leto v Sloveniji najbolj mokro po letu 1965 , RTVslo.si, November 18, 2014.
- ↑ Closure due to snow in front of the Gotthard , Neue Zürcher Zeitung. November 5, 2014. Retrieved November 8, 2014.
- ↑ Severe weather: Deaths after landslide in Switzerland, traffic chaos in Italy , derstandard.at, November 6, 2014.
- ↑ a b Heavy rains wreak havoc along Swiss-Italian border . Euronews , November 16, 2014.
- ↑ a b c landslide near Lugano: Ticino continuous rain claims two deaths . Peter Jankovsky in NZZ online, November 16, 2014.
- ↑ Two dead after landslide: The victims lay under rubble several meters high , 20min.ch, November 16, 2014.
- ↑ Föhnsturm has Tyrol firmly under control , tirol.orf.at, November 4, 2014.
- ↑ Warning of flooding , kaernten.orf.at, November 5, 2014.
- ↑ a b Despite record rain, no dramatic flooding , kaernten.orf.at, November 6, 2014.
- ↑ Rain is easing: the risk of flooding is over in Carinthia , in Kleine Zeitung online, November 7, 2014
- ↑ a b Flood: Verbund rejects guilt and floods: Allegations also in Slovenia , kaernten.orf.at, undated
- ↑ a b The indication of Cévenol is meteorologically incorrect for events in the Maritime Alps: Cévenols in the strict sense of the word are foehn-equivalent rainfall on the Cevennes and the Bouches-du-Rhône; cf. Les pluies intenses : Les épisodes méditerranéens , Météo-France: Dossier Phénomènes météo ; → fr: episode cévenol .
- ↑ a b Two dead after storms in France and Italy , 20min.ch, November 5, 2014.
-
↑ Gard: Les inondations causent quatre morts dont deux enfants , 20minutes.fr, November 15, 2014;
Le bilan des intempéries dans le Gard et en Lozère s'élève à cinq morts après la découverte du corps d'un bébé , francetvinfo.fr, November 15, 2014;
Intempéries: cinq morts dont deux enfants dans le Sud-Est . Le Monde online, November 16, 2014. - ↑ Maltempo: Capri isolata, Veneto e Friuli sott'acqua , Il Mattino online, November 7, 2014.
- ↑ a b Tornadoes and extreme floods , wetter24.de, November 6, 2014 (with videos on the tornadoes).
- ↑ a b Severe weather: Rome's mayor announced the highest level of warning , Die Presse online, November 6, 2014.
- ↑ a b Maltempo, possibile ciclone su coste Sicilia , Repubblica online, 7 November 2014.
- ↑ Maltempo nella Sicilia Orientale, danni per milioni. Allarme ciclone, scuole chiuse anche a Palermo , Repubblica Palermo online, 6 November 2014.
- ↑ La bufera su Misterbianco, tetti scoperchiati e tralicci divelti , Repubblica Palermo online, 7 November 2014.
- ↑ Italy is fighting with floods , wetter24.de, November 6, 2014 (with videos of flash floods around Genoa).
- ^ 1 Killed in Genoa Floods, Italy , Richard Davies in floodlist.com, November 10, 2014.
- ↑ Genova, la nuova alluvione, una vittima a Borgo Incrociati, scuole e strade chiuse , Repubblica Genova online, November 10, 2014.
- ↑ a b Maltempo, tutta la Lombardia è sott'acqua. Esonda il Seveso, un morto nel lago Maggiore , Repubblica Milano online, November 12, 2014.
- ↑ a b c Maltempo, nel Nord Ovest incubo esondazioni. Un disperso a Genova, Milano allagata , Repubblica online, November 15, 2014.
- ↑ a b c d Maltempo, tre morti al Nord. Scontro Burlando-Renzi: colpa di condoni fatti a Roma , Repubblica Milano online, November 16, 2014.
- ↑ a b Maltempo, north in ginocchio: alluvione a Genova e Alessandria, Seveso esonda , blitzquotidiano.it, November 15, 2014.
- ↑ Pioggia, vento, Grandine: Treviso flagellata , la Nuova di Venezia e Trieste online, November 17, 2014.
- ↑ Acqua alta, toccati ieri sera i 120 centimetri , la Nuova di Venezia e Trieste online, November 18, 2014.
- ↑ a b c Nuova ondata di piena del Po, oltre mille gli sfollat , Repubblica Bologna online, November 16, 2014.
- ↑ Emilia col fiato sospeso per il Po. Si rompono gli argini golenal , Repubblica Bologna online, November 18, 2014.
- ↑ a b More Deaths as Flooding Continues in Italy and Louisiana and Genoa - Millions in Unused Mitigation Funds , both Richard Davies in floodlist.com, 14th resp. 15th October 2014.
- ↑ November: Italy's Month for Floods , Richard Davies in floodlist.com, November 15, 2013 (updated).
- ↑ Na Cerkniškem in Planinskem polju lahko spet poplavi ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , Primorske.si, November 9, 2014.
- ↑ Na Ljubljanskem Barju gladina vode počasí upada, v Loški dolini še narašča , siol.net, November 10, 2014.
- ↑ Poplave: Najhuje v občini Ilirska Bistrica. Sledijo nove padavine , RTVslo.si, November 12, 2014.
- ↑ Na poplavljenih območjih se voda umika ( Memento of the original from September 24, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , Primorske.si, November 9, 2014.
- ↑ Plazovi bi se lahko spet začeli premikati , Primorske.si, November 9, 2014.