Khakassia
Subject of the Russian Federation
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Coordinates: 53 ° 24 ' N , 89 ° 51' E

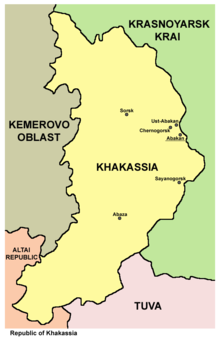
Khakassia ( Russian Хакасия / transcription Chakassija , Khakas Хакас Республиказы ) is a republic in the south of the Siberian Federal Administrative District in Russia . The capital Abakan is located at the southern end of the Krasnoyarsk reservoir on the Yenisei .
geography
Khakassia is located in the south of the Siberian federal administrative district on the northern slope of the West Sayan Mountains on the upper reaches of the Yenisei and its tributary, the Abakan . The capital of the same name Abakan is located at the southern end of the Krasnoyarsk Reservoir . In the north, Khakassia is bordered by the Krasnoyarsk Territory , in the east on Tuva , in the south on the Autonomous Republic of Altai , and in the west on the Altai Region and Kemerovo Oblast . The extension from north to south is 460 km and from west to east about 200 km. The Sayan Mountains occupy about two thirds of the territory.
In Khakassia there are about 1,000 freshwater and saltwater lakes , the largest are the Beljosee , the Lake Shira and Itkulsee .
The climate of Khakassia is continental , with dry, hot summers and cold winters with little snow. The average temperature in January is −18.9 ° C and in July +17.9 ° C. The average rainfall is 300–700 mm per year in the steppe zone and 1500 mm in the taiga and mountain zone .
The area of the Republic of Khakassia, with 61,569 km², makes up around 0.4% of Russian territory; the distance from Moscow to Abakan is about 4200 km.
Flora and fauna
The forests of Khakassia are a natural treasure of the republic. They take up about two thirds of the territory. About 96% of the forests are mountain forests. The conifers make up 75% of the total forest area, a third of which are Siberian stone pines . 20% of Khakassia belongs to the steppe zone .
There are over 1500 plant species, of which about 300 are used economically. About 45 species of birds and 76 species of mammals live on the territory of the republic , including important targets for hunting such as Altai Maral , Siberian deer , musk deer , wild boar and Siberian ibex . There are also bears , sables , foxes and beavers ; in contrast, the red dog and snow leopard are very rare animals. 37 species of fish live in the large and small rivers and lakes, including European grayling , trout and sturgeon .
history
The Khakass state existed for centuries before it fell to the Mongols in the 13th century . At the beginning of the 18th century, Russian rule consolidated, in the 19th century Russian immigration began and some of the Khakass converted to the Orthodox faith .
The Khakassia region was established on October 10, 1930.
During the Stalin era there were several gulag in the Abakan area. The prisoners were used in coal mining, gold mining, the construction of an oil-processing combine, and logging.
After the fall of the Soviet Union, Khakassia became an autonomous republic within Russia in 1991.
population
In the 2010 census, a number of 532,403 residents was determined. The titular nation , the Khakass , are a Turkic people . However, they are in the minority in their republic. Around 80% of the population are Russians . Smaller minorities are Russian Germans , Ukrainians and Tatars . The Schoren are a local minority .
Ethnic relationships changed dramatically during the Stalin era. A huge stream of Slavs (Russians, Ukrainians and Belarusians) immigrated. Deported Germans and Poles joined them during and after the Second World War. They were also joined by many members of other Soviet peoples, namely Mordwinen and Tschuwaschen (1926 688, 1970 6949 people). From the 1980s onwards, numerous Poles and Germans emigrated to their homeland. After the end of the Soviet Union, numerous people of the Soviet nationalities joined them and returned to their regions of origin. For this reason, the population fell from 567,000 in 1989 to 532,000 in 2010 (−6.1%).
The official languages are Khakas and Russian . The population is mainly committed to the Russian Orthodox Church, there is also a Muslim minority.
| Ethnic group | VZ 1926 | VZ 1939 | VZ 1959 | VZ 1970 | VZ 1979 | VZ 1989 | VZ 2002 | VZ 2010 1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| number | % | number | % | number | % | number | % | number | % | number | % | number | % | number | % | |
| Khakass | 44,219 | 49.8% | 45,799 | 16.8% | 48,512 | 11.8% | 54,750 | 12.3% | 57,281 | 11.5% | 62,859 | 11.1% | 65,421 | 12.0% | 63,643 | 12.0% |
| Russians | 41,390 | 46.6% | 205.254 | 75.3% | 314,455 | 76.5% | 349,362 | 78.4% | 395.953 | 79.4% | 450,430 | 79.5% | 438.395 | 80.3% | 427,647 | 79.6% |
| German | 46 | 0.1% | 333 | 0.1% | 10,512 | 2.6% | 10,547 | 2.4% | 11,130 | 2.2% | 11,250 | 2.0% | 9,161 | 1.7% | 5,976 | 1.1% |
| Ukrainians | 836 | 0.9% | 7,788 | 2.9% | 14,630 | 3.6% | 9,480 | 2.1% | 10,398 | 2.1% | 13,223 | 2.3% | 8,360 | 1.5% | 5,039 | 0.9% |
| Tatars | 301 | 0.3% | 3,043 | 1.1% | 3,796 | 0.9% | 3,647 | 0.8% | 4,249 | 0.9% | 4,721 | 0.8% | 4,001 | 0.7% | 3,095 | 0.6% |
| Shear | 99 | 0.1% | 862 | 0.3% | k.Ang. | ?,?% | 887 | 0.2% | 1,015 | 0.2% | 1,207 | 0.2% | 1,078 | 0.2% | 1,150 | 0.2% |
| Other | 1,981 | 2.2% | 9,651 | 3.5% | 19,142 | 4.7% | 17,151 | 3.8% | 18,358 | 3.7% | 23,171 | 4.1% | 19,658 | 3.6% | 25,853 | 4.9% |
| Residents | 88,872 | 100% | 272.730 | 100% | 411.047 | 100% | 445.824 | 100% | 498.384 | 100% | 566,861 | 100% | 546.072 | 100% | 532.403 | 100% |
| 1 8,689 people could not be assigned to any ethnic group. These people are probably distributed in the same proportion as the ethnically classified inhabitants. | ||||||||||||||||
economy
tourism
In absolute terms, the hotel and hospitality industry in Khakassia contributes 1.96 billion rubles to GDP, which corresponds to 1.5 percent of GDP. Thus tourism in Khakassia is of relatively high importance. This is also clear when comparing the territorial units of Russia. Tourism as an economic branch has a high position in Khakassia, this is also evident from the establishment of an independent committee. The republic is rich in medicinal springs . Lakes known for their balneological properties are the Schira, Beljo, Utitschje, Altaiskoje, Tus, Schunet, Chankul and several smaller lakes. In addition, the republic has archaeological monuments, they play a special role for the region.
In the period from 2011 to 2013, the number of national tourists tripled, the number of international tourists increased by 1.5 times. In 2013 there were 398,000 domestic tourists in Khakassia and 2,800 foreign tourists in absolute terms. The Germans make up the majority of these, followed by tourists from the People's Republic of China , Italy and the Baltic States . The tourists also come from Australia and Austria . Communication is a major problem in tourism . Either the experts have a high level of knowledge in the field of history or tourism in Khakassia, or they speak several languages. Furthermore, families, v. a. Russian-Germans and globetrotters are an important target group. In incoming tourism, these are mainly visitors from the Siberian Federal Okrug. People from Kemerovo Oblast particularly like to come here, as they are looking for a contrast to their own, heavily industrialized region. However, guests from Moscow are also often in the region. In addition, local tourists from the European part of Russia in particular make up a particularly high proportion of the “wild” tourists. Khakassia increases awareness of the country through appearances at the ITB (International Tourism Fair Berlin) and through journalist trips.
Among the types of tourism, cultural tourism dominates with 39 percent, followed by bathing tourism with 26 percent. Active and sports tourism follows closely behind with 25 percent, further behind is health tourism with nine percent and business tourism has so far made up a small share of one percent. The number of businesses in the tourism industry is said to have increased by 27% to 46 between 2011 and 2013.
energy
In the capital Abakan , a large industrial complex was built, in which aluminum smelting is particularly important. The energy is generated by a reservoir system of the Yenisei : Sajano-Schuschensker reservoir (1963–1988), Maina reservoir (1979–1987) and Krasnoyarsk reservoir (1961–1967). The share of GDP in energy and water supply in Khakassia is 10.2%. Two thirds of the energy volume of Khakassia is fed into the Siberian power grid .
Extraction of raw materials
In Khakassia coal , iron , molybdenum , gold , barite and bentonite are exploited. In addition, various semi-precious stones and building materials are extracted. The share of barite in Khakassia makes up 27 percent of Russia's total raw material supply. The multitude of natural resources leads to a developed mining , metalworking and wood industry . In addition, the raw materials industry also plays an important role in foreign trade . Aluminum , aluminum products , black metal and black metal products are important export goods. They are mainly exported to the USA , Turkey , Japan , China , the Netherlands , Ukraine , Germany and Korea . The main imports are machines, equipment and chemical products from Kazakhstan , Ukraine, China, Germany, Italy , the Netherlands and Japan.
Agriculture
Even if the agriculture , hunting and forestry sector only ranks tenth in the GDP of Khakassia, the republic is predominantly agricultural. A total of 70 percent of the fall agriculture to livestock and 30 percent to the agriculture . In the period from 2008 to 2010, regional agriculture was supported by the Russian state with around 50 million euros. In addition, there has been a general growth in agricultural areas and yields. Meat production rose by 3.8 percent, that of milk by 10 percent and that of eggs by 23 percent. The meat production in the republic is to be increased fivefold through the construction of a vertically integrated fattening plant and an annual production of 30,000 tons of meat. The investment of the largest local agricultural company APK Mawr in this project is around 180 million euros. In addition, the climatic conditions of Khakassia are well suited for breeding goats and sheep, which is why an investor is being sought for a farm for the production of goat's milk.
Administrative division
The Republic of Khakassia is divided into eight Rajons and five city districts . A total of 6 urban and 82 rural communities are subordinate to the Rajons (status: 2010).
City districts
| Urban district | Residents | Area (km²) |
Population density (inh / km²) |
More places | Number of urban settlements |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II | Abakan | 163,617 | 112 | 1461 | 1 | |
| I. | Abasa | 16,901 | 22nd | 768 | 1 | |
| III | Sayanogorsk | 63,461 | 89 | 713 | Maina , Cheryomushki | 3 |
| IV | Sorsk | 12,982 | 6th | 2164 | 1 | |
| V | Chernogorsk | 78,708 | 118 | 667 | Prigorsk | 2 |
Rajons
| Rajon | Residents | Area (km²) |
Population density (inh / km²) |
Urban population |
Rural population |
Administrative headquarters | More places | Number of urban communities |
Number of rural communities |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Altaysky | 23,509 | 1736 | 13.5 | - | 23,509 | Bely Jar | - | 9 | |
| 2 | Askis | 43,286 | 8201 | 5.3 | 10,848 | 32,438 | Askis (village) | Askis (settlement) , Biskamsha , Vershina Tjoi | 3 | 11 |
| 3 | Be yes | 21,796 | 4536 | 4.8 | - | 21,796 | Be yes | - | 9 | |
| 4th | Bograd | 15,325 | 4524 | 3.4 | - | 15,325 | Bograd | - | 10 | |
| 5 | Ordzhonikidsevskoye | 14,540 | 6611 | 2.2 | 4,567 | 9,973 | Kopjowo | 1 | 8th | |
| 8th | Shira | 27,824 | 6809 | 4.1 | 756 | 27,068 | Shira | Schemchuschny | 1 | 14th |
| 6th | Pocket type | 15,871 | 20012 | 0.8 | - | 15,871 | Pocket type | - | 9 | |
| 7th | Ust-Abakan | 41,331 | 8821 | 4.7 | 15,822 | 25,509 | Ust-Abakan | 1 | 12 |
Remarks:
- ↑ a b number of the district / district (in alphabetical order of the names in Russian )
- ↑ a b Population figures from January 1, 2010 (calculation)
- ^ Urban-type settlements
- ^ Urban-type settlements or municipalities
Cities
There are five cities and eight urban-type settlements in Khakassia . In addition to the republic capital Abakan , Chernogorsk and Sajanogorsk are by far the largest cities.
| City * / City settlement | Russian | Resident October 14, 2010 |
|---|---|---|
| Abakan * | Абакан | 165.214 |
| Chernogorsk * | Черногорск | 72,147 |
| Sayanogorsk * | Саяногорск | 49,887 |
| Abasa * | Абаза | 17,115 |
| Ust-Abakan | Усть-Абакан | 14,578 |
| Sorsk * | Сорск | 12,143 |
education
Khakassia has a well-developed educational landscape. In addition to the State University, the region has the Khakas Business Institute, an Academy of Humanities and a Technical Institute of the Siberian Federal University. The largest university is the Khakas State Katanow University in the capital Abakan, which has a good research base in the humanities and natural sciences. There are also international relationships with universities in China, Germany, France, Mongolia and Portugal. In addition, the university is in close contact with social organizations that focus on the German language and culture, for example the Abakan Center for German Culture, the Association of German Teachers and the Goethe Institute's teaching material center. In 2008/2009 there were 717 students per 10,000 inhabitants in Khakassia, 943 in the Okrug and 961 at the national level.
traffic
The Republic of Khakassia has a road network density of 75 km / 1000 km². The main federal traffic routes include the Yenisei road between Abakan and Ak-Dowurag. In addition, this includes the connection between Khakassia and the Krasnoyarsk region, the Republic of Tuva and other areas of the Russian Federation in east and west Siberia. Great importance is also attached to the construction of the motorway between Abakan and Tashtagol. Furthermore, the transport infrastructure of Khakassia is characterized by rail traffic. The rail network density of Khakassia amounts to 10.8 m / km². The route of the Trans-Siberian Railway runs through Khakassia. It drives routes between Abakan and Taischet, Achinsk and Novokuznetsk. In addition, the Republic of Khakassia is connected by two international airports. One airport is in Abakan, the other in Sayanogorsk.
Attractions
Sapovednik Khakassky
In 1999, the 267.6 hectare Khakassian nature reserve was designated in Khakassia . It is not a contiguous area, but nine sub-areas that are spread over the entire Khakassian republic. In addition to maintaining the flora and fauna, the nature reserve also serves as a research and educational facility.
Ivanovski Osjora ski and nature reserve
The Iwanowskije Ossjora are currently in the planning for a regional nature park, which will cover an area of 50 to 60,000 hectares. In the upper reaches are the rivers Sarala , Isbass and the Black Ijus . The lakes in the high mountains have a very high water quality. You can also find snow fields here that exist all year round and therefore winter mountain sports can be offered all year round. The ski area offers a high level of snow security , the melt does not begin until June, although there are also permanent snow fields. The low avalanche risk is also a great incentive for tourists. Semeinaja (1,293 m), Stolowaja (1,320 m), Transwaalskaja (1,386 m), Ivanovskaya (1,391 m), Saosjornaja (1,657 m), Gus (1,460 m) and Panfilowskaja (1,335 m). The gradient varies between 15 and 51 degrees and the difference in altitude runs from 200 to 400 m. The ski slopes range in length from 700 to 1,500 m.
Sunduki
The Sunduki represent a series of mountains. It stretches from the Schira rajon to Ordschonikidsewskoje . The closest places are Ijus and Schira . The Lake Beljo and the Shirasee are also in the vicinity. The name means "box" and is due to the box-like shape of the rock formations found there. The mountain series consists of five "Sunduki", the highest point being 364 m. This mountain range offers hikers a great backdrop and was already known and signed by Daniel Gottlieb Messerschmidt in 1721 . The representations were adopted in books about Siberia until the 19th century. It is assumed that at that time the seat of the Khan was at the top and the army was gathering down in the valley.
Web links
- Official Website of the Republic of Khakassia (Russian)
- State Tourism Committee of the Republic of Khakassia (Russian, German, English)
- Map of the Gulag in southern central Siberia
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Administrativno-territorialʹnoe delenie po subʺektam Rossijskoj Federacii na 1 janvarja 2010 goda (administrative-territorial division according to subjects of the Russian Federation as of January 1, 2010). ( Download from the website of the Federal Service for State Statistics of the Russian Federation)
- ↑ a b Itogi Vserossijskoj perepisi naselenija 2010 goda. Tom 1. Čislennostʹ i razmeščenie naselenija (Results of the All-Russian Census 2010. Volume 1. Number and distribution of the population). Tables 5 , pp. 12-209; 11 , pp. 312–979 (download from the website of the Federal Service for State Statistics of the Russian Federation)
- ↑ Nacional'nyj sostav naselenija po sub "ektam Rossijskoj Federacii. (XLS) In: Itogi Vserossijskoj perepisi naselenija 2010 goda. Rosstat, accessed on June 30, 2016 (Russian, ethnic composition of the population according to federal subjects , results of the 2010 census).
- ↑ Population of the Russian territorial units by nationality 2010 (Russian) http://www.gks.ru/free_doc/new_site/population/demo/per-itog/tab7.xls
- ↑ a b gks.ru Уровень безработицы (в процентах)
- ↑ turism19.ru
- ↑ AMSARAKOW, Boris (2007) in: Deutsch-Russisches Forum e. V. (Ed.): About the region - The Republic of Khakassia. regionen.ru ( Memento of the original dated November 2, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. 0
- ↑ Amsarakow, Boris (2007) in: Deutsch-Russisches Forum e. V. (Ed.): About the region - The Republic of Khakassia regionen.ru ( Memento of the original from November 2, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link has been inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. 0
- ↑ german.ruvr.ru
- ^ German-Russian Chamber of Commerce Abroad (no year): Republic of Khakassia - economic data. regionen-russland.de
- ^ German-Russian Chamber of Commerce Abroad (no year): Republic of Khakassia - economic data. regionen-russland.de
- ↑ AMSARAKOW, Boris (2007) in: Deutsch-Russisches Forum e. V. (Ed.): About the region - The Republic of Khakassia. regionen.ru ( Memento of the original dated November 2, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. =
- ↑ Численность студентов образовательных учреждений высшего профессионального образования http://www.gks.ru/bgd/regl/b13_14p/IssWWW.exe/Stg/d1/05-29-1.htm
- ↑ GERMAN-RUSSIAN FOREIGN TRADE CHAMBER regionen-russland.de ( page no longer available , searching web archives ) Info: The link is automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. view / siberia / khakassia /
- ↑ Кузнецкий Алатау / ключевые пункты / Ивановские озёра. http://zabroski.ru/kuzneckiy-alatau/point/ivanovskie-ozera
- ↑ priiskovy.ru