Waldeck-Frankenberg district
| coat of arms | Germany map |
|---|---|

|

Coordinates: 51 ° 16 ' N , 8 ° 51' E |
| Basic data | |
| State : | Hesse |
| Administrative region : | kassel |
| Administrative headquarters : | Korbach |
| Area : | 1,848.44 km 2 |
| Residents: | 156,406 (Dec. 31, 2019) |
| Population density : | 85 inhabitants per km 2 |
| License plate : | KB, FKB, WA |
| Circle key : | 06 6 35 |
| NUTS : | DE736 |
| Circle structure: | 22 municipalities |
| Address of the district administration: |
Südring 2 34497 Korbach |
| Website : | |
| District Administrator : | Reinhard Kubat ( SPD ) |
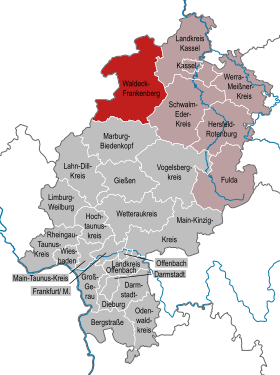
| Location of the Waldeck-Frankenberg district in Hesse | |
The district of Waldeck-Frankenberg is located in the administrative district of Kassel in western North Hesse . The district town is Korbach .
Waldeck-Frankenberg is characterized by a low mountain range with large forests and the Eder , which at Waldeck and Edersee form the second largest reservoir in Germany in terms of area. The population of the district is around 76% Protestant and around 15% Catholic. The proportion of foreigners is around 5.1%. With over 1848 km² it is the largest district in Hesse, ahead of the Schwalm-Eder district and the Vogelsberg district . The two largest cities are in the northern district of Korbach and in the southern district of Frankenberg (Eder) .
geography
location
The district of Waldeck-Frankenberg is located at the transition from the Rhenish Slate Mountains to the Hessian Uplands and thus completely within the German low mountain range. Larger plains can only be found in the north-east near Volkmarsen , in the middle of the circle (Korbach plateau) and in the upper ( Battenberg and Frankenberg) and lower ( municipality of Edertal ) Edertal. The highest point is the 843 m high Langenberg in the Upland near Willingen . In addition, further low mountain ranges are the Upper Hessian parts of the Rothaargebirge near Battenberg as well as the Burgwald and the Kellerwald .
Neighboring areas
The district borders clockwise in the southwest, beginning with the districts of Siegen-Wittgenstein , Hochsauerlandkreis and Höxter (all in North Rhine-Westphalia ) as well as the districts of Kassel , Schwalm-Eder-Kreis and Marburg-Biedenkopf .
Waters
The most important rivers are the Eder , a tributary of the Fulda , and the Diemel , which flows directly into the Weser . There is also the Twiste , a tributary of the Diemel, Itter and Orke . There are no larger natural lakes in the district, but there are several reservoirs , of which the Edersee is the largest. The Diemelsee and the Twistesee also play an important role. Almost the entire district drains into the North Sea via the Weser , only in the southeast the Wohra also flows into the North Sea via Ohm , Lahn and Rhine .
Landmark
The landmark of the district is Waldeck Castle , which is located on the north bank of the Edersee.
Korbach column
A geological peculiarity is the Korbach Fissure , a 20 m deep, up to 3.50 m wide and approximately one kilometer long crevice . It is an important fossil deposit from the Permian period and is located two kilometers south of Korbach city center.
Kellerwald-Edersee National Park
In Waldeck-Frankenberg, the Kellerwald-Edersee National Park has existed since 2004, one of 14 German national parks and the only protected area of this type in Hesse. In 2011 the national park was also declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The goals of the national park are the protection of nature in the national park, further goals are environmental education, recreation, research and the promotion of tourism.
history
The Waldeck-Frankenberg district was established on January 1, 1974 as part of the Hessian regional reform . He was educated
- from the Waldeck in the north to the city of Züschen , in the city Fritzlar in the Schwalm-Eder district was incorporated
- the entire district of Frankenberg in the south and
- the community of Schiffelbach from the Marburg district , which was incorporated into the community of Gemünden an der Wohra .
The larger Waldeck was until 1929 a Free State in the German Reich and before the time of the monarchy , a principality with Bad Arolsen as the capital (to 1655 the mining town of Waldeck ). In 1929 Waldeck was incorporated into the Prussian province of Hessen-Nassau . In 1942, the three districts that had existed since 1850 (renamed as districts in 1939), the Eder district (district town Bad Wildungen ), the Eisenberg district (Korbach district) and the Twiste district (Bad Arolsen district), were combined to form the Waldeck district, with Korbach as County seat. In 1972, the Waldeck district was expanded to include the town of Volkmarsen from the dissolved Wolfhagen district .
The district of Frankenberg, however, historically belonged to Hessen-Kassel , which was part of Prussia ( province of Hessen-Nassau ) from 1866 to 1945 . He was the 1932 Office Battenberg attached, which until then, together with the Office Gladenbach the circle Biedenkopf formed, which until 1866 to Hesse-Darmstadt had heard and was then come to Prussia.
The border between the two old districts still represents a small cultural boundary today. The Benrath line runs approximately between the two old districts and divides the district into a Low German , Waldeck and a Central German , Hessian part. In the Protestant churches, the district is divided between the church of Kurhessen-Waldeck (old districts Waldeck and Frankenberg) and the church of Hesse and Nassau (former Battenberg office). In the Catholic Church, the former Waldeck area belongs to the Archdiocese of Paderborn , the old district of Frankenberg and the core town of Volkmarsen to the Diocese of Fulda and the former Battenberg to the Diocese of Limburg .
Population development
| year | Residents | source |
|---|---|---|
| 1975 | 153,100 | |
| 1980 | 154,700 | |
| 1990 | 157,800 | |
| 2000 | 170,568 | |
| 2010 | 162.275 | |
| 2015 | 156,427 |
politics
District council
The local elections on March 6, 2016 produced the following results, compared to previous local elections:
| Diagram showing the election results and the distribution of seats | |
|---|---|
|
Election of the Waldeck-Frankenberg district council in 2016
% 40 30th 20th 10
0
31.1
28.0
11.3
11.3
8.2
6.9
2.6
0.6
n. k.
Gains and losses
|
|
| Nominations | % 2016 |
Seats 2016 |
% 2011 |
Seats 2011 |
% 2006 |
Seats 2006 |
% 2001 |
Seats 2001 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPD | Social Democratic Party of Germany | 31.1 | 22nd | 34.5 | 24 | 36.0 | 26th | 39.0 | 27 |
| CDU | Christian Democratic Union of Germany | 28.0 | 20th | 30.6 | 22nd | 35.1 | 25th | 34.2 | 24 |
| AfD | Alternative for Germany | 11.3 | 8th | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| FWG | Free community of voters Waldeck-Frankenberg | 11.3 | 8th | 10.0 | 7th | 11.6 | 8th | 10.9 | 8th |
| GREEN | Alliance 90 / The Greens | 8.2 | 6th | 14.3 | 10 | 6.0 | 4th | 5.5 | 4th |
| FDP | Free Democratic Party | 6.9 | 5 | 5.9 | 4th | 7.3 | 5 | 6.6 | 5 |
| THE LEFT. | THE LEFT. | 2.6 | 2 | 2.3 | 2 | 1.7 | 1 | - | - |
| PIRATES | Pirate Party Germany | 0.6 | 0 | 1.1 | 1 | - | - | - | - |
| REP | The Republicans | - | - | 1.4 | 1 | 2.3 | 2 | 3.8 | 3 |
| total | 100.0 | 71 | 100.0 | 71 | 100.0 | 71 | 100.0 | 71 | |
| Voter turnout in% | 50.4 | 51.1 | 50.7 | 56.2 | |||||
District Administrator
Reinhard Kubat has been the acting district administrator since January 1, 2010 . He was elected in a runoff on July 19, 2009 with 54.3 percent of the vote. On July 5, 2015, Reinhard Kubat was confirmed in his office with 60.6 percent of the votes.
Coat of arms and flags
| Banner, coat of arms and flag | |

|

|

|
|
| Blazon : “Divided obliquely by blue and gold; above the growing Hessian lion, divided by silver and red, below the black eight-pointed Waldecker star. " | |
| Justification of the coat of arms: The lion as the heraldic animal of the city of Frankenberg and the Landgraviate of Hesse or their successor states symbolizes the southern part of the district, the former district of Frankenberg. The star is the coat of arms of the former principality of Waldeck and was already featured in the coat of arms of the old Waldeck district. |
economy
The district was and is still one of the traditionally structurally weaker areas in Germany. The remote mountain regions of the upland in particular were still affected by poverty until the first half of the 20th century. This is expressed up to the present day by the relatively low population density of 85 inhabitants per square kilometer; after the Vogelsbergkreis, the second lowest in the state. It should be noted, however, that Waldeck-Frankenberg is by far the largest district in Hesse in terms of area.
In particular in the southern district near Frankenberg and in the cities of Korbach and Bad Arolsen , however, various branches of industry have developed from the 1950s . Among these, the largest employer in the group is the heating technology manufacturer Viessmann, with headquarters in Allendorf (Eder) , which employs over 10,000 people worldwide, of which 4,000 in Allendorf alone, or the internationally known furniture manufacturer Thonet and the Hettich pressure and injection molding plant in Frankenberg, as well as some there world-leading medium-sized companies in the field of so-called hot runner technology . In addition to furniture - and plastics - the rubber industry is an important branch of the company . The largest employer in the northern district is the tire factory of Continental AG in Korbach with around 3400 employees at the site. In total, 42% of the employees in the district work in the manufacturing industry. Agriculture and forestry still play a major role in the rural district: 784 km² of the district area is used for agriculture, 843 km² is forest. This makes up a total of 88% of the total area of the circle. In agriculture, however, only 572 residents are employed as employees in a total of 2220 agricultural businesses, which is only slightly more than one percent of the total number of employees.
The four medium-sized centers in Korbach, Bad Arolsen, Bad Wildungen and Frankenberg are also important locations for the service industry; an important part of this is tourism . The Waldecker Land holiday region (under which the Altkreis Frankenberg is also marketed) is one of the most important holiday regions in Hesse and attracts visitors from all over Germany, especially from neighboring North Rhine-Westphalia and, for historical reasons, also from the Netherlands , as the great-grandmother of former Dutch kings Beatrix , Emma zu Waldeck and Pyrmont , came from the Waldeck Princely House. Winter sports play a major role in the Hessian Upland, and Willingen in particular plays an important role as the venue for the Ski Jumping World Cup . The rest of the district, especially the places near the large reservoirs, are mainly visited in summer. The Edersee plays an important role as a local recreation area for Kassel, 40 km away, and also for the city of Marburg . This was enhanced by the establishment of the Kellerwald-Edersee National Park in 2004. The historic inner cities with many half-timbered buildings are also of interest; Korbach and Bad Arolsen are on the German half-timbered road . This offer is complemented by the opportunity to visit the many castles and palaces in the old district of Waldeck, above all the residential palace in Bad Arolsen , which was built in the 18th century based on the model of Versailles , and the Waldeck Palace.
In the Future Atlas 2016 , the Waldeck-Frankenberg district was ranked 258 out of 402 districts, municipal associations and independent cities in Germany, making it one of the regions with a “balanced risk-opportunity mix” for the future.
traffic
Only in the far north does the district have a direct connection to the German motorway network : in the municipality of Diemelstadt , the exit 64 connects the B 252 with the A 44 . The A 49 runs in the southeast near the district area. The planned closing of the gap on the A4 between the western and eastern parts is to run through the southern part of the district. Until the 1970s, an extension of the A5 from Gießen to Bremen was under discussion, which would have opened up the district in a north-south direction. Today, this is the task of the federal highway B 252 , which connects Marburg via Frankenberg , Korbach and Bad Arolsen with Warburg and Paderborn and in the district area with currently only six through-passages (Ernsthausen, Bottendorf, Herzhausen, Dorfitter, Berndorf and Twiste) on its entire course is relatively well developed in the district.
At the beginning of 2013, after decades of planning , the Federal Ministry of Transport made funds available for the construction of a B 252, which in the long term will bypass all through-roads between Marburg and Frankenberg and thus on the one hand relieve the population, but also ensure better connections to central and southern Hesse and the To benefit the economy in the region. The project is carried out by Hessen Mobil . Other federal highways in the district are the B 236 , which crosses the district starting from Münchhausen via Battenberg and Bromskirchen , the B 251 from Kassel via Waldeck, Korbach, Willingen to Brilon , the B 253 from Bad Wildungen via Frankenberg, Battenberg to Dillenburg , the B 450 from Fritzlar and Wolfhagen to Bad Arolsen and the B 485 from Bad Wildungen to Waldeck to the Sachsenhausen district .
In the district, trains run on the Korbach – Bad Arolsen – Volkmarsen line in the direction of Kassel, the Korbach – Willingen – Brilon Wald line , the Korbach – Frankenberg – Marburg line and the Bad Wildungen – Wabern line . Since autumn 2015, the Korbach – Frankenberg section has been served according to schedule again. Two bridges and two tunnels were renovated for this purpose. Due to the strong competition from private transport , the Bad Berleburg – Allendorf and Nuttlar – Frankenberg routes were shut down a few decades ago, as was the Ederseebahn between Korbach and Bad Wildungen in 1995 because the Buhlener viaduct was in need of renovation . The Ederseebahn cycle path now runs along parts of the latter .
In addition to the bus service in Waldeck-Frankenberg complements call-a-ride Waldeck-Frankenberg to public transport . After registering by telephone, it drives like a normal bus.
Communities
(Residents on December 31, 2019)
|
|
License Plate

On January 1, 1974, the district was assigned the new distinguishing sign KB . It is derived from the district town of Korbach and is still issued today.
Until the 1990s, vehicles from the sub-circles were given special identification numbers:
| area | Letters | numbers |
|---|---|---|
| Korbach district | A to Z | 1 to 9999 |
| AA to ZZ | 1 to 99 | |
| Frankenberg district without the municipality of Vöhl |
AA to AZ | 100 to 999 |
| DA to LZ | ||
| Vöhl municipality in the Frankenberg district | CA to CZ |
Since November 4, 2013, as part of the license plate liberalization , the distinguishing marks FKB (Frankenberg (Eder)) and WA (Waldeck) have been available again.
literature
- Hartmut Wecker: Waldeck-Frankenberg district. Verlag Kommunikation & Wirtschaft, Oldenburg 2007, ISBN 978-3-88363-283-4 .
Web links
- Website of the district of Waldeck-Frankenberg
- Waldeck-Frankenberg district. Historical local dictionary. In: Landesgeschichtliches Informationssystem Hessen (LAGIS).
- Official tourist website of the Ederbergland holiday region
- Official tourist website of the Waldecker Land holiday region
Individual evidence
- ↑ Hessian State Statistical Office: Population status on December 31, 2019 (districts and urban districts as well as municipalities, population figures based on the 2011 census) ( help ).
- ↑ Beech forests are a UNESCO World Heritage Site. In: The world . June 25, 2011, accessed June 20, 2013 .
- ^ Federal Statistical Office (ed.): Historical municipality directory for the Federal Republic of Germany. Name, border and key number changes in municipalities, counties and administrative districts from May 27, 1970 to December 31, 1982 . W. Kohlhammer, Stuttgart / Mainz 1983, ISBN 3-17-003263-1 , p. 415 f .
- ↑ Statistical Yearbook for the Federal Republic of Germany 1976
- ^ A b Michael Rademacher: German administrative history from the unification of the empire in 1871 to the reunification in 1990. Waldeck-Frankenberg district. (Online material for the dissertation, Osnabrück 2006).
- ↑ Hessian State Statistical Office
- ↑ Population in the administrative districts on September 30, 2010 and population processes in the 3rd quarter of 2010. Hessian State Statistical Office, archived from the original on May 10, 2011 ; accessed on May 31, 2019 .
- ↑ Population in the administrative districts on June 30, 2015 and change in population in the 2nd quarter of 2015. Hessian State Statistical Office, archived from the original on March 24, 2016 ; accessed on May 31, 2019 .
- ^ Hessian State Statistical Office: Results of the district elections of 2016 and 2011
- ^ Hessian State Statistical Office: Results of the district elections of 2011 and 2006
- ^ Hessian State Statistical Office: Results of the district elections of 2006 and 2001
- ^ Hessian State Statistical Office: Results of the district elections of 2001 and 1997
- ↑ Viessmann increases sales to 1.7 billion euros. In: Hessische / Niedersächsische Allgemeine . March 16, 2011, accessed June 15, 2013 .
- ↑ Conti manufactures for US industry. In: Waldeckische Landeszeitung / Frankenberger Zeitung . November 9, 2012, accessed June 20, 2013 .
- ^ Economy & Finances in the Waldeck-Frankenberg district. In: meinestadt.de. Retrieved June 20, 2013 .
- ↑ Numbers, data and facts from the Waldeck-Frankenberg district. (No longer available online.) In: lk-wf.active-city.net. Archived from the original on August 10, 2014 ; Retrieved June 20, 2013 .
- ↑ Zukunftsatlas 2016. Archived from the original ; accessed on March 23, 2018 .
- ↑ Federal government provides the first money for circumvention. In: Hessische / Niedersächsische Allgemeine . December 14, 2012, accessed June 20, 2013 .
- ↑ Hessian State Statistical Office: Population status on December 31, 2019 (districts and urban districts as well as municipalities, population figures based on the 2011 census) ( help ).