OT-64 SKOT
| OT-64 (SKOT) | |
|---|---|

OT-64 SKOT in Gdansk (2008) |
|
| General properties | |
| crew | 2 (driver, commander) + 18 infantrymen |
| length | 7.44 m |
| width | 2.55 m |
| height | 2.06 m (tub), 2.71 m (tower top) |
| Dimensions | 14.5 tons |
| Armor and armament | |
| Armor | 10 mm (tower), 14 mm (trough) |
| Main armament | 1 × 14.5 mm machine gun KPWT |
| Secondary armament | 1 × 7.62 mm machine gun PKT |
| agility | |
| drive | air-cooled V-8 diesel engine Tatra T-928-14 180 hp |
| suspension | Wheel suspension 8 × 8 |
| Top speed | 94 km / h (road), 9 km / h (in water) |
| Power / weight | 12.4 hp / ton |
| Range | 710 km |
The OT-64 SKOT ( Czech acronym for: S třední K olový O brněný T ransportér , or in Polish Ś redni K ołowy T ransporter O pancerzony , in German : medium armored wheeled transporter) is an amphibious all-wheel drive troop transport tank (8 × 8) , which was jointly developed and manufactured by Poland and Czechoslovakia (ČSSR) in the 1960s.
history
The first prototype , called SKOT , was built in 1959. It replaced the OT-810 armored personnel carrier , which, apart from a few modifications, was identical to the German Sd.Kfz armored personnel carrier. 251 was from World War II . In 1961 the first test series was made and from October 1963 the vehicles were built in Lublin by FSC ( Fabryka Samochodów Ciężarowych ). Czechoslovakia supplied some assemblies, for example engines.
In 1964 the first vehicles were delivered to both armies and some are still in use today. The OT-64 was also exported to Hungary , India , Iraq , Libya , Morocco , Sudan , Syria and Uganda .
The OT-64 exists in versions 1A, 2A and 2AP.
technology
The OT-64 was the answer to the Soviet BTR-60 . Instead of its two petrol engines, a diesel unit was used in the OT-64. Although this reduced performance, it also reduced the risk of fire and increased the range. The main advantage over the Soviet counterpart was the fully armored interior. The entrance of the OT-64 is at the rear of the vehicle. The OT-64 is equipped with NBC protection system and night vision equipment. It is air-packable and buoyant. Two propellers at the stern serve to drive the boat.
variants

Some variants of the OT-64 SKOT, such as command and recovery vehicles, were built. Some vehicles were also converted for air defense or as tank destroyers. The latter used the missile 9M14 Malyutka as a weapon.
Czechoslovakia
- OT-64 - Original version, used as a troop transport (TTP). The vehicles of the early production were unarmed, but were later retrofitted with a trunnion-mounted 7.62 mm or a 12.7 mm DShK 1938/46 machine gun. In the west they were known as OT-64A and OT-64B , respectively . Some of these vehicles, fitted with 12.7 mm DShK 1938/46, had armor shields around the machine-gun mount.
-
OT-64 - Equipped with the small turret of the OT-65A . However, they were armed with a 7.62 mm twin machine gun instead of the recoilless 82 mm T-21 "Tarasnice" gun.
- DTP-64 ("dílna technické pomoci") - Czech recovery vehicle with towing winches, welding equipment and a hand-operated crane with a payload of one ton. There were two sub-versions, called DTP-64 / M for armored infantry units and DTP-64 / T for armored units.
- OT-64 ZDRAV or ZDR-64 ("zdravotní") - ambulance vehicle
-
OT-64A - Improved version, equipped with the BPU-1 turret of the Soviet armored reconnaissance vehicle BRDM-2 , which is armed with a 14.5 mm KPWT machine gun and a 7.62 mm coaxial PKT machine gun. In western sources this version is often called the OT-64C . In the late 1990s, the turret was replaced in some examples by a trunnion-mounted machine gun for peacekeeping missions. The OT-64A is used as the basis for many command vehicles ("velitelsko-štábní obrněný transportér"), which are equipped with various radio sets, a 1 kW generator and an antenna mast.
- VSOT-64 / R2 R102 - Unarmed radio and command execution.
- VSOT-64 / R2 R105 - Unarmed radio and command execution.
- VSOT-64 / R2 R108 - Unarmed radio and command execution.
- VSOT-64 / R2M - radio and command execution with the tower of the OT-64A.
- VSOT-64 / R3 - Unarmed radio and command execution.
- VSOT-64 / R3MT - Unarmed radio and command execution.
- VSOT-64 / R4MT - Unarmed radio and command execution.
- VSOT-64 / R4RT - Unarmed radio and command execution.
- OT-64A - Equipped with mounts for anti-tank guided weapons on the turret sides.
- OT-64A - Equipped with the new turret with a larger elevation for the armament. Identical to the Polish SKOT-2AP.
- OT-93 - Export version of the OT-64A, in which the original turret was replaced by one from the OT-65 M or OT-62 B. The armament consists of a single 7.62 mm machine gun.
- Cobra armored personnel carrier with a new 30 mm 2A42 turret. So far not in series.
Poland
-
SKOT-1 - Early unarmed model, identical to the OT-64.
-
SKOT-1A - SKOT-1, equipped with a superstructure at the front above the crew room. The structure is a large two-part hatch.
-
SKOT R-3 - Unarmed command vehicle for use at regimental level and above. Equipped with four radio devices, a radio receiver, a relay station and a radio telephone. The crew consists of seven men.
- SKOT R-3M - unarmed radio and command execution for engineer units.
- SKOT R-3Z - SKOT R-3 with modernized radio equipment including a second relay station.
- SKOT R-4 - Unarmed command vehicle in use at division level and in high command. It is equipped with four radio devices, three radio receivers and three radio telephones.
- SKOT-WPT (“wóz pogotowia technicznego”) - technical support vehicle with a light crane.
- SKOT S-260 "Art" ("artyleryjski") - artillery tractor and transport vehicle for ammunition and mortars or anti-tank troops.
- SKOT S-260 “Inż” (“inżynieryjny”) - Equipped with brackets for pulling mechanical mine-layers and mine clearers.
-
SKOT-2 - SKOT-1A with a trunnion mounted MG around the hatch of the superstructure. Two types of machine guns were used - 7.62 mm (first SGMT and later PKT ) or heavy 12.7 mm DShK 1938/46 . The sides of the MG mount are protected with armored plates.
-
SKOT-2A - Polish name for the version with the BRDM-2 tower, which was developed in the late 1960s. The vehicle is equipped with a conical turret and armed with a 14.5 mm automatic cannon and a coaxial 7.62 mm PKT MG. The number of seats in the crew compartment has been reduced from 18 to 10. In western sources this version is often called the OT-64C .
- SKOT 2AM - A small number of Polish SKOT-2A were fitted with mounts for 9M14 Maljutka anti-tank guided weapons on the turret sides. The launchers were protected by steel plates or metal grilles. In the west they were known as the OT-64C (1A) .
-
SKOT R-2 - command vehicle in use at battalion and regimental level. It is equipped with four radios: R-112, R-113 and two R-105. The vehicle is operated by a crew of seven.
- SKOT R-2AM - Unarmed command and fire control variant for artillery units.
- SKOT R-2M - radio and command execution with the tower of the SKOT-2A.
- SKOT R-6 - Unarmed radio and command execution.
- SKOT-2AP - Polish modification with a new WAT anti-aircraft tower , the armament of which consists of a 14.5 mm automatic cannon. The tower offers a higher aiming range for the armament and can therefore be used to combat air targets. A new CGS-90 visor was also installed. This version is known in the West as the OT-64C (2) .
-
SKOT-2A - Polish name for the version with the BRDM-2 tower, which was developed in the late 1960s. The vehicle is equipped with a conical turret and armed with a 14.5 mm automatic cannon and a coaxial 7.62 mm PKT MG. The number of seats in the crew compartment has been reduced from 18 to 10. In western sources this version is often called the OT-64C .
-
SKOT R-3 - Unarmed command vehicle for use at regimental level and above. Equipped with four radio devices, a radio receiver, a relay station and a radio telephone. The crew consists of seven men.
-
KTO WR-02 "Ryś" (KTO stands for Kołowy Transporter Opancerzony - armored personnel carrier with wheels, Ryś is the Polish word for lynx ) - Greatly improved version with an IVECO Cursor 8 engine. The reconstruction will be carried out by the 5th Military Mechanical Institute in Poznań .
- KTO WR-02 "Ryś-2" - export version of the KTO WR-02 "Ryś"
-
SKOT-1A - SKOT-1, equipped with a superstructure at the front above the crew room. The structure is a large two-part hatch.
gallery
SKOT R-2M in the Warsaw Museum of the Polish Army
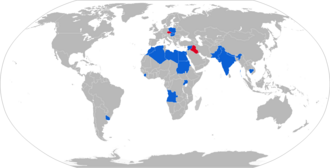
User states
-
 Algeria
Algeria
-
 Cambodia : 26 vehicles, but very few are likely to be operational.
Cambodia : 26 vehicles, but very few are likely to be operational. -
 Czech Republic : 28 OT-64 TTPs in service (as of January 1, 2008). It is planned to replace them with newer vehicles between 2007 and 2012.
Czech Republic : 28 OT-64 TTPs in service (as of January 1, 2008). It is planned to replace them with newer vehicles between 2007 and 2012. -
 Hungary
Hungary
-
 Egypt : 300 vehicles
Egypt : 300 vehicles -
 India
India
-
 Libya
Libya
-
 Morocco
Morocco
-
 Pakistan
Pakistan
-
 Poland : At the beginning of the 1990s, the SKOT was gradually withdrawn from the Polish army . The Patria AMV was purchased as a replacement for the SKOT . In 2005 there were 110 SKOT TTP vehicles and those based on the SKOT in service. Many SKOTs have been sold to private collectors who ensure that the vehicles remain in running order and can be seen regularly at international collectors' meetings.
Poland : At the beginning of the 1990s, the SKOT was gradually withdrawn from the Polish army . The Patria AMV was purchased as a replacement for the SKOT . In 2005 there were 110 SKOT TTP vehicles and those based on the SKOT in service. Many SKOTs have been sold to private collectors who ensure that the vehicles remain in running order and can be seen regularly at international collectors' meetings. -
 Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone
-
 Slovakia
Slovakia
-
 Sudan
Sudan
-
 Syria
Syria
-
 Uganda
Uganda
-
 Uruguay : 90 vehicles
Uruguay : 90 vehicles
Former user states
-
 Czechoslovakia : Assigned to the successor states
Czechoslovakia : Assigned to the successor states -
 Iraq : All destroyed or scrapped
Iraq : All destroyed or scrapped
literature
- Philip Trewhitt: tanks. The most important combat vehicles in the world from World War I to the present day. Neuer Kaiserverlag, Klagenfurt 2005, ISBN 3-7043-3197-X .
swell
- ↑ a b c d OT-64 - SERIES OF 8X8 ARMORED VEHICLES ( Memento from May 1, 2008 in the Internet Archive ). May 1st, 2008 on jedsite.info (via Wayback Machine )
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k SKOT (Polska i CSRR) . On pancerni.abajt.pl
- ↑ Equipment Size in 2008 . On army.cz
- ↑ uzbrojenie ( Memento of October 11, 2007 in the Internet Archive ). October 11, 2007 on militarium.net (via Wayback Machine )
Web links
- About the OT-64 on globalsecurity.org ( Memento from April 28, 2015 in the Internet Archive )
- History on the website of the Czech Ministry of Defense OT-64 (English)
- Photos of different variants of the OT-64 ( Memento from September 22, 2012 in the Internet Archive ) (Czech)