Evangelical Lutheran regional church of Hanover

|
|
| map | |
|---|---|
|
|
| Basic data | |
| Area : | 38,617 km² |
| spiritual direction: |
Regional Bishop Ralf Meister |
| President of the regional synod: |
Matthias Kannengießer |
| President of the Regional Church Office : |
Stephanie Springer |
| Membership: |
EKD , VELKD , Conf. Ev. Churches in Nds. , LWF , WCC |
| Sprengel : | 6th |
| Church districts : | 48 (May 2018) |
| Church district associations: | 12 (May 2018) |
| General associations: | 3 (May 2018) |
| Parish associations: | 58 (May 2018) |
| Parishes : | 1,248 (May 2018) |
| Chapel parishes : | 111 (May 2018) |
| Institution communities : | 9 (May 2018) |
| Parishioners: | 2,532,601 (December 31, 2018) |
| Share of the total population: |
41.4% (December 31, 2018) |
| Official Website: | www.landeskirche-hannovers.de |
The Evangelical Lutheran Regional Church of Hanover is one of 20 member churches ( regional churches ) of the Evangelical Church in Germany (EKD). Like all regional churches, it is a corporation under public law . It is based in Hanover . In December 2018, the church had 2,532,601 parish members, making it the largest regional church in Germany. It is one of the Lutheran churches within the EKD, a member of the United Evangelical Lutheran Church of Germany (VELKD), the World Council of Churches and the Lutheran World Federation . It also belongs to the Confederation of Protestant Churches in Lower Saxony .
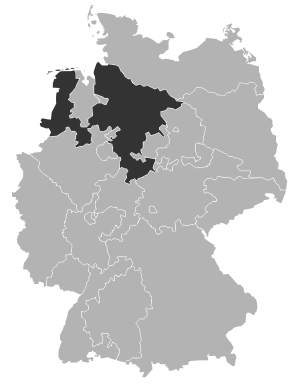
Territory of the regional church
The area of the Evangelical Lutheran Church of Hanover essentially comprises the former Kingdom of Hanover . After its annexation by Prussia after the German War in 1866, there was an independent Protestant church in the Prussian province of Hanover until 1946 , which did not belong to the Old Prussian Union. After the dissolution of Prussia, the state of Hanover was founded from August to November 1946 , which, with minor deviations, was located on the territory of the former Kingdom of Hanover and also saw its tradition. On November 23, 1946, the area became part of the State of Lower Saxony .
The changes in the provincial and state borders in the 1930s were initially not taken into account when assigning areas to the regional church of Hanover. It was not until 1974 that the Ilfeld consistorial district , which was then in the GDR, and whose area had been reclassified to the Province of Saxony in 1932 , was separated from the Hanover regional church. In 1977, the area that came to Hamburg in 1937 through the Greater Hamburg Law was reclassified , with minor deviations, to the North Elbian Church (for both see below under History ). In contrast, the territorial exchange in 1941 between the states of Prussia and Braunschweig, which preceded the formation of the city of Salzgitter in 1942, was taken over directly by the regional churches . That is why today Holzminden belongs to the Hanoverian church, while Goslar belongs to the Brunswick regional church.
Most of Lower Saxony is now part of the Hanover Regional Church. Of the areas in Lower Saxony today, the regional church of Hanover does not include:
- the former state of Oldenburg
- the former state of Braunschweig (with the exception of the Thedinghausen exclave ) and
- the former state of Schaumburg-Lippe
within the limits of 1946.
The following areas outside the current state of Lower Saxony belong to the Landeskirche Hannover:
- from the Free Hanseatic City of Bremen the city of Bremerhaven (with the exception of the United Evangelical Protestant Congregation for the Mayor Smidt Memorial Church ),
- from the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg the island of Neuwerk and the Hamburg-Cranz district ,
- from the state of Hesse the municipality of Nieste as well
- from the state of North Rhine-Westphalia parts of the municipality of Borgholzhausen .
The following area changes between the former states of Oldenburg and Hanover were not taken into account when assigning the regional churches:
- Today's district Vörden (Landeskirche Hannover) of the municipality Neuenkirchen-Vörden is in the district of Vechta .
- The current district of Idafehn (Landeskirche Oldenburg) of the municipality of Ostrhauderfehn is located in the district of Leer .
- The integrated community of Harpstedt (Landeskirche Hannover) is now in the district of Oldenburg .
- The current district of Dedesdorf (Landeskirche Oldenburg) of the municipality of Loxstedt is in the district of Cuxhaven .
- Today's district of Gödens (Landeskirche Hannover) of the municipality of Sande (Friesland) is located in the district of Friesland .
- Today's district of Varrel (Oldenburg regional church) in the Stuhr municipality is in the Diepholz district .
structure
The parishes are corporations under public law with elected church councils, the "church councilors" and the pastors. The church councils are newly formed every six years, with at least two thirds of the members of the church council being elected directly by the parish members. The last church council election took place in March 2018.
Several parishes together form a church district (roughly comparable to a district ), at the head of which is a superintendent ( called provost in the church districts of Uelzen and Lüchow-Dannenberg ). The church districts are also corporations under public law and have the church district council with the church district council and the church district council as organs. The parish council is formed within six months after the new church councils have been formed; until 2012 it was composed of representatives of the parishes, those appointed by the parish council, the superintendent and his deputy and the synodal members from the church district. Since the new formation on January 1, 2013, ordained and non-ordained congregation members in electoral districts have been elected by the members of the church councils instead of the representatives of the parishes. The church districts are grouped into districts (roughly comparable to an administrative district ), with a state superintendent as regional bishop at the head, who is elected by the church senate for ten years, an extension until retirement is possible. The state superintendents wear an episcopal official cross . Until the 1930s, general dioceses existed as subdivisions, headed by general superintendents who had been formed before the formal founding of today's regional church in 1866. The state superintendent is supported by the Ephorenkonvent. All superintendents of the Sprengels belong to the Ephorenkonvent. In contrast to the parish and parish, the Sprengel has no status as a corporation under public law and is not a separate legal entity, so it cannot have its own property or employ staff. People who work for the district are directly employed by the regional church.
As of June 30, 2007, there were eight districts. The number was reduced to six on July 1, 2007; the district of Calenberg-Hoya was dissolved, the districts of Hildesheim and Göttingen were merged and several church districts were assigned to other districts.
Sprengel with their church districts
-
Hanover
- City Church Association Hanover
- Burgdorf
- Burgwedel-Langenhagen (Langenhagen headquarters)
- Grafschaft Schaumburg (seat Rinteln)
- Laatzen-Springe (Pattensen headquarters)
- Neustadt-Wunstorf (Neustadt headquarters)
- Nienburg
- Ronnenberg
- Stolzenau-Loccum (seat of Stolzenau)
-
Hildesheim-Göttingen
- Goettingen
- Hameln-Pyrmont (Hameln headquarters)
- Harzer Land (based in Osterode), until December 31, 2012: Clausthal-Zellerfeld , Herzberg and Osterode
- Hildesheimer Land-Alfeld (seat of Alfeld and Elze)
- Hildesheim-Sarstedt (seat Hildesheim)
- Holzminden-Bodenwerder (headquarters in Holzminden)
- Leine-Solling (seat in Northeim)
- Münden
- Torment
-
Luneburg
- Celle
- Gifhorn
- Hittfeld
- Lüchow-Dannenberg
- Lüneburg, until December 31, 2016: Bleckede and Lüneburg
- Soltau
- Uelzen
- Walsrode
- Winsen (Luhe)
- Wolfsburg-Wittingen (based in Wolfsburg), until December 31, 2012: Wittingen and Wolfsburg
-
Osnabrück
- Bramsche
- Grafschaft Diepholz (Diepholz headquarters)
- Melle-Georgsmarienhütte (Melle headquarters), until December 31, 2012: Georgsmarienhütte and Melle (partially)
- Osnabrück
- Syke-Hoya (Syke headquarters)
-
Ostfriesland-Ems (Emden headquarters)
- Aurich
- Emden-Leer, until December 31, 2012: Emden and Leer
- Emsland-Bentheim (Meppen headquarters)
- Harlingerland (seat of Esen)
- north
- Rhauderfehn (seat Westrhauderfehn)
-
Stade
- Cuxhaven-Hadeln, until December 31, 2012: Cuxhaven and Land Hadeln (seat Otterndorf )
- Bremerhaven
- Bremervörde
- Buxtehude
- Osterholz-Scharmbeck
- Rotenburg (Wümme)
- Stade
- Verden (Aller)
- Wesermünde, until December 31, 2012: Wesermünde-North (Dorum headquarters) and Wesermünde-South (Beverstedt headquarters)
Parishes
In the 48 church districts there are 1,248 parishes, 111 chapel parishes and 9 institutional communities (2002: 59 church districts and 1,384 parishes, 1986 76 church districts and 1,550 church chapels and institutional communities). In the 20th century the number of parishes increased by dividing large parishes, especially in cities. Since 1990 these have partly come together again. Smaller church and chapel congregations with fewer than 300 members were awarded a bonus in the 2010s if they join forces with a larger congregation or enter into close cooperation in a working group.
history
The history of the regional church is inextricably linked with the history of the state of Hanover , which in the 19th century was made up of the following states and areas:
- Principality of Lüneburg ,
- Principality of Calenberg (from which the Electorate of Hanover later emerged),
- Principality of Grubenhagen ,
- Land Hadeln and Amt Neuhaus (both belonging to Saxony-Lauenburg ),
- Counties of Diepholz , Hoya , Lingen , Bentheim , East Friesland and Hohnstein ,
- Lords Spiegelberg and Plesse ,
- Free imperial city of Goslar as well
- Territories of the secularized principalities of Bremen , Verden , Hildesheim , Münster and Osnabrück , the Untereichsfeld ( belonging to Kurmainz ) and the territory of the Imperial Abbey of Loccum .
From 1527 onwards, the Reformation was introduced in almost all parts, mostly following the Lutheran model; The Wittenberg reformer Johannes Bugenhagen , from whom the first church ordinance in the Guelph lands came from, was of particular importance . Only the spiritual territories of Hildesheim, Münster, Osnabrück-Land and Eichsfeld remained Catholic. Some Reformed churches also existed.
The Electorate of Hanover was established in 1692 and gained considerable territory. The territory was expanded again in 1815, when Hanover was elevated to a kingdom, including East Frisia, the counties of Lingen and Bentheim, the rule of Plesse and the Osnabrück and Hildesheim monasteries. With the considerable increase in area there was now a regional church within the Kingdom of Hanover, which had both Lutheran and Reformed congregations, the head of which was the King of Hanover as summus episcŏpus ( Latin for: "supreme bishop").
The church was divided into six relatively independent consistories: In Aurich there was a Lutheran-Reformed simultaneous consistory (for East Frisia). Lutheran consistories existed in Hanover (for the Kurhannöversche core area), in Ilfeld in the Harz (for the former County of Hohenstein ), in Osnabrück (for the former bishopric of Osnabrück ), in Otterndorf (for the Land of Hadeln , existed 1535–1885) and in Stade (1650–1903 for the Landdrostei Stade , until 1885 without Hadeln, then including Hadelns).
In 1866 a "state consistory" was established in Hanover, but the six provincial consistory initially remained. One day after the establishment of the state consistory in Hanover, the Kingdom of Hanover was annexed by Prussia and converted into the Province of Hanover . However, the church remained independent and was not incorporated into the uniate Evangelical regional church in Prussia , which was founded in 1817 . In 1885 and 1903 five of the six provincial consistories were dissolved.
Only Aurich remained as a provincial consistory with equal representation (Lutheran and Reformed). From 1882 - but only its Reformed members - it had become the highest church authority of the Evangelical Reformed Regional Church of the Province of Hanover , from which today's Evangelical Reformed Church (Regional Church) emerged . The Aurich Consistory continued to be responsible for the Lutheran communities of East Frisia . This was continued until after the First World War (elimination of the sovereign church regiment ). It was not until 1922 that the Aurich consistory, with equal representation, was converted into a purely reformed consistory.
In Prussian times the King of Prussia was head of the regional church of Hanover. Spiritual leaders at that time were eight (from 1902 four) general superintendents . In the middle of the 19th century, Gerhard Uhlhorn held office under the numerous names for many years . The names of the last general superintendents of the province of Hanover were:
- in Aurich: Hans Süßmann (1902–1925),
- in Hanover: Carl Schuster (1884–1905), Friedrich Ludwig Möller (1905–1925),
- in Hildesheim: Theodor Hoppe (1903–1925) and
- in Stade: Johannes Remmers (1904–1913), Johannes Schwerdtmann (1913–1922) and August Marahrens (1924–1925, since 1922 substitute).
After the abdication of the kings and the elimination of the sovereign church regiment , Prussia, to which the province of Hanover belonged, became a republic called the Free State of Prussia . The provincial church of Hanover became an independent regional church and received a constitution in 1922. After that, the regional bishop was at the head of the regional church. Furthermore, a regional church convention (from 1946 regional synod) was introduced. The state church office was formed from the state consistory in Hanover. Until the appointment of the first regional bishop in 1925, "the state ministers charged with the provisional administration of the sovereign church regiment" of Prussia, and from 1921 the presidents of the regional consistory in Hanover, acted as heads of the church.
After the transition of the district of Grafschaft Schaumburg from the province of Hessen-Nassau to the province of Hanover in 1932, the area was also reclassified from the regional church in Hessen-Kassel to the Hanoverian regional church in 1933 . The borders of the church district remained unaffected by the later state territorial reforms.
After the Second World War , the Evangelical Lutheran Church of Hanover was a founding member of the Evangelical Church in Germany (EKD) and the United Evangelical Lutheran Church of Germany (VELKD). In 1971 she formed the Confederation of Evangelical Churches in Lower Saxony with the other Protestant churches in Lower Saxony . Since 1976 the former Brunsen and Thedinghausen communities have belonged to the regional church of Hanover after almost 300 years. The parishes had come from the Bremen Church to the Brunswick Church in 1679. In 1974 the consistorial district of Ilfeld , located in the GDR at that time, was separated from the Hanoverian regional church.
In 1977 the North Elbian Evangelical Lutheran Church was founded from four existing regional churches. As part of this merger, the Harburg parish, which is located in Hamburg's urban area, joined the newly founded church. At the same time, the congregations of Cuxhaven, which had previously belonged to the Evangelical Lutheran Church in the Hamburg state , which was merging , separated from their regional church and became part of the Evangelical Lutheran regional church of Hanover. To this day, a merger of the regional churches in Lower Saxony to form a common regional church has occasionally been discussed.
President of the State Consistory in Hanover
- 1866–1883: Carl Lichtenberg
- 1885-1893: Otto Mejer
- 1894–1903: Bodo Voigts
- 1903–1910: Heinrich Franz Chalybäus
- 1911: Wilhelm Heinichen
- 1912–1920: Hermann Steinmetz
- 1921–1924: Ernst Lohmann
Membership development
Like all regional churches, the Hanoverian regional church recorded a decline in membership. On December 31, 2002 it had 3,142,685 parishioners, in 2010 the number was 2,883,510 parishioners. On December 31, 2018, the Hanover regional church had 2,532,601 (41.4%) parish members out of a total population of 6,115,726. In 2004 the Hanover regional church still had an absolute majority (50.3%) with 3,087,195 parish members out of a total population of 6,135,375
Church leadership - constitutional bodies
The Evangelical Lutheran Regional Church of Hanover has six church governing constitutional bodies, these are the regional bishop, the church senate, the regional synod, the regional synodal committee, the regional church office and the bishops' council. The regional bishop presides over the church senate, the bishops' council and the regional church office.
Spiritual guidance
At the head of the Evangelical Lutheran regional church of Hanover is the regional bishop , who is proposed by the church senate of the regional church and elected by the synod for ten years. An extension until retirement is possible. He carries the episcopal official cross of the regional church of Hanover. The office of the bishop is the bishop's office on Haarstrasse in the Hanover district of Südstadt . The market church has been the preaching church of the regional bishop since 1925 . The regional bishop is paid according to salary group B 8 of salary order B.
State Bishops and State Bishops
- 1925–1947: August Marahrens
- 1947–1971: Johannes Lilje
- 1971–1988: Eduard Lohse
- 1988–1999: Horst Hirschler
- 1999–2010: Margot Käßmann
- 2010–2011: Hans-Hermann Jantzen (Episcopal Vicar)
- since March 26, 2011: Ralf Meister
Church Senate
In the Church Senate, all the governing bodies of the regional church work together. In it all questions of the regional church are discussed. Under the chairmanship of the regional bishop are the president of the regional church office, a clerical member of the regional church office (usually the spiritual vice-president), a regional superintendent, the chairman of the regional synodal committee, the president of the regional synod, three other regional synodals and four other members of the regional church who do not belong to the synod, member of the senate. The term of office of the elected members is six years. The Senate's office is located in the Hanover Regional Church Office. The church senate proposes the bishop to be elected (up to three names), appoints the state superintendents, issues their service regulations, supervises them and determines their official residence and sermon place. It appoints the president / vice-presidents and all other members of the regional church office (college) and acts as the highest service authority for the college . He appoints the members of church courts. He appoints ten synodals and can object to resolutions of the regional synod within four weeks. The Senate orders the election of a new regional synod and sets the election day. He participates in church laws, resolutions of the regional synod and declarations of the regional church office, assigns service titles and sets titles. The Senate appoints members of the church bodies and appoints representatives of the regional church in the EKD church conference. In the church senate, the competencies and responsibilities of the regional bishop, the regional superintendent and the regional church office are determined. It issues ordinances with the force of law and issues basic guidelines. The church senate participates in the order and administration of the monasteries as well as the rules of procedure of the regional church office. He exercises the right of grace .
State Synod
Since 1863, the regional church has had a regional synod as the “parliament” . From 1925 to 1945 the parliament was called the Landeskirchentag, from 1945 to 1947 there was a provisional regional synod. Its members, the synodals, are elected every six years in constituencies. The members of the church and chapel boards, the members of the parish councils and the pastors are entitled to vote. The office of the regional synod is located in the regional church office in Hanover. The synod meets about twice a year, usually in the Henrietten Foundation in Hanover. Their tasks are similar to those of political parliaments. During the rest of the time, the Regional Synodal Committee takes on the permanent representation of the Synod. The synod elects a presidium, which is chaired by the president of the regional synod . Before the opening of a regional synod, there is a divine service in which the members make a vow in the hands of the regional bishop. Until a presidium is elected, the first meeting is chaired by the chairman of the regional synodal committee.
The synod forms a number of committees. The seats in the committees and the committee chairs are distributed based on the strength of the two church political groups (corresponding to parliamentary groups in the political field). On the one hand there are the (moderately) conservative synodals, who have come together under the umbrella of the Lebendige Volkskirche (LVK) and the more (left-) liberal faction of the Open Church group (GOK). The latter emerged as the first ecclesiastical political group in the Evangelical Lutheran Regional Church of Hanover in 1969. The LVK followed a few years later.
Both groups meet several times a year and their existence guarantees the efficiency of parliamentary work. Initially, in the 1970s, the LVK was represented somewhat more strongly than the GOK in the synod. Since the 22nd regional synod, the GOK has had a majority of the synodals. In the course of the perspective decisions of the regional church, the 23rd regional synod decided to reduce the number of synodals by 25% to 75 members with the new election of the regional synod in autumn 2007. In February 2014, the 25th regional synod was newly constituted for the legislative period from 2014 to 2020. The 25th regional synod consists of 63 elected members, 10 appointed by the church senate, the Abbot of Loccum and a representative of the Georg-August-Universität Göttingen as members For the first time, two youth delegates were appointed to the state synod, who take part in the meetings without voting rights. Currently (2016) four youth delegates are appointed. The GOK synodal group has 37 members, the LVK synodal group 38. The regional bishop, the members of the bishops' council and the church senate and the authorized representatives of the regional church office can participate in the synod without voting rights and speak after each speech. Furthermore, the head of the office of the regional synod takes part in the conferences.
Bureau
The presidium of the regional synod consists of the president, three vice-presidents and other secretaries. The group chairmen and the chairman of the regional synodal committee take part in the meetings.
Presidents of the regional synod / regional church convention
- Pre-Synod 1863–1869: Alexander Levin Graf von Bennigsen
- 1st regional synod 1869–1875: Friedrich Hermann Albert Freiherr von Wangenheim
- 1st - 4th Regional synod 1875–1893: Friedrich Meyer
- 5th Regional Synod 1893-1894: Wilhelm von der Osten
- 5th Regional Synod 1894–1899: Friedrich von Kaufmann
- 6-7 Regional synod 1899–1911: Georg Lichtenberg
- 8th Regional Synod - 1st Regional Church Congress 1911–1928: Georg Erhard Graf von Wesel
- 2. Landeskirchentag 1928–1931: Wilhelm Barkhausen
- Extraordinary State Church Congress 1931–1932: Anton-Dietrich von Wersebe
- 3rd State Church Congress 1932–1945 / 14. Regional synod 1947–1953: Wilhelm Friedrich Redepenning
- Provisional regional synod 1945–1947: Otto Meyer
- 15th Regional Synod 1953–1959: Johannes Wolff
- 16.-18. Regional synod 1959–1974: Martin Boyken
- 18.-21. Regional synod 1974–1992: Eckart Krömer
- 21-22 Regional synod 1993–1998: Valentin Schmidt
- 23rd Regional Synod 1998-2004: Albrecht Bungeroth
- 23–24 State Synod 2005–2013: Jürgen Schneider
- 25th regional synod since 2014: Matthias Kannengießer
Regional Synodal Committee
The rights of the Synod are exercised between the two meetings in the year of the seven-member State Synodal Committee (LSA) as a separate church governing body. In addition, it has its own rights of consent in the area of finance and legislation, so that synodal participation in the joint church leadership is continuously guaranteed. At the end of the 1st session of the regional synod, the regional synodal committee was re-elected for a six-year term in February 2014. Jörn Surborg - Hildesheim (GOK) has been chairman of the LSA since 2010.
Regional Church Office
The regional bishop is the chairman of the regional church office. The members of the regional church office form the college of the regional church office. Members are, in addition to the regional bishop, the president, the spiritual vice-president, the legally qualified vice-president, the ordinary higher regional church councils and other extraordinary members. In addition to the regional bishop and the president, the college consists of 9 full members (membership is suspended, as of April 2019). All matters of fundamental or significant theological, legal or financial importance are reserved to the college, for example drafts of church laws to the church senate and the regional synod, drafts for the budget, regulations for institutions of the regional church. He makes nominations for the election of superintends (heads of church districts) and appoints pastors in a general church mandate, insofar as this is connected with leadership tasks, and sends representatives to church and non-church organs. The college takes over supervisory measures according to the service or labor law as well as measures according to the disciplinary law and the law of teaching objections. The members support the regional bishop in carrying out his duties. The spiritual members wear an official cross. The regional church office decides as a college and determines the goals of its work within the framework of the law and the resolutions of the other organs. The college meets regularly with the state superintendents (council of bishops) for deliberations.
Council of Bishops
The regional bishop and the regional superintendents ( regional bishops) form the bishops' council. The regional bishop presides. During the church struggle in 1934, Regional Bishop Marahrens appointed representatives or shop stewards to reduce the influence of the provosts who had recently been appointed by the German Christians. He assigned them districts, and a little later the former districts . In February 1935 the formal appointment of the episcopal vicars took place. From then on they formed the Bishops' Council together. In succession to the episcopal vicars, the regional superintendents of the regional church have belonged to the council since 1936. The bishops' council advises on all questions that concern the regional church. He is to be involved in the introduction or modification of agendas, hymn books or catechisms. He advises on the appointment of superintendents (heads of church districts), pastors with special assignments or the appointment of the director of studies and rector of the Theological Academy. Service instructions to the superintendent require the approval of the Bishops' Council.
administration
Regional Church Office
The regional church office of Hanover assumes the function of the highest service authority of the regional church - without prejudice to the supervisory powers of other bodies. It administers the internal and external affairs of the regional church in accordance with the applicable law and the administrative principles established by the church senate and represents the regional church in legal matters. The regional church office oversees the existing bodies in the regional church and the holders of the official positions.
President of the Regional Church Office
The president of the regional church office is paid according to grade B 7.
- 1924–1929: Viktor Lampe
- 1930–1933: Max Schramm
- 1933–1946: Friedrich Schnelle
- 1946–1952: Gustav Ahlhorn
- 1952–1970: Karl Wagenmann
- 1970–1983: Johann Frank
- 1984–2008: Eckhart von Vietinghoff
- 2008 – May 2013: Burkhard Guntau
- since August 30, 2013: Stephanie Springer
Church district offices and administrative offices
The church districts, their parishes and institutions are administered in church district offices. In 2005 the Synod decided to halve the number of church district offices. As of January 1, 2006, there were 43 and as of February 2018 23 church district offices. (including branches) There are also other administrative offices such as the Church Administration Office Loccum and the Administration Office in the House of Church Services , which work for several supra-church institutions and services.
Institutions of the regional church
In Hildesheim, next to the Michaeliskirche , the center for worship and church music (Michaeliskloster) is housed in the regional church. In Göttingen, the church runs a study house and seminar for theology students at the Georg-August University of Göttingen and pastors in the study semester. The Hanover regional church has a central archive . The Center for Health Ethics (ZFG), the Hanns-Lilje-Foundation and the main office for life counseling are located in the Hanns-Lilje-Haus . Together with the regional churches of Braunschweig and Schaumburg-Lippes, the regional church supports the Evangelical Lutheran Mission in Lower Saxony (ELM). The diaconal institutions of the regional church are brought together in the Diaconal Work of Protestant Churches in Lower Saxony , founded in 2014 . Together with the Evangelical Church in Germany, the Hanover Regional Church is responsible for the Social Science Institute of the EKD .
House of Church Services
The House of Church Services (HkD) was founded in 1937 as the Office for Community Service (AfG). Forerunners were from 1918 the Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Volksmission and from 1933 to 1937 the People's Missionary Office I and II. The foundation was made to support numerous free evangelical organizations (Deutsches Evangelisches Männerwerk Hannover, ev. Regional youth service , women's aid and German-Evangelischer Frauenbund , Volksmission) to protect against the prohibition and conformity by the National Socialists and to organize under the umbrella of the official church (see: Church fight ). In 2002 the Office for Community Service was renamed the House of Church Services. Over the years, the structure and organization of the AfG / HkD changed, institutions were added and were outsourced, so from 1956 to 2002 the trombone work belonged to the Office for Community Service and until 2010 the Lutheran Publishing House . The first official residence was the Lutherhaus at Ebhardtstraße 3 in Hanover-Mitte , which is now a listed building. Since 1966, the main office has been on Archivstrasse in Hanover ( Calenberger Neustadt district ). The House of Church Services is present in all districts of the regional church with regional offices. Other institutions and associations in the HkD have their headquarters in the Hanns-Lilje-Haus , which belongs to the institution, and in Odeonstraße in Hanover-Mitte
The House of Church Services is the service and competence center of the regional church of Hanover and supports the work of the regional church and the parishes as a supra-community institution. In the HkD there are more than twenty associations, works, institutions, services and specialist agencies ( women's work , state youth ministry , church service in the world of work , church service in the countryside , missionary services , art and culture , church and Judaism , church in Europe , ecumenism , peace work ua) in the regional church of Hanover combined into one organization . A total of 43 fields of work and other projects (from work with the elderly to the World Day of Prayer, as well as the Church for Democracy initiative - against right-wing extremism , Luther 2017 , the culture prize of the Evangelical Lutheran Church of Hanover or the Loccum – Volkenroda pilgrimage ) are processed and supervised by the HkD. (Status: May 2017) The House of Church Services also includes the Bursfelde Monastery Spiritual Center and the Aid for Chernobyl Children Working Group , which are assigned to departments.
Since 2009, the House of Church Services has been divided into six departments and the administrative office . The house are institutions of the Confederation of Protestant Churches in Lower Saxony, these are the Church Service in Police and Customs of the Confederation of Protestant Churches in Lower Saxony and the Evangelical Adult Education Lower Saxony . Church associations, Evangelisches Dorfhelferinnenwerk Niedersachsen eV , Encounter - Christians and Jews Lower Saxony e. V. associated with the Evangelical Lutheran Central Association for Encounters between Christians and Jews e. V. , Evangelical Family Educational Center Hannover e. V. , Hannoversche Bibelgesellschaft e. V. , institutions of the regional church office and the EMA assigned or connected. The administrative office of the HkD takes on the services and tasks of administration and business management for the house of church services and for 29 other institutions, for example Michaeliskloster Hildesheim, center for pastoral care, church development service of the regional churches of Hanover and Braunschweig as well as the state superintendencies (as of May 2017) .
The House of Church Services has around 240 employees at its Archivstrasse / Brandstrasse headquarters (2002: 270). The facility includes around 90 speakers (pastors of the regional church / deacons / specialist speakers employed under private law) of whom about half have their official seat and focus in the districts. Some speakers have regional church assignments. It is the largest regional church institution. A total of around 700 full-time and part-time employees work in and for the HkD, its facilities, services, specialist units and associations in the regional church and confederation. The House of Church Services is a founding member of Transfair Germany . It is the seat of the joint printing house of the House of Church Services and the Regional Church Office and takes care of the printing of the writings of both offices. It is the publisher of numerous handouts, publications and books. Since 2004 it has received several awards from Ökoprofit .
The institution is dependent and is under the supervision of a board of trustees (representatives from the bishop's council, synod, regional church office, HkD) led by the spiritual vice-president of the regional church office, which gives the house principles and guidelines and monitors the work of the house. The House of Church Services is run by a director, he is the pastor of the regional church (PdL). Staff positions are assigned to the director. The director has u. a. the chair of the management committee, which includes the managing director (head of the administrative office), the six department heads and the head of Evangelical Adult Education in Lower Saxony. Previous leaders were Adolf Cillien (1937–1953, from 1943 also extraordinary member of the regional church office), Theodor Laasch (acting director 1953–1956), Paul Kurth (1956–1961), Rudolf Herrfahrdt (1965–1975), Paul Gerhard Jahn (1975 –1990), Hans Joachim Schliep (1990–1999, from 1994 also extraordinary member of the regional church office) and Dine Fecht (1999–2008). Ralf Tyra has been the head of the facility since 2008 .
Protestant media work
The Evangelische MedienArbeit (EMA) has been responsible for the communication of the Evangelical Lutheran Regional Church of Hanover since 2017 and emerged from the merger of the Evangelical Media Service Center (EMSZ) and the press office of the Regional Church. The media work (EMA) is divided into three work areas, campaigns and design, press officer / theme room and digital agency. The EMA is based in the House of Church Services in Archivstrasse and in the Hanover Regional Church Office, it is a legally dependent institution of the regional church and is headed by a director, Pastor Joachim Lau since July 2020, who is directly assigned to the regional bishop, and one from the regional church office Supervisory board formed in Hanover.
Center for Pastoral Care
The Center for Pastoral Care and Counseling (ZfS) is a dependent institution under the supervision of the regional church office. It includes the specialist services and supraregional bodies for special pastoral care such as those responsible for elderly, AIDS, hospice and deaf pastoral care, the pastoral psychological service , the head of the main office for marriage and life counseling and the pastoral clinic center for clinical pastoral care training . The center coordinates and organizes the work of special and special pastoral care in the area of the regional church and provides basic, advanced and advanced training for church employees in the field of pastoral care. It is managed by a board of trustees and a director. From 2013 to June 2018, Superintendent was a. D. Martin Bergau the leader. Pastor Angela Grimm has been director of the ZFS since August 2018. It is based at Blumhardtstrasse 2A in Hanover.
Evangelical school work
The Evangelical School Work of the Regional Church of Hanover was founded in 2009 and is responsible for the educational and organizational support and coordination of the Protestant schools in the area of the Regional Church and helps to set up new schools. It is a dependent institution under the supervision of the Landeskirchenamt Hannover, to which it is directly assigned. It is headed by a board of trustees and administered by an office based in Hanover.
Facilities in Loccum
The regional church maintains a seminar for preachers in Loccum , which is located in the Loccum monastery . Loccum also houses the Evangelical Academy , the Religious Education Institute and the Lower Saxony Pastoral College , in which the other Evangelical regional churches in Lower Saxony have been participating since 2016. The Evangelical Academy, the Religious Education Institute and the Pastoral College are jointly administered by an administrative office and managed by a management committee, in which the heads of the institutions and the administrative office as well as four representatives (one as chairman) of the Hanover regional church office are members. The heads of the institutions and the administrative office form the leaders' conference.
Commissioner of the Evangelical Lutheran Church of Hanover
The regional church appoints regional church representatives for various topics (peace, environment, repository, art and culture, equality, church and Judaism, ideological issues, etc.). They hold lectures and hold events, training and further education and are the contact for church bodies and governing bodies, as well as for politics, media, science and society.
Hymn books
The congregations of the Evangelical Lutheran Church in Hanover have been singing or singing from the following hymn books in the last few centuries:
- Christian hymn book for the Evangelical Lutheran congregations in the Principality of Osnabrück , 1780, at that time still under the title Christian hymn book for the Evangelical Lutheran congregations in the bishopric of Osnabrück ,
- Hymn book for the Evangelical Lutheran parishes of the city of Osnabrück , Osnabrück, early 19th century,
- Singing book for the Protestant communities in the Principality of Hildesheim , along with a prayer book for church and house devotion; with Royal Great Britain-Hannoverschem Most Gracious Privilegio, 1792, extended edition 1816,
- East Frisian church hymn book in a selection of the best older sacred songs , Aurich, introduced in September 1825,
- Hymnal for the duchies of Bremen and Verden for use in public services and in private prayer, Stade around 1800,
- Hannoversches Kirchen-Gesangbuch with an appendix, prayer book and the epistles. Issued on His Royal Majesty's Most Gracious Order. With royal most gracious privilege, Hanover around 1800,
- Lüneburg church chant book together with a prayer book with the most gracious royal privilege, Lüneburg, before 1850,
- Hanoverian Evangelical-Lutheran hymn book , Hermannsburg 1883,
- Evangelical church hymn book - edition for the Evangelical Lutheran churches in Lower Saxony, Hanover, Hanover 1952,
- Dor kummt een Schipp - hymn book in Low German, published by the Working Group of Low German Pastors in Lower Saxony, Hermannsburg 1991.
- Evangelical hymn book - edition for the Evangelical Lutheran Churches in Lower Saxony and for the Bremen Evangelical Church, Hanover / Göttingen, introduced in Advent 1994 (currently valid hymn book)
Theological attitudes
In the regional church, as in all churches of the EKD, men and women are ordained.
On September 18, 2015, the Church Senate of the Evangelical Lutheran Regional Church of Hanover published a statement on the injustice and failure of theologians of the Reformation churches when innocent people were put to death in the witch hunts , and has pronounced a social rehabilitation of the victims of the witch trials .
In May 2019, the possibility of marriage for same-sex couples was decided.
See also
- List of churches in the Evangelical Lutheran Church of Hanover
- List of disengaged churches in the Evangelical Lutheran regional church of Hanover
literature
- Peter Kollmar, Jens-Peter Kruse (Red.): The Evangelical Lutheran Church of Hanover , ed. from the press and information office of the Evangelical Lutheran Church of Hanover, Kassel: Druckhaus Thiele & Schwarz GmbH, 1988
- Hans Walter Krumwiede : Church history of Lower Saxony . 1st + 2nd partial volume. Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht, Göttingen 1996. ISBN 3-525-55434-6 (standard work)
- Gerhard Lindemann : "Typically Jewish". The position of the Evangelical Lutheran Regional Church of Hanover on anti-Judaism, anti-Semitism and anti-Semitism 1919–1949 (= series of publications by the Society for Research on Germany . Vol. 63). Duncker and Humblot, Berlin 1998, ISBN 3-428-09312-7 .
- Gerhard Uhlhorn : Hannoversche church history in a clear presentation . Reprint of the 1902 edition. Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht, Göttingen 1988. ISBN 3-525-55408-7 (old, but still worth reading)
- Heinrich Große, Hans Otte , Joachim Perels : Preserving without confessing? The Hanoverian regional church under National Socialism . Lutherisches Verlagshaus, Hanover 1996, ISBN 3-7859-0733-8
- Heinrich Große: “Nobody can serve two masters”: on the history of the Protestant Church during National Socialism and in the post-war period . Blumhardt, Hannover 2010, ISBN 978-3-932011-77-1 . Full text .
- Beate Blatz: Heirlooms from the Hanover regional church. 50 years of the Office for Community Service . Edited by the Office for Community Service, Missionshandlung Hermannsburg, 1991, ISBN 3-87546-069-3
- Dirk Riesener : People's Mission-between People's Church and Republic. 75 years house of church services - formerly the office for community service - of the Evangelical Lutheran regional church of Hanover. Lutherisches Verlagshaus, Hannover 2012, ISBN 978-3-7859-1080-1
Web links
- Official website
- Parish dictionary. Evangelical Lutheran regional church of Hanover
swell
- ↑ Landeskirche Hannover: Jurist Kannengießer new President of the Regional Synod ( Memento from February 24, 2014 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ a b c Evangelical Church in Germany - Church membership numbers as of December 31, 2018 , ekd.de, accessed on February 25, 2020.
- ↑ 13 A Church District Order (KKO) - Canon Law online reference work. In: www.kirchenrecht-evlka.de. Retrieved October 16, 2016 .
- ↑ These were the general dioceses of Alfeld , Bockenem , Bremen-Verden , Calenberg , Göttingen , Grubenhagen and on the Harz , Harburg , Hildesheim , Hoya-Diepholz , Lüneburg-Celle .
- ↑ EKD church members on December 31, 2018 , accessed on June 14, 2020
- ↑ Evangelical Church in Germany Table 1: Church members and population by regional churches on December 31, 2004
- ^ Election of the new regional synod on September 29th. Retrieved December 21, 2018 .
- ↑ Archive link ( Memento from October 25, 2014 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ a b c Church Senate. Retrieved December 21, 2018 .
- ↑ 10 A Church Constitution (KVerf) - Canon Law online reference work. In: www.kirchenrecht-evlka.de. Retrieved October 16, 2016 .
- ^ NDR: Market Church in Hanover. In: www.ndr.de. Retrieved October 16, 2016 .
- ↑ 150 A Bishop's Law (LBischG) - Canon Law Online Reference Work. In: www.kirchenrecht-evlka.de. Retrieved October 16, 2016 .
- ↑ http://www.evlka.de/content.php?contentTypeID=4&id=14964 Official press release of the regional church on the election
- ↑ The regional church at a glance. Retrieved December 21, 2018 .
- ↑ The creation of the regional synod was a consequence of the catechism dispute of 1862, see When the King gambled himself away .
- ^ Hannoversche Synod appoints youth delegates for the first time. Retrieved December 21, 2018 .
- ^ Synod met from May 29th to June 1st. Retrieved December 21, 2018 .
- ^ The Presidium of the 25th Regional Synod. Retrieved December 21, 2018 .
- ↑ Regional Church Office. Retrieved December 21, 2018 .
- ^ Council of Bishops. Retrieved December 21, 2018 .
- ↑ 10 A Church Constitution (KVerf) - Canon Law online reference work. Retrieved December 21, 2018 .
- ↑ DWiN editorial staff: Statement by the Diakonie in Lower Saxony on the Good Day Care Act. December 17, 2018, accessed December 21, 2018 .
- ^ House of Church Services is 75 years old. Retrieved December 21, 2018 .
- ↑ http://www.landeskirche-hannovers.de/evlka-de/presse-und-medien/frontnews/2016/11/02
- ↑ Archive link ( Memento from March 11, 2012 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ a b http://www.evlka.de/media/texte/leben/Kapitel/dienste.pdf
- ↑ http://www.kirchliche-dienste.de/themen/
- ↑ http://www.kirchliche-dienste.de/wir_ueber_uns/geschichte
- ^ Website of the House of Church Services ( Memento of February 16, 2011 in the Internet Archive )
- ^ Evangelical Adult Education Lower Saxony (EEB). In: www.eeb-niedersachsen.de. Retrieved October 16, 2016 .
- ↑ Archived copy ( Memento of May 7, 2012 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ http://www.medienbuero.net/index.php?s=content&p=Tacheles
- ↑ Archive link ( Memento from July 27, 2014 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ http://www.kirchliche-dienste.de/wir_ueber_uns/verwaltung/verwaltungsstelle_hkd
- ↑ http://www.kirchliche-dienste.de/Aktuelles/Kuratoren
- ↑ http://www.kirchliche-dienste.de/themen/93/1486/0/0/0.htm ( page no longer available , search in web archives )
- ↑ http://www.kirchenrecht-evlka.de/getpdf/id/20969
- ↑ http://www.kirchliche-dienste.de/specials/75jahre/
- ↑ http://www.evangelische-medienarbeit.de/
- ↑ pastoralklinikum.de. Retrieved December 21, 2018 .
- ↑ New center for pastoral care in the regional church / Martin Bergau appointed director. In: landeskirche-hannovers.de. Retrieved October 16, 2016 .
- ↑ http://www.evlka.de/schuleundkirche/content.php?contentTypeID=1075
- ^ Website of the Pastoral College ( Memento of November 12, 2013 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ http://www.kirchenrecht-evlka.de/showdocument/id/20955/orga_id/EVLKA/search/Akademie# ( page no longer available , search in web archives )
- ^ Evangelical Lutheran Church of Hanover for the social rehabilitation of the victims of the witch trials September 18, 2015
- ^ NDR.de: Landeskirche Hannover introduces "marriage for everyone"