Military area command
Military area commands (WBK) were the command authorities of the Bundeswehr .
The military area commands were set up in 1956 . Until 2001 they were part of the territorial army . By commanders run commands should organize territorial defense in their defensive area. In 2001 the territorial army was disbanded and the military area commands switched from the army to the armed forces base . There they mainly took on joint armed forces tasks in the area of command support and logistics .
The military area commands were dissolved on February 1, 2013. Her orders were then largely taken over by the Territorial Tasks Command of the Bundeswehr and the regional commandos .
history
Prehistory and development in the German Democratic Republic
Already during the Weimar Republic , the territory of the German Reich was divided into military districts with subordinate military substitute districts and military district commands. In addition, during the Second World War , the Reich territory was divided into "Reich Defense Districts" for civil defense with a Reich Defense Commissioner as leader . The replacement army largely organized training and replacement for the field army through the subordinate military district commands . The military district commands, however, had different functions in the Reichswehr and Wehrmacht than the military district commands of the Bundeswehr .
Two military districts emerged in the German Democratic Republic . In the southern part of the set up National People's Army (NVA) the Military District III , based in Leipzig and for the northern part of the Military District V , based in Neubrandenburg one. The military districts were higher command authorities of the land forces of the NVA . In addition to other units, they were subordinate to two motorized rifle divisions and one tank division .
Army structures 1 and 2 (until 1970)
With the establishment of the Bundeswehr, the establishment of a territorial defense organization began alongside the army . In 1956, the Federal Republic was divided into six defense areas, each of which included one or more states . 1956 began the establishment of "territorial command staffs" for one military area each, which were renamed in 1957 in "military area command". Until 1969 they were subordinate to the Territorial Defense Command , which, together with its subordinate departments , formed a separate division of the Bundeswehr alongside the Navy , Air Force and Army .
organization
The following military area commands were set up in 1956:
-
 Military District Command I in Kiel
Military District Command I in Kiel
-
 Military District Command II in Hanover
Military District Command II in Hanover
-
 Military District Command III in Düsseldorf
Military District Command III in Düsseldorf
-
 Military District Command IV in Mainz
Military District Command IV in Mainz
-
 Military District Command V in Stuttgart
Military District Command V in Stuttgart
-
 Military District Command VI in Munich
Military District Command VI in Munich
In 1958, the establishment of “ VP-TV rods ” began. The territorial defense staff were subordinate to the military area commands and, analogous to the civil administrative structure, comprised a country or, in larger countries, an administrative district . The TV staffs were renamed Defense District Commands (VBK) in 1963 . The Defense District Commands were further subdivided into Defense District Commands (VKK) at the district level .
The defense district and defense district commands had their own non-active units such as fighter regiments , telecommunication companies , supply and transport companies, and armor groups . The defense district commands were subordinate to non-active homeland security companies and security trains for tasks of property security . Their number depended on the number and size of the objects to be secured. The infantry units formed the core of the " Territorial Reserve " planned from 1961 , which from 1965 was referred to as the " Homeland Security Force ".
In contrast to units in the field army, the military area commands consisted to a large extent of inactive units , which should grow up quickly in the event of a defense by reservists . The troop units and military departments subordinate to the military area commands could be roughly classified according to their degree of presence as follows:
- Active units: already fully deployed in peacetime. Their material was completely available. Most of the staff were available and were supplemented with individual reservists in the event of tension or defense (staff mob supplementation)
- Partially active units: in times of peace, individual units were fully present. Other sub-units were not active. The active units were partly subordinate to other units during peacetime.
- Non-active units: in peacetime the units consisted only of cadre personnel . Often the squad consisted only of the Mob - Sergeant , who prepared the mobilization, and two to three civilian employees for maintenance of stored materiel. The actual staff consisted of scheduled reservists who only in tension or defense convened would have been. The defense material was partly stored (mainly weapons and weapon systems ), other material such as B. civilian vehicles was also only planned and would have been called up as well (material mob supplement). Inactive units with stored material were also referred to as equipment units .
- A special form of non-active units were cadre units: the majority of the command cadre served in active units during peacetime (also known as " Couleur units "). Defense exercises were supported by these active units and often carried out with their material. In the event of a defense, the cadre staff would have taken over the command of the sub-units of the inactive unit.
assignment
Until 2002, when the " transformation of the Bundeswehr " began, the task of the military area commandos was
- maintaining the freedom of operation of the NATO armed forces (including the German ones),
- civil defense support .
In addition to the technical and troop service requirements for the management of the subordinate troops, the planning work required very precise knowledge of “the country and its people”. In the case of defense cooperation with operating in West Germany was Corps of the Central Army Group , Northern Army Group and LANDJUT provided.
This mandate included in detail:
- The military area command had to prepare all measures in peacetime and to take all appropriate measures in the event of tension or defense :
- to inform oneself about the situation of the civil defense, the military situation and the infrastructure situation and to inform the troops that are in the defense area, civil authorities or directly the population about the military situation and the measures and intentions of the enemy and about the effects of Warn ABC weapons ;
- certain objects, traffic routes and spaces
- to protect against impairment of their use by enemy action on land, in particular "sensitive points";
- to be made available and available for use, in particular military and civil infrastructure of military interest, or to be kept free by directing traffic and managing population movements;
- to block for unauthorized persons or enemies or to paralyze their function;
- to maintain and operate fixed telecommunications equipment;
- To set up and operate reserve hospitals and to protect troops from epidemics and poisoning;
- To replace Bundeswehr personnel in order to maintain the armed forces' freedom of operation.
- The military area command also had on request
- to support the armed forces by providing military forces or aids from the civilian sector, in particular services and material, in order to thereby
- restore the functionality of combat, command and control and supply systems and facilities, or
- to contribute to the supply of the troops ;
- to support the civil authorities in their measures for civil defense, in particular for the restoration of installations and facilities of military interest, in order to thereby
- the governance maintain,
- or to protect the population from enemy influence,
- or to ensure the supply of the population or the troops.
Army Structure 3 (1970 to 1980)
In 1969 the Territorial Defense Command was decommissioned. The tasks of territorial defense were taken over by the army and, in addition to the field army, were run as a separate section of the army under the designation " Territorial Army ". In 1969, the military area commands were subordinated to the newly established territorial commands Schleswig-Holstein , North and South .
The type and strength of the troops directly subordinate to the military area commands in addition to the defense district commands were different in Army Structure 3 and were based partly on geographical conditions (coast, important river crossings for supply roads ( Main Supply Road ) or rail transport lines ), partly on military necessities (proportion of the rear battle zone ( Rear combat zone ) in the area of the weir area commands and distance to the boundaries of the Eastern bloc ). Always they were in the course of the further establishment of the Bundeswehr Military Training Area commandants , military police forces , transportation and hospital associations assumed.
From 1972 a partially active homeland security command (HschKdo) was set up in each of the military area commandos . For the first time , the territorial army had units that were not structured in a purely infantry way , but were also equipped with armored combat vehicles.
The staff departments of the command areas G1 ( personnel / internal command ), G2 ( military intelligence ), G3 (management / organization / training) and G4 ( logistics ) as well as the departments belonged to the staff of a military area command
- Infrastructure / pioneering (military issues in the area of infrastructure with subordinate Wallmeister groups and troops)
- Traffic management (with traffic command offices in the government districts )
- Military geographic service (creation of the map material and the supply of all units of the Bundeswehr within the military area with maps)
- Telecommunications (planning and setting up of the stationary federal defense telecommunications systems and connections. For this purpose, telecommunications command offices at the headquarters of the Oberpostdirektion were subordinate to you ),
- Military motor vehicle (approval of Bundeswehr vehicles and implementation of the general inspection according to § 29 StVZO)
- Defense sector library.
Due to the intermediary function between the Bundeswehr and the civil administration on the one hand and Allied troops on the other hand, the G3 department included corresponding large liaison commands .
Army Structure 4 (1980 to 1992)

In 1982 the homeland security commands in Army Structure 4 were reclassified into six partially active homeland security brigades. Six newly established inactive homeland security brigades supplemented the partially active homeland security brigades. The homeland security brigades were directly subordinate to the military area commands. The Homeland Security Brigades 51 and 56 were assigned to the field army soon after the formation .
From 1985 support commands (Ukdo) were set up with the United States under the Wartime Host Nation Support Agreement . Some of them were subordinate to the military area commands and mainly served to support the mobilization of American forces in Europe.
After reunification , the territorial structures known from West Germany were created in the new federal states in October 1990. The commands of Military Districts III in Leipzig and V in Neubrandenburg that existed when the National People's Army was taken over on October 3, 1990, were reclassified as of December 1, 1990 into the following military area commands subordinate to the newly planned East German Territorial Command:
-
 Military District Command VII with the seat of the rod in Leipzig
Military District Command VII with the seat of the rod in Leipzig
-
 Military area command VIII with headquarters in Neubrandenburg
Military area command VIII with headquarters in Neubrandenburg
On July 1, 1991, the military area commands were merged with the staffs of the divisions to be set up in East Germany in anticipation of the upcoming army structure and renamed " Division / Military Area Command VII" and " Division / Military Area Command VIII".
Army structure 5 (from 1992) and further development
As part of Army Structure 5 (N) (1993–1997), the military area commands were dissolved as independent command authorities and their staffs were merged with existing divisional staffs . The merged associations were given the following names:
| Previous military area command | previous division | new name |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Military area command I / 6th Panzer Grenadier Division |
|
|
|
Military area command II / 1st PzDiv |
|
|
|
Military area command III / 7th Panzer Division |
|
|
|
Military area command IV / 5th Panzer Division |
|
|
|
Military area command V / 10th Panzer Division |
|
|
|
Military District Command VI / 1st Mountain Division |
|
|
Military area command VII / 13th Panzer Grenadier Division | |
|
|
Military area command VIII / 14th Panzer Grenadier Division |
The weir areas remained unchanged in their layout. Only the seat of the "Wehrbereichskommando V / 10th Panzer Division" was not in the state capital Stuttgart, but in Sigmaringen . The territorial commands were decommissioned in 1994. The merged formations were subordinated to the German corps and thus indirectly to the newly established Army Command .
Most of the inactive units and units of the previous military area commands were dissolved, some of which were expressly identified as so-called "WBK-share" within the division. The new staffs were given an additional “Deputy Division Commander and Commander WBK Troops” (renamed “Deputy Commander and General National Territorial Affairs” from 1996 ). In the event of a tension , the staff of the military area commandos would have been divided into a mobile division staff subordinate to NATO and a national military area command staff that remained at the location. The troops would have been assigned accordingly.
The structure of the 10th Jägerregiment " Linzgau " of the "Wehrbereichskommando V / 10th Panzer Division" can be considered as an example: In peace all four battalions were subordinate to the regiment . The active Jägerbataillon 101, the semi-active Jägerbataillon 102 and the non-active backup battalion 108 (provided for securing the Divisions - command posts ) would have been at the 10th tank division. The inactive Jäger Battalion 852 would have been subordinate to the Defense District Command V.
On October 1, 1997, the "Military District Command VIII / 14th Panzer Grenadier Division" was separated. The 14th Panzer Grenadier Division continued to exist as an independent division . Military District Command VIII was disbanded on October 1, 1997 - earlier than all other Military District Command. The organization of the territorial defense in the disbanded military area was transferred to the military area commands I and VII.
Change to the armed forces base and reorganization (2001 to 2006)
As part of the reclassification to the “completely renewed Bundeswehr” in 2001, the territorial army was dissolved and the remaining national structures and tasks were incorporated into the newly created organizational area of the Armed Forces Base. Responsibility for “National Territorial Tasks” changed on October 1, 2001 from the Army Command to the new Armed Forces Support Command , and the new “National Territorial Commander” became the Commander of the Armed Forces Support Command. At the same time, the "military area commands / divisions" were defused and the number of military areas and military area commands reduced from seven to four. The four military area commands were subordinated to the armed forces support command. Individual defense district commands and the still existing non-active units of the military area commands were disbanded.
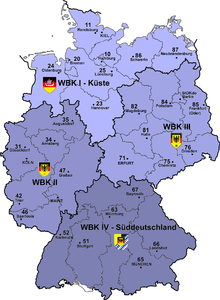
The four new defense areas included the states :
- Defense Area I with Defense Area Command I "Coast" : Bremen , Hamburg , Lower Saxony , Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania and Schleswig-Holstein ,
- Defense area II with defense area command II : Hesse , North Rhine-Westphalia , Rhineland-Palatinate and Saarland ,
- Defense area III with Defense Area Command III : Berlin , Brandenburg , Saxony , Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia ,
- Military area IV with military area command IV "Southern Germany" : Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg .
Since the remaining defense district commands kept their old numbers (the first digit indicated that they belonged to the original military area command), the reorganization was understandable with their assignment to the new military area commands.
List of state commandos and priority formation (2006 to 2013)
assignment
A military area command was responsible for performing territorial military tasks and worked within the military area with the units of the armed forces stationed there (since 2000 also with the Central Medical Service of the Federal Armed Forces ), the departments of the Federal Armed Forces administration , the medium-sized federal authorities and the respective state authorities.
The order in detail included
- ensuring the forces common base operation,
- the support of the armed forces / organizational units in Germany and during missions abroad ,
- the technical and troop management of the subordinate troops,
- the organization of internal aid operations by the Bundeswehr in accordance with Article 35 of the Basic Law ( ZMZ Inland ).
organization
With the dissolution of the Defense District Command (VBK) and the simultaneous establishment of the State Command (LKdo) in 2007, the Defense District Commands essentially adopted their target structure in 2010 as part of the “ Transformation of the Bundeswehr ”. Staff seats and command areas of the military area commands remained unchanged. Following for one country competent state commands were set up:
- Military area command I “Coast” (headquarters in Kiel ) with the state commands of Bremen , Hamburg , Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania , Lower Saxony and Schleswig-Holstein
- Military area command II ( Mainz ) with the state commandos of Hesse , North Rhine-Westphalia , Rhineland-Palatinate and Saarland .
- Military area command III ( Erfurt ) with the state commands of Brandenburg , Saxony , Saxony-Anhalt , Thuringia and the Berlin site command corresponding to a state command
- Military area command IV “Southern Germany” ( Munich ) with the state commandos of Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg
In the countries in which the four military area commands were stationed, the state commands were integrated into the military area commands. The military area commands were subordinate to the state commands for the formation of focal points and various other units and departments. The focus of the military area commands I “Coast” and IV “Southern Germany” was logistics . Military area commands III and IV focused on command support .
In accordance with the political structures of the federal states, the state commandos led 34 district liaison commands (BVK) as liaison commands to the district governments / regional councils and 429 district liaison commands (KVK) as liaison commands to the districts . The district liaison commandos and district liaison commands consisted exclusively of reservists .
Dissolution (2013)
As part of the realignment of the Bundeswehr , the military area commands were dissolved on February 1, 2013. Their tasks were essentially taken over by the Territorial Tasks Command of the Bundeswehr in Berlin and the subordinate state commands .
literature
- Rolf Clement, Paul Elmar Jöris : 50 years of the Bundeswehr . Mittler & Sohn, Hamburg, Berlin, Nonn 2005, ISBN 3-8132-0839-7 .
- Military area command V (Ed.): Military area command V, years 1956–1966 .
- Ferdinand von Senger and Etterlin : The military area command . In: Yearbook of the Army . No. 4 , 1973, ISSN 0075-2282 , pp. 109-115 .
- OW Dragoons: The Bundeswehr 1989 . Territorial Command SCHLESWIG-HOLSTEIN. Territorial Command NORTH. Territorial Command SOUTH. Appendix: Territorial structure. 4th edition. 2.2 - Army, February 2012 ( religte.com [PDF; accessed July 10, 2018]).
Web links
- Jürgen Dreifke: 50 years of the Bundeswehr in the Münsterland. The territorial army. In: Bundeswehr in Dülmen . Retrieved July 14, 2018 .
- Homeland Security Commandos / Homeland Security Brigades. BArch, BH 33. In: invenio. Federal Archives, accessed on July 14, 2018 .
- Territorial Command Schleswig-Holstein / German Authorized Area AFNORTH. BArch, BH 27. In: invenio. Federal Archives, 2004, accessed on July 14, 2018 .
- Military area command I / 6. Panzergrenadier Division. BArch, BH 40-1. In: invenio. Federal Archives, 2004, accessed on July 14, 2018 .
- Military District Command II. BArch, BH 28-2. In: invenio. Federal Archives, accessed on July 14, 2018 .
- Military District Command II / 1. Armored Division. BArch, BH 40-2. In: invenio. Federal Archives, 2004, accessed on July 14, 2018 .
- Military District Command III. BArch, BH 28-3. In: invenio. Federal Archives, accessed on July 14, 2018 .
- Military area command III / 7. Armored Division. BArch, BH 40-3. In: invenio. Federal Archives, 2004, accessed on July 14, 2018 .
- Military area command IV. BArch, BH 28-4. In: invenio. Federal Archives, accessed on July 14, 2018 .
- Military area command IV / 5. Armored Division. BArch, BH 40-4. In: invenio. Federal Archives, 2004, accessed on July 14, 2018 .
- Military area command V. BArch, BH 28-5. In: invenio. Federal Archives, 2004, accessed on July 14, 2018 .
- Military area command V / 10. Armored Division. BArch, BH 40-5. In: invenio. Federal Archives, 2004, accessed on July 14, 2018 .
- Military District Command VI. BArch, BH 28-6. In: invenio. Federal Archives, 2004, accessed on July 14, 2018 .
- Military District Command VI / 1. Mountain Division. BArch, BH 40-6. In: invenio. Federal Archives, 2004, accessed on July 14, 2018 .
- Corps and Territorial Command East / IV. Corps. BArch BH 7-4. In: invenio. Federal Archives, 2004, accessed on July 14, 2018 .
- Military area command VII / 13. Panzergrenadier Division. BArch, BH 40-7. In: invenio. Federal Archives, 2004, accessed on July 14, 2018 .
- Corps and Territorial Command East / IV. Corps. BArch BH 7-4. In: invenio. Federal Archives, 2004, accessed on July 14, 2018 .
- Military District Command VIII / 14. Panzergrenadier Division. BArch, BH 40-8. In: invenio. Federal Archives, 2004, accessed on July 14, 2018 .
- Defense area command I - Coast - (Kiel). BArch, BW 68-1. In: invenio. Federal Archives, 2004, accessed on July 14, 2018 (inventory information on all four SKB WBK).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Sebastian Wanninger, Sina Pawlowski: Second level reached. streitkraeftebasis.de, February 4, 2013, archived from the original on March 4, 2016 ; accessed on June 10, 2016 .
- ↑ Ferdinand von Senger and Etterlin : The military area command . In: Yearbook of the Army . No. 4 , 1973, ISSN 0075-2282 , pp. 109-115 .
- ↑ "(N)" for "(readjustment)"
- ↑ Agreement on civil-military cooperation in the state of Brandenburg ( Memento from January 5, 2013 in the web archive archive.today )
- ^ Government declaration by the Defense Minister, 97th session of the Bundestag 15th period, Item 3, on March 11, 2004 ( Memento of May 10, 2005 in the Internet Archive )