North Dakota
| North Dakota | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
| List of states | |||||
| Capital: | Bismarck | ||||
| State motto: | Liberty and Union, now and forever, one and inseparable Freedom and unity, now and forever, one and inseparable | ||||
| Official language : | English | ||||
| Surface: | 183,112 km² | ||||
| Residents: | 672,591 (2010 Census) | ||||
| Member since: | November 2, 1889 | ||||
| Time zone: | Central: UTC − 6 / −5 Mountain: UTC − 7 / −6 |
||||
| The highest point: | 1,069 m (White Butte) | ||||
| Average Height: | 580 m | ||||
| Deepest point: | 229 m Red River of the North | ||||
| Governor : | Doug Burgum ( R ) | ||||
| Post / Office / ISO | ND / / US-ND | ||||
| Map of North Dakota | |||||
| North Dakota geographic map | |||||
North Dakota ( English [ ˌnɔɹθ dəˈkʰoʊ̯ɾə ] , German North Dakota ) is a federal state of the United States in the north of the United States on the Canadian border. North Dakota is 183,112 km² and has a population of over 750,000 (89% white, 5% Native, 3% Hispanic, 2% black and 1% other). The capital is Bismarck . The climate is cool and temperate.
North Dakota became the 39th state to join the union after the division of Dakota Territory in 1889. North Dakota is nicknamed Peace Garden State ( Peace Garden State ), named after the International Peace Garden on the border with Canada near Dunseith , and Sioux State . The name Dakota is derived from the Indian ethnic group of the Dakota who lived in this area before the submission by the Americans and still lives here today.
geography
Geographical location
To the west are the hilly Great Plains and Badlands . In this area are the White Butte , the highest point in the state, and Theodore Roosevelt National Park . The Missouri River flows through western North Dakota and forms Lake Sakakawea , the third largest man-made lake in the United States , along with the Garrison Dam .
Central Dakota is home to the Drift Prairie and the Missouri Plateau . Lakes, river valleys and gently rolling hills characterize the region. The Turtle Mountains are located in the Drift Prairie near the Canadian border . The geographic center of North America is near the city of Rugby .
To the east is the flat Red River Valley that forms the curving Red River of the North . Like the other rivers in this part of the state, the Red River flows north. At the end of the last Ice Age, the river fed along with others to Lake Agassiz . Today the land around the river is very fertile, which has led to the settlement of many farms and small towns. To the east is Devil's Lake , the largest natural lake in the state.
The White Butte is the highest point in North Dakota at 1,069 meters. It is a prominent elevation in the Badlands of Slope County, in the SW of the state - about 11 km northwest of Amidon. The summit is on private property in Little Missouri National Grassland .
The second highest peak in North Dakota is the Sentinel Butte at 1,045 m near the border with Montana in Golden Valley County, from which the town of the same name takes its name 5 km to the north. The name of the mountain goes back to the killing of two Arikaree guards who were allegedly attacked near the Sioux in 1864.
Neighbore states
North Dakota is bordered to the north by the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba , to the west by Montana , to the south by South Dakota and to the east, across from the Red River of the North and the Bois de Sioux River , by Minnesota .
geology
In the west are some natural resources such as oil and lignite .
climate
The North Dakota climate is a typical example of a continental climate ; the state is far from large bodies of water that could temper the climate. That is why it ranges from oppressively hot and dry summers to bitterly cold winters. Warm air masses from the Gulf of Mexico and cold air masses from the polar regions often create strong winds.
In summer, the meeting of arctic and tropical systems leads to sometimes violent thunderstorms for 20 to 40 days . Tornadoes are not uncommon and mostly occur in the southeastern quarter of the state. In winter the weather tends to be more stable: cold and dry, with occasional snowfall. Even so, the constant wind can cause snowstorms at any time in winter. Heavy snowstorms occur in late winter and early spring.
Spring floods are widespread in the very shallow Red River Valley. In 1997, severe flooding in eastern North Dakota submerged large parts of the Red River Valley and caused great damage in the city of Grand Forks .
population
| Ancestry of the population of North Dakota | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| origin | percent | |||
| German | 41.2% | |||
| Norwegian | 25.2% | |||
| Irish | 7.2% | |||
| English people | 4.5% | |||
| Sweden | 4.2% | |||
| Other | 17.8% | |||
| Origin according to the American Community Survey 2014 | ||||
North Dakota ranks 48th out of 50 states in terms of population. Only Vermont and Wyoming have fewer residents.
People with German ancestors are common all over the state, but especially in the south and the center. Scandinavians are also everywhere. Some counties have large Indian communities (mostly on reservations). North Dakota has the highest percentage of a Russian-German population of all US states. Approx. 20% of all residents of this state can trace their roots back to this. The south (e.g. McIntosh County , LaMoure County , and Emmons County ) was populated almost exclusively by these. Places like Kulm or Strasburg point to the original settlements of the founders in southern Russia, mainly from Bessarabia .
6.9% of the population are under 5 years old, 22.8% are under 18 and 14.2% are 65 or older. The proportion of women in the total population is around 48.7%.
Population development
| Population development | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Residents | ± in% | |
| 1870 | 2405 | - | |
| 1880 | 36,909 | 1,434.7% | |
| 1890 | 190.983 | 417.4% | |
| 1900 | 319.146 | 67.1% | |
| 1910 | 577.056 | 80.8% | |
| 1920 | 646.872 | 12.1% | |
| 1930 | 680.845 | 5.3% | |
| 1940 | 641.935 | -5.7% | |
| 1950 | 619.636 | -3.5% | |
| 1960 | 632.446 | 2.1% | |
| 1970 | 617.761 | -2.3% | |
| 1980 | 652.717 | 5.7% | |
| 1990 | 638,800 | -2.1% | |
| 2000 | 642.200 | 0.5% | |
| 2010 | 672.591 | 4.7% | |
| Before 1900
1900-1990 2000 |
|||
In 2005 the updated population was 636,677, which corresponds to an increase of 369 inhabitants or 0.1% compared to the previous year and a decrease of 5,527 inhabitants or 0.9% compared to 2000. The natural growth compared to the census in 2000 was 10,283 people (40,890 live births, 30,607 deaths). The immigration deficit was 14,881, with 3,687 moving from outside the United States and 18,568 moving domestically.
Since the 1980s, North Dakota has seen a steady population decline due to emigration . Younger people with a university degree in particular left the state. One aspect of the problem is the lack of graduate jobs. The development of economic development programs to provide quality and high-tech jobs has been proposed, but the usefulness of such programs is under debate.
However, the trend changed with the energy boom due to the development of previously inaccessible deposits of oil and natural gas through fracking . Since the turn of the millennium and increasingly after 2010, there has been an economic upswing in the state that has drawn a large number of workers to the assisted areas.
languages
English is the mother tongue of more than 95% of the population.
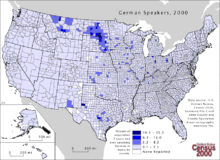
North Dakota has a significant proportion of German speakers. In 2000, German was spoken by 14,931 people in the household, which corresponds to around 2% of the population. In the sparsely populated Counties Logan and McIntosh , over 16% are German-speaking.
There are also speakers of Spanish, Norwegian and indigenous languages.
Religions
The majority of the population is made up of Christians. North Dakota has the lowest proportion of non-denominational people (including atheists) of all states and at the same time the highest church density per inhabitant.
-
Christian : 86%
-
Protestants : 52%
- Lutherans : 35% (especially Evangelical Lutheran Church in America with 174,554 members)
- Methodists : 7%
- Baptists : 6%
- Pentecost Movement : 3%
- Jehovah's Witnesses : 1%
- Catholics : 30%
- Mormons : 1%
- Other Christians: 2%
-
Protestants : 52%
- Buddhists : 1%
- Others: 1%
- Non-denominational: 3%
- No answer: 6%
Biggest cities

The population development in these cities contrasts with that in the countryside. Most of the larger cities grew, due to rural exodus , in the period from 1990 to 2000.
history

Since at least 2000 BC Chr. People live as hunters and gatherers and sedentary farmers in North Dakota. When the first Europeans arrived in the region, several different groups of Native Americans lived there . The Dakota / Sioux , Assiniboine and Cheyenne were nomads and mainly hunted bison herds . This way of life only became possible when riding horses were available in the 18th century . Around 1800 some Chippewa groups also moved to the Red River Valley in eastern South Dakota. Other native American groups such as the Mandan , the Hidatsa , and the Arikara lived mainly from agriculture and trade and only hunted occasionally. Their fortified settlements on the Missouri River became centers of the fur trade in the 18th and 19th centuries .

The first European to reach the area was the French Canadian La Vérendrye , who led an expedition to the Mandan villages around 1738. The inter-tribal trade was arranged so that the tribes of North Dakotas rarely traded directly with the Europeans. Even so, at the time of the Lewis and Clark expedition , the tribes maintained sufficient contact with the Europeans through the fur trade to be aware of the French and Spanish claims to their territory. In 1837/38 an epidemic of smallpox broke out in the villages on the Missouri River , of which around 90% of the native people died.
The Dakota Territory was sparsely populated until the late 19th century, when railways were rapidly being built and the land was being sold on a large scale . A law of February 22, 1889 under the presidency of Grover Cleveland cleared the way to the state for North and South Dakota as well as for Montana and Washington . With the signature of his successor Benjamin Harrison , the admission took place on November 2, 1889. The dispute between the two new states over which of them should be admitted first posed a problem. Harrison instructed Secretary of State James G. Blaine to shuffle the papers and thereby hide the order of the signatures. However, since "North Dakota" is in the alphabet before "South Dakota", North Dakota was first included in the Law Gazette, making it the 39th state before South Dakota.
The territorial governments as well as the first state governments were considered to be very corrupt. In the early 20th century, the strong influence of the Nonpartisan League led to social reforms. The Great Depression hit North Dakota very hard and was the farm crisis intensified in the 1920s. The original North Dakota Capitol burned down in the 1930s. It was replaced by an Art Deco “skyscraper” with a limestone facade that is still standing today.
In the 1950s, the federal government carried out several major construction projects in North Dakota. These included the Garrison Dam and air force bases at Minot and Grand Forks . As oil prices soared and production became profitable, an oil boom began in the Williston Basin in the 1980s. As a result, the population grew to its highest level of almost 700,000 inhabitants. Today the population is around 640,000; this corresponds to the status of the 1920s.
Seven sites in the state have the status of a National Historic Landmark due to their historical significance .
Constitution, politics
State law is based on the Constitution of North Dakota . Changes to the constitution are subject to a referendum . In 1914 the instrument of the constitutional initiative was introduced, so that constitutional amendments can also be introduced through the popular initiative .
legislative branch
Legislation rests with Parliament, the North Dakota Legislative Assembly , which consists of two chambers: the Senate and the House of Representatives . The state is divided into 47 constituencies (legislative districts), each of which elects a senator and two members of the House of Representatives. The senators are elected every four years and the members of the House of Representatives every two years.
executive
The executive power lies with the governor , who is elected by the people every four years. This appoints and dismisses the ministers.
Judiciary
At the lowest court level, there are community and district courts over which the North Dakota Court of Appeals is superordinate. The state's highest court is the North Dakota Supreme Court.
Administrative division
North Country is divided into 53 counties. There are also five autonomous Indian reservations .
Federal level
North Dakota, like its southern neighbor and Montana to the west, is a conservative state, which, however, is dependent on legislative aid for agriculture. This constellation leads to a preference for Republicans , most recently Donald Trump , for the presidency. Overall, the Republicans have won every presidential election since 1948. However, in recent years this has often been countered by an open-minded attitude towards the Democratic candidates for Congress . US Senators for North Dakota are Republican John Hoeven and Republican Kevin Cramer , who won the November 2018 election against Democratic incumbent Heidi Heitkamp ; Republican Kelly Armstrong represents the state in the House of Representatives .
Presidential election
| year | republican | Democrats |
|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 62.96% 216,794 | 27.23% 93,758 |
| 2012 | 58.32% 188,163 | 38.69% 124,827 |
| 2008 | 53.15% 168,887 | 44.50% 141,403 |
| 2004 | 62.86% 196,651 | 35.50% 111,052 |
| 2000 | 60.66% 174,852 | 33.05% 95,284 |
| 1996 | 46.94% 125,050 | 40.13% 106,905 |
| 1992 | 44.22% 136,244 | 32.18% 99,168 |
| 1988 | 56.03% 166,559 | 42.97% 127,739 |
| 1984 | 64.84% 200,336 | 33.80% 104,429 |
| 1980 | 64.23% 193,695 | 26.26% 79,189 |
| 1976 | 51.66% 153,470 | 45.80% 136,078 |
| 1972 | 62.07% 174,109 | 35.79% 100,384 |
| 1968 | 55.94% 138,669 | 38.23% 94,769 |
| 1964 | 57.97% 149,784 | 41.88% 108,207 |
| 1960 | 55.42% 154,310 | 44.52% 123,963 |
Congress elections
- List of members of the US House of Representatives from North Dakota
- List of US Senators from North Dakota
education
North Dakota's premier universities are the University of North Dakota (UND) in Grand Forks and North Dakota State University (NDSU) in Fargo . In addition to several public and private universities and colleges, there are also five colleges that are particularly dedicated to the education of indigenous people.
military
In the north of the state, 150 Minuteman nuclear ICBMs of the 91st Missile Wing of the US Air Force are stationed and are in constant readiness. The headquarters are at Minot Air Force Base .
Culture and sights
literature
An important writer whose works are based in North Dakota is Louise Erdrich .
Museums
- Bonanzaville, United States, West Fargo
- Dakota Dinosaur Museum, Dickinson
- North Dakota Heritage Center, Bismarck
- Fargo Air Museum, Fargo
- North Dakota Museum of Art, Grand Forks
- Plains Art Museum , Fargo
- Roger Maris Museum, Fargo
- North Dakota Lewis & Clark Interpretive Center, Washburn
- Knife River Indian Villages National Historic Site , Stanton
Parks
In the north of North Dakota there is the " International Peace Garden " , which is being transferred to Canadian territory . This landscape garden gave the state its nickname Peace Garden State .
National parks
| National park | location | view |
|---|---|---|
Theodore Roosevelt National Park
|

|
State parks
There are 18 state parks in North Dakota that are administered by the North Dakota Parks & Recreation Department.
Economy and Infrastructure

The real gross domestic product per capita (per capita real GDP) was USD 68,723 in 2016 (national average of the 50 US states: USD 57,118; national ranking: 5). Although less than 10% of the population is employed in agriculture, it continues to play an important role. Important products are cereals, potatoes and flax. North Dakota is the largest producer of barley, sunflower seeds, wheat, and durum wheat in the United States. Cattle and turkey farming are important.
The unemployment rate was 2.2% in March 2020 (US average: 4.4%). North Dakota had the lowest unemployment rate of any state in the country.
raw materials
Oil and gas production has been gaining in importance since oil was discovered at Tioga in 1951 , while lignite mining has declined. Technical progress and the increased oil price have led to an “oil boom” in the region, which has large deposits of tight oil (“fracking oil”). These are now increasingly exploited, currently in the Bakken formation . In March 2012, North Dakota produced 17.9 million barrels of crude oil, so North Dakota overtook Alaska (17.5 million barrels) for the first time and was the second largest oil producer in the USA after Texas. In October 2012, 23.2 million barrels were produced, more than 11% of the total US production of 206.7 million barrels in October 2012.
North Dakota has great potential for generating wind power in the Great Plains, which has been increasingly used since 2008. Before 2008, there was hardly any significant wind power generation, but by 2010 wind power generation rose sharply to 5,236 million kWh, which corresponds to just over 4 percent of total US wind power generation.
traffic
Streets
The main east-west routes are US 2 and Interstate 94 . The state highways 5 and 200 are also significant east-west routes. The major north-south trunk roads are Interstate 29 , US 81 , US 281 , US 83 , and US 85 .
The US 52 runs northwest to southeast from Portal to Jamestown and then together with I-94 to Fargo . The US 12 runs through the extreme southwest of the state and crosses the US 85 in Bowman to Denver and El Paso (Texas) .
railroad
The BNSF Railway and the Canadian Pacific Railway (CP) maintain the most extensive route network in North Dakota. Regional companies are the Dakota, Missouri Valley and Western Railroad (DMVW) and the Red River Valley and Western Railroad (RRVW), which mostly operate on leased branch lines of the BNSF and the CP, which should be closed.
The railway companies that operate in North Dakota include two others in addition to these:
- Dakota Northern Railroad (DN)
- Northern Plains Railroad (NPR)
Former railway companies on the territory of the state were:
- Burlington Northern Railroad (BN)
- Chicago and North Western Railway (CNW)
- Great Northern Railway (GN)
- Milwaukee Road (MILW)
- Midland Continental Railroad
- Northern Pacific Railway (NP)
- Soo Line (SOO)
air traffic
North Dakota has 90 public airports. Bismarck, Devils Lake, Dickinson, Fargo, Grand Forks, Jamestown, Minot and Williston are served by regular services.
Other infrastructure
The KVLY TV mast is located in Fargo , a television broadcast mast with a height of 628.8 meters and thus the fourth tallest structure in the world (as of 2019).
literature
- Robert P. Wilkins, Wynona H. Wilkins: North Dakota: A History. WW Norton and Company, New York 1977, ISBN 978-0-393-24379-6 .
Web links
- Official website of the state of North Dakota. Accessed April 27, 2019 .
Individual evidence
- ^ Density Using Land Area
- ↑ Excerpt from quickfacts.census.gov/ | Population, 2015 estimate .
- ^ North Dakota - Selected Social Characteristics
- ^ US Census Bureau _ Census of Population and Housing . Retrieved February 28, 2011
- ↑ Extract from Census.gov . Retrieved February 28, 2011
- ↑ Excerpt from factfinder.census.gov.Retrieved February 28, 2011
- ↑ US Census 2000
- ^ The Association of Religion Data Archives | Maps & Reports
- ^ First People - Summary of North Dakota History. In: State Historical Society of North Dakota. Retrieved July 20, 2020 .
- ↑ List of NHL by State . National Park Service , accessed October 31, 2018.
- ^ Constitution of North Dakota
- ↑ North Dakota Presidential Race Results: Donald J. Trump Wins. In: nytimes.com. December 13, 2016, accessed June 28, 2017 .
- ^ David Leip: Dave Leip's Atlas of US Presidential Elections. Retrieved November 28, 2018 .
- ^ US Department of Commerce, BEA, Bureau of Economic Analysis: Bureau of Economic Analysis. Retrieved August 27, 2017 (American English).
- ^ US Census Bureau Profile of Selected Economic Characteristics: Data Set: Census 2000 Summary File 3 (SF 3) - Sample Data Geographic Area: North Dakota
- ↑ United States Department of Agriculture: National Agriculture Statistics Service
- ^ Unemployment Rates for States. Retrieved May 18, 2020 .
- ↑ ND becomes nation's second-leading oil producer. Retrieved December 11, 2012 .
- ↑ EIA: North Dakota Oil Production (English)
- ^ US Department of Energy Electricity Generation from Renewable Energy in North Dakota
Coordinates: 47 ° 26 ′ N , 100 ° 20 ′ W