Kent
| Kent county | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Country | United Kingdom | ||
| Part of the country | England | ||
| region | South East England | ||
|
|
|||
| status | Ceremonial and Administrative County | ||
| First mention | Antiquity (as Cantia or Canticum ) | ||
|
|
|||
| Ceremonial county | |||
| surface | 3,736 km² | ||
| Residents | 1,846,478 | ||
| was standing | June 30, 2018 | ||
|
|
|||
| Administrative county | |||
| Administrative authority | Kent County Council | ||
| Administrative headquarters | Maidstone | ||
| ISO-3166-2 | GB-KEN | ||
| surface | 3,544 km² | ||
| Residents | 1,568,623 | ||
| was standing | June 30, 2018 | ||
| ONS code | 29 | ||
| GSS code | E10000016 | ||
| NUTS code | UKJ43 to UKJ46 | ||
| Website | www.kent.gov.uk | ||
|
|
|||
Districts / Unitary Authorities
|
|||
Kent is a traditional county in south east England . It borders on East Sussex , Surrey and Greater London and across the Thames estuary to the county of Essex . Kent is connected to France by the Eurotunnel . The county’s capital is Maidstone .
On a clear day, it is possible to see from the white cliffs of Dover all the way to France. Because of its large number of orchards and hop fields, Kent is also known as the "Garden of England". This designation is now also claimed by other counties in England.
In the northwest there are industrial areas with factories for cement, paper and aircraft. In the south and east, agriculture and tourism are the main sources of income.
Kent's location between London and the European continent meant that it was particularly hard hit during the Battle of Britain during World War II . The east coast of Kent was then also known as the "Hell Fire Corner".
The county's ports provided warships for over 800 years. The Cinque Ports were in the 12-14 Century as well as the port of Chatham in the 16th – 20th centuries . Century of particular importance for the security of the country.
history

Archaeological finds in the quarries at Swanscombe show that ancestors of modern man lived in Kent as early as the Paleolithic. The so-called "Medway megaliths " were built in the Neolithic Age. Other important finds are the Ringlemere Gold Cup and the Roman villas in the Darent river valley .
The name Kent may come from the Brython word cantus , which means something like "edge" or "border", which means the eastern part of the coast. Julius Caesar mentioned 51 BC. The region of Cantium or "Land of the Cantiaci ".
During the Iron Age, the Regni or Regnenses tribe settled in the western part. In the 5th century AD the kingdom of Kent of the Jutes was established in the eastern part .
In 597 Pope Gregory I called Augustine of Canterbury to be the first Archbishop of Canterbury in what is now Kent. The year before, Augustine had been able to convert King Æthelberht to Christianity. The Diocese of Canterbury became England's first bishopric and continues to be the Christian center of the United Kingdom and the Anglican Church to this day .
In the 11th century the residents of Kent gave themselves the motto "Invicta" ("undefeated"), but this was refuted by the subsequent invasion of England in 1066 by William the Conqueror . The residents resisted for a long time, which led to Kent becoming a semi-autonomous palatinate county in 1067 . Wilhelm's half-brother Odo von Bayeux was made ruler of the county, it was treated in the same way as the border regions with Wales and Scotland .
During the Middle Ages and the early modern period, Kent played a major role in various uprisings, notably the Peasants' Revolt of 1381 led by Wat Tyler , Jack Cade's Kent Revolt of 1450, and Thomas Wyatt's 1553 revolt against Queen Mary I. The Royal Navy first used the Medway in 1547 and rented a warehouse at Jyllingham Water . Under Elizabeth I (1558–1603) a small shipyard was built in Chatham . By 1618 further warehouses, a towpath , a dry dock and houses for administrators were built downstream .
Because of the tensions between Great Britain, the Netherlands and France in the 17th century, Kent was increasingly armed with military forces. Several forts were built along the coast following the raid in the Medway , a Dutch attack on the ports in the Medway. The 18th century was dominated by the wars with France. During this time the Medway became the main base for the fleet operating on the Dutch and French coasts. As the clashes shifted more and more into the Atlantic, the ports of Portsmouth and Plymouth took over this task. Chatham was mainly used as a shipyard for repairs and new builds during this period. In times of peace, the yard's workforce was significantly reduced. Also indicative of the county’s military importance is that the first British General Staff map from 1801 was a map of Kent.
At the beginning of the 19th century, the Kent coast was popular with smugglers. Gangs like the "Aldington Gang" brought liquor, tobacco and salt to England and in return transported goods across the English Channel to France. In 1899 the County of London was founded and the former Kent parishes of Deptford , Greenwich , Woolwich , Lee , Eltham , Charlton , Kidbrooke and Lewisham were incorporated there. For this, Penge was incorporated in Kent in 1900.
During World War II, much of the Battle of Britain was fought in the skies over Kent. Between June 1944 and March 1945, about 10,000 flying bombs of the V1 type (called "doodlebugs") were fired from bases in northern France on London. Many of them were destroyed by airplanes, anti-aircraft guns and barrage balloons , but around 2500 of these bombs hit London and Kent.
After the war the borders of Kent were changed several times. In 1965, the Bromley and Bexley counties were reorganized from nine parishes that had previously been Kent.
geography
Kent is in the extreme south east of England. It is bounded to the north by the Thames and the North Sea and to the south by the Strait of Dover and the English Channel . France is within sight, twenty miles away, across the Strait of Dover.
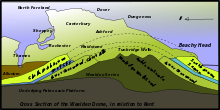
One of the most striking geographic features are the valleys and ranges of hills that run through the landscape in an east-west direction. These are geological remnants of the Wealdsattel , which stretches from eastern France to Sussex and was formed by the earth's movements 20 million years ago. This saddle consists of an upper layer of chalk that lies on top of various layers of green sand , clay, loam and red sandstone . The hills and valleys were formed when the erosion made the clay layers disappear before the rest of the rock.
Sevenoaks , Maidstone , Ashford and Folkestone were built on Greensand while Tunbridge Wells was built on Red sandstone. Dartford , Gravesend , the Medway towns, Sittingbourne , Faversham , Canterbury , Deal and Dover are written on chalk formations.
The eastern part of the Wealdsattel was eroded by the sea. Where the North Downs range of hills meets the coast, the famous chalk cliffs of Dover formed .
The weald is a Mesozoic structure that rests on a Paleozoic pedestal. This is the usual geological precondition for coal deposits. These can also be found occasionally between Deal, Canterbury and Dover at depths of 240 to 400 meters. However, mining would be made considerably more difficult by the high groundwater level. There are two coal fields, one of which extends under the English Channel.
Seismic activity has occasionally been noted in Kent, but its epicentres were off the coast. In 1382 and 1580 there were two earthquakes with a magnitude of 6.0 on the Richter scale . In the years 1776, 1950 and on April 28, 2007 earthquakes occurred with a magnitude of about 4.3. The 2007 earthquake caused damage in Folkestone.
The Kent coast is constantly changing due to tectonic pressures and coastal erosion. Until 960, the Isle of Thanet was an island separated from the mainland by the Wantsum Canal . The canal continued to silt up due to chalk deposits. It was similar in the Romney Marsh and Dungeness , which were also created by silt deposits.
The Medway is the county's largest river. It rises at East Grinstead in Sussex and flows east to Maidstone. There he turns north and crosses the North Downs at Rochester . Then it flows into the Thames at Sheerness . The river is about 112 kilometers long. The tidal range is noticeable in the river as far as the lock at Allington . In earlier times barges could even go as far as Tonbridge . The river forms the border between West Kent and East Kent. The residents of East Kent are called " Men / Maids of Kent " while the residents of West Kent are called " Kentish Men / Maids ".
Demographics
| 2001 census | Kent | South East England | England |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total population | 1,579,206 | 8,000,645 | 49.138.831 |
| Foreigners | 5.8% | 8.1% | 9.2% |
| white | 96.5% | 95.1% | 90.9% |
| Asians | 2.0% | 2.7% | 4.6% |
| Colored ones | 0.4% | 0.7% | 2.3% |
| Christians | 74.6% | 72.8% | 72% |
| Muslims | 0.6% | 1.4% | 3.1% |
| Sikh | 0.7% | 0.5% | 0.7% |
According to the 2001 census, Kent, including Medway, had 1,579,206 residents and 648,308 households. 48.9% of these households were married couples living together, 9% lived in a cohabiting relationship and 8.7% were unmarried parents. 28% of households were individuals, 14.6% were retirees living alone, and 30.4% had children under the age of 16 or adolescents between the ages of 16 and 18. For every 100 women there were 93.9 men.
94.2% of the population's birthplaces were in Great Britain, 0.7% in Ireland, 0.5% in Germany, 0.9% in the rest of Western Europe, 0.3% in Eastern Europe, 0.8% in Africa, 0 , 6% in the Middle and Far East, 0.9% in South Asia, 0.2% in the Middle East, 0.4% in North America, 0.1% in South America, and 0.3% in Oceania.
There were 74.6% Christians, 0.7% Sikhs , 0.6% Muslims , 0.4% Hindus , 0.2% Buddhists and 0.1% Jews . 15.2% said they had no religion, 0.3% had an alternative religion, and 7.8% did not want to state their religion.
government
The county council and its 12 district councils administer most of the county (3,352 km²), while the Medway Unitary Authority administers the densely populated areas (192 km²). The county council meets in Maidstone , while the Medway MPs meet in Strood and Gillingham . At the local level there are around 300 city and local councils.
Since the 2005 election, the Conservative Party has had a majority on the county council. It has 57 of the 84 seats. 21 are occupied by the Labor Party , 6 by the Liberal Democrats and 1 by an independent.
The Medway Council is also ruled by the Conservative Party. Here it occupies 33 of the 55 seats. The Labor Party has 13 seats, the Liberal Democrats eight seats and one seat is occupied by an independent.
Currently, all twelve county councils are also controlled by the Conservative Party, which is not the case in any other county.
Kent is represented by 17 MPs in the House of Commons in London . Ten are from the Conservative Party and seven are from the Labor Party.
Kent belongs to the European constituency of South East England, which has ten members in the European Parliament.
economy
According to the 2001 census, Kent, including Medway, had 41.1% full-time workers, 12.4% part-time workers, 9.1% self-employed, 2.9% unemployed, 2.3% employed students, 3.7% students without Work, 12.3% retirees, 7.3% housewives, 4.3% permanently ill or handicapped and 2.7% non-employed for other reasons.
In the age group 16–74, 16% had a higher education entrance qualification, compared with 20% in the national average.
The average working time was 43.1 hours for men and 30.9 hours for women.
The employees were employed in the following sectors: 17.3% in retail, 12.4% in manufacturing, 11.8% in real estate, 10.3% in healthcare, 8.9% in construction, 8.2% in transportation and logistics, 7.9% in education, 6.0% in public administration and defense, 5.6% in finance, 4.8% public services, 4.1% in hotels and restaurants, 1.6% in agriculture, 0.8% in energy and water supply, 0.2% as miners and 0.1% in private households. Employment rates in the construction industry and in transport and logistics are above average, but below average in the manufacturing industry.
Kent is often referred to as the "Garden of England" because it has many orchards and hop gardens. You can still see many malt houses in the landscape, but these days they have mostly been converted into residential houses. The closer you get to London, the more horticultural companies you will find.
In recent years, more and more farms in the county have disappeared, while industry and services have increased. North Kent is the industrial center of the county. Cement is produced in Northfleet and Cuxton , bricks in Sittingbourne, shipbuilding takes place on Medway and Swale , mechanical engineering and aircraft construction in Rochester. Chemicals are in Dartford, paper is in Swanley and the oil refineries are in Grain . There is also a steel mill for recycling scrap metal in Sheerness and a rolling mill in Queenborough . There are two nuclear power plants in Dungeness, one of which was shut down in 2006.
Cement, papermaking, and mining were important industries for the county as early as the 19th and 20th centuries. Cement production came to the fore in the 19th century when large settlements were built. It was advantageous that the limestone and chalk deposits could be mined in the immediate vicinity in the pits between Stone and Gravesend .
Kent's paper mills were originally on the Darent , a tributary of the Medway, and on the Stour . In the 18th century two more paper mills were built on Len and Loose near Tovil . In the late 19th century, huge new factories were built in Dartford and Northfleet on the Thames and in Kemsley on Swale . Since in pre-industrial times practically every place had its own paper mill, there were at times over 400 paper mills. 28 of these old paper mills are still preserved in the county, plus two replicas.
From around 1900 there were also some coal mines in East Kent. The locations were Chislet, Tilmanstone, Betteshanger and the Snowdown colliery, which was operated from 1908 to 1986.
The west of the county is considered more affluent than the east. This has to do with the proximity to London, as many commuters have settled there. The eastern cities are hoping for the Channel Tunnel Rail Link .
art
Many writers and artists have been inspired by Kent. Canterbury's position as a religious center led to Geoffrey Chaucer's Canterbury Tales , a landmark in English literature. The father of the writer Charles Dickens worked on the Chatham docks. That is why one finds impressions from Chatham and the surrounding area in many of Dickens' novels.
The film and stage actor Trevor Howard (1913–1988) came from Cliftonville .
The painter William Turner spent parts of his childhood in Margate and came back often later. The coast of East Kent inspired many of his works including some of his seascapes.
In the 1930s, the writer and later Nobel Prize winner William Golding worked as a teacher in Maidstone high school, where he also met his future wife Ann Brookfield.
The musician Kate Bush comes from Bexleyheath, the musician and poet David Sylvian from Beckenham .
Pop music producers Xenomania work on their productions in a converted parsonage in Kent.
traffic
Streets

After the Roman invasion of England, a network of roads was built connecting London to the canal ports of Dover, Lympne and Richborough. The road from London to Dover was called Watling Street . Today this road roughly follows the A2, B2068, A257 and A28. The A2 runs from Dartford (A207) via Gravesend, Rochester, Canterbury to Dover; the A20 through Eltham, Wrotham, Maidstone, Charing, Ashford. Hythe, Folkestone and Dover; the A21 around Sevenoaks, Tonbridge, Tunbridge Wells and on to Hastings in East Sussex. Two motorways were built in the 1960s, the M2 from Medway to Faversham and the M20 from Swanley to Folkestone. Parts of the M25 run through Kent, from Westerham to the “Kent and Essex Tunnel” at Dartford. The Dartford tunnel connects to the "Queen Elizabeth II Bridge", with four lanes in each direction. The M26, built in 1980, forms a short connection between the M25 at Sevenoaks and the M20 at Wrotham .
Waterways
The medieval Cinque Ports are all silted up except for Dover. The Medway Estuary had important naval bases and ports for 500 years. The river itself is navigable as far as Tonbridge. There were two canals in Kent, the remaining Royal Military Canal between Hythe and Rye and the Thames and Medway Canal between Strood and Gravesend. This was built in 1824, but bought by the railroad in 1846 and partially replenished. Container ports are Ramsgate and Thamesport .
railroad

The first railroad to carry people was the Canterbury and Whitstable Railway , which opened in 1830. It later merged with the London and Greenwich Railway to form the South Eastern Railway (SER). In the 1850s, the SER had expanded its rail network to Ashford, Ramsgate, Canterbury, Tunbridge Wells and the towns on the Medway. The SER drove to London Bridge Station , Charing Cross Station and Cannon Street Station in London .
There was another railway company in Kent, the London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LCDR). It was originally called East Kent Railway until 1858 and connected the coastal towns in northeast Kent with London's Victoria Station and Blackfriars Station . Both companies merged in 1899 to form the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SECR).
On January 1, 1923, several railway companies were merged by the Railways Act 1921 , and the SECR merged with the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LBSCR) and the London and South Western Railway (LSWR) to form the Southern Railway . In 1948 the railway companies were nationalized and were henceforth called British Rail . In 1996 the railways were privatized again. The lines in Kent have since been operated by Connex South Eastern . Due to financial bottlenecks, the Connex was replaced by the Southeastern .
The Eurotunnel was built in 1994 and the High Speed 1 high speed line in November 2007 leading to St Pancras Station in London. A new station, Ebbsfleet International Station , has opened between Dartford and Gravesend and serves the north of the county. The high-speed lines are designed to provide faster connections to the coastal cities of Ramsgate and Folkestone . The station in Ashford has lost its importance due to the new route.
In addition to the main lines, there are several narrow-gauge railways , museum railways and freight-operated lines. There are three museum railroads, the Spa Valley Railway at Tunbridge Wells on the old tracks of the Tunbridge Wells West Branch, the East Kent Railway on an old coal mine in East Kent and the Kent and East Sussex Railway on the Weald at Tenterden. In addition, there is the tourist-oriented narrow-gauge Romney, Hythe and Dymchurch Railway on the southeast coast along the Dungeness Peninsula.
Finally, there is the former Sittingbourne & Kemsley Light Railway .
air traffic
Some charter flights are handled via Kent International Airport at Manston near Ramsgate and Canterbury and London Ashford Airport at Lydd . Most passengers, however, mainly use the larger London airports Heathrow , Gatwick , Stansted and Luton .
In 2002 it was planned to build an airport with four runways at Cliffe at Hoo in the marshland. This plan was rejected after protests by environmental groups.
education
Kent has three universities: Canterbury Christ Church University with multiple campuses in the east of the county, the University of Kent with campuses in Canterbury and Medway, and the University of Greenwich with campuses in Woolwich , Eltham and Medway.
While almost all of Great Britain had a new school system in the 1970s, Kent, the Medway Unitary Authority and about 15 other administrative units stayed with the old system.
Kent's Department of Education is the largest of any county in Britain.
Cities and Towns in Kent
- Ashford , Aylesford , Allhallows-on-Sea
- Bearsted , Broadstairs , Biddenden
- Canterbury , Charing , Chatham , Cliffe at Hoo , Cranbrook , Crockenhill , Crouch
- Dartford , Deal , Detling , Dover , Dunton Green , Dymchurch
- Eythorne , Edenbridge , Eastry
- Faversham , Folkestone
- Gillingham , Gravesend , Greenhythe
- Hartley-Cranbrook , Hartley-Longfield , Hawkhurst , Herne , Herne Bay , Higham , High-Halstow , Hollingbourne , Hythe
- Kemsing
- Langley , Leigh , Linton , Lydd
- Maidstone , Manston , Marden , Margate , Marsh Green , Martin , Martin Mill , Maxton , Minster-in-Thanet , Minster-in-Sheppey , Monkton
- Netlestead , Nettlestead Green , New Ash Green , New Romney , Northfleet
- Otford
- Paddock Wood , Pembury , Penshurst , Postling
- Queenborough
- Ramsgate , Reculver , Rochester
- Sandwich , Seal , Sevenoaks , Sheerness , Shoreham , Sittingbourne , Stone , Sturry , Swanley
- Tenterden , Thurnham , Tonbridge , Tunbridge Wells
- Upnor , Upchurch
- Walmer , Westerham , Whitstable , Westbrook
Attractions
- Canterbury Cathedral
- Chatham Historic Dockyard, an anchor point on the European Route of Industrial Heritage - ERIH
- Isle of Sheppey
- Isle of Thanet
- White cliffs of Dover
- Leeds Castle
- Sissinghurst - the famous gardens of Sissinghurst Castle, designed by the writer Vita Sackville-West and her husband Sir Harold Nicolson
- Penshurst Castle
- Hever Castle
- Scotney Castle
- Chartwell
- Bodiam
- Batemans
- Pashley Manor Gardens
- Finchcocks
- Bedgebury National Pinetum & Forest
- The Pantiles in Royal Tunbridge Wells
- Turner Contemporary - Margate
literature
- Paul Ashbee: Kent in Prehistoric times . Tempus, Stroud 2005
Web links
- Kent Parishes - forum for history, genealogy and local information
- Kent County Council - County Council website
- Discover the Garden of England - Visitor information for Kent and Sussex (in English)
- Kent Wildlife Trust - Kent Wildlife Trust
- Kent Online - a Kent Messenger Group website
- Camelot Village - Historic Monument Site
- Kent Downs - Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty Website
- Village Net - Photographs and historical information on locations in Kent and East Sussex
- CPRE Kent - Kent's division of the Campaign to Protect Rural England (CPRE)
- historic-kent.co.uk - more information on places in Kent
- BBC - Origin of Place Names in Kent
- Kent Coast in Pictures - Photographs of the coast.
- VisitKent - tourism website
Individual evidence
- ^ A b Mid 2018 Estimates of the population for the UK, England and Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland
- ↑ Kent loses its Garden of England title to North Yorkshire The Guardian June 1, 2006
- ↑ Garden of England title defended BBC June 1, 2006
- ^ Paul Ashbee: Kent in prehistoric times . Tempus, 2005.
- ^ Archbishop of Canterbury . Spartacus.SchoolNet.co.uk. Retrieved June 19, 2007.
- ^ David Bates : The Character and Career of Odo, Bishop of Bayeux (1049 / 50-1097) . Speculum, 1975.
- ^ Peasants' Revolt . Britannia.com. Archived from the original on April 4, 2007. Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved April 20, 2007.
- ↑ Sir Thomas Wyatt, "The Younger" . TudorPlace.com.ar. Retrieved April 20, 2007.
- ^ The Historic Dockyard Chatham --- where legends were created . Jarrold Publishing, 2005.
- ^ The Dutch In The Medway . DeRuyter.org. Archived from the original on May 17, 2007. Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved April 20, 2007.
- ^ Richard Oliver: Ordnance Survey Maps: a concise guide for historians 2nd Ed . Ordnance Survey , 1995, ISBN 1-870598-24-5 .
- ^ South-East England . Smuggler's Britain. Retrieved April 20, 2007.
- ↑ WW2 People's War . BBC. December 9, 2005. Retrieved April 19, 2007.
- ↑ a b c d Frank W. Jessup: Kent History Illustrated . Kent County Council, 1966.
- ^ Greensand Way in Kent . Kent Count Council, 1992, ISBN 1-873010-23-0 .
- ^ Britain's Structure and Scenery, L.Dudley Stamp , Pub Sept 1946, Collins New Naturalist Series.
- ^ Geology of Kent and Boulonnais . The Geology Shop. 2000. Retrieved April 21, 2007.
- ↑ Quake causes Kent Families to Flee Homes . The Guardian. April 29, 2007. Retrieved April 28, 2007.
- ↑ a b Derek Bowskill: Map Of The River Medway .
- ↑ Stephen Rayner: Men of Kent: Sorry ... but we're joining a new tribe , Medway News. October 2004.
- ↑ a b c Neighborhood Statistics . Statistics.gov.uk. Retrieved March 29, 2007.
- ↑ 2005 - Election Results In Kent . Kent Liberal Democrat. Retrieved on April 3, 2007. ( Page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ^ Councilors . Kent County Council. Archived from the original on February 7, 2009. Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved May 13, 2007.
- ^ Democratically elected representatives in Medway . Medway Council. Archived from the original on May 12, 2007. Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved May 13, 2007.
- ↑ UK MEPs . UK Office Of The European Parliament. Archived from the original on September 17, 2007. Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved April 3, 2007.
- ^ Closure of Dungeness Power Station . BBC News. December 31, 2006. Retrieved April 3, 2007.
- ↑ Snowdown Colliery . FreeUK.com. Retrieved April 19, 2007.
- ↑ Charles Dickens . InfoBritain. Archived from the original on April 17, 2007. Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved April 20, 2007.
- ^ The Turner Connection . TurnerContemporary.org. Retrieved June 20, 2007.
- ^ William Golding --- Biography . William-Golding.co.uk. Archived from the original on March 17, 2007. Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved June 20, 2007.
- ^ The lost railway . BBC. Retrieved May 13, 2007.
- ^ A b History of the South Eastern & Chatham Railway . The South Eastern & Chatham Railway Society. Archived from the original on November 1st, 2006. Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved April 22, 2007.
- ↑ Failed rail franchise 'needed time' . BBC. November 13, 2003. Retrieved May 13, 2007.
- ^ Rail workers vote to hold strikes . BBC. April 13, 2006. Retrieved May 13, 2007.
- ^ New station means Eurostar change . BBC. September 12, 2006. Retrieved April 22, 2007.
- ^ Airport plan threatens Dickens' legacy . BBC. September 12, 2006. Retrieved June 20, 2007.
- ↑ Call for end to selective education as 'grammar school areas' fail . The Independent. January 20, 2007. Archived from the original on January 27, 2007. Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved May 14, 2007.
- ↑ [1]
- ↑ National Trust - Sissinghurst Castle Garden ( Memento of the original from October 12, 2009 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (English)
Coordinates: 51 ° 13 ' N , 0 ° 51' E