District of Saalfeld-Rudolstadt
| coat of arms | Germany map |
|---|---|

|

Coordinates: 50 ° 38 ' N , 11 ° 19' E |
| Basic data | |
| State : | Thuringia |
| Administrative headquarters : | Saalfeld / Saale |
| Area : | 1,036.03 km 2 |
| Residents: | 103.199 (Dec. 31, 2019) |
| Population density : | 100 inhabitants per km 2 |
| License plate : | SLF, RU |
| Circle key : | 16 0 73 |
| NUTS : | DEG0I |
| Circle structure: | 26 municipalities |
| Address of the district administration: |
Schloßstraße 24 07318 Saalfeld / Saale |
| Website : | |
| District Administrator : | Marko Wolfram ( SPD ) |
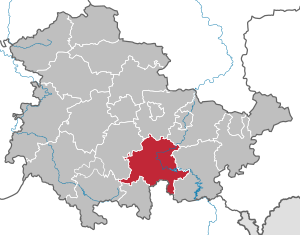
| Location of the Saalfeld-Rudolstadt district in Thuringia | |
The district of Saalfeld-Rudolstadt is a district in the south of the Free State of Thuringia . Despite its geographical location in the south of the state, the district is part of the planning region of East Thuringia .
geography
Neighboring districts are the Weimarer Land district in the north, the Saale-Holzland district in the northeast, the Saale-Orla district in the east, the Bavarian district of Kronach and the Thuringian district of Sonneberg in the south, the district of Hildburghausen in the southwest and the Ilm district in the west. Circle . The Saalfeld-Rudolstadt district is crossed by the Saale River and is located in the Thuringian slate mountains .
history
Emergence
The district of Saalfeld-Rudolstadt has existed since 1994, when - initially with the name Schwarza district - the districts of Rudolstadt and Saalfeld were combined. These emerged from the district offices of the same name, which were renamed districts in 1922. In addition, there was the northern part of the Neuhaus am Rennweg district, founded in 1952, and part of the former Lobenstein district (town of Lehesten and districts).
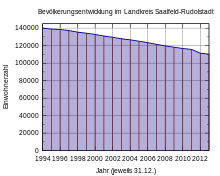
Population development
Development of the population:
|
|
|
|
|
- Data source: from 1994 Thuringian State Office for Statistics - values from December 31st
politics
District Administrator
Marko Wolfram (SPD) has been the district administrator since October 3, 2014 . In the runoff election on September 28, 2014, he won with 57% of the votes in front of his challenger Bernhard Schanze (non-party), who received 43% of the votes. Other candidates were Ulrike Klette (left) and Wilfried Meißner (non-party), who were eliminated in the first ballot on September 14, 2014.
The election on June 28, 2020 was won by Marko Wolfram (SPD) with 58.5% of the vote, ahead of his challengers Maik Kowalleck (CDU) with 23.7% of the vote and Brunhilde Nauer (AFD), who received 17.8% of the vote . The turnout was 42.4 percent. The new term of office begins on October 3, 2020.
Former district administrators
- 1994–2000: Werner Thomas (CDU)
- 2000–2012: Marion Philipp (SPD)
- 2012–2014: Hartmut Holzhey (independent)
District council
The 46 seats in the district council are distributed among the individual parties as follows:
| Party / electoral association | Seats | |
| CDU | 11 (-4) | |
| AfD | 10 (+10) | |
| SPD | 7 (± 0) | |
| Citizens for the district of Saalfeld-Rudolstadt | 7 (+1) | |
| THE LEFT | 5 (-4) | |
| FDP | 3 (+1) | |
| GREEN | 2 (± 0) | |
| Citizens' initiatives against excessive local taxes in the Saalfeld-Rudolstadt district |
1 (-1) | |
| NPD | 0 (-3) |
(As of: local election on May 26, 2019 )
coat of arms
The coat of arms was approved on January 16, 1995 by the Thuringian State Administration Office.
Blazon : “Quartered; Fields 1 and 4: in gold a black, gold nimbly, red armored double-headed eagle, the chest covered with a gold shield with a princely hat, over the eagle heads an imperial crown with red caps, in the claws holding a gold scepter and a gold imperial orb, underneath a red spreader fork over a red comb; Field 2 and 3: divided nine times by black and gold, covered with a diagonal, green diamond wreath. "
An overview of the coats of arms of the towns and municipalities in the district can be found in the list of coats of arms in the Saalfeld-Rudolstadt district .
Cultural institutions and sights
Thuringian State Museum Heidecksburg
The Heidecksburg in Rudolstadt is the most magnificent baroque palace of the 18th century in the Free State of Thuringia. In the high Middle Ages still owned by the Counts of Orlamünde , the Blackburg Counts acquired the castle in 1340 . From 1574 to 1918 it was the residence of the counts and later princes of Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt. Today the castle houses, among other things, the Thuringian State Museum Heidecksburg . It is one of the largest and most visited museums in Thuringia. In accordance with its historically evolved structure of the collection, the specialist work focuses on the many facets of the residential culture at the court of the Princes of Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt. The museum association Thuringian State Museum Heidecksburg, which is sponsored by the district of Saalfeld-Rudolstadt, includes not only the Residenzschloss but also the Friedrich-Froebel-Museum in Bad Blankenburg, the Museum of Hunting and Forestry History in Paulinzella and the Imperial Hall at Schloss Schwarzburg .
Friedrich Froebel Museum Bad Blankenburg
The Friedrich-Fröbel-Museum has been housed in Bad Blankenburg since 1982 in the building in which the “founder” of the kindergarten, Friedrich Fröbel, opened his first “play and employment facility” in 1839, which later became his kindergarten. Friedrich Wilhelm August Fröbel (born April 21, 1782 in Oberweißbach; † June 21, 1852 in Marienthal) achieved world renown through the establishment of the first kindergarten in 1840 in Blankenburg (Thuringia). In the "house above the cellar", in which the Friedrich Froebel Museum is located, the kindergarten was born. Froebel's thoughts on education and upbringing as a whole are as time-bound as they are original and modern. They stimulate pedagogical thinking up to the present day.
Thuringian State Theater Rudolstadt - Thuringian Symphony Orchestra Saalfeld-Rudolstadt
The Rudolstadt Theater is a theater in Rudolstadt in Thuringia. It traces its tradition back to the princely summer theater founded in 1792/93. The Thuringian State Theater Rudolstadt is also the main place of activity of the Thuringian Symphony Orchestra Saalfeld-Rudolstadt. For this reason, the full name is Thuringian State Theater Rudolstadt - Thuringian Symphony Orchestra Saalfeld-Rudolstadt GmbH. The theater is run by a special purpose association to which the district of Saalfeld-Rudolstadt (50 percent) as well as the cities of Rudolstadt (38 percent) and Saalfeld / Saale (12 percent) belong. [1]
Laura Concentration Camp Memorial
The Laura subcamp was one of around 130 subcamps of the Buchenwald concentration camp . It was set up on September 21, 1943 in Schmiedebach in the Thuringian Slate Mountains on the edge of the Oertelsbruch in order to move the weapons production underground. In the Oertelsbruch, an underground oxygen plant and test stands for engines for the A4 rocket (also known as the V-2) were built. A total of around 2,600 prisoners were housed in the concentration camp, at least 560 of whom died as a result of abuse, malnutrition and the consequences of forced labor. On April 13, 1945, the camp was liberated by US soldiers . Since 1979 there has been a memorial in the former main accommodation of the concentration camp, a large field barn. With the end of the GDR, this was first passed into the sponsorship of the Lobenstein district and with the district reform in 1994 into the sponsorship of the Saalfeld-Rudolstadt district. The property, which was originally privately owned, was bought by the Saalfeld-Rudolstadt district, as the ownership of the district was a prerequisite for the approval of subsidies from the State of Thuringia. Between 2011 and 2014, the entire exhibition was revised and the outdoor facilities redesigned. The district has been the operator of the memorial since 2012, with around 4,000 visitors during the season (from April to October). Due to the largely completely preserved original substance, the concentration camp memorial is a specialty among the Buchenwald satellite camps. In the course of the restoration, wall decorations from the prisoners' days were exposed.
Economy and Infrastructure
The Saalfeld-Rudolstadt region not only has a culturally interesting history. The inventive and entrepreneurial spirit has a long tradition here. For example, parallel to JF Böttger, Georg Heinrich Macheleid invented what is known as “white gold” porcelain here in 1760, in 1919 the world's first X-ray tube production was established in Rudolstadt and in 1935 the first industrial production plant for rayon. Today the economic area has a broad branch structure. Determining are u. a. the steel industry, medical technology, machine and tool construction, the chemical and plastics industry, glass and porcelain production and food production. On this basis, the region's economy is always at the forefront when compared to Thuringia, especially in terms of sales and exports. The companies are supported by business development agencies such as the state development company, the municipal business development agency and the innovation and start-up center. Start-ups and expansions are professionally supported here and find space to develop in 30 commercial and 4 industrial areas in the region. Innovation is very important at the location - the Thuringian Institute for Textile and Plastics Research in Schwarza has its share in this as well as international market leaders, e.g. Königsee-Implantate GmbH, the Sandoz competence center aerosols in Aeropharm GmbH, and TRUMPF Medical as Part of Hill-Rom and the Siemens AG-Healthcare Sector Röntgenwerke.
The Saalfeld-Rudolstadt Region Economic Development Agency, as a communal working group, has set itself the goal of better meeting the requirements of effective and targeted economic development in a structure that is unique in Thuringia by bundling specialist skills. With the participation of the district of Saalfeld-Rudolstadt, the cities of Bad Blankenburg, Rudolstadt and Saalfeld, as well as the Innovations- und Gründerzentrum GmbH, tasks of classic economic development are carried out and joint projects are developed. Municipal economic development is a support for companies in all questions of the location, the infrastructure and the financing / funding and of course free of charge.
traffic
With the train station in Saalfeld / Saale , the district has a regional rail hub. The Oberweißbacher Berg- und Schwarzatalbahn operates as one of the first rail lines operated as a profit center by Deutsche Bahn in the south-western district. Due to the new construction of the high-speed line Nuremberg-Erfurt , Saalfeld, like Jena, lost the ICE stop on the long-distance Berlin - Munich line . In this regard, the local politicians are calling for improvements and commitments to protect existing assets, which are of particular importance not only for Saalfeld-Rudolstadt, but also for the Saalebahn. The importance of Saalfeld as a railway junction has grown over time. Not far from Saalfeld in Probstzella , the train distance to Berlin and Munich is 300 km.
The district is crossed by the federal highways 85 , 88 , 90 and 281 . In the respective neighboring districts, the A 4 runs in the north , the A 9 in the east, the A 71 in the west and the A 73 in the south . With regard to the connection to the federal motorways, the district still sees some catching up to do. The distance to the respective motorways is almost the same and too far for the region and its importance. Even if various bypasses up to and including federal motorways bring relief, more direct access to the federal motorways would significantly enhance the region.
Shipping traffic is operated on the Hohenwartetalsperre in the southeast of the district. Several passenger ships offer tours on the reservoir. In addition, the mill ferry enables people to be transferred from one side of the reservoir to the other by car and motorcycle. The northern landing stage of the mill ferry is in the Saale-Orla district. The ferry does not operate all year round.
media
The Ostthüringer Zeitung (OTZ) is predominantly sold in the district's catchment area . OTZ maintains two local editorial offices in Saalfeld and Rudolstadt. Furthermore, three free advertising papers will be distributed.
In the cities of Saalfeld and Rudolstadt there is one cable television provider each, which, in addition to local advertising, sends a small amount of short articles and reports as moving images.
In Saalfeld itself there is the seat of a regional studio of the Mitteldeutscher Rundfunk (MDR) and the seat of the citizen radio SRB . While the MDR provides the district with its radio offerings at least terrestrially, the SRB cannot fully reach the district. Here the local politicians and the administration are trying to significantly improve the supply of the area, although this is associated with difficulties due to the topographical location.
Protected areas
There are 16 designated nature reserves in the district (as of January 2017).
Communities
As a regional center with partial function of a regional center is Saalfeld / Rudolstadt / Bad Blankenburg reported (funktionsteilig).
The basic centers are the cities of Königsee and Oberweißbach / Thür. Wald and the community of Probstzella .
(Residents on December 31, 2019)
|
community-free municipalities
|
|
Administrative communities
(*) Seat of the administrative community
|
|
For the terms "administrative community" and "fulfilling community" see administrative community in Thuringia .
Territorial changes
Communities
- Dissolution of the Weißen community - incorporation into the Uhlstädt community (December 30, 1994)
- Dissolution of the municipalities of Bernsdorf , Burkersdorf , Dittersdorf , Dittrichshütte , Eyba , Kleingeschwenda , Lositz-Jehmichen , Reschwitz , Unterwirbach , Volkmannsdorf , Wickersdorf , Wittmannsgereuth and Witzendorf - reorganization of the municipality of Saalfelder Höhe (January 1, 1997)
- Dissolution of the communities of Drognitz, Neuenbeuthen and Reitzengeschwenda - new formation of the community of Drognitz (January 1, 1997)
- Dissolution of the municipalities of Dorfilm , Hirzbach , Landsendorf , Munschwitz , Schweinbach and Steinsdorf as well as the city of Leutenberg - reorganization of the city of Leutenberg (January 1, 1997)
- Dissolution of the municipalities of Ammelstädt , Breitenheerda , Eschdorf , Geitersdorf , Haufeld , Heilsberg , Milbitz , Sundremda , Teichröda and Treppendorf as well as the cities of Remda and Teichel - reorganization of the city of Remda-Teichel (January 1, 1997)
- Dissolution of the municipalities of Lichstedt , Oberpreilipp and Unterpreilipp - incorporation into the city of Rudolstadt (January 1, 1997)
- Dissolution of the municipality of Neckeroda - incorporation into the town of Blankenhain in the district of Weimarer Land (January 1, 1997)
- Dissolution of the communities of Beutelsdorf , Dorndorf , Engerda , Kirchhasel , Niederkrossen , Rödelwitz , Schloßkulm , Schmieden , Teichweiden , Uhlstädt and Zeutsch - reorganization of the community of Uhlstädt-Kirchhasel (July 1, 2002)
- Dissolution of the Marktgölitz municipality - incorporation into the Probstzella municipality (March 16, 2004)
- Dissolution of the municipalities of Birkigt , Goßwitz , Könitz , Lausnitz and Unterwellenborn - new formation of the municipality Unterwellenborn (February 1, 2006)
- Dissolution of the communities Großkochberg and Heilingen - incorporation into the community Uhlstädt-Kirchhasel (December 1, 2007)
- Dissolution of the municipality of Lichtenhain / Bergbahn - incorporation into the city of Oberweißbach / Thür. Forest (December 1, 2008)
- Dissolution of the municipality of Arnsgereuth - incorporation into the city of Saalfeld / Saale (December 1, 2011)
- Dissolution of the city of Königsee and the municipality of Rottenbach - reorganization of the city of Königsee-Rottenbach (December 31, 2012)
- Dissolution of the municipalities of Saalfelder Höhe and Wittgendorf - incorporation into the city of Saalfeld / Saale (July 6, 2018)
- Dissolution of the municipality of Kamsdorf - incorporation into the municipality of Unterwellenborn (July 6, 2018)
- Dissolution of the municipalities of Mellenbach-Glasbach , Meuselbach-Schwarzmühle and the city of Oberweißbach / Thuringian Forest - new formation of the city and rural municipality of Schwarzatal (January 1, 2019)
- Dissolution of the communities of Dröbischau and Oberhain - incorporation into the city of Königsee-Rottenbach (January 1, 2019)
- Dissolution of the city of Remda-Teichel - incorporation into the city of Rudolstadt (January 1, 2019)
- Dissolution of the communities Reichmannsdorf and Schmiedefeld - incorporation into the city of Saalfeld / Saale (January 1, 2019)
- Dissolution of the communities of Lichte and Piesau - incorporation into the town of Neuhaus am Rennweg in the district of Sonneberg (January 1, 2019)
Administrative communities and fulfilling communities
- Expansion of the Lichte-Piesau-Schmiedefeld administrative community to include the Reichmannsdorf community (November 4, 1994)
- The city of Saalfeld / Saale becomes a fulfilling municipality for Arnsgereuth (May 12, 1995)
- Dissolution of the Saale-Loquitz - Kaulsdorf administrative community becomes a fulfilling municipality for Hohenwarte (October 19, 1995)
- Dissolution of the administrative community Obere Saale - new formation of the city of Leutenberg from the member communities, with the exception of Altenbeuthen, Drognitz, Neutenbeuthen and Reitzengeschwenda; the last three merge to form the new municipality of Drognitz; Kaulsdorf becomes a fulfilling municipality for Altenbeuthen and Drognitz (December 31, 1996)
- Dissolution of the administrative communities Remda and Teichel - new formation of the city of Remda-Teichel from the member communities, with the exception of the communities Lichstedt, which is incorporated into Rudolstadt and Neckeroda, which is incorporated into Blankenhain in the Weimarer Land district (December 31, 1996)
- Outsourcing of the municipalities of Oberpreilipp and Unterpreilipp from the Uhlstädt administrative community (December 31, 1996)
- Dissolution of the administrative community Saalfelder Höhe - new formation of the single community Saalfelder Höhe from the member communities (December 31, 1996)
- The city of Rudolstadt becomes a fulfilling municipality of Kirchhasel (January 1, 1997)
- Dissolution of the Uhlstädt administrative community - reorganization of the Uhlstädt-Kirchhasel unified community from the member communities (excluding Großkochberg and Heilingen ) and the Kirchhasel community, which was previously filled by Rudolstadt; Uhlstädt-Kirchhasel becomes a fulfilling municipality for Großkochberg and Heilingen (June 30, 2002)
- Dissolution of the administrative community Unterwellenborn - new formation of the unified community Unterwellenborn from the member communities (January 31, 2006)
- The community of Uhlstädt-Kirchhasel is no longer fulfilling community for Großkochberg and Heilingen (December 1, 2007)
- The city of Saalfeld / Saale is no longer a fulfilling municipality for Arnsgereuth (November 30, 2011)
- Extension of the administrative community Probstzella-Lehesten-Marktgölitz to include the city of Gräfenthal (December 31, 2013)
- Outsourcing of the Wittgendorf community from the Mittleres Schwarzatal administrative community (July 6, 2018)
- Dissolution of the mountain railway region / Schwarzatal and Mittleres Schwarzatal - new formation of the city and rural community Schwarzatal from the member communities Mellenbach-Glasbach , Meuselbach-Schwarzmühle and Oberweißbach / Thuringian Forest (city); Incorporation of the member communities Dröbischau and Oberhain into Königsee-Rottenbach ; this becomes a fulfilling community for the member communities Allendorf and Bechstedt ; Merger of the other member communities of Cursdorf , Deesbach , Döschnitz , Katzhütte , Meura , Rohrbach (near Saalfeld) , Schwarzburg , Sitzendorf and Unterweißbach and the rural community of Schwarzatal to form the Schwarzatal administrative community (January 1, 2019)
- Dissolution of the Lichtetal am Rennsteig administrative community - incorporation of the member communities Reichmannsdorf and Schmiedefeld into Saalfeld / Saale ; Incorporation of the member communities of Lichte and Piesau to Neuhaus am Rennweg in the district of Sonneberg (January 1, 2019)
Name changes
- from administrative community Probstzella / Loquitzgrund to administrative community Probstzella-Lehesten-Marktgölitz (September 1, 1995)
- from administrative community Lichte-Piesau-Schmiedefeld to administrative community Lichtetal am Rennsteig (December 30, 2004)
- of administrative community Probstzella-Lehesten-Marktgölitz to schiefergebirge (31 December 2013)
- from Königsee-Rottenbach to Königsee (January 1, 2019)
License Plate
On July 1, 1994, the RU (Rudolstadt) and SLF (Saalfeld) vehicles were assigned to the district . From February 1, 1995 only the abbreviation SLF was official. Since November 24, 2012, the distinctive sign RU has been available again.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Population of the communities from the Thuringian State Office for Statistics ( help on this ).
- ↑ District election in Saalfeld-Rudolstadt 2019 In: wahlen.thueringen.de .
- ↑ wahlen.thueringen.de
- ↑ Elections in Thuringia, district council election on June 28, 2020, final result. Thuringian State Office for Statistics, accessed on July 11, 2020 .
- ^ Regional plan East Thuringia of October 28, 2011 , accessed on October 16, 2016