1264
Portal history | Portal Biographies | Current events | Annual calendar
◄ |
12th century |
13th century
| 14th century
| ►
◄ |
1230s |
1240s |
1250s |
1260s
| 1270s
| 1280s
| 1290s
| ►
◄◄ |
◄ |
1260 |
1261 |
1262 |
1263 |
1264
| 1265
| 1266
| 1267
| 1268
| ►
| ►►
Calendar overview 1264
| 1264 | |
|---|---|
|
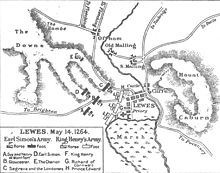
Henry III. and his son Edward are captured by the opposition of the barons, led by Simon V de Montfort, at the Battle of Lewes . |
|
| 1264 in other calendars | |
| Armenian calendar | 712/713 (turn of the year July) |
| Ethiopian calendar | 1256/57 |
| Buddhist calendar | 1807/08 (southern Buddhism); 1806/07 (alternative calculation according to Buddha's Parinirvana ) |
| Chinese calendar | 65./66. (66./67.) Cycle
Year of the Wood Rat甲子 ( at the beginning of the year Water Pig 癸亥) |
| Chula Sakarat (Siam, Myanmar) / Dai calendar (Vietnam) | 626/627 (turn of the year April) |
| Iranian calendar | 642/643 |
| Islamic calendar | 662/663 (turn of the year 23/24 October) |
| Jewish calendar | 5024/25 (22/23 September) |
| Coptic calendar | 980/981 |
| Malayalam calendar | 439/440 |
| Seleucid era | Babylon: 1574/75 (turn of the year April)
Syria: 1575/76 (turn of the year October) |
| Spanish era | 1302 |
| Vikram Sambat (Nepalese Calendar) | 1320/21 (turn of the year April) |
Events
Politics and world events
Second War of the Barons in England
- January 23 : With the Mise of Amiens , the French King Louis IX decides . at the request of the parties to the dispute in the constitutional conflict between King Heinrich III. of England and the opposition of English barons around Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester . The barons are represented by Simon's son Henry de Montfort . Ludwig judges in the spirit of King Heinrich and declares all contracts forced upon the king to be null and void. Contracts that were concluded before 1258 , such as the Magna Charta , are not affected by the judgment. The barons refuse to recognize the arbitration award and again call for war against Heinrich .
- February 14th : Heinrich returns to England and sets up an army within three weeks. The first fights from April onwards are successful for the king and his son Edward . With the support of the Marcher Lords , they conquer several castles of the rebel barons.
- April 7th : Royal troops capture the city of Northampton and Northampton Castle , capturing Simon de Montfort the Younger . Then they conquer Nottingham and Leicester .
- April 18 : Gilbert de Clare , who has so far been waiting for the development in Tonbridge Castle , besieges Rochester Castle together with Montfort .
- May 14 : Heinrich III. and his son Edward are captured by the opposition of the Barons led by Simon V de Montfort at the Battle of Lewes . The king renounces any further resistance and accepts Montfort's Mise of Lewes the following day . After that Heinrich recognizes the Provisions of Oxford again, whereby Montfort allows him to renegotiate on contentious points.
- 23 June : A parliament convened by Simon de Montfort resolves a major change in the government: instead of the 15-member Council of State, a three-member committee is formed, including Montfort, Gilbert de Clare and Bishop Stephen Bersted of Chichester. This committee is to elect a nine-member council of state to advise the king. However, the real power lies with the three-person committee. The king only has symbolic power left.
- August 25 : De Montfort signs a truce with the Marcher Lords. But numerous followers of the king continue the fight.
- December 14th : Simon de Montfort convenes De Montfort's Parliament for January 20th , in which not only barons and bishops, but for the first time also representatives of the knights and the cities take part.
Ireland
- June 18th : The Parliament of Ireland holds its first ever occupied meeting in Castledermot .
Holy Roman Empire
- February 16 : Obizzo II. D'Este becomes lord of Ferrara after the death of his grandfather Azzo VII. D'Este .
- October 12 : Rostock acquires the seaport near Warnemünde .
- The area of today's Upper Austria is mentioned for the first time under the name Austria superior , when Ottokar Přemysl reorganized the administration of the former Babenberg region .
- After the male line of Kyburg died out, the county of Kyburg fell to the Habsburgs . Count Rudolf von Habsburg asserts the inheritance against claims of Count Peter of Savoy . The cities of Winterthur , Diessenhofen , Frauenfeld and Freiburg im Üchtland as well as the county of Thurgau come into his possession.
- The Thuringian War of Succession , which began in 1247 , ended with the Peace of Langsdorf that was concluded the previous year . As a result, Hesse becomes an independent landgraviate under the rule of Heinrich I , the son of Sophie von Brabant . Henry III. von Meissen receives the existing Landgraviate of Thuringia .
- The Fulda prince abbot Bertho II von Leibolz storms Blankenwald Castle, known as the robber barons nest, and razes it.
Eastern Europe
- Beginning of the year: Vaišelga , who previously lived as an Orthodox monk, becomes Grand Duke of Lithuania as the successor to his father Mindaugas I, who was murdered the previous year . He takes up the fight with his father's murderers, Treniota and Daumantas . Treniota is murdered by opponents in the spring.
- September 8th : Duke Bolesław VI. the pious from Wielkopolska enacted the Kalisch statute , which defines the position of the Jews in Poland and forms the basis for their relatively autonomous existence. The statute threatens , among other things, penalties for desecrating Jewish cemeteries and synagogues . The statute contains provisions for the punishment of those who accuse Jews of ritual murder . It regulates the principles of commercial activity by the Jews and guarantees them the inviolability of life and property. The protective function, which has been in effect for centuries, leads - despite repeated ritual murder pogroms - to a considerable increase in the Jewish population in Poland .
- Yaroslav III Yaroslav , son of Yaroslav II of the Rurikids , becomes Grand Duke of Tver and Vladimir . He succeeds his older brother Alexander Newski, who died the previous year, to the Grand Duke's chair. Alexander's son Dimitri had previously been expelled from the important trading city of Novgorod . The recognition of Yaroslav by the local city population also means that he was asserted as Grand Duke.
Crusader States
- After the death of her father Johann II , Isabella from the noble Ibelin family becomes mistress of Beirut .
Central and East Asia
- After four years of fratricidal war, Arigkbugha Khan, supported by traditional tribal chiefs, has to surrender to Kublai Khan in the battle for the khaganate in the Mongol Empire. He is charged in a Reich assembly, but acquitted there.
- July: Ilchan Hülegü , who was closely allied with the new Great Khan but ruled independently in his name in Maragha , convened a meeting (Kuriltai) in his field camp near Tabriz , at which his vassals King David VII of Georgia , King Hethum I of Armenia and Prince Bohemond VI. of Antioch are present. He uses his own administrative officials such as Finance Minister Sams ed Din Gowaini and court astrologer Nasir al-Din Tusi . On this occasion, the two Venetian merchants Niccolò and Maffeo Polo, who have been stuck in Bukhara in the Chagatai Khanate since 1261 , received an invitation to the court of Kublai Khan through a messenger from Hülegü.
- Ahmad Fanakati becomes finance minister in the kingdom of Kublai Khan.
- The Chinese emperor Song Lizong dies childless and is inherited by his nephew Song Duzong , who continues the Song dynasty in China. His reign is marked by the defensive struggle against the Mongols , whereby he largely leaves the business of government to his Chancellor Jia Sidao . He has extensive land expropriations to finance the army, but also has military commanders regularly audited, which makes him unpopular both with the population and with the generals.
City rights and first documentary mentions
- June 22 : Winterthur receives Count of Hapsburg, later Roman-German King Rudolf I , the city charter granted, which also markets law is included.
- November 3rd : The later Berlin district of Schöneberg is mentioned for the first time.
- November 5th : The village of Waldbach (today in Baden-Württemberg) is first mentioned in a document.
- The places Blankenau , Bredenbek , Breitenstein , Dörflingen , Dornwang , Eibach (Hilpoltstein) , Eibach (Nuremberg) Hambach , Kiesdorf auf dem Eigen , Labach , Leckringhausen , Lichtenhagen , Lindenfurterhof , Marbach (Striegistal) , Mischelbach , Möhrsdorf , are also mentioned for the first time. Niederblecher , Olbersleben , Raduhn , Reimenrod , Saalau , Schillerslage , Schmittlotheim , Schönau auf dem Eigen , Severin , Sillenbuch , Stahnsdorf , Verrenberg , Vierow , Wernau .
- The Dražice Castle northeast of Benatek , built by the Prague burgrave Gregor von Litowitz, is first mentioned in a document.
Culture
- February 28th : The Japanese era of Bun'ei begins.
- Walter of Merton founds Merton College at Oxford University .
- around 1264: Jacobus de Voragine writes the Legenda aurea , a collection of saints' lives.
religion
- August 11th : With the bull Transiturus de hoc mundo , Pope Urban IV elevates the Corpus Christi celebration to an official ecclesiastical festival to glorify the Eucharist . The trigger for this decision is the “ blood miracle of Bolsena ”, which he recognized as a real miracle last year . On this occasion Thomas Aquinas wrote five hymns, Pange lingua , Sacris solemniis , Adoro te devote , Verbum supernum prodiens and the sequence Lauda Sion .

Münster Cathedral from Cathedral Square from
- September 30 : After more than 40 years of construction, Bishop Gerhard von der Mark consecrates the third St. Paul Cathedral in Münster, built in Gothic style .
- October 2 : Pope Urban IV, who never entered Rome during his entire term in office , dies in Perugia after a three-year pontificate . No new Pope will be elected until the end of the year .
- The Order of the Augustinians , which is subordinate to the Augustinian Hermits , is founded.
- Johann von Vercelli becomes the sixth master of the Dominican order .
nature and environment
- between July 14th and October 2nd : Great Comet C / 1264 N1 is visible to the naked eye in Europe and China.
Born
- Keizan Jōkin , Japanese monk, one of the founders of the Zen Buddhist Sōtō-shū († 1325 )
- Louis of France , descendant of the Capetians, heir to the French throne († 1276 )
Exact date of birth unknown
- June 1264 or 1269 : Eleanor of England , Countess of Bar († 1298 )
Died
Date of death secured
- February 16 : Azzo VII. D'Este , Margrave of Ferrara (* 1205 )
- April 3 : William Button , Bishop of Bath and Wells
- April 8 : Simon I. Count the front county Sponheim (* 1210 / 1215 )
- April 25 : Roger de Quincy , Anglo-Scottish magnate (* around 1195 )
- May 17th : Wartislaw III. , Duke of Pomerania (* around 1210 )
- August 1st : Johann I , Prince of Mecklenburg (* around 1211 )
- October 2 : Jacques Pantaléon, under the name Urban IV Pope (* before 1200)
Exact date of death unknown
- Spring: Hugo l'Aleman , Lord of Caesarea
- April / May: Robert de Vieuxpont , English nobleman and rebel
- Andrei II , Grand Duke of Vladimir
- Daniel , Prince of Halych-Volodymyr and Volhynia, Grand Prince of Kiev and King of the Rus (* 1201 )
- Isabella of Cyprus , regent of Jerusalem (* around 1210 )
- Johann II , Lord of Beirut (* around 1230 )
- Konrad I , Lord of Frankenstein and presumed builder of Frankenstein Castle
- Otto von Mörnstein , Bishop of Chiemsee and elected Bishop of Lavant
- Song Lizong , Chinese emperor of the Song Dynasty (* 1205 )
- Meinhard Tröstel , Austrian Ministeriale (* after 1200)
Died around 1264
- Vincent von Beauvais , French scholar, pedagogue, Dominican and encyclopaedist (* around 1190 )
Web links
Commons : 1264 - Collection of pictures, videos and audio files