List of sub-national administrative units
This list tries to give an overview of the diversity of the administrative units of the countries of the world, be it states, provinces or regions, to name only the most common.
A.
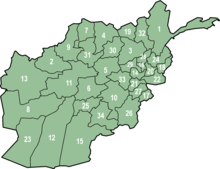
Afghanistan
Since April 13, 2004, Afghanistan has been divided into 34 provinces ( velayat ).
- Levels
- Provinces (34)
- Districts (398)
Egypt
Egypt is divided into 29 governorates (Arabic محافظات muhāfazāt, singular محافظة muhāfaza). Below that in the hierarchy come: Region, City, District, Village.
Albania
The highest level of administrative division in Albania is the Qark , of which there are a total of twelve. Each district is supervised by a prefect appointed by the central government . The Qarqe are divided into three to seven communities ( bashkie ) .
- Levels
- Qarqe (qark) / Prefectures (prefektura)
- Municipalities (bashkia)
The administrative levels of the districts (rreth) between Qark and municipality were lifted.
Algeria
There have been a total of 58 Wilayat in Algeria since 2019. In each there is a wali, a kind of governor who is the highest politician of the Wilaya.
- Levels
- Wilayat
- Daira
- local community
Andorra
Andorra consists of seven parròquies (Sg. Parròquia, literally parishes, actually parishes). The Comuns are the bodies that represent and administer the municipalities, approve and execute the municipal budget, decide and implement their public policy and administer all municipal property. They receive capital from the general government budget to ensure their financial independence.
- parròquia
Angola
Angola is divided into 18 provinces (Portuguese: províncias).
- províncias
- munícipios
Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda is divided into six administrative districts (Parishes) and the two secondary areas (Dependencies) Barbuda and Redonda .
- (parishes or dependencies)
Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea is divided into seven provinces , four of which are on the mainland Mbini and two on the island of Bioko .
Argentina
Argentina has 23 states known as provincias . The capital Buenos Aires forms a federal district (Distrito Federal).
- provincia (and the Federal District Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires)
- departamentos (in the province of Buenos Aires partidos , in the federal district of barrios)
- municipios
- localidades
Armenia
Armenia is divided into eleven provinces (marser, singular mars):
- marser
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan is divided into: 59 rayons (Rayonlar; Rayon - Singular), 11 cities (Şəhərlər; Şəhər - Singular) and an Autonomous Republic (Muxtar Respublika).
- rayonlar and saharlar
Ethiopia
Since 1998, Ethiopia has been divided into nine states according to ethnic criteria, the capital Addis Ababa and the city of Dire Dawa (claimed by Oromiyaa and the Somali region).
Australia
Every state and territory (with the exception of Queensland, which has a unicameral system) has a bicameral parliament, which is usually elected by majority voting. Proportional suffrage is only used in Tasmania. The head of the state government is also referred to as the prime minister. The states have exclusive legislative powers over education, health, justice, police, and transportation. In addition to the government and parliament, every federal state also has its own governor as the direct representative of the monarch.
- states and territories
- local government areas, cities, comtés shires, boroughs, towns, areas
B.
Bahamas
The districts of the Bahamas emerged after the country gained independence in 1973. 21 districts were formed, divided into islands and archipelagos.
Bahrain
Bahrain has been divided into four governorates since September 2014. The country had previously been divided into five governorates since July 3, 2002, and before that into 12 municipal districts.
Bangladesh
Bangladesh is divided into eight administrative units (divisions) named after their capital. These in turn are divided into 64 districts.
- Division (Bangladesh) ( bibhag )
- District (Bangladesh) ( zila )
Barbados
Barbados is divided into 11 parishes that have existed since British colonial times.
Belgium
Belgium has been a federal state since 1993, made up of “communities” and “regions” that overlap. Officially, there is no hierarchy between the federal state, communities and regions; every body has jurisdiction over its territory and within its areas of responsibility. In general, the communities are responsible for people and culture, the regions for economy and territorial matters, and the federal state for the remaining competencies (army, justice, social security, etc.).
- 3 communities : Flemish Community , French Community and German-speaking Community .
- 3 regions : Flemish Region , Wallonia Region and Brussels-Capital Region .
The territory of the three regions is mainly divided by the 10 provinces (which are not regarded as part of the Belgian federal state) and 43 districts (which are only administrative units and not local authorities).
Belize
Belize is divided into six provinces .
Benin
Benins is divided into twelve departments. The departments are divided into 77 communes, which in turn are divided into arrondissements and finally into villages or urban districts.
Bhutan
Bhutan is divided into four administrative regions (dzongdey), which in turn are divided into a total of 20 districts (dzongkhag). With the exception of the Bumthang district (capital Jakar), these have been named after their capitals. Some large dzongkhags are further divided into circles (dungkhag). At the lowest level, the districts are divided into groups of villages called Gewogs.
Bolivia
Bolivia is divided into nine departments. The departments are administered by a prefect (prefecto) who was previously appointed by the president, but who has been elected by the people since 2005 as a concession to aspirations for autonomy. The departments are in turn divided into a total of 112 provinces (provincias), each of which is administered by an appointed sub-prefect (subprefecto). The provinces are in turn subdivided into 324 Municipios.
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Since the Dayton Treaty (also known as the Dayton Peace Agreement ), i.e. since 1995 , Bosnia and Herzegovina has consisted of two entities : the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina ( Federacija Bosne i Hercegovine , also known as the Bosniak-Croatian Federation ) and the Republika Srpska ( Serbian Republic ). The Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina is made up of ten cantons, each of which has considerable powers of their own. The district around the northern Bosnian town of Brčko is directly subordinate to the state as a condominium for both entities.
Botswana
Botswana is divided into ten districts and six cities.
Brazil
Brazil is divided into 26 states and one federal district (Distrito Federal). These are statistically divided into five regions.
Brunei
Brunei is divided into four administrative districts. The four districts are in turn divided into 38 mukims.
Bulgaria
The Bulgarian central state consists of 28 administrative districts (oblasts).
Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso is divided into 13 regions (régions), each of which is administered by a governor. These regions are divided into 45 provinces, which are headed by high commissioners. This includes 350 departments (départements) administered by prefects, which are congruent with the communes (communes urbaines and communes rurales) created as part of the decentralization measures.
Burundi
Burundi is divided into 17 provinces named after their capitals. Bujumbura is the capital of the provinces of Bujumbura Mairie and Bujumbura Rural. The provinces are divided into 129 districts (communes), these in turn are divided into collines (hills).
C.
Chile
Chile is divided into 16 regions, mostly numbered from north to south with Roman numerals (Spanish región) and a capital region, which, however, only play a minor political role, since Chile is a pronounced central state. The 56 provinces are located under the regions.
China
The People's Republic of China is administratively divided into 22 provinces, 5 autonomous areas, 4 cities under the government and the Hong Kong and Macau Special Administrative Areas. In addition, the Chinese leadership regards Taiwan as a “renegade” province of the People's Republic, but the island has never come under its rule since the People's Republic was founded in 1949. Provinces and autonomous areas are composed of prefectures and cities at the prefectural level, which in turn consist of counties and cities at the county level.
Costa Rica
Costa Rica is divided into 7 provinces (provincias).
Cote d'Ivoire
The Ivory Coast (French: Côte d'Ivoire) is divided into 19 regions, which in turn are divided into a total of 58 departments.
D.
Denmark
Since January 1, 2007, the motherland of Denmark has been divided into five regions with a total of 98 municipalities.
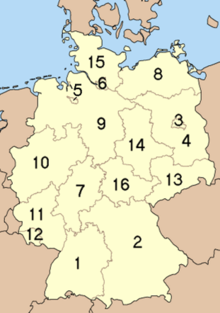
Germany
The Federal Republic of Germany consists of 16 member states , which are referred to as states or federal states, and some of which have different administrative structures.
- Administrative districts : only in North Rhine-Westphalia, Baden-Württemberg, Bavaria and Hesse
- (Land) districts : not in Hamburg, Bremen, Berlin
- Offices : only in Brandenburg, Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania and Schleswig-Holstein
- Local government associations : only in Baden-Württemberg
- Joint municipalities : only in Lower Saxony
- Association communities: only in Rhineland-Palatinate and Saxony-Anhalt
- Administrative associations : only in Saxony
- Administrative communities: only in Bavaria and Thuringia
- Communities
Dominica
Dominica is divided into ten administrative districts ( parishes ).
Dominican Republic
Since July 30, 2004, the country has been divided into ten regions (regiones). These are divided into 31 provinces (provincias) and a national district (distrito nacional), which includes the capital Santo Domingo de Guzmán.
Djibouti
Djibouti is divided into five regions and the capital Djibouti, which has a special status.
E.
Ecuador
For the administration of the state there is a division into 22 provinces ( provincias ), cantons ( cantones ) and Parroquia ( parroquias ); the latter are administrative units under a canton.
El Salvador
The country is divided into 14 provinces (departments):
Eritrea
Since the administrative reform of July 15, 1996, the number of provinces has been reduced to six.
Estonia
Estonia is divided into 15 districts (Estonian pl. Maakonnad, sing. Maakond).
F.
Fiji
Fiji is divided into four divisions and the protected area (dependency) Rotuma with the capital Ahau. The divisions are divided into 14 provinces.
Finland
There are six provinces ( lääni ) in Finland as subdivisions of public administration : Åland, Lapland, Eastern Finland, Oulu, Southern Finland and Western Finland. The provincial administrations are subordinate to the ministries of the State Council in their respective tasks. The provinces are divided into 20 landscapes ( maakunta ), which are based on the historical landscapes from the Swedish era and therefore, in contrast to the provinces, have a traditional regional identity.
France
France is divided into 18 regions (27 regions by 2016), which in turn are subdivided into 101 départements; Departments are divided into arrondissements (333) and these into cantons (2054 constituencies for the departmental council). Of the 18 regions, 13 are in the European heartland (France métropolitaine), including the Mediterranean island of Corsica. The other five regions each consist of only one department and are therefore called overseas departments (Départements et régions d'outre-mer , DROM) . The approximately 35,000 municipalities (communes) are the lowest level of self-government.
G
Gabon
The state of Gabon is divided into nine provinces.
Gambia
The state of Gambia is divided into six divisions.
Georgia
The administration of Georgia is highly centralized. It is divided at the upper level into nine regions (Georgian მხარები, mcharebi, singular mchare), two autonomous republics (Georgian ავტონომიური რესპუბლიკა, awtonomiuri respubliki, singular awtonom respublika) and the capital.
Ghana
The West African state of Ghana is politically divided into 16 regions, each headed by a "Regional Minister" and its own regional court. The regions are in turn divided into districts.
Grenada
Grenada is divided into six administrative districts (Parishes) and the secondary area (Dependency) Carriacou.
Greece
The political structure of Greece has four administrative levels. The state of Greece is divided into 13 administrative regions (Greek diikitikés perifériës / διοικητικές περιφέρειες, singular diikitikí periféria / διοικητική περιφέρεια, περιφέρεια), and fourμοιφέρεια, and fourμομgíς (Greek. nomarchía / νομαρχία, these are divided into Attica, which is an administrative region and a prefecture at the same time). The administrative regions, headed by a general secretary appointed by the national government, serve the administration of national affairs, the prefectures and prefectural districts of Attica have had a prefect and a directly elected prefectural council since 1994, which deals with regional issues. In terms of size, the Greek prefectures are roughly comparable to German districts. Outside of the actual administrative structure is Mount Athos (Άγιον Όρος / Ágion Óros - "Holy Mountain").
Guatemala
Guatemala is divided into 22 departments.
Guinea
Guinea is divided into eight regions and these are divided into 33 prefectures and the Conakry special zone. Unofficially, there is also a subdivision into the regions of Lower Guinea, Upper Guinea, Fouta Djalon (Central Guinea) and Forest Guinea.
Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau is divided into eight regions and an autonomous sector around the capital Bissau. The regions are in turn divided into 37 sectors. For the regions, the respective name of the capital was given in brackets, the sectors are named after their respective capitals.
Guyana
Guyana is divided into ten regions.
H
Haiti
Haiti is divided into ten departments. The departments are divided into arrondissements.
Honduras
Honduras is divided into 18 administrative districts (Departamentos).
I.
India
When the states were reorganized, the respective native language of the residents was used as the basis for drawing the boundaries.
- 28 states
- 8 Union Territories
Indonesia
Indonesia is currently administratively divided into 34 parts, including 31 provinces, 2 special regions and the capital district (daerah khusus ibukota) Jakarta. Recently, some new provinces have been separated from existing ones (around 2003 Irian Jaya Barat and 2004 Sulawesi Barat). The Indonesian government is planning to establish further new provinces. One level below the provinces there are 357 administrative districts.
Iran
Iran is divided into 31 provinces.
Iraq
Iraq is divided into 19 governorates (muhafazat, singular muhafaza).
Ireland
Ireland consists of 4 provinces (Connacht, Leinster, Munster, Ulster), which are again split into districts (counties). In this form, however, these provinces no longer have any significance for the administration of the state. They have grown historically and only play a role in sport since this is organized on a communal basis in Ireland.
Iceland
Politically Iceland is divided into eight regions: Höfuðborgarsvæðið, Suðurnes, Vesturland, Vestfirðir, Norðurland vestra, Norðurland eystra, Austurland and Suðurland. The eight regions are (traditionally, but not administratively) divided into 23 sýslur (Syssel, about counties) and 20 independent municipalities (eight kaupstaðir, seven bæir, one borg and four others).
Israel
Israel is divided into six districts (Mechosot). Center, Haifa, Jerusalem, North, South and Tel Aviv. The administration of the districts is coordinated by the Ministry of the Interior. The Minister of Defense is responsible for the administration of the occupied territories.
Italy
Italy is politically divided into 20 regions (regioni), each with its own government. These regions are divided into a total of 108 provinces (province) and these are divided into about 8,100 municipalities. Five regions have a special statute (statuto speciale) that grants them great autonomy.
J
Jamaica
Jamaica consists of three counties (counties), which in turn are divided into a total of 14 historically grown parishes (districts).
Japan
Japan today has two administrative levels below the central government:
- the 47 prefectures ( to-dō-fu-ken ) and
- the communities ( shi - ku - chō - son ).
They are self-governing local authorities within the meaning of Chapter 8 of the Constitution and the "Law on Local Self-Government" ( chihō-jichi-hō ).
In addition, there are a number of other classifications that are not or no longer administrative units.
- The ancient provinces ( kuni ) and medieval fiefs ( Han ) divided Japan into the 19th century. The provinces were combined into "regions and roads" ( dō ) along important traffic routes .
- The modern regions ( chihō ) combine several prefectures and partly tie in with the dō structure . Some of them are used for joint institutions and administrative cooperation. Various drafts of a special department at the Prime Minister provide for the introduction of a new administrative structure from 9 to 13 regions ( dō-shū ).
- The counties ( gun ) are also of premodern origin. Until 1921 they formed an administrative level between prefectures and rural communities.
- Districts ( ku ) divided 20 "cities by government decree" ( Seirei shitei toshi ), but in contrast to the above Ku Tokyo Metropolitan any communities.
Yemen
Yemen is divided into 21 governorates and a capital district.
Jordan
Jordan is divided into twelve governorates.
K
Cambodia
Cambodia is divided into 24 provinces (Khet) and one province-free city (Krung). The provinces continue to consist of districts (Srok) and municipalities (Khum), the cities of urban districts (Khan) and districts (Sangkat).
Cameroon
Cameroon is divided into ten provinces.
Canada
Canada is divided into ten provinces and three territories. The difference between Canadian provinces and territories is that the provinces are administered by their own provincial governments, while the territories are under more direct control by the federal organs. The provinces manage themselves largely independently, and their parliaments pass their own laws.
Cape Verde
Administratively, Cape Verde is divided into 17 districts (concelhos, singular concelho).
Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan is divided into 14 regions (regions, Kazakh. Oblys, plural Oblystar) and three cities with special status (Kazakh. Qala).
Qatar
Qatar is divided into five regions.
Kenya
The state of Kenya is divided into seven provinces and a capital district.
Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan is divided into 7 areas (kyrgyz. Область / oblast, pl. Областтар / oblasttar) and they are not part of any urban district (шаар / schaar, German city) Bishkek and Osh. The areas are in turn divided into 40 districts (район / rajon, pl. Райондор / rajondor). The city of Bishkek is divided into 4 districts. The districts in turn are subdivided into a total of 473 rural local administrations (айыл өкмөтү / ajyl Ökmötü, German village government) and 22 cities.
Kiribati
The island state is characterized by a system of large local self-government due to the great differences between the individual island groups. The island of Banaba, whose inhabitants are under minority protection, enjoys a special status.
Colombia
Colombia is politically divided into 32 departments and a federal district with the capital (Distrito Capital). Each department has a governor (gobernador) and a departmental council (Asamblea Departamental) who are elected by the people every four years. The departments are further divided into municipalities (Municipios) or municipality-like administrative units (Corregimientos Departamentales abbreviated: CD), which are governed by a people-elected mayor (Alcalde) and a municipal council (Consejo Municipal). There are also four districts (Distritos), also with a mayor and a district council (Consejo Distrital). Bogotá is an exception as a federal district and is still dependent on the Department of Cundinamarca.
Comoros
According to the 2001 Constitution, the Comoros are a Federal Republic.
Congo, Democratic Republic
The Democratic Republic of the Congo is divided into 25 provinces and a capital district (neutral city, French Ville neutre).
Congo, Republic
The Republic of the Congo is divided into twelve departments.
Croatia
Croatia is divided into 20 counties and the capital Zagreb.
Cuba
Cuba is divided into 14 provinces and the Isla de la Juventud Special Administrative Region.
Kuwait
Kuwait is divided into six governorates.
L.
Laos
Laos is divided into 17 provinces (khoueng) and one prefecture (kampheng nakhon). This is followed by a subdivision into around 140 districts and over 11,000 parishes.
Lesotho
Lesotho is divided into ten districts.
Latvia
Latvia is divided into 26 rajoni (Latvian pl., Sing .: rajons). The status of a "rajon" corresponds roughly to that of the typical district in Germany. Seven cities have a special status, and Latvia is divided into five administrative units. Article 3 of the Constitution of Latvia lists four administrative areas that make up the Latvian state territory: Kurzeme ( German : Courland ), Vidzeme , which is the southern part of historical Livonia , as well as Latgale (German: Latgallen ) and Zemgale (German: Zemgals ).
Lebanon
Lebanon is divided into governorates made up of a total of 25 districts. The decision from 2003 to create two more governorates in addition to the six existing ones has been implemented since 2014.
Liberia
Liberia is divided into 15 regions (counties).
Libya
There are currently 22 municipalities in Libya. The Arabic term for a Libyan administrative unit is Schaʿbiyya (plural Schaʿbiyyāt). Until the mid-1980s, Libya was divided into governorates.
Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein is divided into eleven municipalities, which are divided between the two constituencies Unterland and Oberland.
Lithuania
Lithuania consists of 10 administrative districts (lit .: apskritis) The level below are already the 60 self-governing communities.
- see the administrative division of Lithuania .
Luxembourg
The country is divided into twelve cantons and 105 communes. Twelve of these parishes have city status. The municipalities are self-governing bodies which, however, are subject to the legal supervision of the district commissioners appointed by the Grand Duke.
M.
Madagascar
Madagascar is divided into six autonomous provinces (faritany mizakatena), which in turn are divided into 22 regions. Each region is in turn subdivided into circles (fivondronana), of which there are 111 in total.
Malawi
Malawi is divided into three regions (central region, northern region, southern region): The regions are in turn divided into 27 districts, these in turn into 137 chief areas and 68 sub-chief areas.
Malaysia
The Southeast Asian state of Malaysia is divided into 13 states (negeri) and 3 federal territories (Wilayah Persekutuan).
Maldives
The 26 atolls of the Maldives with a total of 1,192 islands are divided into 19 districts ( administrative atolls ) and two cities. They are administered by the atoll chiefs who are appointed by the president. The district around the capital Malé is under direct government administration.
Mali
The state is divided into ten regions and the capital district.
Malta
Since 1993 Malta has been divided into 68 municipalities. For statistical purposes, the municipalities are grouped into six districts (Gozo and Comino, Northern, Northern Harbor, South Eastern, Southern Harbor, Western) and these in turn into three regions (Gozo and Comino, Malta Majjistral, Malta Xlokk). The regions and districts of Gozo and Comino are identical.
Morocco
In 1997, the provinces were merged into regions as part of a decentralization program. At the head of each region is a governor appointed by the king.
Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands consist of two almost parallel chains of islands or atolls.
Mauritania
Mauritania is divided into 12 regions and the capital district.
Mauritius
The island of Mauritius is divided into 9 districts.
Mexico
Mexico consists of 31 states (Estados), each headed by a governor, and the capital Mexico City. The states are divided into Municipios and the capital into 16 Delegaciones.
Micronesia
The island area of Micronesia consists not only of one country, but of several independent countries that were once part of the Pacific Islands Trust Area .
Four Micronesian archipelagos - Yap , Chuuk , Pohnpei and Kosrae - form the Federated States of Micronesia as federal states .
Moldova
The area of Moldova is divided into 5 municipalities (Municipalități; Singular Municipiu) and 32 districts (Raioane; Raion). There is also an autonomous and a renegade area.
Monaco
The distinction between the state and the city of Monaco is purely theoretical, the state consists de facto only of the city (municipality). According to the constitution of 1911, the principality was originally divided into three municipalities: Monaco (Monaco-Ville, Old Town with Prince's Palace), Monte Carlo (northeast) and La Condamine (west and northwest with port area). The reproach to the princely power to proceed according to the motto “divide and rule” led to the fact that in 1917 the three communities were combined into one community. The original communities were henceforth considered to be urban districts (quarters). This means that the principality is currently divided into 10 districts (official numbering; the Le Portier district, which is planned through land reclamation, is anticipated as No. 11). The city districts are subdivided into 173 blocks (îlots) for statistical purposes.
Mongolia
Mongolia is divided into 21 aimags (provinces) and the capital Ulan Bator, which forms an independent administrative unit. The latter also applied to the city of Erdenet until 1994. From this, however, the Orkhon Aimag was created in 1994 together with some Sum des Bulgan Aimags. Likewise the city of Darchan, for which the Darchan-Uul-Aimag was spun off as an enclave from the Selenge-Aimag. Each aimag is divided into a number of sums (comparable to the German districts), these in turn into bags (comparable to our municipalities). There are 329 sums, which are divided into 1,620 bags. A bag often does not exist as a permanent settlement, as its members all move around as nomads.
Montenegro
Montenegro is divided into 21 (large) municipalities (opštine, Sg. Opština), with Nikšić being the largest by area and Podgorica by population.
Mozambique
Mozambique is divided into 10 provinces and the capital district.
Myanmar
Myanmar is divided into seven states, seven regions and a union territory around the capital of the country. The parts of the country that are predominantly populated by the largest ethnic group in Myanmar, the Bamar, are called the region (division until 2008), the areas that are predominantly inhabited by minorities are called the state.
States and divisions are further subdivided into districts and parishes.
N
Namibia
Namibia is divided into 14 regions with a total of 121 constituencies . There are also municipalities, municipalities, towns, villages and settlements.
Nauru
The state of Nauru is divided into 14 districts. In addition to the area and population, the number of historical villages that exist today is given for each district. T. are uninhabited or destroyed. The districts do not play a major role. The borders are the former borders of the former Gaue, which until 1968 consisted of a few villages; these in turn are made up of properties that were owned by families and are still today.
Nepal
Nepal is divided into seven provinces, these consist of 77 districts (जिल्ला, "jilla").
New Zealand
Compared to the federally structured Australia, New Zealand is very centralized. Since a major administrative reform in 1989, there have generally been two levels of administrative structure, which, however, can only decide on a few departments. The first stage are the regions (English Regional Councils); the second level is represented by the districts, which are either referred to as City Council (ie “City Council”), District Council (ie “Council of the District”) or - in the case of the Chatham Islands - as Islands Council (ie “Island Council”). Four of the 16 regions as well as the Chatham Islands are also responsible for the tasks of a district, these are referred to as unitary authorities. Officially, the districts act independently of the regions, so it also happens that a district is located in several regions. Numerous smaller outer areas of the country, such as the Kermadec Islands and the Sub-Antarctic Islands belonging to New Zealand, are administratively directly subordinate to the Minister of Local Government.
Nicaragua
Nicaragua is divided into 15 administrative districts (Departamentos) and two autonomous regions (Comunidades Autónomas). The departments are in turn subdivided into Municipios.
Netherlands
Since January 1, 1986, the Netherlands has been divided into 12 provinces (Dutch: provincies). The provinces in turn are divided into 443 parishes (gemeenten). There are no other regional classifications (such as the districts in Germany). At the head of a province there is a commissaris van de Koningin (commissioner of the queen).
Niger
Niger consists of seven regions and the capital Niamey, which has the rank of a region. The seven regions are divided into 36 departments, which in turn are divided into urban and rural communities.
Nigeria
Nigeria has been divided into states since 1967. In several reforms, the number of states has been increased from twelve to 36 today (since 1996). Before the reorganization in 1967, Nigeria was divided into regions, before independence in 1960 it was divided into provinces. In addition to the federal states, there is the Federal Capital Territory (FCT) around Abuja. On the second level, the states are divided into a total of 774 Local Government Areas (LGA).
North Korea
North Korea is divided into nine provinces and three “special administrative regions”. Two cities are administered directly by the government.
North Macedonia
A new territorial administration law has been in force since August 11, 2004, dividing the state of North Macedonia into 84 municipalities (opštini). The previous 123 municipalities were partially merged, but in the greater Skopje area the previous 8 municipalities were increased to 10.
Norway
The country is divided into 19 administrative provinces ( Fylker ), which are grouped into five statistical regions (landsdel, German part of the country). The smallest province by area is the capital Oslo. As of January 1, 2006, there are 431 municipalities in Norway. In addition to the administrative regions, there are other statistical regions that are not necessarily aligned with provincial borders. Efforts are being made towards an administrative reform with the creation of seven regions, which also includes an enlarged capital region around Oslo.
O
Oman
Oman is divided into eleven governorates (mintaqa), which in turn are subdivided into districts (wilayat, so-called wilaya).
Austria
Austria consists of nine federal states, with Vienna as the federal capital. The other eight countries are divided into 84 districts, which are in turn subdivided into municipalities, as well as 15 statutory cities, which exercise the district administration themselves.
East Timor
East Timor is divided into 13 administrative parishes. These are divided into a total of 65 administrative offices, 442 sucos and 2,225 villages. The island of Atauro belongs to the municipality of Dili , the island of Jaco to the municipality of Lautém . In 2003 the sucos were reorganized and some national borders were moved.
P
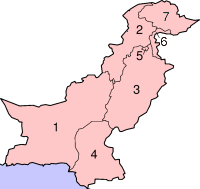
Pakistan
Pakistan is a federal state according to the constitution . It is divided into the four provinces of Balochistan , Khyber Pakhtunkhwa , Punjab and Sindh , each of which has a provincial assembly (Pronvincial Assembly) elected directly by the people for five years . The head of government is the chief minister , who is elected by the provincial assembly and is generally the chairman of the party that forms the largest parliamentary group. However, the chief minister in each province is headed by a governor appointed by the president who, after consulting the president, can dissolve the provincial assembly and form a transitional government.
The capital territory of Islamabad and the tribal areas under federal administration on the border with Afghanistan, which were dissolved in 2018, are or were directly administered by the Pakistani central government, as is the Pakistani-occupied area of Gilgit-Baltistan of the Kashmir region claimed by India . The latter also includes the semi-autonomous Asad Kashmir region , which has its own legislative assembly , a prime minister and a president.
Each administrative unit is divided into districts. The capital territory forms its own district. There are a total of 119 districts in Pakistan, 14 of them in the occupied part of Kashmir. The tribal areas under federal administration are an exception.
Palestinian Territories
The Palestinian Autonomous Areas or the State of Palestine are divided into 16 governorates, five of which are in the Gaza Strip and eleven in the West Bank.
Palau
Palau is divided into 16 administrative states.
Panama
Panama is administratively divided into ten provinces (provincias) and five territories (comarcas), three of which are provincial. In the autonomous territories there is a self-government of the three indigenous ethnic groups Kuna , Ngöbe-Buglé and Emberá-Wounaan .
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea is divided into twenty provinces, one autonomous region and the capital district, the National Capital District. In general, a distinction is made between coastal provinces, highland provinces and island provinces. In addition, the provinces that are in the former mandate of the former German colony of New Guinea can be separated from those of the Australian Papua.
Paraguay
Paraguay consists of 18 administrative regions (departamentos).
Peru
Peru is divided into 24 departments, 195 provinces (Provincias) and 1,828 districts (Distritos). Since the country was regionalized in 2002, the departments have been self-governing units with directly elected bodies. The first national regional elections took place in November 2002. The division of the country into regions (regions) was also planned. In a referendum on October 30, 2005, 78 percent of the population of 16 departments voted against merging them into five regions (Norte, Nor Centro Oriente, Ica-Huancavelica-Ayacucho, Cusco-Apurímac and Arequipa-Puno-Tacna).
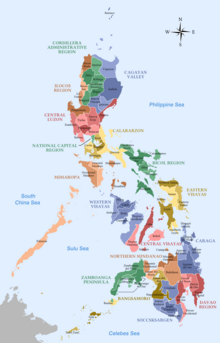
Philippines
The Philippines are hierarchically structured as follows: The lowest administrative level is the barangay . Barangays form towns and cities. The next higher level are the 81 provinces (as of 2018) of the country. These in turn are grouped into 17 districts to simplify administration. Each province is headed by a governor and a lieutenant governor; whereas each city and municipality is headed by a mayor and a city council. Most district government offices have regional offices to support each province. With the exception of the autonomous Muslim districts of Mindanao and Cordillera , the districts do not have their own government like the provinces and cities.
Poland
Since January 1st, 1999 Poland has been divided into 16 voivodeships . They all have their own parliament, a head (voivoda) appointed by the central government, who manages the finances allocated to the voivodships by the central government in Warsaw, and a voivodship marshal (Marszalek) elected by the parliament, who heads a government. The next smaller self-governing unit is the powiat .
Portugal
The relatively small Portugal has a very complex administrative structure. There are five regions, 18 districts and the two autonomous regions of the Azores and Madeira, plus 28 so-called statistical sub-regions. One level below is followed by around 300 districts and 4,200 municipalities. This structure is rather inefficient and expensive, which is why a reform is in progress that will abolish the districts and decentralize competencies.
R.
Rwanda
Since January 1, 2006, Rwanda has been divided into five provinces. Before that, Rwanda was divided into twelve provinces.
Romania
Romania is currently divided into 41 districts ("județ", Pl .: "județe") and a capital (Bucharest = București). This administrative division was made in the 19th century based on the model of the French departments. After 1950, this structure was abandoned in favor of the Soviet model; In 1968, however, the old system that is still in force today was reintroduced. In 1981 the districts of Ilfov and Ialomia were reorganized into the districts of Giurgiu, Călărași, Ialomița and Ilfov. Until 1995 Ilfov was not an independent circle, but dependent on Bucharest.
Russia

Article 65 of the Constitution of Russia names the 83 subjects that make up the Russian Federation: 21 republics, 9 regions ( Kraj ), 46 areas ( Oblast ), 2 cities of federal rank ( Moscow and Saint Petersburg ), 1 autonomous region and 4 autonomous counties . In 2000, President Putin created seven federation districts by decree , each of which combines several federation subjects into a larger unit. The aim of this reform was to strengthen the verticals of power and tighten control over the regional rulers. In January 2010, an eighth federal district was formed with the North Caucasus .
S.
St. Kitts and Nevis
St. Kitts and Nevis is divided into 14 administrative districts (parishes).
St. Lucia
From an administrative point of view, St. Lucia is divided into ten quarters (districts) and the “Central Forest Reserve” area in the center of the island, which is subordinate to the government.
Solomon Islands
The Solomon Islands are a group of islands located southeast of New Guinea in the South Pacific, which extend from north to southeast for about 1,100 kilometers. The southern islands form the state of the Solomon Islands, which is divided into nine provinces and a capital district. Some northern islands are part of Papua New Guinea.
Zambia
Zambia is divided into nine provinces.
Samoa
Samoa is traditionally divided into 11 political districts (itūmālō), some of which consist of spatially disjointed areas (exclaves). The further subdivision into 41 electoral districts (faipule) is based on these. At the local level, there are about 310 villages, including the 45 or so villages that make up the contiguous urban area of the capital, Apia, the country's only city. Each village is still independent and can and does so freely in internal matters. There is neither a central city administration for Apia, nor municipal administrations of the villages or a registration system.
San Marino
San Marino is divided into nine Castelli, which are also independent municipalities.
Sao Tome and Principe
São Tomé and Príncipe is divided into two provinces, these in turn into seven districts.
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia is divided into 13 provinces (mintaqat, singular - mintaqa), plus two regions that are sovereignly neutral, but belong to the kingdom.
Sweden
Sweden is divided into 21 provinces ( län ). These are seldom congruent with the historical provinces ( landskap ), into which the empire was divided up to 1634 (even if the names sometimes suggest it - only Gotland, Skåne and Blekinge are exceptions).
Switzerland
The 26 cantons of Switzerland are the member states of the Swiss Confederation. Each canton has its own constitution and its own legislative, executive and judicial authorities. The article of the Federal Constitution on which this principle is based reads: “ Art. 3 The cantons are sovereign insofar as their sovereignty is not restricted by the Federal Constitution; they exercise all rights that are not vested in the federal government. “No other country in Europe or North America has such a highly fragmented political subdivision as Switzerland, especially if one also takes into account the relatively large autonomy of the Swiss cantons in international comparison and their small size (1,600 km² on average). Many cantons are divided into districts, which in the cantons of Graubünden and Ticino are also subdivided into districts.
Senegal
Senegal consists of eleven regions (régions), which in turn are divided into a total of 34 departments and 109 districts (circonscriptions).
Serbia
Within Serbia there are the autonomous provinces (Serbian: autonomne pokrajine) Vojvodina and Kosovo (Albanian: Kosova, official Serbian name: Косово и Метохија / Kosovo i Metohija, German: Kosovo and Metochien, as a short form of cosmetics), which from 1974 to 1989 a possessed extensive independence within Serbia and Yugoslavia. Under Slobodan Milošević, the autonomy of the two provinces was downgraded to the status before the constitutional amendment of 1974, which led to protests, especially in Kosovo. Since then, the provincial governments have not been elected, but appointed by the central government. The part of Serbia (more than half of the country) that does not belong to these two provinces does not form a separate political unit, therefore there is no official name for it. The term Central Serbia is used informally . For administrative purposes, Serbia is divided into 30 districts (Serbian: Okrug; pl .: Okruzi) (including the city of Belgrade). 18 districts are located in the narrower Serbia, seven in Vojvodina and five in Kosovo. The local self-government units in Serbia are the opštine (Sg. Opština, literally municipality, often more rural districts in terms of size). Of these, there are 108 in narrower Serbia, 54 in Vojvodina and 30 in Kosovo.
Seychelles
The republic consists of 115 islands and is divided into 32 mountain islands (mainly granite stone), which represent the actual Seychelles, and numerous small coral islands, the so-called Outer Islands.
Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone is divided into the four provinces Northern, North Western, Southern and Eastern as well as the area around the capital Freetown (Western Area). The provinces are in turn divided into a total of 14 districts and these are divided into municipal people areas (chiefdoms).
Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe is divided into eight provinces and two cities with provincial status (the capital Harare and Bulawayo). The provinces are divided into 59 districts and 1,200 parishes. The latter in turn usually consist of several localities.
Singapore
The administrative structure of Singapore includes five Community Development Council (CDC) districts, which are administered by mayors (Mayors) and local councils. This structure is completely incompatible with the regional structure of the state planning.
Slovakia
Slovakia is divided into eight regional associations ("kraj"):
Slovenia
Slovenia is divided into 210 municipalities (Slovene občine, Sg. Občina ), including eleven municipalities. However, the creation of regions is being considered.
Somalia
The country is officially divided into 18 regions. Today, however, this classification has only limited meaning.
Spain
Spain is divided administratively into 17 autonomous communities or regions (Comunidades Autónomas), comparable to the German federal states, and into the two autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla. The autonomous communities themselves are divided into a total of 50 (52 including Ceuta and Melilla) provinces (provincias), almost all of which are named after their respective administrative headquarters.
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka is administratively divided into nine provinces and 25 districts.
St. Vincent and the Grenadines
St. Vincent and the Grenadines are divided into 6 administrative districts (parishes).
South Africa
At the end of apartheid in 1994, the former independent and quasi-independent homelands had to be integrated into the political structure of South Africa. This led to the dissolution of the previous four provinces (Cape Province, Natal, Orange Free State and Transvaal), which were replaced by nine new provinces and which now encompass the entire national territory of South Africa. The provinces are again divided into a total of 52 districts. In the great community reform of 2000, many well-known South African cities were united with their surrounding communities and townships.
Sudan
Sudan is divided into 18 states (wilayat), which are again divided into districts.
South Korea
South Korea is politically divided into a special city, a special autonomous city, six independent major cities, eight provinces and a special autonomous province.
Suriname
Suriname is divided into 10 districts.
Swaziland
Swaziland has four administrative districts (regions), which are divided into 59 Tinkhundla , in which there are several umaphakatsi (English: chiefdom ).
Syria
Since 1987, Syria has been divided into 14 governorates (muhafazat, singular: muhafazah), which are named after the respective capital. The district of Quneitra (Kuneitra) in the Golan Heights has been largely occupied by Israel since 1967. The region around Iskenderūn (Alexandrette), called Sanjak Alexandrette until it was incorporated into Turkey, has belonged to Turkey since 1939, but is also claimed by Syria.
T
Tajikistan
Tajikistan is divided into two provinces (вилоятҳо / wilojatho or ولایتها), an Autonomous Province (вилояти мухтор / wilojati muchtor or ولایت مختار), a district directly administered by the central government (Ноҳияҳои тобеъи ҷумҳурӣ or ناحیههای تابع جمهوری) and the capital Dushanbe, which has a special status (шаҳр / schahr resp. شهر) owns.
Taiwan
The province of Taiwan comprises 11 counties and three independent cities. The cities of Taipei, Kaohsiung, New Taipei, Taichung, Tainan and Taoyuan are not part of the province as cities under government control. The Republic of China in Taiwan also controls two counties in Fujian Province .
Tanzania
Tanzania is divided into 31 administrative regions.
Thailand
The administrative division of Thailand into provinces ( Changwat ) , counties ( Amphoe ) , municipalities ( Tambon ) and villages ( Muban ) took place in 1897 under King Chulalongkorn (Rama V) . However, numerous provinces were later created or changed. The 76 provinces can be grouped into 5 regions: North , Northeast ( Isan ), Central Region , East and South . The assignment of the provinces to the regions is not uniform, so a province can sometimes be assigned to one, sometimes to a neighboring region. The provinces are divided into amphoe, which in turn is divided into tambon and then into muban. The name of a province corresponds to the name of its capital. The amphoe of Bangkok is officially called a khet but is sometimes incorrectly called an amphoe.
Togo
Togo is divided into five regions.
Tonga
Tonga is divided into five administrative units (divisions). The distant islands of Niuatoputapu, Tafahi (Cocos Island) and Niuafo'ou, north of Tongatapu and Vava'u, belong to the Niuas division and are administered from the capital Hihifo on Niuatoputapu.
Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago is divided into two cities, three boroughs, nine regions and a ward.
Chad
Since 2002, Chad has been divided into 18 regions.
Czech Republic
Since 2000 the Czech Republic has been divided into 14 higher self-governing territorial units, which are known as kraj. In older literature, kraj is translated as a circle, while German translations continue to include “districts”, and the term “region”, which most kraje use in their German-language self-portrayal, is also useful. In comparison with Germany there are the kraje between the federal states and the administrative districts (closer to the administrative districts); they are headed by a hejtman (German captain) and have their own parliaments. The establishment of the "kraje" was politically controversial for a long time after the fall of the communist government in 1989 and the current situation was initially often criticized as a failure. It was suggested that the kraje are too small and therefore politically too weak.
Tunisia
Tunisia is divided into 24 governorates, the geographic size of which is adapted to their population.
Turkey
Local government is divided into 81 provinces in Turkey.
- 7 regions according to climatic characteristics
- 81 provinces
Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan is divided into five provinces (welaýatlar, singular welaýat) with around 50 districts.
Tuvalu
In German Tuvalu means "eight islands" because originally only 8 islands were inhabited and had their own island councils (elected representatives). The ninth (and southernmost) island, Niulakita, was not settled until 1949 with residents of the overpopulated island of Niutao. Tuvalu is now divided into eight Falekaupule, Niulakita is part of the Falekaupule Niutao.
U
Uganda
Uganda is divided into more than 120 districts, most of which are named after their main town. These are divided into the four regions of the Eastern, Western, Northern and Central Districts, which are of no particular administrative importance. Since the mid-1990s, the top level of the administrative units, which consisted of ten provinces and was divided into just 38 districts, was replaced by an increasingly smaller division. The previous provinces were Nile, Northern, Karamoja, Western, Eastern, North Buganda, Busoga, Central, Southern, and South Buganda.
Ukraine
Ukraine is divided into 24 oblasts (ukr. Область / oblast, districts, literal areas), the Autonomous Republic of Crimea and two cities with special status.
Hungary
Hungary is divided into 19 counties (counties) and 24 cities with county law (including the capital Budapest). In 1999 the country was divided into seven regions, also to meet the requirements of the European Union . The counties, in turn, are subdivided into small areas that correspond to level LAU-1 in the EU's NUTS system .
Uruguay
Uruguay is divided into 19 historically grown departments (including the autonomous city of Montevideo). The departments are headed by the Intendente Municipal, who is elected by the departmental parliaments (junta departamental). Since the state structure is centralized, the 19 provinces (Departamentos) have little self-government.
Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan is divided into 12 provinces (Uzbek. Viloyat, Pl. Viloyatlar), an autonomous republic (Uzbek. Respublika) and a city (shahar) with provincial rank.
V
Vanuatu
Vanuatu has been divided into six provinces since 1994. Their names are composed of the respective first letters of the corresponding islands.
Vatican state
The Vatican State is not divided into sub-national administrative units.
Venezuela
Venezuela is divided into 23 states, the dependent areas of the Dependencias Federales and the capital district.
United Arab Emirates
Administratively, the UAE is divided into the Emirates Abu Dhabi , Dubai , Sharjah , Ajman , Umm al-Qaiwain , Ra's al-Khaimah and Fujairah , which form the federation .
United States
The political units of the United States include the 50 states, which in turn are divided into counties and townships, cities, villages, and other types of parishes, and other independent or subordinate institutions. The most important political entity in the United States after the federal government is the state. In formal legal terms, the states are not subdivisions of the United States, but rather behave in a unique interplay known as parallel sovereignty. The individual states decentralize their sovereign powers in at least two levels. The first level consists of the state-wide agencies that report directly to the state government. Examples of such authorities are the Department of Motor Vehicles, the Statistics Office or the Health Department. The second level consists of the counties (similar to the German district), which are called "Borough" in Alaska and "Parish" in Louisiana. Counties are administrative districts of the state government. A third tier exists in many of the Midwestern states and is known as townships.
United Kingdom
The territorial division of the United Kingdom has undergone major changes several times since the late 19th century, which in some cases led to completely new administrative districts and later to the dissolution of such districts. Nevertheless, some of the names of the old counties are still used today, even though the place no longer belongs to this county.
England is divided into regions which, apart from Greater London, have no administrative functions. Greater London is divided into the City of London and 32 boroughs . The remaining regions are divided into 27 non-metropolitan counties , 6 metropolitan counties and 56 unitary authorities (single-level administrative districts). The 27 non-metropolitan counties are divided into 201 districts and the 6 metropolitan counties are divided into 36 metropolitan boroughs .
Scotland today consists of 32 unitary authorities, including 3 island districts; there is no administrative level above or below them.
Wales is divided into 22 Unitary Authorities, which, however, have different names due to their history and size, so there are three cities, 10 county boroughs and 9 counties.
In Northern Ireland there are 26 districts with the status of a unitary authority, there are no higher or lower administrative units.
Vietnam
Vietnam is divided into 58 provinces and five cities. Each of these administrative units has a parliament and a government, which, however, are subordinate to the central government.
W.
Belarus
Belarus is divided into six administrative districts (woblasts) with 118 districts (Rajons). The capital Minsk has a special status and does not belong to any of the woblasts.
- See also: Administrative division of Belarus .
Z
Central African Republic
The Central African Republic is divided into 14 prefectures, two economic prefectures (Préfectures économiques) and one autonomous city (Commune autonome).
Cyprus
The authority of the government of the Republic of Cyprus has been limited since 1974 to the southern part of the island, which is dominated by Cyprus-Greek. As a result of the Turkish intervention in 1974, the northern part of the island has formed the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus since 1983, which is not recognized under international law . The Republic of Cyprus is officially divided into six districts.