Feldberg lake landscape
| coat of arms | Germany map | |
|---|---|---|

|
Coordinates: 53 ° 20 ' N , 13 ° 25' E |
|
| Basic data | ||
| State : | Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania | |
| County : | Mecklenburg Lake District | |
| Height : | 135 m above sea level NHN | |
| Area : | 199.59 km 2 | |
| Residents: | 4407 (Dec. 31, 2019) | |
| Population density : | 22 inhabitants per km 2 | |
| Postal code : | 17258 | |
| Primaries : | 03964, 039820, 039831, 039882 | |
| License plate : | MSE, AT, DM, MC, MST, MÜR, NZ, RM, WRN | |
| Community key : | 13 0 71 033 | |
| Address of the municipal administration: |
Prenzlauer Straße 2 17258 Feldberger Seenlandschaft |
|
| Website : | ||
| Mayoress : | Constance von Buchwaldt ( SPD ) | |
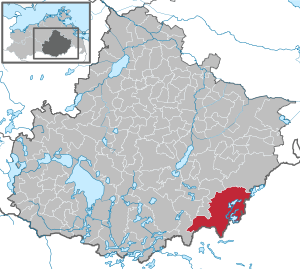
| Location of the municipality of Feldberger Seenlandschaft in the Mecklenburg Lake District | ||
The office free community field Seenlandschaft is located in the southeast of the district Mecklenburg Lake in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. It is shaped by tourism and forms a basic center for its surroundings . Historically, it is part of the Mecklenburg-Strelitz cultural region .
The district of Feldberg has been certified as a Kneipp spa since October 2015. The districts of Carwitz , Fürstenhagen, Lichtenberg, Schlicht, Waldsee and Wittenhagen are state-approved resorts .
geography
Geographical location

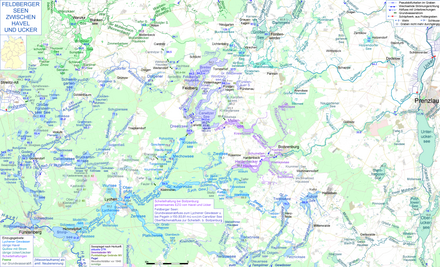
With almost 200 km², the community is the largest in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. It is located in the southeast of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania on the state border with Brandenburg . The name refers to the former town of Feldberg and the numerous lakes in this area, which lies between the Mecklenburg Lake District and the Uckermark Lakes . The largest of the lakes in the municipality are Carwitzer See , Breiter Luzin , Zansen , Schmaler Luzin , Feldberger Haussee , Dreetzsee , Dolgener See and Krüselinsee .
The state border with Brandenburg runs along the Bibelsee , the south bank of the Carwitzer See, the east bank of the Dreetzsee as well as the Krüselinsee, the Küstriner Bach , the Kleiner Mechowsee and the Großer Mechowsee . The area belongs to the terminal moraine of the Pomeranian stage of the Vistula Ice Age . With the bird cherry (north of the latitude Luzin) a height of 166.2 m above sea level. Reached NHN . The community is located in the Feldberger Seenlandschaft nature park . The district of Waldsee is located in the easternmost part of the Müritz National Park .
The municipality of Feldberger Seenlandschaft is surrounded by the neighboring municipalities Möllenbeck in the north, Woldegk in the northeast, Nordwestuckermark in the east, Boitzenburger Land in the southeast, Lychen in the south, Wokuhl-Dabelow in the southwest and Carpin and Grünow in the west.
Community structure
The districts of the municipality are:
|
|
|
|
|
history
On June 13, 1999, the city of Feldberg and the communities of Conow, Dolgen, Lichtenberg and Lüttenhagen merged to form the new community of Feldberger Seenlandschaft.
History of the districts
From 1701, today's districts of the Feldberger Seenlandschaft belonged to the partial duchy, partial grand duchy and Free State of Mecklenburg-Strelitz until its reunification with the Mecklenburg-Schwerin part of the country in 1934.
Carwitz:
Dolgen
During mowing work in August 2009 several holes over five meters deep were discovered in fields near Dolgen. After geological investigations it turned out that these were geological exploration wells from the 1970s, which were carried out in preparation for the Feldberg 1/87 well. This well was used to search for oil and / or natural gas and had a depth of 4920 m.
Feldberg:
Krumbeck was partially owned by the Himmelpfort monastery from 1313 and completely from 1317 and later became a Brandenburg exclave in Mecklenburg-Strelitz. The von Dewitz family had owned the estate since 1797 . In 1811 the estate came to Mecklenburg-Strelitz. Its owners were incorporated into the knighthood in 1825 .
Plain was the domain . Landlord was u. a. August Weißenborn, who had the manor built around 1880. Not far from the manor house are the remains of the fixed house (tower hill) "Maledei" .
Tornowhof was established in 1730 as a dairy from Wittenhagen. In 1870 this was built as an independent estate and the two-story manor house, connected to a one-story administrator's house.
Waldsee was in half-timbered style as a hunting lodge for Erbgroßherzog 1900 Adolf Friedrich V. built. From 1933 the hunting lodge was used by Reichsstatthalter and Gauleiter Friedrich Hildebrandt . Since 1952 it has been the apprenticeship home of the Neustrelitz forestry company. Today it is a hunting hotel.
Weitendorf was a princely farm after 1648 . The manor house dates from 1908 and was after 1947 a. a. School with teacher's apartment and kindergarten.
Wendorf was a manor village with many different owners. The manor house dates from 1857 and was the seat of LPG and consumption after 1958 .
Wittenhagen : The landowner was u. a. from 1506 to 1796 the von Tornow family , followed by the von Rhade family until 1838 . In 1758 a church was built. The classical manor house dates from around 1800.
The former village of Krüselin, located in today's municipal area , has been desolate since 1945.
Population development
|
|
Status: December 31 of the respective year
politics
Community representation
The municipal council consists of 15 members and the mayor. They have been distributed as follows since the local elections on May 26, 2019 :
| Party / list | Seats | Share of votes |
| CDU | 5 | 36.8% |
| SPD | 3 | 20.8% |
| The left | 2 | 13.0% |
| Free voters Feldberger Seenlandschaft | 2 | 10.5% |
| Dolgen voter community | 1 | 8.2% |
| Single applicant Benita customer | 1 | 5.1% |
| Alliance 90 / The Greens | 1 | 4.4% |
| Single applicant Tino Dec | - | 1.2% |
| total | 15th | 100% |
mayor
- since 2009: Constance Lindheimer (SPD), since her marriage in 2019 Constance von Buchwaldt
Lindheimer was elected in the mayoral election on September 24, 2017 with 54.6 percent of the valid votes for a further term of eight years.
coat of arms
|
Blazon : "In silver over a blue shield base, in it three silver waves one above the other, a red wall with a tinned red tower between two battlements, the tower with a square black window."
The coat of arms was made after a suggestion by Dr. Hans Witte designed the main archive in Neustrelitz and adopted it in 1928. It was approved on September 17, 2013 by the Ministry of the Interior and registered under the number 347 of the coat of arms of the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. |
|
|
Justification of the coat of arms: The coat of arms was already adopted in 1928 by the then city of Feldberg and registered under number 43 of the coat of arms of the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. This coat of arms was used as a national emblem by the dissolved city of Feldberg until June 12, 1999. Thus, the coat of arms adopted in 1928 initially lost its status as a national emblem on June 13, 1999 due to the municipal merger. Since its symbolism and tinging are also representative for the new municipality and there is the possibility of continuing the former emblem of a municipality that has merged into it, the previous emblem of Feldberg became the new municipal emblem of Feldberger Seenlandschaft.
In the coat of arms, the base of the shield should be used to indicate the lake-rich surroundings. The wall with the tin tower is reminiscent of the castle of the Veldberghe family, which was built to protect the Mecklenburg border against the Uckermark. This castle, of whose tower only a stump remains today, was the official seat until the 18th century. The town of Feldberg owes its name to the Veldberghe family. |
flag
The municipality does not have an officially approved flag .
Official seal
The official seal shows the coat of arms of the municipal coat of arms with the inscription "GEMEINDE FELDBERGER SEENLANDSCHAFT".
Sights and culture
Buildings
- Carwitz
- Hans Fallada House, residence of Hans Fallada from 1933 to 1945
- Village church from 1706, towerless half-timbered building with pulpit altar from 1714
- Cantnitz
- Village church from the second half of the 13th century, Gothic brick building
- Feldberg
- Feldberg castle wall , remains of a Slavic hill fort from the 9th century
- Former office building / Drostenhaus; 1781 as a two-story half-timbered building over the remains of a castle from the 13th / 14th. Erected in the 14th century, of which a tower stump is still preserved
- Spritzenhaus / Heimatstube from the 19th century based on designs by Friedrich Wilhelm Dunkelberg
- City church from 1872/75, neo-Gothic brick basilica
- Krumbeck
- Lennépark (to the mansion belonging), according to plans by 1832 from Peter Joseph Lenne created
- Manor house from after 1858, single-storey with a mansard roof and two-storey tower as well as company buildings, owned by the von Dewitz family from 1797 to 1945 and since 1996
- Village church from the 14th century, stone building with west tower from 1785, upper part massively renovated after a lightning strike in 1928
- Lichtenberg
- Village church from the 14th century, plastered stone building
- Former mansion in Renaissance style from the 19th century
- Laeven
- Manor house of the domain's independent dairy from 1724, two-storey with six gables from 1924/25
- Lüttenhagen
- Forest and wood museum
- Oak in the cemetery with a chest height circumference of 7.67 m (2016)
- Mechow
- Village church , stone building from the second half of the 13th century
- Simple
- Remains of a tower hill with a permanent house "Maledei"
- Triepkendorf
- Village church from the 13th century, field stone building with half-timbered tower from 1769
- Forest lake
- Waldsee hunting lodge , built in 1901 for the Mecklenburg-Strelitz Grand Duke Friedrich Wilhelm II.
- Wendorf
- Manor house with manor, built in 1856 by F. Menke (based on the building plans of the court architect Friedrich Wilhelm Buttel) as an independent work on the parent house in the Lichtenberg district
- Wittenhagen
- Village church from 1758, octagonal central building with tent roof
- Manor house, classical complex with mansard roof
- Luzin Theater, private theater with 45 seats
- Waking
- Village church, towerless half-timbered building from the 19th century
- Classicist mansion by Friedrich Wilhelm Buttel from 1840
Church in Mechow
Events
In 1965 the Feldberger Carnival Club (FKK) was founded, the first president was Johannes Huebner ("Hannes the Heavenly Dog"). The carnival initially took place in Carwitz and in the Hotel Hullerbusch before the event established itself in Feldberg. There the battle cry "Schlaewitzberg Huneu" arose, which stands for the districts (Schlicht, Laeven, Carwitz, Feldberg, Hullerbusch, Neuhof). There are over 100 members and a children's dance group with around 30 children, the Waldhotel Stieglitzenkrug has been the parent company since the 2000s. In Feldberg there is also its own Rose Monday parade , which is a specialty for Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.
Economy and Infrastructure
economy
In 1855 August Friedrich Erfurth (around 1820–1904) opened a hydrotherapy institute in Feldberg . Since then there has been a spa in Feldberg. In 1998 the rehabilitation clinic at Haussee was opened with 235 beds, a clinic with the departments of cardiology, neurology, orthopedics, psychosomatics and medical wellness. The clinic is a certified MS center. Also in 1998 the Luzin Clinic was opened as a specialist clinic for addictions with 52 places. It treats both alcohol and drug addiction.
traffic
The municipality of Feldberger Seenlandschaft is located on the L 34 state road between Möllenbeck (on the B 198 Neustrelitz - Woldegk federal road ), Feldberg and the state border with Brandenburg south of the Conow district and on the L 341, which connects the Triepkendorf, Feldberg and Schönhof districts.
The community has no rail connection. Until May 28, 2000, there was a connection over the railway line Neustrelitz South Feldberg with the breakpoints Dolgen (Meckl) , Weitendorf (b Feldberg) (until 1995) and the railway station Feldberg (Meckl) . In November 2000, trains ran again to mark the 90th anniversary of the line, but it was shut down on December 22, 2000. In 2005 the company ELS Eisenbahn Logistik und Service acquired the route, until 2015 occasional special trips were offered.
education
- Hans Fallada School Feldberg, Bahnhofstrasse 5
Personalities
Sons and daughters of today's districts
Carwitz
- Wilhelm Moldenhauer (1845–1898), physician and university professor
Feldberg
- Karl von Engel (1826–1896), court and administrative clerk in the (partial) grand duchy of Mecklenburg-Strelitz
- Horst Stolt (* 1933), politician (SPD)
- Wolf-Dieter Firnhaber (1934–1981), politician (CDU)
- Gabriele Lewandowski (* 1960), politician (SPD)
Waking
- Irma Grese (1923–1945), guard in the concentration camps Ravensbrück , Auschwitz-Birkenau and Bergen-Belsen
Personalities associated with the community and its current districts
- Gabriele Meyer-Dennewitz (1922–2011), painter and graphic artist, lived in the Feldberg lake landscape
Carwitz
- Hans Fallada , writer, lived in Carwitz from 1933 to 1944
- Anna Ditzen , wife of Hans Fallada, lived in Carwitz since 1933
- Ruth Werner , writer, lived in Carwitz during the summer months from 1953
- Charly Hübner (* 1972), actor, grew up in Carwitz
Conow
- Friedrich Wilhelm Buttel (1796–1869), architect of the Conow village church
Feldberg
- Robert Kahn (1865–1951), composer, lived in Feldberg
- Reinhard Barby (1887–1974), naturalist and local researcher, lived in Feldberg
- Friedrich Karl Kaul (1906–1981), lawyer, owned a summer house in Feldberg
Krumbeck
- Otto Ernst von Dewitz (1788–1858), landlord in Krumbeck
Lüttenhagen
- Klaus Borrmann (* 1936), head of the Lüttenhagen Forestry Office from 1972 to 2001
literature
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Statistisches Amt MV - population status of the districts, offices and municipalities 2019 (XLS file) (official population figures in the update of the 2011 census) ( help ).
- ↑ Regional Spatial Development Program Mecklenburg Lake District (2011) , Regional Planning Association, accessed on July 12, 2015
- ↑ § 12 of the main statutes of the Feldberger Seenlandschaft community
- ↑ StBA: Changes in the municipalities in Germany, see 1999
- ^ Nordmagazin , NDR television, August 11, 2009
- ↑ "The state of tension in the North German Basin (pdf)"
- ↑ "Regional geologically significant Rotliegend boreholes in the area of the North German Depression (pdf)"
- ↑ Population development of the districts and municipalities in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania (Statistical Report AI of the Statistical Office Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania)
- ^ Result of the local election on May 26, 2019
- ↑ Elections: Kröpelin begins. In: Ostsee-Zeitung , February 18, 2017.
- ↑ Feldberg mayor married. In: Nordkurier , May 15, 2019.
- ↑ The SPD rules in Feldberg. In: Nordkurier , September 24, 2017.
- ↑ Hans-Heinz Schütt: On shield and flag - the coats of arms and flags of the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania and its municipalities . Ed .: production office TINUS; Schwerin. 2011, ISBN 978-3-9814380-0-0 , pp. 433/434 .
- ↑ a b main statute § 1 (PDF).
- ^ Sabine Bock : Stately houses on the estates and domains in Mecklenburg-Strelitz. Architecture and history. Volume 1. (= contributions to the history of architecture and monument preservation, 7.1–3). Thomas Helms Verlag Schwerin 2008, ISBN 978-3-935749-05-3 , pp. 494-504.
- ^ Sabine Bock : The village churches of Cölpin, Holzendorf and Krumbeck. Thomas Helms Verlag Schwerin 2013, ISBN 978-3-944033-04-4 , pp. 38–45.
- ^ Sabine Bock : Stately houses on the estates and domains in Mecklenburg-Strelitz. Architecture and history. Volume 2. (= Contributions to the history of architecture and the preservation of monuments, 7.1–3). Thomas Helms Verlag Schwerin 2008, ISBN 978-3-935749-05-3 , pp. 539-544.
- ^ Entry in the directory of monumental oaks . Retrieved January 10, 2017
- ^ Sabine Bock : Stately houses on the estates and domains in Mecklenburg-Strelitz. Architecture and history. Volume 2. (= Contributions to the history of architecture and the preservation of monuments, 7.1–3). Thomas Helms Verlag Schwerin 2008, ISBN 978-3-935749-05-3 , pp. 999-1004.
- ^ Sabine Bock : Stately houses on the estates and domains in Mecklenburg-Strelitz. Architecture and history. Volume 2. (= Contributions to the history of architecture and the preservation of monuments, 7.1–3). Thomas Helms Verlag Schwerin 2008, ISBN 978-3-935749-05-3 , pp. 1005-1023.
- ↑ Feldberger Karneval Klub (FKK): Club history , accessed on February 19, 2018
- ↑ No train in sight between Feldberg and Neustrelitz. In: Nordkurier , January 5, 2018.