Belgium
The Kingdom of Belgium ( Dutch , French Royaume de Belgique ) is a federal state in Western Europe . It lies between the North Sea and the Ardennes and borders the Netherlands , Germany , Luxembourg and France . Belgium has around 11.4 million inhabitants (2018) on an area of 30,688 square kilometers. With 376 inhabitants per km², Belgium is one of the most densely populated countries. The degree of urbanization in Belgium is almost 98 percent, the highest in Europe. The city of Brussels is the capital and seat of the Belgian royal family and the center of the largest agglomeration. The most populous city is Antwerp ; other major cities are Ghent , Charleroi , Liège , Bruges (Brugge) and Namur .
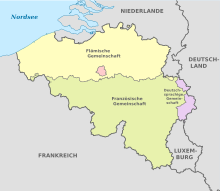
Since independence in 1830 and the constitution in 1831 , Belgium has been a parliamentary hereditary monarchy (see also Belgian monarchy ). The north of the country with the Flemings is Dutch, the south with the Walloons is French (see Flemish and French communities ). The Brussels-Capital Region is officially bilingual, but mostly French-speaking . In the German area in eastern Belgium are Standard German and West Central German dialects spread (see. German-speaking Community ).
The Flemish-Walloon conflict, which has been going on since the 19th century, shapes the often conflicting interests of the representatives of the two major population groups in Belgian politics. Since the 1970s, attempts have therefore been made to counter this problem by decentralizing the state organization. For this purpose, Belgium was converted into a federal state consisting of three regions and three communities . The regions of Flanders , Wallonia and Brussels-Capital as well as the Flemish , French and German-speaking communities have since formed the country's basic political structure. The state structure of Belgium is considered to be complex because, among other things, the territories of the regions are not congruent with those of the communities. The competences of the French and Flemish Communities overlap in the officially bilingual Brussels region, and the small area of the German-speaking Community belongs to the predominantly French-speaking region of Wallonia.
Belgium is a founding member of the European Economic Community (EEC), today's European Union (EU), whose main institutions are based in its capital, Brussels. In addition to the Netherlands and Luxembourg, the Belgian state is also a member of the Benelux Economic Union .
Country name and overview
The name Belgium is based on the Roman province of Gallia Belgica . This northeastern part of Gaul was inhabited by tribes of Celtic (i.e. the Belgians ) and Germanic (i.e. Germani cisrhēnani ) origins. In the 18th century, the French adjective belge or belgique was considered an equivalent of Nederlands 'Dutch'; the short-lived independent Belgian state of 1790 was called z. B. in French États belgiques unis and was mostly called Verenigde Nederlandse Staten in Dutch . Later, the use of belge and belgique was increasingly limited to the southern Netherlands, today's Belgium.
From the High Middle Ages to the middle of the 17th century, Belgium was a haven of cultural and economic creativity and wealth. From the 16th century, Belgium was the theater of many battles between European rulers. B. during the coalition wars (1792 to 1815) and the First and Second World Wars . Belgium participated intensively in the Industrial Revolution and owned the huge colony of the Belgian Congo in Central Africa from 1885 to 1960 . In 1919/20, after Germany lost the First World Crisis, the League of Nations placed the neighboring area of Rwanda-Urundi under Belgium; Belgium administered it as a League of Nations mandate .
geography
Geology and geomorphology
In the wake of the post-glacial Flanders transgression , beach ridges formed , which are still present today as a closed dune belt up to 50 meters high on the Belgian coast . This is followed by a 10 to 20 kilometer wide zone of marshland .
The so-called Flussgeest lies further inland. Here the deposits of the Meuse alluvial fan were covered with sands of great thickness in the last glacial period. In the slightly undulating land, fields and meadows alternate with wooded areas and heather ; in some cases raised bogs also occur. To the west of a line Antwerp-Brussels is the wide Flemish plain. In its northern part it is also covered by sand, in the south it is dominated by clay soils, which are more favorable for agriculture. Here the plain is dominated by a loose chain of Tertiary hills. To the west, the plain communicates with the northern French layered plain, which is largely made up of Mesozoic sediments (→ Paris Basin ).
The valleys of the Sambre and the Meuse form a sharp boundary at a tectonic fault zone, which separates the Tertiary and Chalk plateaus in the northwest from the Ardennes as part of the Rhenish Slate Mountains in the southeast. The heavily forested Ardennes consist of differently resistant paleozoic slates , sandstones , greywacke and quartzites . In Belgium you can reach a height of 694 meters with the Botrange in the High Fens .
In the fault zone of the Haine-Sambre-Maas furrow there are rich deposits of hard coal . There, in the northern French coal mining area , the first continental European mining and heavy industrial area was established in 1830. From 1901 the Limburg coal field was also opened up.
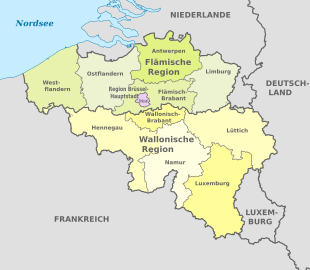
Flanders and Brussels-Capital Region
Flanders forms the northern part of the country and consists largely of flatlands . It is the most populous region in the country. The politically independent capital city region of Brussels is located as an enclave within the Flemish region. This part of the country consists partly of sandy gees - for example in the province of Limburg, which is located in the east of the Flemish region. The Geest is also interrupted by marshland , especially in the area of the rivers. Of these, the Meuse and the Scheldt are the most important. In the far west of Flanders is the 65 km long coast with the port city of Ostend. In particular, the provinces of Antwerp and Flemish Brabant with the area around Brussels are very densely populated.
Walloon Region
The Walloon Region comprises the southern part of Belgium. In terms of area, it is the largest region in the country. Your area in the Ardennes is mountainous and sparsely populated and is cut through by the river valleys of the Maas, Sambre and Ourthe. The most important cities in the region, in particular Liège, Namur and Charleroi, are located along these rivers. In the west of the region there are also Mons as well as Mouscron and Tournai , which are located in a cross-border metropolitan area with the northern French city of Lille . The geographical center of Belgium is located in Nil-Saint-Vincent (municipality of Walhain ) in the densely populated province of Walloon Brabant. The highest point in the country is the Signal de Botrange ( 694 m OP ) in the High Fens in East Belgium near the border with Germany . The highest town in Belgium is Mürringen in eastern Belgium ( 655 m OP ).
Counting
25% of Belgium's land area is used for agriculture. Around 95% of all Belgians live in cities. According to the calculations of the Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences , Belgium has an area of 30,688 km².
This includes
- the Brussels Capital Region 162 km²
- the Flanders region 13,624 km²
- the Walloon Region 16,901 km² (including the German-speaking Community 854 km²)
Waters
There are, among others, the following rivers and canals:
|
|
story
As the province of Belgica - a name introduced by Caesar - what is now Belgium experienced many rulers. In the early Middle Ages it was part of the Frankish Empire and was also politically divided again and again when it was divided. Later it was predominantly part of the Holy Roman Empire and split up into individual duchies and counties.
From the High Middle Ages to the early modern period, the cities of Flanders with their cloth industries were one of the two centers of the European economy (alongside the cities of northern Italy). Politically, the individual territories came under the House of Burgundy , which was inherited by the Habsburgs in 1477 as a result of the marriage of the Burgundian sole heiress Maria of Burgundy to Maximilian I , Archduke of Austria and later Roman-German King and Emperor . In 1555/56 the Habsburgs were divided into a Spanish and an Austrian line. The Dutch provinces were assigned to the Spanish Habsburgs.
In 1579 the Catholic Union of Arras and the Calvinist-Protestant Union of Utrecht were formed . The provinces of the Union of Utrecht broke away from Spain in 1581 and founded the Republic of the Seven United Provinces , whose independence was recognized in the Peace of Westphalia of 1648 after the end of the Eighty Years War . The provinces of the Union of Arras, Flanders and Brabant, were administered as the Spanish Netherlands by a Spanish governor. After the extinction of the Spanish Habsburgs (1700) and the resulting War of the Spanish Succession , the Austrian Netherlands came under the rule of the Austrian Habsburgs in 1714 .
As a result of the absolutist-centralist aspirations of the Austrian ruler Joseph II , the Brabant Revolution took place in 1789 and the short-lived United Belgian States were proclaimed in 1790 . Revolutionary France annexed the Austrian Netherlands between 1792 and 1794, followed by incorporation into the French Republic in 1795. At the Congress of Vienna (1815) the provinces were assigned to the (northern) Netherlands. Brussels became the royal seat of the Dutch king.
In the course of the Belgian Revolution , the country gained independence from the Netherlands in 1830. A parliamentary monarchy was established and Leopold von Sachsen-Coburg was named the first king of the Belgians. Leopold II , son of the first king, acquired the Congo in Africa as a private property. After the atrocities of the Congo (brutal excesses in the economic exploitation of the Congo) became internationally known, Leopold had to cede the area as a colony to the Belgian state in 1908 . During Leopold's reign of terror, an estimated 10 million people were killed in the African country as a result of slavery and forced labor . In 1960 the Congo became independent.
During the First World War , neutral Belgium was invaded by the German Reich in accordance with the Schlieffen Plan and almost entirely taken over by the German army. The German military also took action against civilians with shootings, fires and hostage-taking. Civilian massacres occurred in Dinant and several other Belgian cities. These attacks were justified with partisan activities, the real basis of which, however, is controversial (see Francs-tireurs ). In the course of the trench warfare many cities in Flanders were destroyed and parts of the country devastated. When labor became scarce in the German Reich, tens of thousands of Belgian civilians - Flemings and Walloons - had to do forced labor for the imperial military and the German armaments industry.
After the war, the mixed-language area around Eupen and Malmedy , today's Ostbelgien, became Belgian territory through the Treaty of Versailles after a controversial referendum in 1925. Belgium also took part in the occupation of the Ruhr .
During the Second World War , the country declared itself neutral. In May 1940 it (like the Netherlands and Luxembourg) was occupied by the German Wehrmacht on the so-called western campaign . Belgium remained occupied until 1944/45, minorities such as Jews and Roma were deported to concentration camps. Until its liberation by the Western Allies, it - like half of Europe - suffered from the arbitrary rule of the National Socialist dictatorship and the Jewish population suffered from its persecution and extermination; Cities and landscapes were largely spared from war damage. Only the Ardennes offensive in December 1944 and January 1945 led to severe destruction in the east of the country, especially around Sankt Vith and Bastogne .
The customs and economic unit of Belgium, the Netherlands and Luxembourg, which had been planned since 1944 , was agreed in the Hague Treaty on February 3, 1958 and entered into force on November 1, 1960 (Benelux countries). Belgium is one of the founding states of the European Economic Community (EEC) and has played an important role in the European unification process . The country or the Belgian capital Brussels became the seat of international organizations such as NATO and the European Union.
The internal politics after the Second World War was of a federalization coined the secessionist tendencies of the various language areas, in particular the Flemish north, tried to mitigate. In Flanders, separatist parties get a high percentage of the vote.
See also: List of Prime Ministers of Belgium , Belgian Congo , Flemish-Walloon Conflict and Flemish Movement
politics
Form of government and institutions

Belgium is de jure, i.e. H. purely constitutional, a constitutional monarchy, has de facto developed into a parliamentary monarchy that has been federally organized since the constitutional amendment in 1993 . The federal legislature consists of the king and the two chambers of parliament, the more important Chamber of Deputies with 150 and the Senate with 60 members. The active and passive right to vote for women at the national level did not exist until 1948 on the same conditions as the right to vote for men. The king also belongs to the executive branch, which he forms together with the 15-member federal government , which in turn is presided over by the prime minister as primus inter pares .
The federal institutions are responsible for the judiciary, financial policy, internal security, foreign policy, national defense and social security.
Sovereignty symbols
The Kingdom of Belgium has a flag and a large, medium and small coat of arms.
Political parties
Most political parties split up in the 1960s to 1980s into a Flemish and a Francophone party, and often there is also a German-speaking counterpart. Parties of the same grouping work more or less closely together and sometimes also form factional communities. The German-speaking parties operate exclusively on a regional basis.
| Political party | Seats | annotation |
|---|---|---|
| Flemish parties | ||
| Nieuw-Vlaamse Alliantie (N-VA) | 25th | Conservative separatists, emerged from the Volksunie |
| Vlaams Belang (VB) | 18th | Right-wing populist separatists, formerly Vlaams Blok |
| Christen-Democratisch en Vlaams (CD&V) | 12th | Christian Democrats, formerly CVP |
| Open Vlaamse Liberalen en Democrats (Open VLD) | 12th | Liberals, formerly PVV |
| Vooruit | 9 | Socialists, formerly SP, formerly SP.a |
| Great | 8th | Green, formerly Agalev |
| Francophone parties | ||
| Parti Socialiste (PS) | 20th | Socialists |
| Mouvement Réformateur (MR) | 14th | Liberals, formerly PLP and PRL |
| Ecolo | 13 | Green |
| Center Démocrate Humaniste (CDH) | 5 | Christian Democrats, formerly PSC |
| Démocrate Fédéraliste Indépendant (DéFI) | 2 | Representation of Francophones mainly in Brussels, formerly FDF, 1995 to 2010 joint lists with PRL and MR |
| Nationwide parties | ||
| Partij van de Arbeid / Parti du Travail de Belgique (PVDA / PTB) | 12th | Communists, formerly AMADA / TPO |
Political indices
| Name of the index | Index value | Worldwide rank | Interpretation aid | year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fragile States Index | 27.1 out of 120 | 161 of 178 | Stability of the country: sustainable 0 = very sustainable / 120 = very alarming |
2020 |
| Democracy index | 7.51 out of 10 | 36 of 167 | Incomplete democracy 0 = authoritarian regime / 10 = complete democracy |
2020 |
| Freedom in the World | 96 of 100 | - | Freedom status: free 0 = not free / 100 = free |
2020 |
| Freedom of the press ranking | 11.69 out of 100 | 11 of 180 | Good situation for freedom of the press 0 = good situation / 100 = very serious situation |
2021 |
| Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) | 76 of 100 | 15 of 180 | 0 = very corrupt / 100 = very clean | 2020 |
Flemish-Walloon conflicts
Belgium is characterized by internal turmoil - especially between the Flemish (Dutch-speaking) and Walloon (French-speaking) populations. For this reason, for example, censuses that record the spoken language of the inhabitants have been forbidden since 1961 in order not to stir up new conflicts over and over again on the basis of changing statistical results about the affiliation of certain communities on the language border to one or the other region. In order to defuse the situation in these mixed-language areas, in some cases, community facilities with special minority rights (especially in the school sector) were created.
“Overall, the tensions between the two major ethnic groups in Belgium have decreased in the last generation. There is no end in sight for Belgium, ”said the historian Christoph Driessen in his book History of Belgium in 2018 , pointing out that the separatist parties in Flanders are in the minority and that there are practically no separatist aspirations in Wallonia. Younger Belgians and many immigrants could do less with the language dispute than earlier generations; they follow other identification models in which the question of belonging to one or the other language group is less important. That there is cohesion within Belgium was also shown by the enthusiasm for the entire Belgian team at the 2018 World Cup , in which Belgium took third place. Nonetheless, it can be observed that despite compulsory schooling in the other national language, a good knowledge of Dutch is hardly widespread in Wallonia and fluency in French has decreased in Flanders compared to previous generations. Both population groups lead a largely separate existence, not only in terms of the state structure, but also culturally. In the cultural sector, Flanders has a strong affinity for the Netherlands and Wallonia for France. At the same time, care is taken to ensure that Belgium's multilingualism is demonstrated at the federal political level; top politicians, especially in government offices, must master (or learn) the second national language in order to succeed, and the king consistently delivers speeches aimed at all Belgians in all three official languages.
Political developments since 2008
In March 2008, Flemish and Francophone Christian Democrats ( CD&V and cdH ) and Liberals ( VLD and MR ) as well as the Walloon Socialists ( PS ) agreed to form a joint government with Yves Leterme (CD&V) as Prime Minister.
On December 18, 2008, the Court of Cassation - the highest ordinary court in Belgium - announced in a letter to Chamber Chairman Herman Van Rompuy that Leterme had tried to appeal to the court on the question of the planned sale of the Belgian bank Fortis to the French financial group BNP Paribas to influence; Leterme had denied this shortly before. Leterme resigned the next day.
From December 30, 2008, Herman Van Rompuy (CD&V) led the Belgian federal government , which was composed of the same five-party coalition. However, after being designated the first permanent President of the European Council on November 19, 2009 , he resigned on November 25, 2009. On the same day, Yves Leterme was reappointed Prime Minister and has since led his second federal government in this legislative period. This government collapsed again in April 2010 when the Flemish liberal party OpenVLD announced its withdrawal from the government after internal disputes over a solution to the conflict over the bilingual Brussels-Halle-Vilvoorde constituency .
In the early elections on June 13, 2010 , the Flemish nationalists of the N-VA under Bart De Wever won 27 of the 150 seats, making them the strongest parliamentary group among the Flemish parties. In Wallonia, Elio Di Rupo's socialist PS became the strongest political force. The formation of a government was difficult, and it was not until a year and a half later that Elio Di Rupo was able to form a coalition government , which was appointed on December 5, 2011. As a “tripartite” consisting of the party families of the Socialists, Liberals and Christian Democrats, it did not have a majority among the Flemish parties. With the socialist Elio Di Rupo, a Francophone and a Socialist were elected Prime Minister of Belgium for the first time since the end of the last government of Paul Vanden Boeynants in 1979. The Leterme government remained in office until his election. The time span of 541 days from election to formation of the new government is a record in modern world history.
On July 21, 2013 - the Belgian national holiday - King Albert II abdicated in favor of his eldest son Philippe after he had announced this on July 3, 2013.
In the elections on May 25, 2014 , the socialists in particular lost votes, which meant that the previous government no longer had a majority. The N-VA was able to book further gains. On October 11, 2014, the new government , the Coalition suédoise ("Swedish Coalition") was sworn in under the Francophone Prime Minister Charles Michel . In contrast to the broad coalitions customary up to now, all parties involved, the Flemish nationalists ( N-VA ), Christian Democrats ( CD&V ) and the liberals of both language groups ( MR and OpenVLD ) come from the center-right spectrum. For the first time since 1988, the socialists were not involved in the government that did not have a majority on the Francophone side.
The Michel I government fell in December 2018 over the ratification of the UN Migration Pact , which was rejected by the N-VA and which then withdrew from the government. Thereupon Charles Michel formed the Michel II government without the N-VA members, which, however, resigned before a vote of no confidence on December 18, 2018 and then remained in office, even after the parliamentary elections on May 26, 2019, as there was no new majority found.
After Charles Michel was elected President of the European Council to succeed Donald Tusk , he announced his resignation on October 26, 2019. On October 27, 2019, the King appointed Sophie Wilmès as the new Executive Prime Minister, the first woman in this position since independence 188 years ago. On March 17, 2020, she was sworn in by the King as Ordinary Prime Minister of the Wilmès II government , after all parties except the Walloon Communists, the Flemish Nationalists of the N-VA and the Flemish right-wing extremists of Vlaams Belang in view of the COVID-19 pandemic the support promised. She promised to only take care of the COVID-19 pandemic in Belgium and its consequences and to ask the vote of confidence after six months. After the formation of the government continued to stall and a new coalition was formed, but the quarantine was ordered for one of the informators because of an infection with COVID-19 , the time was extended again.
On October 1, 2020, the new government under Prime Minister Alexander De Croo was sworn in. For the first time, it consists of seven parties from the four party families of the Socialists, Liberals, Christian Democrats and Greens, and is called the “Vivaldi Coalition”. It is considered to be left-liberal, for the first time it has equal representation with ten women and ten men, is significantly younger and has fifteen members of the government who have never held federal political office before. Sophie Wilmès became foreign minister in it.
European politics

Belgium has a strategic geographical position in the heart of Europe, in the middle of a European metropolitan area and close to the largest sea ports. As a result, there is a certain dependence on international trade, with the most important trading partners being the neighboring countries of the Netherlands, Germany and France. This makes Belgium one of the most open economies in the European Union. Against this background, Belgium traditionally pursues a policy of opening up to its European neighbors, on the one hand through the Benelux community, on the other hand within the framework of the Council of Europe and the European Union, of which Belgium is one of the founding members. The country is also a founding member of the European Monetary Union . Eurobarometer surveys regularly show that around two thirds of the Belgian population are pro-European, which is above the EU average of just over 50 percent. The Belgian capital Brussels is the seat of several EU institutions and agencies such as the Commission , Parliament , the Council of Ministers , the Economic and Social Committee or the Committee of the Regions , as well as numerous lobbying groups , non-governmental organizations , etc. that work in the field of European policy.
The Belgian governments since 1945 have worked to build Europe. Under the Belgian Presidency in the second half of 2001, it was decided to convene the Constitutional Convention , which a few years later would produce the Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe (TCE). Belgium campaigned for the ratification process of the TCE and - after its failure - for the preservation of the substance of the TCE in the Treaty of Lisbon , which was signed on December 13, 2007 and entered into force on December 1, 2009.
Belgium's defense policy is based not only on NATO (Belgium is a founding member), but also on the EU within the framework of the Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP). The capital, Brussels, is the seat of both NATO's main bodies and the EU's European Defense Agency , making Belgium the center of Euro-Atlantic defense structures. The country provides troops for the EU battlegroups and participates in EU operations, for example in EUFOR . Thanks to its historical ties to the African country of the Congo , Belgium has established itself as an opinion leader in matters relating to the Great Lakes and Central Africa within the EU and is making a significant contribution to the peaceful stabilization of Eastern Congo.
Due to Belgium's federal structure , which assigns an extraordinary amount of competences to the local level, both the regions and the communities are significantly involved in the formulation of Belgian European policy, but at the same time affected by the implementation of EU political goals - which explains any local differences in implementation. For example, they are responsible for cultural policy and can conclude contracts with foreign countries in this area, so that they have built up an independent profile abroad, for example by appointing cultural officers in some Belgian embassies.
In the second half of 2010, Belgium chaired the Council of Ministers . This Belgian Council Presidency formed the centerpiece of the Trio Presidency with Spain (first half of 2010) and Hungary (first half of 2011). After the entry into force of the Lisbon Treaty, the Belgian Herman Van Rompuy was appointed to the newly created office of President of the European Council ; The Belgian Charles Michel has held this office since December 1, 2019 .
military
The Belgian Armed Forces (Dutch Defensie van België , French Armée belge ) are divided into Army , Navy , Air Force and Medical Corps (Dutch Medische Component , French Corps médical ). In 2006 the Belgian armed forces had a strength of 36,000 men. Voluntary military service was formally abolished in 1994. Belgium spent almost 0.9 percent of its economic output or 4.4 billion US dollars on its armed forces in 2017 .
The land forces are the largest of the armed forces at 24,600. You can fall back on a fleet of 300 battle tanks , 989 armored vehicles and 288 artillery pieces .
The Belgian Air Force (Dutch Luchtmacht , French Force Aérienne Belge ) is the second largest armed force with 6350 men. You have 72 F-16 fighters and 31 helicopters at your disposal.
The navy is organized in a joint Benelux command. It has two Wielingen frigates , six mine hunters and a river patrol ship .
police
The police reform of 2001 created an integrated police force structured on two levels:
- Federal Police (Dutch Federale Politie , French Police Fédérale ), with a general commissioner and three general directorates (the administrative police, the criminal police and the directorate for support and administration). Some of these are also decentralized at the provincial or judicial district level.
- Local Police (Dutch Local Politie , French Police Locale ) with its currently 195 police zones was formed from municipal police units and the gendarmerie (ndl. Rijkswacht ) that existed until 2001 .
Administrative structure
Belgium has been a federal state since 1993, divided into three regions and three communities . There are ten provinces and 43 arrondissements as subordinate administrative units . Local self-government is exercised by the 589 municipalities.
Both the regions and the communities are constituent states of the Belgian federal state; they differ in their territorial delimitation and their competencies. The regions (Dutch west, French régions ) are responsible for large areas of economic , environmental , transport and agricultural policy ; they also exercise legal and, if necessary, technical supervision over provinces, arrondissements and municipalities. The communities (Dutch gemeenschappen , French communautés; formerly often referred to as cultural or language communities) are responsible for the entire education system , cultural policy and other "personal matters" (areas of family, health and social policy, including public hospitals) . Even in comparison with other federal states, regions and communities together have a high level of competencies, and they can also independently conclude contracts with foreign states in their areas of responsibility. International agreements concluded by the Belgian state that affect the competences of the regions or communities require the consent of their parliaments; this applies, for example, to the treaties of the European Union. At the federal level, responsibility for foreign , defense and financial policy , the social security systems as well as the police and the judiciary have remained above all .
The territorial delimitation of the regions and communities is based on the language areas: the Flemish region comprises the Dutch language area, the Walloon region the French and German language area, and the Brussels-Capital region the bilingual French-Dutch area. The Flemish Community exercises its powers on the Dutch and the bilingual language area, the French Community on the French and bilingual language area, and the German-speaking community on the German language area. Regions and communities each have their own parliament and government. However, the Flemish Community and the Flemish Region have merged their institutions so that there is only one Flemish Parliament and one Flemish Government exercising both the region's and the Community's powers.
In addition, at a lower administrative level, Belgium knows the ten provinces that lie within the regions:
- The Flemish Region (Dutch Vlaamse Gewest ) comprises five provinces:
- Antwerp (capital Antwerp )
- Limburg ( Hasselt )
- East Flanders ( Ghent )
- Flemish Brabant ( Leuven )
- West Flanders ( Bruges )
- The Walloon Region (French Région wallonne ) also includes five provinces:
- Hainaut ( Mons )
- Liège ( Liège )
- Luxembourg ( Arlon )
- Namur ( Namur )
- Walloon Brabant ( Wavre )
- The Brussels Capital Region (Dutch: Brussels Hoofdstedelijk Gewest , French: Région de Bruxelles Capitale ) is considered to be provincial. It exercises its responsibilities in the Brussels-Capital Administrative District , which is congruent with the Brussels-Capital Region.
The lowest administrative level is represented by the 581 communes (see also List of Communes in Belgium , List of Communes in Flanders , List of Communes in Wallonia ).
State budget

|
| (Source: Eurostat ) |
The state budget in 2009 comprised revenues (receipts) of 163 billion euros. This was offset by expenses (expenditures) amounting to 183 billion euros. This results in a budget deficit of 20 billion euros or 6.0% of gross domestic product . Between 1995 and 2007, Belgium succeeded in significantly reducing the relative share of national debt in the gross national product. However, this success has been jeopardized by the consequences of the global financial crisis since 2007. On November 25, 2011, the rating agency Standard & Poor’s Belgium downgraded from “AA +” to “AA”. This was justified with the smoldering national crisis, the low growth and the increasing pressure of the financial markets.
The national debt as of June 30, 2016 was 455.3 billion euros or 109.7 percent of the gross domestic product.
In 2006 the share of government expenditure (as a percentage of gross domestic product) was in the following areas:
population
The population of Belgium is usually divided into language groups. Exact data on the distribution have not been collected since the official language border was established in 1962. According to this, the Dutch- speaking Flemings make up almost 60 percent of the population. In this generalized sense, Flemings are not only residents of the provinces of West and East Flanders, but also those of the other Dutch-speaking provinces ( Antwerp , Brabant , Limburg ) and the Dutch-speaking residents of the region Brussels Capital . The Walloons and the francophone residents of the Brussels-Capital Region and its surrounding area, who are usually collectively referred to as French-speaking Belgians , make up a little less than 40 percent of the country's population. In addition, the third population group with an official language area is the German-speaking community in the east of the country; less than one percent of the Belgian population lives here (77,949 on January 1, 2020). Overall, the number of German-speaking East Belgians, including those who live as a minority in mostly francophone rural districts (e.g. Malmedy ), is estimated at 110,000.
The minorities who do not have their own official language area, but whose rights are partly regulated by so-called facilities (relief), include smaller, West Germanic dialects speaking groups in the officially French language area ( e.g. Luxembourgish in the Areler Land and Platdiets in the Low German communities ). As Voyageurs , Gens du voyage or Woonwagenbewoners are both living in Belgium groups of Jeni , Manouche and Roma called also caravan residents of other origin. The number of gens du voyage was estimated at 15,000 to 20,000 people in 2005, 0.15 percent of the Belgian population. The remaining resident population consists of immigrants from many parts of Europe and Africa . Your linguistic situation is not statistically recorded.
In 2012, 25 percent of the total population had a migration background . Since 1945 there have been 2.8 million New Belgians of foreign descent. Of these, around 1.2 million are of European descent and around 1.35 million come from countries outside Europe ( Morocco , Turkey , Algeria , Congo ). Since the relaxation of Belgian citizenship law, more than 1.3 million migrants have acquired Belgian citizenship. The largest group of immigrants are Moroccans (more than 450,000 including their descendants living in Belgium). Turks form the second largest ethnic minority (around 220,000). 89.2 percent of the residents of Turkish origin were naturalized, as well as 88.4 percent of those of Moroccan origin, 75.4 percent of those of Italian, 56.2 percent of those of French and 47.8 percent of those of Dutch origin. The linguistic situation, such as the extent to which the descendants of immigrants still speak the mother tongue of their parents or grandparents, has not been comprehensively recorded statistically.
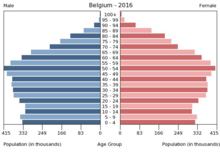
Life expectancy in Belgium between 2010 and 2015 was 80.5 years (women: 83.0 years, men: 78.0 years). The average age in 2016 was 41.4 years. A woman gives birth to a statistical average of 1.7 children.
languages
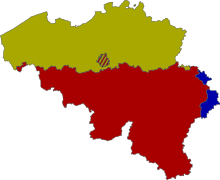
(the bilingual Brussels area is shown in the middle )
In Belgium, three languages have official language status:
- Dutch , often referred to in the past, now less often than Flemish, see Flanders and Belgian Dutch
- French , see Wallonia and Belgian French
- German , see German-speaking Community
After Belgium gained independence in 1830, only French was the official language. In 1873, Dutch was legally recognized as the second official language, but French remained the predominant language of administration and instruction throughout Belgium. In 1919, German was added as the official language in the newly acquired area in the east of the country; Ostbelgien was annexed to the Belgian state after the Versailles Treaty . After the First World War , the majority of Flemings insisted that Dutch should also be used as an administrative and teaching language in schools and universities and that it should be treated as the official language of French. In fact, in the 19th century and well into the 20th century, the majority of the Belgian population spoke local forms of Dutch and French dialects (dialects of Flemish, Brabant, Limburg, Walloon, etc.), which are still the colloquial realization of the standard languages in the Phonetics, partly also in vocabulary and the formation of forms. The colloquial Brussels French contains numerous Flemish elements, since an originally predominantly Flemish-speaking city has gradually been Frenchized through cultural and political change (capital of the newly founded French-speaking Belgian state in 1830); During this language change of large parts of the Brussels population, elements of the Germanic vernacular were incorporated into the local French.
In 1921, the Belgian government established three language areas with territorial monolingualism, which did not take sufficient account of bilingual areas and led to protracted domestic political conflicts: the Dutch language zone in Flanders, the French language zone in Wallonia and the German language zone in East Belgium. Special regulations arose in and around Brussels, which is considered to be bilingual (see language relations in Brussels ), as well as in the later established community facilities along the Romance-Germanic language border. Those educated parts of the population of Flanders, especially in Antwerp and other cities, for whom French was a preferred language and sometimes even their mother tongue were not taken into account; With the exception of the capital Brussels, no allophone language islands were planned in the parts of the country defined as monolingual after 1921. The Flemish-Walloon conflict , which initially had mainly social causes (impoverishment of the Flemish peasantry at the time of the Industrial Revolution , social disadvantage for this section of the population in the country's political and social structure, with the simultaneous economic boom and rise of Wallonia in the 19th and early 20th centuries ), continues to this day, although the socio-economic conditions have changed fundamentally since the decline of the coal and steel industry, which dominated Wallonia, in the second half of the 20th century and the upswing of new branches of the economy in Flanders.
The status of regional languages has been the Romance Lorraine , Champenois , Limburg , Luxembourg, Ripuarian , Picard and Walloon languages since 1990 .
religion

The majority of Belgians belong to Christian churches: around 75 percent of Belgian citizens are Roman Catholics , around 1 percent belong to the United Protestant Church and 8 percent belong to Islamic communities. There are also smaller Christian Orthodox , Jewish , Buddhist and Hindu minorities. The proportion of people who are not religiously bound is around 16 percent.
Belgium has traditionally been a Catholic country. Belonging to the Catholic faith was a major reason for the Belgian Revolution and the split (1830) from the predominantly Protestant north of the United Netherlands, which was formed by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 . The Catholic majority covers all three language areas (Flemish, French, German). With the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven , one of the most important universities in the country is denominationally bound. Rural Flanders in particular was strongly Catholic until the middle of the 20th century; In Wallonia, which was industrialized at an early stage, liberalism and the socialist labor movement caused greater secularization , which also affected the Flemish part of the country in the 1960s.
The United Protestant Church has 45,000 parishioners in 110 parishes, 70 of them Walloon, 35 Flemish, three German and two English speaking with 85 pastors. It is a United Church and thus contains Lutheran and Reformed (Calvinist) elements. There are also Protestant free churches, including the Baptists in Belgium .

In 2011 there were one million people with a Muslim background in Belgium. Muslims make up 22 percent of the population in the Brussels-Capital Region , 4 percent in Wallonia and 3.9 percent in Flanders . The majority of Belgian Muslims live in large cities such as Antwerp, Liège, Charleroi and especially Brussels. The largest group of immigrants are the 400,000 inhabitants of Belgium, who come from Morocco . The approximately 220,000 Turks are the third largest immigrant group and the second largest Muslim population group.
The Belgian federal government recognizes and promotes six religions and one non-denominational worldview: the Roman Catholic Church , the United Protestant Church of Belgium , the Orthodox Church , the Anglican Church , Islam , Judaism and the free spirit community .
homosexuality
In Belgium, homosexuality is socially accepted. Social tolerance towards homosexuals is relatively high. Belgium is considered to be a very liberal country with regard to homosexual rights and their equality . Homosexual acts were decriminalized as early as 1974 ; anti-discrimination laws have also existed since 2003. Belgium was the second country in the world to open marriage to homosexual partners after the Netherlands in 2003. The United Protestant Church has allowed same-sex couples to be blessed since 2007 .
anti-Semitism
Unia , the “Center for Equal Opportunities and Fight Against Racism” in Belgium, registered 101 reports of anti-Semitic crimes in 2018. This is almost double the number of 2017 when 56 anti-Semitic crimes were recorded.
The city of Aalst's carnival parade has been criticized for several years , as it often relies on anti-Jewish stereotypes. An association taking part in the parade, which had already been responsible for anti-Semitic dolls the year before, also used anti-Semitic caricatures in 2020. the mayor of Aalst, Christoph D'Haese from the Nieuw-Vlaamse Alliantie party , did not want to condemn the dolls and caricatures. In this context, UNESCO removed the Aalster Street Carnival from the list of intangible cultural heritage in December 2019 , and the EU Commission has since been asked to initiate criminal proceedings against Belgium under Article 7 of the EU Treaties.
The number of reports of anti-Jewish content on the Internet has quadrupled in Belgium within a year: "Jews are forging a conspiracy against the world" or "Hitler did not finish his work" are sayings that appear regularly. In addition, according to the media, the extreme right-wing Flemish student movement “Schild & Vrienden” is said to have fueled anti-Semitism. Examples of anti-Jewish acts are the attack on the Jewish Museum in Brussels, in which four people were shot dead on May 24, 2014, and the terrorist attacks in downtown Brussels and at Brussels-Zaventem Airport in March 2016.
education
The education system in Belgium is different due to the far-reaching powers of the individual communities, but the higher education system was largely standardized at the inter-community and European level in the course of the Bologna process . The federal authority of Belgium is responsible for the pensions of teachers, the definition of the minimum knowledge for obtaining a diploma and for the school system (from 6 to 18 years of age).
Flemish Community Schools
From the age of two and a half or four years, children in Flanders often attend a kind of kindergarten with preschool (nld. Kleuteronderwijs ). From the age of six they go to elementary school for six years (nld. Basisonderwijs ). The schools are public (Flemish Community), free (subsidized, mostly Catholic) or private (unsubsidized). Many Catholic schools enjoy a higher reputation than state schools. French is taught as the first foreign language from the fifth year of school .
From the seventh year of school onwards, lessons take place in a secondary school. The secondary schools (nld. Secundair onderwijs ) are divided as follows:
- a) first school level (usually from 12 to 14 years of age)
- b) Second and third grade (from 14 to 18 years of age): Choice between
- ASO (general secondary education)
- KSO (secondary art education)
- TSO (technical secondary education)
- BSO (vocational secondary education)
- c) fourth grade (from the age of 18, i.e. after compulsory schooling has expired): mainly nursing schools .
At KSO schools, which are mostly only available in the larger cities, students can also learn modern subjects such as B. comic drawing, computer graphics, etc. choose. The curriculum focuses on English, French and mathematics. The degree ends with the Diploma Secundair Onderwijs ( Abitur ), which enables access to university studies.
Only in the BSO sector can young people leave school before the age of 18 (end of compulsory schooling) if they join an apprenticeship / vocational training.
French Community Schools
Children in the French Community of Belgium can be admitted to a kind of kindergarten ( école gardienne ) from the age of two and a half . From six to twelve years of age, they attend primary school ( enseignement primaire ). The grades are counted from the première primaire to the sixième primaire . From the deuxième primaire , French-speaking students can learn Dutch.
The secondary level ( enseignement secondaire ), like the primary level, comprises six years; it offers two different courses:
- a classical humanistic branch with three years école moyenne inférieure and three years école moyenne supérieure with the diplôme d'humanités degree , which corresponds to the German Abitur .
- a technical and economic branch ( enseignement technique ou professionel ) with six years of instruction and the qualification diplôme technique or diplôme professionnel .
Schools of the German-speaking Community
Schooling has the same age group as in other parts of Belgium: Kindergarten can be attended from the age of three. From the age of five or six you attend a six-year primary school. A further six years are completed in a secondary school. Some schools cover all three age groups, so they can be attended from kindergarten to high school. Other schools can only be attended from kindergarten through the sixth grade, after which you have to change to another school. Some schools are purely secondary schools (seventh to twelfth grade).
French is taught from the first year of school. From the eighth school year, English is added as a third language.
From the ninth grade onwards, in some schools a pupil can choose between social sciences, natural sciences, languages, arts, secretarial services, economics or electronics.
In the language department (modern language branch) a student learns not only English and French but also Italian, Spanish and Dutch.
Teaching is compulsory up to the age of 18, whereby a student can also meet this obligation with an apprenticeship. There you only have to go to vocational school twice a week.
Universities
Belgium has eleven universities :
- Dutch-speaking: Catholic University of Leuven ( Katholieke Universiteit Leuven - KUL), University of Ghent , University of Antwerp (UA), Transnational University of Limburg ( University of Hasselt - UHasselt & University of Maastricht - UM / Netherlands), Free University of Brussels ( Vrije Universiteit Brussel - VUB), Catholic University of Brussels ( Katholieke Universiteit Brussel - KUB);
- French-speaking: Université libre de Bruxelles , Facultés Universitaires Saint Louis à Bruxelles, Université de Liège , École Polytechnique de Mons, Facultés universitaires Notre-Dame de la Paix Namur, Université catholique de Louvain in Louvain-la-Neuve .
There is only one university in the German-speaking area , the Autonome Hochschule in the German-speaking Community .
Individual faculties on an equal footing with universities are the Protestant Theological Faculty of Leuven (Protestant Theological Faculty), the Faculty of Protestant Theology Brussels (Faculteit voor Protestantse Godgeleerdheid) and the Royal Military Academy ( Koninklijke Militaire School / École royale militaire ).
The renowned College of Europe is located in Bruges .
In addition to the universities, there are numerous other Hautes Ecoles / Hogescholen and several art schools (Ecoles Supérieures des Arts) in the three communities .
business
In comparison with the gross domestic product (GDP) of the European Union, expressed in purchasing power standards, Belgium achieved an above-average index of 118 in 2014 (EU-28: 100). Belgium's gross domestic product in 2015 was around 409.4 billion euros. The gross domestic product per capita was 36,500 euros in the same year. Despite its small population, Belgium was the 20th largest exporter of goods in 2016. Thanks to its location in the heart of Europe, it is very closely integrated into the trade network of the European Union. Belgium's most important trading partners are the neighboring countries France, Germany and the Netherlands. In the Global Competitiveness Index , which measures a country's competitiveness, Belgium ranks 20th out of 137 countries (as of 2017-2018). In 2019, the country ranks 48th out of 180 countries in the index for economic freedom .
The unemployment rate was 5.4 percent in June 2019, slightly below the EU average. In 2017, youth unemployment was 19 percent. The total number of employees was estimated at around five million in 2019.
Distribution of the working population by sector (status: 201 and share of total value added in 2016 in brackets):
- Agriculture : 1.1 percent (0.7 percent)
- Industry : 21.5 percent (22.3 percent)
- Service sector : 78.4 percent (77.0 percent)
tourism

The tourism plays a major role in Belgium. In the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Report 2017 of the World Economic Forum, Belgium ranks 21st out of 136 countries. Belgium was visited by 7.5 million foreign tourists in 2016, bringing the country $ 11.8 billion in revenue. Mostly Germans, British, Luxembourgers, French and Dutch visit Belgium. The British also developed a kind of First World War tourism. There are still many old war memorials and cemeteries in West Flanders . In addition, all the holiday resorts on the Belgian North Sea coast ( Knokke-Heist , Bruges , Blankenberge , De Haan , Bredene , Ostend , Middelkerke , Nieuwpoort , Koksijde and De Panne ) are very popular. In addition, the Ardennes are a much-visited holiday region. There are many day trips to be made from the Belgian North Sea coast, for example to the neighboring countries of France and the Netherlands or Great Britain. City tours to Brussels, Hasselt , Ghent, Antwerp and others have also proven to be particularly popular . The city of Bruges is probably the city with the greatest tourism. It is sometimes called the Venice of the North . There is an independent tourist association for Flanders and another for the rest of Belgium.
Energy policy
The country's per capita carbon dioxide emissions are among the highest in the world.
As of 2019, Belgium has two active nuclear power plants . In 1999 parliament decided to phase out nuclear power (see also nuclear energy in Belgium ) and in 2003 a timetable was set up to 2025. However, there were delays in implementation.
media
The federal structure of Belgium is also reflected in the country's media scene. There are three independent media worlds in Dutch , French and German .
The Flemish newspaper market is the largest and is dominated by three publishing groups: Corelio Media (among others publisher of De Standaard , Het Nieuwsblad ), De Persgroep (among others publisher of Het Laatste Nieuws , De Morgen , De Tijd ) and Concentra (among others publisher of Het Belang van Limburg , Metro ). The most important publishing companies in Wallonia are Rossel (among others editor of Le Soir as well as co-editors of L'Echo and Grenzecho ) and IPM / Medi @ bel.
In the broadcasting sector, there are separate public broadcasters for each of the three language communities: VRT (Vlaamse Radio- en Televisieomroep) for Flanders, RTBF (Radio Télévision Belge Francophone) for Wallonia and BRF (Belgian Broadcasting) for the German-speaking community. In addition to the BRF programs, many radio and television programs from nearby Germany are used by the German-speaking East Belgians.
The most important German-language newspaper is the Grenz-Echo , which appears daily in Eupen . Among the magazines include the German-language edition of the Belgian Official Journal (Official Journal of the Belgian Government) in Brussels, the agricultural publication The farmer from St. Vith, the municipal bulletin Eupen currently , the Association of Organ The Public Transport International - Public Transport International of Brussels or the quarterly magazine Geschwënn - zeitschrëft vum Arelerland for German speakers in south-east Belgium around the city of Arlon .
capital
According to a study by Bank Credit Suisse from 2017, Belgium ranked 17th in the world in terms of total national assets . Total real estate, stocks, and cash holdings totaled $ 2,453 billion. The wealth per adult person is 278,139 dollars on average and 161,589 dollars in median (in Germany: 203,946 and 47,091 dollars, respectively). In terms of wealth per inhabitant, Belgium is one of the ten richest countries in the world. Overall, 54 percent of the total wealth of Belgians was financial wealth and 46 percent was non-financial wealth. The Gini coefficient for wealth distribution was 63 in 2017, which indicates relatively moderate wealth inequality. The top 10 percent of the Belgian population owned 47.6 percent of the wealth and the top 1 percent owned 17.5 percent, which is a lower concentration of wealth than most other European countries. The proportion of Belgians with assets over a million dollars is estimated at 3.9 percent of the population.
Regional disparities
Disputes between the Francophone Walloons and the Dutch-speaking Flemings have existed in Belgium since the 19th century (see also Flemish-Walloon conflict ). A current point of controversy has its cause in economic differences between the parts of the country: Since the Walloon regions, which were formerly characterized by the coal and steel industry, are in a recession phase, unemployment there is significantly higher than in the Flemish regions. At the same time, two thirds of the Belgian gross national income is generated in Flanders. The Flemish region pays a solidarity contribution, which in Wallonia is mainly used to finance social benefits. However, these payments are politically controversial in the Flemish region. Growing resentment about the economic weakness of the Walloon region is particularly evident in the Flemish separatist movement, whose main organization is the Vlaams Belang party .
| rank | province | GDP 2017 in million euros |
GDP per capita 2017, PPS , (EU-28 = 100) |
GDP per capita 2017 in euros |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - |
|
77,694 | 196 | 65,000 |
| 1. |
|
85,753 | 140 | 46,600 |
| 2. |
|
17,477 | 131 | 43,700 |
| 3. |
|
47.104 | 125 | 41,500 |
| - |
|
259.786 | 120 | 39,800 |
| - |
|
439.052 | 116 | 38,700 |
| 4th |
|
45.263 | 115 | 38,100 |
| 5. |
|
53,855 | 108 | 35,900 |
| - |
|
15,383,066 | 100 | 30,000 |
| 6th |
|
27,810 | 96 | 32,000 |
| - |
|
101,378 | 84 | 28,000 |
| 7th |
|
30,812 | 84 | 27,900 |
| 8th. |
|
13.008 | 80 | 26,400 |
| 9. |
|
33.202 | 75 | 24,800 |
| 10. |
|
6,880 | 73 | 24,300 |
Key figures

The key economic indicators of gross domestic product , inflation , budget balance and foreign trade have developed as follows in recent years:
| year | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
| Change in% yoy | 1.4 | 0.8 | 3.2 | 1.7 | 2.7 | 2.9 | 1.0 | −2.8 | 2.4 | 1.8 | −0.2 | −0.1 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.7 |
| absolute in billions of euros | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| year | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
| GDP in billions of euros | 387.5 | 391.7 | 400.8 | 410.2 | 421.1 | 437.2 |
| per inhabitant in euros | ||||||
| year | 2013 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
| GDP per inhabitant in thousands of euros | 35,100 | 35,300 | 35,900 | 36,600 | 37,300 | 38,500 |
| Development of the inflation rate in percent compared to the previous year | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| year | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2011 | 2012 |
| inflation rate | 2.3 | 1.8 | 4.5 | 0.0 | 3.5 | 2.6 |
| year | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 |
| Development of the budget balance as a percentage of GDP ("minus" means deficit in the national budget) |
||||||
| Budget balance | −4.1 | −4.2 | −3.1 | −3.1 | −2.5 | −2.6 |
| Billion euros (2014) |
% yoy (2014) |
Billion euros (2015) |
% yoy (2015) |
Billion euros (2016) |
% year-on-year (2016) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| import | 342.2 | +0.6 | 338.1 | −1.2 | 331.5 | −2.0 |
| export | 355.5 | +0.7 | 357.7 | +0.2 | 357.5 | −0.1 |
| balance | +13.3 | +16.9 | +26.0 |
| Export (in percent) to | Import (in percent) of | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
16.7 |
|
14.1 |
|
|
15.5 |
|
13.5 |
|
|
11.3 |
|
9.4 |
|
|
8.9 |
|
8.2 |
|
|
5.9 |
|
4.8 |
|
|
5.2 |
|
4.5 |
|
|
2.7 |
|
4.4 |
| other states | 33.8 | other states | 39.2 |
traffic
Thanks to its central location as a European trading center, Belgium has one of the world's densest infrastructure networks. In 2016, Belgium ranked sixth out of 160 countries in the Logistics Performance Index compiled by the World Bank . The parameters for international shipping and the logistical time required did particularly well.
railroad
Belgium was the first country in continental Europe to have rail links. The state railway company is called the National Company of the Belgian Railways (NMBS / SNCB) and operates one of the most densely developed railway networks in the world. An S-Bahn went into operation for Brussels and the surrounding area on December 13, 2015 , and S-Bahns have also been running in Antwerp , Charleroi , Ghent and Liège since 2018 .
The traditional sleeping car company Compagnie Internationale des Wagons-Lits , which operated, among other things, the luxury trains Orient Express , North and South Express and Ostend-Vienna Express , was founded by Georges Nagelmackers from Liège .
All places along the entire North Sea coast of Belgium are connected to the longest overland tram line in the world, the Kusttram .
shipping
Belgium is an important transit country between Central and Western Europe . The most important port is Antwerp on the Scheldt , one of the largest and most important seaports in the world. The seaport of Bruges-Zeebrugge is also one of the most modern and important in Europe. The port of Ostend had traditional importance as a ferry port until the opening of the Eurotunnel .
Air traffic
The main airport in the country is Brussels-Zaventem . Other airports are Brussels-Charleroi , Liège , Antwerp and Ostend-Bruges .
The Belgian national airline was the traditional Sabena until it went bankrupt on November 6, 2001 . It went on in the SN Brussels Airlines , which in turn merged with Virgin Express to Brussels Airlines .
Road traffic
In 2013, the entire road network comprised around 154,012 kilometers, of which 120,514 kilometers were paved.
Belgium has a very well developed motorway network with a length of 1,756 kilometers in 2010, which - like all other roads in Belgium - is almost completely equipped with street lamps and illuminated at night. However, this lighting is to be restricted in the future to save electricity and thus to protect the climate and consequently remain switched off between 0:30 a.m. and 4:30 a.m. Due to the high volume of foreign traffic, a motorway toll of 60 euros was planned for 2008, which caused heated discussions and has not yet been introduced.
Culture
gastronomy
There is no typical all-Belgian cuisine, as numerous specialties are more likely to be assigned to the Flemish cuisine or the cuisine of Wallonia or are inspired by the culinary arts of neighboring countries, in particular France (more precisely: Lorraine ). But a world-famous invention was made in Belgium that is often misclassified: French fries . Belgian waffles are also a specialty. The best-known waffles are the Brussels and Liège waffles. Belgium is also known for its pralines , which are among the best in the world. Another special feature is the diversity of varieties of Belgian beers , including numerous abbey beers (Abdijbier, Bière d'Abbaye) with higher alcohol content, fermented in a special way beers (eg. As Lambic , Geuze ) or mixed with fruit flavors beers. The most popular types of beer are Jupiler and Stella Artois , both of which belong to the Belgian brewery group AB-InBev .
Sports

A popular sport in Belgium is football . The Belgian 1st league is one of the oldest in the world. In the 1970s and 1980s, the Belgian national team (known as the Red Devils ) was among the best in the world. However, after participating in the 2002 World Cup , Belgium had not been able to qualify for an international tournament for twelve years. In recent years, however, the Belgian national team has once again been among the best in the world, as demonstrated by winning the bronze medal at the 2018 World Cup . ( See also: Football in Belgium )
The national sport in Belgium, however, is cycling. Because of this, Belgium has produced some celebrities in cycling. So were and are Eddy Merckx , Roger De Vlaeminck , Johan Museeuw , Peter Van Petegem and Tom Boonen of the best cyclists in the world. Important one-day classics take place in Belgium, for example Liège – Bastogne – Liège and the Tour of Flanders .
Special mention should also be made of cyclocross , a special cycling discipline that takes place in winter. The domestic races are attended by tens of thousands of spectators. As a rule, three to four of the eight or so World Cup competitions are held in Belgium, as are most of the other competitions with the highest ranking. Belgium dominates the sport like no other country and has by far the largest number of world champions and overall world cup winners, with Sven Nys in particular.
Tennis is also on the rise. The Flemish Kim Clijsters and the Walloon Justine Henin have long been among the best players in the world.
In athletics, Kim Gevaert (100 and 200 m) is European champion and Tia Hellebaut (high jump) Olympic champion.
Rugby Union is also played in Belgium. However, the Belgian national team has not yet qualified for a Rugby Union World Cup . Belgium is one of the participants in the European Rugby Union Championship , where it meets other emerging national teams. Former President of the International Olympic Committee Jacques Rogge was active for the Belgian national team.
Carom and billiard artistique should not be forgotten , in which the athletes René Vingerhoedt and Raymond Ceulemans dominated the scene for years. Billiards is also very important to many amateur and pub players.
The Spa-Francorchamps circuit is one of the most demanding circuits in motorsport. International racing series, including Formula 1 since 1950, are hosted here at regular intervals . One of the highlights is the annual 24-hour race .
With the Circuit Zolder , Belgium has a second race track of national importance. Formula 1 races were also held here from 1973 to 1984. Nivelles-Baulers , the third course on which Formula 1 races took place, no longer exists.
International grade races have already been held several times on the Heusden-Zolder speedway track . The final of the European Grass Track Championship has already been held on the grass track in Alken in the Limburg province .
comics
Comics are generally very popular in Belgium; King Baudouin, for example, was a big avowed fan. People often encounter the Bandes Dessinées (BD for short, French) or Strips (Dutch) in the cityscape. Quality bookstores in Belgium have special BD departments. In addition, comics are offered in large supermarkets.
Comics are a main export item for Belgian publishers, because many internationally known and famous comic artists and authors come from Belgium, which, compared to its size, has produced the most in Europe. The most famous are Willy Vandersteen ( Suske and Wiske ), Jean Graton ( Michel Vaillant ), Morris ( Lucky Luke ), Hergé ( Tintin ), Peyo ( The Smurfs and others), André Franquin ( Spirou and Fantasio , Gaston and Marsupilami ) and Philippe Geluck (Le Chat).
| year | number |
|---|---|
| 1975 | 14th |
| 1985 | 7th |
| 1995 | 8th |
| 2005 | 28 |
In Belgium it is possible to study comics as a major at art schools such as the Royal Academy of Fine Arts and the Institut Saint-Luc in Brussels. This is why the Bandes Dessinées are also dubbed the “ninth art” in Belgium. In Brussels there is a comic museum ( Center Belge de la Bande Dessinée ), in which this art movement is honored on three floors.
music
In the 15th and 16th centuries, the time of the Renaissance , numerous composers from the area of today's Belgium, especially from Hainaut , were leading and style-defining in Europe (the so-called Dutch). Important names are Guillaume Dufay , Johannes Ockeghem , Josquin Desprez , Heinrich Isaac , Jacob Obrecht , Adrian Willaert , Orlando di Lasso . The French composer César Franck was born in Liège, spent the first thirteen years of his life in Belgium and was already musically active there before the family moved to Paris in 1835 .
In jazz the are harmonica player Toots Thielemans , tenor saxophonist and flutist Bobby Jaspar and guitarist Philip Catherine emerged internationally.
The best-known bands of the 21st century include dEUS , Gotye , Hooverphonic and Triggerfinger .
Attractions
Personalities
- Saint Gudula of Brussels and Eibingen is the patroness of the city of Brussels and a Belgian national saint.
- Known painters Pieter Bruegel the Elder , Peter Paul Rubens , Léonard Defrance , James Ensor and the Surrealist René Magritte as well as the friend of Vincent van Gogh , Eugène Boch , and his sister Anna Boch .
- Well-known architects are the Bauhaus architect Henry van de Velde and the Art Nouveau architect Victor Horta .
- World-famous writers are Charles De Coster , Émile Verhaeren , Maurice Maeterlinck , Georges Simenon and Amélie Nothomb .
- For the music world of the 19th century (and beyond) Adolphe Sax was an important figure. Well-known musicians of the 20th century are the jazz musicians Toots Thielemans and Philip Catherine , the singer and chansonnier Jacques Brel , the crossover and pop singer Helmut Lotti and the Flemish singer-songwriter Frederic Sioen . Furthermore, the rock musician Gotye was born in Belgium, who became famous and successful with his hit Somebody That I Used to Know .
- Belgium has been a stronghold of trance music (previously hard trance) since the late 1990s . The groups Ian Van Dahl , Lasgo and Sylver are internationally successful . In the more progressive scene z. B. Push or Yves Deruyter very well known.
- Well-known actors are the action film hero Jean-Claude Van Damme , the actors Benoît Poelvoorde and Johnny Galecki , the actresses Émilie Dequenne , Cécile de France and Jasmin Schwiers . The brothers Jean-Pierre and Luc Dardenne are successful directors .
- Well-known athletes are the tennis players Kim Clijsters and Justine Henin , the soccer players Jean-Marie Pfaff , Marc Wilmots , Emile Mpenza , Daniel Van Buyten and Vincent Kompany , the racing driver Jacky Ickx and the racing cyclists Eddy Merckx , Tom Boonen , Johan Museeuw , Peter Van Petegem and the motocross racer Stefan Everts .
- The comic authors and drawers Hergé ( Tintin ), Morris ( Lucky Luke ), Franquin ( Marsupilami ) and Peyo ( The Smurfs ).
particularities
In Belgium, active euthanasia is allowed, even for minors, and is regulated by a law that provides doctors with special training for this purpose.
In 2017, a total of 2,309 people used active euthanasia, including three minors. In 2009 there were 822 cases, almost 80 percent of them in Flanders.
See also
- List of rulers of Belgium
- List of cities in Belgium
- Brussels-Rundschau (German-language Belgian newspaper)
- Belgian field post
- Women's suffrage in Belgium
- Women's rights in Belgium
literature
- Christoph Driessen : History of Belgium. The divided nation . Verlag Friedrich Pustet, Regensburg 2018, ISBN 978-3-7917-2975-6 .
- Insa Meinen: The Shoah in Belgium. Scientific Book Society, Darmstadt 2009, ISBN 978-3-534-22158-5 .
- Johannes Koll (Ed.): Belgium. History - Politics - Culture - Economy. Aschendorff Verlag, Münster 2007, ISBN 978-3-402-00408-1 .
- Frank Berge, Alexander Grasse : Belgium - disintegration or federal future model? The Flemish-Walloon Conflict and the German-speaking Community. Leske and Budrich, Opladen 2003 (Regionalization in Europe, Volume 3), ISBN 3-8100-3486-X .
- Claus Hecking : The Belgian political system. Leske and Budrich, Opladen 2003, ISBN 3-8100-3724-9 .
Web links
|
Further content in the sister projects of Wikipedia:
|
||
|
|
Commons | - Media content (category) |
|
|
Wiktionary | - Dictionary entries |
|
|
Wikinews | - News |
|
|
Wikisource | - Sources and full texts |
|
|
Wikivoyage | - Travel Guide |
- Official website of the Federal Public Service (Dutch, French, German, English)
- Royal Palace - The Monarchy in Belgium (Dutch, French, German, English)
- Country data from the German Federal Statistical Office
- Database of indexed literature on the social, political and economic situation in Belgium
- Belgiuminfo - German-language current information site
- 175 years ago an opera sparked the Belgian revolution. In: arte.tv. August 25, 2005, archived from the original on April 21, 2020 .
- Link catalog on Belgium at curlie.org (formerly DMOZ )
- CIA World Factbook: data in the CIA Factbook (English)
Individual references and comments
- ↑ a b The role of the monarchy , belgium.be; Accessed April 12, 2020
- ↑ a b The King , The Monarchy in Belgium; Accessed April 12, 2020
- ↑ a b La Belgique est désormais un peu plus grande. In: lalibre.be . January 10, 2019, accessed on January 17, 2019 (French, adjustment of the area to new Eurostat specifications , which means that the base area has increased by 160 km² from 2019 by including beaches at low water).
- ↑ a b Mouvement de la population en 2020. ( XLSX ; 2.56 MB ) In: statbel.fgov.be. Statbel - Direction générale Statistique - Statistics Belgium ( Federal Public Service ), accessed on July 4, 2021 (French).
- ↑ Population growth (annual%). In: World Economic Outlook Database. World Bank , 2020, accessed March 28, 2021 .
- ^ World Economic Outlook Database April 2021. In: World Economic Outlook Database. International Monetary Fund , 2021, accessed June 23, 2021 .
- ↑ Table: Human Development Index and its components . In: United Nations Development Program (ed.): Human Development Report 2020 . United Nations Development Program, New York, pp. 343 ( undp.org [PDF]).
- ^ In front of the Belgian franc ( bfr ), divided into 100 centimes ( c ).
- ↑ European Union: Degree of urbanization in the member states in 2018 . In: de.statista.com . Retrieved December 3, 2019.
- ^ A b Horst Siegemund: Kingdom of Belgium . In: Winfried Steffani (Ed.): Government majority and opposition in the states of the EC . 1991, p. 61-91 ( springer.com ).
- ^ A b Wichard Woyke : The Belgian political system . In: Wolfgang Ismayr (Ed.): The political systems of Western Europe . 3. Edition. UTB, 2004, p. 389-414 ( springer.com ).
- ↑ a b The monarchy in Belgium. ( PDF ; 4.1 MB ) Olivier Alsteens, Director General at the Prime Minister's Public Service Chancellery, archived from the original on May 16, 2011 ; Retrieved August 12, 2014 .
- ^ Bruxelles, singulière et specifique. In: lalibre.be. La Libre Belgique, August 18, 2010, accessed November 13, 2016 (French).
- ↑ Why did Belgium become a federal state? In: ostbelgienlive.be. Ministry of the German-speaking Community of Belgium, accessed July 26, 2017 .
- ^ Christoph Driessen : History of Belgium. The divided nation. Regensburg 2018, pp. 24–32, p. 71.
- ^ Walter Sperling / Adolf Karger (eds.): Fischer Länderkunde - Volume 8: Europa, Frankfurt am Main 1989, pp. 220-225.
- ↑ The Belgian coast. In: belgium.be. Federal Public Service (FPS), accessed June 7, 2021 .
- ↑ Dieter H. Kollmer : The Belgian colonial rule 1908 to 1960 . In: Bernhard Chiari , Dieter H. Kollmer (ed.): Guide to the history of the Democratic Republic of the Congo . 2nd Edition. Publishing house Ferdinand Schöningh, Paderborn u. A. 2006, p. 45 .
- ↑ Jens Thiel: Human basin Belgium. Recruitment, deportation and forced labor in the First World War . Klartext Verlag, Essen, ISBN 978-3-89861-563-1 .
- ↑ Michael Zimmermann : Racial Utopia and Genocide. The National Socialist "Solution to the Gypsy Question" . Hamburg 1996, ISBN 978-3-7672-1270-1 .
- ^ Mart Martin: The Almanac of Women and Minorities in World Politics. Westview Press Boulder, Colorado, 2000, p. 34.
- ↑ Official election results 2019. Accessed June 20, 2019 .
- ^ Fragile States Index: Global Data. Fund for Peace , 2020, accessed March 26, 2021 .
- ^ Democracy Index. The Economist Intelligence Unit, accessed March 26, 2021 .
- ↑ Global Freedom Score. Freedom House , 2020, accessed March 26, 2021 .
- ↑ 2021 World Press Freedom Index. Reporters Without Borders , 2021, accessed June 23, 2021 .
- ↑ Corruption Perceptions Index 2020. Tabular ranking. Transparency International, accessed March 26, 2021 .
- ↑ Jacques Leclerc: L'État belge - Données demolinguistiques. In: axl.cefan.ulaval.ca . Retrieved October 28, 2020 (French).
- ^ Jacques Leclerc: L'aménagement linguistique dans le monde. In: axl.cefan.ulaval.ca . Retrieved October 28, 2020 (French).
- ^ Christoph Driessen: History of Belgium. The divided nation. Regensburg 2018, pp. 219-221.
- ↑ Leterme is Belgium's new head of government. In: Spiegel Online. March 20, 2008, accessed February 20, 2020 .
- ↑ Voltallige regering biedt hair ontslag aan , VRT Nieuws, December 19, 2008 ( Memento of December 20, 2008 in the Internet Archive )
- ^ Yves Leterme nommé Premier ministre. In: lalibre.be . November 25, 2009, accessed April 14, 2020 (French).
- ↑ Open VLD doet deur niet helemaal tight. In: deredactie.be. April 22, 2019, archived from the original on April 25, 2010 ; Retrieved October 22, 2019 (Dutch).
- ^ Elio Di Rupo a été nommé Premier ministre, le gouvernement est dévoilé , rtbf.be, 6 December 2011.
- ↑ Albert II abdicates. In: Spiegel Online. July 3, 2013, accessed December 10, 2014 .
- ↑ René Höltschi: Reformer with severe headwind. In: nzz.ch.ch . October 11, 2014, accessed on July 10, 2020 (preview; full text: registration required).
- ↑ Belgian head of government announces resignation . Welt Online, December 18, 2018.
- ↑ Belga : Sophie Wilmès nommée Première ministre par intérim, première femme à ce poste La Libre October 27, 2019, accessed online on October 27, 2019, 10:56 p.m. CET
- ↑ Daniel Steinvorth: In Belgium the new Prime Minister is the woman of the hour. In: nzz.ch, March 19, 2020, accessed on March 19, 2020.
- ↑ L'installation du gouvernement De Croo Ier . La Libre Belgique , October 2, 2020 edition, pages 4–9.
- ↑ ec.europa.eu
- ↑ Home | SIPRI. Retrieved July 10, 2017 .
- ↑ Provision of data on deficit and debt 2009 (PDF; 427 kB) Eurostat, November 15, 2010, accessed on January 7, 2019 .
- ↑ Rating agency S&P downgrades Belgium to “AA”. derstandard.at, November 25, 2011, accessed on January 21, 2012 .
- ↑ Public debt in the euro area fell to 91.2% of GDP. (PDF; 322 KB) Press release Euro indicators 205/2016. In: ec.europa.eu. Eurostat , 24 October 2016, accessed 26 February 2020 .
- ↑ The Fischer World Almanac 2010. Figures, data, and facts. Fischer, Frankfurt, September 8, 2009, ISBN 978-3-596-72910-4 .
- ↑ Bruno Urmersbach: Share of military spending in GDP in Belgium until 2018. In: de.statista.com. Retrieved October 26, 2019 .
- ^ Jean-Pierre Liégeois: Roms en Europe . Conseil de l'Europe , 2007, ISBN 978-92-871-6050-8 , Annexe 3 - Glossaire du Conseil de l'Europe sur les Roms et les Gens du voyage , p. 295 (French, limited preview in Google Book Search [accessed April 28, 2020]).
- ^ Philippe Masson, homme de voyage. In: cmgv.be. 2015, archived from the original on September 8, 2015 ; accessed on August 28, 2019 (French). Philippe Masson, homme de voyage ( Memento of the original from September 8, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ vzw Alert. Pastoraal voor Voyageurs, Manoesjen, Roms en Roma ( Memento of February 8, 2009 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Les Gens du voyage en Wallonie. (PDF; 1.2 MB) In: cmgv.be. P. 5 , archived from the original on January 12, 2007 ; Retrieved on May 25, 2019 (French, quote freely translated): “The travelers (also called Yenish , especially if they come from the Rhineland, Lorraine or Alsace) form very complex groups of families from European society come from and maintain various close ties with the gypsies. In our regions as in France, the proximity between the groups can be so strong that it is useless to separate them. " Les Gens du voyage en Wallonie ( Memento of the original on 12 January 2007 at the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link is inserted automatically and not yet tested. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Étude de législation comparée n ° 145 - April 2005 - Le stationnement des gens du voyage. In: senat.fr. April 2005, accessed November 4, 2019 (French).
- ↑ a b c d e f g Brussels 2030: moslimmeerderheid of miskennen werkelijkheid? In: npdata.be. February 13, 2012, accessed October 20, 2019 (Dutch).
- ↑ BuG 159 - Report uit het Gewisse - 7 May 2012. In: npdata.be . May 7, 2012, accessed December 15, 2019 (Dutch).
- ↑ a b Voor het first sea Moroccanse dan Italiaanse migrants. In: hbvl.be. May 21, 2007, accessed July 28, 2019 (Dutch).
- ↑ World Population Prospects - Population Division - United Nations. Retrieved July 13, 2017 .
- ^ The World Factbook - Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved August 3, 2017 .
- ↑ J. Kramer, Bilingualism in the Benelux countries, Hamburg: Buske-Verlag 1984, p. 113ff.
- ↑ Liberated, connected, committed. In: de.protestant.link. United Protestant Church in Belgium. Retrieved November 23, 2018 .
- ↑ www.npdata.be
- ↑ Verenigde Protestant Church state inzegening homohuwelijk toe. In: holebi.info. November 30, 2007, accessed December 4, 2018 (Dutch).
- ↑ Cnaan Liphshiz: Belgian carnival float features puppets of grinning Jews, a rat and money bags. In: Jewish Telegraphic Agency website. March 4, 2019, accessed March 31, 2020 (American English).
- ↑ Flora Cassen: 'Jews Don't Get Our Humor': How a Belgian Town Is Doubling Down on Its anti-Semitism. In: Haaretz , October 28, 2019; Rutger Lievens, Cédric Maes: Aalsterse carnavalists laugh opnieuw met joden en Unesco: “Pure provocatie”. In: hln.be . October 21, 2019, accessed September 28, 2020 (Belgian Dutch).
- ↑ Carnival in Aalst no longer cultural heritage. In: juedische-allgemeine.de . December 14, 2019, accessed December 15, 2019.
- ↑ Aalster Carnival again with anti-Semitic motifs. In: juedische-allgemeine.de . February 23, 2020, accessed July 5, 2020.
- ↑ Andreas Kockartz: Jew-hatred: Significant increase in anti-Semitic crimes in Belgium. In: vrt.be . March 2, 2019, accessed February 24, 2020.
- ↑ Gross domestic product (GDP) at current market prices according to NUTS 3 regions. Eurostat , February 26, 2016, accessed on December 3, 2016 .
- ↑ Federal Foreign Office - Belgium - overview , last seen on November 26, 2016.
- ^ A b The World Factbook - Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved August 12, 2017 .
- ↑ At a Glance: Global Competitiveness Index 2017–2018 Rankings. In: reports.weforum.org. Accessed December 11, 2018 .
- ↑ Belgium. (PDF; 230 KB) In: heritage.org. 2019, accessed on February 3, 2020 .
- ↑ Belgium - unemployment rate to 2025. Accessed January 9, 2021 .
- ↑ Belgium - Employed until 2021. Accessed January 9, 2021 .
- ↑ Belgium - Employment by economic sector until 2019. Accessed January 9, 2021 .
- ↑ Services, etc., value added (% of GDP) | Data. Retrieved August 12, 2017 (American English).
- ↑ The Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Report 2017. Accessed July 1, 2017 .
- ↑ “On the right path” - Belgian Foreign Minister confirms nuclear phase-out by 2025. In: aachener-zeitung.de. March 18, 2019, accessed May 26, 2019 .
- ↑ Global Wealth Report 2017: Where Are We Ten Years after the Crisis? In: credit-suisse.com. November 14, 2017, accessed December 13, 2018 .
- ↑ Eurostat. Retrieved July 31, 2019 .
- ↑ Real GDP growth rate - volume. In: ec.europa.eu. Retrieved August 3, 2019 .
- ↑ Main tables, National Accounts including GDP: 2010
- ↑ HICP - inflation rate. In: ec.europa.eu. Eurostat, accessed on 31 July 2019 .
- ↑ a b Germany Trade and Invest GmbH: GTAI - economic data compact. Retrieved July 29, 2017 .
- ↑ Global Rankings 2018 | Logistics Performance Index. Retrieved September 14, 2018 .
- ↑ World Film Production Report (excerpt) ( Memento from July 6, 2011 in the Internet Archive ), Screen Digest, June 2006, pp. 205–207 (accessed June 15, 2007)
- ^ Belgium: euthanasia for minors provided for the first time - health. In: Spiegel Online . September 17, 2016. Retrieved June 9, 2018 .
- ↑ More cases of active euthanasia in Belgium. In: aerzteblatt.de. July 18, 2018, accessed March 13, 2019 .
- ↑ Euthanasia in Belgium: more cases in 2009 - more cases in Flanders. In: brf.be. May 11, 2010, accessed February 1, 2020 .
Coordinates: 51 ° N , 5 ° E