Renault FT
| Renault FT | |
|---|---|

Renault FT |
|
| General properties | |
| crew | 2 (driver and commander / shooter) |
| length | 4.10 m, 5 m (with boom) |
| width | 1.74 m |
| height | 2.14 m |
| Dimensions | 6.5 t (with MG), 6.7 t (with cannon), 7 t (TSF and FT 75 BS) |
| Armor and armament | |
| Armor | 6-22 mm |
| Main armament | a 37mm cannon or a machine gun |
| agility | |
| drive | Renault, 4-cylinder petrol engine, water-cooled 29 kW (39 PS) |
| Top speed | 8 km / h (road) |
| Power / weight | 3.7 kW / t (5 HP / t) |
| Range | 40 km |
The Renault FT (the designation FT17 or FT-17 is common but was never used by Renault) was a French tank of the First World War . The construction of the Société des Automobiles Renault was so successful that it was formative for later armored vehicles.
history
First World War
After Gunther Burstyn , the French artillery officer Jean Baptiste Eugène Estienne (1860–1936) also recognized the value of an armored vehicle traveling on tracks . After the outbreak of World War I, Estienne contacted Louis Renault about this ; this rejected the building for the time being. Renault began developing the FT in mid-1916. Main designer Rodolphe Ernst-Metzmaier was the actual inventor of the advanced features such as the self-supporting armored hull and rotating gun turret . After some prototypes were completed in 1917, the French army ordered 3500 pieces. In addition to Renault , the production order was also distributed to Berliet , Delaunay-Belleville and SOMUA . This led to minor differences, especially on the tower. Many French and some British companies were suppliers . 3,177 pieces were made for the French army , 2,697 of them during the First World War.
Renault also delivered 144 pieces to the American Army in France . In addition, contracts were concluded to have 4400 units built under license in the United States by Van Dorn Iron Works ( Cleveland ), Maxwell Motor Company ( Dayton ) and CL Best (Dayton), the first copies of which, however, were not delivered until October 1918 and therefore not were used more in the First World War. A total of 952 pieces of these licensed buildings, designated as M1917, were manufactured.
The first use took place on May 31, 1918 at Ploisy near Soissons . After the failure of the last German offensive on the Marne in mid-July 1918, the now widely deployed FT played an important role in the counter-offensive of the French troops and the American Expeditionary Forces , beginning on July 18, 1918 at Villers-Cotterêts .
The Battle of Amiens (1918) - it began on August 8, 1918, the Black Day of the German Army - initiated the Allied Hundred Days Offensive .
Interwar period
After the end of the First World War, France used the FT in its colonies . Many copies were exported, so many countries in Eastern Europe - especially Poland - as well as the Dutch armed forces and the Japanese army owned FTs. In some countries the FTs have been modified over time; above all, the armament was adapted to the standards of the respective army.
In the Polish-Soviet War (1920) the tank was used on the Polish side. Unlike the First World War, this conflict was a war of movement . Here, the low speed of the FT had a disadvantageous effect, which is why the transport by rail was forced.
A demonstration took place for use in the South American Chaco War between Bolivia and Paraguay (1932–1935), but the tank did not enter the Chaco area.
In the 1930s, 1580 tanks of the French army were converted to a 7.5 mm Reibel machine gun as the FT modifié 31 . The NC 1 or NC 27 and NC 2 or NC 31 were further developments, but were only produced in small numbers. The Renault FT was later largely replaced by the Renault R-35 in the French army .
The Switzerland bought two 1921 FT and 1939 three more.
Second World War



At the beginning of the Second World War , about 2,700 copies were still in the French army , of which 534 were still in the front line. The rest was used in training units or was stored in depots. They were completely inferior to the German tanks in combat. In 1940 the Wehrmacht captured 1704 tanks in the western campaign . Only around 500 to 600 tanks were completely overhauled in the Renault factory in Paris and used again as tanks. They were designated as Panzerkampfwagen 17R 730 (f) or Panzerkampfwagen 18R 730 (f) . Wehrmacht and Waffen-SS used the tanks for security tasks in occupied areas. The Luftwaffe deployed 100 tanks to secure air bases. The Wehrmacht used numerous FT towers, from unrepaired tanks, in bunkers on the Atlantic Wall . During the Africa campaign , FT towers were also used in the ring stands in front of Tobruk .
In April 1945, three FTs of the air base security from Rotenburg were set out east of Verden to fight against approaching British troops. They were given up operational by the crews in the combat strip of the 7th / 5th Marine Grenadier Regiment near Südkampen and captured by the A Company KRRC ( King's Royal Rifle Corps ).
technology
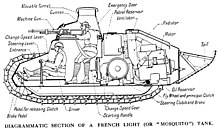
The Renault FT consisted of a self-supporting trough with a crawler mechanism sprung with coil and leaf springs . On each side there was a medium-sized drive wheel at the rear, a large guide wheel at the front and nine small running wheels on four sprung bogies in between . The guide wheel was made of wood and had a steel rim. The chain rolled on six support rollers to the guide wheel. Both the hull and the turret were riveted . The engine, gearbox and 100 liter fuel tank were housed in the rear. The 360 ° rotatable tower sat on the tub in front of it. The driver was accommodated in the front center and reached his place through a hatch that opened on both sides on the front. The commander / gunner in the tower had his own hatch upwards and one in the rear of the tower.
Due to the turret, which was placed quite far forward, the tank was top-heavy and often got stuck upside down in depressions, funnels and trenches during testing in difficult terrain. Even in very muddy terrain, the top-heaviness was a major disadvantage; the front end tended to dig in. To counter this shortcoming, a boom was attached to the stern at the height of the drive wheel. This approximately one meter long boom could then be weighted down to such an extent that it was able to drive convincingly; however, this came at the expense of acceleration and speed. The boom could be removed for transport.
The armor of the FT was a maximum of 16 mm thick, the horizontal plate 8 mm and the floor 6 mm. The turret was also armored 16 mm thick; only the Berliet turret had 22 mm of armor.
There were two openings in the tower in order to be able to use a pistol from the vehicle in emergency situations in close combat .
variants
- FT Char mitrailleur: Basic variant, armed with the Hotchkiss M1914 machine gun with 4800 rounds
- FT Char canon: Basic variant, armed with a Puteaux SA18 37 mm L / 21 short barrel cannon with 237 rounds of ammunition (200 rounds of explosive ammunition , 25 armor-piercing projectiles and 12 shrapnel projectiles)
- FT BS: Assault gun armed with a 75 mm Blockhaus-Schneider gun in the short-barrel version, as it was also used in Galopin rotary sunk turrets .
- FT TSF: command tank with radio . TSF stands for télégraphie sans fil (translated as wireless telegraphy )
- FT modifié 31: FT converted to a 7.5 mm Reibel machine gun in 1931 with 3600 rounds of normal and 450 rounds of armor-piercing ammunition
- Tank M1917: variant made in the United States. 374 vehicles with 37 mm M1916 cannon, 526 with Browning M1919 machine gun and 50 command vehicles
- Fiat 3000 : variant made in Italy
- Russian FT (Russki Reno): 15 copies were built 1919-1920 in Nizhny Novgorod (which was then called Gorky) in the Sormovo plant (Krasnoye Sormovo). In the already cramped tower, a machine gun was housed in addition to the 37 mm cannon. The tanks had FIAT engines.
- Renault Kō-gata Sensha ( Japanese ル ノ ー 甲型 戦 車 , German "Renault tank model A", as the Renault NC 27 was designated with Otsu-gata (model B) ) or type 79 Kō-gata: 13 French FT -Tanks (eight with machine guns, four with cannons) bought by Japan in 1919. In the mid-1920s, these were converted to the Japanese 6.5 mm machine gun type 3 and 37 mm infantry gun type 11 .
- armored Draisine R: In Poland 38 pieces were converted for railroad draisines . The tanks drove the trolley through a new gearbox; they could be disconnected within a few minutes and moved conventionally on chains. On the draisine, the FT could reach over 50 km / h.
Russian copy of the FT-17 (monument in Nizhny Novgorod )
Operational experience
The FT has been described as a very manoeuvrable and operational combat vehicle in all theaters of war. The armor was strong enough not to let rifle projectiles penetrate, but fragments from the inside of the armor could still injure the crew. Towards the end of the First World War, the German tank rifle M1918 was developed, with which the armor could be penetrated, especially directly in front of the driver.
The FT was light enough to be transported to the place of use in the trucks of the time . Renault offered the FU truck for this purpose .
designation
The most common name is FT-17 . Later Renault tank models have names indicating the year they were introduced, e.g. B. Renault R-35 (1935) and Renault R-40 . FT is a Renault-specific coding as it was used for vehicles of this time. Sometimes the code FT is used as an abbreviation for Faible Tonnage d. H. indicated low weight , which is wrong. The number 17 refers to the model year 1917. Renault describes the tank in the associated operating manual as Char d'assault 18 Chevaux / HP for battle tanks 18 horsepower . A sometimes used designation FT-18 for an alleged later version is not officially confirmed.
Remaining vehicles
Around 40 preserved vehicles of various variants can be found around the world, including in the Bovington Tank Museum , the Musée des Blindés and the Thun Tank Museum . This Swiss tank was completely restored inside and out by 2009 and is one of the few roadworthy examples. Another model is exhibited in the War and Resistance Museum in Overloon (Netherlands) (see picture above). Two more specimens were discovered in a scrapyard in Kabul in 2003 and transported to the USA to be restored there, a war-damaged FT is on display in the National World War I Museum in Kansas City (Missouri). A FT is in the Defense Technical Study Collection in Koblenz .
An FT tank was buried as a stationary machine-gun nest in the (neither original nor built) trench system near Barst (on the Maginot Line ) .
See also
literature
- David Miller: The illustrated directory of tanks of the world. Zenith Imprint, 2000, ISBN 978-0-7603-0892-9 limited preview in the Google book search.
- Marshall Cavendish: History of World War I. 2001, ISBN 978-0-7614-7234-6 limited preview in Google Book Search.
- Spencer Tucker: Tanks. ABC-CLIO, 2004, ISBN 978-1-57607-995-9 limited preview in Google book search.
- Steve Crawford: Tanks of World War II. MBI Publishing Company LLC, 2000, ISBN 978-0-7603-0936-0 limited preview in Google Book Search.
- Mark R. Henry: The US Army of World War I. Osprey Publishing, 2003, ISBN 978-1-84176-486-3 limited preview in Google Book Search.
- David Doyle: FT-17 / M1917 WWI Tanks (Walk Around, No. 27023). Squadron Signal Publications, 2011, ISBN 978-0-89747-636-2 .
Web links
- http://www.geocities.com/witekjl/main.html ( Memento from April 22, 2004 in the Internet Archive )
- http://www.militaryphotos.net/forums/archive/index.php/t-46568.html
- FT-17 in the Polish Army http://www.geocities.com/pibwl/ft17.htm ( Memento from February 26, 2008 in the Internet Archive )
- FT in the Czechoslovak Army
Individual evidence
- ↑ www.louisrenault.com ( Memento of the original dated July 6, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ^ Benedict Crowell: America's Munitions 1917-1918 . Government Printing Office, Washington 1919, p. 156 ( Digitized - report by US Secretary of War Benedict Crowell).
- ↑ Spencer Tucker: Tanks. ABC-CLIO, 2004, ISBN 978-1-57607-995-9 limited preview in Google book search
- ^ Photo of a Japanese tank in Manchuria in 1931
- ↑ Alejandro Quesada: The Chaco War 1932-1935. Volume 474 of the Men-at-Arms Series. Osprey Publishing, 2011, ISBN 978-1-84908-416-1 , p. 34. Limited preview in Google Book search
- ↑ Panzermuseum Thun ( Memento of the original from September 23, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. July 2005, p. 2. (PDF; 2.4 MB)
- ↑ Alexander Lüdeke: captured tanks of the Wehrmacht. Great Britain, Italy, Soviet Union and USA 1939–45. Motorbuch, Stuttgart 2011, ISBN 978-3-613-03359-7 , pp. 85-88
- ^ T-17 in the Polish Army ( Memento from October 12, 2002 in the Internet Archive )
- ^ A b Mark R. Henry: The US Army of World War I. Osprey Publishing, 2003, ISBN 978-1-84176-486-3, limited preview in Google Book Search
- ↑ 6 ton tank M1917. In: afvdb.50megs.com. June 21, 2000, accessed January 1, 2015 .
- ^ David Bullock: Armored Units of the Russian Civil War. Osprey Publishing, 2006, ISBN 978-1-84176-545-7 limited preview in Google Book Search
- ↑ Type 79 Ko. In: ww2technik.de. Retrieved January 1, 2015 .
- ^ Steven J Zaloga: French Tanks of World War I , Osprey Publishing , 2011, ISBN 978-1-78096-213-9 , pp. 21-22 [1]
- ↑ Operating instructions of the FT-17
- ^ Dodge 1930 - Loretan Kühler AG. In: loretankuehler.ch. Retrieved January 1, 2015 .
- ^ Rare French Tank Being Taken to US ( Memento from April 10, 2003 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Darryl Levings: KC's National World War I Museum boasts one of the few tanks left from the Great War. In: kansascity.com. May 24, 2014, accessed January 1, 2015 .
- ↑ Report 2010. In: westwalltag.de. Retrieved January 1, 2015 .