Mitsubishi i-MiEV
| Mitsubishi | |
|---|---|
|
Mitsubishi Electric Vehicle
|
|
| Electric Vehicle | |
| Production period: | since 2009 |
| Class : | Microcar |
| Body versions : | Station wagon |
| Engines: |
Electric motor : 49 kW |
| Length: | 3475 mm |
| Width: | 1475 mm without exterior mirrors, with exterior mirror 1792 mm |
| Height: | 1610 mm |
| Wheelbase : | 2550 mm |
| Empty weight : | 1110 kg |
| Stars in the Euro NCAP - Crash Test |
|
The Mitsubishi Electric Vehicle , formerly i-MiEV (三菱· i Mitsubishi i-MiEV, wherein MiEV for M Mitsubishi i nnovative e lectric V ehicle group) is an electric - Kleinstwagen ( K-Car ) of the Japanese car manufacturer Mitsubishi Motors , which on the Mitsubishi i introduced in 2006 is based. The sister models Citroën C-Zero and Peugeot iOn are offered with identical technology . In Germany, the small electric car has been offered under the model name Mitsubishi Electric Vehicle since March 2014 , from mid-2016 only the sister models were sold. C-Zero and iOn were discontinued in summer 2020. The i-MiEV is still sold in Japan and Norway, among others.
Manufacturing and model maintenance
Series production of this vehicle began in Japan on June 5, 2009 . In August and September 2009 a tour of Germany with three right-hand drive vehicles took place, during which the electric vehicles were presented to the public, journalists and companies in some regions.
At the Geneva Motor Show 2009, the “i-MiEV Prototype” was presented alongside the “i-MiEV SPORT AIR”. This is a concept vehicle specially designed for European requirements . The Mitsubishi i-MiEV has been available on the European market since December 2010 . In Germany , the i-MiEV was initially offered at a price of 34,990 euros plus transfer costs. According to Mitsubishi, around 34,000 vehicles had been sold worldwide at the eCarTec 2012 booth in Munich by October 2012.
A facelift was carried out with the 2012 model year, the standard equipment includes heated front seats, an integrated radio-CD / MP3 combination, a switchable warning tone up to a speed of 35 km / h, a remote control for controlling the air conditioning and charging the battery including charge level indicator. The price was reduced to 29,900 or 29,300 euros (Austria / Germany).
In August 2012, the production of the C-Zero and the iOn was temporarily stopped due to low sales figures.
For the 2014 model year, Mitsubishi announced a facelift of the electric vehicle. a. the maximum range has been increased from 150 to 160 kilometers and LED instead of halogen headlights are used. Furthermore, the entry price was reduced by over 5,500 euros to 23,790 euros. The revised electric vehicle will be available in Germany from April 2014. After a delivery stop at Mitsubishi in mid-2016, only the sister models from Citroën and Peugeot are available. (As of 02/2018)
Citroën offered the C-Zero from 21,800 euros with a range of 100 km according to WLTP and gave a guarantee on the electric battery of 8 years or 100,000 km, whichever comes first.
Mitsubishi i-MiEV Cargo, Tokyo Motor Show 2009
Technical specifications
Range and consumption
The 2014 i-MiEV with the 16 kWh battery has a range of 160 kilometers according to the NEDC standard driving cycle ; the previous version has 150 km.
According to the CoC data sheet, the i-MiEV has an energy consumption of 13.5 kWh ⁄ 100 km from the socket ( tank-to-wheel ).
In an ADAC test on a specified route in South Tyrol , the tested Peugeot iOn consumed 12.87 kWh ⁄ 100 km . This corresponds to a consumption of 1.45 liters of petrol.
In a long-term test in Denmark with approx. 740 drivers, approx. 1/4 million journeys over approx. 2.3 million km, an average of 18.3 kWh ⁄ 100 km of power was required, which corresponds to a range of around 80 km. In winter, the average consumption is 22.5 kWh ⁄ 100 km higher and the range is correspondingly lower at 65 km, in summer it is slightly higher at 90 km (consumption 16.8 kWh ⁄ 100 km ; each calculated with 14.5 kWh of usable battery capacity) .
Others
The operation of the fully electric heating at the highest level with 5 kW corresponds roughly to the energy consumption for constant travel at 50 km / h. The range is reduced accordingly.
The maximum speed is 130 km / h.
technology
engine
The sole drive of the i-MiEV is a permanent magnet synchronous motor with an output of 49 kW (67 PS) at 2500–8800 / min and a torque of 180 Nm between 0 and 2000 / min. The electric motor is located under the trunk and drives the rear axle ( rear-wheel drive ). An originally announced wheel hub motor was discarded. The acceleration from 0 to 100 km / h takes about 15.9 s.
Drive battery
The traction battery, which is located in the floor of the vehicle, weighs 200 kg and consists of 88 lithium-ion accumulator cells with cathodes made of lithium manganese oxide (LiMn 2 O 4 ). The cells, each with 50 ampere hours and a nominal cell voltage of 3.7 volts, result in a total voltage of approx. 330 volts. The cell blocks with the designation LEV50-4 come from the supplier GS Yuasa and are given as 109 Wh / kg or 218 Wh / l. The gross capacity of the battery is 16 kWh . In favor of the service life, the battery management system (BMS) allows 80 to 90% of the gross capacity to be used (13–15 kWh net capacity). The battery cost $ 14,000 in 2009, with a later mass production target of $ 800 to $ 1200.
In the sister models Citroën C-Zero and Peugeot iOn, the battery was reduced by 8 cells in 2012 (14.5 kWh gross capacity). The usable capacity is approx. 14 kWh due to an increased degree of discharge (DoD).
In order to guarantee the best possible working temperatures and to optimize the service life, Mitsubishi has set up an air cooling system that is activated by the battery management system if necessary. A battery heater was not used.
In November 2014, a long-term test over three years with a total of 40,000 kilometers was published by the Austrian traffic club ÖAMTC , together with the Vienna University of Technology . As a result, the battery capacity and thus the range has fallen by 17% compared to the nominal value. According to the manufacturer, a capacity reduction of approx. 17% should only occur at more than double the measured value, after approx. 100,000 kilometers driven.
Temperature dependence of the drive battery
Several important statements can be derived from the technical information:
- The battery can only work 100% in the range between +12 and +31 ° C.
- Temperatures> 31 ° C lead to a reduction in performance and> 50 ° C to the destruction of the battery cells.
- Temperatures <12 ° C lead to performance restrictions, but only slightly. The durability is not affected.
- The charging behavior (curve in the upper half) is more restricted by low temperatures than the discharging behavior (curve in the lower half).
The drive battery can only develop its full capacity in warm weather. Only then is a maximum range of 160 km possible. At 0 ° C battery temperature, the battery can only be charged to about 60%. The segment display does not provide any information about this, but the exact range display. If the battery is colder than −20 ° C, it can no longer be charged. Conversely, a fully charged battery in warm temperatures can give up almost 100% of its capacity at −10 ° C, and more than 60% at −20 ° C.
Load capacity
The drive battery can be fully charged in several hours using a normal Schuko socket with 2.7 kW. There is also the option of charging the battery to 80% in 15 to 30 minutes using a DC charging station in accordance with the Japanese CHAdeMO standard with up to 40 kW of power.
Power supply of the components
In addition to the drive battery, the Mitsubishi i-MiEV has a lead battery with 12 volts / 27 Ah for the control units, lighting, power steering, vacuum and water pump and audio system. This is recharged from the drive battery by a DC / DC converter . The drive battery directly supplies the electric motor, air conditioning compressor and vehicle heater with a nominal output of 5 kW. The components are linked via CAN bus , and monitoring via the battery management system.
construction
Another unusual feature for a small car today is that the Mitsubishi i-MIEV a self-supporting aluminum - skeleton body has.
For the European market, the front track is widened by 95 mm and rear by 135 mm; the total width is thus 1475 mm. The overhangs at the front and rear are extended by a total of 55 mm for occupant and pedestrian protection, resulting in a total length of 3475 mm.
Braking system
The vehicle has internally ventilated disc brakes on the front axle and drum brakes with an anti-lock braking system (ABS) on the rear axle .
Registration numbers
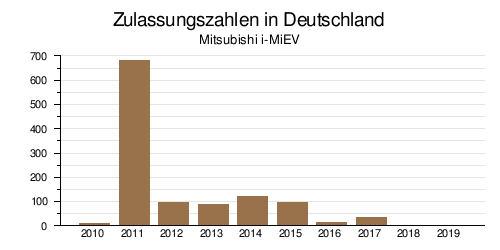
Since the market launch in 2010 up to and including December 2017, only 1,150 Mitsubishi i-MiEVs have been newly registered in Germany. 2011 was the most successful sales year with 683 units. The identical Peugeot iOn was registered 995 times between 2011 and December 2017.
Awards
In 2011 the Mitsubishi i-MiEV received the Plus X Award as the best electric vehicle . Furthermore, in 2012, the first electric car in series production was awarded the winner in the alternative drives class by the FIA automotive association for the second time .
See also
Web links
- Mitsubishi Official Website: Electric Vehicle
- greengear.de: data, facts, pictures
swell
- Automobil Revue , catalog number 2007 (technical data)
- Sprint number 01/2008
Individual evidence
- ↑ Citroen C-Zero 2010 dimensions, boot space and interior. automobiledimension.com, accessed September 13, 2019 .
- ↑ NCAP crash test Mitsubishi i-MiEV
- ↑ NCAP crash test Citroën C-Zero
- ↑ NCAP crash test Peugeot iOn
- ↑ New name, new price. Mitsubishi Electric Vehicle 2014: New name for the i-MiEV. Auto Zeitung, March 24, 2014, accessed October 19, 2017 .
- ↑ http://www.autobloggreen.com/2009/06/04/mitsubishi-launches-production-of-the-imiev/
- ↑ a b The Mitsubishi i-MiEV is cheaper. heise online , accessed on March 17, 2020 .
- ↑ http://www.auto-motor.at/Auto/Neuwagen/Automarken-Automodelle-Neuheiten/Mitsubishi-News/Mitsubishi-i-MiEV-Vienna-Auto-Show.html
-
↑
Price reductions:
- May 2012: mitsubishi-motors.de press release ( memento of the original from July 21, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , accessed June 26, 2014
- March 2014: mitsubishi-motors.de press release ( memento of the original from April 7, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , accessed June 26, 2014
- ↑ Mitsubishi is lowering the prices for its electric city car ( memento of the original from April 7, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , official press release of March 24, 2014
- ↑ https://www.citroen.de/modelle/citroen/citroen-c-zero.html accessed on September 17, 2019
- ↑ CoC data sheet , released July 29, 2011, file number: 710720110722151106
- ↑ News Current Press Portal (October 1, 2012): Electromobility E-cars pass tough practical tests. ADAC: ranges of up to 150 kilometers no problem (accessed on October 14, 2012)
- ↑ Study by the Technical University of Denmark
- ↑ a b SAE International, 2010: AC-System For Electric Vehicles (i-MiEV) (PDF; 1.7 MB), inserted March 1, 2012
- ↑ a b c d Prices, equipment and technical data. (PDF; 7 MB) Mitsubishi Motors, January 1, 2020, accessed on March 17, 2020 .
- ↑ i-MiEV as a handy city electric car , n-tv.de of December 12, 2014
- ↑ atzonline.de ( Memento of the original from August 2, 2009 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. I-MiEV electric car at the start: a lesson for consistent implementation
- ↑ a b c GS Yuasa: Technical Report LEV50-4 ( Memento of the original dated November 10, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (PDF; 534 kB), inserted February 29, 2012
- ↑ a b c Green Car Congress, May 14, 2008: The Battery Pack for Mitsubishi's i MiEV , inserted February 29, 2012
- ↑ FAZ, February 1, 2009. p. 5
- ↑ ÖAMTC long-term test: Destructive verdict for electric cars. Format.at, accessed on November 28, 2014 .
- ↑ Mitsubishi i-MiEV (2015-2018) price and specifications. In: ev-database.org. Retrieved October 31, 2019 .
- ↑ mitsubishi-motors.de, press release ( memento of the original from September 1, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. "best electric vehicle"
- ↑ mitsubishi-motors.de: Press release ( Memento of the original from April 20, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. "Winner (Alternative Drives)"
| Timeline of the Peugeot models since 1945 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | 40s | 50s | 60s | 70s | 80s | 90s | 2000s | 2010s | 2020s | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4th | 5 | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4th | 5 | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4th | 5 | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4th | 5 | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4th | 5 | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4th | 5 | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4th | 5 | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9 | 0 | |
| Microcar | ion | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 106 | 107 | 108 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Small car | 104 | 205 | 206 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 202 | 207 | 208 I. | 208 II | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compact class | 204 | 301 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 203 | 304 | 305 | 306 | 307 | 308 I. | 308 II | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lower middle class | 309 | 408 I. | 408 II | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Middle class | 403 | 404 | 405 | 406 | 407 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 505 | 508 I. | 508 II | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| upper middle class | 504 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 604 | 605 | 607 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Coupe | RCZ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 404 coupe | 504 coupe | 406 coupe | 407 coupe | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minivan | 1007 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crossover | 2008 I. | 2008 II | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3008 I. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUV | 3008 II | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4008 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4007 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5008 II | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compact van | 5008 I. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van | 806 | 807 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Off-road vehicle | P4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pick up | 403 truck | 404 pick up | 504 pick up | Pick up | Land trek | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| High roof combination | Traveler | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Box van | 205 Multi / Fourgonnette | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bipper | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| partner | partner | Rifter | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transporter | D3 | D4 | J7 | J9 | Expert | Expert | Expert | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| J5 | boxer | boxer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Timeline of the Peugeot models from 1889 to 1944 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | 1880s | 1890s | 1900s | 1910s | 1920s | 1930s | 1940s | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4th | 5 | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4th | 5 | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4th | 5 | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4th | 5 | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4th | 5 | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4th | |
| Small car | 1 | 2 | 3 / 4 | 5 / 6 / 7 / 8 | 21 / 24 / 30 / 31 | 37 | 54 | 57 | 69 "Bébé" | B P1 / B3 / P1 "Bébé" [1] | 161/172 "Quadrilette" | 190 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 26 / 27 / 28 | 48 | 126 | 201 | 202 ... | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compact class | 14 / 15 / 25 | 56 | 58 | 68 | VA / VC / VY [1] | V2C / V2Y [1] | VD / VD2 [1] | 159 | 163/163 BS | 301 | 302 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 33 / 36 | 63 | 99 | 108 | 118 | 125 | 173 / 177 / 181 / 183 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Middle class | 9 / 10 / 11 / 12 | 16 / 17 / 19 / 32 | 49/50 | 65/67 | 77 | 78 | 88 | 127 | 143 | 153 | 153 B / BR | 176 | 401 | 402 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18th | 39 | 61 | 71 | 81 | 96 | 106 | 116 | 126 | 138 | 175 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| upper middle class | 23 | 42/43/44 | 62 | 72 | 82 | 92 | 104 | 112/117/122/130/134 | 139 | 145/146/148 | 174 / 184 | 601 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 66 | 76 | 83 | 93 | 135 | 156 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Upper class | 80 | 103 | 113 | 141 | 147/150 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 85 | 95 | 105 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Convertible / Spider | 91 | 101/120 | 133 / 111/129/131 | 136 | 144 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Box van | 13 | 22nd | 34/35 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| minibus | 20 / 29 | 107 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||