License plate (Germany)
The license plate (general terminology also license plate or only indicator ) is in Germany pursuant to Vehicle Registration Regulation (FZV) of the motor vehicle registration authorities issued official identification of vehicles for motor vehicles and possibly their followers . The license plate consists of a distinctive sign (one to three letters, e.g. RA) and the identification number (one or two letters and up to four digits, e.g. KL 8136). For vehicles that are subject to registration, they serve, together with the registration certificate, as proof of the authorization of vehicles for road traffic by a locally and materially responsible road traffic authority (depending on the place of residence or company headquarters). Vehicles for which a general operating license or type approval is sufficient (vehicles that do not require registration) show insurance numbers . These do not count as official license plates for registration purposes , as they are issued by the motor vehicle liability insurance . The term license plate stands for the alphanumeric string as well as the actual license plate.
The list of vehicle registration numbers in Germany contains all currently defined distinctive signs, including all previously abolished and re-introduced after the amendment of the Vehicle Registration Ordinance 2012. For the revoked distinctive signs, i.e. those that may no longer be assigned, see the list of German vehicle license plates that are no longer issued . For all distinctive signs issued so far in Germany with information on the periods of time, see the list of all vehicle registration numbers in the Federal Republic of Germany . The current license plates must be produced in accordance with the DIN 74069: 1996-07 standard.

history
Until 1956
In the German states, some local authorities began to prescribe license plates for bicycles between 1870 and 1890 due to increased cases of hit- and-run, which were issued locally and differed in color. In 1896, the first license plate was attached to an automobile in Baden . On October 1, 1906, the first uniform regulation was enacted, which came into force on October 1, 1907 for the 26 federal states of the German Reich . 10,115 cars, 15,954 motorcycles and 957 trucks were registered at the time.
The uniform designation of the countries in the German Empire began in some larger countries with a Roman number for the territory - I = Prussia , II = Kingdom of Bavaria to VI = Reichsland Alsace-Lorraine - followed by a letter for the administrative district - I A = Berlin , II A = Munich , III A = Stuttgart ... - and finally a sequence of digits. In the Kingdom of Saxony , the code was used in the opposite direction: without a sequence of letters, only using Roman numbers from Ito V. The marks of some smaller states were given one or two letters according to their name, as Afor Anhalt (partly followed by a Roman number). Including the free Hanseatic cities of Bremen, Hamburg and Lübeck, with the characteristics HB, HH, HLthat have been preserved to this day (with an interruption during the occupation).
From 1935 to the end of the Second World War there were military vehicles, depending on the branch of service of the Wehrmacht two letters of the license plate, WH (Wehrmacht Heer) for the army WL (Army Air Force) for the Air Force and WM (Wehrmacht Navy) for the Navy .
After the Second World War, the license plates in the occupation zones of Germany were initially differentiated by color - black on an orange background: the American zone, black on a red background: the French zone, black on a blue background: the British zone, and black on a white background remained in the Soviet zone. In 1947 the four powers decided on a uniform system that was introduced from 1948. The new license plates in the four occupation zones were now kept uniformly white on a black background. Their registration numbers contained two letters at the front (which were written one above the other) for the administrative area, e.g. B. BR for the British Zone Rhineland or AB for the American Zone Bavaria . This was followed by four digits for numbering the vehicles within an administrative area. These marks were valid until the introduction of their own systems in the post-war states of the Federal Republic of Germany and the German Democratic Republic.
In September 1949, the Administration for Traffic of the United Economic Area in Offenbach had pointed out to the federal states that the current vehicle registration system was not up to the increasing motorization, as the four digits of the numbering were no longer sufficient for all vehicles in an administrative district. In November 1951, the Federal Minister of Transport, Hans-Christoph Seebohm ( DP ) , therefore presented a draft for a new identification system that was to replace the previous one. The approval by the Federal Council, which was scheduled for May 14, 1952, was, however, omitted by being removed from the agenda, as the Western powers objected that the replacement of the old system would not be approved by the Soviet Union. This would then only allow vehicles marked according to the old system to drive in or through the GDR area. The corresponding ordinance remained in place until most of the Allied reservation rights had expired as a result of the Germany Treaty and was taken up again and passed at the end of 1955. With the regulation on the amendment of the regulations of the traffic law published on March 14, 1956 ( Federal Law Gazette I p. 199 ) this was introduced for the Federal Republic of Germany and West Berlin , also on December 31, 1956 in Saarland , that on January 1, 1957 was incorporated into the Federal Republic. The old license plates remained valid until June 30, 1958. The GDR had already introduced its own system in 1953 , which was also designed in white with black frames and DIN lettering. GDR license plates were issued until the end of 1990 and remained valid until December 31, 1993.
Development since 1956
After German reunification in 1990, the system was transferred to the new federal states with a slight delay on January 1, 1991. The design and affixing of the license plates are regulated in Section 10 of the Vehicle Registration Ordinance of April 25, 2006.
There are currently two different versions of the license plate in Germany. What they have in common is the black writing on a white background with a black border. On the one hand, these are the older DIN labels used since 1956 , named after their font, which is defined in accordance with DIN 1451 (medium script ) and which replaced the 1949 standardized signs for the three western occupation zones (white script on black background). On the other hand, there are the new Euro plates , which use the FE script (FE = forgery-making). In this case, the letters differ from each other more clearly than in the old DIN font , so that falsifications are made more difficult and automatic recognition with camera systems is made easier (see also toll bridges , truck tolls ). With the introduction of the FE script, it became possible to use the letters B , F , G , for the serial identification number by changing the road traffic licensing regulations , which also governed the licensing of vehicles in Germany until the vehicle licensing ordinance came into force . I , O and Q should be used, which were originally blocked due to the risk of confusion. This means that significantly more combinations are available when assigning labels. The Euro plates were first introduced in 1994 by Berlin and Brandenburg before they were used nationwide. Since November 1, 2000, only the Euro plates have to be attached to the vehicle for new registrations (except for Bundeswehr vehicles). When traveling within the European Union or to Switzerland , the oval nationality symbol (e.g. “D”) on the rear of the vehicle can be dispensed with on vehicles with a Euro license plate .
On September 29, 1989, reflective license plates (special film for particularly strong light reflection on the white surface background) for new cars and also for vehicles with damaged plates were introduced in the Federal Republic of Germany , which had already been on the market since 1967 and for which only 15 percent of the owners decided voluntarily. Bundeswehr vehicles are an exception for military tactical reasons . These reflective license plates, which are now also mandatory for the united Germany, are intended to ensure more safety, for example for vehicles that drive unlit at dusk or in bad weather, as well as in the event of a tail light failure. With the introduction of the new safety labels there was also a price increase from (usually) 20 to 40 DM per label set.
construction
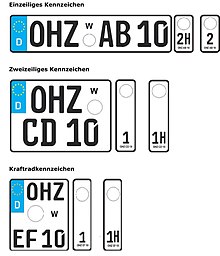
Today's license plates in Germany are designed as Euro plates . They consist of two parts:
- the distinguishing sign of up to three letters,
- the identification number consisting of one or two letters and up to four digits.
Together, however, there is a maximum of eight characters, and a maximum of seven characters for seasonal license plates. For license plates with two lines, as is the case with motorcycles or sometimes used on the rear, only seven characters are allowed for reasons of space, even with narrow font. Between the distinguishing mark and the identification number there is space for the test sticker and the seal of the approval authority . The hyphen after the distinctive sign has been omitted from now on.
Unlike in some other countries, the license plates are assigned to the vehicle and not to the owner . For this reason, the number plate is transferred to the new owner when it is sold, unless the seller de-registers the vehicle before the sale and the purchaser registers with the new number plate.
In Germany, unlike, for example, in Liechtenstein or in some cantons of Switzerland , there are no generally accessible lists from which the owner can be inferred from the license plate.
The time of approval is not noted in the license plate. However, many registration offices (e.g. Erlangen , if no desired license plate is requested) assign the license plates according to a continuous system (previously specified in Section 23 Paragraph II Clause 4 in conjunction with Annex II of the StVZO) (see section Identification number , groups a to e), so that a rough conclusion can be drawn about the period of admission.
Distinctive signs
The distinguishing signs consist of one, two or three letters :
- for the administrative district of the registration authority in which the vehicle is regularly located or
- for the vehicles of the federal and state organs, the Federal Police , the Federal Waterways and Shipping Administration of the Federal , the Federal Agency for Technical Relief , the Bundeswehr , the diplomatic corps in the country and preferential international organizations (eg NATO ).
The distinctive signs of the administrative districts are set or canceled by the Federal Ministry of Transport, Building and Urban Development at the request of the federal states . The establishment and removal of distinctive signs is published in the Federal Gazette . The letter combination of a distinctive sign must not offend against morality. Upon request, administrative districts have been able to use more than one distinctive sign since November 1, 2012 as a result of the license plate liberalization , whereby only such distinctive signs may be requested that were issued before October 25, 2012. Signs whose distinguishing signs have been abolished may continue to be used until the vehicle concerned is taken out of service.
Re-labeling
If the location of a vehicle is relocated to another administrative district, a new registration number had to be applied for there in any case by the end of 2014 (re-labeling requirement). Since September 2008, the federal states have been able to decide whether or not new license plates have to be assigned when changing to another registration area within their own country. Since January 1, 2015, the obligation to re-label has been dropped nationwide.
Identification number
The identification number consists of
- one or two letters. All German capital letters are possible except for the umlauts Ä , Ö and Ü . Sometimes not all combinations are possible (see also the section Miscellaneous ). When authorities mark this area is dropped;
- one to four (deviating up to six) digits without a leading zero. Up to six digits are assigned if they are the only distinguishing features. This occurs with official license plates, because the letters are missing here.
Together with the distinguishing mark, the mark must not have more than eight digits, i.e. H. in the case of distinctive signs with three letters , the identification number may not be longer than five characters.
From July 1, 1956, only the following 20 letters were initially used: A, C, D, E, H, I, K, L, M, N, P, R, S, T, U, V, W, X , Y and Z. With effect from November 7, 1956, only the letter J was used instead of the letter I. With effect from August 12, 1992, the allocation of the three letters B , F and G and, since May 26, 2000, the allocation of the letters I, O and Q were also permitted.
Occasionally you can determine the exact approval district from the number of letters in the middle and the numbers. (see list of all German license plates with a regional division ) . This system is based on the fact that the possible identification numbers are divided into groups:
- Group a (formerly: Ia ): 1 letter, 1–3 digits, i.e. A 1 to Z 999 → 26 × 999 = 25,974 possibilities
- Group b (formerly: Ib ): 2 letters, 1–2 digits, i.e. AA 1 to ZZ 99 → 26 × 26 × 99 = 66,924 possibilities
- Group c (formerly: II ): 2 letters, 3 digits, i.e. AA 100 to ZZ 999 → 26 × 26 × 900 = 608,400 possibilities
- Group d (previously: IIIa ): 1 letter, 4 digits, i.e. A 1000 to Z 9999 → 26 × 9000 = 234,000 options
- Group e (formerly: IIIb ): 2 letters, 4 digits, i.e. AA 1000 to ZZ 9999 → 26 × 26 × 9000 = 6,084,000 possibilities
The specified 7,019,298 possible combinations are theoretical in nature. Some combinations are blocked as unwanted identification numbers, so that the total number of actually usable possibilities is less than indicated above.
These groups are used, for example, when assigning the same distinctive sign to an urban district and to the surrounding district (examples: OL , FÜ , HN , MZ , PS ), in which the assignment to city or country results from the group. But they are also relevant when reassigning distinctive signs. In the old federal states, only group c was initially assigned to one of two districts with the same number. In order to enable shorter license plates, this district was usually assigned all license plates from groups a and b that contain the letters B , F , G , I , O and Q that were not originally assigned .
Not all groups are used by all approval districts. Many, especially smaller districts, only use groups a to c on a regular basis and allow group d and possibly e as a desired identifier. Group e is not possible in districts with a three-digit distinguishing sign. Even in cases in which two registration offices used to issue the same distinctive sign (with the above differentiation) and only one uses it today, the label groups that have become free are often not used. For example, at LD (City of Landau in the Palatinate ) only groups a, d and e and sometimes c are used.
The combination of characters of the identification number and the combination of distinctive signs and identification number must not offend against morality .
Inspection stickers
General inspection
After the distinguishing sign there is a round sticker on the rear license plate above the stamp sticker, which shows the deadline for registering for the next main inspection (colloquially TÜV sticker ).
As a rule, the test badges are stickers that are destroyed when peeled off, which is intended to make falsifications more difficult (e.g. by simply twisting or transferring them to third-party license plates); Individual approval agencies use (as well as for stamp stickers) to this day solid stickers that are clipped into an aluminum holder that is riveted onto the license plate.
The appearance of the badges has remained almost the same since it was introduced in 1960. In 1974 the color scheme was expanded from four to six colors and since the 1974 badge has followed the rhythm that is still valid today, which is repeated every six years. The years 1977 (yellow instead of orange) and 1979 (orange instead of yellow) were exceptions. Since 1975 the badges in the area of the month of December have black segments for better readability. The different colors ensure that expired badges can usually be recognized from a few meters away. Since 1983, the ascending digits have been printed counterclockwise on the inspection sticker so that the month of the due examination can be read off the black segments like on a clock. For example, if the HU is due in August, the "8" is at the top and the black segment appears at "8 o'clock".
Colors of the badges up to 1973
| colour | year | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | 1961 | 1965 | 1969 | 1973 |
| green | 1962 | 1966 | 1970 | |
| yellow | 1963 | 1967 | 1971 | |
| blue | 1964 | 1968 | 1972 | |
Badge colors since 1974
| colour | year | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Brown (RAL 8004) |
1974 | 1980 | 1986 | 1992 | 1998 | 2004 | 2010 | 2016 | 2022 |
| Pink ( RAL 3015) |
1975 | 1981 | 1987 | 1993 | 1999 | 2005 | 2011 | 2017 | 2023 |
|
Green (RAL 6018) |
1976 | 1982 | 1988 | 1994 | 2000 | 2006 | 2012 | 2018 | |
| Orange (RAL 2000) |
1979 | 1983 | 1989 | 1995 | 2001 | 2007 | 2013 | 2019 | |
|
Blue (RAL 5015) |
1978 | 1984 | 1990 | 1996 | 2002 | 2008 | 2014 | 2020 | |
| Yellow (RAL 1012) |
1977 | 1985 | 1991 | 1997 | 2003 | 2009 | 2015 | 2021 | |
- Source: Annex IX - Road Traffic Licensing Regulations (StVZO)
Investigation of the engine management and emission control system

From 1985 to 2009, hexagonal badges were also issued for the examination of the engine management and emission control system (UMA) - initially referred to as the special emission test (ASU), later referred to as the emission test (AU). The test sticker for the UMA was always affixed to the front license plate above the stamp sticker. It followed the color scheme of the inspection stickers for the main inspection and, like this one, was also issued as a hard plastic sticker in some approval districts.
Since diesel vehicles were exempt from the UMA until the end of 1993, they did not receive any test badges until then. The front license plate therefore also provided information about the type of fuel in a vehicle. The color scheme used for the HU badges also applied to the UMA test badges .
The UMA has been part of the general inspection since January 1, 2010. From this point on, the badge on the front license plate was no longer required. Expired badges were usually removed during the next general inspection and no UMA badges were stuck on for new registrations, re-registrations, etc., so that they disappeared from the German streetscape by the end of 2012.
Stamp plaques
Between the distinctive sign and the identification number there is a sticker from the registration authority with the official seal (official: stamp sticker ) of the respective city or district in which the vehicle was registered. At about the same time as the introduction of the Euro license plate , the original gray or white stamp badge was replaced by a larger, multi-colored badge containing the name and coat of arms of the federal state in which the vehicle is registered as well as the name of the registration office. In a transitional phase, however, the old version was stuck on many Euro plates and, in recent years, the DIN plates on many DIN plates the new version of the stamp sticker.
With the old DIN markings, there is a hyphen between the test and stamp plates, which separates the distinguishing mark and the identification number. The first euro plates in Berlin , Brandenburg , Bavaria (more rarely) and Saxony also had a hyphen. However, since the space is no longer sufficient when using the new, larger stamp badges, the hyphen has not been used on the Euro plates since then.
Depending on the district or city, seals were used in different ways: mostly flat stickers, in many districts, especially in southern Germany ( Baden-Württemberg , Bavaria , Rhineland-Palatinate ) as well as in some Thuringian and Lower Saxony approval districts ( Helmstedt , Hameln-Pyrmont , formerly also city of Hanover and district of Celle ), solid plastic stickers (colloquially: "potty seal") were used. In some cases, independent cities and counties with the same distinctive signs (UL, FÜ, HD, LU) used different materials. Some districts also gave the vehicle owner a choice.
New stamp stickers were introduced at the beginning of 2015. These contain (as with the seals of the SicoTra brand already before) the official seal of the licensing authority and - new - an eight-digit printed part number, shown to the right of the state coat of arms as a 2D DataMatrix code and to the left of the coat of arms or above the code as plain text. These seals have a slightly smaller colored coat of arms and a new holographic design, adapted to the additional space required by the code and number. The first “test badges” of the brands SicoTra and SecuRasta for the field test in Ingolstadt were given the old or different hologram design. Likewise, those of the SecuRasta Perfect brand did not yet have a check digit at the end of the pressure piece number. If you remove the official seal from the license plate, a three-digit security code appears underneath, which is also shown as a data matrix. With these official seals, an online decommissioning is possible from 2015 onwards. Since then, solid fuel stickers and official seals have no longer been awarded for civil and official license plates. The Internet-based vehicle registration on the application of i-KFZ3 the competent licensing authorities is currently in addition to the Internet-based readmission and decommissioning possible for a number of other operations. The prerequisites for this are the new identity card with identification function and a card reader.
Bundeswehr approval badge (non-reflective)
Approval badge from the Federal Ministry of the Interior , e.g. for vehicles from the technical relief organization
Approval badge of the Ludwigshafen district with the coat of arms of Rhineland-Palatinate until 2003
Approval badge of the district of Döbeln with the Saxon state coat of arms until 2008
Approval badge of the Mecklenburg Lake District district with the Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania coat of arms until 2014
Approval badge of the Mecklenburg-Strelitz district with the Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania coat of arms until 2011
Registration badge of the state capital Munich with the Bavarian state coat of arms until 2014
Registration badge of the district of Müritz with the Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania coat of arms until 2011
Registration badge of the city of Neubrandenburg with the Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania coat of arms until 2014
Current approval sticker of the independent city of Coburg and the district of Coburg ( Zweckverband Zulassungsstelle Coburg ), right with DataMatrix code and state coat of arms on the top left
Current approval badge of the city of Frankfurt am Main with the Hessian coat of arms , right with data matrix code and city coat of arms at the top left
Current approval badge of the district of Mecklenburg Lake District with the Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania coat of arms , right with DataMatrix code and district coat of arms on the top left
Current approval badge of the district of central Saxony with the Saxon state coat of arms , right with data matrix code and district coat of arms on the top left
Manufacturer
The seals with a diameter of 45 mm come with twelve different versions of adhesive stickers from the SecuRasta , SicoTra , SecuPrint , HöKo , Coloco , ProSecure and Juvikett brands .
The first copies after the introduction of the Euro plates were almost all made by the Munich company SecuRasta . Almost ten years later, the Trautwein company from Herne came onto the market with the silvery reflective SicoTra seal, which, when turned against the light, makes the official seal of the respective approval district appear on the top left and reveals the name SicoTra . SecuRasta then started with SecuRasta Light , which at first glance also has the same silver look; SecuRasta Perfect has also been available as a third since around 2007 .
Some time later, the company Hörauf & Kohler ("HöKo") also began selling adhesive stickers. With the introduction of the new approval badges in 2015, these are also available from the Juvikett brand , whose seals have a dark gray background.
Technical condition
The versions of all license plates in Germany (formats, fonts, colors and, since around the mid-1980s, also reflection ) are regulated in the vehicle registration ordinance and are standardized by DIN 74069. The manufacturing processes and conformity with these rules are monitored by DIN -CERTCO.
Dimensions
Appendix 4 of the Vehicle Registration Ordinance specifies the following dimensions for the license plates:
- a) single-line markings: maximum width: 520 mm, height: 110 mm
- b) two-line license plates: maximum width: 340 mm, for two- and three-wheeled vehicles 280 mm, height: 200 mm
- c) Motorcycle license plate: width 180 mm to 220 mm × height 200 mm
- d) Reduced two-line license plate: maximum width: 255 mm, height: 130 mm.
The motorcycle license plates were newly introduced with the amendment to the Vehicle Registration Ordinance of April 8, 2011, previously the wider two-line license plates had to be used for motorcycles. Reduced two-line license plates are only to be allocated for light motorcycles and for tractors with a design-related maximum speed of no more than 40 km / h and trailers with a design-related maximum speed of no more than 40 km / h, if they are marked with a speed sign for the speed in question .
font
The font used in the Vehicle Licensing Ordinance is the forgery-hindering FE font of the Federal Highway Research Institute , which has a font height of 75 mm in the middle and narrow font variants and a font height of 49 mm for the reduced middle font (only for reduced two-line license plates and motorcycle license plates ) is used. FE font is a non-proportional font ; H. all characters are equally wide. For normal-sized license plates, the middle script can usually be used for up to seven characters . Often, which is eight characters for all characters Engschrift used, but this is not allowed on the system 4 of the vehicle registration Regulation (FZV). Thereafter, the close-up may only be used in exceptional cases, e.g. B. if a correct license plate can not be attached to the vehicle in central letters. This is often the case with US import or tow trucks.
A different font is specified for Bundeswehr license plates and insurance license plates.
For the DIN markings issued up to 2000 with middle letters according to DIN 1451, the following applied: If there was not enough space for the maximum of eight characters, the embossing point could use slimmer characters ( narrow script) . A mixed spelling was mostly used, i.e. H. the registration area in normal width, the identification number in narrow script and the sequence of digits again in normal width.
Attachment to the vehicle

The distinguishing signs and identification numbers must be affixed to a license plate with black lettering on a white, black-edged background (however, the license plate for test, transfer and workshop trips: red; tax-exempt vehicles: green), which are horizontal in the reading direction , easily recognizable, clean and not turned upside down must be attached to the outside of the vehicle. There are minimum and maximum limits with regard to the mounting height; license plates may also only have a certain angle of inclination (max. 30 °). They must not be covered (transparent plastic protection) or covered (trailer coupling, spare wheel). They must be firmly attached to the vehicle, with the exception of the license plates for test, transfer and workshop trips. From a legal point of view , the registration number is a composite document . a. punishable as falsification of documents and misuse of license plates .
In the case of trailers that do not have to have their own registration number (e.g. trailers for agricultural vehicles), the trailer must have a registration number that the owner of the towing vehicle may use for one of his towing vehicles. If the rear license plate of the vehicle is partially or completely covered by a load carrier or cargo carried (e.g. bicycle rack on the trailer coupling), the license plate must be repeated on the vehicle or load carrier. A stamp is not required in both cases ( Section 10 (8) and (9) FZV).
Identification materials
Label plates must be reflective in accordance with Section 10, Paragraph 2, Clause 2 of the FZV and correspond to the standard sheet DIN 74069, July 1996 edition, and have the DIN test and monitoring symbol with the associated registration number on the front. The majority of German license plate blanks are made of aluminum according to these guidelines . Today, the hot stamping process is usually used for production. This process was developed in 1990 and replaced the previous use of solvent-based paints.


A technical innovation are self-luminous plastic license plates that have been approved for general road traffic in Germany since November 2006. These are similar to normal metal signs, are also embossed and have a reflective layer. The special feature is that these are translucent and are illuminated from behind by LED elements in white. This results in uniform and easily legible illumination, which should provide additional security.
At the end of 2006, license plates made of acrylic plastic were also offered as an alternative to metal plates . These look similar to British license plates . These marks are no longer available.
Since November 2013, plastic labels that can be approved under the brand name 3D labels have been on the German market, in which plastic letters are attached to a polypropylene base plate using a plug-in embossing process . The manufacturer cites the flexibility and impact resistance of the materials, a lower weight, a more favorable CO₂ balance and less risk of injury as the advantages of its development compared to aluminum signs . Since the letters are colored through the material, these signs are also insensitive to abrasion during cleaning. Dents and deformations, as is the case with conventional aluminum signs, are not an issue for plastic license plates in 3D optics.
Special identifier
Authority registration number

Authority vehicles registered up to February 28, 2007 bear the abbreviation of the respective registration district in which the authority is based, followed by a sequence of digits. The sequence of digits usually provides information about the authority for which the number plate was assigned:
- Above the municipal administrative level: 1–89, 1XX, 1XXX, 1XXXX
- Courts: 9X, 9XXXX
- municipal administrative level: 2XX, 2XXX, 2XXXX, 3XX, 6XX, 6XXX, 6XXXX
- Police: 3XXX, 3XXXX, 7XXX, 7XXXX
- Civil protection: 8XXX, 8XXXX
- consular posts: 9XX, 9XXX
- other authorities and institutions (some number reserves): 5XX, 5XXX, 5XXXX, 6XX, 7XX, 8XX, 9XXXX
Since March 1, 2007, these official license plates are no longer assigned due to the new Vehicle Registration Ordinance (FZV) - with the exception of the number ranges used by the consular representations. Many districts and cities are now opening new allocation groups or blocking entire sequences of letters for the authorities' fleet. Some cities still reserve combinations for special vehicles, such as B. TX for taxis or S or SW for urban vehicles ( S tadt w orks). For example, the buses of the Berliner Verkehrsbetriebe always have the combination B V XXXX . In Baden-Württemberg, the vehicles of the disaster control units usually have the abbreviation BS or KS (e.g. City of Freiburg) for civil protection or disaster control before the number sequence 8XXX.
Distinguishing signs of the countries



According to Appendix 3 number 3 of the Vehicle Registration Ordinance, vehicles from state governments and authorities have their own distinctive signs. The licensing authority is that of the respective state capital.
| Abbreviation | country | Licensing authority |
|---|---|---|
| B. | Berlin | Berlin |
| BBL | Brandenburg | Potsdam , city |
| ZDP Police Brandenburg | ||
| Teltow-Fläming , district | ||
| Business administration | Baden-Württemberg | Stuttgart , city |
| Stuttgart LPD 1, LKA BW | ||
| Tübingen LPD, RP Tübingen LPD | ||
| Freiburg LPD, PD Freiburg | ||
| Göppingen BPP, Riot Police Headquarters | ||
| Karlsruhe LPD, PD Karlsruhe | ||
| BYL | Bavaria | Munich , city |
| HB | Bremen | Bremen , city |
| HEL | Hesse | Wiesbaden , city |
| HH | Hamburg | Hamburg |
| LSA | Saxony-Anhalt | Magdeburg , city |
| LSN | Saxony | Dresden , city |
| MVL | Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania | Schwerin , city |
| NL | Lower Saxony | Hanover , city |
| NRW | North Rhine-Westphalia | North Rhine-Westphalia police |
| RPL | Rhineland-Palatinate | Mainz , city |
| SAL | Saarland | Saarbrücken , city and city association |
| SH | Schleswig-Holstein | Kiel , city |
| THL | Thuringia | Erfurt , city |
For example, vehicles from the state of Thuringia have license plates in the form THL 4-9999 .
There is a recommendation for the use of the number in front of the hyphen for state codes:
- 1 state parliament
- 3 Prime Minister, State Chancellery
- 4 Ministry of the Interior
- 5 Ministry of Justice
- 6 Ministry of Finance
- 7 Ministry of Transport
Numbers 2, 8 and 9 are not used.
North Rhine-Westphalia
The following rule applies to North Rhine-Westphalia : The number following the distinctive sign is assigned as follows:
- 1 state government
- 3 State Chancellery
- 4, 5, 6 Ministry of the Interior (with police)
- 7, 8 Ministry of the Interior (with civil protection)
The mobility needs of the ministries are generally covered by the state chancellery (NRW 3 – XXXX) . In the case of police vehicles, regional registrations have been waived because the leased vehicles achieve fewer kilometers in urban areas than in rural areas. In order to prevent extreme deviations in the mileage of the vehicles, the vehicles with NRW number can be exchanged continuously.
The other state authorities, however, predominantly use civil authority numbers. However, there is also a certain system here within North Rhine-Westphalia with regard to the letter combination in the identification number: For example, the vehicles of the justice administration usually have JV as a combination, vehicles of the district governments usually BR , vehicles of the financial administration usually FV , the Landesbetrieb Wald und Holz NRW usually uses WH . It should be noted that the vehicles are usually registered at the regular location, for example the vehicles of the Münster district government are registered at the Münster (MS – BR XXXX) , Coesfeld (COE – BR XXX) and Herten (RE – BR XXXX) locations . Of course, not the entire letter combination is used by the respective authority. It is also possible that the relevant authority deviates from the system.
Police license plate
The allocation of the police license plates is currently regulated differently in the federal states after the discontinuation of the official license plates.
Country distinctive signs
In North Rhine-Westphalia , Brandenburg , Rhineland-Palatinate , Baden-Württemberg and the Saarland , the distinctive signs of the respective state administration are currently used for police vehicles according to the models NRW 4 – XXXX , NRW 5 – XXXX and NRW 6 – XXXX as well as NRW 5 – XXX and NRW 6 – XXX (motorcycles), BBL 4 – XXXX , RPL 4 – XXXX , SAL 4 – XXXX and BWL 4 – XXXX , whereby the leading 4 (in North Rhine-Westphalia also 5 and 6) is assigned to the Ministry of the Interior. In Schleswig-Holstein , Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania and Saxony-Anhalt , approvals based on the SH 3XXXX , MVL 3XXXX and LSA 4XXXX models are preferred .
In Baden-Württemberg it was originally planned to keep the police vehicles at the seat of the regional council to which they are assigned ( Freiburg im Breisgau = FR, Karlsruhe = KA, Stuttgart = S and Tübingen = TÜ), or for vehicles of the riot police, at the headquarters of the Riot Police Headquarters ( Göppingen = GP) to allow. The distinguishing marks should be followed by up to two-digit letters and four-digit numbers; Vehicles of the Stuttgart Police Headquarters should have the registration number S PP XXXX . Some vehicles with this scheme have already been registered. Since August 2008, the vehicles have been given license plates according to the BWL 4 – XXXX scheme , whereby the first digit stands for the Ministry of the Interior as the highest service authority.
Civil registration
In some federal states, the systems have been adapted to the normal license plates:
Bavaria
The Bavarian police vehicles of the police headquarters in Upper Bavaria-North based in Ingolstadt , Middle Franconia in Nuremberg , Lower Franconia in Würzburg , Swabia South / West in Kempten (Allgäu) and Upper Palatinate in Regensburg use the IDs IN PP 9XXX , N PP XXX , WÜ PP XXXX , KE PP XXX , R PP XXX and R PR XXX . Those in Augsburg have the identifier A PS XXX , where PS stands for the Swabian North Police Headquarters . A letter BT P 8XXX is enough for the Upper Franconian Police Headquarters in Bayreuth , as well as the Lower Bavaria Police Headquarters in Straubing SR P 1XXX and the Upper Bavaria South Police Headquarters in Rosenheim RO P XXX . On the part of the Munich Police Headquarters , part of the number range from the M PM XXXX area , which is assigned to the registration office of the state capital Munich, is used. A conversion is only carried out for newly registered vehicles, as the conversion should be carried out at no cost. The riot police based in Bamberg use BA P XXXX as a license plate.
Berlin, Hamburg and Bremen
In the city-states of Berlin , Hamburg and Bremen , the numerical codes will be retained according to the previous model.
Hesse
In Hesse , newly registered police vehicles have license plates with the combination WI HP XXXX (always with four digits, with motorcycles also with three digits). The characters HP replace the previous number 3. The next number refers to the police headquarters (PP) or the central police authorities: 1 = PP South Hesse ( Darmstadt ), 2 = PP East Hesse ( Fulda ), 3 = PP South East Hesse ( Offenbach am Main ), 4 = PP North Hesse ( Kassel ), 5 = PP Frankfurt am Main , 7 = PP West Hesse ( Wiesbaden ), 8 = PP Central Hesse ( Gießen ) and 9 = central police authorities (Wiesbaden).
Lower Saxony
In Lower Saxony the police vehicles carry the license plates of the local inspection or management, z. B. CE PI 950 or GÖ PD 599 ( PI for police inspection, PD for police headquarters). Vehicles of the Central Police Directorate Hanover , which also includes the riot police with other departments in Braunschweig and Oldenburg , have the abbreviation H ZD XXXX ( ZD for Central Police Directorate) or PA for the police academies.
Saxony
In Saxony , since March 1, 2007, all police vehicles, including civil ones (with the exception of camouflaged license plates ), have received the code DD Q XXXX (with three or four digits). The riot police are assigned the code group DD Q 7XXX .
Thuringia
In Thuringia , the code EF TP XXXX (always with four digits) was used for police vehicles from 2007 to 2010 . The characters TP replaced the previous number 3. The next number referred to the police headquarters (PD) or the riot police in Thuringia: 1 = PD Erfurt , 2 = PD Gera , 3 = PD Gotha , 4 = PD Jena , 5 = PD Nordhausen , 6 = PD Saalfeld , 7 = PD Suhl and 9 = riot police. The police license plates EF LP XXXX have been assigned centrally in Thuringia since 2011 . The assignment to a specific police headquarters is no longer recognizable.
Distinguishing signs for federal vehicles

- 0 - 1 Federal President
- 0 - 2 Federal Chancellors
- 0 - 3 Federal Minister for Foreign Affairs
- 0 - 4 First State Secretary in the Federal Foreign Office
- 1 - 1 President of the German Bundestag
The license plates of all other company cars of the Bundestag , the Bundesrat , the Federal Government , the Office of the Federal President and the Federal Constitutional Court begin with BD . They are allocated as follows:
- BD 1–… German Bundestag
- BD 3–… Federal Council
- BD 4–… Federal Constitutional Court
- BD 5–… Office of the Federal President , specifically: BD 5–1 Federal President, also 0-1
- BD 6–… Federal Chancellery , specifically: BD 6–1 Federal Chancellor, also 0–2
- BD 6–… Press and Information Office of the Federal Government
- BD 7–… Foreign Office , specifically: BD 7–1 Federal Minister for Foreign Affairs, also 0–3
- BD 9–… Federal Ministry of the Interior
- BD 10–… Federal Ministry of Justice and Consumer Protection
- BD 11–… Federal Ministry of Finance
- BD 12–… Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy
- BD 13–… Federal Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure
- BD 14–… Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture
- BD 15–… Federal Ministry of Labor and Social Affairs
- BD 16–… Federal Finance Administration (Customs)
- BD 18–… Federal Ministry of Defense
- BD 19–… Federal Ministry of Education and Research
- BD 20–… Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation, Building and Nuclear Safety
- BD 21–… Federal Ministry for Family, Senior Citizens, Women and Youth
- BD 22–… Federal Ministry of Health
- BD 26–… Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development
The unallocated code combinations BD 2–… , BD 8–… etc. serve as a reserve.
Identification of the customs authorities
The Federal Customs Administration introduced in 2007 with delivery of new vehicles from the authorities Plate (z. B. HB 123 ) on civilian license plate to (z. B. OS Z 9XXX ).
Since April 1, 2009, the Federal Customs Administration has been issuing license plates with the distinguishing mark BD plus the distinguishing number “16” and a consecutive award number (e.g. BD 16–315 ). The vehicle registration office of the Federal Finance Directorate Southwest - Section RF 5 - is now responsible for this nationwide. This is located at the procurement office of the Federal Finance Administration in Offenbach am Main . The registration sticker reads “Federal Republic of Germany • KfzSt der Bundesfinanzverwaltung”, where “KfzSt” stands for “motor vehicle office”.
Distinguishing marks from federal agencies
Bundesbahn and Bundespost
The Deutsche Bundesbahn (DB) and Deutsche Bundespost (BP) had their own distinctive signs until they were privatized in the 1990s. On the railway, the first two digits - following the DB - coded the vehicle type. In the case of the vehicle registration numbers of the Deutsche Bundespost , a distinction was also made between postal service ( BP 10 to BP 59 ) and telecommunications service ( BP 60 to BP 99 ).
Federal Waterways and Shipping Administration
The Federal Waterways and Shipping Administration uses the distinctive symbol BW , followed by a number that indicates the allocation to the General Directorate for Waterways (GDWS) or one of its branch offices. The approval sticker basically corresponds to the approval authority responsible for the respective seat of the branch office of the GDWS in which the vehicle was registered.
The following key numbers are currently assigned:
| Mark | Department |
|---|---|
| BW 1 XXX | ASt North (Kiel) |
| BW 2 XXX | ASt Northwest (Aurich) |
| BW 3 XXX | ASt Mitte (Hanover) |
| BW 4 XXX | ASt West (Münster) |
| BW 5 XXX | ASt Southwest (Mainz) |
| BW 6 XXX | ASt South (Würzburg) |
| BW 7 XXX | ASt East (Magdeburg) |
| BW 8 XXX | GDWS (Bonn) |
Federal Police
Company cars of the Federal Police have had the identifier BP since April 30, 2006 . Part of the vehicle fleet is still registered with the previous distinctive sign BG for the former designation Federal Border Guard , which has expired since the name was changed.
The license plates of the Federal Police and the former BGS are assigned to the first two digits depending on the vehicle type:
- Kräder : BP 10 to BP 12
- Cars: BP 15 to BP 19
- Off-road cars: BP 20 to BP 24
- Cars (minibuses): BP 25 to BP 29
- Medium off-road cars / trucks: BP 30 to BP 39
- Trucks and buses: BP 40 to BP 49
- Protected vehicles (armored vehicles): BP 50 to BP 54
- Trailer: BP 55
The identifier BP was issued to the Deutsche Bundespost until the end of 1994 .
armed forces
The German Armed Forces are assigned the letter Y for their license plates. Y was chosen because when the Bundeswehr was founded in 1955, all possible combinations such as BW had already been assigned and the distinguishing sign (the registration area) for the likely large number of military vehicles could only consist of one letter, especially since the license plate was also the German one Includes flag. Because no major city in Germany with a Y has incipient name, this letter was Brigadier General Kurt Vogel for the armed forces of the two remaining distinguishing features X and Y selected. ( X is now used for NATO vehicles.)
Furthermore, the German flag , a number up to six digits long and the stamp of the Center for Motor Vehicles of the Bundeswehr (ZKfWBw) are on the license plate, which is not reflective for military (tactical) reasons. Three-digit license plates are also possible for the highest-ranking employees of the armed forces; this also applies to license plates on commercially available vehicles of the Federal Armed Forces in the United States . The numbers are assigned arbitrarily, which means that they are not tied to any system such as vehicle type or unit.
Furthermore, the Bundeswehr uses a normal license plate for vehicles from BwFuhrparkService GmbH , which starts with SU for the Rhein-Sieg district (Siegburg), then bears the letters BW and then any number, e.g. B. SU BW 123 . This means that vehicles belonging to the Bundeswehr can no longer be recognized as such, unless you know the combination of letters in the license plate (if the vehicle does not bear the BW fleet service label ).
There are also some number plates for test drives that are printed in red with a red border. The sequence of digits begins with 06 . Leased or borrowed vehicles also use these license plates, but here the sequence of digits begins with 01 . All vehicles of the Bundeswehr (with the exception of vehicles from the fleet service) are approved by the Bundeswehr Motor Vehicle Center in Mönchengladbach -Rheindahlen. The vehicles of the Bundeswehr are subject to internal monitoring based on the road traffic regulations, e.g. B. the general inspection and the safety check , and are checked in a technical review in accordance with special technical service regulations ( TDv ) by our own staff. Civilian vehicles that are referred to as "commercially available" (HÜ) by the German Armed Forces (e.g. VW Golf or Opel Astra ) can be submitted to an officially recognized test organization (e.g. TÜV , Dekra ) for the main inspection like any civil vehicle. be demonstrated.
The Bundeswehr license plates are still issued in DIN script and not in the new FE script .
Federal Agency for Technical Relief

The service vehicles of the technical relief organization bear the distinguishing mark with the letters THW . Before the introduction of the new Euro license plate, the vehicles of the THW were integrated into the group of official license plates for disaster control. For the time being, the number structure of the official identification numbers was retained (8000–8999; 80000–89999, the number range used for disaster control). Four-digit number combinations are primarily assigned to the full-time organizational units (regional offices, state associations, training centers and management) and five-digit combinations to the local associations. The number plate area has meanwhile been expanded to include blocks with a leading 9 . The license plates are issued by the vehicle registration office at the procurement office of the Federal Ministry of the Interior in Bonn. In addition, the THW also has red transfer numbers with a sequence of digits beginning with 06 .
Seasonal license plates
Season license plates have been issued in Germany since March 1, 1997. After the identification number, the first and last month of the validity period are shown on top of each other, separated by a horizontal line. The admission period can be freely selected between two and eleven months within any twelve-month period, but the beginning and the end of the period must coincide with full calendar months. The big advantage of the season label is that there is no need to register at the beginning of the season and to cancel at the end of the season; as well as motor vehicle tax according to Section 5 (1) No. 5 KraftStG and insurance premiums are only incurred proportionally. You can find these license plates mainly on vehicles that are not used all year round, for example on motorcycles, convertibles and mobile homes , but also on vehicles used for winter service .
When changing from year-round registration to seasonal registration, the Road Traffic Office must be given an insurance confirmation number for the future period, despite the fact that there is year-round insurance coverage . Without this, the change is not possible. The insurance confirmation numbers have replaced the previously required cover cards. It is important that the vehicle may only be used on public roads during the specified operating period or parked on public traffic.
Season IDs can contain a maximum of seven characters, since the eighth digit indicates the period of validity.
There are special license plates for vintage cars as seasonal license plates, the so-called H-season license plates .
Change indicator
Since July 1, 2012 it has been possible to register two vehicles with just one license plate. The prerequisite is that the vehicles fall into the same vehicle class and the vehicle owners can use the license plates with the same dimensions on the respective vehicles. However, the license plate may not be used on both vehicles at the same time. The federal government is assuming registration costs of around 65 euros if a holder applies for a change number plate for two vehicles from the existing stock. Even before it was introduced, it was questioned whether the new license plate would actually generate the desired response from the population, as the federal government did not grant owners of several vehicles any tax savings when using license plates and the insurance industry had not promised any significant benefits. From July to December 2012, only 2,115 exchange number plates were actually issued by the registration offices. The federal government assumed 54,000 approvals per year in advance, so that the regulation is considered a flop.
License plates of historic vehicles
The classic car mark (also H flag called) in which the actual authorization number H is adjusted, is a German marking of a historic motor vehicle according to § 9 FZV that will be awarded to contemporary original state after a test. Another prerequisite is that the vehicle is demonstrably at least 30 years old ("Vehicles that were first put on the market at least 30 years ago." § 2 No. 22 FZV).
The license plate follows the same pattern as regular license plates for civil, government or diplomatic license plates. The only difference is an H as the final character. One restriction is that for single-line labels, the total number of characters without this H must not exceed seven. Example: AB DE 123H . Depending on the engine size of the vehicle, the H license plate can be associated with tax and often insurance benefits . In addition, vehicles with a vintage license plate are exempt from the restrictions associated with a missing particulate matter sticker . Historical license plates with a limited seasonal period (so-called H-seasonal license plates ) may be issued since October 1, 2017.
Thanks to decades of preparatory work by DEUVET - Federal Association for Clubs of Classic Vehicles for the “ Auto Cultural Property ”, the first H license plate issued for historic vehicles was assigned on July 1, 1997. The criteria for awarding an H mark are applied inconsistently: Deviations from the original condition are often tolerated insofar as they were to be found as contemporary modifications 30 years ago or earlier.
Since the beginning of 2010, H markings have been issued in Bremen in the written standard ( DIN 1451 ) used until October 31, 2000 and without a euro bar for an additional processing fee of 100 euros. Between July 2010 and February 2012, the Hessian Ministry of Transport allowed its registration offices to issue signs with the script required before November 2000, also upon request, and to orientate the fee rates on the Bremen model. This made it possible for the owners not to have to mark their vehicle with a Euro plate , which many classic car enthusiasts perceived as inappropriate or annoying . However, this regulation has been repealed since June 2013, since the appearance of the license plates is uniformly prescribed in public road traffic and there are no exceptions for visual reasons.
H markings are not issued if clearly younger components have been installed: Sometimes a more powerful engine of a similar type, which was only available later, is a negative criterion. Initially, even catalytic converter retrofits were rated as accessories that were atypical of the time and given as a reason for rejection; the relevant case law is now clearly environmentally friendly. Badly maintained vehicles are also often denied H status. The condition grades according to DEUVET can be used as a general guide . These classify the condition of a vehicle with school grades (e.g. 1 = very good).
A vehicle that is registered for an H license plate should therefore be in a condition that is no worse than 3 (used condition, small defects, but completely drivable, no rust perforations).
The criteria were changed on November 1, 2011: Until then, the condition of the vehicles had to be at least grade 3 in order to receive an H license plate. The grade 3 is given to vehicles with slight defects and signs of everyday wear, as long as they are ready for use and rust-free. Since then, the testing organizations have had a greater degree of discretion: According to § 2 No. 22 FZV, a good maintenance and conservation status is required to distinguish it from normal old vehicles (guideline for the assessment of oldtimers according to § 23 StVZO of April 6, 2011). The opinion that was widespread shortly after the reform became known that this wording was associated with a tightening of the criteria overlooks the fact that a good state of preservation is not to be equated with a grade of 2. The assessment of the condition worthy of preservation is now to be carried out independently of the definitions of the condition rating system.
Since January 1, 2018, the vehicle registration ordinance has been changed so that the letter H becomes part of the registration number. It therefore appears in both part 1 and part 2 of the registration certificate or on the green card .
Historic vehicles can also be operated with a red license plate (see below) with the code number 07 .
License plate for electric vehicles
After the Electromobility Act passed in 2015 , special license plates for electric vehicles, plug-in hybrid and fuel cell vehicles were introduced in order to be able to introduce and control special rules for electrically powered vehicles. The Federal Association of eMobility e. V. suggested an additional Elabel (analogous to the H label) as a label. In principle, carbon dioxide emissions of a maximum of 50 grams per kilometer driven may be emitted, or the range using only the electric drive unit must be at least 40 kilometers.
Since September 26, 2015, the new E-license plates, which are also available in combination with a seasonal license plate, have been issued by the registration offices. Foreign vehicles that also want to use the license plate rights for electric vehicles require an e-badge instead of the E- plate , which is issued by a registration office for 11 EUR - unless the vehicle has a foreign E-plate or a foreign E -Plaque.
Red license plates

Red license plates have existed in red letters on a white background since at least the 1920s and have consisted of the approval abbreviation and an identification number (without identification letters) since 1956.
According to the current version of the Vehicle Registration Ordinance, red license plates are assigned as:
- Identification number for test drives, test drives and transfer drives (colloquially also: dealer or exchange number ), the number of which starts with 05 or 06 ( § 16 )
- for temporary operation (e.g. trips to participate in events) for classic cars whose number starts with 07 ( § 17 )
Old short-term license plates were also red and were issued according to the same numbering scheme starting with 04 . They have been in the black since 1998; since March 1, 2007 they start with 03 or 04 .
05 and 06 license plates

Red license plates with the sequence numbers 05 and 06 are only issued to motor vehicle manufacturers, motor vehicle parts manufacturers, motor vehicle workshops and vehicle dealers (number starting with 06 ) as well as technical test centers and recognized monitoring organizations (number starting with 05 ) for the purpose of test, test and delivery drives. You are not bound to a vehicle.
For each vehicle a separate page of the vehicle registration booklet is to be used to describe it; the information about the vehicle must be entered completely and in permanent writing before starting the first journey. The vehicle registration booklet must be carried with you on every journey and handed over to the responsible persons on request. Continuous records are to be kept of every test, test or transfer trip, from which the license plate used, the date of the trip, its start and end, the vehicle driver with his address, the vehicle class and the manufacturer of the vehicle, the vehicle identification number and the route can be seen.
07 license plate
Red license plates with the sequence number 07 can also be issued to private individuals, but only for vehicles that are at least 30 years old. Before March 1, 2007, the red 07 number plate was also intended for youngtimers at least 20 years old .
Only test drives and movement drives, test drives for vehicle sales and drives to vehicle meetings may be made with the license plate ; for regular use on the road, these vehicles have to have a regular license plate or a vintage license plate . A vehicle registration booklet for red vintage license plates based on the model in Appendix 10a FZV is provided as proof . The license plate may only be used on the vehicles for which it was issued.
Depending on the registration office, up to ten vehicles can be approved for each red 07 number, but in other cases any number of vehicles can be approved. It is also possible to output several license plates with the same number, for example a large, elongated one for a car and a small square one for a two-wheeler. This license plate is tax-privileged, and insurance companies often offer favorable tariffs for it. The documents to be submitted for approval may vary depending on the approval body.
The red 07 license plate is not only valid in Germany. Due to international agreements with various countries, vehicles with such license plates can also be used abroad.
According to this, the red license plate 07 applies like any other German license plate in the contracting states under the following conditions:
- The data is entered in the vehicle registration document by the authorities (registration office) and this is documented in the vehicle registration booklet (official stamp).
- The license plate may also only be used abroad for the purposes permitted in Germany, i.e. test drives, transfer trips, workshop and adjustment trips as well as trips to and on classic car events.
- If necessary, a green insurance card must be carried according to the general rules.
The use of the red registration number 07 is generally permitted in the following countries:
- all EU member states except Malta and Cyprus,
- in Europe also: Andorra, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Liechtenstein, Macedonia, Monaco, Montenegro, Norway, San Marino, Switzerland, Serbia, Ukraine and Belarus,
- in Asia: Bahrain, Iran, Israel, Kuwait, Pakistan, Philippines, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan,
- in Africa: Ivory Coast, Congo, Morocco, Niger, Senegal, Seychelles, Zimbabwe and South Africa,
- in America: Brazil, Guyana, Cuba and Uruguay.
The registration of oldtimers with a red 07 license plate is in the above. Countries under international law. Although the red license plate and the short-term license plate correspond to international regulations, it may happen that the red vehicle registration, which is also issued with the new short-term license plate, is not accepted abroad because it does not comply with the international road traffic conventions of 1926, 1949 and 1968 . The use of red license plates can occasionally lead to problems abroad. Recognition is recommended at the German ministerial level. However, there is no legal entitlement and no guarantee that this practice will be continued.
Agreements on the mutual recognition of the respective national license plates and test license plates and the corresponding vehicle documents have existed with Austria since 1979 and with Italy since January 1, 1994 . A related agreement with Denmark was terminated in 1990.
Green license plates
Green marks are marks with green letters on a white background and otherwise identical to normal marks. They are for tax-exempt vehicles ( § 3 KraftStG ) such as B. agricultural vehicles, vehicles of non-profit or aid organizations , showman vehicles and self-propelled machines (e.g. cranes and concrete pumps) as well as for sports trailers with a specific purpose (e.g. for pleasure boats, gliders, dogs and horses). The green license plate is only issued by the registration office if the main customs office has approved the tax exemption . Using vehicles with green license plates for other purposes is an offense against the tax law.
If an increased vehicle tax is paid for the towing vehicle (not for cars or motorcycles), a load trailer can be made tax-free; However, this may only be pulled by vehicles that are subject to high taxation. Trailers for container transport that are used in combined transport are tax-exempt, regardless of the tax status of the towing vehicle ( Section 10 KraftStG).
Temporary license plate
Short-term license plates are intended for vehicle transfers, test drives and test drives for a specific vehicle that is not otherwise approved. The legal basis for these license plates is § 16a FZV (test drives and transfer trips with short-term license plates ). Since April 1, 2015, when a short-term license plate is allocated, the technical data of the unregistered vehicle for which the short-term license plate is to be used must be entered in the redesigned registration certificate Part 1 in addition to the vehicle liability insurance that has already been proven. If it is a roadworthy vehicle that does not correspond to an approved type or for which no individual approval has been granted, the vehicle with the registration number may only be moved within the scope of the restriction entered in the registration certificate part 1. There is also a restriction to be entered in Part 1 of the registration certificate if no valid general inspection / safety inspection can be proven for the vehicle . These license plates may only be used with a single vehicle; alternating use with several vehicles is not permitted. These labels are excluded from the regulations regarding the environmental badge.
They are valid for a maximum of five days, the last day of validity is noted in a yellow field on the right, the day above, the month below and the year below, each with two digits. In the case of a natural person, a prerequisite for the issue is the presentation of a valid identity card or a passport along with a registration confirmation and a valid insurance confirmation (eVB number) for up to five days. With many insurance companies it is possible to have the insurance premiums for the short-term registration offset against a subsequent normal registration. Between November 1, 2012 and April 1, 2015, temporary license plates could only be applied for at the registration office of the keeper's place of residence. Since April 1, 2015, it is sufficient to provide proof of the location of the vehicle to the registration office. A nationwide fee totaling 13.10 euros is charged for issuing a short-term license plate. The fee consists of 10.20 euros for the allocation of the short-term license plate + 2.60 euros for the Federal Motor Transport Authority + 0.30 euros for an adhesive seal. (Building No. 221.4, Building No. 124, Building No. 233 of the Annex to the Schedule of Fees for Measures in Road Traffic). The fee can increase by up to EUR 0.60 if up to two additional sheets are issued due to the technical entries.
Appearance
The license plate contains the standard differentiator of the registration area ( no alternative ) and a number that begins with 03 (since March 1, 2007) or 04 . The official stamp sticker is blue (and mostly derived from the old version of the respective approval sticker), and the license plate does not have a euro field on the left edge ( Appendix 4 FZV, sections 1 and 6 and 7 are relevant).
History / precursor
The short-term license plate in its current form replaced the red 04er license plate in 1998, which private individuals could obtain from the registration office for a maximum of five days and had to return. After the abuse of short-term license plates had risen sharply and an increase in the trade in short-term license plates had been ascertained, the law was changed on April 1, 2015. Since then, the abbreviation number has only been assigned if the vehicle corresponds to an approved type or an individual approval has been granted and motor vehicle liability insurance is in place. Due to the vehicle reference, the short-term license plate can no longer be used on another vehicle.
foreign countries
The assignment of a short-term license plate is a national administrative act, and thus the attachment of a short-term license plate to a vehicle that is abroad in order to use it e.g. B. to be transferred to Germany is not permitted (prohibited remote authorization).
For trips abroad, the national registration documents are mutually recognized by the participating states of the Vienna Convention on Road Traffic . However, short-term license plates and the corresponding vehicle registration document are not, strictly speaking, official registration documents, as they permit the use of vehicles outside of the registration process, which in this form does not fall under the Road Traffic Convention. For this reason, different rules may apply to short-term license plates abroad than to regular license plates.
Within the European Union, participation in cross-border public road traffic is generally permitted. Reasons for refusal can be inadequacies in road safety, vehicle theft or the invalidity of the registration certificate.
Export license plate

International short-term approvals with a red border on the right-hand side are approvals for transfer purposes abroad. The date on the red stripe on the right does not indicate the period of validity of the license plate and the associated vehicle registration document, which is always twelve months, but the expiry date of the insurance cover valid in Germany. The vehicle must have been exported abroad before the specified date and may then no longer be driven on German roads. For example, vehicles with expired insurance coverage are sometimes driven abroad. A new insurance may then have to be applied for there. At the beginning, the expiry date was only specified to the month on the red number, later it was changed to an exact date.
The license plate contains the abbreviation of the approval district, a red stamp sticker (which is usually derived from the old version of the respective approval sticker) and a number with two to four digits, followed by a letter that indicates the current series and has no special meaning. Ironically, these international license plates are one of the few license plate types that do not have the Europe feature (star wreath) and the country code.
From 1910 to 1988 the license plate was in the form of an oval shield with a seal from the customs authorities. This seal used to contain the imperial eagle and later the federal eagle. West Berlin was an exception to the seal , as it was not part of the Federal Republic of Germany until 1990.
The old, oval plates were called customs plates and for decades had a double function as
- Export license plate in today's sense, and
- Customs plates for foreign vehicles entering Germany. The foreign license plate had to be unscrewed or covered and exchanged for the customs license plate. When leaving Germany, the customs license plate was given back at the border. Due to international treaties, this function was gradually eliminated.
Diplomatic plates
Vehicle registration numbers of the diplomatic corps begin with the number zero (ambassadors and equivalent persons) or the registration number of the registration district (usually B or BN , other embassy staff and consulates).
To the right of the badges, these labels have a country code and then a one to three-digit number that is usually related to the rank of the holder. Smaller numbers usually indicate a higher rank. Diplomatic plates are not only issued to embassy staff, but also to employees of numerous international (intergovernmental) organizations , but not to German citizens. As personal identification, they restrict the use of such vehicles to holders of a diplomatic ID card (which may also be issued to family members without their own income, but also not to Germans) and drivers in the service of the respective diplomatic missions. Very low-ranking diplomats, e.g. B. Honorary Consul , do not receive diplomatic license plates , but are allowed to affix a CC sticker ( Corps Consulaire ) and, depending on the location , can receive a license plate similar to an official license plate with the abbreviation of the registration area and a sequence of digits starting with 9 .
If a diplomatic license plate is stolen or is lost for other reasons, the vehicle is given an alias number : The previous license plate is supplemented by the letter A and the previous license plate is declared invalid until the blocking period of one year has expired. Then the admissions office may issue it again. If the alias number is also missing, the additional letter B is used, etc.
License plate of NATO

International headquarters of NATO in Germany lead to the registration numbers of their service vehicles as distinguishing characters X , followed by a four-digit number. Even if Section 46 FZV has delegated the tasks of the licensing authority for these vehicles to the Bundeswehr Motor Vehicle Center , vehicles with an X mark are not Bundeswehr service vehicles. The approval and technical monitoring of the vehicles are carried out in accordance with the provisions of the StVZO, the Vehicle Licensing Ordinance, the Motor Vehicle Expert Act and the 15th Exemption Ordinance to the Road Traffic Licensing Regulations.
After that, the vehicles marked with an X have to undergo a regular general inspection and examination of the engine management and emission control system. The safety check can also be carried out by Bundeswehr workshops. This means that these vehicles are in contrast to those of the Bundeswehr with the license plate Y , which are tested by Bundeswehr personnel as part of the Technical Material Testing (TMP).
These signs do not have to be reflective either, and they are not available in the euro version. There are also red marks that start with an X.
More military plates
Members of the Bundeswehr stationed in France (German soldiers and their civilian entourage, i.e. Bundeswehr administration or authorized family members) have their own license plate that begins with DF and has white letters on a black background. This is followed by four digits from 0001 to 9999. The abbreviation DF is a so-called French domain code (state code ) and means Douanes Françaises . It is therefore a customs exclusion indicator.
German soldiers stationed in the Netherlands also have their own registration number. It has yellow letters on a black background and begins with AF . Since the Seedorfer Treaty was changed, the license plate looks different: it has black letters on a yellow background and is indistinguishable from normal Dutch license plates.

The soldiers of the US armed forces stationed in Germany also used a license plate from 2000 to 2005 that is identical to the German one except for the content of the Euroband (so-called lookalike license plate ; starting with AD , AF or HK ; today's license plate HK for the Heidekreis did not exist until 2011 ). Due to safety concerns, since the end of 2005 a regular German license plate has been used for the respective licensing area in which the soldier lives or has his place of work. The identifier IF is still used for company vehicles . Furthermore, QQ is used for transfer license plates and T for red license plates.
Temporary license plates with a red number are also issued with the letter T followed by an abbreviation for the garrison issuing the license and a five-digit number, e.g. B. T GR 00042 from the Grafenwöhr area or T HS 00150 for Hohenfels .
| Abbreviation | garrison | Abbreviation | garrison |
|---|---|---|---|
| TA | augsburg | T HS | Hohenfels |
| T BA | Bamberg | TI | Ingolstadt |
| T bra | Baumholder | TK | Kaiserslautern |
| T BR | Bruchsal | T MA | Mannheim |
| T BW | TS | Stuttgart | |
| T GK | Geilenkirchen | T SP | Spangdahlem |
| T GR | Grafenwohr | T SW | Schweinfurt |
| TH | Heidelberg | TW | Wiesbaden |
Separate license plates exist for soldiers from the following countries who are or were stationed in Germany:
- Belgium (white lettering on a black background) - since the Belgian armed forces withdrew from Germany in 2004, only occasionally seen for military fasteners. These plates have now been replaced by white plates with red letters (typical of the country) and have the fixed combination B – 123 – X (prefixed B , followed by any three-digit number and a letter from A to Z ).
- France (silver writing on a blue background) - since the withdrawal of the French armed forces in Germany in 1999 only members of the French part of the Franco-German Brigade , members of French military fasteners in Germany and members of the last French units in Saarburg (district Trier-Saarburg) and French members of NATO units stationed in Germany.
- Great Britain no longer issues separate license plates for this case. The soldiers there use the regular British license plate, but also German license plates.
- Canada (red font on a white background), two letters and three digits, often with the allocation of the two letters in connection with the stationing location (e.g. WE for vehicles of members of the armed forces stationed in Wesel).
- Netherlands (white letters on a black background).
various
Expansion of the system
The system introduced in West Germany and West Berlin from 1956 should be sufficient for an expected significant increase in the number of motor vehicles while at the same time being able to adapt to changed European political conditions. In this way, the districts in the former GDR could be incorporated into the system in 1991 without major difficulties. The fact that, according to a statement by Transport Minister Hans-Christoph Seebohm at the Federal Council meeting on February 24, 1956, the system could "be extended and applied to Central Germany" contributed to this. The so-called east zone directory may have been created in this context . The latter also included the German Eastern Territories , to which the Federal Republic of Germany was still claiming at the time. After these areas were renounced under international law , these ideas are no longer valid.
In the context of the founding of the city of Lahn , it was decided in 1977 to use the L as a distinguishing sign for the city and the Lahn-Dill district , although its use in the event of reunification for the city and the district of Leipzig was obvious. At the time, it seemed unimaginable that this would happen. Even after the city of Lahn was dissolved again, the distinctive sign for the Lahn-Dill district was retained. It was not until November 1, 1990 that it received the new LDK identifier, which is still valid today . When the L was introduced in Leipzig and in the district of the same name, they managed to use the number groups not yet issued in the Lahn-Dill district for Leipzig license plates, especially the then group IIIb - today group e - (see above under identification number ), were used.
With the regional reform in Saxony-Anhalt in 2007 , expiring distinctive signs were again assigned: HZ was originally issued from January 1, 1991 to December 31, 1993 for the Herzberg district (Brandenburg, today: Elbe-Elster district ). July 2007 used for the Harz district , as well as BK until December 31, 1972 for the former Backnang district (Baden-Württemberg) and since October 1, 2007 for the Börde district in Haldensleben .
The Conference of Transport Ministers of the Länder recommended in April 2011 that the reintroduction of expiring license plates should be made possible by amending the Vehicle Registration Ordinance. In August 2012, Federal Transport Minister Peter Ramsauer announced that cities and municipalities would be free to choose their distinguishing signs in future. In addition to the reintroduction of old license plates, the introduction of completely new distinctive signs should then also be possible. The Federal Council passed the relevant ordinance on September 21, 2012, albeit with the restriction that only expiring distinctive signs should be allowed again in accordance with the demand of the Conference of Transport Ministers. The related First Ordinance amending the Vehicle Registration Ordinance and other road traffic regulations was announced in the Federal Law Gazette on October 25, 2012 and came into force on November 1, 2012.
One of the decisive factors for this decision was the initiative to liberalize the license plates at Heilbronn University. Between 2010 and 2012, the initiative asked over 50,000 people in over 200 cities whether they would like the old license plates to be reintroduced. The evaluation of the survey results showed that more than 72 percent of the people questioned would like the old license plates to be reintroduced.
As a result, distinctive signs that had previously expired were reintroduced in all territorial states with the exception of Saarland from November 9, 2012. Since applications for the reintroduction of old license plates are possible at any time, the number of reintroductions is constantly changing.
Unwanted identification numbers
According to Section 8 of the Vehicle Registration Ordinance, distinctive signs, identification numbers and combinations of distinctive signs and identification numbers that offend morality are not permitted. The administrative regulation for the Vehicle Registration Ordinance recommends that the registration offices not assign any pairs of letters that refer to National Socialist organizations. These are: HJ ( Hitler Youth ), KZ ( concentration camp ), NS ( National Socialism ), SA ( Sturmabteilung ) and SS ( Schutzstaffel ).
AH ( Adolf Hitler ), HH ( Heil Hitler ) and SD ( Security Service ) are only not issued by a few licensing authorities. IS ( Islamic State ) is no longer awarded in Düsseldorf , in the Rhein-Sieg district , in the Marburg-Biedenkopf district and in Darmstadt . Furthermore, combinations with the approval district are undesirable if they are one of the above. Combinations results. For Stuttgart , for example, the identification A , S , and D for Cologne is Z not awarded. However, deviations from this were made in individual cases: For example, in the approval district of the Hannover J region, there was a permissible identification letter that was not further objected to by the responsible minister. In the meantime, license plates with J were no longer issued, but are currently being issued again. Other unassigned letter combinations are in Stuttgart S ED ( Socialist Unity Party of Germany ), in Nuremberg N PD ( National Democratic Party of Germany ), in the district of Nürnberger Land N S and N SU , in the district of Warendorf WAF FE , in the district of Steinburg IZ AN ( Nazi read backwards) in Dithmarschen HEI L . Contrary to the recommendations of the Federal Ministry of Transport, the district of Regensburg in Bavaria issued the pair of letters NS until the beginning of October 2012 . Only after a local newspaper drew the authority's attention to this, such labels were no longer issued. The district of Schwandorf has after the reintroduction of the distinguishing sign BUL the letters BUL LE found to be possible insult to offensive and there is not enough. In contrast, the Aachen Road Traffic Office assigns the pair of letters AB and thus the combination AC AB ( All Cops Are Bastards - 'All police officers are bastards '). The MO RD combination is not used in the Wesel district . In the Rhein-Sieg district, the combination SU FF is not awarded in individual cases.
Since June 2010, the local vehicle registration offices in Brandenburg have no longer assigned new license plates that can be associated with Adolf Hitler, the Hitler salute or similar right-wing extremist symbols . Number plates that end in 88 , 888 , 8888 , 188 , 1888 and 8818 are affected . The combinations HH 18 and AH 18 have also not been issued since then.
Desired license plate
Since at least 1994 it has been possible to obtain a license plate of your choice for a nationwide fee of currently 10.20 euros (building number 221 of the Annex to the Schedule of Fees for Measures in Road Traffic). Almost all registration offices now offer online reservations. An additional fee of 2.60 euros is incurred for such a pre-reservation, whereby the total fee is 12.80 euros for a custom license plate with pre-reservation.
Special approval districts
Even before the amendment to the Vehicle Registration Ordinance came into force, with which since November 1, 2012 , it has been possible to assign multiple distinguishing marks within one licensing area ( license plate liberalization ), there were a number of special features when assigning distinctive marks:
Baden-Württemberg
The municipality of Büsingen am Hochrhein (license plate BÜS , belonging to the district of Konstanz with the license plate KN ), as a German exclave in Switzerland, has had its own distinctive sign since January 1, 1968 to facilitate border controls. Only the letter combinations BÜS-A (duty-paid vehicles) and BÜS-Z (to be declared within two years) are given.
Baden-Württemberg / Saxony-Anhalt
There is a duplication in Backnang / Bördekreis .
Bavaria
On December 1, 2014, the independent city of Coburg and the district of Coburg formed the Coburg licensing office . The vehicles that have been newly registered since then can no longer be differentiated according to the registration district city or district.
The license plate reintroduced in Waldmünchen in connection with the liberalization is the only case nationwide with a “letter turner”. According to the place name it should read WMÜ . Because of the pronounceability and comprehensibility in police radio, it became WÜM at that time.
State of Bremen
In the state of Bremen , the independent cities of Bremen and Bremerhaven have the same distinctive sign with HB , although they are about 60 kilometers apart. The Bremerhaven license plates always have one letter and four digits to distinguish them (group d; see above under identification number ).
Hesse
Hanau , as a town belonging to the district with a special status in the Main-Kinzig district , was allowed to keep the HU label on June 1, 2005 , while all other communities in the district that relocated its seat from Hanau to Gelnhausen received the MKK label . Since June 15, 2016, the HU license plate has also been issued as an alternative license plate in the rest of the Main-Kinzig district.
The special status town of Wetzlar in the Lahn-Dill district became the holder of its own licensing authority on July 1, 2012 and received its own distinctive symbol WZ , which was already used by the district of Wetzlar before the district reform in Hesse .
On a similar basis, the special status town of Rüsselsheim , which belongs to the district, has been striving to obtain its own distinctive sign since 2011, but so far without success.
Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania
After the Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania district reform in 2011 , the former independent cities of Greifswald , Neubrandenburg , Stralsund and Wismar kept their previous distinctive signs, while the newly formed districts received new distinctive signs. Initially, the island of Rügen also retained its former distinctive sign, which was converted into an alternative sign for the district of Vorpommern-Rügen .
Saarland
St. Ingbert (license plate IGB , in the Saarpfalz district with license plate HOM ) and Völklingen (license plate VK , in the Saarbrücken regional association with license plate SB ), as medium-sized towns, have their own distinctive signs according to Saarland municipal law .
Motorcycle license plate
Two-wheelers, trikes and related vehicles today basically only have one license plate that is attached to the rear of the vehicle. In the first half of the 20th century, a curved shield on the front mudguard (lengthways to the direction of travel) was still common on motorcycles , but this was abolished in the post-war period in Germany and other countries due to the endangerment of other road users in collisions. Nevertheless, the use of such license plates is not prohibited to this day, something that is used, for example, on vintage cars.
Since the beginning of April 2011, the Vehicle Registration Ordinance for motorcycles has allowed the use of a motorcycle license plate with the previously small motorcycles and special, for example American vehicles reserved, smaller font; The height of these labels is set to the normal size of two-line labels (200 mm), the width may be between 180 mm and 220 mm. Two-line license plates on motorcycles, like those on cars, can still be up to 280 mm wide if they are provided with characters of normal size.
Insurance indicator
Some vehicle classes are exempt from registration, but must have an insurance license plate as proof of valid insurance in order to be allowed to participate in road traffic:
-
Small motorbikes , mopeds and light vehicles with a design-related maximum speed of 45 km / h
- In the case of two-wheeled vehicles, the cubic capacity must not be larger than 50 cm 3 (internal combustion engine) or the power must not exceed 4 kW (electric motor)
- for three-wheeled vehicles, the same cubic capacity restriction applies to positive-ignition engines and the power restriction to 4 kW applies to other engines
- Motorized patient elevators with an empty weight of a maximum of 300 kg, a maximum permissible total weight of 500 kg, a maximum width of 110 cm and a maximum design speed of 15 km / h
- four-wheeled light vehicles with an empty weight (possibly without batteries) of a maximum of 350 kg. The same restrictions on displacement, maximum speed and power apply here as for small motorcycles
The license plate is issued from March 1st of each year until the end of February of the following year (insurance year) in a different font color and can be purchased from banks and insurance companies. The sign has two lines (three digits and three letters), is portrait format, and is significantly smaller (130 mm × 105.5 mm) than normal license plates. The respective number is not specifically tied to the vehicle, but is usually assigned at random. The insurance company can be identified using the three letters. The license plate is not an official approval because (with a liability insurance) the permission to participate in public road traffic is documented by the ABE of the vehicle. The font colors are black, blue and green on a reflective white background, alternating every year on March 1st. The year in which the license plate is valid is given again in the bottom line. It is therefore not possible to use a license plate again three years later.
On the lower edge is GDV (formerly: HUK Association ). In addition, there are also red license plates that are only given to dealers for test, test and transfer trips. These license plates always start with the letter Z in order to avoid misuse with other insurance license plates , as no special vehicle is entered in the accompanying documents.
Colors of the current license plates from March 1st of the respective year colour year Black
(RAL 9005)1990 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 2008 2011 2014 2017 2020 Blue
(RAL 5012)1991 1994 1997 2000 2003 2006 2009 2012 2015 2018 2021 Green
(RAL 6010)1992 1995 1998 2001 2004 2007 2010 2013 2016 2019 2022
The lack of insurance can be punished as a criminal offense with up to one year imprisonment according to § 6 PflVG . Owners have a right to insurance ( obligation to contract in accordance with Section 5 (2) of the PflVG), which the insurance company cannot avoid; Rejected insurance applications nevertheless lead to a legally valid insurance relationship due to the statutory assumption fiction from § 5 Paragraph 3 and 4 PflVG.
Insurance badge
Since June 15, 2019, an insurance sticker has been mandatory for small electric vehicles as proof of valid insurance in order to be allowed to participate in road traffic:
The insurance badge is a sticker that guarantees permanent adhesion on the vehicle surface. It contains a hologram that makes forgery difficult. The badge is 65 mm high and 52.8 mm wide.
With regard to the font colors and the insurance year, the same rules apply as for the insurance number .
Registration districts with the fewest motor vehicles
Until the license plate was liberalized , the rarest license plate issued in Germany was that of the Büsingen BÜS exclave . Since then, there have been newly introduced license plates that have so far been even rarer. But since the registration districts in question all have a multiple number of inhabitants, it can be a temporary condition. Büsingen is still the smallest registration district in Germany.
The following table shows the registration areas with the fewest registered vehicles in Germany.
(Status: 2005, source: KBA)
Placement 2005 Comparison 1998 As of 2005 Vehicle inventory
in 2005398 Theatrical Version SC 31,077 399 SC ITUC 30,533 400 VK EMD 29,355 401 EMD Theatrical Version 29,127 402 BÖ VK 28,846 403 UTI EA 28,781 404 ZW ZW 27,341 405 EA UTI 25,366 406 BÜS BÜS 812
Umlauts in distinctive signs
The umlauts (Ä, Ö and Ü) are only used for the distinctive signs, but not for the identification numbers. At present, only distinctive signs with 'Ö' (e.g. in GÖ ) and 'Ü' (e.g. in WÜ and ÜB ) are set; the letter 'Ä' has so far only been found in the distinctive sign of the district of Säckingen (SÄK) , which was dissolved on January 1, 1973, which is currently canceled . Nevertheless, a character was developed for the 'Ä' as part of the FE script for the Euro plates that have been used since 1994. The font height of the umlauts (including the dots) is identical to the other letters and numbers in the FE font.
Until 1994, the principle was not to assign combinations for different approval areas, which only differ from each other in the umlaut and the associated vowel, in order to avoid confusion. With the award of the combination BÖ to the Bördekreis in Saxony-Anhalt, this principle was broken in 1996, because the combination BO was already used by the city of Bochum . After this had led to confusion, especially abroad, the BÖ was replaced by BK in 2007 in connection with the merger of the Bördekreis with the Ohrekreis to form the Börde district , but again approved as an option in November 2012 in the course of the license plate liberalization .
License plates in film productions
For motor vehicles that appear as props in film and television productions , fictitious film or so-called game license plates are often used instead of officially approved license plates, since for reasons of data protection officially assigned license plates may only be recognizable in film and advertising recordings if the vehicle owner has given his consent.
Foreign license plates with similar characteristics
- In Australia , some states have special versions of license plates that are similar to the German ones at an additional cost.
- In Victoria the license plate is identical to the German one except for the content of the Euroband. It always starts with V for Victoria (in Germany: Vogtlandkreis ). In addition to the normal Euro size, there is also a smaller format for vehicles with a sign frame according to the US / Australian standard.
- In New South Wales there is a sign similar to that in Victoria, but there it always begins with N for New South Wales (in Germany: Nürnberg or Nürnberger Land ). It is also offered here with white lettering on a black background (negative lettering). In addition to the additional fees of AU $ 400 at the time of issuance (around 310 euros; as of March 2013), the sign also costs an annual luxury tax of AU $ 99 if the vehicle owner wants to personalize the content. The New South Wales Roads Administration recommends this license plate for “people who want to give their vehicle a European touch”.
- In Queensland there are Euro-look-alike numbers that start with a Q for Queensland.
- There may be badges on the license plates of Greek trucks that are very similar to the German TÜV badges, but a serif font is used there.
- Likewise, the plaques used in Lithuania for the main inspection ( Lithuanian TA = techninė apžiūra) are similar to those of their German counterparts .
- The FE font of the German license plate is also used on license plates in Bosnia and Herzegovina , Cameroon , Malta , Namibia , Sierra Leone , Sri Lanka , South Africa , Cuba , Argentina, Paraguay, Brazil and Uruguay .
See also
- Automatic license plate recognition
- Drafts for the license plates in Germany
- Start of validity of the German license plates
- License plate lighting
- License plate (Austria)
- License plates from other countries / license plates by country (category)
- License plate with EU identification
- License plate of the Canadian armed forces in Germany
- List of all license plates of the Federal Republic of Germany
- List of German districts and cities with their license plates
- List of previous German license plate systems
- List of vehicle nationality symbols
- Property search
literature
- Andreas Herzfeld: The history of the German license plate (= contributions to German automobile history . Vol. 1). German Flag Society V., Berlin 2010, ISBN 978-3-935131-11-7 .
Web links
- Overview of the Federal Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure
- Search for the location for the license plate code and vice versa
- Interesting facts about German and European license plates
- Overview of the entire German number plate history
- Further, also historical information on German license plates
- Photos of German license plates, some of them very rare
- Галерея автомотостарины. Номерные знаки. Германия (до 1945 года) .– Photos of license plates in Germany before 1945 with the associated vehicles (sorted alphabetically)
- More information about German license plates
- Funny license plates and combinations
- Further information on transfer license plates (private website)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Michael Ossenkopp: No desired license plate for the emperor. Supplement automobile C2 in the Berliner Zeitung , 22./23. September 2007.
- ↑ a b car numbers: so that the police take notes. In: Der Spiegel 12/1952.
- ↑ Cabinet minutes January 15 , 1952 , cabinet minutes December 21 , 1955 , 154th meeting of the Federal Council on February 24, 1956
- ^ Official Journal of the Saarland, edition 127/1956.
- ↑ Thirty-second ordinance amending road traffic regulations (32nd AmVstVR) . In: Federal Law Gazette 2000 Part I No. 34 . P. 1093. July 20, 2000 .: “Article 13 (e) […] Euro plates […] to be applied from November 1, 2000 […] at the latest, which […] are fitted with a new plate. Marks [...] in the version valid before this date [...] continue to apply. [...] (f) The transitional provision §60 Para. 1b (introduction of the Euro plate) is repealed. "
- ↑ § 8 paragraph 2 FZV in the version valid since November 1, 2012.
- ↑ Art. 2 number 5 b i. V. m. Art. 4 of the First Ordinance amending the Vehicle Registration Ordinance and the Fee Regulations for Measures in Road Traffic of October 8, 2013
- ↑ Section 8, Paragraph 1, Clause 2 of the Vehicle Registration Ordinance in the version that has been in force since November 1, 2012.
- ↑ Annex IX StVZO
- ↑ User manual for web application IKFZ V 1 0 (PDF).
- ↑ Official justification for the first regulation amending the vehicle registration regulation of April 4, 2011 ( Federal Law Gazette I p. 549 ).
- ↑ a b c Art. 1 of the first regulation amending the vehicle registration regulation.
- ↑ License plates: New 3D plastic license plates . Article on the T-Online news portal. Retrieved November 13, 2013.
- ↑ Ordinance on the reorganization of the law on the admission of vehicles to road traffic and on the amendment of road traffic regulations, April 25, 2006 ( Federal Law Gazette I p. 988 )
- ↑ Police on Kennzeichen-Guide.de, accessed on September 20, 2012.
- ↑ kennzeichen-guide.de. Retrieved May 13, 2011.
- ↑ www.kdb.bund.de ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Bundesfinanzdirektion Südwest (BFD SW), procurement office of the Federal Ministry of the Interior ( Kaufhaus des Bundes ), accessed on December 10, 2011.
- ↑ a b Article 1 of the ordinance of 13 January 2012 (Federal Law Gazette I p. 103).
- ↑ Variable license plates - two vehicles, one license plate .
- ↑ New change number plate: the air number plate. In: Spiegel Online , January 18, 2011.
- ↑ Only 2115 variable numbers are a megaflop , accessed on February 18, 2015.
- ↑ Appendix 3 of the 35th BImSchV, exceptions to the labeling requirement.
- ↑ Federal Law Gazette , BGBl. I pp. 522, 553
- ↑ Christian Steiger : We have never been as valuable as we are today. Electric automobility and autonomous driving will change the automotive world quickly and thoroughly ... , in ders. (Red.): Auto Bild Klassik , issue 12/2017 of December 2017, pp. 44–50; here: p. 49
- ↑ Martin Kraut: The thriller with the H mark , in Eckhart Bartels (Ed.) Now drive first ... , p. 27 ff.
- ↑ 57 960 vintage license plates. (PDF; 374 kB) In: Press report 2001. Kraftfahrt-Bundesamt, December 2000, p. 16 , accessed on June 21, 2014 .
- ↑ Decree of the Hessian Ministry of Economics, Transport and Regional Development, Az .: V 3-B - 66 I 02-089 - except for vintage license plates.
- ↑ Bremen gives more weight to the authentic appearance of classic cars . ( Memento from January 18, 2012 in the Internet Archive ) DEUVET - Federal Association for Clubs of Classic Vehicles e. V. Accessed March 7, 2010.
- ↑ In: Oldtimer Markt , No. 9/2010, p. 7 above.
- ↑ http://files.vogel.de/iww/iww/quellenmaterial/dokumente/132474.pdf
- ↑ TÜV Süd: Catalog of requirements for the assessment of classic cars ( Memento from January 31, 2012 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF; 125 kB).
- ↑ Stricter guidelines for H marks. At: rp-online.de .
- ↑ https://www.buzer.de/gesetz/9619/v208931-2018-01-01.htm#t3
- ^ Electromobility Act: Special rights for electric cars. Retrieved October 30, 2014 .
- ↑ bem-ev.de ( Memento from March 27, 2016 in the Internet Archive ), accessed on February 18, 2015.
- ↑ Law on the preferential use of electrically powered vehicles (Electromobility Act - EmoG) § 3 preferential rights
- ↑ BMVI - press releases - special license plate brings privileges in road traffic . bmvi.de.
- ↑ § 9a FZV; 50th Amendment to Road Traffic Regulations
- ↑ No. 259 Schedule of Fees for Measures in Road Traffic (GebOSt); Art. 3 50th Amendment of the Road Traffic Regulations
- ↑ § 9a Paragraph 4 FZV; 50th Amendment to Road Traffic Regulations.
- ↑ § 9a Paragraph 5 FZV; 50th Amendment to Road Traffic Regulations.
- ↑ § 16 Paragraph 3 FZV.
- ↑ Section 16 (3a) of the FZV.
- ↑ Information from ADAC on red vintage license plates abroad ( memento from February 28, 2016 in the Internet Archive ).
- ↑ a b c d Questions and answers on the allocation of short-term license plates since April 1, 2015 ( Memento of November 13, 2016 in the Internet Archive ).
- ↑ European Commission : Explanatory Communication of February 14, 2007 on the registration procedures for motor vehicles brought from one Member State to another (final version in: Official Journal C 68 of March 24, 2007 ). Accessed September 18, 2010.
- ↑ 154th meeting of the Federal Council on February 24, 1956 , page 57
- ↑ Transport ministers of the federal states vote for the reintroduction of old license plates ( memento of April 25, 2015 in the Internet Archive ).
- ↑ Resolution of the Federal Council printed matter 371/12 of September 21, 2012.
- ↑ The comeback of the old license plates .
- ↑ First regulation to change the vehicle registration regulation and other road traffic regulations
- ^ Initiative for license plate liberalization (Heilbronn University, 2012) .
- ↑ Overview map of old license plates reintroduction (status: 09.2013) .
- ↑ § 8 FZV as amended on October 19, 2012 ( Federal Law Gazette I p. 2232 ).
- ^ No IS in Düsseldorf
- ↑ No new registrations with the abbreviation - Marburg bans "IS" from license plates. (No longer available online.) Hessenschau , April 16, 2016, archived from the original on June 19, 2016 ; Retrieved June 19, 2016 .
- ↑ Preferred license plate district Steinburg .
- ↑ Is your desired license plate still available? District of Dithmarschen, accessed on January 6, 2015 : “The letter combinations HJ, KZ, NS, SA u. SS are not awarded nationwide; in Dithmarschen the 'L' is not. "
- ^ Right number - dispute over Nazi license plates on cars
- ↑ Administration: NS on the car: From now on taboo! Mittelbayerische Zeitung , October 9, 2012, accessed on October 9, 2012 .
- ↑ BUL-LE license plate withdrawn from circulation , accessed on January 13, 2014.
- ↑ LTO: Special operating permit for ex-police vehicles: water cannons and tanks as second vehicles .
- ↑ License plate reservation . (No longer available online.) Archived from the original on March 30, 2014 ; accessed on March 29, 2014 .
- ↑ 30 Moerser wanted license plate MO-RD. Rheinische Post , November 13, 2012, accessed on January 18, 2014 : "The request is not granted - MO RD is not allowed."
- ^ Preferred license plate Rhein-Sieg-Kreis ( Memento from March 4, 2016 in the Internet Archive ).
- ^ Rheinische Post from September 18, 2010: Stricter rules against Nazi license plates (accessed in November 2015).
- ↑ a b Info on the BÜS license plate .
- ↑ WÜM: Unique in Germany Mittelbayerische Zeitung from February 19, 2013 - accessed on May 10. 2018
- ↑ Is the RÜS license plate coming? In: Frankfurter Neue Presse. January 30, 2017, accessed September 21, 2019 .
- ↑ Vehicles according to § 3 paragraph 2 number 1 letters d to f
- ↑ Search for insurance for moped license plates at gdv.de.
- ↑ Appendix 12 to the FZV
- ↑ Judgments of the Lübeck district and regional court on compulsory insurance, mandatory contracting and acceptance fiction in the absence of an operating license (PDF; 351 kB).
- ↑ Green light for e-scooter press and information office of the federal government, accessed on May 25, 2019
- ↑ Allocation of film license plates , City of Berlin, accessed on August 28, 2014.
- ↑ Product Range. Retrieved October 30, 2014 .
- ↑ pricing. (No longer available online.) Archived from the original on May 14, 2013 ; accessed on October 30, 2014 .