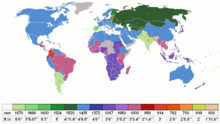
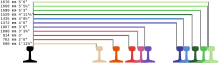List of gauges
This list provides information about the different gauges that can be found in rail traffic around the world .
Normally, the inner distance between the rail heads ("running edges") on a straight line is specified as the gauge. The smallest dimension is measured between the rail heads in the area between the SO (top edge of the rail) and 14 mm below. Exceptions are narrow-gauge railways (0–10 mm) and trams (0–9 mm below the SE). However, since certain railways, especially the French state railways, measure the contact point, deviations can occur. Due to the technical unit in the railway system , the vehicle transfer to France is problem-free despite different definitions.
However, vehicles of the same track width cannot necessarily run on the different routes, since the shape of the wheel flanges also plays a role in addition to the track width . The main factors here are the thickness of the flange and the inner wheel spacing that depends on it, which must only be within a narrow range so that safe guidance in the frogs and guide rails of switches and crossings is possible.
In addition to the track width, the various vehicle gauge lines also prevent liberal use, although a smaller track width does not necessarily mean a narrower clearance profile .
Remarks
Originally, the gauges were defined as feet (foot, abbreviated with ') and inches (inch, abbreviated with "). Due to the non-decadal conversion of 1 foot = 12 inches, the calculation is more difficult If a gauge is based on another measurement (English foot, Castilian foot, Portuguese foot, Prussian foot etc.) this is stated in the second column in the simplest possible form.
- The main gauge of a country is shown in bold type .
- Former gauges are shown in italics (the railway can continue to operate with a different gauge).
- English dimensions:
- Swedish dimensions:
1 Zoll = 24,75 mm1 Fuß = 12 Zoll = 297 mm
Gauges in model building
For track widths of a railway system not designed for passenger transport see
Gauges in passenger transport
Track widths up to 199 mm
Gauges from 200 to 299 mm
| width | Country | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| in mm | Feet & inches | ||
| 203 mm | 8 inches | Netherlands | Leek : Genzelbahn in the Nienoord family park |
| 210 mm | 8¼ in | Great Britain | England : Eastleigh , Brambridge Park Garden Center |
| 241 mm | 9½ inches | Switzerland | Garden railways in Lucerne ( Verkehrshaus ) and Zurich (Katzensee) |
| Great Britain | including: Downs Light Railway (since 1925), Hall Leys Park Railway | ||
| 260 mm | 10¼ in | Great Britain | including: Isle of Mull Railway , Rudyard Lake Steam Railway , Bickington Steam Railway (since 1988), Stapleford Miniature Railway (since 1958) |
Gauges from 300 to 399 mm
Gauges 400 to 499 mm
| width | Country | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| in mm | Feet & inches | ||
| 400 mm | 1 foot 3¾ inches | Germany | Cartoon Express children's railway at kiddy-smile, fairground ride manufacturer: Satorio, Italy |
| 410 mm | 1 foot 4⅛ inches | Germany | only children's tram Frankfurt am Main (since 1960) |
| 450 mm | 1 foot 5¾ inches | Czech Republic | some (former?) factory railways in the Czech Republic |
| 457 mm | 1 foot 6 inches | Great Britain | England : including: Bicton , Bicton Woodland Railway (since 1963), Crewe : Werkbahn Crewe (1862–1932) , Woolwich : Royal Arsenal Railway (1873–192?) |
| Australia | Adelaide : only in the National Railway Museum (? -?) | ||
| New Zealand | Porirua only - Papakowhai : Aotea Railway (? -?) | ||
| United States | including: California : Billy Jones Wildcat Railroad (since 1970), Pennsylvania : Collegeville and Southern Railway (since 2004) | ||
| 483 mm | 1 foot 7 inches | Isle of Man | Great Laxey Mine Railway (since 187?) |
Gauges from 500 to 599 mm
| width | Country | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| in mm | Feet & inches | ||
| 500 mm | As a general rule | worldwide military, industrial, mine, field, garden and forest railways | |
| Germany | Parkeisenbahn Vatterode (1967-2008, reopening August 6, 2016) | ||
| Austria | Vienna : Feldbahn Geriatriezentrum Am Wienerwald (1904–2011), Märchengrottenbahn in Grazer Schloßberg (1968 until closing at the end of 2011; re-tracked to 600 mm, reopened as Grazer Märchenbahn 2014) | ||
| Argentina | Ferrocarril Austral Fueguino (8 km since 1994) | ||
| Denmark | Rördal cement factory in Aalborg | ||
| France | Artouste : Petit train d'Artouste ; Saint-Sulpice-la-Pointe : Chemin de Fer Touristique du Tarn | ||
| Morocco | Casablanca -Berrechid (1908-?) | ||
| Mexico | Yucatán , plantation railways | ||
| Peru | Lima , Sucro district, Parque de la Amistad | ||
| Czech Republic | some (former?) factory railways in the Czech Republic | ||
| 508 mm | 1 foot 8 inches | Great Britain | England : Scarborough North Bay Railway |
| United States | Arizona : Mine railways at Morenci | ||
| 520 mm | 1 Swedish foot 9 inches | Sweden | Industrial line at Sandvikens Järnverk |
| 533 mm | Great Britain | Blackpool Pleasure Beach , Pleasure Beach Express (1933-1970?) | |
| 550 mm | Germany | Mine railways (including roof slate mining Mayen / Eifel) | |
| Czech Republic | Prague : funicular & inclined elevator , cable car of the NH Hotel Prague | ||
| 560 mm | Germany | Berchtesgaden salt mine railway | |
| 575 mm | Germany | Mine railways (including ore mines in Bad Ems and Ramsbeck ) | |
| 578 mm | 1 foot 10¾ inches | Great Britain | Wales : Dinorwic Quarry (until 1969) and Penrhyn Quarry Railway (1798–1962) ( Penrhyn Quarry ) |
| 580 mm | Austria | Wolfsegg Traunthaler coal works in Ampflwang | |
| 585 mm | Germany | Tollwitz-Dürrenberger Railway 1836–1963 | |
| 597 mm | 1 foot 11½ inches | Great Britain | including: England : Lincolnshire Potato Railways (until 1969) Wales : Welsh Highland Railway (since 1922) and Ffestiniog Railway (since 1836), |
Gauges from 600 to 699 mm
Gauges 700 to 799 mm
Gauges 800 to 899 mm
| width | Country | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| in mm | Feet & inches | ||
| 800 mm | 2 feet 7½ inches | Germany | only cog railway sugar factory Schulau (1901–1931) , narrow-gauge factory railway of the Westfalenhütte (1871–1983) , Ernstbahn (1876–1962) , museum field railway Leipzig-Lindenau |
| Austria | Kaprun : only inclined lift Limberg tunnel (1949–?), Not public works railway | ||
| Switzerland | various mountain railways : Schynige Platte Railway (since 1893) of the Bernese Oberland Railway (BOB), Montreux – Territet – Glion – Rochers-de-Naye line of the MTGN (since 1892), Wengernalp Railway (since 1893), Brienz-Rothorn Railway (since 1892), Pilatusbahn (since 1889) and Monte Generoso Railway (Ferrovia Monte Generoso - rack railway - since 1890), Riffelalptram (since 1899) | ||
| France | Luchon : EDF Portillon ( funicular - since 1938) | ||
| Great Britain | Wales : Snowdon Mountain Railway only (since 1896) | ||
| Iran | Tehran-Abd-al-Azim Railway (1888–1962) | ||
| Italy | Crotone – Timpa Grande industrial railway (Ferrovia della Val di Neto - 1920–1955) | ||
| Japan | Kyoto to Mount Kurama , ( funicular ) | ||
| Poland | Warsaw : some suburban railways, all of which have been shut down | ||
| Brazil | Local railway Bertioga - Itatinga on the north coast of São Paulo | ||
| 802 mm | Sweden | eight no longer existing companies, u. a. Bredsjö-Grängens Järnväg (1894–1907), Voxna-Lobonäs Järnväg (1908–1932) | |
| 820 mm | Germany |
Prince Wilhelm Railway (1831–1844) Horse tram Kupferdreh – Neviges (1831–1847) |
|
| Austria | Eisenerzer Bahn (around 1810, non-public works railway) | ||
| 825 mm | Great Britain | England : Volk's Electric Railway , Furzebrook Railway | |
| 828 mm | 2 feet 8½ inches | Great Britain | England : Brighton and Rottingdean Seashore Electric Railway (1896–1901) 2 single tracks, each with 828 mm and 5486 mm total gauge ( four-rail track ) |
| 838 mm | Great Britain | England : Seaton Tramway (since 1971) | |
| 850 mm | Germany | Kunstertalbahn (to the Kunst mine ), 2.4 km long 1882–1924 | |
| Italy | Railway Ponte Tresa - Luino (1885-1924, thereafter umgespurt to 1100 mm) , railway Menaggio - Porlezza (1884-1939) , Mine web Porto Empedocle-Lucia (1881-1950) , mine train-Raddusa Sant'Agostino (1886-1955) | ||
| 860 mm | Germany | Alsensche Kreidebahn Lägerdorf – Itzehoe | |
| 880 mm | Germany | Bavaria : Grassau - Rottau peat railway | |
| Austria | Kaprun : Inclined elevator Limbergstollen - West (1955–?) | ||
| Norway | Sundland Torvströmfabrikk's works railway in Stokke | ||
| 889 mm | Germany | Schlebusch-Harkorter coal railway | |
| 891 mm | 3 swedish feet | Sweden | Standard narrow gauge in Sweden, all railway companies (around 85) with the exception of Roslagsbanan and some museum railways (e.g. Hesselby – Munkebo on Gotland) no longer exist |
Gauges from 900 to 999 mm
Gauges from 1000 to 1099 mm
Track widths from 1100 to 1199 mm
| width | Country | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| in mm | Feet & inches | ||
| 1100 mm | Germany | Braunschweig tram , Schönberger Strand museum tram (three-rail track 1100 mm / 1435 mm), Lübeck tram (1893–1959) and Kiel tram (1881–1985) | |
| France | Mont Cenis Railway (1868–1871) | ||
| Italy | Mont-Cenis rail (1868-1871) , Tram Turin Rivoli (1882-1914 - umgespurt to 1445 mm to 1955) , steam and battery tram Turin Cavour Saluzzo (1882-1950) , steam tram Pinerolo-Cavour ( 1882–1935) , tram Pinerolo – Perosa Argentina (1886–1968) , 3 lines of the Società Varesina per Imprese Elettriche -SVIE- (including the Bettole - Luino Lago railway line 1903–1953 / 55) | ||
| Brazil | Rio de Janeiro : Santa Teresa tram , Estrada de Ferro Cantagalo ( Niterói - Nova Friburgo ) (1873–1965) | ||
| 1106 mm | 3 Austrian feet 6 inches | Austria | Horse-drawn railway Budweis – Linz – Gmunden (1827–1872) and coal railways in Hausruck |
| 1118 mm | 3 feet 8 inches | United States | Pennsylvania : Susquehanna and Eagles Mere Railroad |
| 1130 mm | 3 feet 8½ inches | Canada | Nova Scotia : Cape Breton Railway |
| 1143 mm | 3 feet 9 inches | Great Britain | England : Lynton and Lynmouth Cliff Railway (since 1890) |
| 1156 mm | 3 feet 9½ inches | United States | California : Arcata and Mad River Railroad (1854-1925, converted to standard gauge) |
| 1188 mm | 4 Swedish feet | Sweden | Norbergs Järnväg (1856–1876, converted to standard gauge) |
| Indonesia | Djakarta tram (electric tram 1899–1962 - horse and steam tram 1067 mm) | ||
Track widths 1200 to 1299 mm
| width | Country | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| in mm | Feet & inches | ||
| 1200 mm | Italy | Genoa : Sant'Anna funicular (since 1891 - until 1975 water ballast railway ), Principe – Granarolo rack railway (since 1901) | |
| Switzerland | Mühleggbahn (since 1893 - first water ballast railway , from 1950 cog railway , from 1975 inclined lift ), mountain railway Rheineck – Walzenhausen (since 1896), funicular Neuveville – Saint-Pierre (since 1899), Metro Alpin (since 1994) | ||
| 1217 mm | Sweden | four railway companies: Borås-Herrljunga Järnväg , 42 km, (1863–1899) , Uddevalla – Vänersborg – Herrljunga Järnväg , 92 km, (1866–1899) , Hudiksvalls Järnväg , 16 km, (1860–1887) , Söderhamns Järnväg , 15 km , (1861–1886) , were all converted to standard gauge | |
| 1219 mm | 4 feet | As a general rule | English 4-foot track |
| Great Britain |
England : 17 trams, all shut down
Accrington tram (1907-1932) , Barrow-in-Furness tram (1904-1932) , Blackburn tram (1899-1949) , Bradford tram (1898-1950 - a museum car until 1963) , Burnley tram (1901-1935) , horse-drawn tram Cambridge (1880-1914) , Colne & Trawden tram (1903-1935) , Darwen tram (1900-1946) , Derby tram (1904-1934) , Falkirk tram (1905-1935) , Keighley tram (1904-1924) , tram Nelson (1903–1934) , Oxford horse tram (1881–1914) , Potteries tram (1899–1928) , Rossendale steam tram (1889–1909 - then Rawtenstall tram) , Rawtenstall tram (1909–1932) , Reading tram (1903–1939)
Scotland : Glasgow Subway (since 1896) Wales : Padarn Railway , Saundersfoot Railway (1829–1939) |
||
| New Zealand | former trams in Wellington (1878-1964) and Gisborne (1913-1929) | ||
| United States | former tram in Pueblo (Colorado) , Jeffersonville, Madison and Indianapolis Railroad , Avon, Geneseo and Mount Morris Railroad | ||
| 1245 mm | 4 feet 1 in | United States | Michigan : Hecla and Torch Lake Railroad |
| 1270 mm | Chile | ||
| 1295 mm | 4 feet 3 inches | United States | various coal railways in Pennsylvania , Delaware and Hudson Gravity Railroad (1829–1899) |
Gauges from 1300 to 1399 mm
| width | Country | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| in mm | Feet & inches | ||
| 1365 mm | Spain | Basque Country : Bilbao tram (1896–1964) | |
| 1372 mm | 4 feet 6 inches | As a general rule | Scottish track |
| Great Britain |
England: Seaton Burn Wagonway Scotland : various railways built between 1810 and 1840, later converted to standard gauge |
||
| Japan | (117 km) five lines: Hakodate Tram ; Tokyo Tram: Toden Arakawa Line and Setagaya Line ; Toei Shinjuku Line ( Tokyo Subway ); Keiō line | ||
| Spain | original Spanish colonial trace | ||
| United States | original gauge of several railways in Florida | ||
| 1384 mm | 4 feet 6½ inches | Great Britain | Scotland : Dundee and Newtyle Railway , Newtyle and Coupar Angus Railway , Newtyle and Glammis Railway |
| 1397 mm | 4 feet 7 inches | Great Britain | Wales : Dyffryn Llynfi and Porthcawl Railway (1828–?) |
Gauges 1400 to 1499 mm
Gauges 1500 to 1599 mm
| width | Country | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| in mm | Feet & inches | ||
| 1520 mm | As a general rule |
Russian broad gauge (today) (Developed by reducing the track clearance without changes to the vehicles, new tracks have a gauge of 1520 mm, a car transition between 1520 mm and 1524 mm is possible without any problems.) |
|
| Afghanistan | Rail transport in Afghanistan | ||
| Germany | Mukran (gauge change facility) | ||
| Poland | Foothills off
|
||
| Slovakia | Uzhhorod – Košice railway line (since 1966), Košice – Vienna railway line planned | ||
| Romania | an offshoot from Moldova: Giurgiulești - Galați | ||
| 1524 mm | 5 feet | As a general rule |
Russian broad gauge (originally) Main areas of distribution : former Soviet Union as well as Finland and Mongolia Main areas of application : mainline railways (long-distance traffic), trams and underground trains |
| Russia | Rossijskije schelesnyje dorogi , Trans-Siberian Railway , Kolabahn , Baikal-Amur Mainline | ||
| Armenia | (845 km) Harawkowkasjan Jerkatughi | ||
| Azerbaijan | (2932 km) Azərbaycan Dövlət Dəmir Yolu (since 1880) | ||
| Bulgaria | Varna | ||
| China | (until 1930) | ||
| Estonia | (1200 km) Eesti Raudtee | ||
| Finland | VR-Yhtymä (since 1862) | ||
| Georgia | (1583 km) | ||
| Iran | (94 km) | ||
| Kazakhstan | (15000 km) | ||
| Kyrgyzstan | (428 km) | ||
| Latvia | (1933 km) Latvijas Dzelzceļš | ||
| Lithuania | (1749 km) Lietuvos Gelezinkeliai | ||
| Moldova | Pridnestrovskaya zheleznaya doroga | ||
| Mongolia | Trans-Mongolian Railway | ||
| Tajikistan | (480 km) | ||
| Turkmenistan | (2440 km) Turkestan-Siberian Railway | ||
| Ukraine | Ukrzalisnytsja | ||
| Uzbekistan | (3950 km) | ||
| Belarus | Belaruskaya Chyhunka | ||
| Panama | until 2000, converted to standard gauge , currently on the towing railway at the Panama Canal locks | ||
| United States | among others: originally also in the southern states of the USA (except Florida), Alabama Great Southern Railroad , Mississippi Central Railroad , Louisville tram | ||
| 1537 mm | 5 feet ½ inch | Great Britain | London : London and Blackwall Railway (1840–1849) |
| 1575 mm | 5 feet 2 inches | Ireland | Dublin - Drogheda (1844-1846) |
| United States | Alabama : Montgomery and Eufaula Railroad (until 1870s) | ||
| 1581 mm | 5 feet 2¼ inches | United States |
Pennsylvania track Maryland : Baltimore Pennsylvania tram: Pittsburgh and Philadelphia trams, and in Philadelphia the Market – Frankford Line (since 1907), West Penn Railways |
| 1588 mm | 5 feet 2½ inches | United States |
Louisiana : New Orleans Ohio tram: Columbus (Ohio) trams and Cincinnati Pennsylvania : Aliquippa – West Economy tram (1912–1937) Mobile and Spring Hill Railroad |
Track widths from 1600 to 1699 mm
| width | Country | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| in mm | Feet & inches | ||
| 1600 mm | 5 feet 3 inches | As a general rule | Irish broad gauge |
| Germany | Baden : Baden State Railways (1840–1855), converted to standard gauge | ||
| Ireland | Republic of Ireland ( Iarnród Éireann ) and Northern Ireland ( Northern Ireland Railways ) rail transport in Ireland | ||
| Brazil | second most common track gauge (4057 km), southeast, mid-west and north, Metrô Rio de Janeiro (since 1979) | ||
| Australia | third most common gauge (4017 km), state of Victoria and southeast of South Australia , as well as in Tasmania from 1871–1888 between Launceston and von Deloraine | ||
| New Zealand | Canterbury Provincial Railways (1863–1876), re-gauge to 1067 mm | ||
| 1665 mm | 5 port. Feet | Portugal | Portuguese broad gauge (originally) |
| 1668 mm | As a general rule | Iberian broad gauge (today) | |
| Portugal | Comboios de Portugal | ||
| Spain | Renfe , not the high-speed AVE routes . | ||
| 1672 mm | 6 box. foot | Spain | Spanish broad gauge (originally) |
| 1676 mm | 5 feet 6 inches | As a general rule |
Indian broad gauge , also colonial gauge (in the literature often incorrectly stated for Spain) Main areas of distribution: Indian subcontinent, southern South America Main areas of application: mainline railways (long-distance traffic) |
| Afghanistan | Rail traffic in Afghanistan (originally planned new lines in standard gauge ) | ||
| Argentina | (24,481 km) Ferrocarriles Argentinos , Ferrocarriles General Roca , Sarmiento and Miter networks | ||
| Bangladesh | Bangladesh Railway (since 1862) | ||
| Chile | (3743 km) Empresa de Ferrocarriles del Estado , Santiago – Valparaíso route and south of it | ||
| Great Britain | Scotland : only two routes: Dundee and Arbroath Railway (1838–1847) , Arbroath and Forfar Railway (1839–?) | ||
| India | (42,000 km) Indian Railways , Metro Delhi (since 2002) | ||
| Iran | (97 km between Zahedan and the border with Pakistan) | ||
| Nepal | |||
| Pakistan | Pakistan Railways | ||
| Paraguay | converted to standard gauge | ||
| Sri Lanka | (1508 km) Sri Lanka Railways | ||
| Canada | High-speed network and rail routes between Russia and North America planned; including: Grand Trunk Railway (1852–1873, gauged); Québec : St. Lawrence and Atlantic Railroad (1853- ~ 1873), Intercolonial Railway (1870-1875, gauged) | ||
| United States | San Francisco : BART (since 1972), high-speed network and rail routes between Russia and North America planned; formerly among others: New England , mainly Maine : Maine Central Railroad (1862–1871); Louisiana : New Orleans, Opelousas and Great Western Railroad (1854–1872), Texas : Texas and New Orleans Railroad (1856–1876), Grand Trunk Railway (1852–1873) | ||
Track widths 1700 to 1999 mm
| width | Country | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| in mm | Feet & inches | ||
| 1727 mm | Great Britain | England, Torquay only : Babbacombe Cliff Railway (1926 – today) and Bournemouth - Southbourne : Fisherman's Walk Cliff Railway (since 1935) |
|
| 1750 mm | France | Paris only : Place Denfert-Rochereau - Sceaux ( Ligne de Sceaux ) (1846–1893) | |
| 1800 mm | Germany | only Oberweißbacher Bergbahn (since 1922) | |
| United States | Florida: Hogwarts Express (Universal Orlando Resort) only (since 2014) | ||
| 1829 mm | 6 feet | As a general rule | Bering Lane , original Bering Strait tunnel (TKM-World Link = Yakutsk – Fort Nelson railway line) planned |
| Great Britain | Hastings only : West Hill Cliff Railway (since 1891) | ||
| Russia | Tsarskoye Selo Railway (1837–1897) , then re-gauge to 1524 mm | ||
| United States | Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad , Albany and Susquehanna Railroad , Erie Railroad and subsequent railway companies (until 1880) , rebuilt to 1,473 mm | ||
| India | planned in 1860s (1676 mm built) | ||
| 1850 mm | Canada | Niagara Falls , Falls Incline Railway (since 1966) | |
| 1880 mm | 6 feet 2 inches | Ireland | Ulster Railway (1839-1846) then re-gauge to 1600 mm |
| 1945 mm | 6 feet 4½ inches | Netherlands | Railway Amsterdam – Rotterdam (1839–1866) , Railway Amsterdam – Arnhem (until 1855) , Railway Amsterdam – Haarlem (until 1865) |
| Russia | original gauge Vladivostok – Khabarovsk | ||
| 1981 mm | 6 feet 6 inches | Great Britain | Scarborough only : North Cliff Lift (1930–1996) |
| Israel | only in Haifa: Karmelit funicular | ||
Gauges 2000 mm and more
| width | Country | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| in mm | Feet & inches | ||
| 2000 mm | Great Britain | Scotland : Cairngorms , Cairngorm funicular railway (since 2001) | |
|
2134 mm or 2140 mm |
7 feet or 7 feet ¼ inch |
As a general rule | Brunel broad gauge |
| Great Britain |
England : Great Western Railway , (until 1892) Wales : South Wales Railway (1850–1872) |
||
| Portugal | Azores : Port Railway of Ponta Delgada (1862–1973), Port Railway of Horta (1876–1901) | ||
| 2287 mm | 7 feet 6 inches | Great Britain | Scarborough only : Saint-Nicholas Cliff Lift (1929–2007) |
| 2438 mm | 8 feet | United States |
Johnstown (Pennsylvania) : Johnstown Inclined Plane (funicular, since 1891), West Orange (New Jersey) : Orange Mountain Cable (funicular, 1892–1902) , North American broad-gauge railway planned (never built) |
| 2743 mm | 9 feet | United States | Pennsylvania , Pittsburgh only : Knoxville Incline (funicular), (1890–1960) |
| Japan | Lake Biwa - Kyoto city: funicular railway (1889-1948) | ||
| 3000 mm | Europe | Three-meter gauge, planned for a broad-gauge railway in Europe from 1942 to 1945 during the Third Reich | |
| 3048 mm | 10 foot | Isle of Man | Douglas only : Breakwater Crane Railway (harbor) (1948–197?) |
| United States | Pennsylvania , Pittsburgh only : Fort Pitt Incline , Monongahela Freight Incline (both funiculars), (1882–1935) | ||
| 5486 mm | 18 feet | Great Britain | England : Brighton only : Brighton and Rottingdean Seashore Electric Railway (1896–1901) 2 single tracks with each 828 mm and 5486 mm total gauge ( four-rail track ) |
Gauges of inclined lifts
| width | Country | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|
| in mm | Feet & inches | ||
| 2340 mm | 7 feet 8 inches | Austria | Kaprun only : Inclined elevator Möllpumpwerk (since 1954, not public) |
| 2600 mm | Italy | only Lasa : funicular section of the Lasa marble railway (since 1929) | |
| 3140 mm / 3270 mm |
Poland | five boat lifts in the course of the Oberland Canal in East Prussia , Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship ( funicular railway ) | |
| 8200 mm | Austria | Kaprun only: Lärchwand inclined elevator (since 1941, initially for construction vehicles, later adapted for longer buses) | |
| 9000 mm | Russia | Cogwheel railway of the ship lift on the Krasnoyarsk reservoir | |
Others
Gantry cranes
Cranes for unloading containers from ships at quays at ports are often designed as portal cranes and typically span 2 railway tracks on the land side. The center-to-center distance between the two crane rails is often:
- 15.24 m (50 feet)
- 18 m
- 30.48 m (100 feet) newer facilities
Light gantry cranes that span 1, 2 or 3 railway tracks have center-to-center spacing of the rails of at least 5.5 m, but typically 6, 10 or 14.5 m center-to-center spacing.
Specifically:
- 10.00 m - Rostock Seaport , Pier II
- 35.00 m - Hamburg Container Terminal Altenwerder , Ballinkai, new building
- 40.65 m - new port crane from 2014 in the Danube port of Linz
Arrays of sliding radio telescopes
- The 15 m diameter radio telescopes of the NOEMA project of the Institute for Radio Astronomy in the Millimeter Range (IRAM) on the Plateau de Bure, France can be moved on an approximately right-angled track cross with the 2 rails about 6 m center-to-center.
- The Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array west of Socorro , New Mexico, USA has four-rail tracks - also with curves - for moving and setting up 25 m diameter radio telescopes , which form 2 tracks of (approximately) standard gauge each run in about 7 m track center distance from each other. The antennas are placed in short cross tracks that cross at right angles. Works rail traffic is handled on one of the standard gauge tracks.
Designations of gauges
| Surname | Track width [mm] | Gauge [feet / inches] |
|---|---|---|
| Bosnian track | 760 mm or 762 mm | 2 feet 6 inches (2 '6 ") |
| Brunel broad gauge / Brunel gauge | 2140 mm or 2134 mm | 7 feet ¼ inch (7 '¼ ") |
| Iberian broad gauge | 1668 mm | |
| Indian broad gauge / Indian gauge / colonial gauge | 1676 mm | 5 feet 6 inches (5 '6 ") |
| Irish track | 1600 mm | 5 feet 3 inches (5 '3 ") |
| Italian broad gauge | 1445 mm | |
| Italian meter gauge | 950 mm | |
| Italian narrow gauge | 700 mm | |
| Cape track / CAP track / Japanese track | 1067 mm | 3 feet 6 inches (3 '6 ") |
| Castilian track | 1672 mm | |
| Meter gauge | 1000 mm | |
| Standard gauge / standard gauge / full gauge | 1435 mm | 4 feet 8½ inches (4 '8½ ") |
| Ohio Trail | 1473 mm | 4 feet 10 inches (4'10 ") |
| Pennsylvania Trail | 1581 mm or 1588 mm | 5 feet 2¼ inches (5 '2¼ ") |
| Portuguese broad gauge | 1665 mm | 5 port. Feet |
| Russian broad gauge / Russian gauge | 1520 mm or 1524 mm | 5 feet (5 ') |
| Scottish track | 1372 mm | 4 feet 6 inches (4 '6 ") |
| Swedish track | 1485 mm | |
| Swedish center track | 1188 mm | |
| Swedish narrow gauge | 891 mm | |
| Spanish broad gauge | 1672 mm | 6 box. foot |
See also
literature
- GH Metzeltin: The gauges of the railways. A lexicon on the battle for gauge . German Society for Railway History V., Karlsruhe 1974, OCLC 883123940 .
- Hans G. Wägli: Swiss rail network / Réseau ferré suisse . Published by the SBB General Secretariat. AS Verlag & Buchkonzept AG, Zurich 1998, ISBN 3-905111-21-7 .
Web links
- Rail sides - gauges
- Track construction world - gauges
- German Society for Railway History - Track Gauge Overview
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Neveřejné úzkorozchodné dráhy v Čechách List of (former) non-public narrow-gauge railways in the Czech Republic in the Czech-language Wikipedia
- ↑ Train Rides. ( Memento from December 20, 2017 in the Internet Archive ) National Railway Museum
- ↑ a b c tramz.com
- ^ Rail transport in Peru in the English language Wikipedia
- ↑ SATEB ( Memento from August 31, 2012 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Forest and industrial railways with 760 mm gauge , accessed on December 25, 2017.
- ↑ a b The Magic of the Andes. In: Mike's Railway History. Retrieved February 16, 2012 .
- ^ Glyn Williams: Railways in Nepal. 2018 .
- ^ Glyn Williams: Railways in Nepal. 2018 .
- ↑ tramz.com
- ↑ Online turntable
- ↑ The railways in Peru. ( Memento from May 26, 2012 in the Internet Archive ) (PDF; 33 kB)
- ^ A b Charles Blanchart et al .: Le rail au Congo Belge. Ed. Masoin, Bruxelles 2008, ISBN 978-2-9600471-0-3 , p. 413: Construit à l'écartement de 765mm, la ligne fut mise à l'écartement de 3 '6 "au début des années 1930.
- ↑ tramz.com
- ↑ tramz.com
- ↑ broadspurbahn.de
- ↑ railalbum.co.uk
- ↑ broadspurbahn.de - broad-gauge railways in Japan
- ↑ Walter Strauss: Of iron horses and paths . Hanover 1924, fig. 444.
- ↑ Recommendations of the Working Committee "Shore Edging": Ports and Harbors and Waterways EAU 2004 John Wiley & Sons, 10th edition, 2005, p. 165.
- ↑ ibid. P. 157.
- ↑ Karl Josef Witt (ed.); W. Richwien, et al .: Grundbau-Taschenbuch, Part 3: Foundations and geotechnical structures 2010, 7th edition, Ernst & Sohn; John Wiley & Son, p. 341 f.
- ↑ Karl Josef Witt (ed.); W. Richwien, et al .: Grundbau-Taschenbuch, Part 3: Foundations and geotechnical structures 2010, 7th edition, Ernst & Sohn; John Wiley & Son, p. 340.
- ↑ Port of Linz: Trial operation of the new container crane is getting closer oevz.com, Österreichische Verkehrszeitung, July 15, 2014, accessed July 12, 2020.
- ↑ Map view accessed July 12, 2020. - Approximately 6 m, determined by comparison with the map scale 20 m.
- ↑ Satellite view google.com/maps, accessed July 12, 2020.