Lisbon
| Lisbon | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Basic data | ||||||
| Region : | Lisboa | |||||
| Sub-region : | Lisbon metropolitan area | |||||
| District : | Lisbon | |||||
| Concelho : | Lisboa | |||||
| Coordinates : | 38 ° 43 ′ N , 9 ° 10 ′ W | |||||
| Residents: | 552,700 (as of June 30, 2011) | |||||
| Surface: | 100.03 km² (as of January 1, 2010) | |||||
| Population density : | 5525 inhabitants per km² | |||||
| Postal code : | 1000-1990 | |||||
| politics | ||||||
| Mayor : | Fernando Medina | |||||
| Lisbon district | ||||||
|
||||||
| Residents: | 552,700 (as of June 30, 2011) | |||||
| Surface: | 100.03 km² (as of January 1, 2010) | |||||
| Population density : | 5525 inhabitants per km² | |||||
| Number of municipalities : | 24 | |||||
| administration | ||||||
| Administration address: | Câmara Municipal de Lisboa Paços do Concelho - Praça do Município 1100-365 Lisboa |
|||||
| Website: | www.cm-lisboa.pt | |||||
Lisbon ( Portuguese Lisboa [ liʒˈβoɐ ]) is the capital and largest city of Portugal as well as the administrative district of the same name and is located on a bay at the mouth of the Tagus River in the extreme southwest of Europe on the Atlantic coast of the Iberian Peninsula .
The trading port on the Tagus Bay was called Alis Ubbo before Roman rule . Lisbon, a foundation of the Phoenicians , received Roman city rights under the name Colonia Felicitas Iulia during the time of Julius Caesar . In 711 the place fell like most of the Iberian Peninsula to the Moors ; In the context of the Second Crusade , Lisbon became Portuguese in 1147 and thus again placed under Christian rule. After the relocation of the royal seat of Coimbra , the city was under King Afonso III in 1256 . to the capital of the Kingdom of Portugal . Around 1500 Lisbon experienced a brilliant rise to become one of the most glamorous trading and port cities of the time.
A massive earthquake in 1755 sealed the city's economic decline, which had crept in decades before, and caused a sensation all over Europe. In the 19th century, Lisbon experienced a resurgence.
However, since the last quarter of the 20th century the city has shrunk massively (from over 800,000 inhabitants around 1980 to around 500,000 around 2017); many people have moved to the surrounding area. Lisbon has to struggle with considerable structural problems, among which the dilapidated fabric of many buildings and the enormous road traffic stand out.
Still the largest city in Portugal with the most important port, the seat of government , the highest state and government authorities, several universities and the Academy of Sciences ( Academia das Ciências de Lisboa ), the city is now the country's political, economic and cultural center.
The place is the seat of a number of European Union agencies , including the European Monitoring Center for Drugs and Drug Addiction and the European Maritime Safety Agency . The Community of Portuguese Speaking Countries (CPLP) is also headquartered in Lisbon.
geography
The urban area of Lisbon corresponds to the district of Lisbon and covers 84.7 km² with 506,654 inhabitants (as of 2018). Around 2,400,000 people live in the Lisbon district (as of 2015) and in the Lisbon metropolitan region, with 3,200,414 people (as of 2015), more than 30% of the Portuguese population. The metropolitan area extends over Grande Lisboa on the northern bank of the Tagus and the Península de Setúbal in the south.
Geographical location
Lisbon is located on the Iberian Peninsula . The city is located in a bay on the northern bank of the Tejos river mouth in the extreme southwest of Europe on the Atlantic coast . The Tejo, which spreads just before its mouth, narrows over the last few kilometers to the Atlantic. There the city stretches along the shore. From the bank it rises in steps up several hills. There are high hills and deep valleys in Lisbon. The highest point in the urban area reaches 226 meters. For a long time the city only developed along the Tagus River. The capital has been steadily expanding inland since the 20th century.
geology
The city lies on seven hills, not counting the smaller hills. In Atlantic at the height of Cadiz in an east-west direction runs tectonic rejection, the so-called Gloria sheet shift. Two other tectonic peculiarities, the Gorringe Bank and the Marquês-de-Pombal Fault, lie on the level of the Portuguese south coast. Earthquakes are a consequence of the collision of the northward drifting African plate with the Iberian Peninsula (Eurasian plate). Furthermore, numerous active mud volcanoes in the Gulf of Cadiz indicate continued seismic activity in the region. Due to the past earthquakes , observation points were set up on the sea floor in 2004. They are designed to measure temperature and pressure fluctuations, which indicate stresses in the earth's crust that can discharge in an earthquake.
climate
The climate classification according to Lauer and Frankenberg (1987) assigns the climate of Portugal to the maritime and semi-humid climate of the subtropical climate zone . Due to its location directly on the Atlantic, it is shaped by the temperature behavior of the sea: Summers are not too hot and winters are relatively mild. Temperatures rarely drop below 0 ° C. Snowfall is even less common.
| Lisbon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate diagram | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Average monthly temperatures and rainfall for Lisbon
Source: wetterkontor.de
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The months with the highest rainfall values are October to March. The decisive factor is the location on the cool Canary Current, which sweeps along the coast of Portugal in a southerly direction. It often causes coastal fog in the warm season . In winter, Lisbon is influenced by the Atlantic lowlands, which bring a lot of rain in the coastal area. The average annual precipitation is 656 mm.
etymology
There are different explanations for the origin of the name. Lisbon was called Olissipona or Olisibona by the Goths and Romans . The folk etymology sees a connection with the hero Odysseus . Under Julius Caesar the place belonging to the province of Lusitania was called Felicitas Julia . Others derive the name Lisbon from the Phoenician Alis ubbo . Another theory explains the creation of names with the pre-Roman names of the Tejo river , "Lisse" or "Lucio" .
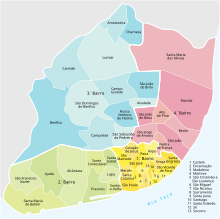
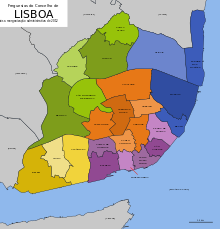
City structure
Up to 2013, Lisbon was divided into 53 municipalities, which in turn were assigned to four districts (bairros) for administrative reasons .
|
|
|
After a long public discussion, on November 8, 2012, the Portuguese Parliament passed Law No. 56/2012 on the reorganization of the municipalities of Lisbon. The territorial reform in Portugal came into effect the following year. Since 2013, Lisbon has been divided into 24 municipalities ( freguesias ):
| local community | Population (2011) |
Area km² |
Density of population / km² |
LAU code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ajuda | 15,617 | 2.88 | 5,429 | 110601 |
| Alcântara | 13,943 | 5.07 | 2,747 | 110602 |
| Alvalade | 31,813 | 5.34 | 5,956 | 110654 |
| Areeiro | 20,131 | 1.74 | 11,551 | 110655 |
| Arroios | 31,653 | 2.13 | 14,876 | 110656 |
| Avenidas Novas | 21,625 | 2.99 | 7,222 | 110657 |
| Beato | 12,737 | 2.46 | 5,178 | 110607 |
| Belém | 16,528 | 10.43 | 1,585 | 110658 |
| Benfica | 36,985 | 8.03 | 4,609 | 110608 |
| Campo de Ourique | 22,120 | 1.65 | 13,395 | 110659 |
| Campolide | 15,460 | 2.77 | 5,573 | 110610 |
| Carnide | 19,218 | 3.69 | 5,209 | 110611 |
| Estrela | 20,128 | 4.60 | 4,372 | 110660 |
| Lumiar | 45.605 | 6.57 | 6,936 | 110618 |
| Marvila | 37,793 | 7.12 | 5,306 | 110621 |
| Misericórdia | 13,044 | 2.19 | 5,950 | 110661 |
| Olivais | 33,788 | 8.09 | 4.178 | 110633 |
| Parque das Nações | 21,025 | 5.43 | 3,868 | 110662 |
| Penha de França | 27,967 | 2.71 | 10,317 | 110663 |
| Santa Clara | 22,480 | 3.36 | 6,699 | 110664 |
| Santa Maria Maior | 12,822 | 3.01 | 4,258 | 110665 |
| Sao Domingos de Benfica | 33,043 | 4.29 | 7,695 | 110639 |
| Sao Vicente | 15,339 | 1.99 | 7,724 | 110667 |
| Santo António | 11,836 | 1.49 | 7,921 | 110666 |
| Lisbon district | 552,700 | 100.03 | 5,525 | 1106 |
history
The city has been ravaged by earthquakes , fires and epidemics several times in its history .
From the beginning to 1147
The Phoenicians founded from v 1000th BC bases in Portugal, probably also on the site of today's Lisbon. They and later the Carthaginians are said to have called the place Alis Ubbo (cheerful bay or funny sea bosom) and used it as the only large natural harbor on the Iberian Atlantic coast . Excavations from Phoenician times can be viewed in the Castelo de São Jorge ; Traces of Greek settlement are far more extensive . If there was not just a trading point here, but actually a Greek city ( polis ), the Greek name of this settlement is unknown. According to Pliny the Elder , Lisbon was later considered a founding of Odysseus .
Under Roman rule, from around 205 BC. BC, the city was initially called Olisipo . Julius Caesar succeeded in the Celtiberian War from 60 BC. From Lisbon to break the last resistance of the indigenous tribes. Under Caesar, Roman veterans were later settled here to control the area; the village received 48 BC The Roman town charter and subsequently became a larger town in the province of Lusitania as Colonia Felicitas Iulia . From 409 AD barbarian tribes from Gaul invaded the Iberian Peninsula. During the late ancient migration period , the Alans , Suebi , Vandals and Visigoths tried to occupy Lisbon. In 468 the Roman city commander Lusidius handed the city over to the Suebi, but shortly after the earthquake of 472, in which large parts of the old Roman city were destroyed, the rule of the Visigoths began. The Visigoths probably renewed the Roman fortress wall.
In 719 Lisbon was conquered by Muslim Moors and later part of the Emirate of Cordoba . Then the city, which was now called al-Ushbuna, experienced its first great boom. Alfonso II won the battle against the Moors at Lugo , penetrated as far as the Tejo and briefly conquered the city in 798. However, Lisbon soon fell back to the Moors. In the Caliphate of Cordoba , the city was one of the most important ports, at the same time Christian Galicians and Leonese tried repeatedly to take the place. In 955 Ordonho III de Leão sent his army to Lisbon to fight the Muslims. Vikings ravaged the city and the surrounding area in 844.
In the 11th century Lisbon was part of the emirate of the Moorish aftasids of Badajoz. From 1093 Count Raymond von Armous, a younger son of Duke Wilhelm I of Burgundy , received from the Leonese King Alfonso VI. transferred rule in Galicia. From there he undertook campaigns against the Moors in the south. He managed to move into Lisbon temporarily after the Muslim ruler of Badajoz had submitted to King Alfonso. But even this conquest (until 1095), like the occupation of Lisbon by Norwegian crusaders under Sigurd 1108 (until 1111), was not yet permanent.
Even when King Dom Alfonso Henriques (Alfonso I) took office, the south of the Iberian Peninsula was still held by the Moors. But in 1147 the siege of Lisbon finally led to the capture of the city by the Portuguese ( reconquista , German "recapture"). Foreign support for the attackers was decisive: The successful siege of the city by a crusader army of the Second Crusade secured Alfonso I the basis for rule over the entire surrounding area. At the end of the 12th century, Saint Anthony of Padua , sometimes also called Anthony of Lisbon , was born in Lisbon.
As the capital of the Kingdom of Portugal until the Spanish occupation
Alfons III moved his residence from Coimbra to Lisbon in 1256 . The city thus became the capital of the Kingdom of Portugal. In 1344 an earthquake shook the city. The great plague , which probably killed more than a third of the country's population from September 1348 to early 1349, also radically decimated the population of the Portuguese capital.
Ferdinand I had a new city wall built after his accession to the throne in 1367. The construction work on the curtain wall was completed around 1370. In the Peace of Alcoutim, Ferdinand I undertook, among other things, to marry a daughter Heinrich II . But then he fell in love with the Portuguese noblewoman Leonore Teles de Menezes and married her instead of the Castilian princess. Angry about the breach of contract, Henry II attacked Portugal and sacked Lisbon in 1373. Ten years later, Lisbon was the scene of the first “bourgeois” revolution in Europe: after the death of Ferdinand I, his widow, Leonore Teles de Menezes, and a lover, took power for six weeks. The resulting tensions and disputes ultimately culminated in the crisis or revolution of 1383 . In Lisbon there was a revolt of the artisan guilds. Supported by large sections of the lower nobility and the bourgeoisie of Porto and Lisbon, the later King John I took the lead in the uprising, killed Leonore's lovers with his own hands and forced Leonore into exile in Castile. His son, Heinrich the Navigator , laid the foundations for Portugal's rise to sea power around 1430, with Lisbon as the most important port.
Under the rule of Manuel I , Lisbon developed into a leading center of world trade. On September 9, 1499, Vasco da Gama received a triumphant reception here after his first trip to India. In 1503 the Casa da Índia was founded in Lisbon , whose activities formed the basis of Portuguese economic and trade policy in the following two centuries. Especially in Lisbon, trade and industry grew, which was in no small part due to the exploitation of the Portuguese colonies in Africa, Asia and South America. As early as 1500 there was talk of a first bloom in Lisbon, which lasted until the middle of the 16th century. The port of Lisbon was one of the largest in the world at that time.
In 1506, at the time of Manuel I, there was a pogrom in the city against the Jews ( Marranos ) who had been forcibly baptized in the years before , which demanded great sacrifices, permanently damaged the city's trade and financial relations and set off a wave of emigration. The first census in Portugal was then carried out between 1527 and 1532. At that time Lisbon had 13,010 households or between 50,000 and 65,000 inhabitants. The city had developed into a European metropolis. However, in 1531 it was shaken again by an earthquake. An unknown number of residents were killed. The estimates are between 1,000 and 30,000 people.
1536 was under Johann III. introduced the inquisition . Four years later, the first public executions of judgments took place in Lisbon. In 1569, a plague epidemic in Lisbon and the surrounding area claimed up to 60,000 lives.
From the Spanish occupation to the great earthquake
King Heinrich I died in 1580 during a campaign in Portugal that the same year the Duke of Alba took possession of Lisbon for the Spanish crown. Two years later he died in Lisbon as the Portuguese Governor General of the Spanish Habsburgs . From the day of the conquest, Lisbon remained occupied by the Spanish for the next 60 years; During this time, Portugal was united in a personal union with Spain. On May 28, 1588, the first ships of the Spanish Armada left the port of Lisbon against England. The departure of the war fleet with 130 ships dragged on until May 30th. The ships were manned by around 27,000 soldiers and armed with over 2,600 cannons.
On December 1, 1640, several Portuguese nobles united to rebel against the Spanish government. France, the great adversary of the Habsburgs (and thus also Spain), saw this as an opportunity to weaken the Habsburgs and encouraged the Duke of Braganza to revolt. The Spanish governor, the Duchess of Mantua , was overthrown in Lisbon and the head of the Braganza family, Duke John II, was proclaimed King of Portugal on December 15, 1640 as John IV . Years of war followed. It was not until 1668 that the Treaty of Lisbon ended the Spanish-Portuguese War and sealed the country's renewed independence.
In 1696, gold and later diamond discoveries in Brazil initiated a second bloom for the Portuguese capital. On December 27, 1703, the Methuen Treaty between England and Portugal was signed in Lisbon. The agreement tied Portugal even closer to England economically, which in the following decades led to a slow economic decline in Lisbon, which now had a population of over 200,000 and was thus a European metropolis.
On November 1, 1755, Lisbon was two-thirds destroyed by a very strong earthquake and a subsequent tsunami . According to current estimates, it had a strength of 8.7 to 9.0 on the Richter scale . Contemporary sources give up to 60,000 fatalities for Lisbon alone; the number may be exaggerated, but modern estimates put up to 100,000 victims across Portugal. The tremors were felt across Europe and North Africa. The city was rebuilt as planned by the Marquis of Pombal . The Baixa , the lower town, with its right-angled streets in the area around Rua Augusta is particularly typical of this reconstruction . In addition to the physical damage caused by the earthquake, it also shook the enlightenment and theistic ways of thinking of many philosophers, who could not identify the cause of this natural disaster, asked the theodicy question and gave up their optimism . Voltaire wrote his Poème sur le désastre de Lisbonne (1756) in response to the quake .
Time after the quake to the First Portuguese Republic

Lisbon recovered in the following years and received its first street lighting with oil lanterns in 1780. The city's first post office opened in 1800. In 1807, Portugal was occupied by French troops. The royal family and the court therefore fled to Brazil . At the end of November 1807, 36 ships with around 15,000 people and the aristocracy of the country left the port of Lisbon. Prince Regent Johann VI. reached Brazil in March 1808. Rio de Janeiro then became the new seat of government.
Typhus broke out in the city in 1811 . Cholera followed in 1833 . 13,522 people died of this within 9 months. During the Miguelistenkrieg , Lisbon , which was occupied by King Michael , was captured by the troops of Peter I on July 24, 1833 . During the September Revolution, Setembrist MPs from Porto arrived in the Portuguese capital on September 9, 1836, headed by Manuel da Silva Passos. They were received triumphantly by the people of Lisbon.
In 1849 the first street lamps were lit with gas. Two years later the Lisbon – Carregado railway line opened. The Treaty of Lisbon decided on April 20, 1859, the division and exchange of Portuguese and Dutch possessions in the Solor and Timor archipelago between Portugal and the Netherlands. In 1873 the horse-drawn tram, called "O Americano", went into operation. The first electric street lights were connected in 1878. The Rossio train station officially opened on June 11, 1890. The Elevador do Município existed from 1897 to 1920.
From the First Portuguese Republic to the present
On October 5, 1910, the First Portuguese Republic was proclaimed on the balcony of the town hall . King Emanuel II then fled into exile in England. This ended the 771-year history of the Portuguese monarchy. On October 19, 1921, the head of government António Joaquim Granjo and a number of other politicians were killed on the night of blood in Lisbon during an uprising by the Republican Guards . A military coup ended the First Portuguese Republic in 1926. Eight years later, the Prime Minister and dictator of Portugal, António de Oliveira Salazar, came to power. He proclaimed the Estado Novo , the "New State", a conservative-authoritarian dictatorship . During the time of the Estado Novo , from 1926 to 1974, the city continued to grow. It was expanded at the expense of the rest of the country.
Portugal remained neutral during World War II; Secret services on both sides were active here; Men like Ian Fleming and Johnny Jebsen worked here, and prisoners like George F. Kennan were exchanged in Lisbon.
The statue of Cristo Rei in Almada , facing the city of Lisbon with outstretched arms, was inaugurated on May 17, 1959 after around ten years of construction. In December 1959 the first metro line opened in Lisbon. In 1966 a suspension bridge across the Tagus to Almada was completed, which is similar to the Golden Gate Bridge in San Francisco . Before the Carnation Revolution , named after António de Oliveira Salazar , it is now called Ponte 25 de Abril (German: "Bridge of April 25").
At the end of April 1974, Lisbon was the center of the Carnation Revolution . With the end of the colonial war in Africa in 1975, there was a wave of refugees from Angola and Mozambique, especially to the greater Lisbon area. A major fire in the old town of Chiado in 1988 destroyed various buildings. In 1994 Lisbon became the European Capital of Culture . Two years later, the Council of Europe and UNESCO passed a new joint general higher education convention in Lisbon, the so-called “ Lisbon Convention ”. In 1998, the 17-kilometer-long Ponte Vasco da Gama motorway bridge over the Tejo was completed on the occasion of the Expo 98 world exhibition .
In March 2000, the European heads of state and government adopted the Lisbon strategy at a special summit . The strategy aims to make the EU the most competitive and dynamic knowledge-based economy in the world by 2010. On December 13, 2007, the Treaty of Lisbon (also known as the EU Basic Treaty ) was signed between the 27 member states of the European Union under the Portuguese Presidency . At the NATO summit from 19. – 20. November 2010 in Lisbon, NATO decided on a new strategic concept. The concept includes building a missile defense shield to protect their entire territory.
From May 8th to 12th, 2018, Lisbon hosted the 63rd Eurovision Song Contest , after Salvador Sobral and Amar Pelos Dois won the 2017 ESC in Kiev .
population
Population development
The population of the city proper is 499,700 (as of 2007); the population for the metropolitan area of Lisbon is according to the Instituto Nacional de Estatística ("National Institute for Statistics") about 2,800,000. The population density of the city itself is 6,658 inhabitants per km². In 2007, 13% of the population were under 15 years old and 24% over 65 years old. The national average in Portugal was only 17% for people over 65 years of age. Women make up more than half of Lisbon's residents, at 54%.
Over the past 30 years, Lisbon has seen a dramatic population decline. Despite the influx of 53,000 people between 1996 and 2001, two more left the city for every new resident who moved to Lisbon in 2001. The newcomers are primarily families who, thanks to their financial resources, can pay for the high housing costs; however, especially younger people and representatives of the middle class have moved away. The trend towards suburbanization that can be observed in the city is counteracted by the gradual relocation of living space to the metropolitan area of Lisbon: This massively increases the number of commuters, so that mobility and transport problems are now a critical factor in everyday life in the city and in terms of the quality of life of their citizens.
Population development of Lisbon (1801-2007)
|
|
|
|
religion
The vast majority of Lisbon residents profess the Roman Catholic faith. The first diocese of Lisbon was founded in the 4th century. When the city was conquered by the Moors, it continued to exist as a partially vacant titular bishopric of the Roman Catholic Church. There are also references to Mozarabic bishops of Lisbon who are not known by name . After the reconquest by Alfonso I , it revived as a Roman Catholic diocese under its bishop, the Norman Gilbert von Hastings (bishop from 1147 to 1166). The Patriarchate of Lisbon was established in 1716.
The Cemitério Alemão cemetery of the German community is located in the municipality of Santo Condestável.
Local politics
City council and local council
The municipal and municipal assemblies are elected by the residents on the basis of proportional representation. The directly elected city council and the municipal council provide the local state power. You are responsible to the respective assembly. The local self-government is financed from local income and own assets as well as from state financial equalization. The budget is drawn up by the municipality or city council and submitted to the respective assembly for decision. In the greater Lisbon area, income of 40 to 50 percent, from real estate tax as well as vehicle and business tax, has contributed to the local budget in recent years.
The Cámara Municipal (German city council) consists of 17 and the Assembleia Municipal (German city council) of 107 members. The members of the community council are elected by the community assembly. The candidate on the first place in the list of the strongest local party takes over the presidency of the municipal council. The mayor is the party with the highest proportion of seats on the city council.
The local elections on October 9, 2005 brought the following results:
| City / Municipal Council | Psd | PS | PCP | BE | PP | PEV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cámara Municipal | 8th | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Assembleia Municipal | 56 | 28 | 13 | 5 | 3 | 2 |
The local elections in the period from 2007 to 2017 brought the following results:
| year | PCP | PS | Psd | CDS | PPM | UDP | APU | AD | CDU | BE | CR | MR | PAN | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | 9.5 | 29.5 | 15.7 | 3.7 | 0.4 | - | - | - | 9.5 | 6.8 | 16.7 | 10.2 | - | |||
| 2009 | - | 44.0 | 38.7 | - | - | - | 8.1 | 4.6 | - | - | - | |||||
| 2013 | - | 50.9 | 22.4 | 1.2 | - | - | - | 9.9 | 4.6 | - | - | 2.3 | ||||
| 2017 | - | 42.0 | 11.2 | 20.6 | - | - | - | 9.6 | 7.1 | - | - | 3.0 | ||||
| Source: Comissão Nacional de Eleições | ||||||||||||||||
mayor
In May 2007, early local elections were necessary because the then mayor of Lisbon, Carmona Rodrigues, had to resign due to a corruption affair. In the election on July 15, 2007, Lisbon's António Luís Santos da Costa elected mayor of the Portuguese capital with a simple majority of 29.54 percent. The turnout was 37.39 percent. On April 6, 2015, the Lisbon residents elected Fernando Medina as the new Mayor of Lisbon.
coat of arms
|
Blazon : “In a wave cut divided by gold and green, below three silver wave bars after the division, growing out of it a black single-masted sailing ship with a silver, left-waving mast flag with double swings and a rolled-up silver square sail , on each of the shipendsa black bird facing each other ( raven and Crow).
Above the coat of arms a schwarzgefugte golden mural crown , down four black round portals, top five patch battlements towers, is ever a black portal, surmounted by two black windows, under the shield a white band with the three-part motto in black capital letters : "MUI NOBRE E - SEMPER LEAL - CIDADE DE LISBOA “( Eng . Very noble and always loyal city of Lisbon ). The lower shield is surrounded by the chain to the attached Order of the Tower and the Sword . " |
|
| Justification of the coat of arms: The coat of arms of Lisbon is adorned by a sailing ship with two ravens. The illustration refers to a legend. Allegedly, the body of the city's saint Vicente de Saragoça was driven in a driverless boat accompanied by a raven and a crow on the Algarve coast, on Cabo de São Vicente . From this place the body was brought to Lisbon and buried there. The city was awarded the Order of the Tower and the Sword. |
Twin cities
Lisbon has twinned cities with the following cities:
Culture and sights
Cityscape


The current cityscape of Lisbon is mainly based on building work from the 18th century. The center of Lisbon is the Baixa . The old town impresses with its tiled facades and medieval, narrow streets. In the inner city districts, structural problems also shape the cityscape. In 1994 the total number of buildings in Lisbon was given as 62,041. Of these, 30.73% of the buildings were from before 1919 and 21.37% from the period between 1919 and 1945. According to surveys by the Lisbon City Center for Territorial Studies in 1992, the estimated renovation costs of the existing housing fell by a third on the buildings between 1850 and 1930.
Since the late 1960s, due to a ban on increasing rents, many property owners have stopped investing in their property as inflation has caused rental income to no longer cover maintenance costs. As a result, thousands of houses in Lisbon fell into disrepair. This law was only repealed in 2012 as part of the reform program to overcome Portugal's economic crisis. As a result, tens of thousands of apartments were renovated; the abolition of the rental price control resulted in the gentrification of entire city districts.
UNESCO world heritage
In 1983 were the Torre de Belém and the Mosteiro dos Jeronimos (Jeronimos Monastery) from the UNESCO for World Heritage declared. The Torre de Belém, which is located in the district of the same name at the mouth of the Tejo , is one of the most famous landmarks of Lisbon. The watchtower was destroyed during the Napoleonic invasion and reconstructed in 1846. In addition to the nearby Mosteiro dos Jerónimos, it is one of the few outstanding buildings of the “Manueline style” that survived the Lisbon earthquake . The Mosteiro dos Jerónimos is located in the Belém district . In addition to the royal tombs, there is also the tomb of the famous seafarer Vasco da Gama . The monastery is considered to be the most important Manueline building , a Portuguese variant of the late Gothic , which also contains some elements of the Renaissance.
Buildings
Sacred buildings
One of the remarkable buildings in Lisbon is the São Vicente de Fora monastery . It was founded in 1147 as an Augustinian monastery by Alfonso I outside the city walls and dedicated to Saint Vincent of Saragossa . Under Philip II , the church and monastery were given their current appearance. Many members of the Portuguese royal family from the House of Braganza were buried in the church.
The Castelo de São Jorge , a fortress with an integrated castle ruin, was used as a royal castle for centuries. The royal collection of documents was located in a tower of the castle, the Torre do Tombo . The castle was largely destroyed in the great earthquake in 1755. After extensive renovation work, the complex is in good condition again.
The main church of the city of Lisbon and the cathedral of the Patriarchate of Lisbon is the Catedral Sé Patriarcal . Construction work on the city's oldest church began in 1147. An earthquake damaged the structure in 1344. In 1380 the western facade was built in the Romanesque style.
In the 17th century the large baroque church Igreja de Santa Engrácia (Eng. Church of St. Engrácia ) was built. The church could not be completed until the 20th century. It was never used as a place of worship and is now used as the Panteão Nacional ( German National Pantheon ). Several presidents and writers and, most recently, football idol Eusébio were buried in the building. There are also some cenotaphs for "Heroes of Portuguese History".
The Convento do Carmo is a monastery of the Carmelite Order built between 1389 and 1423 by Nuno Álvares Pereira . The Carmelite Church was considered a splendid example of Lisbon Gothic . The monastery was badly damaged by the earthquake of 1755. Today only the ruins can be visited.
The historicist style synagogue was built between 1902 and 1904.
Technical buildings
The Aqueduto das Águas Livres has a length of 19 km and extends from Queluz via Caneças to the Mãe d'Água das Amoreiras. This aqueduct is one of the world's largest structures of this type. The most impressive is the aqueduct in the Alcântara valley. The arch bridge has a total length of 941 m. The 66 m high bridge is supported by 109 arches.
The Elevador de Santa Justa , also known as Elevador do Carmo , is a 45-meter-high passenger elevator that connects the Baixa district with the higher Chiado district in downtown Lisbon . In common usage, the three tram-like Lisbon funiculars are sometimes called Elevador , which is actually a vertical elevator.
Representative buildings
The Palácio de São Bento was initially a Benedictine monastery. It was erected in 1598. The Benedictine monks lived in the monastery until 1820. In 1834 the Portuguese Parliament moved into the building. At the back of the building is the Prime Minister's seat.
The Portuguese Foreign Minister is housed in the Palácio das Necessidades, the former royal palace from the 18th century. The palace became the official residence of the royal family under the reign of Queen Maria II . After the proclamation of the republic on October 5, 1910, the building became the seat of the Foreign Ministry.
The Palacete Lambertini is a former city villa in the city center.
António José Dias da Silva, a Portuguese architect, designed the Praça de Touros do Campo Pequeno (German bullring) on Campo Pequeno. The arena was built between 1890 and 1892 after the former Lisbon bullring on Campo de Santana, which was in use between 1831 and 1891, was demolished.
Monuments
The Padrão dos Descobrimentos monument is located in the Bélem district on the banks of the Tagus River. It was created in 1960 under the Salazar regime, exactly 500 years after the death of Henry the Navigator, and is intended to glorify the old days of the seafaring nation Portugal. The bow of a caravel is shown, on which, led by Heinrich the Navigator, other important people from the Age of Discovery are represented. The 54-meter-high tower, with stylized sails on the sides, symbolizes the mast of the caravel.
The Torre Vasco da Gama is a 145 meter high observation tower in steel framework construction, which was built in 1998 for the world exhibition. According to plans by the Portuguese architect Nuno Leónidas, the Vasco da Gama tower is to be converted into a luxury hotel with 178 rooms on 20 floors. The renovation was from 2007 to 2012 and is now called MyRiad. The Oceanário de Lisboa is also located in the area of the former Expo 98 exhibition grounds . It is the second largest oceanarium in the world and is located there in the Park of Nations.
The 113 m high figure of Christ Cristo Rei (Almada), erected in 1959, is located on the southern side of the Tejo, but is considered a symbol of Lisbon.
Expo 98
The world exhibition Expo 98 took place in Lisbon from May 22nd to September 30th, 1998. It was the first in Portugal and the fourth of five so far on the Iberian Peninsula (1888 Barcelona, 1929 Barcelona, 1992 Seville, 2008 Saragossa) and had the motto "Os oceanos: um património para o futuro", in German "The oceans : A legacy for the future ”. 143 countries and 14 international organizations took part in the expo. During the 132 opening days, 10.12 million people visited the 340-hectare World's Fair. Today the popular exhibition area is marketed under the name Parque das Nações .
Parks
The Parque Florestal de Monsanto is the largest park in Lisbon. It is located in the west of the city and covers 800 hectares. It was only created in the 1930s. The largest park in the city center, on the other hand, is Parque Eduardo VII at the upper end of the avenue Avenida da Liberdade in the municipality of Avenidas Novas . The park was named after the British King Edward VII , who visited Portugal in 1903. The third largest park in the city is the Jardim da Estrela from 1852, it is located opposite the Basilica da Estrela . Today it is officially called Jardim Guerra Junqueiro , but is still called Jardim da Estrela in everyday life . The Jardim do Campo Grande , in German "garden of the large field", is a 12.5 hectare park in the municipality of Campo Grande . Also in the north of Lisbon is the 11 hectare Parque Botânico do Monteiro-Mor , which was built in the second half of the 18th century.
Streets, places

The Avenida da Liberdade is a boulevard in Lisbon based on the model of the Parisian Avenue des Champs-Élysées . It connects the Baixa (lower town) , built after the earthquake of 1755, with the higher districts in the north and was continued in the Avenidas Novas from the beginning of the 20th century . A first section of the Avenida was inaugurated in 1882 on the 100th anniversary of the death of the Marques de Pombal and the round square dedicated to him.
In Portuguese, “Miradouro” is a general term for a viewpoint . The Miradouros are among the most beautiful places in the city. They lie on the elevations all around and reveal views of the old town or the Tejo.
The Bairro Alto (Upper Town) is a district of Lisbon that is located above the Baixa business district. It is best known for its nightlife. A Brasileira is one of the oldest and most famous cafes in the city . The café in the Chiado district was founded on November 19, 1905 by Adriano Telles . It was a popular meeting place for intellectuals. The Portuguese poet Fernando Pessoa and the writer Aquilino Ribeiro traveled there . A bronze statue of Pessoa has stood in front of the café since 1988.
Museums
There are numerous museums in Lisbon. The Museu Nacional de Arte Antiga (National Museum of Ancient Art) is one of the most important art museums in Portugal. An important focus of the collection are works by Portuguese artists. It has works by Hieronymus Bosch , Albrecht Dürer , Pieter Brueghel the Younger , Piero della Francesca , Hans Holbein the Elder and Raphael , among others . The Museu Calouste Gulbenkian was built between 1964 and 1969 . The museum's permanent exhibition includes a wide range of art objects from all eras. In 1984 it was expanded to include the Museum of Modern Art. The works of Rembrandt (portrait of an old man) , Claude Monet (still life with bowler hat) and Édouard Manet (the soap bubbles) are among the most famous exhibits in the museum .
The Museu da Marinha (Naval Museum) is located in the Belém district . It is located in part of the west wing of the Mosteiro dos Jerónimos, together with the Museu Nacional de Arqueologia . The Museu de Etnologia (Ethnological Museum) has artifacts from around the world. Most of them come from the former colonies. In 1904 the Museu Nacional dos Coches (Carriage Museum) was opened on the initiative of Queen Amalia. It houses a considerable collection of carriages. The oldest carriage on display comes from King Philip II of Spain in the 16th century. The Museu Colecção Berardo , opened by the industrialist and art collector José Berardo in 2007, is housed in the Centro Cultural de Belém . The art collector has made a considerable collection of modern and contemporary art of the 20th century from Europe and overseas available to the museum.
theatre
In 1854 there were six theaters in Lisbon. Today, in addition to the state theaters, there are several independent festival theaters that offer a rich program of performances. The Teatro Nacional D. Maria II (German National Theater Dona Maria) is the oldest spoken theater in Lisbon and is centrally located on the Rossio. Even older is Lisbon's Teatro nacional de São Carlos , which was built in the Chiado district in the late 18th century. Right next to it is the Teatro Municipal São Luiz . The Teatro da Trindade from the second half of the 19th century is also located in the Chiado . The Teatro Aberto is located near Praça de Espanha . In the Teatro Politeama , in the style of the 1920s, mostly successful musicals are performed. The Companhia Nacional de Bailado CBN ballet troupe moved into the Teatro Camões after the expo . Other ballet ensembles also perform there. Other theaters include the Teatro da Cornucópia , co-founded by Luís Miguel Cintra , the Teatro da Comuna , the Teatro Municipal Maria Matos , the Teatro Taborda , the Teatro Tívoli , the Teatro Villaret founded by Raul Solnado and the Teatro Vasco Santana .
The Cinema Roxy was of historic importance . The Cinema São Jorge is a premiere cinema in the city center, which also houses the international film festivals held in Lisbon, including Lisbon Gay & Lesbian Film Festival , IndieLisboa , DocLisboa and monsters . Another old cinema was the Animatógrafo do Rossio .
music
Fado
The internationally best known of the traditional types of music in Lisbon is the Fado , often sung with a wistful but also sometimes cheerful mood, and usually only accompanied by a classical guitar and a Portuguese guitar . In the evenings, fado is mainly performed in bars in the Bairro Alto and Alfama districts. In addition to the traditional fado bars such as O Faia , Café Luso , Senhor Vinho and many more, the Clube de Fado , which only opened in 1995, has gained some importance in recent years . Internationally, the name of Portugal's most popular Fado singer, Amália Rodrigues , is particularly associated with Fado . The singer Mariza is often called the successor of the artist, who died in 1999, internationally , but names as diverse as Ana Moura , Mísia , Carminho or Cristina Branco have already achieved some international recognition. Among the male singers, Alfredo Marceneiro, who died in 1982, is one of the most influential names. Carlos do Carmo can be considered the most important living singer , while Camané in particular has made a name for himself among the following generations .
Fado has its origins in the slums of Lisbon, where it first appeared in the notorious pubs in the Mouraria district . Whether it originally developed from the songs of Portuguese sailors or from Brazilian musical styles such as Lundum or Modinha can no longer be determined with certainty from today's perspective. The Museu do Fado in the traditional Alfama district is dedicated to the history of fado in detail.
Fado has been on the UNESCO list of intangible world cultural heritage since 2011 .
Classic
The most important opera house in the city is the Teatro Nacional de São Carlos , which opened in 1793 . In addition, concerts and performances take place regularly in a large number of other concert venues, such as the Centro Cultural de Belém . The most important orchestras in the city include the Orquestra Metropolitana de Lisboa , the Orquestra Sinfonietta de Lisboa , the orchestra of the Gulbenkian Foundation , and the Orquestra do Conservatóro Nacional , the orchestra of the National Conservatory in Lisbon, now part of the ESTC .

Jazz, Rock and Co.
Lisbon is home to a multitude of clubs, concert venues and bars of all styles, including the Hot Clube de Portugal, the oldest still existing jazz club in Europe. Thanks to its history as the metropolis of the Portuguese Empire , Lisbon is home to many African immigrants and therefore also a center of African music creation in Europe, with concert halls, bars and a large number of musicians. In the internationally acclaimed series of samplers of the New York Red Hot Organization , the CD Red Hot + Lisbon was released in 1998 for the Lisbon World Exhibition , which is dedicated to these diverse musical influences in Lisbon.
The most varied of subcultures such as punk, gothic, rockabilly, heavy metal, hip-hop, etc. v. m. are present here. The Rock Rendez-Vous concert club played a special role in the development of the various subcultures in the 1980s, thus promoting the emergence of a diverse range of bands in the city.
- → See also : Overview of Lisbon bands and clubs
The Bairro Alto in particular is transformed into a lively nightlife district with its multitude of bars and clubs, but also in the old districts of Alfama and Mouraria , on the Cais do Sodré , or in the modern bar district in the former docks on the river in Alcântara , the Docas , there are a number of music venues for every taste. The city's lively music scene also includes a large number of music labels, such as the internationally renowned jazz label Clean Feed Records . With the Super Bock Super Rock , a big rock festival is taking place in Lisbon, and the internationally known Rock-in-Rio Festival has stopped here several times.
Regular events
Since 1984, jazz fans have been meeting annually at the Gulbenkian Foundation's international jazz festival Jazz em Agosto in the Portuguese capital. The rock music festival Rock in Rio took place in Lisbon in 2006 and 2008. In addition, in addition to other regular trade fairs, an annual tourism fair takes place at the FIL fair .
The following Portuguese film festivals take place in Lisbon every year:
- Doclisboa - International Documentary Film Festival
- Queer Lisboa - the festival of gay and lesbian cinema (Festival de Cinema Gay e Lésbico de Lisboa)
- IndieLisboa - International Festival of Independent Cinema (Festival internacional de cinema independente)
- Monstra - international animated films
- Hola Lisboa - Iberian and Latin American films (Festival de Cinema Ibero-Americano)
- MOTELx - Horror Films (Festival Internacional de Cinema de Terror de Lisboa)
- FESTin - Films of the Portuguese Language Area (Festival de Cinema Itinerante da Língua Portuguesa)
- PLAY - Children's and Youth Films
Annual spring tourism fair in Lisbon.
- Feira Internacional de Turismo
Festival in celebration of the patron saint Anthony of Lisbon .
- Festas de Lisboa , also simply Santo António , annually on June 13th in the old town quarters such as Alfama, Graça, Mouraria, Bica or Madragoa, and with large parades on Avenida da Liberdade and other avenues
Recreation
The traditional seaside resorts of Cascais and Estoril are located in the vicinity of Lisbon. Estoril is considered a retreat for the rich upper class of Lisbon and is located on the edge of the Estremadura . The place became famous for its casino. Estoril is also home to the Autódromo, a racetrack where the Portuguese Grand Prix for motorcycles is held every year. The neighboring city of Cascais is located on a sandy bay in the Atlantic, about 25 kilometers west of Lisbon. From 1870 onwards, the royal family regularly spent the summer in Cascais, which made the place attractive to the nobility and upper classes. The place has a marina with around 600 berths. The Serra da Arrábida nature reserve in the Lisboa e Vale do Tejo region extends west of Setúbal on the coast facing away from the sea. There are a number of rare plants and animals there. The nature park extends with an area of 10821 ha on an up to 8 km wide and 22 km long strip along the coast. Its borders are formed by the cities and villages of Sesimbra and Santana in the west, Azeitão and Quinta do Anjo in the north and Palmela and Setúbal in the east.
Culinary specialties
In the numerous pubs and restaurants and localities, dishes from international and local cuisine are served. However, there are only a few original Lisbon specialties that are not offered elsewhere. The Portuguese cuisine is based on savory and traditionally prepared dishes using meat, fish, vegetables, rice, beans and potatoes. The cod is both specialty and a national dish of Portugal. There are also countless recipes for salted and dried cod . Popular are also sardines , grilled as Sardinhas assadas , also squid , lobsters , crabs , tuna , swordfish , eel , shrimp and other marine animals. Ameijoas na cataplana , a mussel stew with pork , bacon and onions, is also typical . In addition to beef , goat meat (Cabrito) and lamb (Borrego) are often eaten in Portugal .
Internationally known is the Portuguese port wine , a liqueur wine that is mainly drunk with desserts . The specialties also include the Pastel de Nata or Pastel de Belém . The custard tart - consisting of cake or puff pastry, filled with creamy vanilla pudding and dusted with cinnamon and powdered sugar - was probably made by monks of the Jeronimos Monastery in the Lisbon district of Santa Maria de Belém before the 18th century . After the secularization of the monasteries, the monks decided in 1837 to produce delicacies to be sold to the Lisbon residents. Today, many locals and tourists visit the large cafeteria of the factory there to buy the pastéis . Few pâtissiers know the original recipe .
Lisbon in the film
The city is the center of Portuguese cinema . Since the beginning of the art of film, it has also repeatedly been the subject of international and national film productions, be it as a documentary or as a feature film. The focus is on the role of neutral Lisbon in World War II , the charm of its old quarters, and its role for Portuguese culture, especially Fado and the writer Fernando Pessoa.
Sports
Lisbon has various sports facilities. The Estádio da Luz and the José Alvalade Stadium are the largest stadiums in the city. Over the course of its history, the city has repeatedly hosted world and European championships.
World, European and national championships
In Lisbon, who found World Fencing Championships in 1947 , the 1991 FIFA World Youth Championship , the European Short Course Swimming Championships in 1999 , the 2001 IAAF World Indoor Championships , the UCI Road World Championships in 2001 , the World Fencing Championships in 2002 , the World Handball Championship for Men in 2003 and the European Football Championship in 2004 instead.
From 1938 to 1945 the Portuguese Football Cup was held annually in Lisbon.
Since 2004 the international European championships in BJJ (Brazilian Jiu Jitusu) have been held by the IBJJF (International Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu Federation) in Lisbon. It is the most important European championship of this Brazilian sport.
On May 24, 2014, the UEFA Champions League final took place in Lisbon's Estádio da Luz.
Soccer
The football club Benfica Lisbon is the Portuguese record champions and won the European Cup in 1961 and 1962 . The home game venue is the Estádio da Luz . The stadium with a capacity of 65,000 spectators was the venue for three group matches, a quarter-finals and the final of the 2004 European Football Championship. The stadium was completely rebuilt for the tournament.
The Lisbon football club Sporting Clube de Portugal ( Sporting Lisbon ) was the winner of the 1964 European Cup Winners' Cup. The Sporting football team plays its home games at Estádio José Alvalade XXI . The stadium with 52,000 seats was the venue for the 2004 European Football Championship . The stadium, which has been awarded five stars by UEFA, is right next to the old facility.
The Estádio do Restelo is the football stadium of the Club Belenenses Lisbon and is located in the Belém district. The stadium was officially inaugurated on September 23, 1956 and holds around 32,500 spectators.
Other football clubs from Lisbon with a first division past are or were Atlético , Oriental , Casa Pia , Carcavelinhos and CF Unidos , which is now based in the suburb of Pontinha . In the greater Lisbon area, Estrela Amadora , Estoril Praia and FC Alverca are or were first class, while Amora FC , Seixal FC , Fabril Barreiro , FC Barreirense and CD Montijo from the cities on the opposite bank of the Tejo are or were .
The most successful representative of Lisbon in national women's football is CF Benfica .
Other sports
Four clubs from Lisbon play in the handball league LPA: Sporting Clube de Portugal , Sport Lisboa e Benfica , Clube de Futebol Os Belenenses and Boa-Hora . The Lisbon clubs SL Benfica and União Lisboa play in the UZO basketball league . The Lisbon Half Marathon (pt. Meia Maratona de Lisboa) is one of the largest and most important half marathons in the world. It has been held in Lisbon since 1991, usually in March. The first Trans-European Run took place from April 19 to June 21, 2003 and ran from Lisbon to Moscow in 64 daily stages with no rest day . At the end of December 2005, the famous Dakar Rally (formerly Paris-Dakar) began for the first time in the capital of Portugal.
Economy and Infrastructure
economy
The Lisbon area is the most prosperous area in Portugal, with a gross domestic product above the European average (Lisbon generates 45% of Portugal's GDP). 1,300,500 people are employed in the greater Lisbon area. The city's unemployment rate in 2004 was 8%. Lisbon's economy is primarily based on the service industry. The Lisbon seaport is of great economic importance as an interface between land and sea transport, as a maritime service center and as an industrial location. In the Lisbon metropolitan region, the south bank of the Tagus is particularly heavily industrialized. 7 of the 10 largest listed companies in Portugal are based in Lisbon. These include the companies Energias de Portugal , Portugal Telecom and Jerónimo Martins . The Lisbon stock exchange is part of the “multi-country exchange” Euronext with the stock exchanges in Amsterdam, Brussels and Paris .
In a ranking of cities according to their quality of life, Lisbon ranked 38th out of 231 cities worldwide in 2018.
Road traffic
Due to its location on the Tejo, Lisbon could only be reached directly from the south by ferry traffic for a long time. The first bridge was built in 1951 north of the city at a narrow part of the river in Vila Franca de Xira in the north. The Ponte 25 de Abril (1013 m span and 2287 m length) was completed in 1966 and connected Lisbon with Almada on the south side of the Tejo for the first time . Since 1999 there has also been a rail link below the carriageway. The A2 then continues to the east of the country or to Madrid / Spain . With the Ponte Vasco da Gama , one of the longest cable-stayed bridges in the world and the longest bridge in Europe, there has been a direct motorway connection ( A12 / IP1) across the bay between Moscavide / Sacavém on the right and Montijo / Alcochete (Município) / Alcochete or Setúbal with its industries on the left side of the Tagus.
To the north, the A8 motorway connects to Leiria , and the A1 runs along the coast to Porto , the second most important center in the country.
Rail transport
The Portuguese capital, along with Porto, is the main hub of the Portuguese railway network . Four railway lines run towards Lisbon, which - connected by the Linha de Cintura ring line - end at various train stations in the city of Lisbon. The main station is the Santa Apolónia station on Linha do Norte , where all international trains from Spain and France as well as most of the national high-speed trains Alfa Pendular end . Furthermore, in the northeast of Lisbon, the Oriente train station is located , which in future will become the new main train station of the city with the construction of the standard-gauge high-speed RAVE network . The two terminal stations of Cais do Sodré ( route to Cascais ) and Rossio ( route to Sintra ) as well as the Sete Rios and Entrecampos stations on the Linha de Cintura remain for suburban traffic . The line on the south side of the Tagus to Setúbal, operated by the private railway company Fertagus, also begins here.
Ferry traffic
There are several ferry connections across the Tagus to Barreiro , Cacilhas , Montijo , Porto Brandão , Seixal and Trafaria . The landing stages on the right side of the Tejo are: Belem , Cais do Sodré and Terreiro do Paço . The operator of all lines is now the Transtejo & Soflusa , the trademark are the blue and white catamaran ferries , which with 30 knots have shortened the crossing on the Tejo to a third.
Public transport
The public transport is mainly taken over by the two companies Carris ( Companhia dos Carris de Ferro de Lisboa ) and the Metropolitano de Lisboa . The Carris serves over 100 bus routes and six tram routes (12, 15, 18, 24, 25 and 28). The tram traffic is partly carried out with historical carriages (Pt. Eléctricos) , for example on line 28 . On December 15, 2018, one of the historic trams derailed in the Lapa district. The car was destroyed and 28 people were injured. It also operates four elevadores in the city , three of which are funiculars and one is a vertical elevator, the Elevador de Santa Justa . The three funiculars were built towards the end of the 19th century when Lisbon began to replace the horse-drawn tram, which had been in service since 1873, with cable trams from 1890 and later with electric trams. The Lisbon Metro consists of four lines, some of which lead beyond the urban area. The subway network, which is now 38 kilometers long, is being continuously expanded.
Airport
The Lisbon-Portela International Airport is 6 km north of the center and in the extension of the A12 motorway. The construction of the new Novo Aeroporto Lisboa airport has been discussed for some time . On January 10, 2008, Prime Minister José Sócrates announced that it would be built on the Campo de Tiro Alcochete military site north of Alcochete . The Portuguese airlines TAP Portugal , White Airways , Portugália Airlines and EuroAtlantic Airways are based in Lisbon.
port
The port of Lisbon stretches along the city's shoreline for over 10 km. There are also numerous systems on the south side of the Tagus in Trafaria, Porto Brandão, Almada, Seixal, Barreiro and Montijo, which belong to Porto de Lisboa and are operated by the APL port administration, even if they are outside the actual city area. These plants specialize in grain and oil. On the north side in the city of Lisbon, however, mainly containers are handled. There are also direct connections to the train network in Alcântara and Santa Apolónia, where the city's two large container terminals are located. The largest and deepest docks are in Alcântara. In total, the docks of the port of Lisbon enclose a water surface of 430,000 m². Cruise ships often dock in Lisbon to make a stop on the way from Northern Europe to the Mediterranean, the Canary Islands or South America. There are three quays for them at Gare Marítima de Alcântara, Rocha do Conde de Óbidos and Santa Apolónia. For private yachts there are four moorings with the Doca de Alcântara, Doca de Santo Amaro and the Doca de Belém e Doca do Bom Sucesso. There is space for around 1,100 ships in total.
education and Science
Lisbon has several universities and is the most important university city in Portugal alongside Coimbra .
The University of Lisbon was founded in 1288 and confirmed by the Pope in 1290. It is one of the oldest universities in Europe, but was only re-founded in 1911 after a break of more than 400 years. With over 47,000 students in eight faculties, it is the largest university in Portugal. Since 1991 the Torre do Tombo ( Portuguese National Archives ) has been located in a modern building on the university campus. The Lisbon Observatory (pt. Observatório Astronómico de Lisboa) was attached to the University of Lisbon in 1992 and integrated into the Faculty of Natural Sciences in 1995. As the largest clinic, the University Hospital de Santa Maria with 1500 beds also belongs to it. On December 31, 2012, the Technical University of Lisbon merged with the University of Lisbon to form the new University of Lisbon (Universidade de Lisboa).
The Catholic University of Portugal was founded in Lisbon in 1971 as a Catholic public educational institution. Over 11,000 students study in 18 faculties at several regional centers. In 1988, the state distance university Universidade Aberta was founded. In addition to its headquarters in Lisbon, it also has two regional offices in Porto and Coimbra. There are also 16 local study centers in Portugal and one in Mozambique. Other universities in Lisbon include the Lusíada University , the Universidade Nova de Lisboa and the Autonomous University of Lisbon .
The German School in Lisbon is the oldest German school on the Iberian Peninsula and the second oldest of all German schools abroad. It was brought into being in 1848 by a Protestant pastor from the German community in Lisbon. The school was forced to close during World War I in 1916. It reopened in 1922. At the end of the Second World War, school operations ended again. This was resumed after reopening on October 20, 1952.
The Portuguese National Library , founded in 1796, is located in the Campo Grande district of Lisbon . Affiliated to it is the Biblioteca da Ajuda , which dates back to the royal library ( Biblioteca Real ) and is housed in the Palácio Nacional da Ajuda .
Personalities
Lisbon is the birthplace of many well-known personalities. These include the poet Alcipe , the artist Helena Almeida , the UN General Secretary and former Portuguese Prime Minister António Guterres , the President of the European Commission José Manuel Barroso , the doctor and Pope John XXI. , the singer Amália Rodrigues , and the former Prime Minister and President Mário Soares .
In addition, a number of internationally known personalities moved to Lisbon, especially in the 2010s. The best-known names are likely to be the pop musician Madonna , the French fashion designer Christian Louboutin or the former soccer player Éric Cantona , including actors such as the German-Irish Michael Fassbender , the Italian Monica Bellucci , the American John Malkovich and a number of well-known Brazilian actors .
The Canadian musician Bryan Adams , the Italian author Antonio Tabucchi , the German historian Vera Leisner and the British photojournalist Joshua Benoliel can also be found among former residents of the greater Lisbon area .
Awards
In December 2011, the city of Lisbon was awarded the title “European City of the Year 2012” by the London Academy of Urbanism and received the UNESCO award for Fado .
literature
- Johannes Beck: Lisbon. M. Müller, Erlangen 2014, ISBN 978-3-89953-697-3 .
- Johannes Beck: Lisbon and the surrounding area. M. Müller, Erlangen 2012, ISBN 978-3-89953-698-0 .
- Catarina Camarinhas: L'urbanisme de Lisbonne. L'Harmattan 2012, ISBN 978-2-296-47915-9 .
- Rainer Groothuis , Christoph Lohfert (photos): Lisbon: the bright, sad paradise. Introduction: Rafael Chirbes . Edel Momenti, Hamburg 2010, ISBN 978-3-941378-79-7 .
- Gerhard Lauer , Thorsten Unger: The Lisbon earthquake and the disaster discourse in the 18th century, Wallstein 2008, ISBN 978-3-8353-1611-9
- Claus-Günter Frank: Lisbon - Discoveries in Portugal's metropolis . Tübingen 2005, ISBN 3-937667-68-7 .
- Lydia Hohenberger , Jürgen Strohmaier: Lisbon. DuMont, 2005, ISBN 3-7701-6063-0 .
- Annette Hüller: Lisbon. Marco Polo, 2008, ISBN 978-3-8297-0475-5 .
- Susanne Lipps, Heidrun Reinhard: Lisbon. Polyglott-Verlag, 2009, ISBN 978-3-493-55908-8 .
- Sara Lier: Immigrants in Lisbon. Vdm Verlag Dr. Müller, 2008, ISBN 978-3-8364-7226-5 .
- Eva Missler: Lisbon. Baedeker, 2005, ISBN 3-8297-1058-5 .
- António Henrique de Oliveira Marques : History of Portugal and the Portuguese Empire (= Kröner's pocket edition . Volume 385). Translated from the Portuguese by Michael von Killisch-Horn. Kröner, Stuttgart 2001, ISBN 3-520-38501-5 .
- Sabine Scholl : Lisbon. Artemis & Winkler, Düsseldorf 2009, ISBN 978-3-538-07281-7 .
Web links
- City administration website (Portuguese)
- Large-format city map and city view by M. Witkam (1834) (English)
- Illustration of the city in 1598 in Civitates orbis terrarum by Georg Braun and Frans Hogenberg
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b www.ine.pt - indicator resident population by place of residence and sex; Decennial in the database of the Instituto Nacional de Estatística
- ↑ a b Overview of code assignments from Freguesias on epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu
- ↑ https://www.pordata.pt/MicroPage.aspx?DatabaseName=Municipios&MicroName=Popula%C3%A7%C3%A3o+residente+total+e+por+grandes+grupos+et%C3%A1rios&MicroURL=390&
- ↑ Pordata.pt: População residente, Total e por grandes grupos etários, accessed on March 22, 2020 in 2018
- ↑ Statistical Yearbook of the Lisboa Region - 2007, p. 61 (PDF).
- ^ Gerhard Lauer, Thorsten Unger: The Lisbon earthquake and the disaster discourse in the 18th century. Wallstein Verlag, 2008, ISBN 978-3-8353-0267-9 .
- ↑ João C. Duarte, Filipe M. Rosas, Pedro Terrinha, Wouter P. Schellart, David Boutelier, Marc-André Gutscher, António Ribeiro: Are subduction zonesinvading the Atlantic? Evidence from the southwest Iberia margin. doi : 10.1130 / G34100.1
- ^ Johann Jakob Egli: Nomina geographica - language and factual explanation of 42,000 geographical names of all regions of the earth. Georg Olms Verlag, 1973, ISBN 3-487-04571-0 , p. 544.
- ^ Hugo Kastner: From Aachen to Cyprus - Geographical names and their origin. Schlütersche, 2007, ISBN 978-3-89994-124-1 , p. 186.
- ↑ Lisbon. In: Meyers Konversations-Lexikon. 1888.
- ↑ Static.publico.pt: Mapa proposto para as freguesias de Lisboa, accessed on November 1, 2013.
- ↑ Portuguese Law No. 56/2012 - Reorganização administrativa de Lisboa of November 8, 2012 (PDF; 16 MB) ( Memento of the original of November 2, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved November 1, 2013.
- ↑ Cm-lisboa.pt: Comissões instaladoras das novas freguesias tomaram posse, April 17, 2013, accessed on November 1, 2013.
- ↑ Lisboasolidaria: As novas 24 freguesias de Lisboa ( Memento of the original dated November 2, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Retrieved November 1, 2013.
- ^ Eva Missler: Lisbon. 2005, p. 25.
- ↑ Mittelalter-genealogie.de, Alfons 2 , accessed on June 6, 2009.
- ^ Portugal-Info.net accessed on June 6, 2009 .
- ↑ Vikings devastate Lisbon under Björn Járnsiða and Hástein [1]
- ↑ Walther L. Bernecker, Horst Pietschmann: History of Portugal - From the late Middle Ages to the present. P. 10, 11.
- ↑ Looking for Earthquake Sources in the Lisbon Area, 13th European Meeting of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics, Istanbul, Turkey, 3. – 5. September 2007 (PDF) ( Memento from May 22, 2009 in the Internet Archive ).
- ↑ Walther L. Bernecker, Horst Pietschmann: History of Portugal - From the late Middle Ages to the present. P. 36.
- ↑ AH de Oliveira Marques : History of Portugal. P. 105 f.
- ^ Eva Missler: Lisbon. 2005, p. 28.
- ^ Eva Missler: Lisbon. 2005, p. 29.
- ^ Josef Kulischer: General economic history of the Middle Ages and the modern age. 6th edition. Oldenbourg, 1988, ISBN 3-486-41976-5 , p. 221.
- ^ Julius von Minutoli : Portugal and its colonies. P. 240.
- ↑ Walther L. Bernecker, Horst Pietschmann: History of Portugal - From the late Middle Ages to the present. P. 72.
- ^ Julius von Minutoli: Portugal and its colonies. P. 305.
- ↑ Walther L. Bernecker, Horst Pietschmann: History of Portugal - From the late Middle Ages to the present. P. 83.
- ↑ Historical background of the Lisbon Convention ( Memento of the original from April 26, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. .
- ↑ Diário de Notícias 2007, accessed on July 9, 2009 ( Memento of the original from December 29, 2009 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. .
- ^ Report on the Lisbon case study area, Ameixoeira-Galinheiras area, TU-Dresden, 2006 (PDF) accessed on June 6, 2009 .
- ↑ Wolfgang Ismayr: The political systems of Western Europe. VS Verlag, 2009, ISBN 978-3-531-16464-9 , p. 809.
- ↑ Lisboa.pt - Cámara Municipal accessed on March 22, 2020
- ↑ Cm-lisboa.pt Mayor and City Council accessed on June 6, 2009 .
- ↑ Lisboa: Presidente da Câmara Municipal de Lisboa, accessed on March 22, 2020
- ^ Eva Missler: Lisbon. 2005, p. 21.
- ↑ Cm-lisboa.pt - Lisbon homepage, accessed on June 13, 2017 .
- ↑ Anja Bothe: Comparison of the Portuguese and German building planning and redevelopment law with regard to the goal of a socially balanced supply of housing - experiences in the metropolises of Lisbon and Berlin. LIT Verlag, 2004, ISBN 3-8258-7144-4 , p. 227.
- ↑ Thomas Urban , Stadt in Rosa , sz.de , January 10, 2020.
- ↑ whc.unesco.org accessed on 29 June 2009 .
- ^ Eva Missler: Lisbon. P. 154.
- ↑ Structurae.de accessed on June 19, 2009 .
- ^ Lydia Hohenberger, Jürgen Strohmaier: Lisbon. 2005, p. 132.
- ↑ Portaldasnacoes.pt (English) accessed on June 6, 2009 ( Memento of the original from September 25, 2009 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. .
- ^ Johannes Beck: Lisbon and surroundings. Michael Müller Verlag, 2009, ISBN 978-3-89953-458-0 , p. 319.
- ↑ Johannes Beck: Lisbon. Michael Müller Verlag, 2009, ISBN 978-3-89953-459-7 , p. 175.
- ^ Noel Riley Fitch, Andrew Midgley: The Grand Literary Cafes of Europe . New Holland, 2006, ISBN 978-1-84537-114-2 , pp. 114 ff . ( Google Books ). Google Books ( Memento of the original from July 16, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ História - museudoscoches-ipmuseus.pt ( Memento of May 13, 2008 in the Internet Archive ).
- ^ Annette Hüller: Lisbon. P. 78.
- ^ Website Feira Internacional de Turismo (English).
- ^ Website of the Festas de Lisboa (Portuguese).
- ↑ Pastaeis de Belem (flash required) ( Memento of the original from June 4, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. .
- ↑ http://desporto.sapo.pt/futebol/primeira_liga/artigo/2015/04/02/benfica-continua-a-ser-o-clube-com-mais-socios-do-mundo
- ↑ Lisbon.org accessed on June 6, 2009 ( Memento of the original from May 27, 2009 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. .
- ↑ Mercer's 2018 Quality of Living Rankings. Retrieved July 30, 2018 .
- ^ Johannes Beck: Lisbon and surroundings. Michael Müller Verlag, 2009, ISBN 978-3-89953-458-0 , pp. 122-124.
- ↑ Tram accident in Lisbon
- ↑ Lisbon-Umgebung.de accessed on September 17, 2009 ( Memento of the original from September 20, 2008 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. .
- ^ Walter Rüegg, Asa Briggs: History of the University in Europe - Middle Ages. CH Beck, 1993, ISBN 3-406-36952-9 , p. 64.
- ↑ German School Lisbon, accessed on June 19, 2009 ( Memento from November 1, 2009 in the Internet Archive ).
- ↑ Estas celebridades têm (ou já tiveram) casa em Portugal - "These celebrities live (or lived) in Portugal" , article from May 12, 2017 of the news portal Notícias ao minuto (port.), Accessed on August 5, 2018
- ↑ Várias celebridades compraram casa em Lisboa nos últimos meses - "Several celebrities bought houses in Lisbon in the last six months" , contribution of the news channel SIC-Notícias from May 18, 2017 (port.), Accessed on August 5, 2018
- ↑ Lisbon wins European City of the Year 2012 and UNESCO award for Fado ( Memento from May 13, 2012 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ The Academy of Urbanism: Awards 2012, accessed December 19, 2012. (English)