United Kingdom
| United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland |
|||||
| United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland |
|||||
|
|||||
|
Motto : Dieu et mon droit ( French for "God and my rights") |
|||||
| official language |
English (de facto) Officially regional: Cornish , Irish , Scottish Gaelic , Scots , Ulster Scots and Welsh |
||||
| capital city | London | ||||
| form of government and government | parliamentary monarchy ( Westminster system ) | ||||
| head of state | Queen Elizabeth II | ||||
| head of government | Prime Minister Boris Johnson | ||||
| surface |
(79th) 243,610 km² (78th) 248,528 km² |
||||
| population | 66.8 million ( 22nd ) (2019) | ||||
| population density | 275 inhabitants per km² | ||||
| population development | +0.6% (estimate for 2019) | ||||
gross domestic product
|
2020 | ||||
| Human Development Index | 0.932 ( 13th ) (2019) | ||||
| currency | Pound Sterling (GBP) | ||||
| national anthem |
God Save the Queen |
||||
| time zone |
UTC±0 GMT UTC+1 WEST |
||||
| License Plate | UK | ||||
| ISO 3166 | GB , GBR, 826 | ||||
| Internet TLD | .uk , .gb (unused) | ||||
| telephone area code | +44 | ||||
Major cities in the UK |
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland ( English ), abbreviated United Kingdom (English [ juːˌnaɪ̯.tʰɪd ˈkʰɪŋ.dəm ], international abbreviation: UK or GB ), is a European country located on the British Isles off the northwest coast of continental Europe and is the largest island country in Europe.
The United Kingdom is a union of four parts : England , Wales , Scotland and Northern Ireland . In everyday speech it is also simply referred to as Great Britain or England . However, in its actual meaning, England only represents the largest part of the country, while Great Britain refers to the main island of the British Isles (on which the parts of the country England, Scotland and Wales lie).
With a population of over 67 million, the United Kingdom is the fourth most populous country in Europe after Russia , Germany and France . It is a founding member of NATO as well as the United Nations . It is a nuclear power , a permanent member of the UN Security Council and one of the G7 countries. From 1973 to 31 January 2020 it was a member of the EEC and later the European Union respectively .
State name in German
The official long form of the state name is United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland in Germany and Austria , in Switzerland and Liechtenstein the variant United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (without ß and with "of") is used.
In non-official usage, the term Great Britain can be found as an alternative abbreviation of the long form - also in the case of politicians, the media , educational institutions and the British embassies themselves. The vehicle nationality sign was also GB until September 27, 2021 , which was derived from Great Britain . The British themselves refer to their country as UK or Britain for short in everyday language , but less often as Great Britain . The Latin name Britannia comes from the Celtic word brith and means variegated or spotted .
However, Great Britain is really just the name for the largest of the British Isles - or for the former Kingdom of Great Britain (until 1801) which comprised the kingdoms of Scotland and England including Wales. The second largest island - Ireland - is home to Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland .
Despite everything, only the form "British" is available as an adjective for the state name.
The synecdochical term England for the United Kingdom is mainly found on the European mainland and is due to the centuries-long dominance of England and the English official language within the United Kingdom.
Territories associated with the United Kingdom
A number of territories are closely linked to the United Kingdom, but must be distinguished from it under international law. On the one hand , this applies to the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands , which, as crown possessions of the British Crown, are not part of the “United Kingdom” state association. On the other hand, there are 14 overseas territories that are under British sovereignty but are also not part of the United Kingdom.
Through the British Monarchy , the United Kingdom is also in a loose relationship with 15 Commonwealth Realms , each of which is also headed by the British Monarch; However, these are not only independent states, but also form independent monarchies.
geography
The United Kingdom consists of the main island of Great Britain and about one sixth of the island of Ireland. Around the main island are about 800 smaller islands; the main archipelagos are Shetland and Orkney in the North Sea north of Scotland, the Outer Hebrides and Inner Hebrides in the Atlantic Ocean west of Scotland, Anglesey in the Irish Sea north of Wales, the Isles of Scilly in the Celtic Sea south-west of England and the Isle of Wight in the English Channel off the south coast of England. The only land border is on the island of Ireland with the Republic of Ireland; this is 360 kilometers long.
parts of the country
| part of the country | flag | Area (km²) |
Percentage of total area |
Population (2017) |
Percentage of total population |
capital city |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| England |
|
130,395 | 53.5% | 55,619,400 | 84.2% | London |
| Scotland |
|
78,772 | 32.3% | 5,424,200 | 8.2% | Edinburgh |
| Wales |
|
20,779 | 8.5% | 3,125,200 | 4.7% | cardiff |
| Northern Ireland |
|
13,843 | 5.7% | 1,870,800 | 2.8% | Belfast |
| United Kingdom (total) |
|
243,789 | 100.0% | 66.040.220 | 100.0% | London |
England
The largest part of the country is England with an area of 130,395 square kilometers and around 54.3 million inhabitants. Covering around 59 percent of the island of Great Britain, England consists mostly of low plains interspersed with ridges of hills. The Tees-Exe Line , an imaginary line drawn between the rivers Tees in Yorkshire and the Exe in Devon , divides England into two distinct regions.
The northwest and the north are characterized by low mountain ranges of metamorphic and igneous rocks. These include the Cumbrian Mountains and the Pennines . The Peak District in Central England , which adjoins the Pennines to the south, consists of older sedimentary rocks . Other low mountain ranges are Dartmoor and Exmoor in the extreme southwest.
In the south and along the east coast are significantly flatter ridges of younger sedimentary rocks. These include the limestone hills of the Yorkshire Wolds , the Lincolnshire Wolds , the Cotswolds and the Isle of Purbeck on the one hand, and the Southern England Chalk Formation , consisting of the Salisbury Plain , Chiltern Hills , North Downs and South Downs , on the other . The highest mountain in England is Scafell Pike in the Cumbrian Mountains at 978 metres.
The main rivers are the Thames , Severn , Trent , Great Ouse and Humber . The largest cities are London , Birmingham , Manchester , Sheffield , Liverpool , Leeds , Bristol and Newcastle upon Tyne .
Wales
West of England borders Wales ( Welsh Cymru ), which is 20,779 square kilometers in size and has a population of more than three million. The country consists almost entirely of metamorphic low mountain ranges, with elevations generally decreasing from north to south. The highest mountain is Snowdon ( Yr Wyddfa ) with 1085 meters. Snowdonia , the northernmost of the three Welsh mountains, is named after him. In the central part of the country are the Cambrian Mountains , followed by the Brecon Beacons in South Wales .
The longest river in the United Kingdom, the Severn rises in central Wales in the Cambrian Mountains. Most of the population is concentrated in a narrow strip of coastline along the Bristol Channel to the south, with the cities of Cardiff , Newport and Swansea , and the South Wales valleys branching off from the coastal strip.
Scotland

Scotland ( Scottish Gaelic Alba ) is 78,772 square kilometers in size, has around 5.3 million inhabitants and includes the northern part of Great Britain. The country consists of three parts; the Highlands to the north and west, the Central Belt in the center and the Southern Uplands to the south.
The geology of Scotland is largely metamorphic, sediments are relatively rare. Igneous rock, on the other hand, is found in numerous areas, particularly in the southern Highlands and Inner Hebrides. Also the result of primeval volcanic activity is Ben Nevis in the Grampian Mountains , at 1345 meters the highest mountain in Scotland and the entire British Isles . The northern, slightly flatter Highlands are divided from the rest of the country by the Great Glen , a tectonic fault.
Most of the population is concentrated in the Central Belt, in the metropolitan areas of Glasgow , Edinburgh and Dundee . The only major city outside of this region is Aberdeen on the northeast coast. At the southernmost point are the sparsely populated Southern Uplands; they extend along the English border from the Irish Sea to the North Sea. Together, the Central Belt and Southern Uplands are also referred to as the Lowlands .
The west coast of Scotland is highly indented, due to many offshore islands and numerous deep inland fjords (known as Firths in Scotland ). The best known of these estuaries are the Firth of Clyde and the Solway Firth . On the other hand, the east coast is little dissected, with the exception of the Firth of Forth , the Firth of Tay and the Moray Firth , which have more of the character of large estuaries .
Northern Ireland
The smallest part of the country is Northern Ireland ( Irish Tuaisceart Éireann ), which is 13,843 square kilometers in size, has around 1.8 million inhabitants and covers the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland. The terrain is mostly undulating. The only low mountain range is the Morne Mountains in the south-east , the highest mountain is Slieve Donard at 849 metres. Roughly in the middle of Northern Ireland lies Lough Neagh , with a surface area of 388 square kilometers the largest inland lake in the British Isles. The largest cities are Belfast and Derry (Londonderry).
cities
The urbanization rate in the UK was 82.8% in 2016, making it one of the most urbanized countries in the world. The largest city in the United Kingdom is the capital London with over 10 million inhabitants in the metropolitan area. The country is heavily concentrated in its capital, where a sixth of the population lives and which generates almost a quarter of economic output. London is the undisputed economic, cultural and political center of the United Kingdom and is considered one of the most influential cities in the world. Other major metropolitan areas are Manchester (population 2.6m), Birmingham (population 2.5m), Leeds (1.8m) and Glasgow (0.9m). Most metropolitan areas are in the densely populated part of England.
| Top 10 Cities | Top 10 Urban Spaces | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rank | city | population | rank | urban space | population |
| 1 | London | 8,537,673 | 1 | London | 10.356.139 |
| 2 | Birmingham | 1,126,927 | 3 | Birmingham | 2,509,741 |
| 3 | Glasgow | 603,080 | 5 | Glasgow | 990,900 |
| 4 | Liverpool | 565.161 | 7 | Liverpool | 878,052 |
| 5 | Bristol | 560,982 | 11 | Bristol | 648,816 |
| 6 | Manchester | 537,862 | 2 | Manchester | 2,626,139 |
| 7 | Sheffield | 535,782 | 10 | Sheffield | 703,920 |
| 8th | leeds | 493,623 | 4 | leeds | 1,824,753 |
| 9 | Edinburgh | 480,250 | 14 | Edinburgh | 504,390 |
| 10 | leicester | 458,175 | 13 | leicester | 526.018 |
| 19 | southampton | 266,391 | 6 | southampton | 885,693 |
| 17 | Newcastle upon Tyne | 279,534 | 8th | Newcastle upon Tyne | 788,782 |
| 15 | nottingham | 302,029 | 9 | nottingham | 753,777 |
(as of 2015)
climate
The UK is entirely in the temperate zone . The climate is humid and warmer than other areas at the same latitude due to the influence of the Gulf Stream . Due to the country's location in the convergence zone of cold polar and warm tropical air, the weather is very volatile. In general, the climate in the south and east is warmer and drier than in the north and west. The annual rainfall averages 1000 mm in the north and 700 mm in the south. It is the wettest in the western Highlands with over 3000 mm annually, the driest in Essex with 600 mm (in particularly dry years even only 450 mm).
The sky is cloudy for two-thirds of the year, so the average annual sunshine duration is relatively low. On the south coast of England this is 1750 and 2100, in the western part of Scotland it is often less than 1000 hours. The country is relatively rarely affected by natural disasters, but strong storm winds (up to hurricane force ) and flooding can occur , especially in winter . Fog occurs mainly in winter in the mountainous or hilly regions and on the coast.
The highest temperature ever recorded in the UK is 38.5°C on 10 August 2003 at Faversham in Kent , during the 2003 heatwave . It was coldest on December 30, 1995 at Altnaharra in Sutherland with −27.2 °C. Since the average temperature is usually above freezing even in winter, little snow falls. The Scottish Highlands are an exception, where the snow cover is thick enough for winter sports for a few weeks.
effects of climate change
The UK is trending towards warmer winters and hotter summers as a result of climate change , sea levels along the UK coast are rising by around 3mm per year and there are signs of changing precipitation patterns. Climate scientists expect that heatwaves like those of 2003 will become the norm by the 2040s as a result of the climate crisis . Model calculations from 2019 show that London would already be relocated to a different climate zone if the RCP4.5 scenario , which was rated as optimistic, occurred; according to this, the climate in London by 2050 would already be more similar to the previous climate in Barcelona , Spain, than to that in London. Extreme weather events are also becoming more frequent and more intense; for example, it has been shown that the floods in England in 2013-2014 can be traced back to man-made climate change .
Flora and fauna
Because of the relatively mild climate and diverse soils , there is some diversity in plant communities . Originally, the British Isles were covered with large forests , mainly oak and other deciduous forests , particularly in the lowlands . Exceptions were areas of marshland , such as the Fens . At higher elevations, as in Scotland, and on sandier soils, there were large pine forest communities . Due to ongoing deforestation and increased agricultural use, the forest cover has declined over the centuries, so that today about 9 percent of the land area is still covered with trees. Attempts have been made to reforest the forests since the 20th century . There are larger forests today in Scotland and isolated in the south and east of England and in Wales. Occurring tree species are mainly oak species, the common beech , the common ash and elm . Scots pine , Norway spruce and birch species mainly grow in Scotland . The cultural landscapes between the mountains are covered with numerous bogs and various meadows and heaths . There are apple and cherry tree crops. Various species of herbaceous plants are native to much of the country. There are over 1600 species of plants.
The fauna is similar to that in other areas of north-western Europe, but less diverse. The formerly native wolf , the wild boar , the bison and the brown bear have been exterminated. Large wild mammals are red deer and roe deer . Fallow deer , sika deer and water deer are naturalised . Other common native species are the hare , hedgehog , red fox , weasel , shrew and otter . Widespread bird species are the two sparrow species , the thrush , carrion crow , pigeons and finches . The native squirrel is increasingly being pushed out by the released North American gray squirrel and is in danger of disappearing completely. Another originally non-native mammalian species is the mink , a North American relative of the mink. Harbor seals and gray seals live in the coastal regions . Northern Ireland's flora and fauna is largely similar to that of the British mainland.
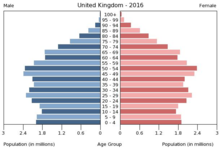
population
demographics
| year | Population (according to census) |
year | Population (according to census) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1801 | 10,500,000 | 1931 | 46,038,000 |
| 1851 | 27,368,800 | 1951 | 50,225,000 |
| 1861 | 28,917,900 | 1961 | 52,807,000 |
| 1871 | 31,484,000 | 1971 | 55,928,000 |
| 1881 | 34,934,500 | 1981 | 56,357,000 |
| 1891 | 37,802,400 | 1991 | 57,439,000 |
| 1901 | 38,237,000 | 2001 | 59,113,000 |
| 1911 | 42,082,000 | 2011 | 63,182,000 |
| 1921 | 44,027,000 | 2016 | 65,648,000 (estimate) |
The population grew from 10.5 million (conducted in the first population census in 1801) to 65.1 million in 2015. The country's industrialization triggered rapid population growth in combination with progressive urbanization . London was the largest city in the world from 1825 and remained so until around 1940. Population growth began to slow in the early 20th century. From the 1960s, momentum accelerated again due to migration from the kingdom's former colonies.
The citizens of the United Kingdom are called Britons. In the 2011 census, the total population of the United Kingdom was 63,181,775. The population was distributed among the individual regions as follows: England 83.9 percent, Scotland 8.5 percent, Wales 4.8 percent and Northern Ireland 2.8 percent. Between 2001 and 2011, the population grew at an average annual rate of 0.7 percent. In 2019, the United Kingdom had 67 million inhabitants. The country is one of the most densely populated countries in the world, with England being significantly more densely populated than Scotland and Wales.
A census is taken simultaneously in all parts of Britain every ten years. The Office for National Statistics collects the data in England and Wales. The National Records of Scotland government agency is responsible for Scotland and the Northern Ireland Statistics and Research Agency for Northern Ireland .
The UK Office for National Statistics forecast the population to be 70 million in 2027 and 73.3 million in 2037.
languages
The United Kingdom does not have a statutory official language , however English is the de facto official language and is spoken as the national language by 95.5% of the population. The pronunciation variant of the Received Pronunciation , which is only spoken by less than 10% of English people in everyday life, mainly in the south of the country, in the region around London, is considered a high-level language. This English is also taught in most schools in Germany. However, three parts of the country have their own official languages: In Wales, both English and Welsh are official languages. In Scotland, the Scottish Gaelic language has been recognized as an official language alongside English since 2005. In Northern Ireland, Irish and Ulster Scots are officially recognized minority languages. In addition, there are various local dialects of English in the United Kingdom , but they have no official status and are mostly of a purely oral nature. Up until recently, dialects and dialectally colored pronunciation were seen as a social flaw in the class-conscious kingdom.
The minority languages are recognized and protected by the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages . In Scotland, in addition to the Scottish Gaelic language , these are also Scots , in Cornwall the Cornish language , in Northern Ireland Ulster Scots and the Irish language . Welsh enjoys equal status with English in Wales. In the United Kingdom, British Sign Language is the sign language of the hearing impaired.
According to the 2001 census, Welsh is spoken by around 20 per cent of the population of Wales (around 600,000 people), Scottish Gaelic by around 60,000 people, Irish by around 20,000 people (7 per cent of the population of Northern Ireland) and Cornish by 3500 people (around 0 .6 per cent of the population of Cornwall).
State names in the regional languages :
- Scots : Unitit Kinrick o Great Breetain an Northren Ireland
- Scottish Gaelic : Rìoghachd Aonaichte na Breatainn Mhòr agus Eirinn a Tuath
- Welsh : Teyrnas Unedig Prydain Fawr a Gogledd Iwerddon
Ethnic groups
| rank | Country | Population (UN estimate) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. |
|
780,000 |
| 2. |
|
700,000 |
| 3. |
|
540,000 |
| 4. |
|
500,000 |
| 5. |
|
320,000 |
| 6. |
|
230,000 |
| 7. |
|
220,000 |
| 8th. |
|
220,000 |
| 9. |
|
210,000 |
| 10 |
|
180,000 |
The population of the United Kingdom (UK) is recorded according to ethnic groups ( ethnic groups or races ) , regardless of citizenship : whites ( whites ), i.e. English, Welsh, Scots and Irish as well as immigrants from other parts of Europe, blacks ( black ) and Asians ( Asian ). This classification is based on a subjective self-attribution. The 2001 census also recorded the Chinese ( Chinese ) as a separate group.
According to the 2011 census, 87.1 per cent of the UK population is white. There are also minorities of 12.9 percent, which consists of several non-white ethnic groups. The largest proportion of non-white people is primarily explained by immigration movements from former British colonies from the Indian subcontinent , Africa and the Caribbean , particularly in the 1950s and 1960s.
The proportion of foreigners and ethnic minorities in the population varies greatly from region to region. The highest proportions are found in London and in the metropolitan areas of England. These include Birmingham , Manchester and West Yorkshire . Relatively few ethnic minorities live in the rural areas of south -west and north-east England , as well as the rest of the country in Wales , Northern Ireland and Scotland . Leicester was the city with the highest proportion of ethnic minorities in 2011. In the same year, 44 percent of London's population was white and British.
In 2011 there were almost 2 million people in the UK who identified themselves as either “Black Caribbean” or “Black African” . This corresponds to about 3 percent of the total population. The majority of West Indian immigrants came as early as the 1950s in the hope of better living conditions; the majority came from Jamaica . Until the end of the 20th century, most blacks in the United Kingdom still came from the Caribbean, but the trend was reversed by increasing migration from African countries such as Nigeria or Ghana , and today the majority describe themselves as "Black African".
In 2011 there were over 1.4 million Indians or of Indian descent living in the UK, with some estimates as high as 1.7 million. Indians make up the largest group of immigrants from a single country. Their share of the population is 2.3 percent. About 44 percent of British Indians are Hindus , followed by Sikhs at 22 percent and Indian Muslims third at 14 percent. Various reasons prompted Indians to emigrate to the UK. In addition to economic reasons and the desire for a higher standard of living, political persecution also played a role.
People of Pakistani origin are the second largest minority in the country. In 2011, nearly 1.2 million British Pakistanis lived in Britain, making up about 1.8 percent of the population. Along with the Indian migrants, most Pakistanis came to Britain in search of work and a better standard of living in the first major wave of immigration in the 1950s. The vast majority of Pakistanis are followers of Islam .
The Bangladeshis, like Indians and Pakistanis, belong to what is known as Asian or British Asian . In 2011, the population group accounted for over 450,000 people. The reasons for their immigration were the civil war and Bangladesh's secession from Pakistan in 1971, as well as the search for work and the hope of a higher standard of living. Most Bangladeshis are also Muslims .
There are over 430,000 Chinese or people of Chinese descent in the UK , which is 0.7 per cent of the total population. Historically, Chinese are one of the oldest migrant groups in the UK. A large wave of immigration occurred in the 1950s, including many migrants from the Hong Kong region . Immigration from China has increased steadily in recent decades.
The English terms Gypsy or Traveler are understood to mean a large number of ethnic minorities, comprising around 63,000 people. The minority closest to the traditional "Gypsies" in their way of life are the Roma , who originated in northern India. The group of Irish Travelers , to be distinguished from the Roma, has its roots in Ireland.
Poles form a large minority in the United Kingdom. As early as World War II there were tens of thousands of Poles in the country; many served on the Allied side . Since the beginning of the 21st century, the number of Polish residents in the UK has increased significantly due to Poland's accession to the EU. In 2011, based on the census, it was assumed that there were almost 600,000 Poles in the United Kingdom.
In 2017, 13.4% of the population were migrants .
education
Education is decentralized and organized differently in England, Wales, Northern Ireland and Scotland. The following information only gives a general overview and is based on the English education system.
Education is compulsory in the UK between the ages of 5 and 16 . The acquisition of education for the child is therefore not exclusively through attending school (preschool from the age of 3, primary school from the age of 5 to 11 and secondary school from the age of 12 to 16 or 18), but also through alternative forms of education such as home schooling possible. However, a School Attendance Order may be issued to children if the local council deems that they are not receiving an adequate education at home. At the age of 16, the “General Certificate of Secondary Education” (GCSE) is taken. Its results determine whether the student can continue to attend school and take A-level exams. Good grades in the A-level examination subjects are a prerequisite for enrolling in a corresponding course at the university. The International Baccalaureate is also offered as a degree. An annual ranking ("League Tables") provides an overview of the performance of the individual schools.
In addition to the state schools, there are fee- based private schools , which about 7 percent of the students attend. In recent years, “academies” and “free schools” have been founded on a large scale as state-financed school types, which have significantly more autonomy in designing the national curriculum and selecting their teaching staff. There is no vocational training offer comparable to Germany (dual system) or it is currently being developed by the British government according to its own principle (“apprenticeship”). Businesses train according to their own needs, and apprenticeship training in craft businesses is largely unknown.
The top 24 of around 180 higher education institutions, including the world's leading research-intensive top universities such as the University of Oxford , University of Cambridge , London School of Economics (LSE), Imperial College and University College London , have organized themselves into the renowned Russell Group. At English universities, domestic and EU undergraduate students pay tuition fees of up to £9,000 per year, which can be pre-funded by a full government loan. In Scotland, there are no undergraduate fees for Scottish and EU students, but there are special rules for Wales and Northern Ireland. The costs for a master's degree are not regulated by law and vary greatly depending on the subject and university.
Foreign language instruction in English state schools is compulsory from the age of 11 to 14. This also applies to learning a foreign language in primary school (Key Stage 2). Since September 2015, secondary school students (from year 7) have had to take a foreign language for their GCSE exams as part of the so-called "English Baccalaureate". Within the last 10 years, the number of German learners at English schools has halved (2016: 50,271 GCSE exams, 3,842 A-Level exams).
In the 2015 PISA ranking , British students ranked 27th out of 72 countries in mathematics, 15th in science and 21st in reading.
Bless you
| Period | life expectancy in years |
Period | life expectancy in years |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1950-1955 | 69.4 | 1985-1990 | 75.1 |
| 1955-1960 | 70.6 | 1990-1995 | 76.3 |
| 1960-1965 | 71.0 | 1995-2000 | 77.2 |
| 1965-1970 | 71.7 | 2000-2005 | 78.4 |
| 1970-1975 | 72.2 | 2005-2010 | 79.7 |
| 1975-1980 | 73.0 | 2010-2015 | 81.0 |
| 1980-1985 | 74.2 |
In international comparison, the British health system was long considered the ideal type of state health service (a so-called "Beveridge system"). However, this integrated system of state financial planning and largely state-run service provision has been in transition to a system of regulated supply markets for some time.
The UK's four national healthcare systems are funded largely from public funds, notably general taxes, earmarked taxes and, albeit to a small extent, social security revenues. Since the National Insurance (NI) contribution rate is set by the state, the National Insurance contributions are considered taxes. The allocation of funds to the service providers in the English National Health Service (NHS) follows a multi-level system of central planning, decentralized allocation and competition. First, the health budget is negotiated between the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Health (DoH) for three years. This is then distributed to local or regional institutions of the national health service on the basis of a complicated formula. The calculation formula is based on various criteria that are intended to ensure that the funds are distributed according to local needs. In 2010, £102 billion was spent on national healthcare in England. Around 50 percent of this expenditure was for treatment in acute hospitals, around 10 percent for primary care. Per capita expenditure on health is significantly lower in Great Britain than in Germany. In 2011, the OECD statistics show per capita expenditure of 3,406 US dollars for Great Britain and 4,495 US dollars for Germany (both in purchasing power parities).
Life expectancy in the UK from 2010 to 2015 was 81.0 years (females: 82.8 years, males: 79.0)
religions


The majority of UK residents (about 59 per cent) identify themselves as Christians . In the last census in 2001, 92 percent of the population answered the optional question about religion . As in other countries, church membership is not the same as religious affiliation. Accurate statistics on church membership are difficult to obtain, as in the UK it is common to become an official member of a church only if you wish to participate in congregational life beyond occasional church attendance. In 1995 only 14 percent of the population were members of churches in this sense. According to polls from 1995, approximately 27 million (45 percent) belong to the Anglican Church , 11 million (19 percent) to other Protestant churches in the broadest sense and just under 6 million (10 percent) to the Roman Catholic Church . The Black Churches (Churches of the Blacks), which had been founded in major English cities by immigrants from the (former) British colonies in the Caribbean and Africa since the late 1940s, have experienced strong growth since the 1970s .
Major Churches (roughly classified by size and influence) include
- in England the
- Church of England ( Anglican ) – Supreme Governor of the Church of England is the reigning British monarch
- Roman Catholic Church with the Bishops' Conference of England and Wales
- United Reformed Church ( Reformed )
- and the Methodist Church of Great Britain in England, Wales and Scotland
- in Wales the
- Church in Wales (Anglican)
- Roman Catholic Church
- Presbyterian Church of Wales (Calvinist-Methodist)
- United Reformed Church (Reformed)
- in Scotland the
- Church of Scotland (Reformed/ Presbyterian )
- Roman Catholic Church with the Scottish Bishops' Conference
- United Reformed Church (Reformed) (developed in Scotland from the Congregational Union or Church and other Reformed congregations)
- Scottish Episcopal Church , member church of the Anglican Communion
- in Northern Ireland the
- Church of Ireland (Anglican)
- Roman Catholic Church with the Irish Bishops' Conference
- Presbyterian Church in Ireland
- as well as other Presbyterian churches , see also Northern Ireland (religion)
| religion | proportion absolute |
proportion relative |
|---|---|---|
| Christians | 33.243.175 | 59.3% |
| Muslims | 2,706,066 | 4.8% |
| Hindus | 816,633 | 1.5% |
| Sikhs | 423,158 | 0.8% |
| Jews | 263,346 | 0.5% |
| Buddhists | 247,743 | 0.4% |
| other | 240,530 | 0.4% |
Over 14 million inhabitants (25.1 percent) do not belong to any religion.
story
antiquity
It is assumed that at the end of prehistory large parts of the island of Great Britain were settled by Celtic tribes. These maintained close connections with Gaul . In the year 55 BC The first campaign began by the Roman provincial governor Gaius Julius Caesar . The conquest of Britain, with the exception of Scotland , took place in AD 43 and led to Roman rule lasting about 400 years. When the Romans retreated, Angles , Saxons and Jutes arrived on the island, pushing the Celts back into what is now Wales and Scotland.
England, Scotland and Wales in the Middle Ages
In the early Middle Ages, the Kingdom of Strathclyde arose in the south of what is now Scotland . The Kingdom of Scotland was formed in the 10th century by the union of Picts and Celtic Scots from the petty kingdom of Dalriada .
Meanwhile, the Anglo-Saxons created seven independent petty kingdoms in what was later to be named England: Wessex , Sussex and Kent to the south, East Anglia and Essex to the east, Mercia in the center and Northumbria to the north. Within this power constellation, known as the heptarchy , there were repeated struggles for supremacy. In the 9th century, kingdoms also had to defend themselves against attacks by Danish Vikings , who brought large parts of the country under their rule with the Danelag . From the late 9th century, the Wessex kings managed to both push back the Vikings and establish their hegemony over the other Anglo-Saxon kingdoms.
In 1066, the Norman conquest of England began with the invasion of Duke William II , which led to Norman rule over England after the Battle of Hastings . The French-speaking Anglo- Normans exerted a lasting influence on the country's culture and language and established feudalism in England. However, over the centuries, the descendants of the conquerors eventually assimilated into Anglo-Saxon culture and society. In the mid-12th century, Anglo-Norman nobles from England and Wales began conquering Ireland. For a long time, however, the dominion of the English king on the smaller neighboring island was limited to the area around Dublin known as The Pale .
After the conquest of Wales by King Edward I , much of the island of Great Britain was under one rule from 1283. However, Edward's successors from the House of Plantagenet failed in their attempt to conquer Scotland . Following the Declaration of Arbroath , the kingdom in the north of the island of Britain retained its independence, leading to centuries of rivalry between England and Scotland . The Scottish kings entered into a strategic alliance with France , to whose crown the English monarchs had raised inheritance claims since the 14th century and with which they got into long-lasting conflicts, especially during the Hundred Years' War .
Formation of the United Kingdom
In the early modern period, the Reformation and the introduction of Protestant state churches in England and Scotland led to conflict. The Principality of Wales , which had been under the control of England since 1283, also became a de jure part of the English Kingdom by the Act of Union 1536 . Ireland was incorporated into a personal union from 1541 , forming the Kingdom of Ireland . In the early 17th century, following rebellions against English rule, lands were confiscated from Catholic Gaelic nobility in what is now Northern Ireland. Protestant settlers from England and Scotland were settled there as part of the so-called Ulster Plantations . Thus, in the north of Ireland, a section of the population arose that, religiously and nationally, always felt that it belonged to Great Britain and not to Ireland.
After the death of the childless Queen Elizabeth I , her heir, King James VI, ascended. of Scotland from the House of Stuart , ascended to the English throne as James I in 1603. Under him England and Scotland were united in personal union, but remained independent kingdoms with their own parliaments, laws and administrations. As a result of the English Civil War between the English Parliament and James's successor , Charles I , the monarchy was abolished in 1649 and the republican Commonwealth of England was established under the Lord Protector Oliver Cromwell . Through bloody but successful campaigns, the republic united all three later parts of the empire, England, Scotland and Ireland, into a centrally governed state for the first time.
Although the republic was abolished in 1660 and the separation between the three kingdoms was reintroduced with the monarchy, the House of Commons maintained its primacy in the English constitution. Instead of an absolutist one , a constitutional monarchy developed with a parliamentary system of government . The Act of Union , approved by Parliaments in London and Edinburgh in 1707, united the kingdoms of Scotland and England into the Kingdom of Great Britain.
In the 18th century, it rose to become a global sea power and created the British Empire , which included numerous overseas colonies in North America, Africa and Asia. The Act of Union 1800 united the Kingdom of Great Britain with Ireland to form the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland in 1801 .
The United Kingdom in the 19th and 20th centuries

On November 21, 1806, the French Emperor Napoleon imposed a continental blockade on the British Isles. It remained in force until 1814. It was intended to bring Britain to its knees with economic warfare and protect the French economy against European and transatlantic competition. Great Britain opened up new sales markets, particularly in North America.
The United Kingdom, the dominant industrial and maritime nation in the 19th century, played a significant role in the development of modern democracy , literature and science. Great Britain advocated a balance of power on the European continent ( Pax Britannica ) and concluded changing alliances for this. At its peak, the British Empire covered two-fifths of the world's land area, conquered in many wars.

Entry into the First World War in 1914 met with the approval of all parties except for a group in the Labor Party around Ramsay MacDonald . The British fought with France , Russia and (from 1917) with the USA against Germany and its allied Central Powers until victory in 1918.
In 1922, 26 Irish counties formed the Irish Free State (from 1937 Éire , from 1949 Republic of Ireland). The remaining 6 counties in the province of Ulster remained with the United Kingdom, despite Irish resistance. The current state name "United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland" has been used since 1927.
Following the German invasion of Poland , the United Kingdom and France declared war on Germany in 1939. In May 1940 Winston Churchill , who had been a member of the cabinet since 1939 and had long warned against appeasement , became prime minister. After the fall of France, Churchill mobilized all the country's forces for the war, so that a German invasion of Britain could be prevented by a successful air war . German missile and bomber attacks destroyed Coventry , parts of London and parts of other cities, and killed over 32,000 civilians. From the end of 1942, Great Britain achieved military successes: on the one hand in the Tunisia campaign led by General Bernard Montgomery , on the other hand in the invasion of Sicily and the subsequent Italian campaign , finally in the landings in France in 1944 and the final defeat of Germany in 1945 .
Since World War II

The country lost its position as a world power as a result of the two world wars, although it was on the winning side both times. In the second half of the 20th century, the British colonial empire was dissolved except for a few small remnants ( decolonization ): British India became independent in August 1947, the states of India , Bangladesh and Pakistan emerged (see Partition of India ). In Africa z. e.g. British Somaliland gained independence on 26 June 1961 and Nigeria on 1 October 1961 (see Decolonization of Africa ).
The Labor Party won the first post-war elections in Great Britain on July 5, 1945, and party leader Clement Attlee became Prime Minister of the United Kingdom. Contributing to Churchill's defeat was his reputation as "brilliant but unsound"; the electorate did not trust him to lead a peace government after the war years. However, in 1951-1964 government reverted to the Conservatives (Churchill, Eden, Macmillan, Douglas-Home - see British General Election 1951 ) after the Labor Party had worn itself out in factional struggles. The periods of government and the problems of the post-war period were briefly outshined by the coronation of Elizabeth II as head of state (queen) in 1952, after George VI. had died.
Although the British economy did not recover to the extent that Germany, Japan or the USA did after the Second World War, there was still a shortage of labour. As a result, numerous migrants came from the 1950s, primarily from Commonwealth countries such as India , Pakistan , Bangladesh , Nigeria , Kenya and the Caribbean .
In the Suez Crisis (1956/57) with Egypt, Great Britain suffered a defeat and with it a severe setback in its economic and colonial policy.
From 1969 onwards, civil war-like conditions prevailed in Northern Ireland , which only came to an official end with a peace agreement ( Good Friday Agreement ) in 1998. The conflict is about a religion, identity and power struggle between the two population groups, the English -born Unionist Protestants and the Irish-born, predominantly Irish nationalist Catholics .

In 1973, Great Britain joined the European Community after domestic opposition and the veto of France (see Member States of the European Union ). Until then, the EG had only its six founding members; on January 1, 1973 the UK, Ireland and Denmark joined. The Labor Party reigned again in 1974-1979.
Due to economic difficulties and increased deindustrialization in the 1970s and 80s, the Conservative government under Margaret Thatcher (1979-1990) implemented reforms and pursued an economic policy of monetarism to combat inflation and reduce national debt. In addition, there were deregulations in the labor market and in the financial sector. State-owned companies have also been privatized and some subsidies have been abolished. This led to increased unemployment figures in some cases, but also to economic growth, especially in the service sector. In 1990 there were violent protests against a new poll tax, which was abolished in 1992 and replaced by another tax. The Thatcher era also saw the reconquest of the Falkland Islands occupied by Argentina in 1982 . The Conservatives were in power until 1997. In 1997 , New Labor won the general election, with Tony Blair as leader , becoming prime minister. On July 1 of the same year, the British crown colony of Hong Kong was returned to China.
In 1999, as part of a constitutional reform (e.g. Scotland Act 1998 ), Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland were given their own parliaments . In 1998, the Human Rights Act 1998 was passed, which stipulates that all human rights enshrined in the European Convention on Human Rights expressly also apply in the United Kingdom.
From 2001 Britain participated with the United States in the War on Terror in Afghanistan , and in the Iraq War between 2003 and 2011.
Tony Blair resigned as Prime Minister in 2007 and was succeeded by former Chancellor of the Exchequer Gordon Brown . Brown lost the 2010 General Election in Britain and was succeeded by David Cameron ( Tories ).
On September 18, 2014, a referendum was held in Scotland on whether Scotland should remain in the United Kingdom, and the majority of voters rejected Scotland's independence from the United Kingdom.
In a referendum on June 23, 2016 on whether the United Kingdom should remain in the European Union , 51.9 percent of voters with a turnout of 72 percent voted in favor of leaving the European Union, the so -called BREXIT . David Cameron had campaigned to remain and therefore announced his resignation, effective October. His party friend Theresa May took over the office of prime minister on July 13 . May formally initiated the exit from the EU in accordance with Article 50 of the Treaty on European Union on March 29, 2017 by written notification to the European Council. The scheduled exit was scheduled to take effect on March 30, 2019, 12:00 a.m. At the request of the UK government, the EU agreed to postpone the exit date to October 31, 2019. After the British Parliament had not given its consent to the present withdrawal agreement by this date either, the EU granted a further extension of the deadline until the end of January 2020. Following resolutions by the British and European Parliaments in January 2020, the United Kingdom left the European Union on January 31, 2020 at 23:00 local time (24:00 CET). Therefore, a passport has been required for EU citizens to enter the UK since October 1, 2021 . If you live on the island, your identity card will suffice as before .
A remaining point of contention between the United Kingdom and the European Union remains the customs status of the province of Northern Ireland. According to the exit agreement, Northern Ireland forms an economic area with the European Union, which results in a customs border with the British mainland.
See also:
- History of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland , History of the United Kingdom
- history of Great Britain
- British Empire , Commonwealth of Nations
politics

The United Kingdom is a unitary state and formally a constitutional monarchy . The Head of State is currently Queen Elizabeth II. She is also the Head of State in 15 other independent Commonwealth countries . The country's constitution is not codified. Rather, it consists of common law , enacted statutes of constitutional status and the common law , collectively known as British constitutional law. Since there is no difference between statutes and so-called constitutional law, the British Parliament can implement "constitutional reforms" by making ordinary Acts of Parliament . It has the power to amend any constitutional element, written or unwritten, but subsequent governments may reverse or reverse those changes as well. However, there are laws with de facto constitutional status, such as the Bill of Rights . In principle, the courts have a great deal of freedom to formulate laws, since the British legal system is based on the principle of common law (cf. "conventions") and the correct interpretation of precedents by courts.
Initially, the Magna Carta (1215) was the first basic law of the state, but it only granted certain rights to a small upper class of nobles ( Council of Barons ). Nevertheless, the United Kingdom is considered to be the country in Europe with the oldest democratic tradition, since parliament has steadily gained in importance since the Glorious Revolution (1688/89) and the associated Bill of Rights.
The United Kingdom is governed and administered centrally, but in the course of " devolution " (decentralization) since the 1990s, powers have been transferred to Scotland , Wales and Northern Ireland to varying degrees . As the fourth and largest nation in the United Kingdom, England does not have its own executive and legislative powers. In the aftermath of the failed Scottish independence referendum in 2014, further powers were transferred to Scotland, which also have an impact on the devolution structure in the other parts of the country. The important elections to the regional parliaments in Belfast, Cardiff and Edinburgh took place in May 2016.
In local elections, women had active voting rights from 1869 and passive ones in 1907. According to Martin, this right was limited to women who paid taxes and only applied in some parts of the country. On February 2, 1918, the Representation of the People Act gave women restricted suffrage: the minimum voting age for women was 30. Women could also only vote if they paid at least £ 5 a year in taxes as single people or their husbands, female heads of household or University graduates were. The age limit was introduced in order not to create a numerical balance between women and men. For men, on the other hand, universal suffrage from the age of 21 applied from 1921. For men who had served in the military and met certain residency and property requirements, the age limit was 19. Full equality with men regarding the right to vote was achieved on July 2, 1928.
government
The UK is formally a constitutional monarchy as the British monarch can in theory depose the government but in practice does not exercise this right due to centuries of customary law. It is therefore a de facto parliamentary system of government in the form of a parliamentary monarchy , based on the Westminster system . The monarch usually appoints the leader of the largest party in the House of Commons as prime minister. In theory, however, he has the right to appoint any British citizen as Prime Minister, provided they are not members of the House of Lords. Today, this freedom of choice is only relevant when there is no clear majority in parliament ( hung parliament ).
The Prime Minister of the United Kingdom assumes the role of Head of Government , although among the traditional Great Officers of State he formally ranks only second to the Lord Chancellor as Lord High Treasurer . He also assumes leadership of the party that holds the majority in Parliament and chooses the ministers in the British Cabinet who are appointed by the monarch and form Her Majesty's Government . Formally, however, the Cabinet is only a committee of the Royal Privy Council ( Privy Council ). Prime Minister has been Boris Johnson since July 2019 (see also Boris Johnson I and II Cabinet ).
houses of Parliament
The British Parliament is bicameral and consists of the House of Lords ( Upper House ) and the House of Commons ( Lower House ). It sits in the Palace of Westminster in London . The members of the House of Lords are now mostly members of the non-hereditary gentry of merit, some nobles with hereditary titles of peerage, and 26 Anglican bishops . Members of the House of Commons are elected by first-past-the-post system. The democratically legitimized House of Commons is the dominant branch of parliament today, where all laws are introduced and passed. Due to parliamentary sovereignty , there is no constitutional jurisdiction in the UK.
head of state

The monarch, currently Queen Elizabeth II , is the head of state of the United Kingdom and also of 15 other sovereign states in the Commonwealth of Nations and the Crown Dependencies . He is also the head of the Church of England , the state church of the kingdom. Together with Parliament, it is the sovereign holder of executive , legislative and judicial powers .
Only when the monarch gives royal approval ( Royal Assent ) to a law passed by the other two chambers of Parliament does it come into force. However, this was last refused in 1708 under the reign of Queen Anne and is therefore actually only considered a formality today. The monarch can continue to enact laws as King/Queen in Council ( Royal Prerogative ) on the recommendation of the Prime Minister or Crown Council , which can, however, be rescinded by Parliament. However, this form of direct royal legislation plays a subordinate role today and is only used as secondary legislation (in the form of administrative regulations ). However, as part of the Brexit process, royal prerogatives briefly came into the public eye again when Theresa May briefly attempted to declare the United Kingdom's withdrawal from the EU in this way (without consulting Parliament).
Other rights, such as the dissolution of parliament , pardons , the awarding of orders or a declaration of war , also fall under the sole sovereignty of the monarch, but in practice are only exercised on the recommendation of the prime minister. Nowadays the monarch therefore has practically only a ceremonial role. Its power is limited by common law and public opinion, and breaching this practice would immediately lead to a constitutional crisis. In 1867, the constitutional theorist Walter Bagehot generally attributed three basic rights to constitutional monarchs: "The right to be heard, the right to give advice, and the right to warn." The incumbent prime minister meets weekly with the monarch for an intimate exchange of views current whereabouts.
Political Indices
| Index name | index value | World Rank | interpretation aid | year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fragile States Index | 38.3 out of 120 | 149 of 178 | Country stability: very stable 0 = very sustainable / 120 = very alarming |
2020 |
| democracy index | 8.54 out of 10 | 16 of 167 | Full democracy 0 = authoritarian regime / 10 = full democracy |
2020 |
| Freedom in the World Index | 94 out of 100 | — | Freedom status: free 0 = not free / 100 = free |
2020 |
| Press Freedom Index | 21.59 out of 100 | 33 out of 180 | Satisfactory situation for press freedom 0 = good situation / 100 = very serious situation |
2021 |
| Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) | 77 out of 100 | 11 of 180 | 0 = very corrupt / 100 = very clean | 2020 |
military

The UK has around 150,000 troops and, at US$55.5 billion, had the highest military spending in Western Europe in 2015 and is considered one of the leading military powers in the world. Traditionally and for geographical reasons, the Navy and Air Force have a relatively large weight compared to the Army in the armed forces of the UK.
The army has a target strength of around 82,000 soldiers (in 2010 it was 102,000 soldiers). The UK was ranked 74th out of 155 countries in the 2018 Global Militarization Index (GMI). According to the Global Firepower (2018) ranking, the country has the 6th strongest military capability in the world and the 3rd strongest in Europe.
The UK has had nuclear weapons since 1952 . Their stock has been significantly reduced since the end of the Cold War ; Great Britain's nuclear deterrent potential , which is currently stationed exclusively on nuclear submarines , is to be modernized. The army currently has 249 main battle tanks. The Air Force has around 250 combat aircraft and around 600 other aircraft. The Royal Navy is one of the largest navies in the world with 65 warships and 11 submarines. In June 2017, the new aircraft carrier HMS Queen Elizabeth (R08) went on sea trials for the first time; it has cost around £3.5 billion.
The British armed forces maintain a number of military bases abroad. This includes several bases in Germany with around 5,200 soldiers (as of 2015) and two British territories on Cyprus with around 7,000 soldiers. Apart from the United States , no country has more soldiers stationed abroad than the United Kingdom.
War on Terror
The United Kingdom is an ally of the United States in the " War on Terror ". It has served with air and ground forces in the Iraq War and is involved in the war in Afghanistan . In 2000, an anti-terror law (Terrorism Act 2000) was ratified . After the terrorist attacks on September 11, 2001 in the United States , the "Anti-Terrorism, Crime and Security Act" was introduced into Parliament in November 2001. It was passed and came into force on December 14, 2001. Another Anti-Terrorism Act was passed in response to the July 7, 2005 terrorist attacks in London . Britain has been accused of committing human rights abuses in the fight against terrorism . Twelve suspects in connection with terrorist attacks have already been held for several years without charge in maximum security prisons in Great Britain under the possibilities of the Anti-Terrorism Act. According to Amnesty International , prisoners were tortured and mistreated by British and American soldiers during the Iraq war.
foreign policy
The UK still has a wide web of connections from the days of the British Empire, when it was the most powerful country in the world.
The UK sees itself as a power of global reach and responsibility. It is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council, the North Atlantic Alliance ( NATO ), the G7 , the G20 and the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe ( OSCE ) and was a member of the European Union (EU) until 31 January 2020. Efforts to maintain close relations with the USA, the central importance attached to NATO in terms of security policy and the preservation of the ability to act independently are the basis of British foreign policy. In the future, the relationship with the European states will have to be redefined.
Among the European countries, Germany is the most important partner alongside France (bilateral defense agreement of November 2010); In the global context, it is the United States with which the United Kingdom maintains a “special relationship” based on shared historical and cultural roots, also in order to maintain the special transatlantic connection. It was one of the few countries to support the American invasion of Iraq in 2004 (“ Coalition of the Willing ”). The United Kingdom intends to build on these close ties with the USA in the future. Among other things, both countries want to negotiate a free trade agreement after the UK leaves the EU.
In the future, the government is aiming, among other things, for intensified economic and political relations with India and the People's Republic of China . She also wants to strengthen the importance of the Commonwealth .
administrative division
Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland have their own regional parliaments and governments headed by a so-called “first minister” (comparable to a prime minister in Germany or a governor in Austria). Nevertheless, the United Kingdom is a central state - the individual parts of the country are therefore not independent member states . England has no state administration. The formation of a Northern Assembly was rejected by a large majority in a referendum on 4 November 2004. The tasks of a head of state in England are carried out by the parliament and government of the United Kingdom. It has meanwhile become customary for MPs from other parts of the country to abstain in Parliament if a decision only affects England (see also the West Lothian Question ).
The lower administrative levels have been restructured several times since the late 19th century, and further changes are to be expected in the future. Since the Middle Ages, England has traditionally consisted of 39 counties, Scotland 34, Wales 13 and Northern Ireland six counties . Today there are 25 administrative counties in England, 57 unitary authorities , six metropolitan counties and Greater London (see also England's administrative structure ). Wales is divided into 22 and Scotland into 32 Unitary Authorities (there called Council Areas ). There are eleven districts in Northern Ireland which also have Unitary Authority status. However, the names of the old counties are often still used in everyday usage in all parts of the country.
Dependent Territories (officially British Overseas Territories ):
- Akrotiri and Dekelia (military bases in Cyprus)
- anguilla
- bermuda
- British Virgin Islands
- British Antarctic Territory
- British Indian Ocean Territory
- Falkland Islands
- Gibraltar
- Cayman Islands
- Montserrat
- Pitcairn Islands
- Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
- South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
- Turks and Caicos Islands
Territories subject only to the British Crown and not to the United Kingdom ( British Crown Dependencies ):
Both have their own legislatures and legal systems , but are represented by the UK Government in the area of defense and international relations .
The British monarch is the head of state of the United Kingdom and a large number of other independent Commonwealth countries.
police
Police forces in the UK are not organized in a unified manner. In rural areas, police forces from the defense or interior ministries are responsible for public security. The uniforms are largely identical. There is also the Metropolitan Police Service ( Scotland Yard ) for Greater London and the Police Service of Scotland for Scotland . In addition, the secret service MI5 operates domestically.
crime
England and Wales is a region of common jurisdiction within the United Kingdom. The National Bureau of Statistics has been conducting victimization studies here at regular intervals since 1982 . Randomly selected people are asked whether and, if so, in what form they have been victims of crime in the past year. It shows an increase until 1995 and since then a decline in crime . This corresponds to the typical course in a country in the western world .
An advantage of victimization studies over police statistics is that they also look at unreported cases. When analyzing long-term trends, however, the changing level of social tolerance can have a falsifying effect. In particular, cases of physical harm and sexual assault are more likely to be classified as criminal today than they were decades ago.
The time course shows a steady increase up to the peak in 1995. After that, the numbers fell almost continuously. Excluding credit card fraud and computer fraud , total victimization decreased by 68% from 1995 to 2019. The decrease in violent crime was 70%, robbery 48% and theft 68%.
The homicide rate is used as an index for comparisons of propensity to violence over long periods of time and over large geographical distances. In 2017, the United Kingdom had 1.2 cases per 100,000 inhabitants (for comparison: the average in Europe was 3 cases per 100,000 inhabitants, in Germany it was 1 case, the global average was 6.1; the lowest value is reached in Singapore with 0.2 cases per 100,000 inhabitants).
law
At the sub-national level, the United Kingdom has three legal systems , each originating from a specific geographic area with different historical backgrounds: English law , Scottish law and Northern Irish law. Since 2007, following the passage of the Government of Wales Act 2006 by the UK Parliament , there has also been purely Welsh law, but unlike the other three, it is not a separate legal system in itself. It is just primary and secondary law drawn up by the National Assembly for Wales and interpreted in accordance with the teachings of English law. It does not affect English common law (unless such law supersedes a common law rule because it is a superordinate legal form). There is significant overlap between these three legal systems and the three jurisdictions of the United Kingdom, namely England and Wales , Scotland and Northern Ireland. By default, each jurisdiction is subject to each jurisdiction, and the legal systems of each jurisdiction support the relevant jurisdiction by jurisprudence. However, it should be noted that in private law a person in certain jurisdictions may claim the rights of other jurisdictions, e.g. B. a company in Edinburgh (Scotland) and a company in Belfast (Northern Ireland) which can contract under English law. This is not applicable in public law (e.g. criminal law) where a code of procedure is established in each legal system. Superordinate are laws of the United Kingdom, also (less commonly) referred to as British law. British law arises when laws apply to the United Kingdom and/or its citizens as a whole, most obviously constitutional law, but also other areas such as tax law.
The UK does not have a unified legal system because it was created by a political union of previously independent countries. Article 19 of the Treaty of Union, enacted by the Act of Union 1707 , created the Kingdom of Great Britain but guaranteed the continued existence of Scotland's separate legal system. The Act of Union of 1800 , which united Great Britain and Ireland into the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, contained no such provisions but retained the principle of separate courts in Ireland , of which the part known as Northern Ireland still remains is part of the United Kingdom.
The Supreme Court of the United Kingdom is the country's highest court for all criminal and civil matters in England and Wales and Northern Ireland, as well as for all civil matters in Scottish law. The Supreme Court is also the final court for the interpretation of UK law. Its decisions can be expressly overturned by Parliament on the basis of the doctrine of parliamentary sovereignty. The Supreme Court was created in October 2009, replacing the House of Lords ' Appeals Committee . In England and Wales, the court system is led by the High Courts of England and Wales, which consist of the Court of Appeal, the High Court of Justice (for civil matters) and the Crown Court (for criminal matters). The courts of Northern Ireland follow the same pattern. In Scotland, the highest courts are the Court of Session for civil cases and the High Court of Justiciary for criminal cases. Sheriff courts have no equivalent outside of Scotland as they deal with both criminal and civil matters.
The Judiciary Committee of the Privy Council is the highest court of appeal for several independent Commonwealth countries, the British overseas territories and the British Crown possessions. There are also immigration courts with jurisdiction in the UK - the Asylum and Immigration Court and the Special Immigration Appeals Commission.
business

The UK is one of the most deregulated and privatized economies in the world. The British economy is the origin of what has come to be known as 'Anglo-Saxon capitalism', based on the principles of liberalisation , the free market , low taxation and light regulation. With a gross domestic product (GDP) of around 2.85 trillion US dollars (2015), the country is the sixth largest economy in the world and has the second largest gross domestic product in Europe after Germany . It ranked eighth in purchasing power parity (PPP) in 2013 . At 28,300 euros, per capita GDP is in the upper European reference range. In comparison with the gross domestic product of the European Union, expressed in purchasing power standards , the United Kingdom has an index of 110 (EU-28 in 2015: 100). Economic growth was 2.2 percent in 2015. In the Global Competitiveness Index , which measures a country's competitiveness, the United Kingdom ranks 8th out of 137 countries (as of 2017–2018). The country ranked 12th out of 180 countries in the 2017 Economic Freedom Index . The employment rate reached a historic high of 73.6 percent in early summer 2015. The unemployment rate was 4.1% in April 2018, well below the EU average and at its lowest level since the 1970s. In 2017, youth unemployment was 11.7%. In 2014, 1.3% of all workers worked in agriculture, 15.2% in industry and 83.5% in the service sector. The total number of employees in 2017 is estimated at 33.5 million.
The history of Jaguar Land Rover is an exemplary reflection of the rise and fall of the British automobile industry in the 20th century. In the 1930s and 1940s, the Jaguar models defined the style of luxury cars . From the mid-1970s, the manufacturer got into financial difficulties, was sold to international competitors several times in the following decades and has belonged to the Indian Tata Group since 2007 . The Industrial Revolution originated in the United Kingdom. Initially there was a concentration on heavy industry with emphasis on shipbuilding , steel production and mechanical engineering . Also, for a long time in the 19th century, Britain was at the forefront of industrializing the manufacture of textiles . Between 1803 and 1857 the number of looms in commercial use increased from around 2,500 to over 250,000. In 1023 textile production in Britain was at its peak before capacity was reduced in favor of a shift to India.
The colonies and protectorates of the British Empire have long been a ready market for British products. During the 20th century, the industrial sector gradually lost importance. The service sector grew. In 2016, it accounted for around 79% of gross domestic product.
The service sector is dominated by financial service providers such as banks and insurance companies. The City of London with its privileged special rights is the largest financial center in the world. The City is home to the London Stock Exchange , Lloyd's of London , the Bank of England and numerous banks including HSBC , Citigroup and Barclays . The City of London has the largest concentration of foreign bank branches in the world. The Scottish capital Edinburgh is the fifth largest financial center in Europe and the headquarters of well-known companies such as the Royal Bank of Scotland and HBOS . The strong current account deficit, which reached a record level in 2014, is compensated for by the permanent import of capital. Tourism is also of great importance; with over 29 million tourists, the United Kingdom was the world's eighth most important tourist destination in 2016. Tourism revenue for the same year was $39.7 billion. Per capita wealth in the UK is $288,806 per adult , according to Credit Suisse . The country has one of the highest per capita wealth in the world and the fourth highest total national wealth of any country. However, inequality is significant and the Gini coefficient for wealth distribution was 73.2, indicating high inequality. There were an estimated 961,000 millionaires and over 100 billionaires in the UK in 2016.
Today, industrial production still accounts for around one sixth of gross domestic product. An important branch is the automotive industry , even if all companies are now in foreign hands. The aerospace and defense industries are dominated by BAE Systems and Rolls-Royce with a significant share of the world space industry. An important mainstay is the chemical and pharmaceutical industry; two of the world's ten largest pharmaceutical companies , GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca , are headquartered in the UK.

British agriculture is small by European standards, accounting for 0.9 percent of gross domestic product. On the other hand, the country has large reserves of coal , natural gas and oil . Industrial extraction of mineral resources contributes 10 percent to the gross domestic product, which is a high proportion for an industrialized country. This proportion is expected to decrease as coal, gas and oil production peaked around 2000. Great Britain has been a net importer of crude oil since 2005 and the production volume in 2010 was only 45.9 percent compared to the maximum amount reached in 1999 ( peak oil ). Natural gas and coal have also had to be imported in increasing quantities for a number of years. Major global British companies in this industry include BP and Royal Dutch Shell . The British Isles have a very large potential for regenerative energies, especially in the field of wind power and current and tidal power plants, which has only been used to a small extent so far. However, the proportion of regenerative energies, including solar energy , in the total energy supply is increasing. According to estimates, in 2020 [outdated] about 4 percent of the energy demand could be covered by solar energy alone. The government ( cabinet Cameron II ) is (as of 2015) committed to expanding nuclear energy and has named eight locations.
The UK has the largest current account deficit of any major industrialized country . In 2014 it was 5.1 percent of total economic output. This was a record value since the end of the Second World War. The last time a current account surplus was achieved was in the 1980s. The main cause is not the trade deficit that has existed for a long time , but the declining net returns on (falling) British investments and assets abroad with rising domestic consumption. The current account deficit has been compensated for by foreign capital inflows for a long time, which could, however, decrease sharply if interest rates rise in the USA (2015/16) or after Brexit and then lead to a devaluation of the British currency.
state budget
In 2015, the state budget included expenditure equivalent to 1.134 trillion US dollars , which was offset by income equivalent to around 1 trillion US dollars. This results in a budget deficit of 134 billion US dollars or 4 percent of gross domestic product (GDP). In 2018, the budget deficit was still 1.5 percent of GDP.
At the end of 2013, the government debt amounted to 87.2% of gross domestic product. In the course of the banking and financial crisis since 2007 , national debt has risen sharply. In February 2013, the US rating agency Moody's downgraded the United Kingdom's credit rating from the top rating of "AAA" to "Aa1" due to the country's increasing debt and weak economy.
| year | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| national debt | 34.0 | 34.1 | 35.7 | 38.3 | 39.5 | 40.3 | 41.7 | 49.7 | 63.7 | 75.2 | 80.8 | 84.1 | 85.2 | 87.0 | 87.9 | 87.9 | 87.1 | 86.8 |
| budget balance | −0.4 | −2.5 | −3.1 | −3.6 | −3.0 | −2.8 | −2.6 | −5.2 | −10.1 | −9.3 | −7.5 | −8.1 | −5.3 | −5.3 | −4.2 | −2.9 | −1.9 | −1.5 |
In 2015, government spending (as a percentage of gross domestic product) accounted for the following areas:
Regional differences
| position | region | GDP/capita, PPS , (EU28=100) (2015) |
GDP per capita in € (PPS) (2015) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | London | 184 | 53,200 |
| 2. | South East England | 118 | 33,900 |
| – |
|
108 | 31,200 |
| 3. | East of England | 101 | 29,200 |
| 4. | Scotland | 100 | 28,900 |
| – |
|
100 | 28,900 |
| 5. | Southwest England | 97 | 28,100 |
| 6. | Northwest England | 92 | 26,600 |
| 7. | East Midlands | 88 | 25,500 |
| 8th. | West Midlands | 88 | 25,400 |
| 9. | Yorkshire and the Humber | 86 | 24,800 |
| 10 | North East England | 80 | 23,100 |
| 11. | Northern Ireland | 78 | 22,600 |
| 12. | Wales | 76 | 21,900 |
The United Kingdom is strongly characterized by regional disparities in wealth. The former industrial north of England is struggling with structural change and has fallen behind the rest of the country. The level of prosperity in Northern Ireland and Wales is also below the national average. The country's wealthiest regions are the south-east of England and the capital region of London, leaving the rest of the country far behind. London accounts for a significant portion of the country's financial and industrial resources and accounts for more than a quarter of total economic output.
metrics
| year | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
| % change yoy | 2.5 | 2.6 | −0.6 | −4.3 | 1.9 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 2.0 | 2.9 | 2.3 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.4 |
| absolute (in billion US dollars) | per capita (in thousand US dollars) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| year | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | year | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
| GDP in billion US$ | 2,659 | 2,638 | 2,825 | GDP per capita (US$ thousand) | 40.5 | 39.9 | 42.5 |
| in billion euros and its change compared to the previous year in percent | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | ||||
| billion euros | % yoy | billion euros | % yoy | billion euros | % yoy | |
| import | 636.4 | +1.0 | 641.3 | +0.8 | 669.6 | +4.4 |
| export | 411.5 | −11.4 | 442.1 | +7.4 | 487.1 | +10.2 |
| balance | −224.9 | −199.3 | −182.6 | |||
| Export goods (share in %) | Import goods (share in %) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemicals | 15.8 | Chemicals | 11.7 |
| machinery | 14.0 | automobiles and parts | 11.3 |
| automobiles and parts | 11.7 | machinery | 9.8 |
| other vehicles | 5.0 | food | 7.9 |
| oil | 4.3 | electronics | 7.6 |
| Export (in percent) to | Import (percentage) from | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
13.4 |
|
13.7 |
|
|
9.6 |
|
9.5 |
|
|
6.8 |
|
9.4 |
|
|
6.5 |
|
8.2 |
|
|
5.8 |
|
5.6 |
|
|
5.7 |
|
5.2 |
|
|
5.3 |
|
4.0 |
|
|
29.2 |
|
65.4 |
|
|
46.9 |
|
44.4 |
currency
The currency in the United Kingdom is the pound sterling , abbreviated GBP for Great British Pound . The currency symbol is £ .
power supply
The UK economy is suffering from the sharp rise in gas prices in 2021 . Dozens of energy suppliers are threatened with bankruptcy because they can no longer afford the high gas purchasing costs. In the UK, 23 million households, 85 percent of the total population, heat their homes with natural gas. 40 percent of the electricity is generated in gas -fired power plants. Shortly after the year 2000, the UK was still self-sufficient with its own North Sea natural gas ; today (2021) it is one of the major natural gas importers in Europe.
See also List of UK nuclear reactors and en:List of UK nuclear reactors
traffic


In 2018, the United Kingdom was ranked 9th out of 160 countries in the Logistics Performance Index , which is compiled by the World Bank and measures the quality of infrastructure .
road traffic
The transport network is oriented in a north-south direction and mainly extends radially from London. Traffic drives on the left , unlike in most other countries. The road network is around 388,000 kilometers long. Around 3,500 km of these are motorways that have been built since the 1950s.
In addition to the motorways, there is also a dense network of four-lane dual-carriageways (A roads) on which all types of vehicles are permitted and which intersect with other roads. This type of road is also referred to as a dual carriageway and corresponds to the highway-like roads in German-speaking countries. Multi-lane roads have so-called "U-Turns" (German: Halbkreiswende) or roundabouts (roundabouts) at regular intervals.
The Highway Agency , an agency under the Department for Transport, is responsible for the maintenance of motorways and trunk roads in England . Local governments are responsible for the rest of the road network in England. In Scotland , road network maintenance falls within the remit of Transport Scotland , in Wales the Welsh Parliament and in Northern Ireland Roads Services (a department of the Department for Regional Development).
Toll roads are rare in the UK, however there are numerous toll bridges such as B. the Humber Bridge . In 2003, the first toll motorway was opened, the Motorway M6 Toll , which relieves the Motorway M6 near Birmingham . Some cities have a congestion charge (e.g. the London Congestion Charge ).
Since February 4, 2008, a Low Emission Zone (LEZ) has also been set up in the greater London area. According to the Transport for London supervisory authority, it is the largest environmental zone in the world. From February 4, 2008 to January 2012, the emission ceilings will be gradually increased. However, no cars are affected, but smaller transport vehicles and buses up to trucks. Before entering the zone with one of these vehicles, it must be registered beforehand. If the vehicle does not meet emission standards, a daily fee will be charged. Unregistered vehicles risk a fine.
The speed limit on freeways is 70 mph (113 km/h), extra-urban up to 60 mph (97 km/h) and urban 30 mph (48 km/h). In the United Kingdom, traffic drives on the left .
When it comes to road traffic, the country is one of the safest in the world. In 2013, the UK had a total of 2.8 road deaths per 100,000 inhabitants. For comparison: In Germany there were 4.3 deaths in the same year. A total of 1,827 people lost their lives on the road. The country has a high motorization rate in global comparison. In 2016 there were 544 motor vehicles per 1000 inhabitants in the country (in Germany there were 610 vehicles).
rail transport
The railway network in Great Britain is the oldest in the world. The skeleton forms the five main routes radially from London, West Coast Main Line , East Coast Main Line , Midland Main Line , Great Western Main Line and Great Eastern Main Line . These are supplemented by numerous regional lines and dense suburban networks in the metropolitan areas. The Channel Tunnel Rail Link is operationally separate from the rest of the rail network and built to the same specifications as the TGV network in France.
The world's first passenger railway was the Stockton and Darlington Railway , opened in 1825, and the Liverpool and Manchester Railway , opened in 1830, was the world's first railway between two major cities. As a result, hundreds of railway companies were founded, which, after numerous mergers, consolidated into four companies in 1922. In 1948 the railways were nationalized and the route network was then reduced to less than half. In 1994 and 1995, the state railway British Rail was divided into infrastructure, maintenance, rolling stock, passenger and freight companies, which were privatized in 1996 and 1997.
The UK's privatized rail network consists of two independent sub-networks, in Northern Ireland and in Great Britain. Since 1994, the latter has been connected to mainland Europe by the Eurotunnel . The Northern Ireland network is connected to that in the Republic of Ireland. The rail network is a total of 16,878 kilometers long, more than half less than in the 1950s. Of these, 4,928 km are electrified and 12,591 km have two or more tracks. The top speed for decades was 125 mph (200 km/h ) on the Intercity lines. On the Channel Tunnel Rail Link , which connects London with the Eurotunnel, Eurostar trains travel at up to 300 km/h.
air traffic
The United Kingdom is one of the most important hubs for world air traffic. With around 200 million passengers per year (including 125 million at London airports), the total number of passengers is the largest in Europe. The country's largest airport is London Heathrow , followed by London Gatwick and Manchester Airport . The largest British airline is British Airways .
maritime transport
Due to the island location of the country, the spatial separation of Northern Ireland from the rest of the country and the many offshore islands, shipping has traditionally been of great importance. Around 95% of all goods reach the UK by ship (representing 75% of the total value). The main ports are Felixstowe , Tilbury , Southampton and Teesport .
traffic
Two main hubs for the wired internet ( Apollo ) and telephone connection ( Atlantic Crossing 1 ) between Europe and the US are in the UK.
Culture
Due to the influence of the British Empire, cultural customs from the United Kingdom have spread around the world. The country is still one of the largest exporters of cultural products worldwide.
kitchen
British cuisine (especially English) has long had a reputation for being bland, monotonous, stodgy, and flavorless, and for combining unfamiliar flavors (e.g., mint sauce with lamb ). The traditional combination of meat, potatoes and vegetables ( meat and two veg ) finds its most established form in the Sunday roast . Potatoes also play a crucial role in other ways and are prepared in a variety of ways, but mostly in the form of mash. Pies with meat filling are widespread. The British breakfast is an extensive cooked meal known all over the world. Among the cold dishes, sandwiches cut diagonally are prominent. The epitome of British fast food is fish and chips . Cakes are preferred for dessert. England is also known for its Cheddar cheese .
The cuisine of Scotland has some differences. Above all, the food culture of the upper classes took over numerous characteristics of French cuisine as a result of the Auld Alliance .
The most popular non-alcoholic drink is tea . British tea culture is part of the British way of life. Coffee , on the other hand, played a rather subordinate role. The light alcoholic beverages are dominated by the beer types ale and stout , as well as the sparkling apple wine cider . Gin and whiskey are common among the high -proof. For centuries the British market has been the main outlet for sweet wines such as sherry , port and Madeira .
media
There is a diverse range of media in the United Kingdom, which also have a great influence internationally due to the spread of the English language.
The BBC is the country's public broadcaster and is also the oldest and largest in the world. Funded by compulsory broadcasting fees and partly by advertising, it operates several television and radio stations , both domestically and internationally. BBC World , the BBC's international news channel, is broadcast around the world and the BBC World Service radio station broadcasts programs in 33 different languages. BBC television's main competitors are ITV , Channel 4 , Channel 5 and Sky .
The BBC, which operates ten national and over 40 local stations, dominates radio broadcasting. The most popular radio station by listenership is BBC Radio 2 , followed by BBC Radio 1 . In addition, there are more than 200 commercial radio stations, most of which are locally based. The largest private stations are Absolute Radio (formerly Virgin Radio), Classic FM and talkSPORT . By far the most important local radio station is Capital Radio from London.
Until a few years ago, British newspapers made a strict distinction between ' broadsheet ' newspapers, with high-quality articles, and tabloid newspapers, which are tabloids . Due to the greater readability, numerous "quality newspapers" have switched from broadsheet to tabloid format, so that at least this distinction has disappeared. The highest circulation of any British newspaper is the Monday to Saturday tabloid The Sun , while its sister newspaper , the News of the World , dominated the Sunday newspaper market until it was discontinued on 10 July 2011. The highest circulation of the so-called quality newspapers are The Daily Telegraph and The Times , to the right of center on the political spectrum, and The Guardian and Daily Mirror , to the left of center. The leading business newspaper is the Financial Times .
In 2019, 93 per cent of UK residents used the internet .
The use of social media is playing an increasingly important role. In January 2011, the gross reach of social networks was 27.2 million people living in the UK. As elsewhere, the trend in the UK is towards increased use of online and mobile media. The most popular online service is the BBC news portal, which is also very popular internationally. The Guardian and Daily Mail websites are also widely read both nationally and internationally.
Movie
The UK has had a significant film industry for over a century. While film production reached an all-time high in 1936, the 'golden age' of British cinema is believed to have been the 1940s, during which time directors David Lean , Michael Powell (with Emeric Pressburger ) and Carol Reed made their critically acclaimed works. Many British actors have achieved worldwide fame and recognition such as Maggie Smith , Michael Caine , Sean Connery , Daniel Day-Lewis , Gary Oldman and Kate Winslet . Some of the largest box office films to date have been made in Britain, including the third and fourth highest grossing film series of all time ( Harry Potter and James Bond ), the former being British-American. The identity of the British film industry, particularly as it relates to Hollywood , has often been debated. Its history has often been influenced by attempts to compete with American industry. Producer Alexander Korda 's career was marked by this goal, with the Rank organization attempting this in the 1940s and Goldcrest in the 1980s. Numerous British-born directors, including Alfred Hitchcock and Ridley Scott , and performers such as Charlie Chaplin and Cary Grant , have found success largely through their work in the United States.
In 2009, British films grossed around US$2 billion worldwide and had a market share of around 7% worldwide and 17% in the UK. UK cinemas totaled £1.1bn in 2012 from 172.5m admissions.
In 1999 the British Film Institute published a list of the 100 best British films of the 20th century.
literature

The earliest literature on modern United Kingdom territory (apart from works in Latin ) was written in the various Celtic languages of the islands. Thus the tradition of Welsh literature goes back to the 6th century; the early medieval Mabinogion is a collection of tales by the Welsh bards. The tradition of Irish poetry can also be traced back to the 6th century, with the Ulster cycle being particularly important in Northern Ireland . Old English literature produced works like Beowulf or Cædmon's Hymns , but the educated elite preferred Latin. Well-known authors in this language include Bede Venerabilis and Geoffrey of Monmouth .
After the Norman conquest of England , Anglo-Norman literature brought influences from mainland Europe to the British Isles. English literature proper developed from the late 14th century with the rise and spread of the London dialect of Middle English . The first writer of English-language literature known by name is Geoffrey Chaucer , author of the Canterbury Tales . After the introduction of printing to England by William Caxton in 1476, literature flourished in the Elizabethan era, particularly in the realms of poetry and drama . William Shakespeare in particular stands out from this period .
The 18th century saw the dawn of the English novel . Famous authors of this period include Daniel Defoe , Samuel Richardson and Henry Fielding . After a period of decline, Scotsman Robert Burns revived interest in literature in the 'language of the people', with the Rhyming Weavers of Ulster being influenced by Scottish literature in Scots . The following two centuries produced an unprecedented variety of literature. In the early 19th century, Romantic poetry resembled that of the Renaissance , with authors such as William Blake , William Wordsworth , John Keats and Lord Byron . The Victorian Age was the golden era of the realist English novel, represented by Jane Austen , the Three Brontë Sisters , Charles Dickens , William Thackeray , George Eliot and Thomas Hardy . Specialists in historical novels included Walter Scott and Robert Louis Stevenson .
The First World War produced British 'war poets' such as Wilfred Owen , Siegfried Sassoon , Robert Graves and Rupert Brooke , who wrote (often in a paradoxical style) about their expectations of war and/or their experiences in the trenches. In the wake of the Celtic Revival there has been an increased appreciation of traditional Irish literature. Since Ireland's independence in 1922, Irish literature has been seen as a distinct movement from British literature. The Scottish Renaissance of the early 20th century modernized English-language Scots literature and also led to the introduction of new forms in Scots and Gaelic literature .
In the course of the 20th century the English novel developed a much greater diversity, which was further enriched by immigrant writers. The novel has remained the dominant form of literature to this day. Other famous novelists include Arthur Conan Doyle , DH Lawrence , George Orwell , Salman Rushdie , Mary Shelley , JRR Tolkien , Virginia Woolf , Graham Greene , HG Wells , and Joanne K. Rowling . Influential poets include Elizabeth Barrett Browning , Ted Hughes , John Milton , Alfred Tennyson , Alexander Pope , and Dylan Thomas , among others .
The following British authors won the Nobel Prize in Literature : Rudyard Kipling (1907), John Galsworthy (1932), TS Eliot (1948), Bertrand Russell (1950), Winston Churchill (1953), William Golding (1983), Harold Pinter (2005) and Doris Lessing (2007).
architecture
The earliest evidence of architecture in the UK are Neolithic megalithic monuments such as Stonehenge , Avebury and West Kennet Long Barrow . Skara Brae on the Orkney Islands is one of the best preserved Neolithic settlements in the world. Stone round houses and towers ( brochs ) from the Iron Age are mainly known from Scotland. The Celts built only wooden buildings, so nothing of them has survived. The Romans built the first cities, the most important being Aquae Sulis ( Bath ), Camulodunum ( Colchester ), Deva ( Chester ), Eboracum ( York ), Londinium ( London ) and Verulamium ( St Albans ). Many Roman buildings are still standing today, the thermal baths in Bath are particularly worth mentioning.
The Romans were followed by the Anglo-Saxons and other Germanic peoples. Their dwellings usually consisted of a wattle and daub reinforced with clay. The stone churches, which often give an indication of how old a settlement is, lasted longer. A typical example of Anglo-Saxon architecture is Wing Parish Church in Buckinghamshire .
In the two centuries following the Norman Conquest in 1066, numerous significant castles such as the Tower of London , Caernarfon Castle in Wales and Carrickfergus Castle in Northern Ireland were built to keep the population in check. While the Crown mainly encouraged the building of defences, the clergy and nobility paid homage to God by building numerous cathedrals, first in the Norman , later in the Gothic style. The practice of reinforcing virtually all large buildings with fortifications ended with the advent of the Tudor style and the construction of the first representative country houses such as Montacute House and Hatfield House , and castles such as Hampton Court Palace .
During the English Civil War (1642-1649) buildings suffered sieges for the last time in British history. Numerous castles such as Corfe Castle were destroyed in attacks by Oliver Cromwell's army . After the end of this war, buildings were only erected for residential and commercial purposes; Design and appearance pushed the idea of defense completely into the background. Before the war, Inigo Jones was known as the first significant British architect and a co-founder of Palladianism . His most important works are the Queen's House and the Banqueting House .
After the reinstatement of the monarchy in 1660 and the Great Fire of London in 1666, London missed an opportunity to create a new metropolis using modern architectural styles. Although Christopher Wren , one of the most important British architects of the time, was commissioned to design and rebuild many of the destroyed churches, his overall plan for rebuilding the capital was rejected on cost grounds. His most important building is St Paul's Cathedral , built between 1675 and 1708 .
In the early 18th century, Baroque , popular in Europe , also made its way to the British Isles, during which time Blenheim Palace , for example, was built by John Vanbrugh and Nicholas Hawksmoor . However, the Baroque was soon replaced by Palladianism. A further development of Palladianism in the second half of the 18th century was Georgian architecture , represented by country houses such as Woburn Abbey and Kedleston Hall . Architects of this architectural style and its neoclassical and romantic successors respectively include Robert Adam , William Chambers and James Wyatt .
Almost as a throwback to the symmetry of Palladianism, the neo- Gothic style seems almost medieval ; the best-known example of this phase is the new Palace of Westminster , designed by Charles Barry . By the mid-19th century, technology had advanced enough for steel to be used as a building material. This is how Joseph Paxton built the Crystal Palace , arguably the most iconic structure of the Victorian era. While many new building methods were introduced to British architecture in this era of progress, leading architects such as Augustus Pugin ironically insisted on a backwards-looking style.
In the early 20th century, Arts and Crafts Movement design became popular. The architectural form of this style, which had developed from the works of 19th-century architects such as George Devey , found its culmination in the buildings of Edwin Lutyens . Arts and craft in architecture is symbolized by an informal, non-symmetrical form, often the buildings were decorated with mullion and lattice windows, multiple gables and tall chimneys. This style lasted until World War II . Post-war Reconstruction was dominated by Modernism or Brutalism , particularly from the late 1950s to the early 1970s.
Modern building has remained the driving force behind British architecture to this day, although its influence is felt far more on commercial buildings than on residential buildings. The two leading contemporary British architects are Richard Rogers and Norman Foster . Rogers' most famous buildings are probably the Lloyd's building and the Millennium Dome , while Foster created the skyscraper 30 St Mary Ax (also known as "Gherkin") and London's City Hall , among others.
science

England and Scotland have been leading centers of the scientific revolution since the 17th century. The UK led the Industrial Revolution in the 18th century and has continued to produce important scientists and engineers. Among the most important theorists of the 17th and 18th centuries are Isaac Newton , who described universal gravitation with his law of gravitation and formulated the laws of motion , laying the foundation for classical mechanics , and Charles Darwin in the 19th century, whose theory of evolution natural selection was fundamental to the development of modern biology and James Clerk Maxwell who formulated the classical electromagnetic theory; and more recently Stephen Hawking , who has advanced important theories in the fields of cosmology, quantum gravity, and the study of black holes.
Major 18th-century scientific discoveries include hydrogen by Henry Cavendish , 20th-century penicillins by Alexander Fleming , and the structure of DNA by Francis Crick and others. Well-known British engineers and inventors of the Industrial Revolution include James Watt , George Stephenson , Richard Arkwright , Robert Stephenson and Isambard Kingdom Brunel . Other significant engineering projects and applications by people from Britain include the steam locomotive developed by Richard Trevithick and Andrew Vivian , the 19th century electric motor by Michael Faraday , the lightbulb by Joseph Swan and the first practical telephone patented by Alexander Graham Bell and im 20th century The world's first working television system by John Logie Baird , the jet engine by Frank Whittle , the basis of the modern computer by Alan Turing and the World Wide Web by Tim Berners-Lee .
Scientific research and development remains important at UK universities, with many science parks being established to facilitate collaboration with industry. Between 2004 and 2008, the United Kingdom produced 7% of the world's scientific research and had an 8% share of scientific citations, the third and second highest in the world (after the United States and China respectively). The country had the fifth-highest output of scientific and technical articles in the world in 2016. Since 1901, 132 Britons have received a Nobel Prize , second only to the United States. Major scientific journals produced in the UK include Nature , the British Medical Journal and The Lancet .
Britain has been one of the largest recipients of research funding from the European Union. Over the period 2007-2013, the UK received EUR 8.8 billion out of a total of EUR 107 billion for research, development and innovation in EU Member States, associated countries and third countries. At the time, this represented the fourth largest proportion in the EU. The European Research Council awarded 79 projects in the UK in 2017, more than any other EU country.
Sports

Sport plays a significant role in the UK. In the individual sports, however, there are sometimes clear regional and social differences. In large parts of the English and Scottish lower social classes (“ working class ”), football is by far the most popular team sport, whereas in Wales and in middle and higher social classes (“ upper class ”) of England and Scotland, rugby union (15-a-side Rugby) is usually the number one team sport. In the traditional industrial cities of northern England, the variant of rugby league (thirteen rugby) is also very popular. Like rugby union, cricket is a more socially 'elitist' sport. These circumstances mostly have historical causes. In the English working-class areas of the big cities, for example, it was not possible to play rugby without lawns, whereas football only required a backyard. The upper class secondary schools all had grass pitches where rugby and cricket could be played. Over time, the sport in question also became a way of identifying with its class . Especially if you look at the ranks of spectators at a rugby union match or a football match, for example with the English national teams, you can see clear differences in the clientele today. Violence among and by fans has long been a huge problem in English football but has never been a factor in rugby .
Significant individual sports are athletics , fencing , darts , golf , motor sports and horse racing . The rulebook of many major sports developed in the United Kingdom. For example, England is considered the "motherland of football". In addition, e.g. tennis , squash , golf, boxing , rugby, cricket, snooker , billiards , badminton and curling .
The four parts of the country have separate national teams in most team sports. However, joint teams from all four "home nations" are sent to the Olympic Games (but not to the Commonwealth Games ). These formally start under the designation "Great Britain and Northern Ireland", but this is usually shortened to "Great Britain". Club championships are also held separately in most team sports; "British" championships are therefore rather rare. Winter sports are not widespread because, despite the location in the high northern latitudes, only a few regions get enough snow.
In addition to the football championships, the most well-known sporting events include the Wimbledon Championships (tennis), The Ashes (cricket), the Six Nations tournament (rugby union), the London Marathon (athletics), the Open Championship (golf) and the Grand Prix of Great Britain (Formula One), the Motorcycle Grand Prix , the World Speedway Championship Grand Prix of Great Britain , the Boat Race (rowing) and Royal Ascot (horse racing). In addition, London has hosted the Olympic Games three times (1908, 1948 and 2012).
public holidays
In the UK, bank holidays are the days when most businesses and non-essential services are closed, although some bank holidays see an increasing number of retail outlets (especially the larger ones) open. Trading restrictions apply on Sunday and Christmas Day in England and Wales and on New Year's Day and Christmas Day in Scotland.
The United Kingdom does not currently have an official national holiday . As a partial substitute, the monarch's birthday is commemorated as a central national holiday - under Queen Elizabeth II , this day is celebrated as the Queen's Official Birthday (regardless of her actual birthday on April 21) on an annually re-determined date, usually in late May or early June . However, this day is also celebrated in the other Commonwealth Realms , whose head of state is Elizabeth II (sometimes with a different date), and is therefore not exclusively British and, due to its annually changing date, not a real national fixed day. Especially in recent years there have been repeated efforts to make Britain Day or UK Day a fixed date for the national holiday.
When it comes to public holidays in the UK, there are regional differences between the four parts of the country.
| Holiday ( German ) | Holiday ( English ) | date | Valid | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| England | Northern Ireland | Scotland | Wales | |||
| New Year | New Year's Day | January 1st | • 1 | • | • 2nd | • 1 |
| January 2nd | • 1 | |||||
| Saint Patrick's Day | Saint Patrick's Day | 17. March | • 1 | |||
| Good Friday | good friday | Easter Sunday − 2d | • | • | • | • |
| easter monday | Easter Monday | Easter Sunday + 1d | • | • | • | |
| Early May Bank Holiday | Early May Bank Holiday | First Monday in May | • | • | • | • |
| Spring Bank Holiday | Spring Bank Holiday | Last Monday in May | • | • | • | • |
| Battle of the Boyne | Battle of the Boyne | July 12 | • 1 | |||
| August Bank Holiday | August Bank Holiday | First Monday in August | • | |||
| Last Monday in August | • | • | ||||
| 1st Christmas Holiday | Christmas Day | 25 December | • 1 | • 1 | • 1 | • 1 |
| 2nd Christmas Day | Boxing Day | December 26th | • 2nd | • 2nd | • 2nd | • 2nd |
1 If the public holiday falls on a weekend, it will be made up for on the following Monday.
2 If the public holiday falls on a weekend, the following Tuesday is a work-free day.
See also
- Royal Mail (national postal service)
literature
- Johann N. Schmidt : Britain 1945–2010. Culture, politics, society (= Kröner's pocket edition. Volume 305). Kröner, Stuttgart 2011, ISBN 978-3-520-30501-5 .
- Frank Welsh, The Four Nations: A History of the United Kingdom. Yale University, New Haven 2002, ISBN 0-300-09374-8 .
- Hans box Diek, Karl Rohe, Angelika Volle (ed.): Great Britain: history, politics, economy, society. 2nd, updated and expanded edition. Campus, Frankfurt/New York 1999, ISBN 3-593-36193-0 .
- Jim Bulpitt: Territory and Power in the United Kingdom: An Interpretation. Manchester University, Manchester 1983, ISBN 0-7190-0937-5 .
web links
|
More content in Wikipedia
's sister projects:
|
||
|
|
Commons | – Media content (category) |
|
|
Wiktionary | – Dictionary entries |
|
|
Wikiquote | – Quotations |
|
|
wikisource | – Sources and full texts |
|
|
Wikivoyage | - Travel Guide |
- Welcome to GOV.UK - UK Government Portal
- The home of the Royal Family (English; JavaScript and cookies required)
- Statistics - UK Statistical Office
- Search for date - UK Government's public data search engine
- Queen and the Church of England at www.royal.uk (English; JavaScript and cookies required)
- Country profile of the Federal Statistical Office
- UK information in the CIA Factbook
- Database of published literature on the social, political and economic situation in the United Kingdom
- Neville Wylie , Sacha Zala , Kaspar von Gruyeres , Beat Kümin : Great Britain. In: Historical Lexicon of Switzerland . January 11, 2018 .
itemizations
- ↑ The UK Government signed the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages in 2000 and ratified it in 2001 in respect of Welsh in Wales, Scots and Gaelic in Scotland and Ulster Scots and Irish in Northern Ireland. Manx and Cornish were subsequently added. European Charter for regional or minority languages ( Memento of 7 June 2011 at the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Note: formally a constitutional monarchy .
- ↑ CIA World Factbook : United Kingdom (land and sea area).
- ↑ Eurostat : United Kingdom.
- ^ Population, total. In: World Economic Outlook Database. World Bank , 2020, accessed April 19, 2021 (English).
- ↑ Population growth (annual %). In: World Economic Outlook Database. World Bank , 2020, accessed April 19, 2021 (English).
- ↑ World Economic Outlook Database April 2021. In: World Economic Outlook Database. International Monetary Fund , 2021, retrieved 20 June 2021 (English).
- ↑ Table: Human Development Index and its components . In: United Nations Development Program (ed.): Human Development Report 2020 . United Nations Development Programme, New York, p. 343 ( undp.org [PDF]).
- ↑ a b population, total. In: World Economic Outlook Database. World Bank , 2020, accessed April 19, 2021 (English).
- ↑ www.eda.admin.ch , Federal Department of Foreign Affairs.
- ↑ Population estimates for the UK, England and Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland: mid-2017. Retrieved July 26, 2018.
- ↑ a b United Kingdom: Countries and Major Urban Areas.
- ↑ Met Office climate and weather statistics ( Memento of 14 December 2005 at the Internet Archive ) .
- ^ a b UK Climate Change Risk Assessment 2017.
- ↑ J.-F. Bastin et al.: Understanding climate change from a global analysis of city analogues. In: PLoSOne. No. 14(7), 2019, e0217592. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0217592 .
- ↑ Nathalie Schaller et al. (2016). Human influence on climate in the 2014 Southern England winter floods and their impacts. Nature Climate Change , 6(6), 627. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate2927 .
- ↑ UK Population Estimates 1851 to 2014 – Office for National Statistics. Retrieved July 10, 2017 .
- ↑ What Were the Largest Cities Throughout History? In: ThoughtCo . ( thoughtco.com [accessed 10 July 2017]).
- ^ "BBC News - Census shows 'highest' Scottish population ever" , accessed 17 March 2017.
- ↑ ONS Overview of the UK population: February 2016 , accessed 17 March 2017.
- ↑ Geography - Census Geography ( Memento of 4 June 2011 at the Internet Archive )
- ↑ National Population Projections 2012 , accessed May 14, 2015.
- ^ "Pew Research Center - Origins and Destinations of the World's Migrants, from 1990-2015" → Source : United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs-Population Division (numbers are rounded). ( page no longer available , search web archives ) Retrieved 4 March 2017.
- ↑ ONS Guidance and Methodology - "Ethnic group" , accessed 7 March 2017.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h "ONS 2011 Census: Ethnic group, local authorities in the United Kingdom" , accessed 8 March 2017.
- ↑ "Movement and settlement in the UK" , accessed 7 March 2017.
- ^ "ONS - What are migration levels like in your area?" , accessed 10 March 2017.
- ↑ 2011 Census: Leicester 'most ethnically diverse' in region . In: BBC News . 12 December 2012 ( bbc.com [Accessed 10 July 2017]).
- ↑ "Black Britons - The next generation" , accessed 8 March 2017.
- ^ "British Indians: a remarkable story of success" , accessed March 8, 2017.
- ^ "ONS - DC2201EW - Ethnic group and religion" , accessed 8 March 2017.
- ↑ a b "The diverse origins of Britain's Muslims" , accessed 8 March 2017.
- ^ "The Chinese in Britain: personal tales of a journey to a new land" , additional text.
- ↑ Most immigrants to the UK now come from China, figures show. Retrieved March 10, 2017.
- ↑ Dale Farm: Who are the UK's travellers? Retrieved March 10, 2017.
- ↑ "How Britain and Poland came to be intertwined" , accessed 10 March 2017.
- ^ "Why Poles love coming to Britain" , accessed 10 March 2017.
- ↑ Migration Report 2017. (PDF) UN, accessed 30 September 2018 (English).
- ^ a b Educating your child at home. In: www.gov.uk. Retrieved April 11, 2021 (English).
- ↑ a b Culture and Education. Retrieved July 10, 2017 .
- ↑ PISA study – Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development. Retrieved April 14, 2018 (English).
- ^ Source: UN World Population Prospects - Population Division - United Nations. Retrieved July 15, 2017 .
- ↑ Federal Agency for Civic Education (bpb): Health policy in Great Britain. Retrieved July 10, 2017 .
- ↑ World Population Prospects - Population Division - United Nations. Retrieved July 10, 2017 .
- ↑ Census reveals decline of Christianity and rise in foreign born to one in eight , guardian.co.uk, 11 December 2012, accessed 13 January 2013.
- ↑ Laure Chamarel: Des Églises noires made in England . In: L'Actualité religieuse dans le monde , vol. 1983, issue 8, pp. 6–8.
- ^ "Religion Data from the 2011 Census" , accessed April 26, 2016.
- ↑ Brexit - but without Cameron. result of the referendum. In: tagesschau.de. Tagesschau (ARD) , June 24, 2016, retrieved June 24, 2016 .
- ↑ Entering the UK: EU citizens need a passport. September 30, 2021, retrieved October 2, 2021 .
- ↑ Domestic Policy. Retrieved July 10, 2017 .
- ↑ Dolf Sternberger, Bernhard Vogel, Dieter Nohlen, Klaus Landfried (eds.): The election of parliaments and other state bodies. Volume 1: Europe. De Gruyter, Berlin 1969, ISBN 978-3-11-001157-9 , p. 620.
- ^ a b c Mart Martin: The Almanac of Women and Minorities in World Politics. Westview Press Boul396der, Colorado, 2000, p. 396.
- ↑ Caroline Daley, Melanie Nolan (eds.): Suffrage and Beyond. International Feminist Perspectives. New York University Press New York 1994, pp. 349-350.
- ↑ Benjamin Isakhan, Stephen Stockwell: The Edinburgh Companion to the History of Democracy. Edinburgh University Press 2012, p. 343.
- ↑ June Hannam, Mitzi Auchterlonie, Katherine Holden: International Encyclopedia of Women's Suffrage. ABC-Clio, Santa Barbara, Denver, Oxford 2000, ISBN 1-57607-064-6 , p. 44.
- ↑ Dolf Sternberger , Bernhard Vogel , Dieter Nohlen , Klaus Landfried (eds.): The election of parliaments and other state bodies. Volume 1: Europe. De Gruyter, Berlin 1969, ISBN 978-3-11-001157-9 , p. 621.
- ↑ Krista Cowman, "Female Suffrage in Great Britain." In: Blanca Rodríguez-Ruiz, Ruth Rubio-Marín: The Struggle for Female Suffrage in Europe. Voting to Become Citizens. Koninklijke Brill NV, Leiden and Boston 2012, ISBN 978-90-04-22425-4 , pp. 273–288, p. 273.
- ↑ Walter Bagehot, The English Constitution. Section III.2. Quote: To state the matter shortly, the sovereign has, under a constitutional monarchy such as ours, three rights-the right to be consulted, the right to encourage, the right to warn. And a king of great sense and sagacity would want no others. He would find that his having no others would enable him to use these with singular effect. gutenberg.org.
- ↑ Audiences | The Royal Family In: royal.uk , accessed 13 February 2019.
- ↑ Fragile States Index: Global Data. Fund for Peace , 2020, accessed 19 April 2021 (English).
- ↑ The Economist Intelligence Unit's Democracy Index. The Economist Intelligence Unit, accessed April 19, 2021 .
- ↑ Countries and Territories. Freedom House , 2020, accessed April 19, 2021 (English).
- ↑ 2021 World Press Freedom Index. Reporters Without Borders , 2021, accessed 20 June 2021 (English).
- ↑ Transparency International (ed.): Corruption Perceptions Index . Transparency International, Berlin 2021, ISBN 978-3-96076-157-0 (English, transparencycdn.org [PDF]).
- ↑ a b GFB, United Kingdom Military Strength Globalfirepower, last seen 24 July 2017.
- ↑ Statista. Countries with the highest military spending in 2014 Statista.com last seen on June 24, 2016.
- ↑ FAZ.net July 30, 2017: Military power on the way to the sidelines .
- ↑ GLOBAL MILITIZATION INDEX 2018. (PDF) Max M. Mutschler, Marius Bales \ BICC, accessed 10 February 2019 .
- ↑ Countries Ranked by Military Strength (2018) Globalfirepower, accessed 10 February 2019.
- ↑ Ewen MacAskill Defense correspondent: HMS Queen Elizabeth aircraft carrier to take to the seas . In: The Guardian . 26 June 2017, ISSN 0261-3077 ( theguardian.com [accessed 13 July 2017]).
- ↑ Laws Against Terror ( Memento of 27 September 2007 at the Internet Archive ) In: cafebabel.com .
- ↑ UK: Detention Policy Impedes Effective Counter-Terrorism - Foreign Citizens Being Detained Unrestrictedly and in Contempt ( Memento of 26 June 2004 at the Internet Archive ) In: hrw.org .
- ↑ AI calls for systematic investigation of all allegations of torture and ill-treatment by an independent body - Amnesty International. (No longer available online.) In: amnesty.de. September 14, 2003, archived from the original on December 23, 2014 ; retrieved 22 February 2015 .
- ↑ " Theresa May defends UK ties with Saudi Arabia ". BBC News. 4 April 2017.
- ↑ The bright side of Brexit? A US-UK trade deal . In: POLITICO . 23 June 2016 ( politico.eu [accessed 13 July 2017]).
- ↑ Foreign Policy. Retrieved July 10, 2017 .
- ↑ Helmut Weber: Law and Jurisdiction. In: Hans Kastendiek, Karl Rohe, Angelika Volle (ed.): Great Britain: history, politics, economy, society. 2nd, updated and expanded edition. Campus, Frankfurt/New York 1999, ISBN 3-593-36193-0 , pp. 178-193; here: p. 178 .
- ↑ Crime in England and Wales: year ending Dec 2016 .
- ↑ Michael Tony , Why Crime Rates Are Falling Throughout the Western World . In: Crime & Justice . tape 43 , no. 1 , 2014, p. 1–63 , doi : 10.1086/678181 (English, alternative full-text access: scholarship.law.umn.edu ).
- ↑ Michael Tony , Why Crime Rates Are Falling Throughout the Western World . In: Crime & Justice . tape 43 , no. 1 , 2014, p. 6 , doi : 10.1086/678181 (English, alternative full-text access: scholarship.law.umn.edu ).
- ↑ Crime in England and Wales: year ending June 2019 . Figures are from Table 2a: Crime Survey for England and Wales (CSEW) incidence rates and numbers of incidents for year ending June 2019 and percentage change , accessed 1 December 2019.
- ↑ United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime: Global Study on Homicide. Booklet 1. Executive Summary . Vienna 2019, p. 7 (English, unodc.org ).
- ↑ United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime: Global Study on Homicide. Retrieved January 5, 2020 (English).
- ↑ "The UK has three legal systems, operating in England and Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland" , on direct.gov.uk .
- ↑ The Treaty (act) of the Union of Parliament 1706. Scottish History Online, accessed 10 January 2019 .
- ↑ UK Supreme Court judges sworn in BBC News .
- ↑ Constitutional reform: A Supreme Court for the United Kingdom. ( Memento of 5 February 2009 at Internet Archive ) (PDF). Department for Constitutional Affairs.
- ^ Great Britain: Gross domestic product (GDP) in current prices from 2004 to 2015 (in billion US dollars) , last seen on June 12, 2016.
- ↑ IMF : World Economic Outlook Database, April 2009.
- ↑ Countries with highest Gross Domestic Product (GDP) , last seen June 12, 2016.
- ↑ Gross domestic product (GDP) per capita in PPS. Eurostat , 1 June 2016, retrieved 4 December 2016 .
- ↑ At a Glance: Global Competitiveness Index 2017-2018 Rankings . In: Global Competitiveness Index 2017-2018 . ( weforum.org [accessed 22 December 2017]).
- ↑ heritage.org .
- ↑ Home – Eurostat. Retrieved August 8, 2018 .
- ↑ Unemployment, youth total (% of total labor force ages 15-24) (modeled ILO estimate) | Data. Retrieved August 8, 2018 (US English).
- ↑ The World Factbook - Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved August 6, 2018 (English).
- ↑ Anders Clausager: Automobile industry 1945-2000: A key industry between boom and crisis . Editors: Stephanie Tilly, Florian Triebel. Oldenbourg, 2013, p. 205-230 .
- ↑ Richard Leslie: Power from Steam: A History of the Stationary Steam Engine . Cambridge University Press, 1993, ISBN 0-521-45834-X , pp. 244 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ ons.gov.uk (Office for National Statistics): Index of service , accessed 28 March 2017.
- ↑ UNWTO 2017. (PDF) World Tourism Organization, accessed 14 August 2018 .
- ↑ credit-suisse.com: Global Wealth Report.
- ↑ A million British households are now millionaires – even excluding their houses In: telegraph.co.uk .
- ↑ Roger Harrabin: Solar energy 'could provide 4% of UK electricity by 2020'. BBC News 24 March 2015, retrieved 26 March 2015 .
- ↑ Susanne Preuss, Marcus Theurer: Swabians fear British nuclear power plant Hinkley Point. faz.net, May 30, 2015, accessed May 30, 2015.
- ↑ Gerald Hosp: Britain's Other Deficit. In: NZZ, international edition, December 23, 2015, p. 9.
- ↑ a b "ukpublicrevenue" , accessed 14 February 2017.
- ↑ Government Statistics. Retrieved January 28, 2015 (English).
- ↑ Credit rating: Moody's revokes Great Britain's AAA status at zeit.de, February 22, 2013 (retrieved on February 23, 2013).
- ^ "UK government debt and deficit as reported to the European Commission: July to Sept 2016" , accessed 14 February 2017.
- ↑ Eurostat - Annual government debt. Retrieved September 28, 2019 .
- ↑ Budget balance. Retrieved August 28, 2019 .
- ↑ GDP by region. (PDF) Retrieved April 23, 2018 .
- ↑ GDP growth (annual %) | Data. Retrieved September 15, 2018 (American English).
- ↑ GDP (current US$) | Data. Retrieved July 10, 2017 (US English).
- ↑ GDP per capita (current US$) | Data. Retrieved September 15, 2018 (American English).
- ^ a b c Germany Trade and Invest GmbH: GTAI - economic data compact. (PDF) Retrieved 25 July 2017 .
- ↑ FAZ.net / Philip Plickert September 20, 2021: Gas crisis hits Britain to the core
- ↑ Global Rankings 2018 | Logistics Performance Index. Retrieved January 3, 2019 .
- ↑ Low emission zone website. Transport for London, retrieved October 6, 2009 .
- ↑ Global status report on road safety 2015. Retrieved 30 March 2018 (British English).
- ↑ UK newspaper circulation figures , The Times, 12 May 2006.
- ↑ Individuals using the Internet (% of population). World Bank , retrieved April 19, 2021 (English).
- ↑ An overview of the most important social media platforms in Great Britain. (No longer available online.) Social Media Switzerland, archived from the original on March 13, 2011 ; retrieved March 14, 2010 .
- ↑ Harry Potter becomes highest-grossing film franchise . In: The Guardian . London ( theguardian.com ).
- ↑ UK film - the vital statistics. ( Memento of 11 December 2011 at Internet Archive ) UK Film Council .
- ↑ ( page no longer available , search web archives: UK cinema annual admissions ) Cinema Exhibitor's Association .
- ↑ Dafydd Johnston: The literature of Wales . University of Wales Press, Cardiff, 2004, ISBN 0-7083-1265-9 .
- ↑ Anglo-Saxon literature.
- ↑ Hans Ulrich Seeber: English literary history. Metzlersche JB Verlagsb., 1993, ISBN 3-476-00911-4 .
- ↑ NF Blake: William Caxton and English Literary Culture. Hambledon Press, London 1991, ISBN 1-85285-051-5 .
- ↑ The Burns Encyclopedia.
- ↑ Herbert F. Tucker: A companion to victorian literature and culture. Blackwell, Malden, Mass. 2004, ISBN 0-631-20463-6 .
- ↑ Poets and poetry of the Great War.
- ↑ List of Nobel Laureates in Literature.
- ↑ Prehistoric Britain - Barrows, stone circles, henges, and such.
- ↑ Guy de La Bedoyere: The Buildings of Roman Britain . NPI Media Group, 2001, ISBN 0-7524-1906-4 .
- ↑ Anglo-Saxon architecture.
- ↑ Castles in England and Wales.
- ↑ Tudor architecture in England 1500-1575.
- ↑ Elizabethan architecture in England 1550-1625.
- ↑ Rudolf Wittkower: Palladio and English Palladianism . Thames & Hudson, 1983, ISBN 0-500-27296-4 .
- ↑ Lisa Jardine: On a Grander Scale: The Outstanding Life of Sir Christopher Wren . HarperCollins, New York 2003, ISBN 0-06-019974-1 .
- ↑ Georgian architecture.
- ↑ Gothic revival architecture.
- ↑ Victorian art and architecture.
- ↑ J. Gascoin: A reappraisal of the role of the universities in the Scientific Revolution. In: David C. Lindberg, Robert S. Westman (eds.): Reappraisals of the Scientific Revolution . Cambridge University Press, 1990, ISBN 0-521-34804-8 , p. 248.
- ↑ C Hatt: Scientists and Their Discoveries . Evans Brothers, London 2006, ISBN 0-237-53195-X , pp. 16, 30 and 46.
- ↑ Scientific and technical journal articles. Retrieved January 5, 2019 .
- ↑ Nobel Prize Winners By Country. Retrieved January 5, 2019 (English).
- ↑ How much research funding does the UK get from the EU and how does this compare with other countries? Royal Society, 23 November 2015, retrieved 13 June 2016 .
- ↑ Boost for hopes of post-Brexit co-operation as EU awards Britain more research grants than anywhere else. In: The Telegraph. September 6, 2017, retrieved September 19, 2017 .
- ↑ ERC Starting Grants 2017. (PDF) European Research Council, September 6, 2017, accessed September 19, 2017 .
- ↑ UK bank holidays. Retrieved January 13, 2019 (English).
Coordinates: 52° N , 0° W