1916
Portal history | Portal Biographies | Current events | Annual calendar | Daily item
◄ |
19th century |
20th century
| 21st century
◄ |
1880s |
1890s |
1900s |
1910s
| 1920s
| 1930s
| 1940s
| ►
◄◄ |
◄ |
1912 |
1913 |
1914 |
1915 |
1916
| 1917
| 1918
| 1919
| 1920
| ►
| ►►
Heads of State · Elections · necrology · Art Year · Literature Year · Music Year · Movie Year · sports year
| 1916 | |
|---|---|
|
The ten-month battle for Verdun ended without any significant shift in the course of the front. |
|
| The Battle of the Somme , with over a million killed, wounded and missing soldiers, the battle with the greatest losses in World War I, did not change the course of the front. | The Arab revolt against the Ottoman Empire begins in the Middle East . |
| The Mexican expedition under General John J. Pershing begins in the USA . | |
| The Austrian Emperor Franz Joseph I dies. | |
| 1916 in other calendars | |
| Armenian calendar | 1364/65 (turn of the year July) |
| Ethiopian calendar | 1908/09 (September 10-11) |
| Baha'i calendar | 72/73 (March 20/21) |
| Bengali solar calendar | 1321/22 (beginning of April 14th or 15th) |
| Buddhist calendar | 2459/60 (southern Buddhism); 2458/59 (alternative calculation according to Buddha's Parinirvana ) |
| Chinese calendar | 76th (77th) cycle
Year of the Fire Dragon丙辰 ( since February 14th , before that Wood Bunny乙卯) |
| Chuch'e ideology (North Korea) | Chuch'e 5 |
| Chula Sakarat (Siam, Myanmar) / Dai calendar (Vietnam) | 1278/79 (turn of the year April) |
| Dangun era (Korea) | 4249/50 (October 2/3) |
| Iranian calendar | 1294/95 (around March 21) |
| Islamic calendar | 1334/35 (October 27-28) |
| Japanese calendar |
Taishō 5 (
大 正 元年); Koki 2576 |
| Jewish calendar | 5676/77 (September 27-28) |
| Coptic Calendar | 1632/33 (September 10-11) |
| Malayalam calendar | 1091/92 |
| Minguo calendar (China) | Year 5 of the Republic |
| Rumi Calendar (Ottoman Empire) | 1331/32 (March 1) |
| Seleucid era | Babylon: 2226/27 (turn of the year April)
Syria: 2227/28 (turn of the year October) |
| Suriyakati Calendar (Thai Solar Calendar) | 2458/59 (April 1) |
| Tibetan calendar | 1662 |
| Vikram Sambat (Nepalese Calendar) | 1972/73 (April) |
events
Politics and world events
First World War
Political and diplomatic developments
- January 24th: A German-Afghan friendship and trade treaty ensures that Afghanistan will recognize its sovereignty .
- January 26: In the House of Commons one is conscription law adopted. It initially applies to all single men between the ages of 18 and 41.
- February 4th: The Austrian Emperor Franz Joseph I donates the War Cross for civil merit in four classes.
- February 22nd: With the House-Gray Memorandum , Edward Mandell House , US President Woodrow Wilson's representative to the Entente and British Foreign Secretary Edward Gray conclude a secret agreement on the entry of the United States into the First World War .
- March 9: After Prime Minister Afonso Costa gave the order in February to confiscate all German merchant ships in Portuguese waters, the German Empire declares war on Portugal . On March 15, Austria-Hungary follows with the declaration of war.
- March 12: At the third Chantilly conference in the French town of the same name , further strategic plans of the Allies are discussed.
- March 16: A grand coalition government is formed in Portugal due to the country's entry into the First World War . António José de Almeida will succeed Afonso Costa as head of government, but he will remain finance minister.
- May 16: In the secret Sykes-Picot Agreement limits the UK and France their colonial spheres of influence in the Middle East for the period after the collapse of the Ottoman Empire in World War I from. The agreement negotiated by François Georges-Picot and Mark Sykes contradicts the Hussein-McMahon correspondence , in which Sir Henry McMahon , British High Commissioner in Egypt , the leader of the Hejaz , Hussein ibn Ali , Sherif of Mecca, the Arab independence in the case of a successful Arab uprising , albeit in very vague formulations.
- June 18: After a vote of no confidence over ongoing military failures, Italian Prime Minister Antonio Salandra resigns . He is succeeded by his 78-year-old party colleague Paolo Boselli after two others have refused office.
- June 22: Greek Prime Minister Stephanos Skouloudis resigns. After him come in quick succession Alexandros Zaimis , Nikolaos Kalogeropoulos and, on October 10th, Spyridon Lambros . The government installed by Constantine I in Athens, however, only controls the south of the divided country . A republican counter-government under Eleftherios Venizelos is established in Thessaloniki .
- July 6th: Liberal David Lloyd George succeeds Herbert Kitchener, who died a month earlier in the sinking of HMS Hampshire, as British Secretary of War.
- August 28: Italy declares war on the German Reich.
- August 29th: Erich von Falkenhayn is replaced as Chief of the Supreme Army Command by Paul von Hindenburg and Erich Ludendorff . Two days later they presented the Hindenburg Plan , an extensive list of demands to expand arms production.
- October 21: The Austrian Prime Minister Karl Graf von Stürgkh is murdered by the Social Democrat Friedrich Adler in the dining room of the Vienna Hotel Meissl & Schadn .
- October 28: Ernest von Koerber is appointed by Emperor Franz Joseph I to succeed Stürgkh as Austrian Prime Minister. The Koerber II Ministry is sworn in on October 31 .
- The census of Jews in the German army takes place on November 1st . The decree of the Prussian War Minister Adolf Wild von Hohenborn of October 11th reacts to the anti-Semitism widespread in the German officer's corps and the propaganda intensified by anti-Semitic associations, parties and the media that Jews are " shirkers " who use all kinds of excuses to join the armed forces withdrawn and freed from it disproportionately often.
- November 5th: The Central Powers proclaim the reign of Poland in the Warsaw Royal Castle on the territory of the Russian province of Vistula - without a king and without a more precise definition of the borders. The anti-German movement Narodowa Demokracja (National Democracy), which has its stronghold in the province of Poznan and whose leader Roman Dmowski is in Paris, continues to reject any cooperation with the Central Powers.
- November 11th: The Czechoslovak National Committee is established. The task of the organization is to prepare for the takeover and draft a constitution in Czechoslovakia . The founding members include Edvard Beneš , Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk and Milan Rastislav Štefánik .
- November 15: The fourth Chantilly Conference deals with strategic planning for the war year 1917.
- November 21: The Austrian Emperor Franz Joseph I dies of pneumonia. His successor is his nephew Karl I.
- December 1: The Office for People's Nutrition , which was still decided under the Stürgkh Ministry , begins its work in Austria-Hungary.
- December 5: Herbert Henry Asquith resigns as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom . Two days later, David Lloyd George succeeds him as leader of the coalition government with the Conservatives. Asquith's supporters go into opposition, so that the Liberal Party is divided. The new Prime Minister pursues a war policy aimed at a complete defeat of the German Reich.
- December 13: Ernest von Koerber , who does not have a good relationship with Emperor Karl I, resigns from his position as Austrian Prime Minister.
- December 20: Heinrich Clam-Martinic is appointed as the new Austrian Prime Minister.
- December 30th: The Entente rejects a peace offer from the Central Powers .
"Home front"
- The Internationale Gruppe around Rosa Luxemburg , Franz Mehring and Karl Liebknecht is organized nationwide in Germany . On January 1, she adopts the guidelines on the tasks of international social democracy , written by Rosa Luxemburg while she was in custody, as her program. On January 27, the first of the so-called illegal Spartacus letters , which implements the group’s goals, appears. That is why the vernacular gives the group the name Spartacus , so that it is now called itself the Spartacus group .
- January 12: Karl Liebknecht is expelled from the SPD . Otto Rühle then resigned himself from the parliamentary group out of solidarity.
- March 24th: The SPD chairman Hugo Haase speaks surprisingly in the German Reichstag against the war and the acceptance of the note budget, which the SPD parliamentary group wanted to accept. He and 17 other MPs are expelled from the SPD parliamentary group and forced to resign as party leader. The excluded MPs form the Social Democratic Working Group .
- May 1: Karl Liebknecht speaks at an illegal anti-war rally in Berlin on Potsdamer Platz and is arrested. Thereupon spontaneous solidarity strikes with around 50,000 participants.
- July 1: Propaganda in the First World War : The 1916 war exhibition in Vienna's Prater opens.
- August 23: The arrested Karl Liebknecht is sentenced to four years and one month in prison for high treason .
- November / December: The so-called turnip winter begins.
- December 6th: In the German Reich, the law on patriotic auxiliary service comes into force, according to which men between the ages of 17 and 60 who were not drafted into the army or who did not work in an agricultural or forestry business before 1916 Be obliged to work in the armaments industry or in an operation essential to the war effort.
Western front

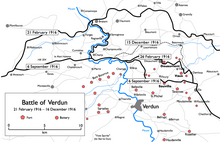
- February 21: The Battle of Verdun begins with a shell launch by the 38 cm German naval gun Langer Max on Verdun , which is in the Warphémont forest and is supposed to destroy a bridge over the Meuse in vain . After that, the 1220 German guns of all calibres opened fire on the French positions and the hinterland at the same time. For the first time, the Germans used twelve tethered balloons in a coordinated manner. The field airmen provide information for battlefield reconnaissance .
- February 21 to December 18: Over 700,000 German and French soldiers are killed or wounded in the Battle of Verdun . At the end of the battle, the course of the front on the western front is almost unchanged.
- February 25: German troops capture Fort Douaumont .
- February 26th: General Philippe Pétain becomes the new French commander in the front line around Verdun.
- February 27th: The French captain Charles de Gaulle becomes a German prisoner of war.
- April 1: Nurse Gabrielle Petit is executed for espionage for the British secret service in the German-occupied General Government of Belgium .
- April 16: The French army expeditionary force requested by France lands in Marseille.
- April 18: The Escadrille La Fayette of the French Air Force, consisting mainly of US war volunteers, is founded.
- April 28: Robert Nivelle , a supporter of the offensive à outrance , becomes the new French commander around Verdun.
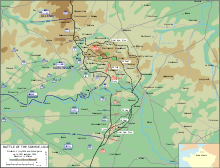
- June 24th to June 30th: British units prepare for the Battle of the Somme with seven days of barrage .
- July 1: The Lochnagar mine is blown up and the Battle of the Somme begins, which will be the battle with the greatest losses in the First World War . July 1st goes down as the most loss-making day in British military history. Since the British are convinced that the German positions have been destroyed by the immense gunfire, the attacking troops are allowed to advance in dense ranks at marching speed. There, however, they get caught in unexpectedly strong machine-gun fire and suffer heavy losses. Only in a few places do they succeed in capturing the foremost German trenches, which, however, have to be abandoned again after a short time.
- July 3: British units conquer Mametz and Fricourt .
- July 6th to 14th: The Trones forest near Longueval changes hands 18 times.
- July 14th: British units break into German positions deeply.
- July 19-21: The Battle of Fromelles ends in disaster for the First Australian Imperial Force.
- September 15: The British use tanks in the war for the first time in the Battle of the Somme .
- October 24th: Fort Douaumont , hotly contested in the Battle of Verdun , is retaken by the French.
- November 18: The Battle of the Somme ends. About 1.2 million British, German and French soldiers were killed or wounded in the battle. The battle brings the Allies a small gain in terrain.
Mountain war between Italy and Austria-Hungary
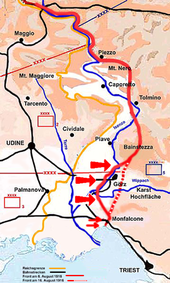
- March 11 to March 16: The Fifth Battle of the Isonzo will only take place at the request of the Entente . France and Great Britain wanted to relieve their soldiers in the Battle of Verdun . The losses on both sides are around 2,000 men after five days.
- May 15 to June 25: With the South Tyrol offensive , Austria-Hungary tries to advance into Pavia and Venice , encircle the Italian forces east of the Piave and thus neutralize or at least relieve the heavily pressed Isonzo front. The latter succeeds, even if only temporarily. On June 18, the order to withdraw is issued. The reason for this is the Brusilov offensive started by Russia on June 4th , the catastrophic effects of which on the Austro-Hungarian eastern front can only be absorbed with troops from the South Tyrolean region. From the night of June 24th to June 25th, the front was therefore moved back to positions that were easier to defend by a strip of about three to four kilometers.
- June 26th to July 8th: The Italian counter-offensive brings no significant gains in terrain.
- August 5th: Italian units carry out mock attacks south of Gorizia , near Selz and Monfalcone .
- August 6 to August 16: During the Sixth Isonzo Battle , the first gas attack by Austro-Hungarian troops takes place. The poison gas is released into the opposing positions in the "blowing process" from pressure bottles using the wind conditions. The battle ends with the capture of the city of Gorizia by Italian units. However, it is not possible to advance beyond the straightened front and take Trieste as planned .
- September 14th to September 18th: The Seventh Battle of the Isonzo ends after a few days without any significant success for the Italian attackers.
- October 9th to October 12th: In the Eighth Battle of the Isonzo, the attacking Italians achieve a minimal gain in terrain.
- October 31 to November 4: The ninth battle of the Isonzo brings the Austro-Hungarian army to the brink of collapse, but after the Italian units have hesitated too long, they can regroup and stabilize the front.
Eastern Front and Balkans
- January 5th: After the victorious Serbian campaign of the Central Powers and the Austro-Hungarian occupation of Serbia , the Austro-Hungarian campaign in Montenegro under Stephan Sarkotić von Lovćen begins .
- January 9: The last British troops have to evacuate the Turkish peninsula of Gallipoli . The British attempt to conquer the Dardanelles has failed.
- January 13th: Austrian troops reach the Montenegrin capital Cetinje . King Nikola goes into exile in Italy.
- January 23: The Austrians occupy Scutari .
- January 25: Montenegro , an ally of Serbia , has to surrender and signs an armistice. In the campaign, the country lost around 40% of its army and over 10% of its total population. This is followed by the Austro-Hungarian occupation of Montenegro from 1916 to 1918 .
- February 9th: Austrian troops occupy Tirana .
- February 26: Viktor Weber von Webenau becomes Governor General of occupied Montenegro.
- March 18: The battle of Lake Narach begins with a Russian offensive and ends with a Russian defeat at the end of March.
- June 4 to September 20: The Russian Brusilov offensive on the Eastern Front brings large territorial gains, but the high loss of life causes the morale of the Russian army to decline.
- July 3 to July 29: The Baranowitschi Offensive ends with a loss-making defeat of the Imperial Russian Army and an accompanying destabilization of Russia.
- August 27: Romania declares war on Austria-Hungary in the hope of increasing territory . The Romanian army made an advance to Transylvania under General Constantin Prezan , but came to a halt in front of Sibiu .
- September 1st: Bulgaria declares war on Romania. The next day, Bulgarian units march into Dobruja .
- September 6th: Bulgarian-German troops capture Tutrakan fortress .
- September 12: The Allies begin an offensive on the Salonika Front in the direction of Monastir .
- October 9: The Entente powers install a counter-government under Eleftherios Venizelos in Thessaloniki, which they occupy . Objective: overthrow the Greek king.
- November 17th: The Central Powers reach Little Wallachia .
- November 21: The Central Powers conquer Craiova .
- November 25th: The Greek counter-government declares war on the German Reich.
- November 29th: In the Romanian theater of war , the Central Powers start the attack on the capital Bucharest .
- December 1st to 6th: The Central Powers defeat Romania in the Battle of the Argesch , thus opening the way to Bucharest. As the Romanian troops retreat to the capital, they burn down the oil and grain fields near Ploieşti .
- December 7th: German troops capture the Romanian capital Bucharest . King Ferdinand I flees to Iași .
- The city of Auschwitz , which belongs to Austria-Hungary, built a barrack camp for the Saxons .
Ottoman Empire
- January 6th: The Battle of Sheikh Saad is the first of several attacks by the British Indian Army on the Mesopotamia Front that resulted in a breakthrough to the troops trapped in the city of Kut by the Ottoman Army under Halil Kut and Colmar von der Goltz under Charles Vere Ferrers Townshend as a goal. After heavy fighting, the British succeed in conquering the trenches on the left bank of the Tigris and capturing two cannons. But the right side of the river is held by the Ottoman troops. The British-Indian troops were not able to drive the Ottomans out of Sheikh Saad until January 9th . These withdraw to the wadi 16 kilometers away .
- January 9: The last British units leave the Gallipoli peninsula after the evacuation .
- January 10 to February 16: The Battle of Erzurum , a major winter offensive by the Imperial Russian Army under Nikolai Nikolayevich Yudenich during the Caucasus campaign ends with the capture of the city of Erzurum .
- January 13: In the battle of the Wadi, the Ottomans under Nureddin Pascha and Colmar von der Goltz achieve a tactical victory against the British-Indian troops.
- January 20: Enver Pascha replaces Nureddin Pascha with Halil Kut as Commander-in-Chief of the Ottoman Army on the Mesopotamia front , after he and Colmar von der Goltz have given a German command of the siege of Kut .
- January 21: In the battle of Hanna , the British-Indian troops again fail to end the siege of Kut .
- March 8: Fenton Aylmer fails in the Battle of Dujaila with another attempt to free the troops trapped in Kut.
- March 15 to June 30: Due to the beginning of the Arab revolt, the German Stotzingen mission is unsuccessfully canceled.
- April 29: After a five-month siege , the British army trapped in the Iraqi city of Kut , under General Townshend, has to surrender. More than 10,000 men are taken prisoner by the Ottoman Empire. The Ottoman troops then launch an offensive in the direction of Iran .
- June 5: The Arab revolt against the Ottoman rule on the Arabian Peninsula begins: Faisal , the son of the Grand Sherif of Mecca , declares the independence of the Arabs and, supported by the British TE Lawrence, begins guerrilla actions against the Ottoman Empire , among others in Transjordan . The insurgents conquered Mecca on June 11th. However, the uprising then came to a standstill due to the stubborn resistance of individual Turkish garrisons, especially the troops of Ömer Fahrettin Pasha stationed in Medina .
- June: With the support of the German Asia Corps under Friedrich Kress von Kressenstein , the Ottoman Empire makes another unsuccessful attempt to advance to the Suez Canal on the Palestine front. Immediately afterwards, the British, under their Commander-in-Chief Archibald Murray, begin the gradual reconquest of the Sinai Peninsula and, after the Battle of Magdhaba on December 28, they can take Al-Arish .
- July 2: After defeating Russian units, the Ottoman army takes the Iranian city of Kermanshah .
- November 2: Hussein ibn Ali , Emir of the Hejaz and one of the leaders of the Arab revolt , has himself proclaimed King of Arabia by his supporters. Despite the Hussein-McMahon correspondence, Great Britain and France only recognize him as King of the Hejaz .
The war in the colonies
- January 9th: The blockade breaker Marie leaves Wilhelmshaven to supply the troops in German East Africa with clothing, medicine, ammunition, provisions and weapons.
- January: A large Allied force under South African leadership advances from several sides into German East Africa .
- February 15: After Carl Zimmermann and most of the German Schutztruppe went over to the neutral colony of Spanish Guinea / Río Muni and were disarmed there, the last fighting units of the German colony of Cameroon surrender to the Allies under Ernst von Raben . Zimmermann and his units were brought to Fernando Póo Island until the end of the war .
- After circumnavigating the Cape of Good Hope on March 4th, Marie reached the Sudi Bay in German East Africa unnoticed on March 16th .
- Iyasu V , Emperor of Ethiopia , attacks the Anglo-Egyptian South Sudan. There, German agents staged an uprising by Christian Africans and Muslim Darfuris, while pro-Turkish Senussi from Libya are supposed to advance through Egypt to Northern Sudan. However, Iyasu's venture failed at the outset, his clearly inferior Ethiopian troops were quickly defeated in May, while Anglo-Egyptian troops quickly and inexorably advanced into Addis Ababa .
- August: The Allies have conquered all important places in German East Africa except Dar es Salaam .
- September 4th: Allied troops occupy Dar es Salaam.
- September 27th: Faned by British agents, a revolution begins by the nobles of Shewa against the Ethiopian Emperor Iyasu V with the aim of putting Zauditu , the daughter of Menelik II on the throne.
- October 27: Zauditu's supporters decisively defeat Iyasu and his father in the Battle of Segale .
Sea and air war
- January 29th: The military airship LZ 79 drops bombs over Paris during the First World War . On the way back, the zeppelin was hit in the stern and had to make an emergency landing in German-occupied Belgium.
- February 8: The German submarine U 21 sinks the French armored cruiser Amiral Charner off Beirut.
- February 14: Twelve Austro-Hungarian planes bomb Milan . In return, the Italian Corpo Aeronautico Militare attacked the city of Ljubljana with Caproni bombers .
- February 26: The German submarine U 35 under the command of Lothar von Arnauld de la Perière sinks the French troop transport Provence II off Cape Matapan on the southern tip of the Greek peninsula of Peloponnese . Around 1,000 people are killed in the process.
- February 27: The British passenger steamer Maloja is sunk by a German submarine two miles off Dover , drowning 155 passengers and crew. The sinking of the Maloja is one of the greatest losses for the British shipping company P&O .
- February 29: An artillery battle between the British auxiliary cruiser Alcantara and the German auxiliary cruiser SMS Greif ends with the sinking of both ships. 264 men are killed.
- March 24th: When the steamship Sussex was torpedoed during World War I, it did not sink, but around fifty passengers were killed, including the composer Enrique Granados and the former tennis player Manliffe Francis Goodbody . Several US passengers are injured, prompting US President Woodrow Wilson to call for an end to unqualified submarine warfare on April 18 . The reaction of the German government is the so-called "Sussex pledge" of May 4th, with which the Americans are assured not to attack passenger ships in the future, not to sink merchant ships until weapons have definitely been identified on board and also for them Ensure the safety of passengers and crew.
- 24./25. April: The shelling of Lowestoft and Great Yarmouth is in the political context of the Irish Easter Rising . Through the combined air and sea operation of the Imperial Navy against the English east coast , parts of the British Grand Fleet are to be provided in order to turn the British-German balance of forces at sea, which is unfavorable for the German Empire, to the advantage of the Imperial Navy through a German victory. However, there are only minor fighting without any further consequences.
- May 31/1. June: The German deep-sea fleet and the British Grand Fleet meet in the Skagerrak . More than 8,500 sailors lost their lives in the Battle of the Skagerrak . The greatest naval battle of the First World War ends in a draw, the naval blockade of the Royal Navy remains in place.
- June 5: With the British Minister of War Lord Kitchener on board, the armored cruiser HMS Hampshire hits a mine in the North Atlantic and sinks.
- August 10: Oswald Boelcke is appointed commander of the newly established Prussian Jagdstaffel 2 . The squadron's fighter pilots include the young lieutenants Manfred von Richthofen and Erwin Böhme .
- November 6th: The British ocean liner Arabia is sunk by the German submarine UB 43 without warning off Cape Tenaro on the south coast of Greece, killing eleven people.
- November 21: The sinking of the British hospital ship HMHS Britannic by a German sea mine (or a torpedo) near Greece kills 30 people and injures 40.
Other events in Europe
- January 1: Camille Decoppet becomes President of Switzerland .
- April 1: Bulgaria replaces the previous Julian (Orthodox) calendar with the Gregorian calendar.
- April 24th: In front of the main post office in Dublin , Patrick Pearse reads out the Easter proclamation on behalf of a Provisional Irish Government , marking the start of the Easter Rising in Ireland . The uprising was bloodily suppressed by April 29th.
- April 30th: The German Reich and Austria-Hungary are the first countries in the world to introduce summer time to increase the number of hours of usable daylight. May 1st starts on April 30th at 11:00 p.m.
- December 17th jul. / December 30th, Greg. : The Russian traveling preacher and influential advisor to the tsarist family Grigori Rasputin is murdered. The main perpetrators are members of the Russian nobility such as Prince Felix Felixowitsch Jussupow and Dmitri Pawlowitsch Romanow as well as the right-wing extremist Duma deputy Vladimir Mitrofanowitsch Purishkewitsch .
America and the Caribbean
- March 14th: The United States sends an expeditionary army of 12,000 men under the command of John Pershing to Mexico to capture the rebel leader Pancho Villa , who on March 9th attacked the small garrison town of Columbus in the US state of New Mexico . By June, the US units succeeded in several skirmishes and skirmishes in decimating the Villistas involved in the attack on Columbus and subsequently operating in small units, but they did not manage to capture or kill Villa. The presence of American soldiers on Mexican territory not only increases Villa’s popularity there, but also creates an ongoing conflict with the Mexican government under Venustiano Carranza , who repeatedly calls on the US government to withdraw its armed forces. Armed clashes between Mexican and American armies with dead and wounded on both sides finally bring the two states to the brink of war. The US armed forces then withdraw a large part of their units, but remain present in Mexico.
- July 30: The Black Tom explosion of 1,000 tons of ammunition in Jersey City , probably caused by sabotage by German agents, kills up to seven people and damages the Statue of Liberty .
- August 4: The USA buys the Virgin Islands from Denmark as a naval base in the Caribbean for US $ 25 million .

- NOV 7: In a very tight decision of the Democratic incumbent wins Woodrow Wilson in the US presidential election over his Republican challenger Charles Evans Hughes , becoming confirmed for a second term.
China
Yuan Shikai , who only proclaimed the Empire of China in December of the previous year , wants to introduce a new calendar and proclaims year 5 of the republic to be Hongxian year 1 . In doing so, however, he encounters not only resistance from forces loyal to the republic, but also from the military. Since his support in the population is very weak, he postpones his official coronation again and again. On March 1st, the preparations will officially be stopped. The monarchy is abolished on March 22nd. The year Hongxian 1 will end on March 23rd and the Republican calendar will be reinstated. Yuan's reign as emperor only lasted 83 days.
With his death on June 6th, Yuan's presidency ends and former Vice President Li Yuanhong takes over. This appoints Duan Qirui as his prime minister and reinstates the national assembly and provisional constitution of the republic. Vice-president will be Cai E , one of the bitterest opponents of Yuan, who will, however, die in November at the age of 33. As a result of the uprisings during the brief imperial rule, the central government in Beijing lost control of large parts of the country. The army is quickly splintering into factions of warlords fighting each other, known as the Northern Militarists , and China is slipping into what has become known as the warlord era .
Other events in Asia
- February 3: In the presence of the Viceroy Lord Curzon , the courthouse of the newly established Patna High Court is opened. The High Court is the Supreme Court for the Province of Bihar and Orissa, formed in 1912 .
- October: The Ōkuma Shigenobu cabinet resigns because of the Ōura scandal . Terauchi Masatake becomes the new Prime Minister of Japan .
- November 3: Qatar under Emir Abdullah bin Jassim Al Thani becomes a British protective state after the last Ottoman troops left the country last year .
business
War economy
- January 15: The first journey of the Balkanzug from Berlin to Constantinople, replacement for the Orient Express , which has been discontinued since the beginning of the war , begins. A total of twelve railway administrations from Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria and the Ottoman Empire are involved in the Balkans move. The journey of the trains, which run twice a week, takes just under three days. The Balkan train quickly became popular and also used by prominent passengers, although because of the war it was not classified as a luxury train , but as a normal express train.
- May 22nd: The War Food Office is founded in the German Reich under President Adolf Tortilowicz von Batocki-Friebe . It is supposed to ensure the security of the people's food during the First World War. Nevertheless, at the end of the year, caused by the potato rot , among other things , there is a famine, the so-called turnip winter .
- November 24th: The Central European Sleeping Car and Dining Car Corporation is founded with the participation of Deutsche Bank , Dresdner Bank and other banks from Austria-Hungary . The aim is to limit the dominance of the Franco-Belgian Compagnie Internationale des Wagons-Lits ( CIWL ).
Patents
- February 29: The American civil engineer Arthur Hale receives a patent for the motorway junction he invented in the shape of a clover .
Business start-ups
- March 7th: The Bayerische Flugzeugwerke emerged from the flying machine works owned by Gustav Otto , which went bankrupt at the beginning of the year . The day is considered to be the official founding date of what would later become the Bayerische Motoren Werke ( BMW ).
- July 15: One month after the first B&W Seaplane they developed , William Edward Boeing and George Conrad Westervelt found the Pacific Aero Products Company in Seattle , which developed into the aircraft manufacturer The Boeing Company . The United States Navy will conduct a flight test beginning August 10th . The second machine will be completed in November.
- July 22nd: Under the name Der Kriegsbote , the first edition of the Allgemeine Zeitung appears in Windhoek , today Namibia's oldest daily newspaper and the only German-language daily newspaper in Africa.
- August 27: The first Russian rifle and machine gun factory is founded in Kovrov as a joint venture between the Petrograd industrialists WA Hippius and DL Lurie and the Danish entrepreneurs Karl Winter and Sören Jensen.
- September 6th: Clarence Saunders opens one of the first supermarkets in the world with its Piggly Wiggly Store .
- September 19: In truth, in Leipzig which is Dux automobile works AG founded; the manufacturer of small to medium-sized trucks and passenger cars emerges from the automotive division of Polyphon Musikwerke .
- November 19: The film company Goldwyn Picture Corporation is founded by Samuel Goldfish and his two partners Edgar and Archibald Selwyn in Fort Lee , New Jersey.
- Fiat in Turin founds the subsidiary Società Italiana Aviazione (SIA) to manufacture aircraft .
science and technology
Antarctic exploration
- March 16: The members of the Ross Sea Party , who have set up depots for the planned endurance expedition to the South Pole since September 15 of the previous year , return to their base camp. A man died of scurvy and exhaustion during the strenuous activity. When trying to reach Cape Evans on May 8th, two more members of the expedition went missing.
- April 8: The ice floe, on which the stranded members of the Endurance Expedition have been since the end of the previous year, breaks apart, which is why the lifeboats are launched the next day. On April 14th they reach the remote Elephant Island .
- April 24: Ernest Shackleton and five members of the endurance expedition in Antarctica set sail from Elephant Island in the James Caird lifeboat to organize aid for the crew who remained behind in South Georgia .
- May 10: After a crossing with heavy storms, the six men reach South Georgia and land in King Haakon Bay . However, the island is only populated on the north coast, which is why the expedition has to cross the unexplored interior of the island because the condition of the lifeboat no longer allows circumnavigation.
- May 20: After a 36-hour hike, Shackleton, Tom Crean and Frank Worsley arrive at the whaling town of Stromness . The next day, the remaining three men from King Haakon Bay are also rescued.
- May 22nd: The ship The Southern Sky to rescue the other members of the expedition leaves South Georgia, but encounters impenetrable pack ice off Elephant Island .
- June 10: A steamer made available by the Uruguayan government embarks on another rescue operation, but also has to give up because of the pack ice.
- August 30th: After another unsuccessful attempt, the Chilean steamer Yelcho finally succeeds in recovering all members of the expedition from Elephant Island.
- Only in September can the men turn to the rescue of the Ross Sea Party , which however does not succeed by the end of the year.
mathematics
- Hermann Weyl formulates Weyl's embedding problem for the first time .
Science and medicine
- February 1: The Danish astronomer Holger Thiele discovers the asteroid (1847) Stobbe .
- March 20: Albert Einstein publishes the article The basis of general relativity in the journal Annalen der Physik .
- Oskar Dressel succeeds in synthesizing the drug suramin . Suramin or suramin sodium is the first effective remedy for sleeping sickness .
- The American astronomer Edward Barnard discovers Barnard's arrow star .
Teaching and Research
- October 14: The Perm State University is founded as an offshoot of the University of Saint Petersburg in the Ural region.
- The Christian Yanjing University in Beijing is founded.
Others
- April: The SPAD S.VII , a single-seat biplane - fighter aircraft of the French manufacturer Société Pour L'Aviation et ses Dérivés , has its first flight .
- September 2nd: The German library is inaugurated in Leipzig .

- October 16: The longest railway line in the world, the Trans-Siberian Railway , is completed with the opening of the Khabarovsk bridge over the Amur .
- Daimler builds the first armored or tracked vehicles in Germany.
- The German physicist Wolfgang Gaede presents the diffusion pump with mercury as a propellant.
Culture
architecture
- Beginning of the construction of the Piesteritz industrial estate as a residential location for the Reich nitrogen plant in Wittenberg .
Movie
- MAY 15: The silent film The Floor Walker ( The shop supervisor ) by and starring Charlie Chaplin appears in the United States. It is Chaplin's first film for Mutual Films . The action climaxes in a turbulent chase on an escalator .
- The documentary and propaganda film The Battle of the Somme will open in British cinemas on August 21 . Around 20 million people - almost half of the population at the time - saw it within six weeks.
- September 5: The groundbreaking epic film Intolerance ( Intolerance ) of D. W. Griffith has its premiere. The work becomes the first flop in film history .
- October 2: The Pawnshop ( The Pawnshop ) , a comedy film directed by Charlie Chaplin, has its world premiere. The film established Chaplin's collaboration with Henry Bergman .
- DECEMBER 4: Charlie Chaplin's comedy The Rink ( The Rink ) comes into the American cinema.
literature
- November 18: In the US newspaper The Saturday Evening Post first appears Jeeves Takes Charge ( Jeeves takes the helm ) of PG Wodehouse , the short story that the first meeting of Bertie and Jeeves portrays.
- December 29: James Joyce published the autobiographical novel A Portrait of the Artist as a Young Man ( A Portrait of the Artist as a Young Man ). In the Bildungsroman he uses the stream of consciousness narrative technique for the thoughts of his alter ego Stephen Dedalus for the first time .
Music and theater
- January 14th: World premiere of the operetta Der Sterngucker by Franz Lehár in the Theater in der Josefstadt in Vienna.
- January 15: The world premiere of the Singspiel Das Dreimäderlhaus by Heinrich Berté takes place at the Raimund Theater in Vienna . The central figure of the operetta is the composer Franz Schubert , whose music Berté has based his score in a slightly edited form. The libretto was written by Alfred Maria Willner and Heinz Reichert . It is based on the novel Schwammerl by Dr. Rudolf Hans Bartsch .
- January 28th: The operetta Liebeszauber by Oscar Straus is premiered at the Bürgertheater in Vienna.

- February 5: Hugo Ball and Emmy Hennings found Cabaret Voltaire in Zurich , the birthplace of Dadaism . In June Ball will perform his first phonetic poem Gadji beri bimba here .
- March 3: African American Angelina Weld Grimké's play Rachel , one of the first plays to address racially motivated violence, premieres in Washington in response to the racist silent film The Birth of a Nation . Initially little noticed, it is now considered a pioneer of the Harlem Resistance .
- March 5: Eugen d'Albert's opera Die toten Augen with the libretto by Hans Heinz Ewers and Marc Henry premiered with great success at the Dresden Hofoper . The conductor is Fritz Reiner .
- March 28: The two one-act operas Der Ring des Polykrates and Violanta by Erich Wolfgang Korngold are premiered at the Court Opera in Munich. They are so successful that Korngold will become one of the most performed opera composers in Germany and Austria over the next few years.
- April 1: Die Schneider von Schönau , a comic opera in three acts by the Dutch composer Jan Brandts-Buys with the libretto by Ignaz Michael Welleminsky , is premiered at the Dresden Court Opera. The opera gave the composer international success.
- October 15: The world premiere of the opera Das Höllisch Gold by Julius Bittner takes place in Darmstadt. The opera becomes the composer's greatest success.
- December 2: The operetta Die Rose von Stambul by Leo Fall is premiered at the Theater an der Wien in Vienna. The work with the libretto by Julius Brammer and Alfred Grünwald belongs to the so-called silver operetta era .
- December 5th: The world premiere of the chamber opera Savitri by Gustav Holst takes place in Wellington Hall in London.
- September 6th: The musical comedy The Testament by Wilhelm Kienzl is premiered at the Vienna Volksoper . The libretto comes from the composer based on motifs by Peter Rosegger .
society
- February 11: Anarchist and peace activist Emma Goldman is arrested in New York after giving a lecture on birth control .
- July 1: Charles Vansant, 25 , was attacked and fatally injured by a shark while swimming near Beach Haven , Long Beach Island , New Jersey . There will be four more shark attacks on the New Jersey coastline by July 12th . Years later, the attacks inspired Peter Benchley to write the novel Jaws .
- September 13: For killing a circus trainer, the cow elephant Mary is hung to death after an animal trial in front of 2,500 onlookers in Erwin, Tennessee.
- October 16: Nurse Margaret Sanger opens the first US family planning and birth control clinic in Brownsville, New York City, along with her sister and a like-minded woman . Nine days later, the three women are arrested by the police.
- November 15: A tropical convalescent home is founded in Tübingen .
- November 18: The purchase of supposed whale meat from Norway triggers the Haakjöringsköd case , which is now considered a prime example of the legal principle of falsa demonstratio non nocet .
- The Volksgarten Nymphenburg near Munich, at its time the largest amusement park in Germany, will be demolished after 26 years.
Disasters
- January 14th: The dikes on the Dutch Zuider Sea break in a storm . Large areas are flooded.
- January 16: A large part of the Norwegian city of Bergen is destroyed by a major fire.
- March 5: The Spanish luxury liner Príncipe de Asturias hits a rock off Santos on the Brazilian coast and sinks in just five minutes. 445 passengers and crew members die. It is one of the greatest tragedies in the history of Spanish steam shipping.
- August 28: A series of tremors begins in the relatively sparsely populated Nantou district in China, which cost 71 lives by January 7, 1917. Agriculture and forestry are suffering severe damage.

- September 18: When the dam on the White Desse in the Jizera Mountains breaks , 62 people die. 33 houses have completely disappeared, 69 heavily damaged. 307 people become homeless and 1020 lose their jobs.
- November 3: 90 people died in the collision of the passenger ferry Connemara with a coal freighter off Greenore on the coast of County Louth, Ireland .
- December 13: A Nasschnee avalanche come on the Marmolada about 300 soldiers killed, who fought in the Italian-Austrian mountain warfare.
Minor accidents are listed in the sub-articles of Disaster .
nature and environment
- April 3: The Treysa meteorite hits a forest near Rommershausen .
- August 1: The Hawaii National Park in Hawaii is established.
- August 6: The area around Lassen Peak in northern California is declared Lassen Volcanic National Park . At this point the volcano is in a phase of increased volcanic activity.
- August 9: In the US state of New Mexico is Capulin Volcano National Monument established.
- August 25: The United States creates the National Park Service . It is his responsibility to make the managed places accessible and to preserve the natural landscape and fauna as well as historical monuments.
- August 29: On the island of Tasmania are the Mount Field National Park and the Freycinet National Park created protected areas for nature.
Sports
- APRIL 10: The Professional Golfers Association of America , the American Association of professional golfer , is founded in New York City.
- As part of the Campeonato Sudamericano 1916 from July 2nd to 17th, the South American Football Confederation CONMEBOL is founded on July 9th .
Nobel Prizes
| price | person | country | Reason for awarding the prize | image |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nobel Price for physics | not awarded | |||
| Nobel Prize in Chemistry | not awarded | |||
| Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine | not awarded | |||
| Nobel Prize in literature |
Verner von Heidenstam (1859–1940) |
|
"As a recognition of his importance as a spokesman for a new era in our beautiful literature" |

|
| Nobel Peace Prize | not awarded |
Born
January
- January 1: Murray Alexander Armstrong , Canadian ice hockey player and coach († 2010)
- January 1: Giacomo Neri , Italian football player and coach († 2010)
- January 3: Erik Alfred Ågren , Swedish boxer († 1985)
- January 3: Maxene Angelyn Andrews , American singer († 1995)
- January 3: Antonio Estévez , Venezuelan composer († 1988)
- January 3: Bernard Greenhouse , American cellist and music teacher († 2011)
- January 4: Slim Gaillard , American jazz singer († 1991)
- January 4: Jan Kotík , Czech painter († 2002)
- January 4th: Willy Mattes , Austrian composer, arranger and conductor († 2002)
- January 5: Dora Grabosch , German painter († 1994)
- January 7: Elena Ceaușescu , Romanian politician and wife Nicolae Ceaușescus († 1989)
- January 7: Fernando Sancho , Spanish actor († 1990)
- January 7th: Paul Keres , Estonian-Soviet chess player († 1975)
- January 9: Fernando Lamas , Argentine actor and film producer († 1982)
- January 10: Sune Bergström , Swedish biochemist and Nobel Prize winner († 2004)
- January 10: Josef Hindels , Austrian resistance fighter in the 3rd Reich († 1990)
- January 11: Zikmund Schul , German composer († 1944)
- January 12: Pieter Willem Botha , South African Prime Minister and President († 2006)
- January 12: Jay McShann , American blues musician († 2006)
- January 15: Maurice Bavaud , tried to shoot Adolf Hitler in 1938 († 1941)
- January 15: Christel Peters , German actress († 2009)
- January 15: Denise Soriano , French violinist († 2006)
- January 18: Horst Adamietz , German journalist († 1985)
- January 19: Harry Huskey , American mathematician and computer engineer († 2017)
- January 20: Johan Adolf Pengel , politician and Prime Minister of Suriname († 1970)
- January 21: Miquel Asins Arbó , Spanish composer, conductor and teacher († 1996)
- January 21: René Hernández , Cuban pianist and arranger († 1987)
- January 21: Pietro Rava , Italian football player and coach († 2006)
- January 22nd: Henri Dutilleux , French composer († 2013)
- January 22nd: Riza Lushta , Albanian football player († 1997)
- January 23: Marshall Clagett , American historian († 2005)
- January 23: David Douglas Duncan , American photographer († 2018)
- January 23: Olaf Andreas Gulbransson , architect and church builder († 1961)
- January 23: Paul B. Johnson junior , American politician († 1985)
- January 23: Airey Neave , British politician († 1979)
- January 24th: Rafael Caldera , Venezuelan politician and former president († 2009)
- January 25: Frederick Valentine Atkinson , British mathematician († 2002)
- January 25: Hans Coppi , member of the Rote Kapelle resistance group († 1942)
- January 26th: Hans Martin , German composer, choir director and organist († 2007)
- January 27: Helle Hirsch , German-American student and resistance fighter († 1937)
- January 30th: Benno Kusche , German opera singer († 2010)
- January 30: Hans Joachim Sewering , German doctor († 2010)
- January 31: Carlos Jiménez Mabarak , Mexican composer († 1994)
- January 31: Sangoulé Lamizana , Burkinabe politician († 2005)
- January 31: Frank Parker , American tennis player († 1997)
February
- February 2: Vincent Pasquale Biunno , American lawyer († 1991)
- February 3: Jean Margéot , Bishop of Port-Louis and Cardinal († 2009)
- February 5: Ugo Locatelli , Italian football player († 1993)
- February 5: Daniel Santos , Puerto Rican singer and composer († 1992)
- February 6: Clifford Griffith , American racing driver († 1996)
- February 7: Floyd K. Haskell , American politician († 1998)
- February 7th: Helmut Schubert , German soccer player († 1988)
- February 8: Al Coppage , American football player († 1992)
- February 8: Hans-Hugo Hartmann , German racing car driver († 1991)
- February 10: Ahiam Shoshany , French-Israeli sculptor († 2005)
- February 10: Edward R. Roybal , American politician († 2005)
- February 11: Wilhelm Koch-Hooge , German actor († 2004)
- February 12: Damián Iguacén Borau , Spanish bishop († 2020)
- February 12: Helmut Gröttrup , German engineer and inventor († 1981)
- February 13: Jagjit Singh Aurora , Indian Lieutenant General († 2005)
- February 13: Willi Bars , German soccer player († 2000)
- February 13: Ruth Geede , German writer († 2018)
- February 14: Hans-Wolrad Dölling , German General (†)
- February 14: Sally Gray , English film actress († 2006)
- February 14: C. William O'Neill , American politician († 1978)
- February 14: Oskar Wielgos , German chess problem composer († 1986)
- February 16: Karl Brunner , Swiss economist († 1989)
- February 16: Dương Văn Minh , South Vietnamese politician and general († 2001)
- February 16: Josef Rommerskirchen , German politician († 2010)
- February 17: Karl Wald , soccer referee considered the inventor of the penalty shootout in soccer († 2011)
- February 18: Maria Altmann , American entrepreneur and art collector († 2011)
- February 19: Eddie Arcaro , American jockey († 1997)
- February 20: Julius Juzeliūnas , Lithuanian composer and music teacher († 2001)
- February 22nd: Gertrud Burgsthaler-Schuster , Austrian opera singer († 2004)
- February 23: Franz Adis , German politician († 2005)
- February 23: George Abel , Canadian ice hockey player († 1996)
- February 24: Guglielmo Gabetto , Italian football player († 1949)
- February 25: Reinhard Bendix , American sociologist of German origin († 1991)
- February 26: Mordecai Seter , Israeli composer († 1994)
- February 28: Svend Asmussen , Danish jazz musician and actor († 2017)
- February 28: Wilhelm Heidel , Romanian field handball player († 2008)
- February 29: Dinah Shore , American singer, actress and golfer († 1994)
March
- March 1: Krystyna Feldman , Polish actress († 2007)
- March 2: Bernard Stevens , English composer and conductor († 1983)
- March 3: Paul Halmos , American mathematician of Hungarian origin († 2006)
- March 3: Benno Sterzenbach , German theater and film actor († 1985)
- March 4: Giorgio Bassani , Italian writer and publicist († 2000)
- March 4: Hans Jürgen Eysenck , German-British psychologist († 1997)
- March 4: Ernest Titterton , nuclear physicist († 1990)
- March 6: Hermann Axen , SED functionary and member of the Politburo of the SED Central Committee († 1992)
- March 6: Virginia Gregg , American actress († 1986)
- March 7: Theodor Bergmann , German agricultural scientist and author († 2017)
- March 8: George Sylvester "Red" Callender , American jazz bassist (double bass and tuba) († 1992)
- March 8: Peter Gingold , German resistance fighter († 2006)
- March 8: Yvon Petra , French tennis player († 1984)
- March 8: Robert Wolfgang Schnell , German writer († 1986)
- March 9: Jack Ferrante , American football player († 2006)
- March 9: Puey Ungphakorn , Thai economist, administrative specialist and university lecturer († 1999)
- March 10: Hans Drachsler , German politician († 1996)
- March 11: Erkki Aro , Finnish orienteer († 1993)
- March 11: Ferdy Mayne , German actor († 1998)
- March 11: Harold Wilson , British politician and Prime Minister († 1995)
- March 13: Jacque Fresco , American futurologist († 2017)
- March 13: Frank Licht , American politician († 1987)
- March 14: Ove Andersson , Swedish football player († 1983)
- March 15: Charley Brock , American football player († 1987)
- March 15: Gomikawa Jumpei , Japanese writer († 1995)
- March 15: Harry James , American trumpeter and band leader († 1983)
- March 15: Blas de Otero , Spanish lyric poet († 1979)
- March 16: Gerhard Ernst Erich Ahnfeldt , German draftsman and painter († 1964)
- March 16: Mercedes McCambridge , American actress († 2004)
- March 16: Benjamin A. Smith , American politician († 1991)
- March 18: Winton Dean , English musicologist († 2013)
- March 18: Louis Toebosch , Dutch composer and professor († 2009)
- March 20: Pierre Messmer , French politician († 2007)
- March 21: Ken Wharton , English Formula 1 racing driver († 1957)
- March 25: Nikolai Peiko , Russian composer († 1995)
- March 25: Jean Rogers , American actress († 1991)
- March 26: Christian Boehmer Anfinsen , American biochemist († 1995)
- March 26: James Gayfer , Canadian military bandmaster , clarinetist, organist and choir director, composer and music teacher († 1997)
- March 26: Sterling Hayden , American actor and author († 1986)
- March 28: Jess Willard , American country musician († 1959)
- March 29: Jacob Asher , British cameraman († 1991)
- March 29: Eugene McCarthy , American politician († 2005)
- March 30th: Carl Helmut Steckner , German painter, journalist and regional researcher († 2003)
April
- April 1: Otto Schulmeister , Austrian journalist, editor-in-chief († 2001)
- April 2: Oleg Lundstrem , Russian jazz musician († 2005)
- April 5: Gregory Peck , American actor († 2003)
- April 7: Robert Freitag , Austrian actor († 2010)
- April 9: Eladio Acosta Arteaga , Colombian religious and archbishop of the Archdiocese of Santa Fe de Antioquía († 2012)
- April 10: Bel Abbey , American Indian researcher and folklorist († 1992)
- April 10: Hans-Egon Hass , German lawyer, Germanist and university professor († 1969)
- April 11: Alberto Ginastera , Argentine composer († 1983)
- April 11: Hartwig Zürn , German prehistorian and state curator in Northern Württemberg († 2001)
- April 12: Robert Austrian , American bacteriologist, immunologist and physician († 2007)
- April 12: Movita Castaneda , American film actress († 2015)
- April 12: Russell Garcia , American composer and arranger († 2011)
- April 14: Henning von Arnim , German chief finance president († 1990)
- April 14: Paul Bürks , German actor, dubbing and radio play speaker († 1995)
- April 14: Pehr Edman , Swedish biochemist († 1977)
- April 17: Sirimavo Bandaranaike , Prime Minister of Sri Lanka († 2000)
- April 18: José Joaquín Trejos Fernández , Costa Rican politician († 2010)
- April 19: Bruno Chizzo , Italian football player († 1969)
- April 19: Gerhard Wendland , German pop singer († 1996)
- April 20: Phil Walters , American racing driver († 2000)
- April 21: George Arents , American racing driver († 1992)
- April 21: Eldon Rathburn , Canadian composer, pianist, organist and music teacher († 2008)
- April 22: Julian Edward George Asquith , British diplomat and colonial administrator († 2011)
- April 22: Yehudi Menuhin , American-British violinist and conductor († 1999)
- April 25: Luis Herrera de la Fuente , Mexican conductor and composer († 2014)
- April 25: Marco Tulio Maristany , Venezuelan singer († 1984)
- April 26: Werner Bischof , Swiss photographer († 1954)
- April 26: Morris L. West , Australian writer († 1999)
- April 27: Peter Keetman , German photographer († 2005)
- April 27: Jan Rychlík , Czech composer († 1964)
- April 28: Hildegard Grube-Loy , German watercolor painter († 2002)
- April 28: Ferruccio Lamborghini , car maker and father of the Lamborghini car brand († 1993)
- April 28: Ilsemarie Schnering , German actress († 1995)
- April 29: Lars Korvald , Norwegian politician and Minister of State († 2006)
- April 30: Otto Bertram , Air Force officer in the Third Reich and in the Bundeswehr († 1987)
- April 30: Claude Elwood Shannon , American mathematician († 2001)
May
- May 1: Glenn Ford , American actor († 2006)
- May 1: Rong Yiren , Chinese businessman, politician and ex-Vice President of China († 2005)
- May 5: Weli Muhadow , Turkmen composer († 2005)
- May 6: Robert Henry Dicke , American physicist and astrophysicist († 1997)
- May 7: Alejo Benedicto Gilligan , Argentine bishop († 2007)
- May 8: Chinmayananda , founder of the Chinmaya Mission († 1993)
- May 8: João Havelange , Brazilian football official († 2016)
- May 10: Milton Babbitt , American composer († 2011)
- May 10: Alfred Weidenmann , German author and director († 2000)
- May 11: Camilo José Cela , Spanish writer and Nobel Prize winner († 2002)
- May 13: Jack Anglin , American country singer († 1963)
- May 13: Margot Antillano , Venezuelan theater, television and film actress († 1975)
- May 14: Hermann Böhm , German motorcycle racer († 1983)
- May 14: Lance Dossor , British-Australian pianist and professor († 2005)
- May 14: Del Moore , American actor and comedian († 1970)
- May 15: Vera Gebuhr , Danish actress († 2014)
- May 16: Ephraim Katzir , Israeli scientist and politician († 2009)
- May 17th: Bele Bachem , German graphic artist, book illustrator and set designer († 2005)
- May 17: Lenka Reinerová , German-Czech writer and journalist († 2008)
- May 19: Blair Lee III. , American politician († 1985)
- May 20: Luise Ermisch , activist and candidate of the Politburo of the Central Committee of the SED († 2001)
- May 20: Carl Malsch , provost in Jerusalem, chief pastor in Hamburg († 2001)
- May 20: Trebisonda Valla , Italian athlete and Olympic champion († 2006)
- May 21: Erich Dittmann , German painter, graphic artist, draftsman († 1999)
- May 21: Martinus Osendarp , Dutch athlete and Olympian († 2002)
- May 21: Harold Robbins , American writer († 1997)
- May 21: Tan Siew Sin , Malaysian Minister of Finance († 1988)
- May 22: Gleason L. Archer , American classical scholar and Old Testament scholar († 2004)
- May 22: Gordon Binkerd , American composer and music teacher († 2003)
- May 22: Arno Peters , German historian, geographer and economist († 2002)
- May 22: Alfred Pfeifle , German tenor († 1986)
- May 22: Anna Teluren , German actress and theater director († 2018)
- May 23: Horst Krüger , German General († 1989)
- May 24th: Ottilie Graszl , Austrian table tennis player († 1993)
- May 26: Halil İnalcık , Turkish historian († 2016)
- May 26: Moondog , American composer († 1999)
- May 28: Walker Percy , American writer († 1990)
- May 28: Christa Siems , German folk actress († 1990)
- May 29: Simone Berteaut , French author († 1975)
- May 29: Arthur Seldon , British economist († 2005)
- May 30: Joseph William Kennedy , American physicist († 1957)
- May 31: Bernard Lewis , British-American publicist and historian († 2018)
June
- June 1: Jean Jérôme Hamer , Cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church († 1996)
- June 2: William R. Laird , American politician († 1974)
- June 3: Leslie Thorne , American racing car driver († 1993)
- June 4: Robert Francis Furchgott , American scientist and Nobel Prize winner († 2009)
- June 4: Gaylord Nelson , American politician († 2005)
- June 6: Hamani Diori , Nigerien President († 1989)
- June 6: Jack Miller , American politician and lawyer († 1994)
- June 8th: Luigi Comencini , Italian film director († 2007)
- June 8: Francis Crick , English physicist and biochemist († 2004)
- June 8: Adolph Hofner , American country musician († 2000)
- June 9: Jurij Brězan , Sorbian writer († 2006)
- June 9: Robert McNamara , American politician († 2009)
- June 10: Heinz Mäde , German painter († 2004)
- June 12: Georg Pfligersdorffer , Austrian classical philologist († 2005)
- June 13: Helmut Zahn , German chemist († 2004)
- June 14: Wilhelm Aduatz , Austrian architect († 1978)
- June 14: Heinz-Joachim Heydorn , German educator († 1974)
- June 14: Dorothy McGuire , American actress († 2001)
- June 14: Georg Henrik von Wright , Finnish philosopher († 2003)
- June 15: Gene Force , American racing driver († 1983)
- June 15: Walter Hellman , Swedish-American world champion in checkers († 1975)
- June 15: Horacio Salgán , Argentine orchestra leader († 2016)
- June 15: Herbert A. Simon , American social scientist and Nobel Prize winner († 2001)
- June 16: Ebenezer Ako-Adjei , Ghanaian politician, lawyer, publisher and journalist († 2002)
- June 16: Hank Luisetti , American basketball player († 2002)
- June 18: Gaston Allaire , Canadian musicologist and teacher, organist and pianist, composer († 2011)
- June 18: Jean Géraud André , French film architect and set designer († 1980)
- June 18: Julio César Turbay Ayala , Colombian politician and president († 2005)
- June 21: Anthony J. Armentano , American politician († 1987)
- June 21: John Ngu Foncha , Cameroonian politician († 1999)
- June 21: Herbert Friedman , American physicist († 2000)
- June 22: Richard Eastham , American singer and actor († 2005)
- June 23: Ernst Willimowski , German-Polish soccer player († 1997)
- June 23: Siegfried Wünsche , German motorcycle racer († 2000)
- June 24: William B. Saxbe , American lawyer and politician († 2010)
- June 24: Ruth Shaw Wylie , American composer and music teacher († 1989)
- June 25: Erich Zöllner , Austrian historian († 1996)
- June 26: Karlrobert Kreiten , German pianist († 1943)
- June 27: Bill Spear , American racing driver († 1979)
- June 28: Manfred Steffen , German actor († 2009)
- June 29th: Óscar Cristi , Chilean show jumper († 1965)
- June 29: Runer Jonsson , Swedish writer and journalist († 2006)
- June 29: Ruth Warrick , American actress († 2005)
- June 30: R. Clark Jones , American physicist († 2004)
- June 30: Karl Neumann , German writer for children and young people († 1985)
- June 30: Manuel Simó , Dominican composer, conductor and music teacher († 1988)
July
- July 1: Olivia de Havilland , American actress († 2020)
- July 2: Ken Curtis , American singer († 1991)
- July 2: Hans-Ulrich Rudel , German Air Force colonel in World War II († 1982)
- July 3: John Kundla , American basketball coach († 2017)
- July 4th: Iva Ikuko Toguri D'Aquino , Japanese-American radio presenter († 2006)
- July 6: Harold Norse , American author, poet († 2009)
- July 6: Unica Zürn , German draftsman and prose writer († 1970)
- July 8: Peter Pasetti , German actor († 1996)
- July 9: Edward Heath , British Prime Minister († 2005)
- July 11: Alexander Mikhailovich Prokhorov , Nobel Prize in Physics, Soviet physicist († 2002)
- July 11: Gough Whitlam , Australian politician and Prime Minister († 2014)
- July 12: Ernst Engelbrecht-Greve , German politician († 1990)
- July 14: Natalia Ginzburg , Italian author († 1991)
- July 16: George Gilbert Ashwell , American biochemist († 2014)
- July 17th: Arnold Edelstein , Romanian cartoonist and illustrator († 2008)
- July 17: Aleksander Gieysztor , Polish medieval historian († 1999)
- July 18: Kenneth Armitage , British sculptor († 2002)
- July 18: Patrick Gray , FBI executive director from 1972 to 1973 († 2005)
- July 19: Ildefonso Aroztegui , Uruguayan architect († 1988)
- July 22nd: Gino Bianco , Italian racing driver († 1984)
- July 22: Marcel Cerdan , professional middleweight boxer († 1949)
- July 24th: Fred Hall , American politician († 1970)
- July 24: John D. MacDonald , American writer († 1986)
- July 27: Amha Selassie I , Crown Prince of Ethiopia († 1997)
- July 27: Siegfried Reda , German composer († 1968)
- July 28: Tilly Lauenstein , German theater actress († 2002)
- July 29: Charlie Christian , American jazz guitarist († 1942)
- July 30: Friedrich Adler , German engineer († 1996)
- July: Bernard Yago , Archbishop of Abidjan and Cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church († 1997)
August
- August 1: Fiorenzo Angelini , Italian Cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church († 2014)
- August 2: Michael Gough , British archaeologist († 1973)
- August 2: Hans Peter Schanzlin , Swiss musicologist († 1991)
- August 3: Hertha Feiler , Austrian actress († 1970)
- August 4th: Heinz Lanker , German actor († 1978)
- August 4th: Carlos Ramírez , Colombian singer and actor († 1986)
- August 6: Dom Mintoff , Maltese politician († 2012)
- August 7: Lawrence Trevor Picachy , Archbishop of Calcutta and Cardinal († 1992)
- August 7th: Anton Eric Scotoni , Swiss entrepreneur († 2011)
- August 10: Coutoucou Hubert Maga , President of Benin († 2000)
- August 11: Johnny Claes , Belgian racing driver († 1956)
- August 11: Paul Dupuis , Canadian actor († 1976)
- August 12: Ralph Nelson , American director and screenwriter († 1987)
- August 14: Wellington Mara , American football legend († 2005)
- August 14: Dioris Valladares , Puerto Rican composer, arranger, singer, band leader, guitarist and percussionist († 2001)
- August 15: Heinz Oestergaard , German fashion designer († 2003)
- August 15: Ueli Prager , Swiss catering entrepreneur († 2011)
- August 15: Joseph-Marie Raya , Lebanese Archbishop († 2005)
- August 16: Kurt Fichtner , Minister for Ore Mining and Metallurgy of the GDR († 2003)
- August 18: Margareta Erichsen , German painter and illustrator († 2006)
- August 18: Moura Lympany , English pianist († 2005)
- August 19: Dennis Poore , British racing car driver († 1987)
- August 20: Bernard Archard , British actor († 2008)
- August 20: Paul Felix Schmidt , Baltic-German chess player († 1984)
- August 20: Richard Stücklen , German politician († 2002)
- August 21: Robert Gagné , American experimental psychologist and educator († 2002)
- August 22nd: Anthony Michaelis , English science journalist († 2007)
- August 24th: Léo Ferré , French poet, composer, singer and anarchist († 1993)
- August 25: Van Johnson , American actor († 2008)
- August 25: Ernest Majo , German composer and professor († 2002)
- August 25: Frederick Chapman Robbins , American medic († 2003)
- August 26: Walter Aichinger , Austrian politician († 1994)
- August 26: Milton Soares Gomes dos Santos , Brazilian composer († 1974)
- August 28: Charles Wright Mills , American sociologist († 1962)
- August 28: Jack Vance , American science fiction writer († 2013)
- August 29: Consuelo Velázquez , Mexican composer († 2005)
- August 30: Antoine Andrieux , French politician († 1983)
- August 30: Heinz Frehsee , German politician († 2004)
- August 31: Robert Hanbury Brown , English physicist and radio astronomer († 2002)
- August 31: John S. Wold , American politician († 2017)
September
- September 1: Dorothy Bundy , American tennis player († 2014)
- September 1: Heinrich Schiemann , German science journalist († 2002)
- September 2: Liu Baiyu , Chinese writer and cultural politician († 2005)
- September 3: Alexander Koblenz , Latvian chess player, trainer and journalist († 1993)
- September 3: Helmut Sinn , German aviator and watch manufacturer († 2018)
- September 5: Daniel Paul Arulswamy , Bishop of Kumbakonam († 2003)
- September 8: René Touzet , Cuban pianist, composer and band leader († 2003)
- September 9: Peter Beauvais , German director († 1986)
- September 9: Tatjana Lietz , Latvian-German painter, language and art teacher († 2001)
- September 10: Jack M. Campbell , American politician († 1999)
- September 10: Heinrich Heitsch , career officer, lieutenant general of the NVA, († 1986)
- September 11th: Josef Gauchel , German soccer player († 1963)
- September 12: William Alonzo Anderson , American jazz trumpeter († 1981)
- September 12: Tony Bettenhausen , American racing driver († 1961)
- September 12: Mary Stewart , British writer († 2014)
- September 13: Roald Dahl , Welsh writer († 1990)
- September 14: Luis Corvalán , Chilean politician and General Secretary of the Communist Party of Chile († 2010)
- September 15: Antonio Branca , Swiss Formula 1 racing driver († 1985)
- September 15: Ettore Puricelli , Uruguayan-Italian football player and coach († 2001)
- September 16: Robert Bradshaw , St. Kitts and Nevis politician († 1978)
- September 17: Yumjaagiin Tsedenbal , politician of the Mongolian People's Republic († 1991)
- September 20: Rudolf-August Oetker , German entrepreneur († 2007)
- September 20: Paul Parin , Swiss ethno-psychoanalyst and writer († 2009)
- September 21: Luis Carlos Meyer , Colombian singer and composer († 1998)
- September 23: Aldo Moro , Italian Christian Democratic politician († 1978)
- September 23: Omar Ali Saifuddin III. , Sultan of Brunei († 1986)
- September 23: Günter Poser , German admiral and politician († 2003)
- September 25: Jessica Anderson , Australian writer († 2010)
- September 25: Tolia Nikiprowetzky , Russian composer († 1997)
- September 25: Friedrich Thielen , German politician († 1993)
- September 26: Fritz Köthe , German painter and graphic artist († 2005)
- September 27: Eckhard Hess , American psychologist and ethologist († 1986)
- September 28: Peter Finch , British theater and film actor († 1977)
- September 28: Ernst Wille , German painter († 2005)
- September 29: Minao Shibata , Japanese composer († 1996)
- September 29: Josef Traxel , German tenor († 1975)
- September 30: Hassan Abdulaziz al-Saaty , Egyptian sociologist
October
- October 2: Leonard C. Lewin , American writer and satirist († 1999)
- October 2: Ángel Suquía , Archbishop of Madrid and Cardinal († 2006)
- October 3: Ardyth Alton , American cellist and music teacher († 2007)
- October 3: Louise Behrend , American violinist and music teacher († 2011)
- October 3: James Herriot , English veterinarian and writer († 1995)
- October 3: Russell W. Peterson , American politician († 2011)
- October 4: Witali Ginsburg , Russian physicist and Nobel Prize winner († 2009)
- October 5: Wolfram Röhrig , German pianist and conductor († 1998)
- October 6: Vern Sneider , American writer († 1981)
- October 6: Franz Vit , German politician († 2005)
- October 7: Walt Whitman Rostow , American economist, economic historian and politician († 2003)
- October 8: John W. King , American politician († 1996)
- October 10: Bernard Heuvelmans , Belgian-French zoologist († 2001)
- October 11: Luis Kalaff , Dominican singer, guitarist and composer († 2010)
- October 12: Wilhelm Muster , Austrian writer and literary translator († 1994)
- October 14: Jack Arnold , American film director († 1992)
- October 15: Hassan Gouled Aptidon , Djiboutian politician († 2006)
- October 15: Karl Ebert , Auxiliary Bishop of the Apostolic Administrator in Erfurt and Meiningen († 1974)
- October 15: Fritz Wedel , German politician († 1964)
- October 16: Werner Buxa , German officer and author († 1998)
- October 16: Pierre Meyrat , French racing driver († 1969)
- October 17: Knut von Kühlmann-Stumm , German politician († 1977)
- October 17: Tadeusz Paciorkiewicz , Polish composer and music teacher († 1998)
- October 17: Friedrich Schoenfelder , German actor and voice actor († 2011)
- October 18: Anthony Dawson , British actor († 1992)
- October 19: Karl-Birger Blomdahl , Swedish composer and conductor († 1968)
- October 19: Jean Dausset , French physician and hematologist († 2009)
- October 19: Emil Gilels , Russian pianist († 1985)
- October 20: Hans Walter Berg , ARD foreign correspondent in Asia († 2003)
- October 22: Erwin Ammann , German politician († 2000)
- October 22: Fanita English , American psychoanalyst
- October 23: Philip Rosenthal , German entrepreneur and politician († 2001)
- October 23: Maria Rosseels , Flemish-Belgian writer and journalist († 2005)
- October 24: Pierre Sancan , French pianist, conductor and composer († 2008)
- October 25: Noel Gilroy Annan , British intelligence officer († 2000)
- October 25: Max Caflisch , Swiss typographer, book designer and font connoisseur († 2004)
- October 26: François Mitterrand , French politician, President of France († 1996)
- October 27: Kazimierz Brandys , Polish writer († 2000)
- October 28: Erich Mende , German lawyer and politician († 1998)
- October 28: Simon Pierre Tchoungui , Cameroonian politician († 1997)
- October 29th: Slim Aarons , American photographer († 2006)
- October 30: Kurt Hübner , German theater director, actor and theater director († 2007)
- October 30: Charles E. Potter , American politician († 1979)
- October 30: Heinz Spitzner , German actor († 1992)
- October 31: Earl Songer , American country musician († 1972)
November
- November 3: Harry Lampert , American cartoonist and author († 2004)
- November 5: Franz K. Opitz , Swiss painter and photographer († 1998)
- November 5: Madeleine Robinson , French actress († 2004)
- November 6: Ray Conniff , American composer, arranger, orchestra conductor and trombonist († 2002)
- November 7th: Joe Bushkin , American jazz pianist († 2004)
- November 8: Peter Weiss , German writer, painter and graphic artist († 1982)
- November 9: Fernando Fernández , Mexican actor, singer, screenwriter and director († 1999)
- November 9: Helmut Wandmaker , German entrepreneur and book author († 2007)
- November 10: Louis le Brocquy , Irish painter († 2012)
- November 10: Paul Leyhausen , German zoologist and behavioral scientist († 1998)
- November 11: Robert Carr, Baron Carr of Hadley , British politician († 2012)
- November 11th: Wilhelm Stuellen , German judge and revisionist († 2006)
- November 12: Paul Emery , British racing car driver and designer († 1993)
- November 12: Jean Papineau-Couture , Canadian composer († 2000)
- November 12: Talbot Rothwell , British author and screenwriter († 1981)
- November 14: Roger Apéry , Greco-French mathematician († 1994)
- November 14: Sherwood Schwartz , American television producer and screenwriter († 2011)
- November 16: Herbert C. Abramson , American music producer († 1999)
- November 17: Shelby Foote , American writer and historian († 2005)
- November 17: George Silk , American war and sports photographer († 2004)
- November 21: Sid Luckman , American football player († 1998)
- November 23: Michael Gough , British actor († 2011)
- November 23: Ken Kavanaugh , American football player and coach († 2007)
- November 24: Forrest J. Ackerman , American editor, publisher and author († 2008)
- November 27: Chick Hearn , American sports reporter († 2002)
- November 27: Bernhard Hartmann , German economist and business economist († 1989)
- November 28: Ramón José Velásquez , Venezuelan politician and president († 2014)
- November 29: Valentino Bucchi , Italian composer († 1976)
- November 29: John Arthur Love , American politician († 2001)
- November 29: Gerhard Wacher , German politician († 1990)
- November 30th: Günter Ortmann , German handball player († 2002)
- November 30th: Heinz Raack , German table tennis player († 2003)
December
- December 1: Frans Hendrik Breukelman , Dutch Reformed pastor and professor of theology († 1993)
- December 2: Charlie Ventura , American jazz musician († 1992)
- December 5th: Paul Aste , Austrian luge and bobsleigh athlete
- December 6: Kristján Eldjárn , Icelandic President († 1982)
- December 7th: Jean Carignan , Canadian fiddle player († 1988)
- December 8: Richard Fleischer , American director († 2006)
- December 8: Ernst Maria Lang , German architect and cartoonist († 2014)
- December 9th: Dieter Andersen , German clergyman, state superintendent of the district of Lüneburg and bishop († 1994)
- December 9: Kirk Douglas , American actor († 2020)
- December 9: Wolfgang Hildesheimer , German writer and painter († 1991)
- December 10: Ruedi Walter , Swiss folk actor and cabaret artist († 1990)
- December 11th: Dámaso Pérez Prado , Cuban musician and composer († 1989)
- December 11th: Jakob Streitle , German soccer player († 1982)
- December 15: Kenshiro Abe , Japanese Jūdō teacher († 1985)
- December 15: Maurice Wilkins , New Zealand physicist († 2004)
- December 16: Gerhard Dabel , German writer and head of the Kinderlandverschickung service at the Reich Youth Leadership († 1984)
- December 18: Betty Grable , American actress and pin-up girl († 1973)
- December 18: John Simms , American politician († 1975)
- December 18: Karl Schnell , German General († 2008)
- December 18: Anselm Strauss , American sociologist († 1996)
- December 19: Roy Ward Baker , British film director and producer († 2010)
- December 19: Elisabeth Noelle-Neumann , German pollster († 2010)
- December 19: Jack Charles Stanmore Agazarian , Armenian-French-British agent († 1945)
- December 20: Gonzalo Rojas , Chilean poet († 2011)
- December 23: Dino Risi , Italian film director and screenwriter († 2008)
- December 24th: Hans Affentranger , Swiss racing driver († 2005)
- December 24th: Lalo Guerrero , American singer, guitarist and songwriter († 2005)
- December 24th: Carlo Rustichelli , Italian film music composer († 2004)
- December 25: Ahmed Ben Bella , Algerian politician and head of state († 2012)
- December 25: Graciela Naranjo , Venezuelan singer and actress († 2011)
- December 26th: Helmut Eder , Austrian composer († 2005)
- December 26: Rüdiger Proske , German journalist and book author († 2010)
- December 27: Werner Baumbach , German general of fighter pilots and bomber pilot in World War II († 1953)
- December 27: Friedrich von Bömches , German painter († 2010)
- December 27: Johnny Frigo , American jazz bassist and violinist († 2007)
- December 30th: Georg Årlin , Swedish actor († 1992)
Exact date of birth unknown
- Edward Sidney Aarons , American writer († 1975)
- Abdullah Afeef Didi , Maldivian translator and politician († 1993)
- Abd ar-Rahman Arif , President of Iraq († 2007)
- Samuel Armato , American swing musician († 2014)
- Mario Escobar , Chilean tenor saxophonist († 1984)
- Helen Kotas Hirsch , American horn player († 2000)
- Pedro Lerma , Spanish pianist and music teacher († 2003)
Died
January February
- January 4th: Godefroid Kurth , Belgian historian (* 1847)
- January 8: Rembrandt Bugatti , Italian sculptor (* 1884)
- January 9: Tadeusz Ajdukiewicz , Polish portrait, genre and military painter (* 1852)
- January 12: Léon César Autonne , French engineer and mathematician (* 1859)
- January 13: Victoriano Huerta , Mexican general and President of Mexico (* 1850)
- January 14: Otto Ammon , German anthropologist (* 1842)
- January 17th: Marie Bracquemond , French impressionist painter (* 1840)
- January 18: Česlovas Sasnauskas , Lithuanian composer (* 1867)
- January 21: George Musgrove , Australian opera and theater entrepreneur (* 1854)
- January 23: Isa Boletini , Albanian politician (* 1864)
- January 23: Wilhelm Riedel , German cloth manufacturer and benefactor (* 1829)
- January 25: Ferenc Szoldatits , Hungarian painter (* 1820)
- January 26: William Shakespeare Burton , English genre painter (* 1824)
- January 27: Cesare De Sanctis , Italian composer, church musician and music teacher (* 1824)
- January 30th: Julius Pohlig , German engineer and pioneer in cable car construction (* 1842)
- February 6: Rubén Darío , Nicaraguan writer (* 1867)
- February 8: Arwed Emminghaus , German economist (* 1831)
- February 8: Gustav Falke , German writer (* 1853)
- February 10: Naftali Amsterdam , Russian rabbi (* 1832)
- February 12: Richard Dedekind , German mathematician (* 1831)
- February 13: Vilhelm Hammershøi , Danish painter (* 1864)
- February 13: Carlos Antonio Mendoza , third President of Panama (* 1856)
- February 14: Adolf von Auer , German lawyer (* 1831)
- February 17th: Miklós Konkoly-Thege , Hungarian astronomer (* 1842)
- February 17th: Maurice Vignaux , French world billiard champion and specialist book author (* 1846)
- February 19: Afonso Arinos de Melo Franco , Brazilian lawyer and writer (* 1868)
- February 19: Ernst Mach , physicist, philosopher and scientific theorist (* 1838)
- February 20: Klas Pontus Arnoldson , Swedish journalist, politician and Nobel Peace Prize laureate (* 1844)
- February 28: Henry James , British writer (* 1843)
March April
- March 2: Carmen Sylva , Romanian queen and writer (* 1843)
- March 4th: Franz Marc , German painter and co-founder of the artists' association "Blauer Reiter" (* 1880)
- March 8: Rudolf Oetker , German chemist and entrepreneur (* 1889), son of August Oetker
- March 10: Edward Farley , Australian singer (* 1846)
- March 11: Henry G. Davis , American entrepreneur and politician (* 1823)
- March 12: Marie von Ebner-Eschenbach , Austrian writer (* 1830)
- March 14: Benjamin F. Shively , American politician (* 1857)
- March 16: William Taylor Thornton , American politician (* 1843)
- March 20: Stephen Wallace Dorsey , American politician (* 1842)
- March 22nd: Fritz Schenck , German physiologist (* 1862)
- March 24th: Enrique Granados , Spanish composer and pianist (* 1867)
- March 25th: Ishi , the last survivor of the Yahi Indians (* around 1860)
- March 25: Emilie Wedekind-Kammerer , German actress and singer (* 1840)
- April 4: Albert Mauritz Atterberg , Swedish chemist and soil mechanic (* 1846)
- April 9: Wilhelm Sauer , German master organ builder (* 1831)
- April 14: Gina Krog , Norwegian women's rights activist (* 1847)
- April 27: Bruno Schmitz , German architect (* 1858)
- April 30: Paul Schlenther , German theater critic, writer and theater director (* 1854)
- April 30th: Otto von Herff , German doctor and professor (* 1856)
May June
- May 1: Rudolf Hirth du Frênes , German painter (* 1846)
- May 2: Jules Blanchard , French sculptor (* 1832)
- May 10: Robert Kraft , German writer (* 1869)
- May 11: Max Reger , German composer and organist (* 1873)
- May 11: Karl Schwarzschild , German astronomer and physicist (* 1873)
- May 12: James Connolly , Irish politician (* 1868)
- May 13: Sholem Alejchem , Yiddish writer (* 1859)
- May 17: Wilhelm Anton Michael Graf von Attems-Petzenstein , Austrian field marshal lieutenant (* 1848)
- May 17th: Wilhelm Hübbe-Schleiden , German explorer, theosophist and writer (* 1846)
- May 17th: Gaston Salvayre , French composer (* 1847)
- May 20: Georges Boillot , French automobile racing driver and fighter pilot in World War I (* 1884)
- May 27: Joseph Gallieni , French Marshal and Minister of War (* 1849)
- May 28: Iwan Franko , Ukrainian poet (* 1856)
- May 28: Albert Lavignac , French musicologist and composer (* 1846)
- May 29: Hugo Jentsch , German high school teacher, regional historian and researcher of prehistory (* 1840)
- May 29: Jan Otto , Czech publisher (* 1841)
- May 31: Gorch Fock , German poet (* 1880)
- June 1: Anna Schramm , German soubrette and actress (* 1835)
- June 2: Paul von Bruns , German surgeon (* 1846)
- June 5: Horatio Herbert Kitchener , British general and politician (* 1850)
- June 5: Karl August Lingner , German industrialist (* 1861)
- June 6: Yuan Shikai , Chinese army leader, president and self-appointed emperor (* 1859)
- June 18: Helmuth Johannes Ludwig von Moltke , Prussian general (* 1848)
- June 18: Max Immelmann , German ace pilot in World War I (* 1890)
- June 23: Heinrich Hansjakob , German folk writer (* 1837)
- June 25: Thomas Eakins , American painter (* 1844)
- June 27: Ștefan Luchian , Romanian painter (* 1868)
July August
- July 4th: Alan Seeger , American poet (* 1888)
- July 6: Kurd Adler , German poet (* 1892)
- July 6th: Odilon Redon , French impressionist painter (* 1840)
- July 8: Henriette Johanne Marie Müller , Hamburg original (* 1841)
- July 15: Ilya Ilyich Metschnikow , Ukrainian zoologist and bacteriologist, Nobel Prize winner (* 1845)
- July 16: Luigi Forlano , Italian football player (* 1884)
- July 16: Sir Victor Alexander Haden Horsley , British physiologist and neurologist (* 1857)
- July 18: Mite Kremnitz , German writer (* 1852)
- July 23: Thomas MacDonald Patterson , American politician (* 1839)
- July 23: William Ramsay , British chemist and Nobel Prize winner (* 1852)
- July 24th: Eugène Anthiome , French composer (* 1836)
- July 27: Karl Klindworth , German composer and conductor (* 1830)
- August 3: Roger Casement , Irish independence fighter (* 1864)
- August 9: Lily Braun , German writer (* 1865)
- August 13: Pierre de Ségur , French writer (* 1853)
- August 16: Umberto Boccioni , Italian painter and sculptor (* 1882)
- August 17th: Johann Hinrich Fehrs , German narrator and poet (* 1838)
September October
- September 10: Lucy Walker , British mountaineer (* 1836)
- September 14th: Pierre Duhem , French physicist and scientific theorist / historian (* 1861)
- September 15: Raymond Asquith , British lawyer (* 1878)
- September 15: Isidore Legouix , French composer (* 1834)
- September 17: Seth Low , American educator and politician (* 1850)
- September 20: August Leskien , German Indo-Europeanist and Slavist (* 1840)
- September 23: Oliver Godfrey , British motorcycle racer and aviator in World War I (* 1887)
- September 25: Julius Ernest Wilhelm Fučík , Czech composer and conductor (* 1872)
- October 1: Emil Deckert , German geographer (* 1848)
- October 4: William Warner , American politician (* 1840)
- October 6: Marie Wieck , German pianist and singer (* 1832)
- October 10: Hope Bridges Adams Lehmann , suffragette and first German doctor with state examination (* 1855)
- October 11: Otto I , Bavarian King (* 1848)
- October 15: Karl Marbach , Catholic auxiliary bishop in Strasbourg (* 1841)
- October 18: Ignacio Pinazo , Spanish painter (* 1849)
- October 21: Karl Reichsgraf von Stürgkh , Austrian Prime Minister (* 1859)
- October 22: Arnold Woldemar von Frege-Weltzien , German manor owner and politician (* 1841)
- October 22: Herbert Kilpin , English football player and coach (* 1870)
- October 25: Giulio Cottrau , Italian composer (* 1831)
- October 25: William Merritt Chase , American painter, developed his own American Impressionism (* 1849)
- October 28: Cleveland Abbe , American astronomer and meteorologist (* 1838)
- October 28: Oswald Boelcke , German fighter pilot (* 1891)
- October 31: Tina Blau , Austrian painter (* 1845)
- October 31: Charles Taze Russell , Bible Student (* 1852)
- October: Bagher Khan , Iranian military leader and revolutionary (* 1861)
November December
- November 1: Gustav Tweer , German aerobatic pilot and aviation pioneer (* 1893)
- November 7th: Marie Heim-Vögtlin , Swiss doctor (* 1845)
- November 8: Ernst Möller , German football player (* 1891)
- November 8: Frederic Woodman Root , American composer and music teacher (* 1846)
- November 11th: Francisco António da Veiga Beirão , Portuguese politician (* 1841)
- November 14th: Hector Hugh Munro ("Saki"), British writer (* 1870)
- November 15: Henryk Sienkiewicz , Polish writer (* 1846)
- November 21: Franz Joseph I , Emperor of Austria, King of Bohemia and Apostolic King of Hungary (* 1830)
- November 22nd: Jack London , American writer (* 1876)
- November 23: Lanoe Hawker , British military pilot in World War I (* 1890)
- November 23: Eduard Nápravník , Czech conductor and composer (* 1839)
- November 24th: Adelheid Marie von Anhalt-Dessau , Duchess of Nassau and Grand Duchess of Luxembourg (* 1833)
- November 24th: Hiram Maxim , American-British inventor (* 1840)
- November 27: James Cutler Dunn Parker , American composer (* 1828)
- November 27: Émile Verhaeren , Belgian poet (* 1855)
- November 28: Marthinus Theunis Steyn , President of the Orange Free State (* 1857)
- November 30th: Dorrit Weixler , German silent film actress (* 1892)
- December 3: Victor Occellier , American-Canadian singer (* around 1865)
- December 4: Preston Lea , American politician (* 1841)
- December 5: Hans Richter , Austro-Hungarian conductor (* 1843)
- December 5: Gustav Sack , German writer, poet and playwright (* 1885)
- December 8: Germán Riesco Errázuriz , Chilean politician (* 1854)
- December 14: Norbert von Hellingrath , German Germanist and Hölderlin expert (* 1888)
- December 15: Wilhelm Merton , German entrepreneur, founder of the metal company in Frankfurt am Main (* 1848)
- December 19: Thibaw Min , King of the Konbaung dynasty in Burma (* 1859)
- December 20: William Wallace Gilchrist senior , American composer (* 1846)
- December 25th: Wilhelmine von Hillern , German writer and actress (* 1836)
- December 27: Nikolai Feopemptowitsch Solowjow , Russian composer and music teacher (* 1846)
- December 27th: Hugo Süchting , German chess player (* 1874)
- December 28: Carl Hintze , German mineralogist and crystallographer (* 1851)
- December 28th: Eduard Strauss , Austrian composer and Kapellmeister (* 1835)
- December 30th: Rasputin , Russian monk and politician (* 1869)
Exact date of death unknown
- Angelo Ferni , Italian violinist (* 1845)
- Edward Kreiser , American organist and composer (* 1869)
- Lewanika I. , Litunga (King) of Barotseland (* around 1842)
Web links
- https://www.dhm.de/lemo/jahreschronik/1916/ (Living virtual museum online)