1917
Portal History | Portal Biographies | Current Events | Annual Calendar | Article of the day
◄ |
19th Century |
20th Century
| 21st Century
◄ |
1880s |
1890s |
1900s |
1910s
| 1920s
| 1930s
| 1940s
| ►
◄◄ |
◄ |
1913 |
1914 |
1915 |
1916 |
1917
| 1918
| 1919
| 1920
| 1921
| ►
| ►►
| 1917 | |
|---|---|
| The United States enters World War I. | |
| The Russian Tsar Nicholas II is overthrown by the February Revolution . |
Vladimir Ilyich Lenin travels from Zurich to Petrograd
in a sealed train . |
|
With the October Revolution , the Bolsheviks take power in Russia . |
|
| 1917 in other calendars | |
| Armenian calendar | 1365/66 (July turn of the year) |
| Ethiopian calendar | 1909/10 (10/11 September) |
| Baha'i calendar | 73/74 (20/21 March) |
| Bengali solar calendar | 1322/23 (beginning of the year April 14 or 15) |
| Buddhist calendar | 2460/61 (Southern Buddhism); 2459/60 (alternative calculation according to Buddha's parinirvana ) |
| Chinese calendar | 76th (77th) cycle
Year of the Fire Serpent丁巳 ( at the beginning of the year Fire Dragon 丙辰) |
| Chuch'e ideology (North Korea) | Chuche 6 |
| Chula Sakarat (Siam, Myanmar) / Dai calendar (Vietnam) | 1279/80 (April turn of the year) |
| Dangun era (Korea) | 4250/51 (October 2nd/3rd) |
| Iranian calendar | 1295/96 (around March 21) |
| Islamic calendar | 1335/36 (17/18 October) |
| Japanese calendar |
Taishō 6 (
大正元年); Koki 2577 |
| Jewish calendar | 5677/78 (September 16/17) |
| Coptic calendar | 1633/34 (10/11 September) |
| Malayalam calendar | 1092/93 |
| Minguo Calendar (China) | Year 6 of the Republic |
| Rumi Calendar (Ottoman Empire) | 1332/33 (March 1) |
| Seleucid era | Babylon: 2227/28 (April turn of the year)
Syria: 2228/29 (October turn of the year) |
| Suriyakati Calendar (Thai Solar Calendar) | 2459/60 (April 1) |
| Tibetan calendar | 1663 |
| Vikram Sambat (Nepalese calendar) | 1973/74 (April) |
The year 1917 is determined by the international events that take place against the formative background of the First World War . The entry of the United States into the war on the Entente side, triggered by the unrestricted submarine warfare of the German Empire and the intercepted Zimmermann dispatch to Mexico at the beginning of the year, explains the slow rise from an industrial superpower to a political world power . The Entente's increased tank warfare and their surplus of material and troops let the strategic initiative pass to them.
In the Russian Empire , social and political tensions led to the fall of the ruling Tsar family , the Romanovs , in the February Revolution , whose representatives were in turn overthrown by the October Revolution and the subsequent civil war . The establishment of a Soviet system , the USSR , laid the seeds for the East-West conflict and allowed Russia to grow into a world power of communist design over the next few decades.
The political and socio-economic upheavals that the war demands of the countries involved mark the end of the so-called “long 19th century” , the break in monarchical tradition towards the politicization of the masses. Due to these complex phenomena, which give the year 1917 a caesura character, it is also referred to as an epoch year .
events
politics and world affairs
First World War
Political and diplomatic developments
- January 16: Arthur Zimmermann , the German State Secretary for Foreign Affairs , transmits an encrypted telegram to the German ambassador in Washington, Johann Heinrich von Bernstorff . On January 19, he forwarded the Zimmermann telegram to the German ambassador in Mexico, Heinrich von Eckardt . In it, the German Reich proposes an alliance to Mexico in the event of the United States entering the war. Germany offers Mexico support for regaining territory lost to the United States in the 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo . The telegram is intercepted by British naval intelligence agency Room 40 , led by William Reginald Hall , and deciphered over the next few weeks.
- January 22: US President Woodrow Wilson proclaims “peace without victory” in a speech before the United States Congress.
- January 30: The Supreme Army Command establishes the Image and Film Office ("BUFA"); this operates psychological warfare and propaganda in the First World War .
- February 1: At the urging of the Supreme Army Command, the German Reich resumes unrestricted submarine warfare with Imperial approval . As a result, the United States broke off diplomatic relations with the German Empire on February 3 . Ambassador Johann Heinrich von Bernstorff is expelled.
- March 1: US Secretary of State Robert Lansing releases details of the Zimmermann cable intercepted in January to the press .
- March 4: US President Woodrow Wilson begins his second term.
- April 6: The United States declares war on Germany .
- April 7: In his Easter message , the German Kaiser Wilhelm II held out the prospect of constitutional amendments after the end of the war, in which the Prussian three -class electoral system would also be replaced by a secret and direct electoral system.
- April 13: The Committee on Public Information is established in the United States by executive order as a propaganda tool .
- April 23: The Democratic Party of Russian Citizens of German Nationality is founded in Latvia .
- April 23: The Kreuznach War Goals Conference between the German Reichsleitung under Chancellor Theobald von Bethmann Hollweg and the Supreme Army Command under Paul von Hindenburg and Erich Ludendorff takes place at the Main Headquarters of the Third Supreme Army Command in Kreuznach . The resulting Kreuznach program contains far-reaching demands for annexations in both the west and the east. A second conference follows on May 17th and 18th, at which the war aims are agreed with Austria-Hungary.
- April: The Bandō prisoner of war camp is set up in Japan.
- May 7: John J. Pershing is appointed commander in chief of the newly formed American Expeditionary Forces .
- May 18: Woodrow Wilson signs the Selective Service Act , introducing conscription in the United States.
- May 21: The British Imperial War Graves Commission for the maintenance of war graves is established.
- May 30: The Austrian Reichsrat – convened by Emperor Karl I – meets for the first time since 1914.

- 2–19 June: 1917 Stockholm Peace Conference
- June 11: King Constantine I of Greece abdicates under pressure from France and goes into exile in Switzerland with Crown Prince George . His second son Alexandros becomes the new king . The counter-government under Eleftherios Venizelos enters the war on June 29 on the side of the Entente.
- June 15: The Espionage Act is passed in the United States, criminalizing the disclosure of military information.
- June 23: Heinrich Clam-Martinic resigns as Prime Minister of Austria . Ernst Seidler von Moistenegg is appointed as his successor . In order to solve the nationality problems of Cisleithania , Seidler, despite concerns about trialism , strives for a constitutional reform in which, while retaining the crown lands, circles that are as nationally uniform as possible and have their own autonomy are to be created. This creates an increasing contrast to the authoritarian Foreign Minister Count Ottokar Czernin .
- July 6: The majority factions in the Reichstag of the German Empire , the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD), the Progressive People's Party (FVP) and the German Center Party , form the Intergroup Committee as an unofficial body . The immediate reason for founding the company is the Reichstag debate on the drafting of a peace resolution , which Member of Parliament Matthias Erzberger initiated with his speech during the meeting of the Reichstag Main Committee in the morning.
- July 6: A majority in the Canadian House of Commons passes the Military Service Act . Almost all English-speaking MPs vote in favor of the law, while all French-Canadian MPs vote against. From January 1, 1918, the government tried to enforce conscription .
- July 9: During the Oath Crisis , several units of the Polish Legions refuse to take the oath of allegiance to the German Empire and Austria-Hungary. Thousands of legionnaires are then demoted or interned. The approximately 1,100 legionnaires who took the oath are integrated into the Polish Wehrmacht , which was newly formed in April .
- July 13: Under pressure from the Supreme Army Command , Kaiser Wilhelm II dismisses Chancellor Theobald von Bethmann-Hollweg , who had spoken out in favor of universal and equal suffrage and had criticized unrestricted submarine warfare; his successor is Georg Michaelis . However, actual power now rests with Quartermaster General Erich Ludendorff .
- July 17: Due to the anti-German sentiment during the First World War, the British King George V drops his family name Saxe-Coburg and Gotha and henceforth calls himself Windsor .
- July 19: The German Reichstag passes the peace resolution calling for a mutual peace agreement to end the First World War.
- July 20: The Corfu Declaration paves the way for the establishment of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes under the rule of the Karađorđević dynasty . It is signed in Corfu by Serbian Foreign Minister Nikola Pašić and Ante Trumbić , the chairman of the Yugoslav Committee , an association of South Slavic politicians from the Habsburg monarchy founded in exile . Entente powers Great Britain and France support the declaration.
- 1 August: The Apostolic Exhortation Dès le début marks the culmination of Pope Benedict XV's efforts at peace. It met with little response from the warring parties.
- 1 November: German Chancellor Georg Michaelis resigns after three months in office, and is succeeded by Georg von Hertling .
- 2 November: In the Balfour Declaration , British Foreign Secretary Arthur Earl of Balfour pledges land in Palestine to the representative of the Zionist movement , Lord Rothschild , for the establishment of a Zionist "national home". The British government under David Lloyd George , which has been in office since the end of last year , expects the promise to mobilize additional resources during the war and long-term strategic advantages.
- November 7: France, Britain and Italy form the Allied Supreme War Council at the Rapallo Conference .
- November 28 Leon Trotsky proposes an armistice to the warring parties. While the Entente refuses, the Central Powers agree.
- December 7: The United States declares war on Austria-Hungary .
- December 9: In Brest-Litovsk , the delegations of Russia and the Central Powers meet for the first time to negotiate a ceasefire. Despite mutual personal dislike of the negotiators, a ceasefire agreement is signed on December 15.
- December 17: Prime Minister Robert Borden wins Canada 's general election with the Unionist Party , a short-lived coalition of Conservatives and some pro-conscription Liberals, the largest majority ever won by any party in a federal election. Candidates from the opposition Liberal Party , who support their party leader Wilfrid Laurier , are predominantly being elected in the French-speaking province of Quebec , where conscription has met with unanimous opposition.
"Home Front"
- 7 January: 138 delegates and 19 members of the Reichstag take part in the Reich Conference of the Social Democratic opposition in Berlin, convened by the Social Democratic Working Group .
- April 6 to 8: Former members of the Social Democratic Party of Germany found the Independent Social Democratic Party of Germany (USPD) at the second Reich Conference of the Social Democratic opposition in Gotha. Hugo Haase and Georg Ledebour are elected chairmen , Wilhelm Dittmann becomes executive secretary. The Spartakusbund around Rosa Luxemburg and Karl Liebknecht also joins the extremely heterogeneous faction, which is mainly united by their opposition to the war. Large parts of the SPD will convert to the USPD in the next few months. The Social Democratic Party calls itself the Majority Social Democratic Party of Germany .
- April: There are mass strikes in the German Reich , which are directed against the insufficient supply situation as a result of the swede winter .
western front
- 9 February to 15 March: Under the alias of Operation Alberich , German forces on the Western Front prepare to withdraw to the Siegfried Line. This is intended to shorten the course of the front and thwart the Allied attack plans. The withdrawal is carried out from March 16 to 20 under the leadership of Army Group "Kronprinz Rupprecht" . The area to be cleared on both sides of the Somme is systematically devastated before the withdrawal in order to make it largely impossible for the enemy to use it for military purposes. Around 200 towns and the infrastructure are completely destroyed; more than 100,000 civilians are deported . From the German point of view, the enterprise is successful and surprises the military leadership of the Entente . But it also strengthens the reputation of the Germans as "barbarians".
- February 13: Mata Hari is arrested for espionage in Paris and taken to Saint-Lazare women's prison after her appearance before the magistrate of the court-martial . Her trial begins on July 24th and lasts only one and a half days in camera.
- March 27: German soldiers blew up the keep of Coucy Castle , one of the most important medieval feudal castles in Europe, in Picardy , despite numerous protests from historians on both sides .
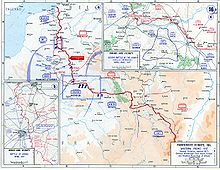
- April 9 Battle of Arras begins. By May 16, British and Canadian troops succeeded in taking a strategic ridge near Vimy from German troops, but without achieving a decisive breakthrough. British losses during the battle amount to 150,000 men, the Germans are slightly lower.
- April 16: Under General Robert Nivelle , the French army launches a major offensive against the Chemin des Dames, which is considered impregnable. The second battle of the Aisne had to be stopped at the end of May because of the heavy losses.
- End of April: The first extensive mutinies in the French army occur . By June 10, around 25,000 to 50,000 men were refusing to carry out orders.
- May 21: Battle of Messines begins. It is best known for the simultaneous detonation on 7 June of a group of mines previously dug by Allied troops under German positions, ending on 21 June in a British victory and German withdrawal.
- May 27: Mutiny breaks out among around 30,000 French soldiers at Missy-aux-Bois in north -eastern France .
- June 4 France forms the Blue Army from Polish émigrés.
- June 13: John J. Pershing , commander in chief, American Expeditionary Forces , arrives in Paris with his staff. Barely two weeks later, on June 26, the first combat troops of the 1st Infantry Division landed at Saint-Nazaire . Pershing wants to train his soldiers well before they are sent into battle, which is why American troops only move into trenches on the Western Front at the end of October. He also considers the Entente's plan to deploy its troops at the front under foreign command to be unacceptable. This initially caused great tension between the US militaries and their European allies.
- July 12: In the course of the gas war during the First World War , German troops used mustard gas for the first time near Ypres .
- July 31: After days of artillery fire, the Third Battle of Ypres begins with a major offensive by the British 5th Army . The German 4th Army under Commander-in-Chief General Friedrich Sixt von Armin , which had been warned by the bombing , drew on appropriate reserves to defend itself. The onset of heavy rain turns the battlefield into a mudfield, making tank deployment impossible and the trenches flooded. The offensive continued on August 16, but had to be called off at the end of August due to renewed bad weather.
- October 12: As part of the Third Battle of Ypres , the First Battle of Passchendaele begins .
- October 15: A firing squad shoots dead dancer Mata Hari , who has been found guilty by a military court of double espionage and high treason , in the ramparts of Vincennes Castle .
- October 23-25: French troops regain control of the Chemin des Dames hills in northern France at the Battle of Malmaison .
- October 26 Second Battle of Passchendaele begins.

- November 6: The Third Battle of Ypres ends with the conquest of the completely destroyed town of Passchendaele by Canadian divisions .
- November 20: The British Army launches an offensive against the Germans at Cambrai , using several hundred tanks . The Battle of Cambrai , which lasted until December 6th, claimed tens of thousands of dead and injured and ended without a decision for either side.
Mountain warfare between Italy and Austria-Hungary
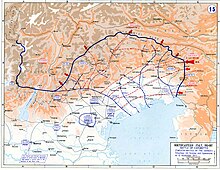
- May 12 to June 10: The tenth Battle of the Isonzo brings heavy losses on both sides only small gains for the Italian attackers.
- August 17th to September 12th: In the eleventh Battle of the Isonzo, the Italian army is able to record successes, but fails to achieve its goal of conquering Trieste . Both sides not only suffer heavy casualties in the fighting, but are also increasingly weakened by rampant diseases such as dysentery and typhoid.
- October 24: Beginning of the Battle of Karfreit , in which Austria-Hungary advances against Italy to the Piave
- November 10: The first of three Piave battles in World War I begins. Austria-Hungary tries to win the war against Italy.
eastern front
- January 5th to 11th: The battles on the Aa between Russia and the German Reich do not bring any notable success for either side. The Russian offensive under Radko Dimitriev , hampered by a mutiny by two Siberian regiments, is answered with a German counter-offensive under Friedrich von Scholtz on January 23 . After three days, the temperature drops to -38 °C, which makes it impossible for both sides to continue fighting.
- Early March: February Revolution begins in Russia . After the tsar's abdication, the provisional government under Georgi Lvov continued the war for the time being .
- July 1 Russian Kerensky Offensive begins. It ends on July 19 with a counter-offensive by the Central Powers. Only the Battle of Zborów brings success for the Russian army .
- July 19: The Central Powers ' Tarnopol offensive begins. It ends on July 25 with the occupation of eastern Galicia by the Central Powers.
- September 1–5: The Battle of Riga ends with German troops entering Riga .
- September/October: Operation Albion
- October 17: Battle of Moon Sound
- December: After the October Revolution, there is an armistice on the Eastern Front .
The Fronts of the Ottoman Empire
- January 23: Arab Revolt : Supported by British warships, an army of 10,000 Bedouin warriors led by Faisal and TE Lawrence captures al-Wajh after heavy fighting .
- March 11: During the First World War , British troops take the city of Baghdad , which belongs to the Ottoman Empire , without much resistance.
- March 26: The British Egyptian Expeditionary Force makes the first unsuccessful attempt to capture the city of Gaza .
- On May 9, TE Lawrence sets out with the Sherif Nasir and a few men on a journey through the Nefud desert to Maʿan in order to recruit more warriors there for sabotage actions in the vicinity and finally for the capture of Aqaba . They are soon joined on the journey by Auda ibu Tayi , a Howeitat tribal chief . With his help, the Turks finally succeeded in beating the Turks in front of Akaba at Abu l-Lisan on July 1st. The Arabs were able to take Aqaba without a fight on July 6th. With supplies now embarking in the city, the Bedouins are now able to take the Arab Revolt to Palestine and Syria and carry out several sabotage actions against the Hijaz railway and telegraph poles. On October 8th, the British expeditionary forces manage to break through at Gaza and advance further north through Palestine.
- Mid-July: At the request of the Ottoman army command under Enver Pasha , Erich von Falkenhayn takes over the leadership of Army Group F , whose forces have been newly formed in Iraq and near Aleppo. After lengthy arguments with the Turkish leadership, on September 7 he was appointed as an Ottoman field marshal and commander-in-chief of two Turkish field armies in Palestine .
- 31 October: Edmund Allenby , since June 28 replacing Archibald Murray in command of the British Egyptian Expeditionary Force , begins a successful offensive against the Ottoman Army on the Palestine front . With the Australian 4th Light Horse Brigade and the British 5th Mounted Brigade, he led one of the last successful cavalry attacks in history during the capture of Be'er Sheva . On November 7th he takes Gaza , which has been heavily fortified by the German commanders of the Ottoman troops. Ottoman resistance then collapses and Allenby is able to conquer Jaffa on November 16th. On November 19 he opens the Battle of Jerusalem , which ends on December 9 with the capture of the city .
- 5 December: Revolutionary Russia and the Ottoman Empire sign the Erzincan Armistice , ending hostilities on the Caucasus Front.
The War in the Colonies
- February: A unit of the Schutztruppe for German East Africa under Max Wintgens breaks away from the main body of the troop and begins autonomous guerrilla operations in the west and north of the German colony. The remnants of this force surrendered at Luitaberg southeast of Kondoa on October 1st . The remaining forces under Paul von Lettow-Vorbeck are increasingly concentrated near the Mozambican border. The last radio of the Schutztruppe was destroyed, meaning that there was no longer any communication with Germany.
- October 15-18: Germans defeat British at Battle of Mahiwa , suffering heavy casualties.
- November 25: The German Schutztruppe from German East Africa under Paul von Lettow-Vorbeck defeats Portuguese troops under João Teixeira Pinto at the Battle of Ngomano and secures the passage across the Rovuma border river into Portuguese East Africa . From there they continue their bush war against the Allies.
- 3 November: A last attempt to supply the Schutztruppe with supplies by the airship LZ 104/L 59 from Berlin-Staaken via Bulgaria fails. On November 21, the airship turns back over Sudan and returns to Bulgaria. In flight, it sets a long-distance record. LZ 104 covered a distance of 6,757 kilometers in 95 hours and five minutes .
Sea and Air War
Due to the difficult overall military situation, the Supreme Army Command urged Wilhelm II to allow unlimited submarine warfare; on January 8, the Kaiser agreed. On January 9, Chancellor Theobald von Bethmann-Hollweg presented all the counter-arguments again, but in contrast to the discussions in 1915 and 1916, he no longer raised any fundamental objections. On January 9, 1917, the Privy Council decides to open unrestricted submarine warfare on February 1 without further negotiations and advance notices. This means that submarine commanders can attack "any ship using any available weapon without notice". The neutrals will receive a brief notification to this effect on January 31st. By December 31, 6.141 million GRT of Allied shipping and 1.127 million GRT of neutral shipping were sunk by the German U-boat fleet, consisting of approximately 110 operational boats.
- January 9: The German submarine U 32 under the command of Kurt Hartwig sinks the British battleship Cornwallis in the Mediterranean . Since the ship can be kept under control for a long time before sinking, only 15 people are killed.
- January: Manfred von Richthofen is given the command of Jagdstaffel 11 .
- February 3: The German submarine SM U 53 under captain lieutenant Hans Rose boards the US freighter Housatonic south of the Isles of Scilly . After the crew has boarded lifeboats, the ship is scuttled.
- February 7: The British passenger liner California is sunk by the German submarine SM U 85 off the south coast of Ireland without warning . 41 people die.
- February 17: When the French troop carrier Athos is sunk in the eastern Mediterranean by the German submarine SM U 65 under the command of Hermann von Fischel , 754 crew members, soldiers and passengers die.
- February 25: The British ocean liner RMS Laconia is sunk by a German U-boat off the coast of southern Ireland without warning; 12 people die. The death of two Americans creates political tension.
- March 11: SM U 53 under Hans Rose sinks the former Cunard Line passenger ship Folia , which has been converted into a cargo ship , killing seven crew members.
- April 4: German submarine UC 35 sinks British passenger liner City of Paris off Cap d'Antibes ( Côte d'Azur ) . All 122 people on board die.
- April 10: The British hospital ship HMHS Salta runs into a sea mine off Le Havre and sinks. Of the 205 people on board, 130 die.

- April 15: The former ocean liner Cameronia , converted into a troop transport , is sunk east of Malta by the German U-boat U-33 . 210 people die.
- April 17: The British hospital ships Donegal and Lanfranc are torpedoed and sunk by German U-boats. A total of 81 people are killed, including some German prisoners of war.

- 22 April: A Royal Aircraft Factory SE5 is used for the first time on a Royal Flying Corps patrol flight over France. Starting in the summer, together with the Sopwith Camel , it made a significant contribution to achieving air supremacy for the Allies on the western front and maintaining it until the end of the war.
- April 24: 180 nautical miles west of Fastnet Rock , the British passenger and cargo steamer Abosso is sunk by the German submarine U 43 ; 65 passengers and crew perish.
- May 4: The former ocean liner Transylvania , converted into a troop carrier, is sunk by the German U-boat U 63 in the Gulf of Genoa . 412 soldiers and crew members die.
- 15 May: An Austro-Hungarian attack on the Otranto Lock between the Adriatic and Ionian Seas leads to the Battle of the Straits of Otranto , the largest naval battle in the Adriatic during the war. Without losing a ship, the Austrian Navy , under the command of Miklós Horthy , inflicts great damage on the Entente and is able to break through the barrier. However, the battle changes little in the overall strategic situation in the Adriatic and the barrier can be rebuilt a little later.
- August 2: Edwin Harris Dunning 's Sopwith Pup becomes the first pilot to land on a moving ship, the British aircraft carrier HMS Furious . Five days later, trying again, he falls and drowns.
- August 13: The troop carrier Turakina is sunk by the German submarine U- 86 southwest of Bishop Rock at Land's End .
- September/October: Operation Albion
- 17 October: Battle of the Shetland Islands ends in Imperial Navy victory over Royal Navy .
- November 17: In the German Bight , a naval battle breaks out between British and German naval forces off Heligoland , which is broken off without a decision being made.
- November 28: Off the island of Anglesey , the British passenger and cargo steamer Apapa is sunk by two torpedoes by the German U-boat U 96 ; 77 passengers and crew perish.
- December 6: SM U 53 under Hans Rose sank the United States Navy destroyer USS Jacob Jones . Two officers and 64 sailors are killed. It is the first US Navy destroyer to be lost to enemy action.
- December 12: The sea battle off Bergen ends with another German victory over British units.
- December 30: The British troop carrier Aragon is sunk by a torpedo off the port of Alexandria by the German submarine UC-34 . 610 British soldiers and crew members perish.
- December 31: The British troop carrier Osmanieh runs into a sea mine laid by the German submarine UC 34 off Alexandria and sinks within a few minutes. 199 people are killed, including eight British nurses.
The revolution in Russia
February revolution and overthrow of the tsar
- December 19, 1916 Jul. / January 1, 1917 greg. : Grigory Rasputin , advisor to Tsar Nicholas II , is recovered dead from the Neva . Tsarina Alexandra Fyodorovna demands the immediate execution of the main perpetrators, but Prince Felix Yusupov is only banished to his family estate in Rakitnoye , and Dmitri Romanov is transferred to the Persian front. All other assassins remain unmolested, Vladimir Purishkevich even continues to give speeches as a Duma deputy .
- February 14th / February 27th greg. : The opening of the Duma will be accompanied by a mass demonstration calling for energetic action.
- 21 february july / March 6th greg. : A strike breaks out in the Putilov works , an armaments factory in Petrograd . As a result, the directorate ordered the lockout of 30,000 men. A protest demonstration against the catastrophic supply situation promptly ensued. The protests spread like an avalanche to other companies. Thousands demonstrate with red flags on Nevsky Prospect .
- 23 february july / March 8th greg. : There is another strike in the Putilov works. Workers in Petrograd go on general strike , the actual February revolution begins. As in 1905, workers' committees form councils, so-called soviets , which represent the demands of the demonstrators and try to enforce them politically. The councils are headed by an executive committee, which initially consists mainly of Mensheviks and SRs .
- 24 february july / March 9th greg. : Tsar Nicholas II gives the order to shoot at the insurgents of the February revolution . The following afternoon, members of the Volhynian Guards regiment fired on the rebels in the capital, killing sixty people. In other places, however, the troops are allied with the demonstrators.
- February 26th / March 11 greg. : Nicholas II telegraphically dissolves the Duma, which, however, refuses to disband.
- 27 Feb Jul / March 12 greg. : The Volhyn Guards Regiment in Petrograd switches to the side of the revolution. The Preobrazhensk and Lithuanian Guards regiments follow. Several commanders are shot and the insurgents are supplied with weapons. In the afternoon the building of the Duma is also occupied by armed soldiers and workers, and in the evening the Petrograd Soviet meets in the session hall of the Duma . The still incumbent tsarist government imposed a state of siege on Petrograd .
- 28 february july / March 13 greg. : The uprising spreads to Moscow , where it takes a similar course as in Petrograd.
- March 1st July / March 14 greg. : The Petrograd Soviet issues Order No. 1 , according to which only government orders that do not contradict those of the Soviet are to be obeyed. This marks the beginning of the so-called “ dual power ” of the government and the Soviets.
- March 1st July / March 14 greg. : Mikhail Alexeyev , the chief of staff and thus de facto commander of all armies, calls on Nicholas II to abdicate.
- 2 mar july / March 15 greg. : Tsar Nicholas II abdicates in favor of his brother Mikhail , who renounces his throne the following day; thus ends the Romanov dynasty. A provisional government is formed under Prince Georgi Lvov . Minister of Justice will be Alexander Kerensky , Minister of Foreign Affairs Pavel Miliukov and Minister of War Alexander Guchkov . The tsar's arrested ministers are transferred to the Peter and Paul Fortress .
- 7 mar july / March 20 greg. : Mychajlo Hruschewskyj is elected chairman of the People's Council in Ukraine , which was founded three days earlier .
- 8 mar july / March 21 greg. : Nicholas II is arrested and, after being interned in Zarskoje Selo , banished to Siberia with his family.
Journey of Lenin and October Revolution
- 27 mar july / April 9th greg. : Lenin's journey in a sealed car from Zurich via Germany and Sweden to Russia begins. The intermediary for the company is the accompanying Swiss socialist Fritz Platten . Other passengers included Lenin's wife Nadja Krupskaja and his lover Inessa Armand , Mieczysław Broński (with daughter Wanda Brońska ), Moissei Charitonov , Karl Radek , Sarra Rawitsch , Georgi Safarov , Grigory Zinoviev and Grigory Sokolnikov .
- 30 mar july / April 12 greg. : On the railway ferry Drottning Victoria , the tour group crosses over from Sassnitz to Trelleborg in Sweden. She then travels on to Tornio in Finland via Stockholm .
- April 3rd / April 16 greg. : Lenin's tour group arrives at the Finnish railway station in Petrograd, where they are received by several thousand people. Georgian Mensheviks Nikolos Cheidze and Irakli Tsereteli deliver welcoming speeches.

- April 4th / April 17 greg. : Vladimir Lenin gives a speech to the Petrograd Soviet, where he outlines his April Theses for the first time. In it he criticizes, among other things, the provisional government for its capitalist orientation and calls for the establishment of a republic based on the Soviets, nationalization of the land and the means of production, and the unconditional peace agreement with Germany.
- April 18th / May 1st greg. : In the Miliukov Note , the Russian government assures the Allies that they will fulfill their obligations to the alliance and that the war will be continued, and rules out the conclusion of a separate peace with Germany. The letter leads to the so-called April Crisis in Petrograd, where the population reacts again with strikes.
- April 29th / May 12 greg. : Minister of War Alexander Guchkov resigns as a result of the April Crisis.
- May 2nd / May 15 greg. : Foreign Minister Pavel Miliukov resigns.
- June: First All -Russian Central Executive Committee elected at First All-Russian Congress of Soviets June 3-24 in Petrograd . Nikolos Tschkheidze becomes chairman.
- July 3rd / July 16th greg. until July 7th / July 20 greg. : The Bolshevik-inspired July Uprising in Petrograd fails. The declared general strike failed, as did a poorly coordinated uprising by the Kronstadt sailors and Red Guards . A demonstration they were accompanying in St. Petersburg was shot up by government cadets. The dual power ended in favor of the provisional government.
- July 8th / July 21 greg. : After the resignation of Georgi Lvov, Alexander Kerensky takes over the presidency of the Provisional Government in addition to the Ministry of War and Navy .
- Aug 27th / 9 September greg. : Lavr Kornilov , supreme commander of the Russian armed forces, attempts a failed coup against the Kerensky government.
- 1 september july / September 14 greg. : Prime Minister Alexander Kerensky proclaims the Russian Republic demanded by the radical left after the February revolution . The Bolsheviks , meanwhile, are planning an uprising .
- october 25th / November 7th greg. : The October Revolution begins in Petrograd with a signal shot from the cruiser Aurora . The Winter Palace , the seat of the provisional government, is stormed and all members of the government except Prime Minister Alexander Kerensky are arrested. The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic is founded.
- october 26th / November 8th greg. : The decree on land worked out by Lenin is published in Izvestia . The confiscation of lands from landlords, churches and state domains without compensation won the rural population over to the Bolsheviks. On the same day, the government of Soviet Russia unanimously passed the Decree on Peace , which was also published in Izvestia .
- october 27th / November 9th greg. : Lev Kamenev becomes chairman of the All- Russian Central Executive Committee and thus head of state of the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic. He was replaced by Yakov Sverdlov just 12 days later . Furthermore, 13 People's Commissariats are created by decree and the Council of People's Commissars is set up.
- 12 Nov Jul / November 25th greg. : The elections to the Constituent Assembly are held, from which the SR Party emerges by far as the strongest force. The Bolsheviks received just under a quarter of the votes.
- 23 Nov-July / December 6th greg. : The Soviet Russian government chaired by Lenin instructed Felix Dzerzhinsky , a member of the Petrograd Military Revolutionary Committee (MRKP) , to set up a special commission to combat the strike by tsarist officials, which began just a few days after the October Revolution . On December 7th July / December 20th greg. the secret police Cheka will come into being, from which the GPU will emerge.
- 2 december july / December 15th greg. : The Supreme Council for National Economy is established by decree. This is on an equal footing with the people's commissariats and has the task of organizing the entire economy and finances of Russia.
independence aspirations
- 2 Nov Jul / November 15 greg. : The Bolsheviks declare a general right of all peoples of the Tsarist Empire to self-determination .
- 7 Nov Jul / November 20th greg. : The Central Council of Ukraine proclaims the autonomous Ukrainian People's Republic within the federative new Soviet Russia . Capital will be Kiev . In December 1917, Soviet Russian units of the former Russian Army and Red Guards begin a military offensive into Ukraine. The Ukrainian-Soviet War begins.
- 21 Nov Jul / December 4th greg. : A Declaration of Independence drafted by Pehr Evind Svinhufvud is presented to the Finnish Parliament .
- 23 Nov-July / December 6th greg. : In Helsinki , the parliament declares the independence of the former Grand Duchy of Finland from Russia.
- Nov 29th / December 12 greg. : Uprisings of the Bolsheviks in Kiev , Odessa and Vinnyzja are put down by units of the Ukrainian People's Republic.
- 2 december july / December 15th greg. : The previous governorate of Bessarabia proclaims the Moldovan Democratic Republic , which at this point in time is not striving for full independence but wants to remain part of a new, reformed Russian state and in return wants to have extensive autonomy.
- 13 december july / December 26th greg. : Soviet units capture the Ukrainian city of Kharkiv. On December 17th July / December 30th greg. the Ukrainian People's Republic of the Soviets is declaimed there.
- 18 december july / December 31 greg. : Soviet Russia recognizes Finland's independence.
Portugal
- 25 April: Finance Minister Afonso Costa succeeds António José de Almeida and becomes Prime Minister of Portugal for the third time . The new government consists only of democrats and non-partisans close to them, but is tolerated by the liberal evolutionists .
- June 12: In Portugal, the Afonso Costa government declares a state of emergency after allegations of corruption killed in violent demonstrations.
- December 5: A military revolt begins in Portugal, with Captain Sidónio Pais taking power.
- December 8: After the December 5 coup , Prime Minister Afonso Costa leaves Portugal and goes into exile in France. Sidónio Pais becomes the new head of government, suspends the constitution and proclaims the República Nova . President Bernardino Machado , who refused to hand over his office, was briefly arrested and then also had to go into exile in France.
Other events in Europe
- January 1: Edmund Schulthess becomes the new President of Switzerland .
Other events in America
- January 27: In Costa Rica , Secretary of War and Navy Federico Alberto Tinoco Granados , with the help of the military, staged a coup against President Alfredo González Flores , who was taking refuge in the US Embassy. A constituent assembly convened by Granados elects him president of the country in April.
- February 5: Mexico's first constitution is promulgated during the Mexican Revolution . Venustiano Carranza becomes Mexico's first constitutional president in May .
- February 7: The United States ends the Mexican Expedition against Pancho Villa and withdraws its troops from Mexico.
- March 2: US President Woodrow Wilson signs the Jones–Shafroth Act . With this, Puerto Rico becomes an organized but unincorporated territory of the United States .
- April 1: After a referendum held late last year, Denmark sells the colony of the Danish West Indies to the United States for $25 million , which renames it the United States Virgin Islands . James Harrison Oliver is appointed first Governor of the US Virgin Islands by President Woodrow Wilson. Edwin Taylor Pollock will temporarily represent him until he arrives at his new place of work .
Asia
- July 1: After a military coup, eleven-year-old Puyi is crowned Emperor of China for the second time in the Forbidden City . After 12 days, however, this restoration attempt is already over.
- November 2: The Lansing-Ishii Agreement between the United States and the Japanese Empire over their interests in China . The negotiators of both nations are former Japanese Foreign Minister Ishii Kikujirō and US Secretary of State Robert Lansing . The open door policy should be maintained.
Australia
- August 2-September 8: At times, more than 100,000 workers took part in the 1917 Australian General Strike , which emanated from New South Wales . However, the strike is ended without success, and numerous strikers are subsequently fired or transferred to other jobs with lower wages. The strike was triggered by the introduction of a new cost and performance control system, a Taylorism system, for railway and streetcar workers.
business
war economy
- July 24: The War Economy Enabling Act is passed in Austria . In it, the imperial and royal government is empowered by the emperor and the Reichsrat to enact the necessary decrees for the functioning of the economy and the supply of the population by decree and also to change laws.
- December 22: The standards committee of German industry (precursor to DIN ) is founded.
Company formations and takeovers
- 17 April: Henry Ford founds the Henry Ford & Son subsidiary in Cork , establishing the motor industry in Ireland .
- April 24: Polyphon Musikwerke AG takes over Deutsche Grammophon Gesellschaft .
- July 31: The Neue Republikanische Blatter appear for the first time in Switzerland .
- September 25: Anglo American is founded by Ernest Oppenheimer to exploit the gold deposits of South Africa's East Rand .
- October 16: Investors from several states participate in the formation of the Companhia de Diamantes de Angola ( Diamang ), which will focus on diamond mining in Angola .
- December 13: Deutsche Luft-Reederei , a predecessor of Lufthansa , is founded.
- The Austrian Tourist Office is founded in Vienna. The state organization is initially entrusted with the development of a ticket system for the Austrian State Railways .
Other Economic Events
- March 13: The German Leather Museum , created on the initiative of Hugo Eberhardt , is opened in Offenbach am Main .
- April 15 to 29: The first sample fair in Basel is held.
- August 4: French engineer Lucien Lévy applies for a patent for a method of superimposing radio signals. As a result, his circuit principle prevailed over others.
- October 6: The Swiss railway company Langenthal-Melchnau-Bahn opens the meter- gauge narrow -gauge railway line from Langenthal via Roggwil and St. Urban to Melchnau , which is located in the cantons of Bern and Lucerne . The Langenthal-Melchnau railway is managed by the Langenthal-Jura-Bahn , which was founded in 1907 .
science and technology
Antarctic research
- January 10 Refitted in New Zealand , the Aurora arrives at Cape Evans on the west coast of Ross Island , Antarctica , and picks up the last seven survivors of the Ross Sea Party to take them to Wellington, arriving on February 9. This ends the failed Endurance Expedition , which set out in 1914 under the leadership of Ernest Shackleton to cross Antarctica.
natural sciences
- July 6th: The Kaiser Wilhelm Society for the Advancement of Science decides to found the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Physics on October 1st. This initially does not have its own institute building, the address of the institute is the private address of the first director Albert Einstein in Berlin-Schoeneberg .
- August 19: The American paleontologist Charles Walcott finds fossilized in the Burgess Shale the extinct species Fasciculus vesanus , which lived on Earth about 510 million years ago in the Cambrian .
- Robert Innes , director of the Republic Observatory in Johannesburg, discovers the star Proxima Centauri .
Technical achievements
- December 15: After more than two years of construction, the first train crosses the Metropolis Bridge over the Ohio between the city of Metropolis , Illinois and McCracken County , Kentucky . The steel bridge, which is almost two kilometers long, has the world's longest simple truss girder of a railway bridge at 220 meters and was originally designed for a double-track expansion, which was never implemented.
- The American Eugene Clark produces the first forklift truck .
- Technicolor is used for the first time in the film The Gulf Between with a 2-color process. However, the process leads to a great disappointment, as the cinema projectionist does not manage to adjust the two cinema projector prisms in such a way that the two colored partial images are correctly superimposed on the screen.
Teaching and Research
- March 26: Chulalongkorn University is founded in Bangkok as the first university in Siam (today's Thailand).
Culture
Visual arts

- 10 April: The first issue of the Dada magazine The Blind Man is published in New York to mark the opening of the Society of Independent Artists ' first exhibition .
- April: The Ready-made Fountain by Marcel Duchamp , a marked “R. Mutt" autographed commercial urinal from a plumbing store , is rejected by the board of the Society of Independent Artists .
- Commissioned by his friend and art dealer Leopold Zborowski , Amedeo Modigliani painted a series of nudes, including the oil paintings Nu couché ( Reclining Nude ) and Reclining Female Nude on White Pillow . The works will be shown on December 3 at the artist's only solo exhibition at the Berthe Weill Gallery, which, however, is closed by the police on the first day.
- The Dutch artist group De Stijl is founded. She is committed to a geometric-abstract, "ascetic" form of representation in art and architecture and a purism limited to functionality . Founding members are painter and art theorist Theo van Doesburg , painters Piet Mondrian and Georges Vantongerloo , architects Robert van't Hoff , JJP Oud and Jan Wils , painters Vilmos Huszár and Bart van der Leck , and poet Antony Kok .
Movie
- The premiere of Charlie Chaplin's silent comedy Easy Street , scheduled for January 22, has had to be postponed by two weeks due to several mishaps on the set. The "comical parody of Victorian reformatory melodramas" is considered one of the artist's early masterpieces.
- February: During a studio visit, Roscoe Arbuckle spontaneously invites the initially skeptical vaudeville comedian Buster Keaton to appear in one of his films. The Butcher Boy is considered Keaton's screen debut.
- March 1st: With the first of four parts of Let There Be Light! directed by Richard Oswald , the first educational film was released in cinemas and received a positive response from the general public and non-bourgeois critics. Archconservative and military circles, on the other hand, are fiercely fighting the plant.
- June 17: The tragic comedy The Immigrant , starring Charlie Chaplin and Edna Purviance , premieres. Clips from the film are used in the McCarthy era as "evidence" of Chaplin's alleged anti-Americanism.
literature
- March 8: The British publishing house Methuen Publishing publishes the short story collection The Man with Two Left Feet by PG Wodehouse .
- Spring: The Siuru literary group is founded in Estonia.
- June 4: The Pulitzer Prize , one of the most important awards for journalism and literature in the United States, donated by journalist and newspaper publisher Joseph Pulitzer , is presented for the first time at Columbia University .
- In the field hospital after the Battle of the Somme , JRR Tolkien drafts the first drafts of his later work The Silmarillion .
- Leonard and Virginia Woolf found The Hogarth Press in their living room .
music and theatre
- January 29: Georg Kaiser's expressionist stage play The Burghers of Calais premieres at the New Theater in Frankfurt am Main, directed by Arthur Hellmer . The play is a great success with the public and brings the author's artistic breakthrough.
- January 30: The one-act opera Eine Florentinische Tragedy by Alexander von Zemlinsky has its world premiere at the Hoftheater in Stuttgart . The text is based on the poem A Florentine Tragedy by Oscar Wilde in the German translation by Max Meyerfeld.
- February 23: The premiere of César Cui 's opera Mlada takes place at the Mikhailovsky Theater in Saint Petersburg, but the work, written in 1872, arouses no interest.
- April 26: Hugo von Hofmannsthal 's comedy Die Lästigen is premiered in the Kammerspiele of the Deutsches Theater in Berlin.
- April 28: Georg Kaiser 's play From Morning to Midnight , written in 1912, premieres in Munich.
- May 11: The Opera Turandot. A Chinese fable by Ferruccio Busoni based on Carlo Gozzi will be premiered together with the Capriccio Arlecchino or The Windows conducted by the composer at the Stadttheater Zürich .
- May 12: The dance play A fából faragott királyfi ( The Wooden Prince ) by Hungarian composer Béla Bartók to a libretto by József Újfalussy after Béla Balázs has its world premiere in Budapest.
- June 12: Hans Pfitzner 's musical legend Palestrina is premiered at the Prinzregententheater in Munich under the direction of Bruno Walter with Karl Erb in the title role with an extraordinary success.
- June 18: The drama So it is by Luigi Pirandello has its world premiere in Milan.
- August 25: The world premiere of Leon Jessel 's operetta Schwarzwaldmädel takes place in Berlin. The libretto is by August Neidhart .
- October 6: The operetta Three Old Boxes by Walter Kollo with the libretto by Herman Haller is premiered at the Theater am Nollendorfplatz in Berlin . The lyrics are by Rideamus aka Fritz Olive .
- December 11: Hans Pfitzner 's work Das Christ-Elflein is premiered in its second version, which has been reworked into a dramatized opera , at the Dresden Court Opera under the direction of Fritz Reiner and with Grete Merrem-Nikisch in the title role. The original poetry comes from Ilse von Stach . In contrast to Pfitzner's first version, the second version is a success.
society
- 4 June: King George V of Great Britain institutes the Order of the Companions of Honor in recognition of outstanding achievement in the fields of art, music, literature, science, politics, industry and religion.
- June 7: Businessman Melvin Jones forms the Lions Club in Chicago .
religion
- 12 mar july / March 25 greg. : The Georgian Orthodox Church declares its independence from the Russian Orthodox Church , to which it has been subordinate since 1811. On September 15th / September 28 greg. With Kyrion II , a Catholicos patriarch is elected again for all of Georgia. However, the restored autocephaly of the Georgian Orthodox Church will remain controversial within Orthodoxy for decades to come.
- May 13: The three children Lúcia dos Santos , Jacinta and Francisco Marto allegedly have a Marian apparition in Fátima , Portugal , which is followed by four more until October 13.
- May 27: Pope Benedict XV. puts into effect the Codex Iuris Canonici suggested by the First Vatican Council , commissioned by Pope Pius X and largely developed by Pietro Gasparri . This is the first time that Latin canon law has been codified in a centralizing legal code . The strengthening of papal legal competences , which was criticized as Roman centralism , was promoted by the Vatican also out of the devastating experience of papal powerlessness in the face of the First World War . Among other things, episcopal ordinations must no longer fall under the control of national politics.
- October 13: At midday, in Fátima , Portugal , the Virgin Mary makes her final appearance to the three shepherd children, Jacinta Marto , Francisco Marto , and Lúcia dos Santos . The miracle of the sun takes place in the presence of tens of thousands of people.
disasters
ship disasters
- January 14: Japanese battleship Tsukuba sunk after fire and ammunition rack explosion in Yokosuka Bay. The result was 305 deaths among the 817-strong crew.
- August 30: The French passenger liner Natal collides with an oncoming cargo ship near Marseilles and sinks in just ten minutes. 105 of 503 passengers and crew die.
- December 6: The largest accidental man-made explosion to date occurs in the port of Halifax on Canada's east coast. The French ammunition freighter Mont Blanc collides with the Norwegian ship Imo , catches fire and explodes. The accident killed at least 1,946 people and injured many more thousands. The explosion is so powerful that it triggers a tidal wave and violent earthquakes, while the enormous blast uproots trees, bends railroad tracks and destroys numerous buildings.
earthquake
- January 21: An earthquake of unknown magnitude in Bali , Indonesia kills about 15,000.
- July 30: A 6.5 magnitude earthquake in China kills around 1,800.
fire disasters
- May 21: A major fire breaks out in Atlanta , destroying 1,938 buildings and making about 10,000 people homeless. However, there is "only" one fatality to be lamented.
- August 18: The Great Fire in Thessaloniki begins. The flames can only be finally extinguished the following day. 32 percent of the city is destroyed, and about 70 percent of the jobs are destroyed by the fire. Thousands of residents become homeless.
other disasters
- January 13: In one of the world's worst rail accidents, a train packed with wounded Russian soldiers and refugees derailed at the train station in the Romanian town of Ciurea . The accident claims between 600 and 1000 lives.
- August 4: The rupture of the Tigra Dam in India causes a tidal wave that kills around 1,000 people.
- July 10: In the case of the Pragerhof railway accident , a transport of ammunition loaded with sea mines explodes at Pragerhof station in present-day Slovenia on the Spielfeld-Strass-Trieste Centrale railway line . 43 people die and 75 others are injured.
- December 12th: train crash near Modane /France, at least 543 dead
Minor accidents are listed in the sub-articles of Disaster .
nature and environment
- February 26: With the signature of the American President Woodrow Wilson , on the initiative of Senator Key Pittman , Mount McKinley National Park is created in Alaska .
- March 5: The Treysa meteorite , which had fallen almost a year earlier, is found in a forest near Rommershausen based on calculations by Alfred Wegener .
Sports
- May 9: Norwegian football club Rosenborg Trondheim is founded under the name Odd .
- 30 September to 14 October: Uruguay defends their title in the 1917 Campeonato Sudamericano .
- October 29: The Berlin senior gymnastics manager Max Heiser gives fixed rules to the “torball game” he designed for women in 1915 and renames the game handball .
- November 22-26: Due to disagreements in the Eastern Canadian National Hockey Association , the leaders of the Montréal Canadiens , Montreal Wanderers , Ottawa Senators and Québec Bulldogs join forces and, after several meetings, form the National Hockey League . First matchday of the first season is December 19th.
Nobel prizes
| price | person | country | Justification for the award | image |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nobel Price for physics |
Charles Glover Barkla (1877–1944) (awarded 1918) |
|
"for his discovery of the characteristic X-ray radiation of the elements " |

|
| Nobel Prize in Chemistry | not awarded | |||
| Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine | not awarded | |||
| Nobel Prize in literature |
Karl Gjellerup (1857–1919) |
|
"for his diverse, rich poetry, which is based on high ideals" |

|
|
Henrik Pontoppidan (1857–1943) |
|
"for his rich portrayal of contemporary Danish life" |

|
|
| Nobel Peace Prize |
International Committee of the Red Cross (founded 1863) |
Based in Geneva, Switzerland |
campaigned for prisoners of war and wounded and for the respect of the Geneva Convention during the First World War |

|
Born
January
- January 1: Erwin Axer , Polish theater director († 2012)
- January 1: Jule Gregory Charney , American meteorologist (d. 1981)
- January 2: Zainab al-Ghazali , Egyptian Islamic propagandist (died 2005)
- January 2: Pierre Salama , French classical archaeologist and epigraphist (died 2009)
- January 3 Pauline Davis , US politician (died 1995)
- January 3: Alexander Spoerl , German writer (died 1978)
- January 4 George Casalis , French Evangelical Reformed pastor (d. 1987)
- January 4: Georg Schaeffler , German entrepreneur (died 1996)
- January 5: Robert Antelme , French writer (died 1990)
- January 5: Silvia Eisenstein , Argentine-Venezuelan pianist, composer, conductor and music teacher (died 1986)
- January 5: Wieland Wagner , German opera director and set designer (died 1966)
- January 5: Fred Wander , Austrian writer (died 2006)
- January 5: Jane Wyman , American actress (died 2007)
- January 7: Ulysses Kay , American composer (died 1995)
- January 7: Paul Limberg , German crop production scientist (died 1997)
- January 8 Len Younce , American football player (d. 2000)
- January 10: Hilde Krahl , Austrian actress (d. 1999)
- January 11: Cornelius Brown , Canadian ice hockey player (d. 1996)
- January 11: Max Lang , Swiss musician, composer and conductor (d. 1987)
- January 13: Sergio Grieco , Italian film director and screenwriter (d. 1982)
- January 16: Luigi Agustoni , Swiss theologian, church musician and professor († 2004)
- January 16: Justin Ahomadegbé-Tomêtin , President of Benin († 2002)
- January 16: Ibrahim Shams , Egyptian weightlifter (d. 2001)
- January 17 – MG Ramachandran , Indian film actor and politician (d. 1987)
- January 18: Robert Carricart , French-American actor (d. 1993)
- January 19: Rudolf Maros , Hungarian composer (died 1982)
- January 20 Bruno Heck , German politician (died 1989)
- January 20: K-Ximbinho , Brazilian clarinetist, composer and arranger (died 1980)
- January 22: Rainer Brambach , Swiss writer (d. 1983)
- January 22: Peter Steiner , Swiss advertising figure and musician († 2007)
- January 23: Lotte Buschan , German opera singer (died 1994)
- January 24: Ernest Borgnine , American actor (died 2012)
- January 25: Jânio Quadros , President of Brazil (died 1992)
- January 25: Enrique Sáenz-Valiente , Argentine marksman and automobile racer (d. 1956)
- January 26: Edgar Barth , German racing driver (d. 1965)
- January 26: William Verity , American businessman and politician (died 2007)
- January 28 Abdel-Kader Zaaf , Algerian cyclist (d. 1986)
- January 30: Paul Frère , Belgian racing driver, journalist and author († 2008)
- January 31: Hans Posegga , German composer, pianist and conductor († 2002)
February
- February 1 – Ray Bray , American football player (d. 1993)
- February 2 Herman Feshbach , American physicist (died 2000)
- February 2: Hans Friedrich , German politician, MP (died 1998)
- February 2: Karl Gass , documentary film director and film functionary of the GDR († 2009)
- February 2: Đỗ Mười , Vietnamese politician (died 2018)
- February 4: Franz Josef Bach , German politician and member of the Bundestag (died 2001)
- February 5: Otto Edelmann , Austrian singer († 2003)
- February 5: Yamada Isuzu , Japanese actress († 2012)
- February 6: Emmanuela Aichinger , German Abbess of Tettenweis Monastery (died 2005)
- February 6 Zsa Zsa Gabor , American-Hungarian actress (died 2016)
- February 6 Arnold Spielberg , American electrical engineer (d. 2020)
- February 6: Hermann Schmidt , German politician (died 1983)
- February 8: Wilhelm Karl Ferdinand Schubert , German SS-Oberscharführer and block leader in Sachsenhausen concentration camp († 2006)
- February 10: Danny Kladis , American racing driver (d. 2009)
- February 10 Syria Poletti , Italian-Argentinian writer and journalist (died 1991)
- February 12: Al Cervi , American basketball player and coach (d. 2009)
- February 12: Karl Wilhelm Struve , German prehistorian and early historian (died 1988)
- February 12: Joseph Wresinski , French cleric and founder of the ATD Fourth World human rights movement (died 1988)
- February 14 Herbert A. Hauptman , American mathematician and biophysicist (died 2011)
- February 15: Gösta Andersson , Swedish wrestler (died 1975)
- February 16 Adalbert Pilch , Austrian painter and graphic artist († 2004)
- February 16 Willi Weyer , German sports official (died 1987)
- February 18: Luigina Amendola , Italian actress (d. 1968)
- February 18: Hans Otto Lenel , German national economist (died 2016)
- February 19 – Carson McCullers , American writer (died 1967)
- February 19 Margarete Neumann , German poet and writer († 2002)
- February 19 Fritz-Rudolf Schultz , German politician (died 2002)
- February 20: Josef Haiböck , Austrian general (died 2002)
- February 22: Louis Auriacombe , French conductor (died 1982)
- February 22 – Jane Bowles , American writer (died 1973)
- February 23: Herbert Wunsch , Austrian table tennis player (died 1970)
- February 24: Hans Hartwig , German composer († 2012)
- February 25: Anthony Burgess , British novelist (died 1993)
- February 26: Robert La Caze , French racing driver (died 2015)
- February 26 – Robert Taft Jr. , American politician (died 1993)
- February 27: John Connally , US politician, Governor of Texas, Secretary of the Treasury (d. 1993)
- February 28: Ernesto Alonso , Mexican actor, television director and producer († 2007)
- February 28 Max Jones , British jazz writer and journalist (died 1993)
March
- March 1: Robert Lowell , American poet (died 1977)
- March 1: Cliffie Stone , American country musician, host and producer (d. 1998)
- March 2 Desi Arnaz , Colombian musician and actor (d. 1986)
- March 2: Babiker Awadalla , Sudanese politician (died 2019)
- March 6: Samael Aun Weor , Colombian occultist (died 1977)
- March 6: Will Eisner , American comic artist († 2005)
- March 6: Oswald Karch , German racing driver (d. 2009)
- March 7: Robert Erickson , American composer (died 1997)
- March 8: Petar Hristoskov , Bulgarian composer, violinist and music teacher († 2006)
- March 8: Leslie Fiedler , American literary scholar and critic († 2003)
- March 9: Walter Hilsbecher , German writer (died 2015)
- March 9: Ian Watt , British literary critic and literary historian (died 1999)
- March 11: Günter Goetzendorff , German politician (died 2000)
- March 12: Leonard Chess , Polish-American entrepreneur (d. 1969)
- March 12: Millard Kaufman , American screenwriter († 2009)
- March 12: Googie Withers , American actress († 2011)
- March 14: Jack Davis , Australian playwright and poet (died 2000)
- March 14: Gerhard Müller-Menckens , German architect and university lecturer († 2007)
- March 15: Elfie Mayerhofer , Austrian film actress and singer (d. 1992)
- March 16: Louis C. Wyman , American politician (died 2002)
- March 19 Dinu Lipatti , Romanian pianist and composer (died 1950)
- March 19 László Szabó , Hungarian chess player (died 1998)
- March 20: Augustin Augustinović , Croatian religious priest, missionary and writer (d. 1998)
- March 20: Jigael Jadin , Israeli archaeologist, politician and Chief of Staff of the Israeli Army (died 1984)
- March 20: Vera Lynn , British singer († 2020)
- March 20: Gottfried Schädlich , German officer and writer (died 2007)
- March 21: Anton Coppola , American musician and composer († 2020)
- March 23 Oscar Shumsky , American violinist and music educator (died 2000)
- March 24: Constantin Andreou , Greek-French painter and sculptor (died 2007)
- March 24 – Otto Rösch , Austrian politician and lawyer († 1995)
- March 26: Rufus Thomas , American blues musician († 2001)
- March 26: Billy Wallace , American country, rockabilly musician and songwriter (d. 1978)
- March 27: Cyrus Vance , US Secretary of State under Jimmy Carter (d. 2002)
- March 30: Els Aarne , Estonian composer († 1995)
- March 30 Thaddäus Schwabl , Austrian alpine skier (d. 1993)
- March 31 Dorothy DeLay , American violin teacher (d. 2002)
April
- April 2: Maria Holst , Austrian theater and film actress (d. 1980)
- April 2: Iris von Roten , Swiss lawyer, journalist and women's rights activist († 1990)
- April 3: Tibor Andrašovan , Slovak composer and conductor († 2001)
- April 3: Rembert van Delden , German politician (died 1999)
- April 3: Fredy Reyna , Venezuelan cuatro player and music educator († 2001)
- April 3: Stanley Solomon , Canadian violist and music manager († 2015)
- April 5: Robert Bloch , American author (died 1994)
- April 6 Leonora Carrington , British-Mexican painter and writer (died 2011)
- April 7: RG Armstrong , American actor (died 2012)
- April 7 Albert Sing , German soccer player and coach (died 2008)
- April 8th; Winifred Alice Asprey , American mathematician and computer scientist (died 2007)
- April 9: Johannes Bobrowski , German poet, storyteller, poet and essayist († 1965)
- April 9: Brad Dexter , American film actor and film producer († 2002)
- April 9: Rolf Kauka , German comics artist and publisher (father of Fix and Foxi ) († 2000)
- April 10: Robert B. Woodward , American chemist (d. 1979)
- April 11: Morton Sobell , US Soviet agent (died 2018)
- April 12: Robert Manzon , French Formula One racing driver (d. 2015)
- April 14: Valerie Hobson , British actress (d. 1998)
- April 16: Charlotte Salomon , German painter (died 1943)
- April 18: Shimao Toshio , Japanese writer (died 1986)
- 22 April Leopold Abse , Welsh lawyer, politician (Labour Party), gay rights activist and author (died 2008)
- April 22 – Åke Magnus Andersson , Swedish footballer (d. 1983)
- April 22 Erik Arnberger , Austrian cartographer (died 1987)
- April 22: Erna Steuri , Swiss ski racer († 2001)
- April 25 Ella Fitzgerald , American jazz singer (d. 1996)
- April 25: Jean Lucas , French racing driver (d. 2003)
- April 26: Ieoh Ming Pei , Chinese-American architect (died 2019)
- April 27 Denzil Best , American jazz musician (d. 1965)
- April 28: Robert Woodruff Anderson , American novelist, playwright, and screenwriter († 2009)
- April 29: Paul Affolter , Swiss Customs Officer (died 2005)
- April 29: Urie Bronfenbrenner , American developmental psychologist (died 2005)
- April 29 Maya Deren , American director (d. 1961)
- April 29: Celeste Holm , American actress (died 2012)
- April 30 Bea Wain , American singer and radio host († 2017)
May
- May 1: Aimé Barelli , French jazz trumpeter and band leader († 1995)
- May 1: Fyodor Chitruk , Russian animator and film director (died 2012)
- May 1: Danielle Darrieux , French actress († 2017)
- May 1: Wendy Toye , British actress (died 2010)
- May 2: Félix López , Dominican songwriter (died 1969)
- May 3: Kiro Gligorov , Macedonian politician (died 2012)
- May 7: Domenico Bartolucci , Italian cardinal and choir director of the Sistine Chapel († 2013)
- May 7: David Tomlinson , British actor (died 2000)
- May 8: John Anderson Jr. , American politician (died 2014)
- May 8: Miguel Bernad , Filipino cleric and journalist (died 2009)
- May 9 Fay Kanin , American screenwriter and film producer († 2013)
- May 10: Kurt Brand , German science fiction writer (died 1991)
- May 11: Thomas Burton Adams Jr. , American politician (died 2006)
- May 11: Wilhelm Auerswald , Austrian physiologist and university lecturer († 1981)
- May 11: Eva Garza , Mexican singer (d. 1966)
- May 12: Rika Unger , German sculptor († 2002)
- May 13: Marietheres Angerpointner , German actress († 2005)
- May 14: Heinz Alisch , German composer (died 1993)
- May 14: Lou Harrison , American composer († 2003)
- May 14 Norman Luboff , American composer and choir director (d. 1987)
- May 16: George Gaynes , American actor (died 2016)
- May 20 Tony Cliff , British socialist (died 2000)
- May 21: Raymond Burr , Canadian actor (died 1993)
- May 23: Edward N. Lorenz , American meteorologist († 2008)
- May 24 Florence Knoll , American designer and architect († 2019)
- May 24: Ross Thatcher , Canadian politician (died 1971)
- May 25 Theodore Hesburgh , Roman Catholic priest and university professor (died 2015)
- May 25: Josef Rudnick , German entrepreneur and politician (died 2009)
- May 26: Isabella Nadolny , German writer († 2004)
- May 28: Papa John Creach , American violinist (d. 1994)
- May 29: Miguel Ablóniz , Italian guitarist, educator and composer († 2001)
- May 29: John F. Kennedy , American politician, 35th President of the United States (died 1963)
- May 29 Hansmartin Decker-Hauff , German historian and genealogist (died 1992)
- May 31: Jean Rouch , French director († 2004)
June
- June 1: Erich Aehnelt , German veterinarian and university lecturer († 1974)
- June 1: Otto Esser , German Employers President (died 2004)
- June 1: William S. Knowles , American chemist (d. 2012)
- June 2: Heinz Sielmann , German wildlife filmmaker and TV presenter († 2006)
- June 4: Robert Merrill , American opera singer (baritone) († 2004)
- June 6: Kirk Kerkorian , American entrepreneur and billionaire (died 2015)
- June 7: Gwendolyn Brooks , American writer (died 2000)
- June 7 Alfred Charles Gimson , English linguist (died 1985)
- June 7: Dean Martin , American singer, actor and entertainer (d. 1995)
- June 8 – Otto Betz , German theologian and university professor († 2005)
- June 8 Jacques Labrecque , Canadian folk singer and record producer (d. 1995)
- June 9: Eric Hobsbawm , British historian (died 2012)
- June 9: Norbert Neugebauer , Croatian film director and screenwriter († 1992)
- June 11: Franz Hesse , German Protestant theologian and university teacher († 2013)
- June 12: Gottfried Honegger , Swiss graphic artist, painter and sculptor († 2016)
- June 13: Augusto Roa Bastos , Paraguayan novelist (died 2005)
- June 14: Lise Nørgaard , Danish journalist, writer and screenwriter
- June 14: Atle Selberg , Norwegian professor of mathematics (died 2007)
- June 15 Lillian Bassman , American painter and photographer († 2012)
- June 15: John B. Fenn , American chemist and Nobel laureate (d. 2010)
- June 15: Leon Payne , American country music artist (d. 1969)
- June 15 Karl Steinbuch , German cyberneticist, communications engineer and information theorist (died 2005)
- June 16: Rudolf Keller , German chess player (died 1993)
- June 16: Aurelio Lampredi , Italian designer of automobile and aircraft engines (d. 1989)
- June 16: Irving Penn , American photographer (died 2009)
- June 17: Wolfgang Liebe , German pharmacist (died 2017)
- June 18: Rudolf Angelides , Austrian architect (died 2000)
- June 18: Cövdət Hacıyev , Azerbaijani composer († 2002)
- June 18 Theo Schöller , German entrepreneur (died 2004)
- June 19: Rolf Hachmann , German prehistorian (died 2014)
- June 19 Dave Lambert , American jazz singer (d. 1966)
- June 19: Joshua Nkomo , Zimbabwean politician (died 1999)
- June 20: Felice Filippini , Swiss writer and painter (died 1988)
- June 20: Gerhard Meier , Swiss writer († 2008)
- June 22: George Fonder , American racing driver (d. 1958)
- June 22: Jean Hubeau , French composer, pianist and music educator (d. 1992)
- June 23: Dominic Ignatius Ekandem , Archbishop of Abuja (died 1995)
- June 25: Nils Karlsson , Swedish cross-country skier (died 2012)
- June 26: Karin von Arronet , painter, graphic artist and art teacher († 2006)
- June 26: Pavel Alexandrovich Solovyov , Soviet engine designer (d. 1996)
- June 28: Bert De Cleyn , Belgian footballer (d. 1990)
- June 29 Hellmuth Gensicke , German historian and archivist (died 2006)
- June 30: Susan Hayward , American film actress (d. 1975)
- June 30: Lena Horne , American singer († 2010)
July
- July 1: Rolf Rodenstock , German businessman, chairman of the Federation of German Industries (1978–1984) († 1997)
- July 4: Jean Hémard , French racing driver (d. 1982)
- July 6 Arthur Lydiard , New Zealand athletics coach (d. 2004)
- July 7: Yakovos Bilek , German basketball coach (died 2005)
- July 7 Larry O'Brien , American manager, third commissioner of the NBA (d. 1990)
- July 8 Eduardo Federico Acosta y Lara , Uruguayan historian and anthropologist (died 2014)
- July 9: Kay Aldridge , American actress (d. 1995)
- July 9 Antonino Janner , Swiss diplomat (died 1982)
- July 12: Andrew Wyeth , American painter (died 2009)
- July 14 Arthur Laurents , American novelist, screenwriter, and film director (died 2011)
- July 14: Ludwik Stefański , Polish pianist and music teacher (died 1982)
- July 15: Robert Conquest , British historian and writer (died 2015)
- July 16: Jack Austin , British pioneer of European Buddhism (died 1993)
- July 16 Andy Marefos , American football player (d. 1996)
- July 17 Gustavo Arriola , American comic artist († 2008)
- July 17 Phyllis Diller , American comedian and actress († 2012)
- July 17 – Kenan Evren , Turkish General and President (died 2015)
- July 17: Margarete Mitscherlich , Danish-German psychoanalyst, physician and author († 2012)
- July 18 Paco Escribano , Dominican humorist (died 1960)
- July 18: Henri Salvador , French singer († 2008)
- July 19: William Scranton , American politician (died 2013)
- July 19: Fulbert Youlou , Congolese President (d. 1972)
- July 21: Luigi Cantone , Italian fencer and Olympic champion (d. 1997)
- July 22: Jurij Chěžka , Sorbian poet (died 1944)
- July 22: Adam Malik , Indonesian Minister of Foreign Affairs (died 1984)
- July 23: Gisela Voß , German athlete († 2005)
- July 25: Fritz Honegger , Swiss politician (died 1999)
- July 26 Alberta Adams , American blues singer († 2014)
- July 26: Bertil Nordahl , Swedish footballer (died 1998)
- July 27: Bourvil , French actor (died 1970)
- July 28: Brigitte Schröder , wife of Gerhard Schröder († 2000)
- July 28: Gerhard Wollner , German actor and cabaret artist († 1997)
- July 29: Jean-Jacques von Allmen , Swiss Protestant clergyman and university teacher (died 1994)
- July 29: Rochus Misch , German SS man (died 2013)
August
- August 3: Rudolf Gnägi , Swiss politician (died 1985)
- August 3: Denis Harbour , Canadian singer († 2009)
- August 3: Antonio Lauro , Venezuelan composer and guitarist (d. 1986)
- August 4: John Fitch , American racing driver (d. 2012)
- August 4: Karl Wlaschek , Austrian entrepreneur (died 2015)
- August 6: Robert Mitchum , American actor (d. 1997)
- August 6: Christiane Volger , German forest scientist (died 2008)
- August 10: Bäiken Aeshimov , Soviet politician (died 2010)
- August 11: Inge Aicher-Scholl , creative artist and writer; Sister of the Scholl siblings († 1998)
- August 11: Dik Browne , American comic artist (d. 1989)
- August 11 Spencer Mathews King , American diplomat (died 1988)
- August 12: Adolf Burger , eyewitness of the counterfeiting workshop of the Sachsenhausen concentration camp and survivor of several concentration camps († 2016)
- August 12: Ebba Haslund , Norwegian writer (died 2009)
- August 13: Ulrich Hausmann , German archaeologist (died 1996)
- August 15: Hans Bals , German politician, MP († 2004)
- August 15: Oscar Romero , Roman Catholic bishop (d. 1980)
- August 16: Luigi Accogli , Italian bishop and Vatican diplomat (died 2004)
- August 16: Roque Cordero , Panamanian composer († 2008)
- August 17: Gianni Agus , Italian actor (died 1994)
- August 18 Caspar Weinberger , US politician and Secretary of Defense (died 2006)
- August 19: Laurence Aarons , Australian politician (died 2005)
- August 19 Hermann Aichinger , Austrian architect (died 1965)
- August 19 Heinz Benthien , German table tennis player (died 1981)
- August 22: Kō Arima , Japanese soccer player and coach
- August 22: Samuel Dolin , Canadian composer and music educator († 2002)
- August 22: Per Anders Fogelström , Swedish writer (died 1998)
- August 22: John Lee Hooker , American blues musician (d. 2001)
- August 23: Itō Keiichi , Japanese writer († 2016)
- August 23: Tex Williams , American country singer and band leader (d. 1985)
- August 25: Lou van Burg , Dutch-German show host and entertainer (d. 1986)
- August 25: Mel Ferrer , American actor, film director and producer († 2008)
- August 25: Lisbeth Movin , Danish actress and director († 2011)
- August 26: Walther Killy , German literary scholar (died 1995)
- August 26 William French Smith , American lawyer and politician (died 1990)
- August 28: Claire-Lise de Benoit , Swiss writer († 2008)
- August 28: Jack Kirby , American comic artist (d. 1994)
- August 29: John Leonard King , British business leader (died 2005)
- August 30: Denis Healey , British politician (died 2015)
- August 31 György Aczél , Hungarian cultural politician (died 1991)
- August 31: Lucrecia Kasilag , Filipino composer († 2008)
September
- September 2 – Laurindo Almeida , Brazilian jazz musician (d. 1995)
- September 2 Nazaire De Wolf , Belgian composer and band leader († 1983)
- September 3: Paul Zoungrana , Archbishop of Ouagadougou and Cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church († 2000)
- September 4: Henry Ford II , grandson of Henry Ford, President of Ford Motor Company from 1945 to 1960 (d. 1987)
- September 4: Geoff Love , British bandleader (died 1991)
- September 5: Jean Bertin , French aeronautical engineer (d. 1975)
- September 6: Philipp Freiherr von Boeselager , German resistance fighter (died 2008)
- September 6: Hilde Sommer , German track and field athlete
- September 7: Jenny Aloni , German-Israeli writer (died 1993)
- September 7: John W. Cornforth , Australian chemist (d. 2013)
- September 9: Rolf Wenkhaus , German actor (died 1942)
- September 10 Algirdas Savickis , Lithuanian painter (died 1943)
- September 10: Miguel Serrano , Chilean politician and writer (died 2009)
- September 11: Herbert Lom , Czech-British actor († 2012)
- September 11 - Ferdinand Marcos , Philippine politician and President (d. 1989)
- September 12: Jürgen Seydel , German karateka (died 2008)
- September 12: Han Suyin , Chinese doctor and English-language writer († 2012)
- September 13 Joseph "Piney" Armone , American mobster (d. 1992)
- September 13: Robert Ward , American composer († 2013)
- September 14: Rudolf Baumgartner , Swiss violinist and conductor († 2002)
- September 14 Mack Hellings , American racing driver (d. 1951)
- September 15: Richard Anthony Sayer Arnell , British composer and conductor (d. 2009)
- September 15: Hilde Güden , Austrian coloratura soprano and chamber singer († 1988)
- September 16: Alexander Schmorell , co-founder of the resistance group White Rose († 1943)
- September 17: Isang Yun , Korean composer (d. 1995)
- September 18 József Asbóth , Hungarian tennis player (d. 1986)
- September 18: June Foray , US voice actress († 2017)
- September 19: James Bowes-Lyon , British officer (d. 1977)
- September 20 Red Auerbach , American basketball coach (d. 2006)
- September 20: Fernando Rey , Spanish actor (d. 1994)
- 20 September: Władysław Rubin , auxiliary bishop of Gniezno and cardinal (died 1990)
- September 21: Vincas Bartuška , Lithuanian canonist, professor of canon law, apostolic protonotary and monsignor (died 2010)
- September 21: Ernst Vasovec , Austrian writer (died 1993)
- 24 September: Otto Günsche , SS Hauptsturmfuhrer and Hitler's personal adjutant († 2003)
- September 25: Heimo Kuchling , Austrian art theorist († 2013)
- September 26: Jürgen Thimme , German classical archaeologist (died 2010)
- September 27 Sally Amato , American singer and actress († 2000)
- September 27: Louis Auchincloss , American writer (died 2010)
- September 29: Christoph Barth , Swiss Protestant clergyman and university teacher († 1986)
- September 30 Park Chung-hee , South Korean politician (died 1979)
- September 30: Buddy Rich , American jazz drummer (d. 1987)
October
- October 1 Cahal Daly , Irish Archbishop and Cardinal (died 2009)
- October 2: Christian de Duve , Belgian biochemist (died 2013)
- October 3: Erich Apel , SED functionary and chairman of the state planning commission († 1965)
- October 4 Luis Carniglia , Argentine soccer player and coach (d. 2001)
- October 4: Violeta Parra , Chilean folk musician (d. 1967)
- October 5: Robert Adams , British sculptor (died 1984)
- October 5 Allen Ludden , American presenter and actor (d. 1981)
- October 6: Maria von Schmedes , Austrian singer and actress († 2003)
- October 7: June Allyson , American actress (died 2006)
- October 8 Rodney R. Porter , English biochemist (d. 1985)
- October 8: Franz Schädler , Liechtenstein ski racer († 2004)
- October 10: Thelonious Monk , American jazz pianist and composer (d. 1982)
- October 11 – John Adriano Acea , American jazz pianist (d. 1963)
- October 11: José d'Angelo Neto , Brazilian Archbishop (died 1990)
- October 13 – Hugo Lindo , Salvadorian writer, diplomat and politician (died 1985)
- October 13: Ulrich Sahm , German diplomat and ambassador (died 2005)
- October 15: Arthur M. Schlesinger , American historian († 2007)
- October 17 Marsha Hunt , American film actress
- October 19 Kalcidon Agius , Maltese writer, playwright and politician (died 2006)
- October 19 Yevgenia Petrovna Antipova , Soviet-Russian painter and art teacher (died 2009)
- October 19 Walter Munk , American oceanographer and geophysicist (died 2019)
- October 20 Stéphane Hessel , French resistance fighter, diplomat and author (died 2013)
- October 20: Jean-Pierre Melville , French film director (d. 1973)
- October 21 Lindanor Celina , Brazilian writer († 2003)
- October 21: Dizzy Gillespie , American jazz musician, composer, singer and band leader († 1993)
- October 21: Heinz Oskar Vetter , German trade unionist and politician (died 1990)
- October 22: Joan Fontaine , American film actress († 2013)
- October 22: John Tolan , American racing driver (d. 1986)
- October 24: Ladislav Nižňanský , Slovak commander († 2011)
- October 25: Lee MacPhail , US baseball official (died 2012)
- October 27: Arne Andersson , Swedish athlete (died 2009)
- October 27 Oliver Tambo , South African anti-apartheid politician (d. 1993)
- October 28: Harold Brown , Canadian pianist (died 2011)
- October 29: Harold Garfinkel , American sociologist (died 2011)
- October 30: Anna Marly , Russian-born French singer-songwriter († 2006)
- October 30: Maurice Trintignant , French racing driver (d. 2005)
- October 31 – Heinz Musculus , German caricaturist, draftsman and illustrator (died 1976)
November
- November 1: Wolfgang Ruge , German historian (died 2006)
- November 2: Ann Rutherford , American actress (died 2012)
- November 5: Jacqueline Auriol , French pilot, became the first woman to break the sound barrier († 2000)
- November 6: András Mihály , Hungarian composer (died 1993)
- November 6: Edgar Whitcomb , American politician (died 2016)
- November 7: Ján Arpáš , Slovak footballer (died 1976)
- November 7: Lev Yefimovich Kerbel , Soviet sculptor († 2003)
- November 7: Helen Suzman , South African politician (d. 2009)
- November 8: Gustav Georg Gunter Angenheister , German geophysicist (died 1991)
- November 10: Ion Cubicec , Salvadoran music educator and composer (d. 1998)
- November 10: Lloyd Cutler , American attorney (died 2005)
- November 10: Avelina Landín , Mexican singer (d. 1991)
- November 11: Sepp Arnemann , German cartoonist (died 2010)
- November 12: Jo Stafford , American singer († 2008)
- November 14: Ansley Coale , American demographer (died 2002)
- November 15: John Whiting , British playwright (died 1963)
- November 15: Hans Vießmann , German engineer and entrepreneur (died 2002)
- November 16: Giovanni Alberti , Italian racing driver (died 2019)
- November 19: Indira Gandhi , Indian politician and prime minister (died 1984)
- November 20: Robert Byrd , American politician (died 2010)
- November 20: Heiner Gautschy , Swiss radio and television journalist († 2009)
- November 22: Hugh Gregg , American politician (died 2003)
- November 22: Fritz Hillebrand , German motorcycle racer (died 1957)
- November 22: Andrew Fielding Huxley , British biophysicist and physiologist, Nobel laureate († 2012)
- November 22: Kurt Locher , Swiss civil servant (died 1991)
- November 22: Jean-Etienne Marie , French composer (died 1989)
- November 23: John Newland , American film director, actor and screenwriter († 2000)
- November 23 Karl Wild , German ice hockey player and coach (d. 1975)
- November 24: novella Hamilton Richards , Antiguan writer and politician (died 1986)
- November 25: Amal al-Atrasch , Syriac-Druze singer and actress (d. 1944)
- November 25: Jean-Pierre Dautel , French conductor and composer (died 2000)
- November 25: Luigi Cardinal Poggi , Italian Curia cardinal (died 2010)
- November 28 Werner Krusche , German Protestant theologian (died 2009)
- November 29: Pierre Gaspard-Huit , French film director and screenwriter († 2017)
- November 29: Merle Travis , country musician and songwriter (d. 1983)
- November 29 Herbert Zimmermann , German radio reporter (died 1966)
December
- December 1: Gerd Schmückle , German general (died 2013)
- December 3 Manuel Solís Palma , 41st President of Panama († 2009)
- December 5: Ken Downing , British racing driver (d. 2004)
- December 5: Wenche Foss , Norwegian actress († 2011)
- December 6 Kamal Jumblat , Lebanese politician (died 1977)
- December 6: Hans Verbeek , Member of the German Bundestag (died 1966)
- December 7: Ernst Siegfried Hansen , editor-in-chief and general secretary of the Bund deutscher Nordschleswiger († 1980)
- December 7: Ottorino Volonterio , Swiss racing driver († 2003)
- December 8: Albert Baldauf , German politician and MP (died 1991)
- December 9: James Jesus Angleton , American agent (d. 1987)
- December 9: James Rainwater , American physicist (d. 1986)
- December 12: Joseph-Albert Malula , Archbishop of Kinshasa and Cardinal (d. 1989)
- December 14 – Walter Edwin Arnoldi , American mechanical engineer (d. 1995)
- December 14: Carl-Henrik Hermansson , Swedish politician (died 2016)
- December 14: Elyse Knox , American actress (died 2012)
- December 15 Karl-Günther von Hase , German diplomat and director of ZDF († 2021)
- December 15: Hilde Zadek , German-Austrian opera singer († 2019)
- December 16: Arthur C. Clarke , British science fiction writer († 2008)
- December 17: Kriangsak Chomanan , Prime Minister of Thailand (1977–1980) († 2003)
- December 18: Ossie Davis , American actor (died 2005)
- December 18 – Eddie "Cleanhead" Vinson , American jazz musician (d. 1988)
- December 19: Eduardo Catalano , Argentine architect (died 2010)
- December 19 – Chucho Martínez Gil , Mexican singer and composer (d. 1988)
- December 20: David Bohm , American quantum physicist (d. 1992)
- December 21: Diana Athill , British author and literary critic († 2019)
- December 21: Heinrich Böll , German writer and winner of the Nobel Prize in Literature (died 1985)
- December 21: Ivor Dean , British actor (died 1974)
- December 22: Marthe Gosteli , Swiss women's rights activist († 2017)
- December 26 – Joe Osmanski , American football player (d. 1993)
- December 26: Rose Mary Woods , US secretary to Richard Nixon († 2005)
- December 28 Mouloud Mammeri , Algerian-Kabyle writer, anthropologist and linguist (died 1989)
- December 29: David Hampshire , British racing driver (d. 1990)
- December 30: Wesley Tuttle , American country music artist (d. 2003)
- December 31 Italo Astolfi , Italian track cyclist (died 2004)
- around December 31: Suzy Delair , French actress and singer († 2020)
Exact date of birth unknown
- Karim Ahari , Persian agricultural engineer and diplomat
- John James Atherton , English footballer (died 1961)
- Mashal , Afghan miniaturist (d. 1998)
Died
January February
- January 1: Agnes Dean Abbatt , American painter (born 1847)
- January 1: Dominique Jules-Antoine , German veterinarian and politician (born 1845)
- January 2: Edward Tylor , British anthropologist (b. 1832)
- January 6: Carl Leonhard Becker , German painter and engraver (b. 1843)
- January 6: Hendrik Peter Godfried Quack , Dutch historian and economist (born 1834)
- January 10: William Frederick Cody, known as Buffalo Bill , American bison hunter and showman (b. 1846)
- January 10: Martha Fontane , daughter of Theodor Fontane and role model for several of his novel characters (b. 1860)
- January 11: Hans Chemin-Petit , German composer (b. 1864)
- January 11: Wayne MacVeagh , American politician (b. 1833)
- January 14: Carl Börger , German organ builder (b. 1846)
- January 15: Alfredo Lobos , Chilean painter (b. 1890)
- January 17: Viktor Gluth , German composer and music teacher (b. 1852)
- January 17: Lionel Allen Sheldon , American politician (born 1828)
- January 18: Bernhard Schmidt , German classics scholar (b. 1837)
- January 20: Alejandro Ferrant y Fischermans , Spanish painter (b. 1843)
- January 22: Emma Miller , British-Australian suffragette, pacifist, trade unionist and founding member of the Australian Labor Party (b. 1839)
- January 23: Emil Eberhard Heinrich von Abel , German jurist and politician (born 1825)
- January 23: Jesko von Puttkamer , German colonial official and governor of Cameroon (b. 1855)
- January 24: Hermann Schubert , German sculptor (b. 1831)
- January 27: Ernst Sars , Norwegian historian (b. 1835)
- January 29: Olga von Lützerode , German nurse and benefactor, founder and head of the Clementinenhaus (b. 1836)
- January 31: Otto Finsch , merchant, ethnologist, ornithologist (b. 1839)
- February 1: Margarethe von Witzleben , founder of the movement for self-help and self-awareness of people who are hard of hearing in Germany (b. 1853)
- February 2: Sophie Beier , German writer (b. 1870)
- February 4: Frédéric de Rougemont the Younger , Swiss evangelical clergyman and entomologist (b. 1838)
- February 5: Friedrich Hahn , German geographer (born 1852)
- February 8: Henry E. Burnham , American politician (b. 1844)
- February 10: Émile Pessard , French composer (b. 1843)
- February 10: John William Waterhouse , British painter (b. 1849)
- February 11: Charlotte Lady Blennerhassett , German writer and historian (b. 1843)
- February 11 Bernhard Listemann , German-American violinist and music teacher (b. 1841)
- February 16: Octave Mirbeau , French writer (b. 1848)
- February 17: Emile Auguste Carolus-Duran , French painter (b. 1837)
- February 17: Josef Riehl , significantly involved in the development of Tyrol (* 1842)
- February 18: Ezequiel de Baca , American politician (b. 1864)
- February 23: Jean Gaston Darboux , French mathematician (b. 1842)
March April
- March 1: Jaro Pawel , Austrian gymnastics teacher and Germanist (b. 1850)
- March 3: Hermine Villinger , German writer (b. 1849)
- March 7: Eugen von Aichelburg , Austrian politician (b. 1852)
- March 8: Ferdinand Graf von Zeppelin , German airship designer (b. 1838)
- March 9: Hōshō Kurō , Japanese nō actor (b. 1837)
- March 9 Wilhelm Meyer , German classical scholar and medievalist (b. 1845)
- March 14: Antonio Vanegas Arroyo , Mexican publisher (b. 1852)
- March 14: Zenas Ferry Moody , American politician (b. 1832)
- March 15: Paul Puget , French composer (b. 1848)
- March 15: Kristofer Randers , Norwegian writer (b. 1851)
- March 16: Karl Heinrich Gisbert Gilhausen , German engineer and politician (b. 1856)
- March 17: Cæsar Peter Møller Boeck , Norwegian dermatologist (b. 1845)
- March 17: Franz Brentano , German philosopher and psychologist (b. 1838)
- March 19: Christian Schmidt , German soccer player (b. 1888)
- March 21: Alfred Einhorn , German chemist (b. 1856)
- March 23: Adolf Ritter von Guttenberg , Austrian professor of forestry (b. 1839)
- March 23: Joseph Anton Friedrich August Freiherr von Hövel , German politician and government president (b. 1842)
- March 23: Louis Schmeisser , German weapons designer (b. 1848)
- March 26: Georg Froböß , German evangelical clergyman (b. 1854)
- March 30: Gottfried Karl Wilhelm Asselmann , German clergyman and local historian (b. 1851)
- March 31: Emil Adolf von Behring , German physician and Nobel Prize winner (b. 1854)
- April 1: Scott Joplin , American musician (ragtime composer) (b. 1868)
- April 2: Jindřich Kafka , Czech composer (b. 1844)
- April 8: Richard Olney , American politician (b. 1835)
- April 12: Otto Stockmayer , German evangelical minister, evangelist and author (b. 1838)
- April 14: Ludwik Lejzer Zamenhof , Polish ophthalmologist ( Esperanto founder) (b. 1859)
- April 14: William T. Watson , American politician (b. 1849)
- April 20: Zygmunt Ajdukiewicz , Polish painter (b. 1861)
- April 23: Karl Altrichter , German writer (b. 1844)
- April 23: Robert Koehler , German-American painter (b. 1850)
- April 24: Oscar Blumenthal , German novelist and playwright (b. 1852)
- April 29 Richard Applin , British fighter pilot (b. 1894)
May June
- May 1: William Knox D'Arcy , British entrepreneur (b. 1849)
- May 5: Richard Leopold Oskar Anders , German sculptor and university teacher (b. 1853)
- May 7: Charles Johnson Brooke , White Raja of Sarawak (b. 1829)
- May 8: Thomas McArthur Anderson , United States officer (b. 1836)
- May 10: Joseph B. Foraker , American politician (b. 1846)
- May 11: Otto Klauwell , German composer (b. 1851)
- May 14 Joseph Choate , American jurist and diplomat (b. 1832)
- May 16: Fernand Halphen , French composer (b. 1872)
- May 20: Friedrich "Fritz" Ludwig Tilman Achelis , German merchant and politician (b. 1840)
- May 20: Ernest Leroux , French bookseller and publisher (b. 1845)
- May 25: Édouard de Reszke , French opera singer (bass) of Polish origin (b. 1853)
- June 2: Philipp Friedrich Mader , German theologian and priest (b. 1832)
- June 2: Oscar Schuster , German physician and alpinist (b. 1873)
- June 3: Louis Gathmann , engineer and inventor (b. 1843)
- June 9: Thomas McKenny Hughes , British geologist and paleontologist (b. 1832)
- June 12: Teresa Carreño , Venezuelan pianist and composer (b. 1853)
- June 15: Friedrich Robert Helmert , German geodesist and mathematician (born 1843)
- June 17: Ernst Stöhr , Austrian painter, poet and musician (b. 1860)
- June 17: Karl Zilgas , German soccer player (b. 1892)
- June 20: James Mason Crafts , American chemist (b. 1839)
- June 22: Yevgeny Franzevich Bauer , Russian film director (b. 1865)
- June 26: Dragutin Dimitrijević , Serbian officer (b. 1876)
- June 27: Gustav von Schmoller , German economist and social scientist (born 1838)
- June 30: Jonathan Chace , American politician (b. 1829)
July August
- July 1: Julius Falkenstein , German physician and traveler to Africa (b. 1842)
- July 2: William Stevenson Hoyte , English organist, composer and music teacher (b. 1844)
- July 2: Adolf Ferdinand Weinhold , German chemist and physicist (b. 1841)
- July 9: Wilhelm Langheld , German officer (b. 1867)
- July 13: Oskar Telke , German physician (b. 1848)
- July 14: Octave Lapize , French cyclist (b. 1887)
- July 16: Philipp Scharwenka , German composer and music teacher (b. 1847)
- July 17: Gustav Denhardt , German explorer of Africa (b. 1856)
- July 19: Franz Arndt , German Protestant theologian (b. 1848)
- July 20: Iwan von Müller , German classical scholar (b. 1830)
- July 20: Ignaz Sowinski , Austrian architect (b. 1858)
- July 27: Emil Theodor Kocher , Swiss physician and Nobel Prize winner (b. 1841)
- July 28: Alfred Victor Robert Auger , French fighter pilot (b. 1889)
- July 28: Ernst Sandberg , German physician (b. 1849)
- August 1: Enric Prat de la Riba , the first President of the Mancomunitat de Catalunya (b. 1870)
- August 1: Ludwig Rochus Schmidlin , Swiss Roman Catholic clergyman, educator and church historian (b. 1845)
- August 1: Christian August Volquardsen , German ancient historian (b. 1840)
- August 3: Ferdinand Georg Frobenius , German mathematician (b. 1849)
- August 6: Richard McBride , Canadian politician (born 1870)
- August 7: Edwin Harris Dunning , British pilot (b. 1892)
- August 11: Hermann Sökeland , German museum director (b. 1848)
- August 12: Gustav Kampmann , German painter and printmaker (b. 1859)
- August 13: Eduard Buchner , German chemist, Nobel laureate (b. 1860)
- August 15: Philippine von Edelsberg , Austrian opera singer (b. 1838)
- August 15: Gustav Körte , German archaeologist (b. 1852)
- August 17: John W. Kern , American politician (b. 1849)
- August 20: Alexander Georg Aster , German architect and non-fiction author (b. 1849)
- August 20: Adolf von Baeyer , German chemist (b. 1835)
- August 20: Robert von Mendelssohn , German banker, art collector and patron (b. 1857)
- August 29: Albert Grey , British politician and statesman (b. 1851)
September October
- 5 September: Albin Köbis , German sailor and a leader of the Sailors' Rebellion (b. 1892)
- September 5: Marie Schröder-Hanfstängl , German opera singer and singing teacher (b. 1847)
- September 8: Charles Lefèbvre , French composer (b. 1843)
- 9 September: Madge Syers , British figure skater, first world and Olympic champion in women's figure skating (b. 1881)
- September 12: Désiré André , French mathematician (b. 1840)
- September 15: Kurt Wolff , German fighter pilot in World War I (b. 1895)
- September 20: José Gallegos y Arnosa , Spanish painter, sculptor and architect (b. 1859)
- September 21: Grete Trakl , Austrian pianist and sister of Georg Trakl (b. 1891)
- September 25: Thomas Ashe , Irish independence campaigner (b. 1885)
- September 25: Bernhard von Gaza , German rower (b. 1881)
- September 27: Edgar Degas , French painter and sculptor (b. 1834)
- October 1: Ivan Aguéli , Swedish itinerant Sufi, painter and author (b. 1869)
- October 4: David Gallaher , New Zealand rugby union player (b. 1873)
- October 9: Hussein Kamil , Sultan of Egypt and King of Anglo-Egyptian Sudan (b. 1853)
- October 9: Duncan Mackinnon , British rower (b. 1887)
- October 10: Sarah Aaronsohn , Jewish pro-British spy in Ottoman Empire (b. 1890)
- October 13 Florence La Badie , American silent film actress (b. 1888)
- October 13: Rudolf Schneider , German naval officer and U-boat commander in World War I (b. 1882)
- October 15: Donald M. Dickinson , American politician (b. 1846)
- October 15: Mata Hari , Dutch dancer (b. 1876)
- October 16: Walter Flex , German poet (b. 1887)
- October 20: Aleksander Eduard Thomson , Estonian composer (b. 1845)
- October 21: Paul O. Husting , American politician (b. 1866)
- October 27: Georgine Galster , German theater actress (b. 1848)
- October 27 August Wilmanns , German classical scholar and librarian (b. 1833)
- October 30: Heinrich Gontermann , German pilot in World War I (b. 1896)
- October 30: Otokar Kopecký , German violinist (b. 1850)
- October 31: Margarete Lenk , German writer (b. 1841)
November December
- November 1: Ferdinando Gianella , Swiss engineer, architect and politician (b. 1837)
- November 2: Rudolf Heinrich , German politician (b. 1845)
- November 3: Léon Bloy , French writer (b. 1846)
- November 11: Liliʻuokalani , Hawaiian Queen (b. 1838)
- November 12: Hans Bachmann , Swiss painter (b. 1852)
- November 15: Hans Adam , Bavarian officer (b. 1886)
- November 15: Émile Durkheim , French sociologist (b. 1858)
- November 15: John W. Foster , American politician (b. 1836)

- November 17: Auguste Rodin , French painter and sculptor (b. 1840)
- November 20: Frederick Herbert Torrington , Canadian organist, conductor, composer and music teacher (b. 1837)
- November 22: Teobert Maler , Austrian photographer, discoverer and researcher of Maya ruins (b. 1842)
- November 23: James Peabody , American politician (b. 1852)
- November 24: Hermann Vöchting , German botanist (b. 1847)
- November 25: João Teixeira Pinto , Portuguese colonial officer (b. 1876)
- November 26: Leander Jameson , British physician and politician (b. 1853)
- November 30: William E. Chandler , American politician (b. 1835)
- December 1: George A. Banker , American bicycle racer, world champion 1898 (b. 1874)
- December 8: Alexander Kisch , Rabbi (b. 1848)
- December 8: Mendele Moicher Sforim , writer (b. 1836)
- December 10: Mackenzie Bowell , Canadian politician (b. 1823)
- December 11: Hedwig Arendt , German theater actress (b. 1856)
- December 13: Ebe W. Tunnell , American politician (b. 1844)
- December 19: Anna Magdalena Appel , German ballet dancer and Grand Duchess (b. 1846)
- December 20: Lucien Petit-Breton , French cyclist (b. 1882)
- December 21: Wilhelm Trübner , German landscape painter (b. 1851)
- December 22: Franziska Xaviera Cabrini , US saint (b. 1850)
- December 25 Karl Voll , German art historian (b. 1867)
- December 26: Friedrich Lange , German journalist and politician (b. 1852)
- December 28: John Randolph Thornton , American politician (b. 1846)
- December 30: Rudolf Hirzel , German classics scholar (b. 1846)
- 31 December: Johannes Gallandi , Prussian lieutenant colonel and genealogist (b. 1843)
- December 31: Wilhelm Neumann-Torborg , German sculptor (b. 1856)
Exact date of death unknown
- Reinold Aßmann , German jurist and politician (born 1822)
- Heinrich Aufhäuser , German banker (born 1842)
- Ludwig Auspitz , German theater actor and opera singer (born 1859)
- Sakurama Banma , Japanese Nō actor (b. 1835)
web links
- http://www.dhm.de/lemo/html/1917/ (living virtual museum online)