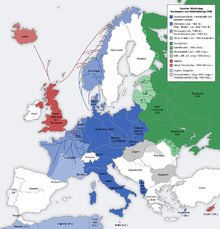
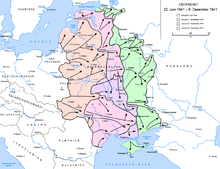
Chronology of the Second World War
This calendar overview represents an incomplete chronology of the Second World War . It is not an independent representation of the Second World War, but primarily serves to find Wikipedia articles on a date or event or its assignment to a period.
From the second half of 1941 onwards, the war in Europe and adjacent areas, or the war in Asia and the Pacific , are shown every six months separately according to theaters of war for better clarity . A detailed chronology of the entire Pacific War can be found under Chronology of the Pacific War .
At the end of the chronology of all events there is a separate brief overview of the important conferences during this time.
prehistory
The post-war years, 1919 to 1932
1919
- February to May: After the November Revolution of 1918, the German Reich is reorganized as a democracy and republic (so-called Weimar V) . Friedrich Ebert becomes the first Reich President.
- March 2-6: Founding of the Comintern with the goal of world revolution
- April 28th: Foundation of the League of Nations
- June 28: Signing of the Treaty of Versailles (peace agreement on the First World War )
- November: The period in which the stab in the back legend was created to defame Republican institutions
1920
- 1919/20: a cordon sanitaire against the Soviet Union is created in the Paris suburb agreements
- August 13-25: in the battle for Warsaw , an advance of the Red Army into Europe is stopped
- October: Founding of the Economic Reconstruction Association, in which German right-wing organizations and Russian emigrants striving to restore the old order in the Soviet Union organize
1921
- March 18: End of the Polish-Soviet War in the Peace of Riga
- December 13: Washington Four Power Agreement between the United States , the United Kingdom , the French Republic and the Japanese Empire
1922
- February 6: The Washington Naval Conference decides to limit armaments at sea
- April 16: Treaty of Rapallo , rapprochement between Germany and the Soviet Union
- October: March on Rome , Mussolini conquers power in Italy
1923
- January 11: French and Belgian troops march into the Ruhr area ( occupation of the Ruhr )
1924
- January 20-30: 1st National Congress of the Kuomintang
- September 1: the Dawes Plan comes into force - the annual reparation payments are adjusted to the economic strength of the Weimar Republic
1925
- April 15: Signing of the contract for the establishment of the Secret Aviation School and test site of the Reichswehr in the Soviet Union
- May 12: the former Prussian Field Marshal Paul von Hindenburg is elected as Reich President
- June: General Theodoros Pangalos takes power in Greece
- 5th-16th October: Germany recognizes the western borders created by the Versailles Treaty in the Locarnopakt
1926
- January 26th: Foundation of the Stega , the Reichswehr secretly plans to mobilize the armaments industry
- September 30th: Foundation of the International Crude Steel Community , which is celebrated as an important element of European understanding and thus the preservation of peace
- December 11th: the second volume of Hitler's “Mein Kampf” appears, in it he calls among other things for the conquest of the Soviet Union as a living space in the east
1927
- January 23: Foundation of the OSSOAWIACHIM , a defense organization for the military training of Soviet youth
- August: in the Phoebus scandal (Lohmann affair), the Reichswehr's secret armament program is exposed
1928
- August 27: Briand-Kellogg Pact to outlaw war
- November: Battleship debate in Germany at the beginning of the second Müller cabinet
1929
- February to June: the Young Plan is negotiated
- February 9: Litvinov Protocol to Renounce Violence in International Disputes
- April 3: Persia signs the Litvinov Protocol
- OCTOBER 24: Black Thursday , the American stock market crash triggers the Great Depression of
- 1929: Construction of the Stalin Line begins
1930
- January 14th: the French Parliament approves the construction of the Maginot Line
- April 22nd: the London Fleet Agreement is signed
- May 1st: the French politician Aristide Briand presents a European plan for the creation of a “ European Federal Union ”
- July 11: The German government rejects Briand's Europe Plan
- September 14: The NSDAP receives 18.3% of the votes in the 1930 Reichstag election , making it the second strongest force after the SPD (24.5%)
1931
- August: Founding of the Central European Business Day , which aims to unify Central Europe under German leadership
- September 18: after the Mukden incident, Japanese occupation of Manchuria during the Manchurian crisis . Part of Japan's expansion policy
- November 7: Mao Zedong , now chairman of the All-China Executive Committee and chairman of the Council of People's Commissars, proclaims the "Chinese Soviet Republic"
1932
- January 7th: Stimson Doctrine , the US declares not to recognize territorial changes through violence
- 28 January to 5 May: Battle of Shanghai , which ends with a ceasefire brokered by the League of Nations, which declared Shanghai a demilitarized zone.
- July 25: Signing of the Polish-Soviet non-aggression pact
- August: Anti-War Congress in Amsterdam
- September 13: Establishment of the Reich Board of Trustees for Youth Training for Defense Education , following the efforts of Generals Groener and Schleicher
Preparations, armament
The years 1933 to 1937
1933
- January 30: Hitler was appointed Chancellor by President Hindenburg - is often associated with the term seizure named
- February 3: Hitler announces his habitat program to the leaders of the Reichswehr ( Liebmann recording )
- February to October 1933 (with interruptions): second international disarmament conference in Geneva
- February 28: The presidential decree for the protection of the people and the state invalidates the civil rights of the Weimar constitution and is an important formal milestone in Hitler's "seizure of power" and the elimination of the democratic constitutional state . The reason was the Reichstag fire the night before
- March 4: Roosevelt announces Good Neighbor Policy
- March 24th: the law to remedy the misery of the people and empire (Enabling Act) comes into force immediately after its promulgation
- March 28th: Japan leaves the League of Nations
- April 4: Decision to found the Reich Defense Council
- May 5: Ratification of the extension of the German-Soviet friendship treaty
- May 17: Hitler's "Peace Speech" before the Reichstag
- June 9: Reichsbank transfer moratorium
- October 10: Law on tax breaks for expenses for civilian air defense purposes
- July 15: Signing of the four-party pact between Italy , France , Great Britain and Germany, it brings international recognition of the new regime
- July 20: Reich Concordat between the Holy See (Vatican State) and the German Empire
- September 2nd: Non-aggression pact between Italy and the Soviet Union
- October 14: Germany leaves the Disarmament Conference, leaves the League of Nations
- December 14: With the Feder-Bosch Agreement , the production of synthetic gasoline starts , which is a prerequisite for the Second World War
1934
- 1934: Introduction of the Mefo change to finance rearmament
- January 26th: German-Polish non-aggression pact
- February 9: Balkan Pact between Turkey , Greece , Romania and Yugoslavia
- March 17th: Roman protocols on economic cooperation between Italy, Austria and Hungary
- April 12: The Nye Committee or officially the US Senate Investigating Committee "Senate Munitions Investigating Committee" begins its work (April 1934 - February 1936) on the influence of the arms industry on the First World War
- June 27th: French politician Louis Barthou's proposal for an "East Locarno"
- June 30 to July 2: The so-called Röhm Putsch leads to the elimination of the SA and secures the role of the Reichswehr as the sole bearer of arms, at the same time an important domestic part of the safeguarding of the new dictatorial form of rule of the National Socialists
- July 25 to 27: July Putsch , a failed Nazi coup attempt in Austria, Chancellor Dollfuss is murdered in his office premises
- August 1st: The “Law on the Head of the German Reich” unites the offices of the Reich President and the Reich Chancellor, the previous Reich President Hindenburg dies the next day, and on August 19, 1934 the unification of the offices is confirmed by a referendum.
- August 20: new text of the oath of the Reichswehr, the soldiers are now sworn in personally on the "Führer of the German Reich and the people, Adolf Hitler, the commander-in-chief of the armed forces "
- September 18: Entry of the Soviet Union into the League of Nations
1935
- January 7th: Laval-Mussolini Pact between France and Italy
- January 13th: vote in Saarland ; 91 percent vote in favor of a return to the German Reich, and the Anschluss takes place on January 17th
- March 16: General conscription is introduced in Germany, as a result Germany begins expanding the air force and building submarines
- April 11-14 : Stresa Front
- May 2nd: Franco-Soviet assistance pact , some historians argue that the introduction of conscription in Germany was a reaction to negotiations on a Franco-Soviet alliance
- May 16: Czechoslovak- Soviet assistance pact
- MAY 21: foreign policy speech to the Reichstag Hitler emphasized readiness for peace, while new Defense Act and a secret "Reich Defense Law," which the economy to arms production required to newly created Office "plenipotentiary for the war economy" is with bay occupied
- June 18: German-British naval agreement - the strength of the German navy must not exceed 35 percent of the strength of the British navy
- August 2: The World Congress of the Comintern referred to fascism as "shock troops of the international counter-revolution", which for a crusade against the Soviet Union enters and calls the Popular Front for the overthrow of Nazism from
- August 31: 1st neutrality law in the USA forbids the export of weapons to opponents in the event of disputes
- September: Foundation of the Anglo-German Fellowship
- SEPTEMBER 15: Nazi Party Rally in Nuremberg, Nuremberg Laws , Jews civil rights are revoked, the Nazi Party flag, the swastika is more Reichsflagge
- October 3: Italian attack on Ethiopia , the League of Nations imposes an arms embargo and a credit and raw material freeze on Italy, the USA continues to supply fuel
1936
- January 15: Japan refuses to restrict its fleet and leaves the London Fleet Conference
- February 4: Wilhelm Gustloff , national group leader of the NSDAP foreign organization in Switzerland, is shot dead by David Frankfurter in Davos, who wanted to protest against anti-Semitism in Germany.
- February 6th: 1936 Winter Olympics in Garmisch-Partenkirchen, the Summer Olympics will be held in Berlin from August 1st to 16th, 1936
- February 27th: The French National Assembly approves the Franco-Soviet military pact with 353 votes to 164, approval in the Senate on March 12th
- March 7th: The Wehrmacht invades the Rhineland, which was demilitarized after the First World War
- May: Election victory of the Popular Front in France.
- May 12: Foundation of the Reichskolonialbund (co-ordination of the German colonial movement ).
- July 16: Beginning of the Spanish Civil War , also known as Spanish Civil War called; was fought between the democratically elected government of the Second Spanish Republic ("Republicans") and the right-wing putschists under General Francisco Franco ("Nationalists"). It ended in 1939 with the victory of the nationalists, especially with the help of the fascist allies from Italy and Germany. It was followed by the end of the Republic in Spain and the Francoist dictatorship (1939–1976), which lasted until Franco's death in 1975 .
- July 21: on the fifth day of the uprising, the nationalists captured the Ferrol naval base in northwestern Spain with two brand new cruisers. In particular, Franco helped the first airlift in history to move troops from the Spanish colonies to the mainland with German help, thus circumventing the republican naval blockade in the Strait of Gibraltar and thus consolidating a bridgehead he controlled.
- August: In his secret memorandum on the four-year plan, Hitler postulates a Soviet will to attack and demands: “I. The German army must be operational in four years. II. The German economy must be capable of war in four years "
- Italy is in Ethiopia Chemical Weapons a
- Italy leaves the League of Nations
- October 1: The Reich Court Martial was re-established as the highest instance of the Wehrmacht courts (compare conscientious objection and desertion )
- November: the Condor Legion is set up for use in Spain
- November 25th: the Anti-Comintern Pact between the German Reich and the Japanese Empire is signed, in 1937 Italy and other countries joined
- December 11: Edward VIII abdicates , the pro-German British King Edward VIII is forced to abdicate
1937
- 7th / 8th February: German pilots of the Condor Legion are involved in the Málaga massacre of Spanish nationalists of civilian refugees. 3,000 to 5,000 refugees were killed.
- March 31 and April 26: German pilots fly devastating air raids on Durango and Gernika (Guernika) for the putschist army in Spain
- May 1: Roosevelt signs the revised Neutrality Act
- June: Start of the “purge” of the Red Army by Stalin in the Soviet Union
- July 5th: according to an instruction dated in this way, the putschists set up a first Spanish concentration camp based on the German model in Miranda de Ebro during the so-called Spanish Civil War . The camp was managed by Gestapo member (and embassy employee) Paul Winzer until 1947 ( concentration camp commandant ). There was also a tour with Himmler.
- July 7: the Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) begins with the incident at the Marco Polo Bridge
- it brings the end of the Chinese-German cooperation
- In some representations, but historically controversial, the beginning of the Second Sino-Japanese War on July 7, 1937 is given as the actual beginning of the Second World War. Thus the Asian theater of war is emphasized / overemphasized in the importance of the conflict of many states.
- October 5th: With the sensational foreign policy quarantine speech , the American President Franklin D. Roosevelt calls for the aggressor states Germany , Italy and Japan to be put under “quarantine” and an end to American isolationism and the appeasement policy of Great Britain and the United Kingdom Of France
- November 5: Hitler specifies his war aims in front of the German generals ( Hoßbach protocol (also: Hoßbach protocol))
- November 6th: Italy joins the Anti-Comintern Pact
- December: case green (several instructions Hitler to the Armed Forces planning prepare the subsequent capture of Czechoslovakia), outwardly Hitler solves the in the subsequent period with different statements to Czechoslovakia Sudetenkrise from
- See also the map for this period: Image with the borders of the German Reich from December 31, 1937 (i.e. before the annexations, conquests in connection with the Second World War)
- 1937: Rowehl's command begins aerial espionage over the Soviet Union
- 1937: Heinz Guderian publishes his book “Achtung Panzer!” On the Blitzkrieg strategy
- December 11th: Italy leaves the League of Nations
1938
- February 4th: Blomberg-Fritsch crisis : Dismissal of War Minister Werner von Blomberg and Commander-in-Chief of the Army Werner von Fritsch , resignation Foreign Minister Konstantin von Neurath , successor Joachim von Ribbentrop , formation of a High Command of the Wehrmacht (OKW) under General Wilhelm Keitel with new ones Responsibilities through a Führer decree, General Walther von Brauchitsch becomes the new Commander-in-Chief of the Army (OBdH)
- March 12: Invasion of German troops and “Anschluss” of Austria to the German Reich (initially unofficially “ Greater German Reich ”); preceded by: Austrofascism (cf. Austria in the time of National Socialism )
- April 10th: A referendum in Austria confirms the connection to Germany
- May 17: The Naval Expansion Act allows US fleet spending to increase by $ 1 billion in ten years
- May 20: the so-called May crisis or weekend crisis - Czechoslovakia carries out a partial mobilization due to incorrect reports about German troop movements
- May 30th: Hitler's directive “Green” (in the new version) begins with the words: “It is my irrevocable decision to destroy Czechoslovakia by military action in the foreseeable future. Waiting for or bringing about the politically and militarily appropriate point in time is a matter for the political leadership. "
- July 29th: Battle of Lake Chassan , Japanese troops capture two Soviet heights on the border with Manchuria
- See also: on the use of chemical and biological weapons by the Japanese Army in the Battle of Wuhan
- August 13: the express plan decides that German industry will be ready for war in autumn 1939
- August 18th: Resignation of the Chief of Staff of the Army Ludwig Beck , successor on November 1st General Franz Halder
- the Sudeten crisis accumulated in the separation of the Sudetenland from Czechoslovakia - Munich Agreement of September 29, 1938 - on October 1, it was followed by the invasion of German troops
- October 5th: the President of the Czechoslovak Republic, Edvard Beneš , resigns his office and fled to London , one day later the Slovaks declared the autonomy they longed for within Czechoslovakia, which will be recognized by Prague a day later .
- October 19: Instruction from the Propaganda Ministry to the German press that "the self-confidence of the German people in their own strength and their military means should now be strengthened"
- November 9th / November 10th: the November pogrom (downplaying "Reichskristallnacht"), the centrally organized murder, abuse and robbery by NSDAP organizations of Jewish Germans throughout the German Reich is the beginning of the massively intensified persecution. Hundreds are murdered. In the weeks that followed, thousands were blackmailed abroad in concentration camps to transfer their property to the Nazis and to flee, possibly with their families. The Second World War, which was triggered a few months later, expressly (Hitler) turned against “Judaism” or “World Jewry”.
- November 10, 1938: The Reich-wide Central Association of German Citizens of Jewish Faith is banned by the Nazi authorities
- November 22nd: the Autonomy Act renames the Czechoslovak Republic , this state, which is dependent on the German Reich, was also called the Second Republic , in terms of foreign policy the entire process is perceived as a victory by Hitler over Great Britain and France without bloodshed, at the same time there is the interpretation (especially through N. Chamberlain ) that this prevented a war with Germany, plus the term appeasement policy (appeasement policy )
- November 24th: Hitler's directive on the “coup d'état of Danzig”
- December 6: Franco-German declaration by the two Foreign Ministers Ribbentrop / Bonnet (no border disputes, consultation in the event of conflicts)
1939, January to August
- January 24th: Reinhard Heydrich takes over the contract from Göring to "solve the Jewish question"
- January 27th: the Z-Plan to build up a large fleet by 1947/48 comes into force
- January 30th: In a speech in the Reichstag, Hitler announces the “annihilation of the Jewish race in Europe” in the event of a new world war
- February 14th: The Bismarck was launched
- February 27: France and England recognize Franco's government
- March 10: the so-called “chestnut speech” of Stalin; it is generally understood as a signal that the Soviet Union is ready to come to an understanding with Germany
- March 13th: Hitler puts pressure on the Slovak Prime Minister Jozef Tiso , who has already been deposed by the Czechs, to proclaim an independent First Slovak Republic (under German protection / pressure)
- March 14th: the Slovak parliament, which emerged from elections, unanimously votes for independence
- March 15: Destruction of the remaining Czech Republic contrary to the Munich Agreement (German troops march into the Czechoslovakian territories known as the remaining Czech Republic ), establishment of the Reich Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia
- March 15: Understanding between German and British industry in the Düsseldorf Agreement
- March 21st: the German Foreign Minister again talks to the Polish Ambassador in Berlin about the "annexation of Danzig" to the German Reich and calls for extraterritorial access to East Prussia
- March 22nd: forced return of the Memelland from Lithuania to the German Reich
- March 23: Slovakia becomes a state closely bound to Germany through the protection treaty
- March 24th: a coup attempt by the National Socialists with the help of the Volksdeutsche movement in the Principality of Liechtenstein fails
- March 26th: Poland finally rejects the German offers made since October on Danzig and the corridor and initiates a partial mobilization of the armed forces
- March 27: Spain joins the Anti-Comintern Pact
- March 28: Spanish general Franco's insurgent troops conquer Madrid
- March 31: British-French guarantee for Poland
- April 3: Hitler's internal directive to the military to work out a plan of aggressive war against Poland ( Weiß case )
- April 7-12: Italian occupation of Albania
- April 17th: American President Roosevelt demands long-term non-aggression declarations from Germany and Italy for 31 countries
- April 27: UK government decides to introduce compulsory military service for 20 and 21 year olds
- April 28: In the Reichstag speech, Hitler announces the German-British naval agreement and the German-Polish non-aggression pact of 1934
- May 11th - August 30th: Japanese troops attack soldiers of the Mongolian People's Revolutionary Army , allied with the Soviet Union , in order to enforce territorial claims. The Japanese-Soviet border conflict begins, in which Japan also uses biological weapons . High Japanese casualties (Battles of Khalkhyn Gol - Battles of Nomonhan) ended with an armistice.
- May 11: Poland rejects an offer of assistance from the Soviet Union
- May 15 to May 17: Franco-Polish military meetings in Paris
- May 19: Signing of the Franco-Polish military agreement by the French Chief of Staff Maurice Gamelin and the Polish Minister of War Tadeusz Kasprzycki , France undertook an offensive with the majority of its troops after 15 days in the event of a German attack on Poland or threat to its vital interests in Danzig to begin against Germany
- May 22nd: Signing of the steel pact between Germany and Italy
- May 23: Hitler announced in a speech to the Commander-in-Chief ( Schmundt Protocol ) that he had decided to attack Poland. He stated: "So the question of protecting Poland is omitted and the decision remains to attack Poland at the first suitable opportunity."
- May 26: With the "Military Training Act" Britain leads the military one
- May 31: German-Danish non-aggression treaty
- June 7th: With the "Strategic and Critical Materials Stock Pilling Act", the American Congress decides to buy up and stockpile essential raw materials worth 100 million dollars
- June 7: Estonia and Latvia sign a non-aggression treaty with Germany
- The National Socialist propaganda on the Polish Corridor that began, which had been suppressed until then, indicates that from now on Poland will be targeted, and the governments of Poland, Great Britain and France sign assistance agreements
- the general staff planning for the war against Poland, code-named Fall Weiß , will be completed by June 15
- July 5: Decision of a conference of the SS with the OKW under the direction of Heydrich to set up initially five, then 16 police task forces for tasks behind the front line
- July 18: Goering's confidante Helmuth Wohlthat arrives in London and conducts secret negotiations with Horace Wilson (Head of the Home Civil Service under Neville Chamberlain ) and Robert Hudson about a German-British understanding. These are made public through the British press
- July 26th: Intelligence services - two-day secret meeting of French, British and Polish cryptologists / code breakers / deciphers in the Kabaty forest of Pyry near Warsaw. Poland's secret service gave all its knowledge of Enigma encryption to the allies. They astonish them with Enigma replicas and their knowledge of their methodology. As a result, the supposed secret radio traffic of the Wehrmacht in Bletchley Park (GB) was soon largely deciphered.
- News service Bletchley Park (BP) and War Office Y Group (WOYG), Government Communications Wireless Stations (GCWS, the British radio monitoring service ; this corresponds to on the German side:
- B-Dienst (a department of the MND - Naval Intelligence Service of the German Navy)
- July 31: Chamberlain announces a military mission to the Soviet Union.
- August 6: Soviet ten-year plan to build a fleet of 15 battleships of the Soviet-Soyuz-class
- August 11: British and French military missions arrive in Moscow to negotiate an alliance against Germany
- August 17: the German-Soviet economic agreement on Soviet raw material deliveries enables Hitler to plan a war without fear of the effects of another naval blockade , which led to the German defeat in World War I and forced approval of the Versailles Treaty in 1919
- August 19: Conclusion of the German-Soviet economic agreement as a preliminary stage to the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact between the two foreign ministers.
- August 21: from Wilhelmshaven : the battleship Admiral Graf Spee leaves for the Atlantic and the liner " SMS Schleswig-Holstein " (old name) for a "visit" to Gdansk - with landing troops hidden on board -
- August 22nd: At Hitler's address to the commanders-in-chief on August 22nd, 1939 , Hitler announced the impending attack on Poland
- August 24: German-Soviet non-aggression pact , Eastern Europe is divided into spheres of interest in a secret additional protocol (also known as the Hitler-Stalin Pact or Molotov-Ribbentrop Agreement)
- August 24: Roosevelt's message to Mr. Hitler, with the request in the interest of “world peace” to fully respect the “territorial integrity” of the other nations and to settle disputes in “direct negotiations”
- August 25:
- Offer from Hitler / the German Reich to Great Britain, for freedom of action in the East he wants to forego any border adjustments in the West and declares himself ready to defend the British Empire with the German army in the event of an attack by third parties
- Signing of an assistance agreement between Poland and Great Britain in the event of a German attack on Poland
- Japan announces the Anti-Comintern Pact
- The beginning of the mediation efforts of Birger Dahlerus between Hitler and GB / Fr
The course of the war from 1939 to 1945
| year | Europe and Western Hemisphere | Asia and Pacific | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1939 | |||
| 1940 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | ||
| 1941 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jul – Dec | |
| 1942 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1943 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1944 | Eastern Europe | Western Europe | |
| Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1945 | Jan – May | Jan – Sep | |
1939
Gdansk and Poland are occupied. The Red Army also invades Poland, Lithuania and Finland. Annexation of further areas and establishment of a German special zone of occupation, the Generalgouvernement, in Poland. Massive reprisals against the civilian population, in particular the massive kidnapping and murder of Jewish Poles, begins (as a special force for this: police task forces). A planned intervention by Great Britain and France against Germany and the Soviet Union no longer materializes.
Events in 1939 just before the start of the war:
- August 25: at 3:02 p.m. Hitler gave the order to begin the attack on Poland on the morning of August 26, but canceled the start of the attack at 8:00 p.m.
- August 26th: the cancellation does not reach a German commando unit, it attacks the station of Mosty , ( occupation of the Jablunka pass )
- AUG 28: introduction of food stamps and motor gasoline -Bezugsscheinen in Germany
- August 28th: Mobilization of the Netherlands , those born after 1924 are drafted, the army reaches the strength of 280,000 men
- August 29: Polish fleet ordered into British waters (12:55 p.m., Operation Beijing )
- August 30th:
- Polish mobilization - Polish army, deployment
- Switzerland: Corps commander Henri Guisan (1874–1960) becomes General and Commander-in-Chief of the Swiss Army by parliamentary resolution
-
August 31: An SS commando unit fabricated a Polish attack on the Gleiwitz transmitter . This is supposed to provide Hitler with the propaganda pretext for an attack on Poland.
- The 16-point plan is read out on German radio .
- Issue of "Instruction No. 1 for Warfare" ( military code name of the planning: the "White case")
The attack on Poland
-
September 1st: Without a previous declaration of war , the German Wehrmacht attacks Poland ( attack on Poland ). For information on the organization of the military, see the schematic structure of the Wehrmacht on September 1, 1939 and the Polish Army before the Second World War . At 04:45 a.m., the Schleswig-Holstein liner fired at the fortified ammunition depot on the Westerplatte in the port area of the Free City of Danzig . Two German army groups (approx. 1.5 million soldiers) cross the Polish border. During the attack on the Vistula Bridge near Dirschau , there were first battles.
- Battle at Krojanty . This battle later gave rise to the myth that the Polish cavalry attacked German armored troops with bare sabers.
- German air raids on Wieluń , Krakow and Warsaw
- At 10:00 a.m. Hitler gives
- To mark the beginning of the war arrested the Secret State Police (Gestapo) in the war-Promotions numerous leaders of the dissolved unions and battered opposition parties.
- According to the Worek plan , the five submarines of the Polish Navy mine the coastal areas against sea landings and artillery attacks. Due to the German air superiority, the submarines are not in a position to act offensively and the individual commanders break off the operation independently in mid-September and call at neutral or allied ports.
- Estonia , Latvia , Lithuania , Finland , Norway and Switzerland declare their neutrality
- After taking the Gdańsk post office , Gauleiter Albert Forster announced the annexation of the city to the German Empire .
- The first Polish prisoners are transferred to the newly established Stutthof concentration camp near Danzig. 65,000 people died there by the end of the war.
- The British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain is a war government and appoints Winston Churchill to the First Lord of the Admiralty . He had already warned of a threat from the Nazi state during the 1930s and criticized the appeasement policy .
- The British Dominions Australia and New Zealand declare war on the German Empire. The Dominions of Newfoundland and the Union of South Africa will follow on September 4th and 6th, Canada on September 10th.
- The British Viceroy in India, Lord Linlithgow, declares, without consulting the leading Indian forces, a state of war with India on the side of Great Britain (As a result, the governments of the Congress Party resigned in the seven provinces of India they governed and there was a mass movement against the Deployment of Indian soldiers)
- Italy ( Axis Powers ), allied with the German Reich, declares itself to be "non-belligerent"
- The sinking of the British passenger ship Athenia by the U 30 opens the fighting of the Atlantic battle
- Violent attacks on ethnic Germans in the Polish city of Bromberg kill between 700 and 1,200 people ( Bromberg Bloody Sunday ).
- Mobilization of the Swiss Army .
- The Japanese Empire declares its neutrality
- To implement the state-directed war economy that occurs in the German Reich war economy regulation in force
- The Slovak state , allied with the German Reich, enters the war against Poland.
- The United States declares its neutrality and sets up a neutrality patrol .
- Due to the lack of relief attacks by the Western powers and after the declaration of neutrality by its ally Romania , Poland remains militarily isolated
- General mobilization in the Soviet Union
- SS-Obergruppenführer Reinhard Heydrich gave the task forces operating in the rear area of the front the order "to render the leading strata of the population in Poland as harmless as possible."
- In the Ciepielów massacre , members of the Wehrmacht murder 250 Polish prisoners of war .
- After the German victory in the Battle of Radom , 60,000 Polish soldiers are taken prisoners of war.
- German units begin the siege of the Hel peninsula .
- Start of a Polish counter-offensive on the Bzura .
- The British government sends the first four divisions of an expeditionary army to provide military support to France . By May 1940, the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) had 394,000 soldiers (twelve divisions) and was subordinate to John Vereker, 6th Viscount Gort .
- German troops capture the Brest fortress . The Polish government flees Lublin and resides in Romania.
- U 29 sinks the British aircraft carrier HMS Courageous .
- September 18: Soviet and German troops establish contact with each other near Brest-Litovsk
- September 19: the Battle of the Bzura (Battle of the Vistula) ends with a Polish defeat
- September 19: the Soviet army arrives in Vilnius
- September 21: Heydrich's order , as head of the German security police, to set up Jewish residential areas (concentration camp assembly camps) specifies in detail how the task forces should proceed (see Aktion Reinhard later )
- September 22nd: General Heinz Guderian and Brigade Commander Semjon Kriwoschein hold a joint German-Soviet military parade.
- 27./28. September: Bombing of Warsaw by the air force and artillery
- In Wejherowo (Neustadt), psychiatric patients are murdered by German SS troops. A German military hospital was then set up in the affected clinic.
- September to December: Shortly after the start of the war in Poland, members of the Schutzstaffel (SS) and the “Volksdeutsche Selbstschutz” murdered several thousand people in the woods around the village of Wielka Piaśnica near Danzig between September and December 1939. The Piaśnica massacre is considered to be the first systematically carried out mass murder by the National Socialists in German-occupied Europe. The victim groups were members of the Polish and Kashubian intelligentsia , Polish prisoners of war, patients in German and Polish psychiatric clinics and, as the largest group, Gestapo prisoners deported from the Reich.
- September 28th:
- the Polish capital surrenders; that ends the battle for Warsaw
- Signing of the German-Soviet border and friendship treaty in Moscow (modification of the border between these two countries)
- September 29: Surrender of the Polish fortress of Modlin
- October 4: Hitler's secret pardon for war crimes committed in Poland
- October 6: The last Polish troops surrender after the Battle of Kock
- October 8: the Peace Treaty of Brest-Litovsk between Germany and the Soviet Union is taking the " fourth partition of Poland "
- It follows: permanent occupation of Poland until 1944/1945 , including annexations in the German-Polish border area in violation of international law
- October 26th: the Nazi functionary, Reich Minister and lawyer Hans Frank becomes Governor General of the not the German. Richly incorporated parts of occupied Poland (the Generalgouvernement ). Frank had his official residence initially in Łódź , from November 1939 in Krakow , in the Wawel Castle . This division and the appointment of Frank reduced the military's sphere of influence. Commander-in-Chief Blaskowitz regarding his position as chief of civil administration (CdZ).
- Further acts of war
- September, see also: on the use of chemical and biological weapons by the Japanese army in the battle of Changsha
- September 26th: the French government bans the Communist Party
- September 27: Hitler's instructions to the Army High Command to work out the attack plan " Fall Gelb " (the western campaign)
- October 6: Germany offers peace to the Western powers
- October 7: the area around Marijampolė , Lithuania , known as Suwalken , is occupied by the Wehrmacht in accordance with a German-Soviet agreement; later renamed by the occupying forces in the Sudauen district .
- October 11: Soviet-Finnish negotiations begin on the transfer of bases
- October 14: the German submarine U 47 sinks the British battleship “ Royal Oak ” in Scapa Flow
- October 19: Arrival of the first three transports of Jews forced to work from Vienna (from Aspang train station ; among others) according to the Nisko plan to create a barrack camp for a "Jewish reserve" in Nisko , Poland, near the border with the Soviet-occupied part Poland. (The plan will be canceled in November)
- October 29: The German U 34 sinks the British civilian freighter Malabar (7976 GRT), part of the Anglo-American convoy HX 5A
- November 1st: Introduction of stand courts ( military jurisdiction )
- November 3: The US lifts its general arms export ban for Great Britain and France only
- November 6th: During the special campaign in Krakow , over 180 professors and other university members are kidnapped from the Jagiellonian University by German occupiers and imprisoned in concentration camps.
- November 8: Unsuccessful bomb attack by Georg Elser on Hitler and the assembled National Socialist leadership in Munich's Bürgerbräukeller
- November 23: At Hitler's address to the commanders-in-chief on November 23, 1939 , Hitler announced his decision to attack France and Great Britain soon
- November 27: the Soviet Union stages the Mainila incident
- November 30: Soviet troops engage in so-called " Winter War " Finland on
- Sweden supported Finland without officially giving up neutrality
- a planned intervention by Great Britain and France against the Soviet Union no longer materializes
- December 7th: Beginning of the Battle of Suomussalmi , in which two Soviet divisions are crushed (until January 1940)
- December 14th: Exclusion of the Soviet Union from the League of Nations because of its attack on Finland
- December 17: Captain Hans Langsdorff (1894–1939) ordered the ironclad Admiral Graf Spee to be sunk in the mouth of the Río de la Plata off Argentina so that the ship and its technical equipment could not fall into the hands of the superior units of the Royal Navy . The entire ship's crew was evacuated beforehand. He thus negated the order to fight.
- December 18th:
- Poland, in the form of the government in exile in London , declares a state of war with the Soviet Union
- The aerial battle over the German Bight proves British bomber operations by day without escort to be unrealistic, as a result, the Royal Air Force develops its concept of night bombing
- 1939: Construction of the Soviet Molotov Line begins
| year | Europe and Western Hemisphere | Asia and Pacific | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1939 | |||
| 1940 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | ||
| 1941 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jul – Dec | |
| 1942 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1943 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1944 | Eastern Europe | Western Europe | |
| Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1945 | Jan – May | Jan – Sep | |
1940
- In 1940 the German Reich attacks Denmark and Norway, which is then occupied by them. Invasion of Belgium, Luxembourg, the Netherlands and northern France (the so-called Western Campaign ) leading to the occupation of Paris. The evacuation of over 300,000 Allied soldiers near Dunkirk succeeds. German air raids on Great Britain. Hitler's military fail to achieve the main goal of keeping Britain out of the war or forcing it to surrender. The Soviet Union occupies the Baltic States and Romanian Bessarabia. Planning for the war against the Soviet Union. The conclusion of a three-power pact between Italy, Japan and the German Reich, which other states subsequently join, is a success for Hitler in foreign policy.
First half of 1940
- January 5: Leslie Hore-Belisha (1893–1957), British Minister of War, Secretary of War from 1937 to 1940, is dismissed by PM Chamberlain . The background were u. a. anti-Semitic prejudice against him.
- January 10th: Mechelen incident : a German military aircraft has to make an emergency landing in Belgium, an air force officer carries parts of the deployment plan with him, the then planned attack date of January 17th is postponed
- January 19: French Prime Minister Daladier orders the preparation of Operation Pike to bomb the Soviet oil refineries
- January 30th: The battle of South Henan lasts a month and ends with a Chinese victory
- February 5: Planning of the landing of four German divisions in Narvik
- February 11: Economic agreement between Germany and the Soviet Union for a further year
- Under the term Generalplan Ost (GPO), a number of plans, planning sketches and lecture materials on a possible new settlement structure as a planning basis for the colonization and “Germanization” of parts of eastern Central and Eastern Europe are presented
- February 16: Altmark incident , the German transport ship "Altmark" is attacked in Norway by a British destroyer
- February 17th: the Mannerheim Line in Finland is broken by Soviet troops
- February 21: Hitler's instructions for further planning in the Scandinavian region
- February 24th: The sickle-cut plan officially becomes the basis for German attack planning in the west
- February 25 to March 21: attempts at mediation by Sumner Welles
- March 1: The Weser Exercise company - the occupation of Denmark and Norway - is decided on the German side, the aim of the planned company is to import further iron ore from neutral Sweden and Finnish nickel into the German Reich. Great Britain wanted to prevent these raw material deliveries
- March 12: Peace of Moscow between Finland and the Soviet Union: parts of Karelia , Lapland and the fishing peninsula are ceded to the Soviet Union
- March 13th: The peace treaty ends the winter war
- March 14th: The Chinese army wins the battle for Shanggao by April 9th
- March 17th: The General Plenipotentiary for Construction, Fritz Todt , is appointed Reich Minister for Armaments and Ammunition and thus controls practically the entire German war economy
- MARCH 20: new French government under Paul Reynaud dissolves the government of appeasement politician Édouard Daladier from
- From March 30 or May 16, 1940: the “Extraordinary Pacification Action” (mostly abbreviated to AB-Aktion ) in Poland was a mass murder campaign by the German occupying forces, carried out jointly by SS task forces and local ethnic German self-protection units . It was genocidal in character; In the spring and summer, about 7,500 people were arrested in the General Government as part of this action , sentenced to death by alleged SS courts and murdered. (Period March 30 - June 1940, but lasted beyond that and after June 22, 1941 (attack on the USSR) was extended to eastern Poland, which had been occupied by the Soviet Union from September 17, 1939. German war crimes )
- March 31: the auxiliary cruiser Atlantis under Captain B. Rogge left Kiel for a 600-day cruiser war (including the South Atlantic and Indic).
- April 3, Katyn, Russian SFSR : Members of the Soviet People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (NKVD) begin (April 3 to May 11) with the murder of around 4,400 captured Poles, mostly officers, in a forest near Katyn, 20 kilometers to the west from Smolensk . This act was one of a series of mass murders of between 22,000 and 25,000 career or reserve officers, police officers and other Polish citizens, including many intellectuals. See also the Katyn Memorial (opened in 2000)
- April 8: Allied, no longer running, Operation Wilfred was German shipments of iron ore from Sweden through neutral Norwegian waters as part of the plan R4 prevent
- April 9: Start of the German invasion of Norway and Denmark (Weser exercise company)
- Invasion of Denmark under the code word Weserübungen-Süd (16 dead on the Danish side), government and king remain in the country
- The Norwegian coastal battery Oscarsborg (from 1856) sinks the heavy cruiser Blücher off Oslo . With this gain in time, King Håkon VII ends up in exile in England.
- Landing of a German mountain infantry division off Narvik (Norway)
- May 3 Rjukan is occupied with the only heavy water factory in the world in Vemork . It fell into German hands undamaged , but it was found that the entire supply of heavy water had already been given up. This could have been a warning sign for the army command that the Allies were also interested in the use of nuclear fission (German uranium project ). There later Operation Gunnerside (see film project Operation Swallow).
- 10th of April:
- April 13th:
- Great Britain begins Operation Valentine, the occupation of the 18 Danish Faroe Islands in the North Atlantic to secure the Atlantic route to North America . At times, 2000 soldiers are stationed there during the war.
- heavy naval battles between British and German destroyers at Narvik ; the German fleet unit is largely destroyed.
- April 14 to April 19: extensive Allied formations, including Polish soldiers and parts of the Foreign Legion , land in Norway
- May 3rd: The Luftwaffe sinks two Allied destroyers off Namsos
- May 7th: The Battle of South Shanxi ends on May 27th with the Japanese victory
- 10th of May:
- Beginning of the German campaign in the west (see main article: Chronology of the campaign in the west in 1940 , schematic war organization of the Wehrmacht on May 10, 1940 )
- seven German armies attack (yellow case) the neutral states of the Netherlands, Belgium and Luxembourg . Presentation of a diplomatic note to the ambassadors of these countries at 5:45 a.m. with the claused declaration of war that the Reich will ensure their neutrality militarily
- the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg is occupied
- Already on this day the Belgian Fort Eben-Emael , which was considered impregnable, was taken by German paratroopers
- the Dutch government had tried to be neutral at first, the invasion of the Netherlands began
- Winston Churchill becomes British Prime Minister
- British troops occupy Iceland (this makes the planned German invasion, Operation Icarus , obsolete)
- Beginning of the German campaign in the west (see main article: Chronology of the campaign in the west in 1940 , schematic war organization of the Wehrmacht on May 10, 1940 )
- May 13th:
- Queen Wilhelmina and the Dutch royal family and the rest of the government flee into exile in London; a Dutch government in exile is formed there. This was followed by a varied resistance in the home country until 1945 .
- Churchill's blood-sweat-and-tears speech
- 13th to 15th May: Battle of Sedan : after breaking through the Ardennes , German armored troops fight for the crossing over the Meuse near Sedan
- May 14th:
- the German air strike on Rotterdam kills 800 - the surrender negotiations had already started.
- Surrender of the Dutch troops
- the Nazi functionary Seyß-Inquart , who until then was Deputy Governor General in occupied Poland, becomes German Reich Commissioner for the Netherlands
- General Friedrich Christiansen was the German Wehrmacht Commander in Chief from May 29, 1940 to April 7, 1945, and from November 10, 1944 to January 28, 1945 also Commander in Chief of the 25th Army deployed there .
- General Guderian crossed the Meuse with his tank group , the British Royal Air Force suffered heavy losses
- May 15: the British cabinet decides to wage a strategic aerial warfare against the German Reich
- 17th of May:
- Counterattack by the French 4th Panzer Division under Charles de Gaulle canceled - Bataille de Montcornet on the Aisne
- Brussels is handed over without a fight
- May 19: the German 6th Army reaches the river Schelde and advances to Abbeville . The advance is so rapid that the British and French units in northern France are cut off; they withdraw to Dunkerque (Dunkirk)
- May 20: The Committee to Defend America by Aiding the Allies, which calls for material and moral support for the Allies in the fight against Germany, announces its founding.
- May 23: After the occupation of the Netherlands , SS leader Hanns Albin Rauter was appointed "General Commissioner for Security" and Higher SS and Police Leader "Northwest" at the Reich Commissioner for the Netherlands Seyß-Inquart. In his position as police commander and the highest-ranking SS leader in the Netherlands, Rauter was responsible for the deportations of around 110,000 Dutch Jews to the extermination camps (around 6,000 survived), the fight against the Dutch resistance and the harsh occupation conditions. Around 300,000 Dutch people were deported to the Reich for forced labor and their properties were confiscated. The general strike organized by the Dutch resistance in February 1941 was bloodily suppressed at Rauter's orders.
- May 24th: Hitler's controversial stop order for the armored forces of Army Group A
- May 26th - June 5th: the Battle of Dunkirk begins; on June 4th capture of Dunkerque
- May 27: British Operation Dynamo (evacuation of over 300,000 Allied soldiers) starts near Dunkirk. Will be completed on June 4th.
- May 28: Belgian army surrenders
- May 29: German-Romanian oil-weapons pact
- May / June: Polish civilians are massacred in Poland as part of the AB action and the Palmiry massacre
- June 1: A squadron of the Condor Legion flies over the border to Switzerland when attacking France . Swiss airmen shot down 11 of them German machines in the defensive position.
- June 4: three Swiss aircraft are shot down in a subsequent German “punitive expedition”
- June 5th: German offensive on the Aisne and Somme
- June 6th: the Reich government protests against the Swiss "air raids" and asks the Swiss Federal Council to apologize (repeated on June 19th)
- June 8th: Allied expedition forces, which had been successful up to then, withdrew from the Narvik area
- June 9th: Soldiers of the 6th Infantry Division cross the Seine
- June 10th:
- the Norwegian military surrenders, King Håkon VII and the government go into exile in Britain
- From this time: Shetland Bus , around 600 Norwegians fled to the British Shetland Islands in 1940 by fishing boats . From 1941 to 1945 373 refugees were saved in this way. Conversely, Norwegian resistance fighters and 192 agents were smuggled into Norway via this route (locations Lunna and Scalloway near Lerwick and Telavåg ; losses: 33 men and seven ships).
- Mussolini decides to go to war against the two Western Allies
- 10-13 June: Operation Cycle, approx. 11,000 British and other Allied soldiers evacuated from Le Havre
- June 11th: First Italian air raids against British Malta (bombing), initially no attempt at invasion, blockade - British name: Second large siege of Malta (until November 1942)
- 14th June:
- • Paris is occupied, previously partially evacuated by the French military ( Paris in WWII )
- • The German Army Group C breaks through the Maginot Line and the fortress of Verdun is taken
- 15-25 June: Another British evacuation, Operation Aerial , of more than 215,000 Allied soldiers from Cherbourg , St. Malo and other ports to England
- June 17th: ... the HMT Lancastria , used as a troop transport, is sunk by the German Air Force in front of the Loire estuary .
- 17th of June:
- Ex-Marshal Philippe Pétain , Prime Minister of the newly formed French government, explains France's defeat
- The Soviet Foreign Minister Molotov congratulates the German Reich on its victory over France
- Soviet troops occupy the Baltic states on the same day
- June 18: Charles de Gaulle , Military Secretary of State in exile in London, calls on the French (with Churchill's support) in his radio appeal later called Apell de Londre on BBC London (with the support of Churchill) to keep fighting - the appeal of London / June 18 . He then founds the Committee for Free France (France libre) and from the French participants in the Narvik expedition and from the 130,000 men who were disembarked from Dunkirk in time, the first volunteers as French units in the British Army ( Forces françaises libres ). As a result, various civil groups of the Resistance , but also partisan units , emerged in France .
- June 19: Le Mans is captured and occupied
- 20th June:
- At the behest of the Federal Council, the Commander in Chief of the Swiss Army, General Henri Guisan , ordered the aircraft to be left on the ground with immediate effect.
- The transfer of the 45th French Army Corps to internment in the Jura under General Marius Daille is granted by the Swiss Federal Council (around 43,000 French and Polish soldiers at Goumois . In the following period, the Swiss Army was partly in favor of interning them until the end of the war foreign military personnel.)
- June 21: Hitler negotiates with the French government (État français , Vichy regime) in the forest of Compiègne
- June 22nd: Signing of the Franco-German armistice (Compiègne) , French called Armistice de Rethondes ; ( to the place and the railway carriage )
- June 25th: the German-French Armistice goes into effect at 1:35 a.m.
- June 25: Public statements by the Federal Council (government) to the Swiss people on the ceasefire in the neighboring country via radio and in the Neue Zürcher Zeitung and at the same time a secret, Rütli report , issued by Commander-in-Chief Henri Guisan on the Réduit plan in the event of an attack by the Axis powers . Two parts of a cautious policy of deterring the Axis powers. Named after the Rütliwiese on Lake Lucerne (place where orders were issued in central Switzerland).
- June 26th: Dönitz visits Lorient . As a result, the decisions to expand this and the four other bases for submarines are made. The first two Koroman bunkers will be completed by December 1941. They were part of the "Atlantic Wall" and the " Atlantic Battle " (trade war with submarines; alongside Brest , Saint-Nazaire , La Rochelle and Bordeaux )
- June 28 to July 4: Soviet occupation of Bessarabia and northern Bukovina
- June 30 and next days: the British Channel Islands near the French north-west coast are occupied by German troops, Guernsey surrenders on June 30, Jersey on July 1, Alderney on July 2 and Sark on July 4 after a partial evacuation of the civilian population
- June: William Stephenson opens the British Security Coordination (BSC, British secret service network in the USA) in New York City
| year | Europe and Western Hemisphere | Asia and Pacific | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1939 | |||
| 1940 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | ||
| 1941 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jul – Dec | |
| 1942 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1943 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1944 | Eastern Europe | Western Europe | |
| Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1945 | Jan – May | Jan – Sep | |
Second half of 1940
- July 3: Operation Catapult , sinking of the French fleet in North Africa in Mers-el-Kébir by the British Force H (Admiral Somerville). 1297 French sailors died and 350 were wounded. Similar missions before Oran and on July 8th in Dakar .
- July:
- Division of France into a German-occupied part and the unoccupied southeast part of the Vichy regime under Marshal Pétain (État fr.)
- General de Gaulle is from 1940 the organizer of the external military resistance with fled units: later called "Leader of Free France", from exile in London (see London appeal, radio address, June 18 )
- the Resistance - the resistance within France is formed, supported by trade unions, the socialist and communist parties, but also by conservatives who do not want to collaborate with Pétain and the Germans
- Mid-July: Creation of the British Special Operations Executive (covert military operations)
- July: the Battle of Britain begins from the Channel coast of occupied France with attacks on shipping traffic in the English Channel (partial blockade)
- July 19: USA, the Two-Ocean Navy Act provides for a 70 percent increase in the US Navy
- July 25th:
- Rütli report , orders issued by the Swiss Mayor Guisan (withdrawal of troops from the border, Réduit strategy)
- Code name "Otto", a "preferred Wehrmacht program", the plan for the larger west-east railway lines through the Generalgouvernement, in particular the railway line from Radom via Demblin to Lublin , to be restored or expanded from October . Franz Halder , Chief of the General Staff of the Army since September 1938, commissioned his staff on June 19 or July 3, 1940 to prepare it . This plan was expanded after July 31, merged with other plans and, in December (see 18.), the war preparations of the OKW and OKH ( Barbarossa case ) were based.
- July 31: Hitler decides to attack the Soviet Union in the spring of 1941 in order to eliminate it as England's mainland sword.
- August 6: Estonia's forced accession to the Soviet Union, annexation
- August 7: Churchill and de Gaulle agree on the Accord of Checkers ( Checkers treaties), after the United Kingdom respects the integrity of all French possessions and the "integral restoration and independence and greatness of France" and receives.
- August 8: The detailed invasion plan against Ireland under the code name Enterprise Green is handed over to the German high command - General Field Marshal Fedor von Bock was in charge . The invasion was supposed to flank the Sea Lion Company (England) and was done with its task.
- August 11: Operation Razzle begins to destroy the German harvest with fire chips
- August 13: "Eagle Day" during the Battle of Britain: massive air raids on Royal Air Force bases in southern England
- August 17th: Hitler imposes an import blockade on the British Isles
- August 20: The Chinese Communists open the Hundred Regiments Offensive , which will last until December 5, towards the end of which there is a rift between Peng Dehuai , the military leader of the Communists, and Mao Zedong
- August 21: The British Allied Forces Act 1940 gives certain governments in exile the right to own troops in the United States. To station kingdom as an expression of their sovereignty. In practice, they were then combatants in the British armed forces and integrated into their management structure.
- 24./25. August: First (unplanned) dropping of German bombs on the British capital London , followed by the first British air raid on Berlin the following night
- August 30th: Second Vienna arbitration award by Germany and Italy: Romania has to cede parts of Transylvania to Hungary
- August: Use of the French naval port as a submarine base (German and Italian navy)
- September 2: Destroyer-by-base agreement
- September: Conscription is introduced in the USA with the Selective Training and Service Act
- September 4th: Foundation of the America First Committee , an isolationist organization which is directed against the participation of the USA in the war
- September 7: Air raids on London begin (300 German bombers and 600 fighters; until May 16, 1941)
- September 22nd: Japan invades northern French Indochina . The USA and Great Britain then impose an embargo and freeze Japan's financial resources
- The headquarters of the Japanese Southern Army under Marshal Terauchi Hisaichi was in the former French colony of Vietnam from 1941 to summer 1943 and from autumn 1944 to the end of the war . The French, Vichy-oriented colonial administration under Admiral Jean Decoux was not eliminated (collaboration). The Japanese policy of occupation resulted in a famine in the final year of the war that killed over a million people.
- 23 to 25 September: in the battle of Dakar ( Operation Menace ), a British-French attempt (with De Gaulle's forces for a free France (Forces fr. Libres) ), the port and the city of Dakar in French West Africa (AOF ) fails , in what is now Senegal )
- September 27th: on the initiative of Adolf Hitler , the three-power pact was agreed between the German Empire, the Empire of Japan and the Kingdom of Italy . Internationally used names are Patto tripartito, Tripartite Pact or Berlin Pact . It was also referred to by the contracting parties as the Berlin-Rome-Tokyo axis and the three parties involved as the axis powers . Signing in the Great Hall of the New Reich Chancellery , Berlin; for Japan by Ambassador Saburō Kurusu .
- October 12th: The Seelöwe company is postponed indefinitely
- October 23: The Hitler-Franco meeting at the Hendaye border station (on the German side in France) does not lead to the abolition of neutrality of Spain in 1940 either (Franco declaration on December 7: No German march through to Gibraltar (company Felix) )
- October 28: Beginning of the Greek-Italian war , Italian units attack from the Italian colony Albania from Greece to Italy can Bulgaria do not win as allies
- November 3rd: the Greek army successfully counterattacked, by November 14th the Italian units were on the defensive and were pushed back across the borders of Albania
- November 8th to 12th: The campagne du Gabon or bataille de Libreville is the name given to the conquest of Gabon by Forces françaises libres (FFL, under De Gaulle )
- November 11th: from the auxiliary cruiser Atlantis in the South Pacific the Engl. Freighter SS Automedon with a mailbag of extensive British secret material on board that could be made available to Japan. Automedon incident - the tea service; an assessment of the situation and strategy in the Far East (as of August 1940; Chiefs of Staff Appreciation of Far Eastern Strategy )
- 11./12. November: British attack on the Italian naval base Taranto , three battleships are incapacitated , in particular by the first use of an aircraft carrier, the Illustrious , against an enemy fleet
- November 12th to 13th: Visit of the Soviet Foreign Minister Molotov in Berlin, an extension of the three-power pact to form a continental bloc against England, on the Soviet Union does not take place - Hitler is already determined to go to war against the Soviet Union
- November 14: German air raid on Coventry (568 people were killed in this attack)
- Start of broadcasting of Germany Calling , German propaganda shortwave transmitter in around 30 languages, daily 147 hours of programming (until April 30, 1945) - identifier Germany calling! Here are the Reichssender Hamburg, station Bremen
- December 8: Start of Operation Compass , during which the Allies in North Africa under the command of General Richard O'Connor were able to repel Italian troops 800 km south of Sidi Barrani in Libya as far as Bardia from December 8 to February 9, 1941 a sudden victory at Fort Capuzzo in July, this was the first Allied operation in North Africa
- December 13th: In view of the defeats of the Axis partner, Hitler issues instructions for a German campaign in the Balkans with the Plan Marita
- December 16: British air raid on Mannheim (Operation Abigail), considered the first British bombing raid with terrorist intent and experiment for later incendiary attacks, internally justified as retaliation for the air raids on Coventry and Southampton,
- 16./17. 23rd and 23rd December: two accidental air raids by the Royal Air Force on Basel and Zurich , two dead, possibly a result of the Swiss blackout measures.
- December 18: Hitler issues " Instruction No. 21 " to the OKW to prepare for war against the Soviet Union under the new code name Case Barbarossa , until then the code name "Otto" was in effect (see July).
- December 29: German air raid on London leads to the second city fire ( Second Great Fire of London )
| year | Europe and Western Hemisphere | Asia and Pacific | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1939 | |||
| 1940 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | ||
| 1941 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jul – Dec | |
| 1942 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1943 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1944 | Eastern Europe | Western Europe | |
| Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1945 | Jan – May | Jan – Sep | |
1941
- In 1941 the war was widened again in many places. In order to support Italy in its invasion of Africa, Hitler orders the deployment of German troops in Libya. They succeed in advancing to Egypt (the port of Tobruk is initially held by British troops). The invasion of the Balkans leads to the invasion of Crete and Greece. The sinking of the battleship Bismarck represents Hitler's weak point in the Atlantic. In Asia, the cooperation between the Kuomintang and the communists in the war against Japan ended. The Battle of Britain, the German aerial warfare to conquer Great Britain, ended in favor of the Royal Air Force. With the withdrawal of German troops from France to the east, London is literally getting air again. On June 22nd, Hitler started the war against the temporary contracting party, the Soviet Union, with the company "Barbarossa". In mid-August, parts of the rapidly advancing Wehrmacht turned south-east towards Ukraine as far as Crimea and north towards Leningrad. The alliance between the United Kingdom / Great Britain and the USSR is established. Great Britain and the USA agree on the Atlantic Charter. By conquering southern Indochina to Malaysia, Japan can increase the pressure on China's supply routes. The Japanese advance in the Pacific comes to a halt in New Guinea. The German attack on the Soviet Union comes to a standstill in front of Moscow and Leningrad, and in the counter-offensive the Allied side has for the first time made major gains.
First half of 1941 in Europe and the Mediterranean
- January 10th: Planning for the Felix company , attack on the fortress of Gibraltar - cf. October 23, 1940, were discontinued
- January 19: East Africa campaign : start of the British offensive against the colony of Italian East Africa
- January 29th to March 27th: secret American-British staff talks in London lead to the ABC-1 war plan , in which the principle "Germany first" is established.
- February 2 to March 27: Battle of Keren , Eritrea , British troops defeat the Italians
- In February the German General Rommel received an order to support the unsuccessful ally Italy with the Africa Corps in its defense in North Africa
- February 15: From this date, Cichociemni , Polish soldiers trained as parachutists after the invasion of Great Britain in 1939, supported the Home Army for the first time . They were also subordinate to her after landing. The first jump took place at Dębowiec . The last jump took place on December 28, 1944. Of the 316 soldiers who jumped off, 112 were killed. Nine of them were convicted after the war by the so-called communist people's courts during the Stalinist era . Of the 91 Cichociemni soldiers who took part in the Warsaw Uprising in 1944 , 18 died during the fighting.
- February 15 and 26: a deportation train each from Vienna-Aspang station with around 1,000 captured Jewish citizens from Vienna drives to a collection camp in the east of occupied Poland in Opole Lubelskie . (Those who still survived after one year in prison were murdered from there on March 31, 1942 in the Belzec extermination camp and in May and October 1942 in the Sobibor extermination camp . Only 28 of these two deportation transports are known.) On the 19th, another train leaves to camp Kielce .
- FEBRUARY 18: the US lend-lease (English: "Lend-Lease Act") in the US Congress
- February 22nd and 23rd: after a large-scale raid against Jews in the Netherlands, there was the “ February strike ” against the deportations , which was bloodily suppressed
- February 28: The German army marches in from Romania near Giurgiu from south of Bucharest across the Danube and near Dobruja in Bulgaria (see History of Bulgaria )
- Bulgaria later joins the Axis powers in the war against Yugoslavia and Greece
- in December 1941 it declared war on Great Britain and the US - but not on the USSR
- February 1941: manned German weather stations on Svalbard and NE Greenland (last cleared Ripfjorden on September 4, 1945) - on the other hand, a Danish Sirius patrol deployed in Greenland (Danish: Nordøstgrønlands Slædepatrulje)
- March 1: Heinrich Himmler and a delegation from IG Farben meet for a tour and joint planning at Auschwitz concentration camp
- March 9: Italian major offensive in Albania turns into a disaster
- March 11th: With the Lend & Lease Act, the US Congress creates the legal basis for the previously practiced support for Great Britain, the country, like the Soviet Union later , will be relieved of the country with arms and aid supplies on a large scale USA supplied
- March 25: Yugoslavia joins the three-power pact, the result are demonstrations and a coup against the government of Prince Regent Paul, whereupon the accession is revoked 12 days later
- March 27: “Instruction No. 25” on the destruction of Yugoslavia in connection with the planned campaign against Greece
- March 28: Due to the defeat in the Battle of Cape Matapan against British units, the Italian fleet loses its effective operational capability in the Mediterranean
- March 30th: Hitler announces war against the Soviet Union in a speech to 200–250 soldiers in the Reich Chancellery
- April 1: The military coup in Iraq ends on May 31 with the capture of Baghdad by British troops (including the Arab Legion )
- April 8th: This airstrike on the city of Coventry (and the previous one on November 14th) was the heaviest bombing raid of the war to date, and thus also a massive war crime . These attacks coined the term " Coventrieren " in German propaganda ( language used by the National Socialists, here to avoid explanations of content ).
- April 6th ff .: Balkan campaign against Greece and Yugoslavia :
- Units of the German Wehrmacht cross the Yugoslav and Greek borders, fighting for the Metaxas line For the organization of the military forces, see the schematic structure of the Wehrmacht on April 6, 1941 .
- A series of air raids on Belgrade begin, around 500 to 600 German aircraft will be deployed by April 7th, and after the end of the war the commanding General Alexander Löhr was convicted and executed for this attack
- April 9th: Salonika occupied
- April 10th: the Croatian capital Zagreb is occupied
- April 12th: Belgrade is occupied
- April 17th: unconditional surrender of Yugoslavia
- April 21: 223,000 Greek soldiers capitulate in Epirus after their route of retreat is cut off
- Britons have also been stationed in Greece, meanwhile, build a defense to the Thermopylae on
- April 24th: these positions are overrun, whereupon the Allies launch an amphibious evacuation operation in which 50,000 soldiers are shipped to Crete and Egypt
- April 25th: OKW issues “Directive No. 28” ( Operation Merkur ) on an airborne invasion of the island of Crete
- April 27th: the Wehrmacht advances in Athens a
- April 8th: As part of Operation Columba , the British Army obtained vital information from the occupied countries of Western Europe by means of carrier pigeons
- April 9: The Danish envoy in Washington signed an agreement on the American military protection of Greenland
- April 10th: German troops reach Tobruk fortress in Libya and begin a seven-month siege
- April 13th: Japanese-Soviet Neutrality Pact
- April 15: That night alone, around 1000 people died in the Belfast Blitz (series of air strikes, Northern Ireland; 7.4. - 6.5.) In the practically undefended Belfast .
- May 2 to June 1: Great Britain prevents Iraq from joining the Axis powers in the Anglo-Iraqi War
- May 2 to June: Preparation of the Green Portfolio of Economic Guidelines for the Occupation in the Soviet Union.
- May 5: Stalin's speech to the graduates of the Soviet military academies
- May 9th: Capture of the German submarine U 110 together with an intact Enigma M3 machine and all secret documents (see " Ultra ") by the British destroyer HMS Bulldog
- May 10: Hitler's deputy in the NSDAP leadership, Rudolf Hess , flies to Scotland in a Messerschmitt Bf 110 to allegedly negotiate peace with the Duke of Hamilton , in the course of which he becomes a British prisoner of war and is later convicted as a war criminal, His flight is publicly described by the Nazi regime as treason and Hess is declared crazy
- May 13: With the martial law decree of the High Command of the Wehrmacht for the area "Barbarossa" (Soviet Union) of May 13, 1941 , the courts- martial were deprived of jurisdiction against civilians in the war zone (and transferred to the Higher SS and Police Leaders (SSPF) )
- May 20: Airborne battle for Crete (Op. Merkur), 593 transport aircraft bring German airborne units to Crete, the Allies, including New Zealanders and Australians , defend Crete for a week. Operation "Merkur" was only successfully completed by the German troops with heavy losses.
- May 27: US President Roosevelt declares an unlimited national emergency
- May 30th: During the night, the Air Force mistakenly bombed the neutral Irish capital, Dublin
- strengthened from May: North Atlantic Route as a supply line from the USA for GB and northern sea convoys in the SU, also HX convoys and their German combat under the umbrella term Atlantic battle
- June 6th: the commissar order of the Chief of the High Command of the Wehrmacht Keitel - official guidelines for the treatment of political commissars - is one of the well-documented violations of international law by the German Wehrmacht, issued with reference to an instruction from Hitler dated May 14, five weeks before the invasion the Soviet Union for the murder of prisoners of war from the Red Army
- June 8th to July 14th: in the Syrian-Lebanese campaign , the British and the Free French take control of the League of Nations mandate for Syria and Lebanon
- June 14: Hitler's speech to the commanders-in-chief on June 14, 1941 on the Eastern campaign
- June 15-17: a British attempt to lift the siege of Tobruk ( Operation Battleaxe ) fails
- June 18: the German Reich and Turkey sign a friendship and non-aggression treaty
- June 22nd: Beginning of the German-Soviet War
- Three Army Groups (North, Center, South) were ready for the attack, Army Group North (von Leeb) was supposed to conquer the Baltic states and advance to Leningrad , the main load was on Army Group Center (von Bock), it was supposed to advance to Moscow and was accordingly well armed, the Army Group South ( von Rundstedt ) was to conquer the Ukraine , units from allied or conquered countries of the Axis powers were also involved in the campaign, attacks against the Soviet Union are also being carried out from occupied Norway, they are aimed particularly at Murmansk and the local railway connection, the " Murman Railway ", and the port. For the organization of the forces, see Schematic war organization of the Wehrmacht on June 22, 1941 and Schematic war organization of the Red Army on June 22, 1941 .
- General plan east , hunger plan (strategic basis)
- the Molotov Line was a Soviet defense system that had been built along the border with the German Reich or the General Government established on the basis of the German-Soviet Treaty of Friendship of 1939
- The Balkan campaign had postponed the time of attack on the Soviet Union by four weeks, so the attack did not take place until June 22nd, this delay and an unusually early onset of winter mean that the advance cannot proceed as planned and the operational goal of achieving it the Arkhangelsk - Astrakhan line , although it was calculated on the German side that supplies to the Wehrmacht could only be made possible up to a line running along Pskov , Kiev and the Crimea , Hitler demands the conquest of Moscow as part of a single line , uninterrupted campaign
- In the early morning hours of June 22nd, the advance of 149 divisions across the Soviet border begins , two divisions are operating from Finnish territory , eight divisions were stationed in Norway, one division is ready in Denmark, 38 remain in the west, two divisions are fighting this time in North Africa and seven divisions stand in the Balkans
- Despite many hints, the lower and middle leadership of the Soviet Union are not prepared for an attack, many of the Soviet soldiers on the border surrender without resistance, while the motorized German troops initially advance quickly
- One consequence of the winter war in Finland was that Stalin began a comprehensive reorganization in the Red Army , in the course of which many officers who had been exiled to Siberia in the purges of 1936/37 are being rehabilitated; this contributes significantly to the Red Army has a greater combat strength than the German leadership expected
- Soviet war production is relocated behind the Urals , where it is inaccessible to the German air force
- as a direct reaction to the Soviet attack, Finland took part in the 1941 Continuation War in the German Russian campaign to recapture the lost territories
- June 22nd: Romania and Italy declare war on the Soviet Union
- June 23-29 : Tank battle near Dubno-Lutsk-Rivne
- June 23: The Göring program envisages the quadrupling of the Luftwaffe
- June 27: Hungary declares war on the Soviet Union
- June 29th:
- the Soviet leadership declares the defensive actions to be the " Great Patriotic War "
- Against the war conventions, special German SS Einsatzgruppen kill thousands of prisoners of war and civilians (mass murders, war crimes) directly behind the advancing front lines, as in Poland
- shortly before that, Minsk and Bialystok had already been included in a cauldron battle and were occupied shortly afterwards
| year | Europe and Western Hemisphere | Asia and Pacific | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1939 | |||
| 1940 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | ||
| 1941 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jul – Dec | |
| 1942 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1943 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1944 | Eastern Europe | Western Europe | |
| Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1945 | Jan – May | Jan – Sep | |
Second half of 1941 in Europe, Mediterranean
- Mass killings in 1941 in Lviv (Lemberg), Ukraine, after the German occupation
- July 1: Broniki case , Soviet massacre of German soldiers
- July 3: Stalin's radio address . He now interprets the war as the “Great Patriotic War” or calls for the liberation of Europe from fascism. He names partisan warfare and scorched earth politics as weapons .
- July to August 8th: Kessel battle near Uman
- July 4th: about four weeks after the Wehrmacht took Pinsk , the 2nd SS cavalry regiment under the command of Franz Magill murdered about 9,000 Jewish men between August 5th and 13th around six kilometers outside the city.
- July 10th - September 10th: Battle of the Smolensk Valley
- July 12th: a mutual aid agreement between the Soviet Union and Great Britain is signed, both sides agree not to conclude a unilateral armistice with Germany
- Between July 13, 1941 and August 19, 1944: long unsuccessful air raids on Ploieşti (oil production facilities in Romania) by the Allied powers
- 21./22. July: Start of the German air raids on Moscow , which by a radar network of RUS-1 and RUS-2 is protected
- July 26: the US and England declare a fuel embargo on Japan
- July 29 to August 1: Harry Hopkins agrees to deliver American aid to the Soviet Union in Moscow
- JULY 30: the Sikorski-Maisky agreement between the Polish government in exile and the Soviet Union is signed, it provides for the establishment of diplomatic relations and the establishment of a Polish army in the Soviet Union before
- July 31 - August 21, 1941, planning of the Kamenets-Podolsk massacre (see below August 27 - 31)
- August 7th: Stalin becomes Supreme Commander of the Red Army
- August 8: first Soviet air raid on Berlin .
- August 14: The Atlantic Charter of President Franklin D. Roosevelt and Prime Minister Winston Churchill specifies the ideas of a new world order after the war, it is considered one of the birth documents of the later United Nations
- August 23 to September 26: Battle of Kiev
- August 25 to September 17: Successful Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran (English: Operation Countenance - Russian: Sochuwstije ): the occupation of the formally neutral country serves to secure the Iranian oil fields and the establishment of a southern supply line for the Soviet Union
- August 27 to 31: mass shooting of 23,600 deported Hungarian Jews by SS units and the 320 police battalion, the Kamenets-Podolsk massacre in Soviet territory ( Ukraine ); beforehand, the plan was agreed with the armed forces (from July 31 to August 21). For the first time in the Soviet Union, thousands of civilians were murdered indiscriminately, regardless of age or gender.
- August 30: first successful Soviet offensive near Jelnja and at the same time the first withdrawal of German troops
- September 4th: "Greer" incident, the American destroyer USS Greer reports the position of a German submarine to a British aircraft and pursues the submarine, the submarine shoots a torpedo at the American destroyer, the "Greer "Throws depth charges, which leads to the" Shoot on sight "order of the American President on September 11th
- September 8: Beginning of the Leningrad blockade (today St. Petersburg ). It lasted over two years until January 18, 1944. The military capture of the city was forbidden to the Wehrmacht by Hitler. The civilian population of the metropolis is systematically starved by German troops .
- September 10th: End of the battle near Smolensk
- September 13th: on this day the Finnish Tarmo drove as part of the bogus company "Nordwind" - a German-Finnish company to cover the German occupation of the Estonian islands Hiiumaa and Saaremaa against the Red Army fleet
- September 15: The OKW issues an order to take and shoot civilians hostage (in connection with attacks on members of the Wehrmacht behind the front) - atonement order
- September 30: Mass murder in the Babyn Yar valley near Kiev of over 30,000 people from the city's Jewish population, after the 6th Army had occupied Kiev, mainly by Einsatzgruppe C of the SS , until November 1943, further mass shootings took place in the city a total of between 150,000 and 200,000 Soviet prisoners of war and civilians were murdered.
- Establishment of the London Controlling Section (LCS) under Oliver Stanley to coordinate the Operation Bodyguard (fortitude , diversion , concealment of the later invasion, strategic deception ) under the Joint Planning Staff
- October 2: 1. Moscow Protocol on Aid Deliveries to the Soviet Union under the Loan and Lease Act ; Deliveries are planned to be worth $ 1 billion by June 1942
- October 2 to the end of October: in the course of the German attack on Moscow ( Operation Taifun ) there is a double battle at Vyazma and Bryansk , the autumn muddy season forces the attacks to cease
- 6./7. October: In the tank battle near Mtsensk , a rapid advance on Tula can be repulsed
- October 12: More than ten thousand Jewish men, women and children are shot on Bloody Sunday in Stanislau . This mass murder in Ivano-Frankivsk , now part of western Ukraine, is considered to be the beginning of the “final solution” in the part of Poland known as the General Government.
- October 22nd: So-called hostage shooting by the Wehrmacht in a quarry near Châteaubriant (Massacre of Ch.) Of 27 prisoners from the Vichy camp Camp de Choisel and a further 21 prisoners elsewhere as so-called reprisal for Lieutenant Karl Hotz who was shot in Nantes .
- October 31: The US destroyer USS Reuben James (neutral country) is torpedoed near Iceland, killing over 100 US marines
- November 1st: Stationing of submarines for the " Atlantic Battle " ( trade war with submarines in La Rochelle (until August 1944))
- November 6th: Stalin speaks on the radio for the second time to the entire Soviet population, he announces the imminent victory over Germany
- November 7th:
- Red Army military parade in Moscow's Red Square
- Sinking of the Soviet passenger ship Armenija (1928) off Gurzuf (Crimea) in the Black Sea. Before this date it was used as a troop transport. It is unclear whether it was marked as a hospital ship when it was used to clear the Sevastopol hospitals. As a result of the attack by (at least) one German aircraft, 4,700 to 4,800 people died in the rapid sinking, and figures of over 7,000 are also mentioned.
- November 14th: The British aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal is sunk by the German submarine U 81 east of Gibraltar
- November 17th: so-called torchmen order
- still in November:
- The battle for Moscow begins with the new German offensive , and this attempt did not bring the Wehrmacht any resounding success either (October 2, 1941 to January 31, 1942)
- The US is revising its neutrality laws , US merchant ships may be armed and deliver war material to warring states
- November 17th to December 2nd: Battle of Rostov
- November 18: British Operation Crusader offensive begins in North Africa
- on November 26th a second attack followed, a successful breakout from Tobruk
- On December 7, the Africa Corps withdrew to the Gazala Line, and the Africa Corps under Rommel attacked Tobruk again in January 1942
- November 20: Around 1,000 people are deported on a first train from Munich to Lithuania and murdered there. In another 42 transports up to 1945, almost all Munich residents persecuted as Jews were deported to the east.
- November 25: Extension of the Anti-Comintern Pact by 5 years, accession of Romania, Bulgaria, Slovakia, Croatia, Finland and Denmark
- November 28: Italian colonial rule in East Africa ended with the lost Battle of Gondar (October 18 to November 28) against Commonwealth troops
- December 1941: Creation of the Indian Volunteer Legion of the Waffen-SS , initially as an army organization from British-Ind. Prisoners of War in North Africa. Compare: Boses Azad Hind and StaLag Annaburg
- December 5: at the Battle of Moscow , the Red Army begins its comprehensive counter-offensive with reserves brought in from Siberia under General Zhukov
- December 11: Germany and Italy declare war on the United States after the start of the Pacific War (see below)
- December 14th: Great Britain, USA and Bulgaria declare war on each other, Romania declares war on the USA; India declares it to Japan
- December 16: Hitler gives the order to stop on the Eastern Front, but the Wehrmacht is pushed back further by the end of the year
- December 22 to January 14, 1942: Allied Arcadia Conference in Washington (DC)
| year | Europe and Western Hemisphere | Asia and Pacific | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1939 | |||
| 1940 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | ||
| 1941 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jul – Dec | |
| 1942 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1943 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1944 | Eastern Europe | Western Europe | |
| Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1945 | Jan – May | Jan – Sep | |
Second half of 1941 in Asia and the Pacific
- July 3: The German HSK 7, the former merchant ship Schiff 41 Komet (Ex-Ems, after the river; built in 1937; converted as a lighter HSKr.) Sets out on a pirate voyage in the Far East to cross the (Soviet controlled) Northeast Passage to get into the planned area of operations in the Pacific . (Return to Hamburg via Cape Horn and Cherbourg on November 30, 1941)
- July 24th: Japan also occupies southern Indochina, the USA reacts by freezing Japanese assets, which practically brings exports to Japan to a standstill, Great Britain and the Netherlands join in this step
- September 6th: Japan tries to take the city for the second time in the battle for Changsha , but on October 8th this attempt fails again
- October 18: Government reshuffle in Japan, Tōjō Hideki becomes Prime Minister
- November 14th: With the Hull Note , the USA gives Japan a final ultimatum regarding its sphere of interest in China
- November 26th: The Japanese attack fleet Kidō Butai leaves domestic waters for Pearl Harbor
- See also: on the use of chemical and biological weapons by the Japanese Army in the Battle of Changde, Unit 731
- December 7th: Japan starts the Pacific War by attacking the possessions of the USA, Great Britain and the Netherlands
- Japan begins the invasion of Southeast Asia with the landings at Kota Bharu in northern Malaysia and further landings in Thailand ( Japanese invasion of the Malay Peninsula )
- Japanese planes of the Kidō Butai fly the attack on Pearl Harbor , the most important US base in the Pacific on Hawaii , all eight battleships of the US Pacific Fleet sink or suffer damage
- (belated) delivery of the 14-point telegram (it is considered a Japanese declaration of war) in Washington by Nomura Kichisaburō
- December 8th:
- the US declares war on Japan so that the United States can enter World War II
- At least now we must speak of the beginning of another world war
- Beginning of the Battle of the Philippines
- The US base Guam is captured by Japanese troops (west of the Mariana Islands)
- In the course of the Japanese invasion of Thailand, there is a battle for Prachuap Khiri Khan
- December 8th to 25th: Japanese troops conquer the British colony of Hong Kong , the Japanese occupation of Hong Kong lasts until the end of the war
- National China declares war on Japan
- December 9th: the Netherlands (government in exile) declare war on Japan
- 10th of December:
- Japanese troops occupy Makin and Tarawa during the Battle of the Gilbert Islands (also Operation Galvanic)
- Sinking of the HMS Prince of Wales and HMS Repulse - parts of the so-called Force Z
- December 14th: India declares war on Japan
- December 16: The Japanese invasion of Borneo begins. It was completed by around mid-March 1942.
- December 20: Japanese troops capture the US- annexed Pacific Atoll in the Battle of Wake
- December 24th: Another Japanese attempt to take the city of Changsha fails in the third battle for Changsha (until January 15, 1942)
| year | Europe and Western Hemisphere | Asia and Pacific | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1939 | |||
| 1940 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | ||
| 1941 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jul – Dec | |
| 1942 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1943 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1944 | Eastern Europe | Western Europe | |
| Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1945 | Jan – May | Jan – Sep | |
1942
- After the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor in December, the war year 1942 was followed by the first German deportations of Jews from France, the fighting over the Tobruk and El Alamein fortresses, increasingly massive air raids on German cities, but also on Tokyo, the conquest of the Philippines, the attack Heydrich marked in Prague; German troops reach the Don, followed by the German attack on Stalingrad and in a counterattack its encirclement; Beginning of the Manhattan Project, the Allied landing in Northwest Africa. After the Japanese invasion of the Dutch East Indies in January and the naval advance into the Indian Ocean, the year brings the first Australian and US successes against Japan in the Battle of Midway and New Guinea.
First half of 1942 in Europe, Mediterranean area
- January 1st: In the White House in Washington, 26 nations sign the UN Declaration in which they commit themselves to a joint fight against the Axis powers . The 26 signatory states call themselves the United Nations . a. The Soviet Union, the USA, Great Britain, China, Belgium, Greece, the Czechoslovak Republic, India, Luxembourg and Holland count; seven more nations by October 1943, and ten more nations by the end of the World War, have joined this declaration.
- January 2: 33 German spies from the Duquesne spy ring are convicted. The largest espionage case in United States history. They were arrested on June 29, 1941 by the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI).
- January 8th: Beginning of the Demyansk Kessel Battle by the Red Army, Kessel until relief on April 21
- From January 1942: the first " Eastern workers " ( forced labor ) are deported to the German Reich by train, from 1942 to 1944 a total of around three million people from the Soviet Union are transported to Germany to do forced labor
- First counter-offensive to overcome the blockade of Leningrad: Ljubaner operation . She failed. After heavy attacks, the offensive was ended in April 1942.
- January 8 to April 20: Fighting for Rzhev (Rzhev-Vyazma operation and its follow-up fights until December 1942)
- January 14th: At the Arcadia Conference, the Americans and British decide to form a joint committee of their general staffs, the Combined Chiefs of Staff
- January 14th ff: German submarines sink 23 merchant ships off the US coast at the company Paukenschlag
- January 18: The battle for Cholm begins
- February 1: Vidkun Quisling becomes Prime Minister in occupied Norway
- in February: Introduction of the more strongly encrypted Enigma-M4 (Ultra) for the encryption of German submarine radio traffic leads to the so-called black-out of the decryption of enemy radio messages on the part of the Allies for 10 months (successful since January 1940)
- After February 8 ( Fritz Todt's fatal plane crash ), Hitler appoints the architect Albert Speer as Reich Minister for Armaments and Munitions and as General Inspector for German Roads, General Inspector for Fortifications, General Inspector for Water and Energy , (in addition in 1943 as Reich Minister for Armaments and War Production ) and Fritz Sauckel as General Representative for Labor Use (GBA)
- February 11: Construction of the British Maunsell sea forts, "HM Forts" for air and coastal defense, especially the estuaries (Maunsell Sea Forts and Maunsell Army Forts, construction started August 1942), code name Uncle (U) and a number
- 11th to 13th February: Cerberus company : Return of the warships Gneisenau , Scharnhorst and Prinz Eugen lying in Brest through the English Channel to Germany
- February 14: The British Bomber Command is instructed in the so-called Area Bombing Directive to use its forces without restrictions and with a focus on working-class quarters in German industrial cities
- February 15: The Gestapo deported a group of Jews from Bytom (Beuthen) to Auschwitz main camp and murdered them immediately. The mass murder of Jews in this German concentration camp in occupied Poland begins.
- February 16: German-Italian submarine attack on Aruba (part of the Caribbean battle )
- February 25th: The 1st Polish Armored Division was established in eastern Scotland on the orders of General Sikorski .
- 27./28. February: With Operation Biting near Bruneval near Le Havre, the British Army captured the main components of a German radar radio measuring device in an airborne company . Their evaluation yielded important information about the state of German radar technology .
- March 6: The German counterintelligence succeeds in the Hague with the arrest of the "Gruppe RLS" (British code name: "Ebenezer"), the decryption of the recorded radio traffic of the espionage network and the long-term access to it: the England game , also known as Operation North Pole , led to the Many Dutch agents are arrested.
- March 27: the first train with Jewish deportees leaves France from Compiègne from the Royallieu concentration camp in the direction of the extermination camps with 1112 deportees; Of these, only 19 people survived until 1945, followed by 78 more trains with 75,721 deportees, of which only 2,500 people experience 1945 in freedom again
- 28/29 March: Heavy air raid on Lübeck , the militarily insignificant city was attacked because of its favorable location and the half-timbered construction of its old town to test new methods of attack, one month later German retaliatory attacks begin ( Baedeker Blitz )
- In March: the Nazi deportations of Jews from the vassal state of Slovakia begin in consultation with the Jewish advisor D. Wisliceny , the so-called Aktion David (an easily understandable cover name). Around 60,000 prisoners were deported to the Auschwitz and Lublin concentration camps for murder.
- April 3: About 1,000 people persecuted as Jews are deported on a second train from Munich “to the East” and murdered there; see. November 20, 1941
- April 5: In instruction No. 41 on Operation Blau , Hitler set the goals of the three Army Groups in the Soviet Union for this summer, Army Group South to the Donets industrial area ; Capture the north wing of the Army Group with the 6th and 4th Panzer Army and the Romanian 4th Army, the Donbogen and Stalingrad, then further advance towards the Caucasus and Baku
- April 11: Cowes ( Isle of Wight ), air strikes (also on the following days)
- April 23rd and April 27th: Bombing of Rostock
- April 26th - 30th: Destruction of the village Telavåg ( Norway ) as a so-called punitive action by the Gestapo against the so-called Shetland Bus escape route and the imprisonment of the population; 54 of the 268 deportees were killed, others later died as a result
- April: The plans for Operation Roundup (later expanded as Operation Bolero ) and Operation Sledgehammer were presented to the Allied military command in April 1942. They contained the basics of the later Operation Overlord and Operation Neptune . The execution, which did not come about in this way, was planned for the first half of 1943. The rate for personnel and material was initially significantly lower than for the 1944 landing in Normandy.
- May 4th: the Polish destroyer Błyskawica , lying in port, took part in the defense of the attacked Cowes (160 bombers). After the German air raids, the crew of the Błyskawica also took part in the fire fighting in the city. The warship escorted a total of 83 convoys during the war, damaged 3 submarines through fire and shot down four air force machines. Involved in Operation Torch .
- May 4th and May 7th: bombing of Stuttgart
- May 5th: Operation Ironclad , beginning of the English Occupation of the island of Madagascar, which was controlled by Vichy France until then (had no effect on the talk of the Madagascar plan by the Nazi leaders)
- May 8th to 20th: In the Trappenjagd company , German associations expel the Red Army troops that had landed on the Kerch peninsula ; the Germans take 170,000 prisoners
- May 12: Soviet offensive to capture Kharkov ( Battle of Kharkov ) begins
- May 23: Parts of the Soviet attack troops are encircled near Kharkov and destroyed by the end of the month (240,000 prisoners)
- May 26:
- Great Britain and the Soviet Union sign a formal treaty of alliance in London, valid for 20 years after the end of the war
- The start of the Theseus company , the German attack on the Gazala Front in Libya, at Bir Hakeim and Bir el Harmat , French (of the Forces françaises libres ) and Jewish troop units in the British army delay Rommel's attack to such an extent that the majority of the 8 British Army can withdraw in an orderly manner
- May 27th: Operation Anthropoid : Attack on the head of the Reich Main Security Office (RSHA) and at the same time deputy Reich Protector in Bohemia and Moravia, Reinhard Heydrich , in Prague , Heydrich succumbs to the consequences of the attack on June 4th
- May 22: Mexico declares war on Germany
- May 29: American-Soviet discussion in Washington about a second European front in 1942 (participants: Franklin D. Roosevelt, Harry L. Hopkins, George C. Marshall , Ernest J. King and Cordell Hull, as well as the Soviet ambassador Maxim M. Litvinov)
- May 30th: Operation Millennium : the British Bomber Command gathers over 1000 bombers for the largest air raid of the war to date, targeting Cologne ; by 1945, 262 air raids on the city followed
- Against the Soviet offensive to overcome the blockade of Leningrad: Lyuban operation directed German counterattack (destruction of the Soviet 2nd shock army)
- June 2: Battle of the Crimea for Sevastopol (June 7) ends on July 5
- June 6: US declaration of war on Romania, Bulgaria and Hungary
- June 9: Heydrich's largest funeral ceremony to date takes place in Berlin, the village of Lidice and the hamlet of Ležáky are destroyed as retaliatory measures, and there are around 1700 victims of the wave of terrorism following the Heydrich attack in the whole of the Czech Republic

- June 11: American-Soviet Treaty on the Principles of Mutual Assistance in Warfare in consideration of the American Congress Act of March 11, 1941 ( Lending and Lease Act )
- June 13th to 27th: Operation Pastorius (German sabotage attempt in the USA)
- June 19: The Military Intelligence Training Center is founded in Camp Ritchie , Maryland, a training camp in which, in the further course of the war, mainly young Germans who have fled are trained to become news specialists ( Ritchie Boys )
- June 21: Tobruk's Allied Commander Major General Hendrik B. Klopper surrenders, Rommel is promoted to General Field Marshal
- the further advance should take place through Egypt, the city of Alexandria should fall and the Suez Canal should be occupied; Shortly before El Alamein , British units built a 65-kilometer-wide defense belt
- June 28: the German summer offensive ( blue case ) in the Soviet Union begins with the attack on Voronezh
| year | Europe and Western Hemisphere | Asia and Pacific | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1939 | |||
| 1940 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | ||
| 1941 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jul – Dec | |
| 1942 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1943 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1944 | Eastern Europe | Western Europe | |
| Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1945 | Jan – May | Jan – Sep | |
First half of 1942 in Asia and the Pacific
- January 11: Japanese invasion of the Dutch East Indies begins . the Dutch surrendered on March 1st, Dutch residents were taken prisoner
- 11th to 12th January: Battle of Tarakan (Dutch Borneo)
- January 23: Rabaul on the northeastern tip of New Britain ( New Guinea ) is captured by Japanese troops and expanded as a fortress base in the following years. From the opponents' point of view, this was the beginning of the
- Battle of New Guinea (the New Guinea campaign 42-45), the Allied advance along the north coast of New Guinea. This strategic movement opened up positions of attack against Japan that were decisive for the war. Duration until August 1945.
- January 25: Thailand declares war on the Allies on the side of Japan
- January 31st: the Malay Peninsula is completely occupied by the Japanese
- January 31 to February 15: Japanese siege of Singapore
- February 1: US attack on Japanese positions in the Marshall and Gilbert Islands
- February 2nd: Japanese air raids on Java
- February 24th: Battle of the Strait of Makassar
- February 14th to March 28th: Japanese invasion of Sumatra
- February 15th: British base Singapore is occupied by the Japanese
- February 19: First Japanese air raid on Darwin (on the north coast of Australia ), killing 243 people and injuring 300 to 400 people
- until February 20th: Defeat of the ABDACOM coalition in the sea battle in the Strait of Badung
- February 20th: Timor (NL) is conquered
- February 23: Japanese submarine I-17 bombs an oil refinery near Ellwood, California
- February 24th: Sea battle off Balikpapan , Borneo
- February 25th:
- Japan. Troops land north of Surabaja on Java
- In a riot in New Zealand's Featherston POW camp , 48 Japanese and one New Zealander are shot dead by the guards. The background was a sit-in strike by prisoners as a form of refusal to work.
- February 27 to March 1: Battle of the Java Sea
- March 1st: Battle of the Sunda Strait
- March 1-10 : Japanese invasion of Java , also known as Operation "J"
- 8th of March:
- Japanese landing in New Guinea near Lae and Salamaua
- Rangoon , the capital of the British colony of Burma , today Yangon, is captured by the Japanese army
- March 12th:
- the Americans land in New Caledonia and set up a base on Nouméa
- Dutch East Indies falls to Japan
- March 13: Japan lands in the Solomon Islands
- 19./20. March: US General MacArthur manages to withdraw to Australia
- March 23: Japanese capture of the Andaman Islands in the Bay of Bengal
- March 30: Start of Japanese Operation C , the Japanese major attack on Allied bases in the Indian Ocean
- April 5: The 1st group of the allied formations for the defense of Ceylon left the port of the Addu Atoll . Group 2 followed on the morning of the following day.
- April 5: A Japanese fleet of five aircraft carriers attacks a British base in Ceylon as part of Operation C and sinks two British heavy cruisers
- the Bataan death march begins in the Philippines
- April 9th: attack on Trincomalee
- April 17th: The Japanese conquer central Burma
- April 8: A Japanese unit from Rabaul lands in western New Britain
- April 18:
- an American air strike on Japan's main islands ( Doolittle Raid ), 16 B-25B launched from the new Hornet aircraft carrier , bombs facilities in Tokyo , Yokohama and Nagoya .
- As a result, the Japanese begin the battle of Zhejiang-Jiangxi on the Chinese mainland in search of the pilots who landed there , in which 250,000 Chinese civilians are killed
- MacArthur is appointed Supreme Commander of Allied Forces in the Southwest Pacific Area (SWPA) by the US President, GHQ in Melbourne
- April 19: Japanese landing in Dutch New Guinea
- April 30th: Japan cuts ties with China by capturing Lashio in Burma
- April: British Admiral JF Somerville relocates the headquarters of the British Eastern Fleet (formerly in Singapore) from Trincomalee near Colombo , Ceylon (now Sri Lanka ), under Japanese pressure to Mombasa- Kilindini, Kenya in East Africa
- May 1: Japan takes Mandalay in Burma
- May 3: Japanese invasion of Tulagi , Operation MO (Mo Sakusen or Port Moresby Operation)
- May 6th: the Philippines are completely conquered by Japan
- May 6-8: Battle of the Coral Sea , southern advance of the Japanese invasion fleet on Port Moresby stopped
- on the 8th: an aircraft carrier , the USS Lexington , was hit several times, caught fire and finally sunk itself. In 2018 the hull of the wreck was located and filmed again approx. 3000 m under water.
- May 11: the Okinoshima , the flagship of the Japanese invasion fleet heading for Nauru , is sunk by the US submarine S-42 , the fleet turns
- MAY 16: the allied troops withdraw from Burma to India back
- May, from May 5th: Madagascar , from the French cooperating with Germany. Vichy regime controlled, occupied by British troops to secure retreat positions - Operation Ironclad (until November 8th)
- June 4-6: Battle of Midway . Japan loses all four deployed fleet carriers (out of a total of six at this point in time), the USA one of three carriers
- June 6: the battle for the Aleutian Islands (American territory southwest of Alaska) begins; it did not end until August 15, 1943 with the reconquest. Japanese troops occupy the western islands of Attu and Kiska. In addition, construction of a road connection through the Canadian part of Alaska.
- June 20: Japanese submarine I-26 bombarded Estevan Point on Vancouver Island , British Columbia
- June 21: Fort Stevens , Oregon , in the northwestern United States, is shelled by the Japanese submarine I-25
- June 25: US maritime patrol aircraft PBYs bomb Japanese base on Tulagi
- July 3rd: Guadalcanal falls under Japanese control
- 21 July:
- July 29th: Kokoda Airfield in New Guinea is captured by Japanese units on the way over the Owen Stanley Mountains , aiming at Port Moresby
| year | Europe and Western Hemisphere | Asia and Pacific | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1939 | |||
| 1940 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | ||
| 1941 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jul – Dec | |
| 1942 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1943 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1944 | Eastern Europe | Western Europe | |
| Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1945 | Jan – May | Jan – Sep | |
Second half of 1942 in Europe, Mediterranean
- June 28 to November: German summer offensive in southern Russia, planned as a " blue case ". Modified carried out as a company Braunschweig . The plan includes the advance to the Caucasus and the lower Volga.
- July to November 1943: in Aktion Reinhardt , almost all Jews and Roma from occupied Poland, the Generalgouvernement , over two million Jews and around 50,000 Roma from five districts (Warsaw, Lublin, Radom, Krakow and Galicia) in the three extermination camps in Belzec , Sobibor and Treblinka murdered
- from June 29th: Conquest of Liepāja . Most of the more than 7,000 Jewish residents were murdered in the following massacres in Liepāja by Wehrmacht and SS troops in what the perpetrators called hostage shootings . Over 3000 of them from December 15 to 17, 1941 near Šķēde.
- July: Destruction of the allied convoy PQ 17 in the North Sea
- JULY 1: German troops take the Soviet-occupied Latvia's capital Riga a
- From July 16: Paris - on the first and second day of the summer vacation, more than 4,000 French police officers arrested 13,000 Jewish people, children and adults, and interned them, among others, in a raid on the instigation of the Nazi authorities. a. eponymous for this first action on this scale in occupied France, in the sports palace for cycling races: Rafle du Vélodrome d'Hiver . About ten thousand people managed to escape capture on these days by escaping. In the following weeks, Pithiviers and Drancy are the most important collection camps for prisoners until they are transported to Auschwitz for the Nazi mass murder . Less than 2 percent of these prisoners from France experience the end of the war. In addition to the franz. Collaboration , the valuation as a war crime against the civilian population in an occupied country is important for these acts.
- July 2nd - 13th: Operation Seydlitz (fighting by Soviet and German cavalry units near Rzhev)
- July 4th: End of the battle for Sevastopol 1941–1942 , "Operation Störfang" ends with the conquest of the fortress and the capture of around 100,000 Red Army soldiers
- July 1 to July 31: first battle of El Alamein ; German-Italian offensive with the aim of penetrating the Suez Canal gets stuck there
- July 18: First flight of the Me 262
- Skirmishes in the German summer offensive in southern Russia
- July 21: A protest rally takes place in New York City against the mass murder of hundreds of thousands of Jews in Europe
- July 21st German forces cross the Don , first step for the advance on Stalingrad
- July 23: Rostov is captured
- July 23: in directive No. 45 , Hitler ordered that instead of attacking one after the other simultaneously into Stalingrad and into the Caucasus
- August 4th: Stavropol is captured
- August 9: Krasnodar and the Kuban are crossed
- July 28th: Order 227 of the Soviet High Command (later Stawka) with the slogan: “Don't step back!”
- July 30 to October 1: First Rzhev Sychovka operation (see Battle of Rzhev )
- The Romanian allies of the German army succeed in rolling up the Soviet defense on the east coast of the Sea of Azov from the north and opening the Taman Peninsula from "backwards"
- August 4: The Swiss Federal Council , aware of their persecution, confirms in a resolution the rejection at the borders, especially of Jewish Germans, even if the foreigners affected by this could face serious disadvantages (dangers to life and limb). (according to Federal Council protocol on August 4, 1942)
- 8/9 August: Limited Soviet attack against the siege forces (Operation Stormwind) in preparation for the performance and radio broadcast of the Leningrad Symphony by D. Shostakovich in the city ( Leningrad Blockade ). The music was then also transmitted to the German positions via loudspeakers. (Compare 19 Aug.)
- August 11: Beginning of the Wirbelwind company , a German tank offensive against the Soviet "Sukhinichi front arc "
- August 15: After two unsuccessful Royal Navy operations since June, a third convoy with essential supplies arrives in the ports of Malta ( Operation Harpoon , Vigorous , Pedestal in August. This broke the blockade of the Mediterranean islands again.) This continued to ensure British air superiority across the Sicilian Strait ( Strait of Sicily before Africa).
- August 16: Dt. Kriegsmarine - The armored ship Admiral Scheer leaves for Operation Wunderland against the Northeast Passage and the Soviet icebreakers there
- August 19: Operation Jubilee (English: Dieppe Raid ), the landing operation / invasion near Dieppe at the mouth of the Arques in the English Channel (original plan: Operation Rutter ) is canceled after heavy Canadian and British losses. 6,000 Allied soldiers landed in Normandy. You should open a second front against Hitler's Germany. This first attempt at landing failed - the Allies had to withdraw with heavy losses.
- August 19: Sinyavinsk Operation (First Ladoga Battle), start of the second Soviet counter-offensive to overcome the blockade of Leningrad (until October 10, stalemate, losses Wehrm / RA about 1: 2)
- August 21st to September 21st: in the so-called General Commissioner of Belarus , mass murders of civilians are committed at the company mala fever (over 11,000 dead)
- August 21: German mountain troops climb the Elbrus massif and hoist a swastika flag
- August 22nd: Brazil declares war on Germany and Italy. Germany is thus losing an important rubber supplier. From September 1944: active participation with expeditionary force
- August 23: around 1000 planes begin to drop incendiary bombs on Stalingrad, at the same time German tanks penetrate the outskirts for the first time
- August 26th: the attack on Tuapse which had started is halted after two days
- August 30th to September 6th: the continuation of the German offensive in North Africa fails in the Battle of Alam Halfa
- September: Leslie Groves , is promoted to Brigadier General and takes over the management of the weapons project of the OSRD, now named after the location of George C. Marshall's headquarters in the Manhattan Constructions District ( Manhattan Project ) and begins in the highest secrecy in the desert of New Mexico with the construction of Site Y , a research town near Los Alamos - scientific. Direction: J. Robert Oppenheimer - on building the atomic bomb; This also included the espionage of the Alsos missions , based on Roosevelt's signature of June 28 under Executive Order 8807 for the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD)
- August 31: the port city of Anapa is taken
- September 6th: Novorossiysk , the main base of the Black Sea Fleet, is captured
- In the high mountains, German troops occupy the most important pass crossings and temporarily move south on a broad front - they are in the Abkhazian mountain village of Pschu , 20 kilometers off the coast of the Black Sea near Gudauta , east of the Elbrus, the German and Romanian troops are standing on the river sections of the Baksan and des Terek to Naurskaja , north of it the front is lost on the Kuma , in the Nogaier steppe and in the Kalmyk steppe
- Maikop with its oil reserves is captured and held until January 1943, Grozny , cf. Transcaucasus Front of the Red Army
- September 13th: with the German attack on the inner defensive belt of Stalingrad , the five-month battle of Stalingrad begins (the German attempt to conquer the city is described under the attack on Stalingrad )
- September 17: Laconia order to German submarines on how to behave in the recovery of survivors of an attack at sea
- September: Completion of the " general settlement plan" by the RKF planning office. It describes the intended population shifts of around 12 million people in the Soviet Union if the war was won
- September 24: Two agents from the British intelligence service Special Operations Executive (SOE), Lise de Baissac (1905–2004) and Andrée Borrel (1919–1944, murdered in the Natzweiler concentration camp ) are parachuted to northern France. They explore u. a. possible landing sites for the allied invasion. (L. Baissac can be highly decorated for this after the war)
- September 30 (until Aug. 12, 1944): the German television station Paris , in French. Paris-Télévision, after the first test broadcasts in Paris from the converted “Magic City” dance palace, starts broadcasting an ongoing television program to look after the German troops, especially the injured in military hospitals (hospital television)
- October 10: Beginning of the Battle of Bowmanville, a two-day prisoner-of-war revolt against the shackling of captured German officers in the Bowmanville prisoner of war camp ( Bowmanville (Clarington) prisoner of war camp 30, Ontario , Canada; connection with the Dieppe company on August 19 )
- October 10: End of the Sinjawinsk Operation (First Ladoga Battle) in a stalemate situation (Wehrm / RA losses roughly like 1: 2)
- 13./14. October 1942: mass shootings / murders of Polish civilians ( persecution of Jews ) occur in the so-called Misoch Ghetto
- October 18: After illegal by the Hague Regulations command command of Hitler to the Wehrmacht were Allied commandos (Engl. Commandos ) killed immediately or the security service of the SS passed (SD). The order was kept top secret and generally obeyed.
- October 23rd: the new British commander in Africa, FM Bernard Montgomery , starts the counterattack with the second battle of El Alamein and wins on November 4th, the long retreat of the Axis powers to the west begins
- 30th of October:
- After 170 days of military resistance, the siege of the Adzhimushkai quarries (near Kerch in the Crimea) ends . Of the 13,000 Red Army soldiers defending the catacombs, only 48 survived.
- the British destroyer HMS Petard arrives at the German submarine U 559 and is able to hide the discovery of the German radio documents. Subsequently (December 12th) the radio traffic (Ultra) was deciphered again with the new Enigma-M4 encryption machine .
- November 8th to 11th: Operation Torch , British-American troops land at Casablanca (Morocco) as well as Algiers and Oran (Algeria) and thus initiate the two-front war in North Africa, the German side reacts with Company Anton (see below) ): the Wehrmacht occupies southern France and Tunisia . The USS Texas provides effective artillery support.
- November 9th to 12th: Operation Hubertus : German storm pioneers are to bring the decision in the battle for the Stalingrad industrial complexes
- November 11th: Occupation of the south of France
- Company Anton (planning in place since May 1942) 1st Army and 7th Army advanced parallel to the Spanish border and Mediterranean coast.
- Nice , Grenoble (previously unoccupied France ) are occupied by Italian troops - Italian occupation zone in France (to the left bank of the Rhone extended) - 4th Army occupied the Côte d'Azur and the Italian division landed on the island of Corsica , which otherwise remained largely unoccupied.
- The crew of the submarine Casabianca (Q 183) (monument since 2004 in Bastia ) of the French navy can break out of the port under fire before the German capture of Toulon in November 1942 and move to Algiers , French North Africa, and the FFL connect. (Between December 1942 and 1944, the Casabianca carried out seven secret missions during which it transported weapons, equipment and people to Corsica and Provence in support of the Maquis , called Pearl Harbor.)
- November 13th:
- Tobruk is back in British hands
- the first fighting occurs between US and German troops
- From November: Preparations for Army Group Africa - Italian / German battles for Tunisia until May 13, 1943
- November 19-23: Operation Uranus : Counter-offensive by the Red Army near Stalingrad, breaking the Romanian lines in the north and south, a few days later these two wedges unite near Kalatsch on the Don , thus encircling the 6th Army in Stalingrad General Paulus feels bound by Hitler's order to halt and cannot bring himself to give the order to break out (retreat), which was still possible at the time
- November 22nd: the auxiliary cruiser Atlantis under Captain B. Rogge is sunk by the British heavy cruiser HMS Devonshire between Brazil and West Africa. He was able to sink 19 merchant ships with almost 128,000 GRT and raise three ships with 18,253 GRT as prizes.
- Since November: Corpses buried in the German extermination camp Belzec have since been exhumed en masse and burned on large grates from railroad tracks to remove traces of the Shoah .
- November 25 to December 21: Second Rzhev Sychovka operation ( Operation Mars ; part of the fighting for Rzhev )
- November 27th: The Vichy fleet was scuttled by order of the Admiralty of the Vichy regime after the German company Anton ( Mediterranean fleet in the naval port of Toulon )
- December 12th to 23rd: Operation Wintergewitter : Relief attack by the 4th Panzer Army under General Hoth, which brings up to 60 kilometers to the trapped troops in Stalingrad, fails
- In “ Aktion Zamość ” (November 27, 1942 to August 15, 1943) the population was rounded up by SS / police commandos and transported to the Zamość assembly camp. By August 1943, 110,000 Poles were transferred from 300 villages to SS, police and Wehrmacht units expelled, 34 villages were dealt with, allegedly because of resistance and partisan activity, similar to Lidice , followed by the military anti-partisan actions "Aktion Werwolf I / II", a division of the Polish Home Army and the 3rd company "Grzmot" of the peasant battalions (Bataliony Chłopskie) , altogether about 400 men, fought against the 1900 strong German security troops, 7000 people were killed in the German retaliatory measures for the resistance, on June 30, 1943 Himmler declared the entire “ Generalgouvernement ” a gang fighting area , the action was stopped by O. Globocnik
- December 2nd: first controlled chain reaction in the USA ( Manhattan Project )
- December 4th: American bombing of Naples
- December 12th: The British destroyer HMS Petard landed the German submarine U 559 in the Mediterranean on October 30, 1942 -> as a result, the German radio traffic encrypted with the Enigma-M4 was again successful
| year | Europe and Western Hemisphere | Asia and Pacific | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1939 | |||
| 1940 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | ||
| 1941 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jul – Dec | |
| 1942 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1943 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1944 | Eastern Europe | Western Europe | |
| Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1945 | Jan – May | Jan – Sep | |
Second half of 1942 in Asia and the Pacific
- Death Railway (German: Todeseisenbahn or rail line of death ) is a name for the railway connection that the Japanese army had prisoners of war built between Burma and Thailand between June 1942 and October 1943 (see film Die Brücke am Kwai )
- July 31: American B-17s launch a seven-day bombardment of Tulagi and Guadalcanal
- August 7th: American troops begin the Battle of Guadalcanal in the Solomon Islands , the fighting until the Japanese surrendered until February 8th, 1943
- August 9: Battle of Savo Island
- August 21: Battle of Alligator Creek (Japanese defeat; incorrectly called Tenaru)
- August 24-25: Battle of the Eastern Solomon Islands
- August 28th: the Japanese start the Tokyo Express supply route to Guadalcanal
- September 13th: the battle at Bloody Ridge lasts until September 16th
- October 11th to October 12th: Battle of Cape Esperance
- October 25-27: Battle of the Santa Cruz Islands
- November 13-15: Naval Battle of Guadalcanal
- November 30th: Battle of Tassafaronga
- August 13th: in New Guinea the Japanese advance along the Kokoda Trail over the mountains to Port Moresby
- August 25th: Oceania and Nauru are captured by Japanese units
- September 5: In the Battle of Milne Bay (since Aug. 25), the Allies (Australian soldiers) defeat Japanese land forces (on the eastern tip of Papua New Guinea) for the first time
- September 9th: A Japanese light aircraft launched from submarine I-25 drops bombs in a forest near Mount Emily , Oregon, to start forest fires
- September 17th: the Japanese advance on New Guinea comes to a halt at Ioribaiwa within sight of Port Moresby
- September 24th: Japanese forces begin invading Gilbert Islands on Maiana
- September 29: repeated bombing of a forest in Oregon from aboard a Japanese I-25 light aircraft (submarine)
- October 2nd:
- a US battalion takes Funafuti on the Ellice Islands , a
- B-17 bombers attack Japanese. Base Rabaul to
- October 28: Australian forces recapture Kokoda Airfield in New Guinea
- December 13: Buna in New Guinea falls to the US
- December 14th: Gona in New Guinea falls to the USA
| year | Europe and Western Hemisphere | Asia and Pacific | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1939 | |||
| 1940 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | ||
| 1941 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jul – Dec | |
| 1942 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1943 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1944 | Eastern Europe | Western Europe | |
| Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1945 | Jan – May | Jan – Sep | |
1943
- Key words for the war year 1943 are: Soviet armies achieve victory in Stalingrad - a first major German surrender. In March, German troops recaptured the area as far as the central Donets, but after several Soviet counter-offensives in the following months, the Wehrmacht had to retreat along the entire eastern front. The militarily insignificant uprising in the Warsaw ghetto was a lasting moral victory for the Jewish prisoners. The Atlantic battle is lost for the German submarines. Allied troops land in Sicily. Italy leaves the alliance with Hitler. The air sovereignty of the Allies in Europe is becoming more and more overwhelming. With the reconquest of the Solomon Islands, the American tactic of island jumping begins in the Pacific.
First half of 1943 in Europe, Mediterranean area
- January 10th: Seven Soviet armies with 1,000,000 soldiers attack the German troops in Stalingrad in a large-scale counter-offensive, whose 6th Army had meanwhile been split into two pockets
- 11 January: Höfle telegram with figures on the Jewish victims of the extermination camps of Aktion Reinhardt in 1942
- January 12th to 30th: Start of Operation Iskra (2nd Ladoga battle), during which Schlüsselburg and thus a narrow supply corridor for the besieged Leningrad are recaptured on 18th
- January 13th to 27th: Operation Ostrogoschsk-Rossosh (part of the Voronezh-Kharkiv operation ), leads to the destruction of the Hungarian 2nd Army, allied with the German Reich, and parts of the Italian 8th Army .
- January 18: Occupation troops under F. v. Collectors , at least 1000 men, attempted for the first time to deport the prisoners in the Warsaw ghetto to extermination camps and encountered organized, massive and initially successful resistance.
- JANUARY 21: On the Casablanca Conference , the Combined Bomber Offensive decided
- January 12: Hitler issues the Adolf Hitler tank program to quadruple armored vehicle production
- 23 January: British units occupy Tripoli, in March and April the Axis powers are finally included in the Tunisia bridgehead ( Tunisia campaign ), resistance is still being offered on the Mareth Line , regiments from Penal Division 999 are deployed
- January 26th: At the Casablanca Conference, the Allies proclaim the demand for the "unconditional surrender" of the Axis powers as a target
- January 29: Military jurisdiction - For cases of military disintegration, the Ordinance of January 29, 1943 (RGBl. I p. 76) gave the People's Court responsibility for cases of “public disintegration” as well as cases of “deliberate evasion of military service” (Section 5 Paragraph 1 No. 1 and 3 of the Special War Criminal Law Ordinance. This abolished the jurisdiction of the courts-martial and the Reich court martial ).
- January 31: In the morning of the Battle of Stalingrad , Red Army troops broke into the “Univermag” department store , in whose basement the headquarters of the 6th Army were located. After further attacks by the Soviet troops, the 71st Infantry Division in the southern basin gave up ( Gen. F. Roske ). GF F. Paulus was captured after the surrender. On the same day the middle kettle ( Gen. W. Heitz ) also surrendered .
- February to April: Operation Winterzauber , a mass murder by SS forces as part of the alleged anti-partisan fight in northern Belarus and western Russia
- The National Memorial of the Republic of Belarus today commemorates over 600 "burned villages" and the victims from over 5000 villages.
- February 2: The last isolated units surrender. Paulus, who was promoted to General Field Marshal on the 30th , only had the option of surrendering in view of the hopeless situation , whereupon almost 100,000 soldiers were taken prisoner. Only about 6,000 of them will return to their homeland after the war. The death toll is many times higher on both sides, and the Battle of Stalingrad also marks a psychological turning point in the war.
- February 16: The city of Charkow is abandoned by troops of the Wehrmacht and Waffen-SS against Hitler's orders in order to avoid an impending encirclement
- February 18: Nazi Propaganda Minister Joseph Goebbels calls for " total war " in the Sportpalast speech
- February 21: a German counter-offensive begins (“ third battle for Charkov ”), by March 5 the area as far as the central Donets is recaptured; in the process, considerable gains in land and a closed front were established again, thus preventing the collapse of the eastern front, which could potentially be imminent in spring 1943, until March 14th, Kharkov was recaptured by Waffen SS troops
- February 22: Sophie (1921–1943) and Hans Scholl (1918–1943) and their friend Christoph Probst are executed as members of the “ White Rose ” resistance group
- February 27: Beginning of the Rosenstrasse protest by women against the deportation of Jews from Berlin
- March 5th: The five-month Battle of the Ruhr begins with an air raid on Essen
- March 8 : Departure of the Allied convoy HX 229 from New York, which suffered the most casualties of all HX convoys up to its destination port of Liverpool .
- March 13: Assassination attempt on Hitler on the return flight from Smolensk with OB Günther von Kluge fails. Were involved Henning von Tresckow and Fabian von Schlabrendorff
- March 22nd: In the Belarusian village Khatyn , 152 people (including 76 children) are murdered by the SS special unit Dirlewanger and the village is destroyed, in Khatyn the memorial of the Republic of Belarus stands today on behalf of 185 other villages burned down with their residents in this republic
- March 27: In the successful attack on the Amsterdam residents' registration office, resident documents were destroyed to make the Gestapo's persecution in the city more difficult
- April 1: A total of 84 people died in the Allies bombed Switzerland between 1939 and 1945. In the accidental bombing of the city of Schaffhausen , which was darkened under German pressure, 40 people were killed that day and 270 were injured, some seriously. In October 1943, the Swiss Air Force resumed its interception measures, which had been suspended since June 1940 under German pressure, and tried to force Allied bombers to land in Switzerland.
- April 19: Uprising in the Warsaw Ghetto : the remaining inhabitants of the ghetto are to be deported to extermination camps, most of them to Treblinka , the Jewish Fighting Organization (Polish Żydowska Organizacja Bojowa or ŻOB or ZOB ) defends itself in the uprising in the ghetto that lasts several weeks. The uprising was bloodily suppressed by the SS under Jürgen Stroop by May 16, later there was a concentration camp in Warsaw on this site
- May 13: German troops surrender in Tunisia
- May: the Battle of the Atlantic is for the German submarines lost
- June 11 and 13: The garrisons of the islands of Pantelleria and Lampedusa surrendered to British troops without a fight after a series of bombings ( Operation Corkscrew ; with Mussolini's approval due to lack of water).
| year | Europe and Western Hemisphere | Asia and Pacific | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1939 | |||
| 1940 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | ||
| 1941 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jul – Dec | |
| 1942 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1943 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1944 | Eastern Europe | Western Europe | |
| Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1945 | Jan – May | Jan – Sep | |
First half of 1943 in Asia and the Pacific
- January 29th: The Battle of Northern Solomon Islands begins with the Battle of Rennell Island
- February 8th: After the Japanese have withdrawn, Guadalcanal is in American hands
- February 25: First of General MacArthur's RENO plans to retake the Philippines is presented
- In February, Japanese troops occupy Kwangtschouwan (Guangzhouwan) , a French leased area. As Territoire de Kouang-Tchéou-Wan, it was under the governor of French Indochina (Vietnam). It lies in the area of a bay of the Chin. Sea on the South China Peninsula Leizhou (north of the island of Hainan ).
- March 2: The planes of the Royal Australian Air Force and the US Navy win the battle in the Bismarck Sea , which lasts until March 4, preventing a supply of around 7,000 Japanese soldiers to New Guinea
- March 27: Battle of the Komandorsky Islands to intercept a Japanese supply convoy for the troops in the Aleutian Islands
- April 18: Japanese admiral Yamamoto Isoroku is shot down in his plane while approaching Bougainville (in the Solomon Islands, the planner of the attack on Pearl Harbor)
- May 12th: The battle for West Hubei begins in mainland China and ends on June 3rd with a victory for the Chinese Revolutionary Army
- May: US troops capture Attu island - western Aleutian island, southwest of Alaska (part of the Battle of the Aleutians since June 6, 1942)
- June 20 to August 25: Battle of New Georgia
- June 30th: Operation Cartwheel begins ( Rabaul , New Britain; part of the Battle of New Guinea )
Second half of 1943 in Europe
- July 5 to 16: The Citadel company is supposed to clear the so-called front balcony near Kursk and encircle and destroy large parts of the Red Army. The operation culminates in the greatest tank battle in history; the attack anticipated by the Red Army stalled
- Soviet counter-offensive at: July 12-August 18 Oryol ( Operation Kutuzov ) with the aim of parts of Army Group Center encircle
- July 12: The National Committee for Free Germany is founded
- August 1: Operation Tidal Wave : during an air raid on the oil fields of Ploieşti (Romania), 53 of 177 US bombers are shot down
- August 3rd Operation Rail War Strike against the German rail network
- 3rd to 23rd August: the Belgorod-Kharkov operation (Battle of the Kursk Arch) leads to the final reconquest of Kharkov
- August 7th to October 2nd: Smolensk Operation (also Operation Suvorov)
- August 16 to September 22: the Donets Basin operation leads to the reconquest of the economically important Donets Basin
- August 26th to December 20th: the Battle of the Dnepr leads u. a. to recapture Kiev
- After several Soviet counter-offensives, the Wehrmacht had to retreat along the entire front
- October 30: the foreign ministers of the three leading allies adopt the Moscow declaration on the basis of their further cooperation
- From November 18: the final air raids on Berlin begin
- from December 24th: Dnepr-Carpathian operation of the Red Army (until April 17th, 1944)
on the western fronts:
- July 10th: Operation Husky , Allied landing in Sicily
- July 19: Rome / Feltre : After air raids on Genoa, Turin and Milan by the British Air Force, the first war attack on Rome took place , involving over 500 US bombers. Italy's dictator Mussolini found out about this during meetings with Hitler in Feltre (Veneto).
- July 22nd: the Sicilian regional capital Palermo is occupied by the Allies
- 24./25. July: Beginning of massive air raids on Hamburg (mainly by more than 700 RAF bombers each, also 2 attacks by US bombers; cover name in the planning phase was Operation Gomorrah ; lasted until August 3; on average, a major attack took place every other night. ) Min. 35,000 people, almost all civilians, die.
- July 25th: the Great Fascist Council accuses its leader Mussolini of failure, the "Duce" is thereupon on the orders of the Italian King Victor Emanuel III. arrested. Pietro Badoglio is appointed as the new Prime Minister
- from July: the internment of some 20,000 Italian military personnel in Switzerland , which flee across the border in Ticino
- August 14th: Rome is repeatedly declared an open city. (At the beginning of June 1944, FM Kesselring declared Rome an “open city” and withdrew all troops except for a rearguard.)
- August / September: Start of Operation Barclay , deception maneuvers with a fictitious British 12th Army, which is mainly stationed in Egypt through fictitious radio communications and regular exercises. The German enemy should be distracted from the goal of the next invasion.
- August 17th:
- Portugal allows the Allies to use the Azores as a military air base (expansion of Lajes Field )
- Operation Double Strike : USAAF suffers heavy losses in an air raid on Regensburg and Schweinfurt
- Company course , operation of German and Italian troops for the rapid evacuation of Sicily near Messina (see July 10th)
- 18 August Operation Hydra : Air raid by the Royal Air Force on the German rocket research facility in Peenemünde
- September 3:
- The Cassibile armistice between the (formally still existing) Kingdom of Italy under the government of Pietro Badoglio, the USA and Great Britain is signed by General G. Castellano . This leads to Italy's withdrawal from the fighting.
- Start of the Allied invasion of Italy ; two British divisions land on mainland Italy with little resistance (boots)
- September 8th: after the Italian armistice with the Allies, the German Wehrmacht initiates the Axis case, in which all Italian troops are disarmed and Rome is occupied
- September 9th: Operation Avalanche : Landing of the 5th US Army in the Gulf of Salerno
- The Wehrmacht occupies the parts of Italy that have not yet been liberated by the Allies, including the capital Rome (not the Vatican State )
- September 12th: German paratroopers in the company Eiche manage to free Mussolini from Italian captivity on Gran Sasso in Abruzzo . Mussolini was first brought to East Prussia , then to Hirschberg Castle , in order to lead a puppet government in northern Italy a little later ( Republic of Salò ) and thus only apparently to continue Italy's struggle as a German ally
- 21./22. September: Massacre in Kefalonia : after the Italian soldiers stationed on the Greek island of Kefalonia oppose their disarmament, around 5000 captured Italians are shot by German mountain troops between September 18 and 23 (war crimes)
- September 23 (until April 25, 1945): The Italian Social Republic (also Italian Repubblica Sociale Italiana - RSI, Republic of Salò) dependent on the Nazi state . The seat of government was Salò on Lake Garda and from 1944 Milan with the pro forma head of state B. Mussolini.
- September 27th: Beginning of the uprising of the civilian population known as the Four Days of Naples until September 30th, in which they freed themselves from the occupation of German troops shortly before the approaching Allied troops.
- September 29th: a second Allied-Italian armistice of Malta is signed on board the HMS Nelson by the generals Dwight D. Eisenhower and Pietro Badoglio , also Italian Armistizio lungo. He extended the September 3rd.
- The deception operation Fortitude (North / South) begins (separately for Norway and the Channel coast with General Patton as allied mayor ) from autumn 1943 up to the mock invasion on Pas de Calais on June 5, 1944
- October 1st: capture of Naples (5th US Army)
- thereafter: withdrawal of the German troops to the Gustav Line , about 100 kilometers south of Rome, via the Volturno, Barbara and Bernhardt Lines
- October 5th: all of Corsica is liberated (from November 11th 1942 there was initially an Italian and later also a German occupation), so that the liberation of Europe from the south was approached to mainland France
- October 13: Italy's declaration of war - the Badoglio government declares that a ceasefire condition fulfilled with it, war against the German Reich, a powerful partisan army of 256,000 women and men operated alongside the official Italian associations , which in 1944 took on about ten Wehrmacht- divisions bind
- October 16: German troops (involvement of the Wehrmacht? Under the command of Theodor Dannecker ) capture over 1000 Jewish residents of Rome in a raid and deport them on the 18th to the Auschwitz-Birkenau concentration camp (only 16 of these 1023 Italian prisoners Jews will see the end of the war)
- October 26th: the Shetland bus , instead of fishing boats, the three converted American submarine hunters Hessa, Hitra and Vigra drive the route under Norwegian command for the first time
- November 18, 1943: British air forces bomb Lund , Sweden
- December 1943 to July / August 1944: Establishment of the Arras Defense Center (abwehr Arras or Ast Arras for short, also 430) of the German military defense in Arras, Pas-de-Calais, to secure the V1 bomb launch sites and for escort protection the missile parts there (V1 = Fieseler Fi 103; see also: retribution weapon )
- In December, US President Roosevelt gives General Eisenhower the post of Supreme Allied Commander in Europe , SHAEF . He moved into Thatched House Lodge in Richmond Park as quarters southwest of London for the period until May 1945. From March 1944, the HQ is close to Camp Griffiss in Bushy Park .
- December 20th to 28th: Battle of Ortona , also known as "Italian Stalingrad", around the deep-water port on the east coast, which is important for supplies (German Paratrooper Reg. 3 of the 1st Division and Canadian 1st Infantry Division)
| year | Europe and Western Hemisphere | Asia and Pacific | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1939 | |||
| 1940 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | ||
| 1941 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jul – Dec | |
| 1942 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1943 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1944 | Eastern Europe | Western Europe | |
| Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1945 | Jan – May | Jan – Sep | |
Second half of 1943 in Asia and the Pacific
- June 21st: during the reconquest of the Solomon Islands , the American army begins the tactic of island jumping
- June 30th: Operation Cartwheel to isolate Rabaul begins
- July 5th: Battle of the Solomon Islands'
Kula Gulf
- August 6th: Battle of the Solomon Islands Vella Gulf
- August 17th: Battle of Horaniu near Vella Lavella in the Solomon Islands
- August 15: US troops land on the evacuated island of Kiska - one of the western Aleutian islands , southwest of Alaska. End of the battle for the Aleutians since June 6, 1942
- September 4th: New Guinea is in Allied hands
- September: The previously neutral Portuguese colony of Macau , a city and port on a Chinese peninsula, comes under a Japanese protectorate. It comes to America several times. Bombing of fuel depots.
- October 6th: Battle of Vella Lavella (until October 7th)
- October 21: The Indian Chandra Bose founds an Indian government in exile under Japanese protection under the name Azad Hind (Free India)
- November 1st: US Marines land at Bougainville in the Solomon Islands
- November 2:
- the sea battle at the Kaiserin Augusta Bay begins
- Capture of the Chinese city of Changde , Hunan Province (formerly Langzhou) by the Japanese, recaptured in the following battle for Changde by December 20th
- November 20: November 28: The Americans conquer the archipelago in the Battle of the Gilbert Islands
- November 26th: After the Battle of Cape St. George , the Solomon Islands are completely in American hands
- December 26th: Landing at Cape Gloucester in the western part of New Britain
| year | Europe and Western Hemisphere | Asia and Pacific | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1939 | |||
| 1940 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | ||
| 1941 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jul – Dec | |
| 1942 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1943 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1944 | Eastern Europe | Western Europe | |
| Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1945 | Jan – May | Jan – Sep | |
1944
- The war year 1944 is characterized above all by important successes of the Allies: In January the siege ring around Leningrad is broken. In the west the invasion of Normandy succeeds; Paris is set free. In the east, the Red Army succeeds in throwing back the Army Groups Central and South decisively. Only in East Prussia does the offensive stop temporarily in October. In Italy the Allies advance north of a line between Rimini and Rome. In Asia alone, a Japanese offensive in China leads to a land connection to Indochina and thus to a partial success of the Axis powers. But in October the Philippines are liberated and the Imperial Japanese Navy is destroyed.
- (For this year an additional subdivision has been made for the theaters of war in Eastern and Western Europe).
First half of 1944 in Eastern Europe
- January 14: Start of the successful Soviet attack on the German siege ring around Leningrad , the Leningrad-Novgorod Operation , (until March 1; sub-operations: Krasnoseljsk - Ropschaer, Novgorod - Lugaer, Kingissepp - Gdower and the Staraya Russa - Novorschewer operation)
- the Soviet Union adds: their spring offensive has further territorial gains and the Wehrmacht runs until Peipussee back
- February 7-27: a series of Soviet air raids on Helsinki with over 2000 bombers (February 6/7, 16/17, 26/27 February). They were answered with attacks on airfields near Leningrad.
- February 22: Soviet bombing of Stockholm (approx. 30 bombs, reason remained unknown)
- March 2nd: OKW bullet decree , secret order to shoot (war crimes) officers who escaped from German prisoner-of-war camps ( Stalag , Oflag ) by the SD / SS (not generally for officers of the British and American armed forces who have been captured)
- In March: Start of the hay campaign, which continued until the summer of 1944 . 30,000 to 50,000 ten to fifteen year old children were deported from Eastern Europe to Germany to be used as slave labor.
- March 12th to 19th: In the Osaritschi Wehrmacht concentration camp for 40,000 so-called disabled civilians (south of the Belarusian city of Bobrujsk ), at least 9,000 people are murdered by the 9th Army in just one week with the participation of Sonderkommando 7a of Einsatzgruppe B. Not only during the transport, but also after internment, the guards of the 35th Infantry Division often shot at children for the slightest reason or without any reason, including children. According to Belarusian sources, there may have been a total of 20,000 deaths there.
- March 19: Operation Margarethe , occupation of the hitherto allied Hungary by German troops
- April 8: The Battle of the Crimea begins
- April 25th: Start of the Braunschweig offensive of the SS units in Croatia
- 12th of May:
- the Crimean peninsula, with its large ports, etc., is again in Soviet hands
- The US Air Force begins the air raids on the Leuna works and on Brüx (Most) , its fuel offensive against the industrial plants for the production of synthetic fuel
- June 9th: the offensive on the Finnish front on the Karelian isthmus , the Vyborg-Petrozavodsk operation , begins (until August 9th), at the end of June this attack comes to a halt at the old 1940 border
- June 22nd: Operation Bagration , also a major offensive in the Vitebsk- Orsha area - start of the break-up of Army Group Center , whereby the Red Army reaches shortly before Warsaw and East Prussia, on July 3rd Minsk is recaptured by the Soviet Army, 100,000 German soldiers are guessed in prison
- June 25th: Battle of Tali-Ihantala between armed forces of the Soviet Union and German-backed Finnish troops
- June 26: Ryti-Ribbentrop declaration of consent , military alliance between the Republic of Finland and the German Reich
| year | Europe and Western Hemisphere | Asia and Pacific | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1939 | |||
| 1940 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | ||
| 1941 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jul – Dec | |
| 1942 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1943 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1944 | Eastern Europe | Western Europe | |
| Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1945 | Jan – May | Jan – Sep | |
First half of 1944 in Western Europe
- January: in Ireland - the first large-scale training maneuver (duck) for the Operation Neptune invasion
- January 1: Field Marshal Erwin Rommel becomes the new Commander in Chief of Army Group B
- January 2nd: Heavy air raid on Berlin by the British Air Force
- 21./22. January: Start of the Steinbock operation of the Luftwaffe , which will intensify the air raids on London and other English cities by May 29th (see below)
- January 22nd: Battle of Anzio (English Operation Shingle) , Allied units land in Italy south of Rome surprisingly behind the German front line and form a bridgehead there
- January: The expansion of Lajes Field on the Azores island of Terceira is completed. Important US aircraft supply route in the Atlantic (in use since December 2, 1943)
- January 30 to February 8: At the Brazzaville Conference , De Gaulle and other representatives of France Libre met with 20 governors from the African colonies of France . The Brazzaville Declaration formulated the following objectives, among other things: parliamentary participation, opening up the public service to the indigenous population , and abolition of forced labor.
- February 8: Allied plans for Operation Overlord , the landing in northern France, are completed
- February 13: The Hurtigruten passenger steamer Irma is sunk in the bay of Hustadvika by two motor torpedo boats of the Norwegian Navy ; 61 people die
- February 15th: Battle of Monte Cassino : around the Monte Cassino mountain monastery - final offensive May 11th to 18th
- February 22nd: American planes bomb the Dutch city of Nijmegen ; around 800 fatalities, the attack had the German city of Kleve as its target
- March 18: during an Allied air raid on the city center of Frankfurt am Main there was a fire. a. the St. Paul's Church from
- March 22nd: Another heavy bombing raid on Frankfurt am Main wipes out the historic old town ; Among other things, the Katharinenkirche is destroyed, 1001 people die
- March 24th: on the orders of the SS Police Chief of Rome H. Kappler, 80 to 90 SS men murder 335 hostages in the massacre in the Ardeatine Caves (322 of the victims could be identified, among others Generalfeldmarschall Kesselring, SS- 1947/48 Obersturmbannführer Kappler, Lieutenant General Mälzer and Colonel General Eberhard von Mackensen convicted of shooting hostages)
- 26./27. March: Massacre on the Plateau des Glières in the Savoier Alps northeast of Annecy and Thônes ; after fighting since January by units of the 157th Reserve Mountain Division and the French Vichy militia
- April 1: US planes unintentionally bomb the city of Schaffhausen in Switzerland
- April 2: In the Ascq massacre, 86 civilians are murdered by members of the 12th SS Panzer Division "Hitler Youth"
- 27./28. April: Approx. 1000 Allied dead during a landing exercise in Devon , Exercise Tiger , from friendly fire and a German speedboat attack from Cherbourg on it. (The Slapton Sands Memorial reminds of this. The exercise provides important information in preparation for the landing four weeks later)
- May 12th: Allied troops advance into Rome in Italy
- May 18: the 2nd Polish Corps under the leadership of General Władysław Anders takes Monte Cassino after massive Allied losses,
- the further advance on Rome from the south begins
- MAY 25: unite the allied forces her two fronts in Italy and pushing the German troops to the "Green Line" between La Spezia and Rimini back
- January 21 to May 29: Operation Steinbock , the bombing of London and engl. Ports, is set according to loss rates of up to 10 percent. Also referred to as Baby Blitz by the British .
- June 4th: Rome is left / liberated without resistance, Field Marshal Albert Kesselring , Commander in Chief of the German Army Units in Italy, refuses to fight in the “Eternal City”. He declares it an open city. Withdraw all troops except for a rearguard. Troops of the 5th US Army march in.
- June 5th: the Tonga airborne operation is part of the preparation for the invasion of northern France. a. The Pegasus Bridge (Bénouville Bridge until 1944) and the Horsa Bridge south of the Sword beach section near Ranville / Caen are taken
- June 6: D-Day for Operation Overlord ( code name for the Allied liberation of northern France), the Western Allies land in Normandy (the landing itself is code-named Operation Neptune ) and build a rapidly widening beachhead around the next Weeks of fierce fighting, the operation is based on invasion plans drawn up from 1941 onwards , which were drawn up in concrete form from 1943 by the British General Frederick E. Morgan
- June 8th to 15th: Battle of Carentan to connect the American. Beach Heads Utah Beach and Omaha Beach
- the battles in the British-Canadian sector ( Sword - (GB), Juno - (Ca), Gold Beach (GB)) are known as the Battle of Caen or Engl.
- Battle for Caen ; individual operation names in the addition. thus (June – August 1944) are: Operation Perch (June 9th to 14th, see below); Epsom June 25-30, Windsor July 4-5, Charnwood July 7-9, Jupiter July 10-11, Goodwood July 18-20, Spring (July 25th to 27th), Bluecoat (July 30th to August 7th), the German company Liège (counterattack, August 6th to 8th), Totalize (August 7th to 10th), Tractable (August 14th to 7th). to 15 August) and the final fights in the Falaise Pocket, the pocket of Falaise (16 to 20 August, see below).
- June 9: Resistance fighters cordon off an area near Grenoble east of the Rhone , which will be the first liberated zone within France from July 3 - (partisan) République du Vercors . Recaptured by the Wehrmacht from July 21st (action Bettina, see there).
- June 10th:
- Oradour massacre in Oradour-sur-Glane near Limoges, the 3rd company of SS Panzergrenadier Regiment 4 "Der Führer" murdered almost all the inhabitants (642 people) of the village, allegedly as reprisal, and destroyed the entire village
- Distomo massacre (218 victims of the 4th SS Police Panzer Grenadier Division) near Delphi, Greece
- June 12: The German Air Force fires V 1 missiles at London for the first time (Fi 103)
- June 13th: the tank battle near Villers-Bocage resulted in losses of the British tank forces advancing as part of Operation Perch and attacking SS Tiger tanks
- 17th of June:
- Beginning of the Battle of Cherbourg with air raids and bombardment of the city and the fortress. On the 21st, the USS Texas begins artillery support.
- The Danish territory of Iceland , which has been occupied by British troops since May 10, 1940 and US troops since 1941, declares itself to be an independent Democratic Republic ( Icelandic Lýðveldið Ísland ). Denmark is still under German occupation at this time .
- June 25: Opération Zebra, in support of the Résistance intérieure française with weapons, the Allies flew parachute containers with weapons from Italy to four bases of the Maquis with around 200 bombers during the day. Similar again on July 14th.
- June 26th: Capture of the port of Cherbourg after a German partial capitulation
| year | Europe and Western Hemisphere | Asia and Pacific | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1939 | |||
| 1940 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | ||
| 1941 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jul – Dec | |
| 1942 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1943 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1944 | Eastern Europe | Western Europe | |
| Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1945 | Jan – May | Jan – Sep | |
First half of 1944 in Asia and the Pacific
- January 31 to late April: American forces begin the battle for the Marshall Islands
- February 3: US troops win the Battle of Kwajalein in the Pacific , with the atoll of the Marshall Islands , for the first time in this war a Japanese defended island is captured within its territory
- FEBRUARY 4: Japanese units penetrate through Burma as far as northern India before
- February 7th: Kwajalein in the Marshall Islands falls to the Americans
- February 17 to February 23: Operation Catchpole (capture of Eniwetok Atoll)
- February 17 to February 18: Operation Hailstone (attack on Truk Atoll )
- February 23: Series of air raids on Tokyo begins, and 334 US bombers are deployed by March 9
- February 29th: American units land on the Admiralty Islands
- March 8th - July 3rd: Battle of Imphal , Nagaland / India and
- April 4 - June 22: Battle of Kohima , Nagaland / India (British victory stops the Japanese invasion along the Imphal-Kohima road ; later Tipaimukh Road , National Highway NH-150, Manipur)
- April 19: Start of the Japanese offensive Operation Ichi-gō in the direction of southeast China to open a land connection to Indochina and capture the Allied air force bases (until December 1944)
- JUNE 5: 77 US B-29 Superfortress bombers attack the railway factories of Japan in Bangkok on
- June 15 to August 10: American forces capture the islands of Saipan and Tinian , which have been occupied by Japan since the First World War , in the Battle of the Mariana Islands ; the US territory of Guam (conquered December 8, 1941). The largest overseas US military air base will then be built on Tinian. (The B-29 bombers Enola Gay and Bockscar also took off from the island with the atomic bombs to Hiroshima and Nagasaki - August 6 and 9, 1945)
- June 15th: American B-29 bombers launched attacks on the main Japanese islands from Chinese bases
- June 19 to June 20: Battle of the Philippine Sea - directed against the Japanese naval Operation A-gō
| year | Europe and Western Hemisphere | Asia and Pacific | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1939 | |||
| 1940 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | ||
| 1941 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jul – Dec | |
| 1942 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1943 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1944 | Eastern Europe | Western Europe | |
| Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1945 | Jan – May | Jan – Sep | |
Second half of 1944 in Eastern Europe
- JULY 3: The Red Army captured Minsk back
- July 13, 1944 to August 29: Red Army's 1st Ukrainian Front offensive : Lviv-Sandomierz operation , consisting of three sub-operations: Lviv , Stanislavov and Sandomierz operations ; The most important results were the defeat of large units of Army Group South in the Brody pocket , the conquest of western Ukraine and the south-eastern regions of Poland, the Vistula is reached
- July 17: 57,000 German prisoners of war are taken into captivity through Moscow
- July 23: The Majdanek concentration camp (in the suburb of Lublin ) is the first of the German extermination camps to be liberated by Allied troops, here the Red Army, followed by internationally acclaimed press reports
- July 24th: German troops withdraw from the Narva bridgehead
- Early August: a Soviet bridgehead was formed on the Vistula near Sandomir
- August 1st: the Warsaw Uprising of the Polish Home Army begins, on October 2nd, after 64 days - without the support of the Soviet Army - the High Command of the Polish Home Army surrenders
- 5th of August:
- an Allied air raid on Magdeburg kills 683 people
- In the Black Sea, the Soviet submarine sinks SC-215 , the MS MV MEFKÜRE , which has over three hundred Jewish refugees on board. The ship sailed under Turkish registration and carried the neutral flags of the Republic of Turkey and the Red Cross . It went in convoy with the Bulbul and Morina ships , each of which carried over 300 passengers. There were eleven survivors.
- August 16-20: In Operation Doppelkopf , the German 3rd Panzer Army succeeds in temporarily reestablishing the land connection between Army Groups Center and North
- August 18: the Red Army reaches the East Prussian border
- August 20: Operation Jassy-Kishinev : the 2nd and 3rd Ukrainian Fronts of the Red Army begin a summer offensive with around 900,000 soldiers against the Army Group of Southern Ukraine in Romania
- August 23: King Michael of Romania declares an armistice with the Soviet Union ( royal coup d'état in Romania 1944 ), a little later Romania enters the war against Germany after the air force bombed Bucharest on the 23rd and 24th , this change of front had already taken place several months earlier in negotiations with the Allied powers. The Soviet Union occupies the country.
- Withdrawal of the German armed forces from Greece
- 26./27. August: First bomb attack on Königsberg by British bombers
- 29./30. August: The city center is almost completely destroyed in the second night attack on Königsberg
- August 29th: the Slovak national uprising breaks out. On October 27th he was bloodily suppressed
- September 2nd: Finland demands that Germany evacuate its territory, the so-called Lapland War begins on September 19th. In the armistice with Moscow, Finland was obliged to expel the previously allied German troops by military means within 14 days. Since this deadline could not be met, a sham war arose. The city of Rovaniemi burned down completely in a fire triggered by the explosion of an ammunition train . The fighting dragged on until the spring of 1945. The German troops retreated north to escape to Norway. The last occupied place in Finland was evacuated on April 27, the village of Kilpisjärvi.
- September 3: The 20th Mountain Army initiates Operation Birke , the disengagement movement in Finland
- September 5th: the Red Army takes Bulgaria ; Bulgaria declares war on Germany, which is followed by a communist coup d'état there on September 9th
- 14./15. September: The Wehrmacht tries in vain in Operation Tanne Ost to occupy the Finnish island of Hogland
- September 16 to November 24: In the Baltic operation of the Red Army, the Baltic region comes largely under the control of the Soviet Union again, the German Army Group North is cut off in the Kurland basin and has to be supplied via the Baltic Sea
- September 19: Finland had to cede the Petsamo area to the Soviet Union in an armistice
- October 1: Red Army troops enter Yugoslav territory for the first time
- October 2nd: the Warsaw Uprising ends with the surrender of the Polish Home Army , which submitted to the London government in exile, and the Germans almost completely destroyed the city
- October 6: Beginning of the Debrecen operation of the allied Soviet and Romanian troops against the German-Hungarian Army Group South
- October 7th: In the German concentration camp Auschwitz-Birkenau there is an uprising of the Jewish Sonderkommando (the prisoners who had to operate the gas chambers and crematoria), female prisoners smuggled in explosives from their forced labor in an arms factory and crematorium IV was partially destroyed
- October 10: The Red Army reaches the German border in East Prussia
- 7th to 29th October: in the Petsamo-Kirkenes operation , the Red Army conquers the German bases in northern Finland
- October 13th:
- in the northeast of the draws Army Group North from Riga to Kurland back
- British units back in Athens a
- 15th October:
- Coup of the Arrow Cross in Hungary , supported by Germany , Reichsverweser / dictator Miklós Horthy is arrested in the Panzerfaust company by SS troops under the orders of Skorzeny in the Budapest Castle and forced to abdicate by threatening to shoot his son
- In East Prussia , the Soviet Union's offensive came to a halt in October after initial successes
- October 19: the destruction of Warsaw ordered by Adolf Hitler begins
- October 20: Soviet units and Yugoslav partisans under Josip Broz Tito conquer the capital Belgrade in the course of the Belgrade operation
- October 21: Nemmersdorf massacre : the Red Army conquers the village of Nemmersdorf for a few hours and shoots at least 23 civilians there, the majority of them women and children, this is considered the first documented crime of the Red Army on German soil
- November 24th: The unarmed Swedish passenger ship Hansa is sunk in the Baltic Sea off the island of Gotland by a Soviet submarine without warning, 84 civilians die
- December 25th: Battle of Budapest , completely enclosed by the Red Army
| year | Europe and Western Hemisphere | Asia and Pacific | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1939 | |||
| 1940 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | ||
| 1941 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jul – Dec | |
| 1942 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1943 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1944 | Eastern Europe | Western Europe | |
| Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1945 | Jan – May | Jan – Sep | |
Second half of 1944 in Western Europe
- July 19th: Caen is completely occupied - see above from June 8th Battle of Caen
- July 20: The attack on Hitler by Count Claus Schenk von Stauffenberg on July 20 and the associated military coup (" Operation Valkyrie ") fail completely (attack on Hitler in the Wolfsschanze headquarters near Rastenburg in East Prussia)
- 200 people from the circle of conspirators will therefore be executed in the next few days and weeks (including 20 generals, 26 colonels, diplomats, a minister, the head of the Reich Criminal Police Office; chief presidents, police presidents and regional presidents)
- July 25: Operation Cobra : in Normandy the Americans in the room to take Saint-Lô an attempt to break out of their bridgehead sector, which in the following days in the west to the constriction of the Cotentin -Halbinsel until after Avranches leads
- July 31: After the tank battle of Avranches , they break through the German western front
- August 6th: Operation Liège : the Germans under the leading OB West , Field Marshal Günther von Kluge , start a counterattack at Mortain , the operation is stopped again after two days - see above under Battle of Caen
- August 12-21: a large part of the German troops in Normandy is wiped out in the Falaise pocket
- August 12: four Waffen SS companies shoot almost all residents of the Italian village of Sant'Anna di Stazzema after partisan attacks ; 560 victims, most of them women and 116 children
- August 12: With Operation PLUTO (Pipe-Lines Under The Ocean), the allies succeed in laying a 130-kilometer-long submarine fuel pipeline between the Isle of Wight and Cherbourg . In October 1944 a pipeline from Dungeness to Cherbourg followed, and still later one through the Dover Strait .
- Allied air war plans: Operation Thunderclap (not implemented)
- August 15: Operation Dragoon begins a second invasion of southern France on the Côte d'Azur between Toulon and Cannes . The French and Americans can quickly advance into the interior of the country without decisive resistance
- August 17th: after heavy bombing of Saint-Malo , the city commander Colonel Aulock surrenders
- August 22nd:
- Grenoble is evacuated by the German troops and jointly by the Maquis de l'Oisans and American. Troops freed
- the wave of arrests at Aktion lattice is started by the Gestapo throughout the Reich; many former political opponents are arrested and interned
- August 25: The battle for Paris begins
- the German city commandant General Dietrich von Choltitz refuses Hitler's order to destroy the city and surrenders with his troops without a fight
- the Allies overstretch in their rapid advance to the German Siegfried Line their supply lines, the development of new supply routes is achieved by the Red Ball Express . From August 25th to November 16th the code name for the supply trips for the military. Replenishment (ammunition, fuel, food - on average far more than 3 million liters of petrol were used per day!) With around 6,000 trucks over a cordoned off route from Cherbourg to behind the front, which is further away every day, beyond Paris. This organization and its importance also shows the historical change to the first great motorized war - at the same time a further development of the overlord planning - replaced by the possible use. of the port of Antwerp . The route was u. a. Supplemented by workshops and rest areas for drivers.
- Until September 1, German air raid on Paris and with rockets ( V1 , V2 ) on northern France and London
- August 28: In Marseilles , after a week of fighting, the Wehrmacht units surrender to French troops
- August 29: French and American troops hold a victory parade in Paris
- the southern part of the Netherlands was liberated from the advancing Allies in the second half of 1944; the north of the country only at the end of the war
- September 1st / 2nd: 107 imprisoned members of the French espionage network (Réseau, SR) Alliance are murdered by SS members in the Natzweiler-Struthof concentration camp .
- September 1st: The Canadian 2nd Infantry Division (two years earlier involved in the Dieppe raid) marches into the abandoned Dieppe without a fight. The Allied supply ships landed in the port of Dieppe on September 7th.
- September 3: Brussels is liberated
- September 4th: Antwerp is liberated / British troops occupy it (other places in the NL are not initially liberated - Dolle Dinsdag )
- from September 6: approx. 3200 German air raids with V2 rockets on cities, especially on London (1358) and Antwerp (Belgium, 1610) by March 1945
- September 6th: Bomb units destroy around 80 percent of the city center of Emden , the submarine construction there is hardly affected
- From September 10th: Partisan Republic of Ossola (Italian Repubblica dell'Ossola) a partisan republics or "liberated zones", zona liberata , founded by partisans for 44 days (one of approx. 20 temporarily asserting itself) , in northern Italy around Domodossola (until 19 October 1944; part of the resistance in Italy against fascism )
- September 11th: American units cross the German border northwest of Trier
- 11./12. September:
- Air raid on Darmstadt , the Royal Air Force (RAF) is testing the tactics of the fan attack for the first time
- the so-called air battle over the Ore Mountains (after German attacks on the bombers, the following US Mustang fighter planes fight )
- September 12th: Roetgen is the first municipality on German soil to be occupied by Allied forces
- 12./13. September: there were a total of 53 nights with air raids on Stuttgart , during which the British RAF dropped 75 heavy air mines , 4,300 high-explosive bombs and 180,000 incendiary bombs. More than 1,000 people fell victim to the subsequent firestorm
- September 14th: Maastricht (NL) is liberated by US troops
- September 16: Major General Elster surrenders with 19,600 men on the Loire Bridge from Beaugency to American troops, Elster commanded the rearguard when German troops withdrew from France, most of them were on foot and barely able to fight, his unprecedented surrender leads to a conviction a German military court
- September 17th: The 1st Polish Armored Division liberated the city of Ghent together with Belgian resistance fighters .
- September 17th to 27th: at the Market Garden airborne operation fights u. a. the II. SS Panzer Corps against British and American units around Arnhem . Crossing the Rhine does not succeed.
- after losing the Atlantic ports on the English Channel ( Battle for Brest ), the German navy is continuing its submarine warfare of Norway from continuing
- September 20: The British government issued a communiqué announcing the formation of the Jewish Brigade within the British 8th Army from volunteers from the Mandate area in Palestine
- September 25: Hitler orders the paramilitary " Volkssturm " to be set up, made up of older people, young people and UK employees aged 16 to 60
- September 29th: The 1st Polish Armored Division liberates the Dutch city of Breda after two days of hard fighting with no civilian casualties. All soldiers in the division were made honorary citizens of the city.
- On the orders of Prince Bernhard and the Dutch government-in-exile in London, many Dutch railway workers went on strike in September 1944 and went underground in order to paralyze German supplies.
- September to April 1945: Hongerwinter (Eng. Hungerwinter) towards the end of the German occupation of the Netherlands , especially during the months of October 1944 to April 1945. The densely populated area of Holland in the Netherlands was mainly affected . From September 1944, a German blockade prevented this region from being supplied with food and fuel from the more rural regions ( war crimes ). The famine that began in October 1944 affected 4.5 million people whose food supplies had already been rationed in the previous years of the war. The aforementioned rail strike is viewed indirectly as a trigger. The number of people who died from this famine is now estimated at 18,000 to 22,000.
- October 1: In the Marzabotto massacre , the Wehrmacht and SS murder over 800 civilians near Bologna
- October 2 to November 8: Battle of the Scheldt estuary (French: Bataille de l'Escaut, English Battle of the Scheldt) to open the port of Antwerp to allied supplies
- October 5: Air raid in Saarbrücken ; 361 people die
- October 6th: The Debrecen operation of the Red Army begins
- October 7th: Red Army's Petsamo-Kirkenes operation begins
- October 7th: About 80% of Kleve is destroyed by two British air raids, as is Emmerich, about ten kilometers away
- October 15: Air raid on Braunschweig
- October 18th:
- the first heavy air raid on the city of Bonn devastated the city center
- Battaglia dei Bagni di Craveggia , border incident involving Italian partisans who fled to Switzerland ( Onsernone Valley )
- October 21: Battle of Aachen : the Allies conquer Aachen , the first German city and penetrate at this point for the first time by the Western Wall
- October 31: Air raid on Gestapo headquarters in Aarhus was flown with 24 British bombers
- November 6th: British air raid on Koblenz
- November 8: the battle at the mouth of the Scheldt , which began on October 2, is decided in favor of the Canadian armed forces , the German armed forces have to clear the area from Antwerp to the Meuse
- November 12th to December 19th: Battles for Alsace and Lorraine
- November 16: Bombing of the Rhenish cities of Heinsberg , Jülich , Euskirchen and Düren as part of Operation Queen , mainly Euskirchen and Düren are destroyed
- NOVEMBER 22: US Army takes Metz a
- 23 November: Advance on and liberation of Strasbourg / Strasbourg from US troops and the French 2nd division blindée
- November 25: The Brazilian expeditionary force Força Expedicionária Brasileira in the ranks of the Allies opens the battle of Monte Castello with an attack on positions of the Wehrmacht near Bologna
- November 29th: the Wehrmacht evacuates Shkodra ; all of Albania is liberated
- November 30th: Operation Elster begins , attempted infiltration (espionage, diversion) against the USA, especially the Manhattan Project
- December 4th: Air raid on Heilbronn - 282 Lancaster bombers of the RAF; 6500 people die in the process
- December 5th: the British military intervention in Greece against the Greek People's Liberation Army ELAS begins
- December 16, 1944: the German Ardennes offensive is initiated; it is intended to prevent the Allies from advancing further
- December 17th: A combat group of the 1st SS Panzer Division Leibstandarte SS Adolf Hitler under the command of J. Peiper murdered US prisoners of war in the Malmedy massacre
- December 24th: the Belgian troop transporter Léopoldville is sunk in the English Channel off Cherbourg by a German submarine, 736 people die
| year | Europe and Western Hemisphere | Asia and Pacific | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1939 | |||
| 1940 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | ||
| 1941 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jul – Dec | |
| 1942 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1943 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1944 | Eastern Europe | Western Europe | |
| Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1945 | Jan – May | Jan – Sep | |
Second half of 1944 in Asia and the Pacific
- August: the Chinese city is captured with the fourth battle for Changsha
- August 5: Japanese prisoners of war attempt what is probably the largest prison escape in history in the internment camp near Cowra , Australia ; 231 Japanese and four guards die in the process; 108 Japanese are wounded, and all those who fled are back in military custody nine days later
- August 11: Liberation of the islands of Saipan, Tinian and Guam (June 15 - August 11; Saipan battle ends on July 8; Japanese water-air offensive Operation A-Gō / Battle of the Philippine Sea, 19/20. July ; Tinian, Aug. 1 ; Guam, Aug. 10 )
- August 16: In the Battle of Guilin-Liuzhou (Henan-Hunan- Guangxi ) the Japanese succeeded by November 24th against troops from Chiang Kai-shek in capturing airfields in south-east China on which US Air Force bombers and fighter planes are stationed are
- August 22nd: the Japanese withdraw from India again
- September 15 to November 25: Battle of the Palau Islands
- September 23: Soldiers of the 81st Infantry Division take the Ulithi Atoll (today part of Yap of the Federated States of Micronesia ). It offered anchorages for 700 ships and was quickly expanded to become a naval base. For seven months until early 1945, the lagoon was the largest U.S. anchorage in the world.
- October 20th: the recapture of the Philippines begins with the American landing on Leyte - fighting until December 31st
- October 24th to October 25th: victory in the sea and air battle in the Gulf of Leyte brings the destruction of the Japanese navy ; shortly afterwards there was a long-prepared first kamikaze attack u. a. on the aircraft carrier USS St. Lo , which led to its sinking.
- November 24th: Heavy air raids by Allied bombers on Tokyo from Tinian. Of 111 B-29s , only 59 aircraft reach the target area, the Musashino aircraft factory. The bombs were dropped from a height of around 10,000 meters with radar target search as area bombing. 16 of the 399 tons of high-explosive bombs hit the aircraft factories.
- December 15th: American troops land in Mindoro , Philippines
| year | Europe and Western Hemisphere | Asia and Pacific | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1939 | |||
| 1940 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | ||
| 1941 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jul – Dec | |
| 1942 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1943 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1944 | Eastern Europe | Western Europe | |
| Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1945 | Jan – May | Jan – Sep | |
1945
- The last year of the war was initially marked by a conference of foreseeable victors: the Yalta conference. In the weeks that followed, the liberation of the concentration camps was associated with terrible observations for the Allied soldiers. In the Pacific, the Philippines, Indochina, Burma and China are liberated. The victory in the battle for the Seelower heights opens the way to Berlin. The Rhine is crossed in March. On April 30th, the Red Army hoisted a flag on the Reichstag. After the capitulation on May 7, Europe was liberated from the Nazi regime. The first atomic bomb was dropped on Hiroshima on August 6th. After the surrender of the emperor, the Japanese army was ordered to cease all fighting on August 16 and the signature ceremony on the battleship USS Missouri in Tokyo Bay ended the Second World War on September 2.
January to May 1945 in Europe and the Atlantic
- 1st - 25th January: German company Nordwind , last offensive on the western front
- 11 January: the Gotthard line (railway) is bombed by the Allies near Chiasso, an SBB train driver dies
- January 12th: The Red Army's Vistula-Oder operation begins
- January 13 to April 25, 1945: East Prussian operation by the Red Army. It advances north, cutting East Prussia off from the rest of the empire; the German population is fleeing (permission from their own government comes very late), some of them across the frozen Baltic Sea or by ship .
- January 14th to January 26th: Operation Blackcock (Rur Triangle). This will against the 15th Army (in fact it was the 25th ), the front towards the Rhine ahead
- January 16: devastating air raid on Magdeburg ; this causes a firestorm
- January 17th: Warsaw is liberated
- January 20th ff .: La poche de Colmar - between January 20th and February 9th, the bridgehead in Alsace is taken by Allied troops
- January 27th: first Soviet units reach Küstrin
- January 27: Liberation of the concentration camps in and around Auschwitz , which the SS had largely evacuated from prisoners by means of death marches, by the Red Army
- January 30th:
- The troop transport Wilhelm Gustloff , which is not marked as a hospital ship, is sunk by a submarine off the coast of Pomerania (several thousand drowned)
- Start of the Malta Conference between the Combined Chiefs of Staff (Chiefs of Staff of the USA and Great Britain) and the Foreign Ministers of both countries in preparation for the Yalta conference with Stalin (see 4.2.). The meeting ended on February 2 aboard the cruiser USS Quincy in the port of Malta. It was only on the last day of the conference that President Roosevelt and Prime Minister Churchill met there .
- 31 January:
- the fortress front Oder-Warthe-Bogen , also Ostwall, is broken through by the Red Army after three days of fighting
- After the successful Soviet winter offensive, the Red Army stood at the end of January 1945 along the Oder and Neisse rivers from Stettin to Görlitz almost 80 kilometers from Berlin
- 2. February :
- Mauthausen concentration camp : Mühlviertel hare hunt (so titled breakout of Soviet prisoners of war)
- During the battle for Küstrin , the Soviet troops passed north and south of the old town on an island in the Oder and the Küstrin fortress. The two bridgeheads were fiercely contested in the second half of March 1945. However, the Wehrmacht succeeded neither in removing the bridgeheads nor in holding the fortress. From here the advance on Berlin began on April 16, 1945.
- February 4-11: Allied Yalta Conference on the Crimean Peninsula (Black Sea)
- February 7: US Operation Veritable in the Kleve area, known in German as the Battle of the Reichswald , until February 22.
- February 9th: the Swiss Federal Council forbids further coal transit from Germany to northern Italy
- February 9th: the first refugees arrived in occupied Copenhagen on a refugee ship . Hundreds of thousands of people, mainly from Eastern Pomerania , Danzig, and West and East Prussia , were evacuated across the Baltic Sea before the approaching Soviet troops. Schools, hotels and sports facilities were requisitioned by German authorities for their reception. Around 6,580 refugees had died in the country by the end of the war. After the Wehrmacht troops withdrew from Denmark in May 1945, around 250,000 refugees were housed / imprisoned in Denmark in barracks and camps previously used by the Wehrmacht. The last refugees were only brought to Germany from there in February 1949.
- February 10 to April 4: Battle of East Pomerania
- February 11th: The Hungarian capital is captured by the Red Army in the Battle of Budapest
- February 12: Varkiza Agreement , disarmament and demobilization of the Greek People's Liberation Army ELAS
- 13th February:
- Air raids on Dresden begin (until April 17th)
- the last defenders of Budapest , besieged since December 25, 1944, capitulate.
- February 14th to 14th: the British Army's Operation Columba , which uses carrier pigeons to transport information essential to the war effort from the occupied countries of Western Europe, is suspended. In three and a half years, 17,000 birds were caged there. Ten percent made it back and delivered about 1,000 messages.
- February 23, 1945: US troops ( 9th US Army ) cross the Rur near Linnich, Jülich and Düren at the start of Operation Grenade . Your goal is to advance between Neuss and Rheinberg to the Rhine and to conquer an intact Rhine bridge. (until March 11th)
- February 23 to March 3: Second phase of Operation Veritable , now as Operation Blockbuster
- 22./23. February: Operation Clarion : 3500 bombers and around 3000 warplanes from the USA-AF and the RAF attack numerous railway hubs and stations in smaller cities as well as marshalling yards, trains, river transport ships, ports, bridges and other traffic facilities in daytime attacks.
- Air raid on Pforzheim with a firestorm
- February 27th: Switzerland bans all transit traffic (especially on the Gotthard Railway ) between Germany and Italy
- March 6th : Cologne on the left bank of the Rhine is captured (the last bomb attack took place on March 2nd, 1945). The cathedral is apparently almost intact .
- March 7th: the bridge at Remagen is taken by surprise by US troops, the city of Remagen is then bombed by the German side with V1 shells .
- March 16: from 9:15 p.m. to 9:42 p.m. the bombing raid on Würzburg, which destroys 80 percent of the core city
- March 19: Hitler's order for destructive measures in the Reich , later called Nero order, see also ARLZ measures of the Wehrmacht
- March 22:
- Hildesheim is almost completely destroyed in an air raid
- the Arab League is founded in Cairo
- American troops cross the Rhine near Oppenheim
- March 23-27: Anglo-American Operation Plunder (Rhine crossing between Emmerich and Wesel , Churchill's visit to the front ). The main attack took place in the British sector at Wesel and Rees. The attack included the Varsity and Flashpoint operations . 29 divisions are involved.
- 25th March:
- Aachens' new mayor, Franz Oppenhoff (1902–1945), a conservative lawyer appointed by the US military government, was murdered in his house after almost five months in office. Initially, a group from the Nazi organization Werwolf was held responsible for this. Today it is assumed that Oppenhoff was murdered on the orders of Heinrich Himmler .
- Start of the Bratislava-Brno operation
- Air raid on Prague , 650 US planes
- March 26th: Americans occupy Limburg adL , coming from Remagen
- March 26th to 28th: US troops occupy Frankfurt am Main, which was badly damaged by bombing
- March 29th:
- American troops occupy Mannheim , Wiesbaden and Fulda
- Soviet troops penetrate Austrian territory for the first time near Klostermarienberg
- March 30th to March 31st: French troops cross the Rhine near Speyer and Germersheim
- March 31: Beginning of the capture of Würzburg
- Bis 21st 1. April : the Ruhr pocket , losses on the German side about 10,000 deaths and 325,000 prisoners; 1,500 dead in the 1st and 9th US Army
- April 1st: Proclamation of a "Werewolf station" about the resistance of the population against the occupation. The programs will be broadcast until the end of April.
- April 4: Hungary is completely captured by the Red Army after the failure of the Lake Balaton offensive
- April 5th:
- Lieutenant Colonel Josef von Gadolla is shot dead in Weimar because of his refusal to give orders in Gotha (handover of the city)
- Beginning of the Battle of Crailsheim (until April 21)
- April 6th:
- Soviet troops reach Vienna , the battle for Vienna begins
- The revolt of SS members of the Georgian Infantry Battalion 822 "Queen Tamara" against her further war effort is described as the " Georgian Uprising " on Texel (NL) (until May 20th)
- April 6th to 9th: Königsberg is captured by Soviet troops
- 12. April:
- Death of Franklin D. Roosevelt in Warm Springs (Georgia) after a long illness; his successor as the 33rd President of the USA will be constitutionally Harry S. Truman
- After taking office, the Roosevelt ministers will initially remain in office at the request of the new president.
- Handover of the city of Braunschweig to the US Army
- April 13th: End of the battle for Vienna (since 6th): Soviet troops also conquer Lower Austria , Burgenland and Styria
- April 16: The battle for the Seelow Heights begins
- April 16-18: the Red Army gains the upper hand, after April 19 the way to Berlin was open
- around the same time the siege ring around Breslau was closed further south
- Beginning of the battle for Nuremberg
- April 16-18: Action Rhineland for the surrender of Düsseldorf without a fight . Military occupation on April 18th
- April 18: US troops in Magdeburg
- April 19th:
- April 20: Victory parade of the Americans on the Nuremberg main market after the fighting ended
- APRIL 21: the first French army occupied Freiburg and Stuttgart and penetrates later to Vorarlberg ago
- April 23:
- Berlin is completely enclosed; Beginning of the battle for Berlin
- German Jews, including Rabbi Martin Riesenburger, were also hiding on the grounds of the Jewish cemetery in Weißensee . He reports on the first Soviet soldier whom those hiding there greet.
- The Flossenbürg concentration camp is liberated by American troops
- The Haigerloch research reactor for atomic bombs is found south of Stuttgart in a relatively inconspicuous castle cellar by the American special unit Alsos and dismantled on April 24th. The scientists involved there are captured.
- April 25th:
- US and Soviet troops meet in Torgau on the Elbe ; they celebrate Elbe Day together
- Bomber formations of the Royal Air Force and the 8th USAAF Air Force attack Bad Reichenhall , Berchtesgaden and Freilassing in a coordinated manner . The main focus is on the railway line to Berchtesgaden as a supply line to any Alpine fortress and the facilities on and near Obersalzberg . Over 200 people die in the air raid on Bad Reichenhall .
- April 26th: British troops occupy Bremen ; later they march further northeast and take Lübeck (May 2nd) and Hamburg (May 3rd), while the US Army marches into Wismar .
- April 27th:
- “ Proclamation on the independence of Austria ” in Vienna
- American and French troops liberate the Kaufering / Landsberg concentration camp command
- Regensburg is handed over to the Americans without a fight after the last Wehrmacht units left the city the day before
- Rebellion of the Bavarian freedom campaign around Munich, which is crushed within a short time
- Genoa is conquered
- April 28th:
- Failure of the relief attempt of the 12th Army under General Wenck for Berlin
- (April 25-28) The Halbe pocket , southeast of Berlin, can be closed by the Red Army
- US troops, coming from Kempten im Allgäu , enter Austrian territory near Vils ( Tyrol )
- French troops reach Austrian territory at Lochau in Vorarlberg near Bregenz
- Italian partisans shoot the fascist "Duce" Mussolini, who fled government troops , on Lake Como
- April 29th:
- Hitler wrote his “ political testament ”.
- under the new chancellor Karl Renner that occurs in Vienna Provisional Government of Austria together
- Liberation of the Dachau concentration camp by US troops
- Operations Manna and Chowhound begin; Humanitarian military operations of the Allied Air Forces under the tolerance of the German occupation forces to rescue the starving Dutch population, the Royal Air Force supported by Australian, Canadian, New Zealand and Polish forces has from April 29th to May 7th food from heavy bombers over parts of the Netherlands thrown off who suffered from the Hongerwinter . The United States Army Air Forces flew similar missions May 1 through May 8, Operation Chowhound . Since the supply flights alone would not be sufficient, the Allies and the German side also agreed to supply food with trucks in the Rhenen area (Operation Faust) and on the waterway to Rotterdam as part of an armistice.
- April, 30th:
- the Red Army hoists a Soviet flag on the Reichstag building
- Adolf Hitler kills himself in the bunker under the Reich Chancellery ; There are more suicides there, on the days before and after many NS members tried to escape from their bunker system
- Munich (American) and Stuttgart (French) are occupied
- May 1 : After Hitler's death, Admiral Dönitz becomes, in accordance with Hitler's testamentary decree, de facto "President of the Reich" without a designated election; he calls on the radio to continue the war in the East.
- 2.May:
- Admiral Dönitz in the (main) quarters in Flensburg - Mürwik names a so-called executive government under the previous Reich Finance Minister Graf Schwerin ( Dönitz government )
- the German troops in Berlin capitulate to the Red Army
- The Großdeutsche Rundfunk ends its broadcasts on May 2nd at 12:50 a.m. with the Reichsender Berlin
- the German partial capitulation in Italy (Operation Sunrise) of April 29 comes into force
- the British army marched in Trieste a
- May 3rd:
- At 8:00 a.m., a delegation led by the newly appointed Commander-in-Chief of the Navy, Admiral General von Friedeburg , arrives at the British headquarters and reads a letter from Keitel offering the surrender of the Wehrmacht units operating in the area between Berlin and Rostock
- May 4th:
- the Reichssender Hamburg begins with the announcement "This is Radio Hamburg, a station of the allied military government" under British management
- von Friedeburg signs the partial surrender of the troops of the Commander-in-Chief Northwest to the British Field Marshal Montgomery on behalf of Dönitz. This comes into force on the morning of May 5th in northwest Germany, the Netherlands and Denmark
- According to the rainbow order , which had existed for a long time, but was canceled by Dönitz on the evening of May 4, 1945 , many submarines lying in the harbors were sunk themselves ; the submarines that were still in service call at British or American ports after May 8th
- At the Brenner Pass , US troops advancing south meet units of the 5th US Army , which had occupied Northern Italy from the south, including the remaining fascist state that calls itself the Italian Social Republic
- Salzburg is taken by US troops without a fight
- In the Altaussee salt mine of Nazi looted art , miners and the salt works managed to remove the explosives from the mine and to temporarily close the tunnel entrances by blasting them. The art treasures housed there were saved from destruction and a few weeks later the Americans were able to salvage them and restore them for the most part.
- 5th of May:
- the Army Group G surrendered in Munich
- the military commander of Linz surrenders; US troops liberate the Mauthausen concentration camp in Austria , the last of the concentration camps
- Beginning of the so-called Prague Uprising
- May 6th:
- Berlin is taken as a whole by the Red Army
- a German delegation ( Jodl , von Friedeburg, Oxenius ) arrives at the headquarters of the SHAEF in Reims , where they are authorized by Dönitz by telephone to sign an unconditional surrender
- US troops under George S. Patton reach Pilsen in the Czech Republic
- May 7th:
- Continuation of the meeting of Colonel General Jodl in Reims with the Allied Commander in Chief, General Eisenhower
- At 2:41 a.m., Colonel General Jodl signed the unconditional surrender of the Wehrmacht and all branches of the armed forces in Reims , which should come into force on May 8, 11:01 p.m. Central European Time, which corresponds to 0:01 a.m. German summer time
- Lutz von Schwerin-Krosigk announced the surrender and the end of the Second World War on the Reichsender Flensburg at 12:45
- May 8: VE-Day (for English Victory in Europe Day , day of victory in Europe, often translated as Liberation Day . This means the victory over Nazi Germany or the liberation from National Socialism), people celebrating in photos of these often the V-sign is shown from the index and middle fingers
- Admiral Karl Dönitz , as Hitler's successor, announced the unconditional surrender of the Wehrmacht between 12:30 and 12:40 p.m. on the Flensburg radio station
- Soviet troops occupy Dresden
- British troops and Yugoslav partisans reach Klagenfurt ( Carinthia ), resolution of the prohibition law by the new provisional government of the Republic of Austria
- In the west, on May 8th, the Channel Islands and the cities of Lorient , St. Nazaire and La Rochelle are still under the control of German troops , to the south the Alpine region and islands of the Aegean Sea and in the north Schleswig-Holstein and Norway
- May 8th and 9th: almost two million German soldiers flee from the Soviet sphere of influence to the areas controlled by the Western Allies, especially from Bohemia ( Czechoslovakia ), which was not initially occupied
- seven German submarines in action at the Atlantic, U-190 , U-234 , U-805 , U-858 , U-873 , U-889 , and U-1228 are heading for the American coast and surrendering there until 19 May 1945. The boats U-530 and U-977 flee to Argentina and arrive there months later
- For most people in Europe the end of the war was a happy day - in Germany it was " liberation " initially for many prisoners, people in hiding, forced laborers and opponents of the defeated regime, but a large part of the population experienced the day with mixed feelings: on the one hand, an expected military one Defeat and a moral “collapse” (which triggered the suicides of “convinced” or prominent National Socialist activists and functionaries), on the other hand, the budding hope of a new beginning
- May 9:
- Repetition of the signing of the unconditional surrender in Berlin-Karlshorst to the Soviet Union, on the German side Field Marshal Wilhelm Keitel signs
- the unconditional surrender of the Wehrmacht comes into effect on all fronts in Europe
- Soviet troops enter Graz ( Styria ) without a fight
- May 22nd: on this date the war diary of the High Command of the Wehrmacht ends
| year | Europe and Western Hemisphere | Asia and Pacific | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1939 | |||
| 1940 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | ||
| 1941 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jul – Dec | |
| 1942 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1943 | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1944 | Eastern Europe | Western Europe | |
| Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | Jan – Jun • Jul – Dec | |
| 1945 | Jan – May | Jan – Sep | |
January to September 1945 in Asia and the Pacific
- January 9: Landing of the Americans on the main Philippine island of Luzon ( Battle of Luzon )
- February 19: The island is conquered by the Americans in the battle for Iwo Jima
- March 3: Manila is liberated
- The battle for Mindanao begins (through August)
- The battle for the Visayas begins
- March: The colonial troops of the French Vichy regime, which had cooperated with Japan, leave French Indochina
- 9th March:
- Heavy air strike by American bombers on Tokyo kills over 100,000 people
- In the course of the annexation of Indochina by Japanese troops, the French. Admiral Jean Decoux captured. This formally ends the French Colonial rule that had been de facto Japanese since 1940
- March 18: Air raids on Kyushu
- March 21st:
- Burma is completely liberated
- The Battle of West Henan-North Hubei begins in mainland China
- March 26th to June 30th: Battle of Okinawa , the American. Troops occupy the Okinawa Islands
- March 26th: The Kerama Islands are occupied
- April 1: US Army and Marine Corps units land on the main island of Okinawa Honto
- April 7th: The battleship Yamato , which is to be used in Operation Ten-gō against the invading forces, is sunk
- June 1st: Naha, the island's capital with the Shuri fortress , falls after weeks of fighting over the barrier-like mountain ranges
- April to June: Battle of West Hunan in China
- May 1st to August 15th: Borneo is liberated from the Allies in the course of Operation Oboe
- May 3: Rangoon (Burma) is liberated

- July 16: The Trinity test , the first successful detonation of an atomic bomb (nuclear weapon) , takes place very close to Los Alamos , in Alamogordo
- August 6: at 8:16 am local time, the first atomic bomb (bomb name Little Boy ) was dropped on Hiroshima from the Enola Gay bomber , around 90,000 people died immediately
- August 8th: the Soviet Union declares war on Japan, according to the Potsdam Agreement , and invades Manchuria . Operation Auguststurm is the subsequent military-historical name for the offensive of the Soviet Union. In its course, the Japanese vassal states Manchukuo and Mengjiang , Korea , the prefecture of Karafuto (South Sakhalin ) and the Kuril Islands were conquered by September 2 .
- August 9: at 11:02 am local time, the second atomic bomb (Fat Man) explodes over Nagasaki , killing around 36,000 people immediately
- August 15: Tennō Hirohito (Emperor) reads in the radio speech Gyokuon-hōsō , German about the "transmission of the imperial (literally: diamond) voice" of the imperial decree to end the war at 4 pm, Japanese time. With this decree, he instructs the Japanese government to accept the Potsdam Declaration , the actual decree will be signed on August 13th or 14th and the speech will be recorded on record, on August 14th there will be another attempted coup in the palace district to prevent their radiation and surrender. Although the commanding General Mori Takeshi is shot in the process, the coup is suppressed. On August 16, the army was ordered to cease all fighting
- August 17th: Nationalists proclaim independence in Indonesia , (only after military conflicts, called “police actions” , Indonesia is formally granted independence on December 27th, 1949, until 1962 the Dutch western part of the island of New Guinea remains under the colonial power )
- August 28: Air Force technicians land as the first American unit on the Atsugi airfield near Tokyo in Japan
- August 30th:
- the first regular US occupation troops arrive in Tokyo Bay and go ashore
- British troops march back to Hong Kong a
- September 2, 1945 : The Japanese surrender is signed on the battleship USS Missouri in Tokyo Bay, formally ending World War II
- September 12th: Japanese partial capitulations followed in China (September 9th in Nanjing ) and Singapore (September 12th)
Post-war events
- Founding of the United Nations (UN; the Charter was signed in San Francisco on June 26, 1945)
Europe 1945
- After the occupation of Hungary by Soviet troops on April 4, a Stalinist phase of the political system begins there
- April 25th: last battle of retreat of German troops in Finland ( Lapland War )
- May 4: Karl Scharnagl is appointed Lord Mayor of Munich by the American occupation forces
- May 6th: The Hanover local association of the Social Democratic Party of Germany , initiated by Kurt Schumacher , is brought into being and is the first nucleus for the reconstruction of the SPD
- May 9: Vilhelm Buhl becomes Prime Minister of Denmark
- May and the following period: the situation of the approximately 250,000 German refugees in Denmark: after the withdrawal of the Wehrmacht troops from Denmark, they found shelter in barracks and camps previously used by the Wehrmacht. The last refugees were only brought to Germany from there in February 1949.
- May 10: Soviet units enter Prague
- occupied post-war Austria
- May 23: arrest of the remnants of a "Reich government" under Grand Admiral Karl Dönitz in Flensburg - Mürwik (cf. Dönitz government )
- June 5: The Allied Control Council takes over the supreme government in occupied Germany through the Berlin Declaration
- From the end of the war, the Allies try to return the so-called Displaced Persons (DPs; e.g. former forced laborers, refugees, concentration camp prisoners; between 6.5 and 7 million DPs) from Germany, Austria and Italy to their home countries; this cannot be done within happened a few days, for temporary accommodation is made up of former military barracks and other mass accommodation DP camp (ger .: DP camps ), prisoners of war do not fall within that concept, by the end of 1946, almost six million DPs can "repatriated" are, for approximately one However, for a variety of reasons, returning home is out of the question for a million people
- June 21: the Czechoslovak President Edvard Beneš orders the expropriation of the property of the Sudeten Germans ( Beneš decrees )
- July 17th to August 2nd: Winner conference from Potsdam on defeated Germany: conclusion of the Potsdam Agreement with the agreement on the 5 D: denazification , demilitarization , democratization , dismantling , decentralization
- July 27th: after winning the general election, Clement Attlee takes over the office of British Prime Minister from Winston Churchill
- September 26: The Friedland reception center for returning prisoners of war , refugees and displaced persons from Eastern Germany and Eastern Europe is created near Göttingen
- During Operation Deadlight , 115 surrendered German submarines were sunk by the British Navy between November 27, 1945 and February 12, 1946
- November 11th: the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg receives its own zone of occupation in Germany with the cities of Bitburg and Merzig

War crimes and war crimes trials
- United Nations War Crimes Commission (UNWCC) for the preservation of evidence and criminal penalties for war crimes committed by the Axis Powers (founded October 1943 in London, active until March 1948)
- Office of Strategic Services (OSS), an intelligence service of the US Department of War (1942–1945)
- Camp Ashcan , Allied prison camp in Bad Mondorf , Luxembourg (May to September 1945)
- Camp Dustbin, allied prison camp in Frankfurt am Main
- Beginning of denazification by the Allies with a tribunal procedure (defused by " Persilscheine ")
- October 10, 1945: by order of the Allied Control Council , all National Socialist organizations are dissolved
- October: Stuttgart Confession - Statement by Protestant Christians on the attitude of the churches in the Nazi era
- November 14, 1945: Opening of the 1st Nuremberg Trial (war crimes trial in Germany before an International Court of Justice)
- Follow -up trial against the Wehrmacht High Command and other follow-up trials (see also the article Crimes of the Wehrmacht )
- January 5, 1946: The trial of 23 former concentration camp doctors for crimes against humanity begins before a US military court in Nuremberg
- September 30 and October 1, 1946: pronouncement of the verdicts in the main trial of the Nuremberg trials
- October 12, 1946: Control Council Directive No. 38 aims at the arrest and punishment of war criminals , National Socialists and militarists as well as the internment , control and surveillance of potentially dangerous Germans
- October 16, 1946: Execution of the death sentences in the war crimes trial before the International Court of Justice
- May 16 to July 16, 1946: the Malmedy trial was one of 286 Dachau trials before American military courts against German war criminals
- 30 July-1 August 1946: the secret trial of ex-general Andrei Vlasov for treason ended with the death sentence on August 1 in Moscow's Taganka Prison was completed
1947
- March 11-29, 1947: Höss trial in Warsaw , Poland; against the former concentration camp commandant Höß (Auschwitz)
- 24 November to 22 December 1947 Auschwitz Trial , Kraków , Poland
- January 2, 1947 Start of a four-week war crimes trial against Professor Solms Wilhelm Wittig (Director General of DASAG) and others before the British Military Court in Braunschweig because of their participation in the mineral oil security plan , also known as the Geilenberg program , to implement 350,000 people, including 100,000 concentration camp prisoners , work and thousands died
1948
- February to October 1948: The High Command of the Wehrmacht , also known as the General Trial , is the last and one of the longest of the twelve follow-up trials in Nuremberg against those responsible for the Nazi regime.The indictment against generals of the OKW is filed on November 17, 1947, negotiations last from February by October 1948 (169 days); the verdict is announced on April 14, 1949.
- Denmark, Copenhagen: The trial before the Copenhagen District Court against the four German defendants Werner Best , Hermann von Hanneken , Günther Pancke and Otto Bovensiepen is called the Great War Crimes Trial . You were convicted of crimes committed in Denmark during the German occupation of Denmark. Hanneken was acquitted by the appellate body.
1955
- the last German soldiers and SS members return from Soviet captivity
1963 and later
- The Frankfurt Auschwitz Trials are six German criminal trials against members of the SS guards at the concentration camp before the jury court in Frankfurt am Main in 1963/1966 and in the 1970s; they triggered the statute of limitations debate
2002
The armed forces justice overturned convictions for desertion
- See also: Code names of Nazi secret objects , death marches , so-called end- phase crimes and their prosecution in Germany and Austria after 1945, forced labor (general)
economy and politics
- June 10, 1945: Marshal Zhukov orders in his order No. 2 in the Soviet occupation zone , "to allow the formation and activity of anti-fascist parties"
- November 23: in the American zone of occupation in Germany, parties at the state level are admitted
- December 27: the International Monetary Fund (IMF) is founded
Asia and Pacific
- About the prisoner-of-war camps of a total of 320,000 Allied soldiers in Japanese custody
- September 4, 1945: Japanese units surrender on Wake
- September 5: British troops return to Singapore
- September 6: The US launches Operation Magic Carpet to bring as many soldiers home from the Pacific as possible by Christmas
- September 8: The Supreme Commander for the Allied Powers (SCAP), the allied GHQ - Allied Military Government, was relocated from Yokohama, to Tokyo across from the imperial residence . It was the highest occupation authority in Japan during the occupation. Chief was Gen. until 1951. Douglas MacArthur (1880-1964).
- September 9: Japanese troops in Nanjing , China and Korea capitulate
- September 13th: Japanese troops capitulate in Burma
- War Crimes Trials:
- Tokyo Trials (1946–1948), ( Tōkyō Saiban or 東京 裁判; actually: International Military Tribunal for the Far East )
- End of 1948: Death sentence and execution of Tōjō Hideki (born 1884), General of the Imperial Japanese Army, 40th Prime Minister (Prime Minister and Minister of War from October 17, 1941 to July 22, 1944; seriously injured himself when he was arrested )
- Far Eastern Commission
- War crimes trials in the Dutch East Indies (1946–1949)
Post-war era 1945 to 1949 Consequences and effects
Memorial stones and graves of the Unknown Soldier were soon erected in the theaters of war and in the capitals . They became the location of annual thanksgiving and commemoration ceremonies. Peace memorials and museums about the Second World War followed a little later .
Europe
- the Soviet Union installs communist governments in the part of Europe it occupies
- The change of government in the USA in 1945 also led to a change of policy, Harry S. Truman struck a strictly anti-communist and anti-Soviet course, based on economic superiority and later on the nuclear weapon monopoly
- these conflicts subsequently lead to the so-called Cold War era between the USA and the Soviet Union
- Main article on the flight and expulsion of German civilians from regions of Central and Eastern Europe with very different status (1945–1950)
- in August, 63 former employees of the naval intelligence service, u. also Max Kupfer and Heinrich Böx, from S. Delmer with a staff of editors and archivists from London the German News Service , the first new news agency in Germany built by the Western Allies in Hamburg. As his successor, the German Press Service was founded on January 1, 1947, which was transferred to the German Press Agency in 1949 .
- October 2-15: 3 test kills under British supervision of three V2 (A4) missiles west of Cuxhaven over the North Sea. About 600 involved German prisoners of war; Code name: Operation Backfire . American parallel rocket secret project leads to Operation Overcast and Paperclip (cf. later Hermann Oberth Society )
- 1946
- January 11, 1946: Abolition of the monarchy, proclamation of the People's Republic of Albania by Enver Hoxha
- The deportation / expulsion of over 2 million Germans from Czechoslovakia (expatriation) in 1945 and 1946 officially begins in January (see Beneš decrees )
- May 25, 1946: independence of Jordan
-
Paris Peace Conference (July 29 to October 15), also known as the Conference of the 21 Nations , the winners negotiate the terms of peace with the “smaller” war losers Italy , Romania , Hungary , Bulgaria and Finland at this conference
- It was not until 1990 that the two-plus-four treaty (complete: treaty on the final regulation with regard to Germany), a state treaty between the Federal Republic of Germany, the German Democratic Republic as well as France, the Soviet Union, Great Britain and the United States of America, came into being on the peace settlement of the Allies with Germany . It came into force on March 15, 1991. Germany has finally been freed from restrictions under occupation law.
- September 6, 1946: the American Secretary of State announces that he wants to unite the economy of the zones of occupation in Germany, only Great Britain agrees to do so
- Mass construction of Nissen huts (Nissen-Huts or Quonset huts) to accommodate the bombed-out population and refugees in Schleswig-Holstein and Hamburg in the following winter
- October 20, 1946: last free state election in the Soviet occupation zone
- The Operation Black Tulip , the expulsion of about 3,700 German descent from the Netherlands, started in 1946 and was discontinued late 1948 (legalization of related expropriations 1967)
- 1947
- The Marshall Plan , officially the European Recovery Program ( ERP for short ), becomes the US economic reconstruction program for the devastated Western Europe , the program is later named after the US Secretary of State (and 1953 Nobel Peace Prize laureate ) George C. Marshall, on whose initiative it is going back. It was worked out primarily by William L. Clayton and George F. Kennan in the US State Department , and the plan will be adopted at a meeting of European states on June 6th
- 1948
- March 20, 1948: the ruling Allied Control Council meets for the last time, Soviet Marshal W. Sokolowski leaves the Control Council
- March 31/1. April: The Faroe Islands are given extensive autonomy within the Kingdom of Denmark
- April 3: US President Harry S. Truman signs the Marshall Plan , which frees up US $ 5.3 billion for the reconstruction of Europe
- April 16: Creation of the Organization for European Economic Cooperation ( OEEC )
- June 20: Currency reform in the three German western zones , 40 Deutsche Mark per person are paid out on presentation of identification and food cards
- June 23: Introduction of its own currency in the Soviet zone of occupation (SBZ; Deutsche Mark of the German Central Bank , Berlin)
- In June 1948, the Soviet Union begins blocking supplies to the western sectors of Berlin - this is known as the first battle of the Cold War and ended in the defeat of Stalin's policies
- July 1, 1948: Frankfurt documents formulate lines of development towards the desired independence
- October 2: the Soviet Union begins building nuclear weapons in Siberia
- February 1948 and May 1949: Division of Germany into East and West (February 1948 London Six Power Conference , May 1949 Foreign Ministers Conference of the Allies in Paris
- from 1949
- GG of the Federal Republic of Germany on May 23, 1949, on October 7, 1949, the Second German People's Council , which had already been elected in the Soviet Zone by the Third People's Congress , met as the Provisional People's Chamber and declared the "Constitution of the German Democratic Republic" to be the law applicable there)
- Economic miracle - around 1948–1965
- 1990: Two plus four treaty (complete: treaty on the final settlement with regard to Germany), a state treaty between the Federal Republic of Germany, the German Democratic Republic as well as France, the Soviet Union, Great Britain and the United States of America on the peace settlement of the Allies with Germany. It came into force on March 15, 1991. Germany has finally been freed from restrictions under occupation law.
America
After the Second World War, liberal American business circles feared the loss of important sales markets and trading partners because of the economic decline in Europe. The economic strengthening of Europe also benefits American exports.
From 1947 the USA followed a so-called containment policy , formulated as the Truman Doctrine against the USSR. The governments and economies of European countries including Turkey are also to be tied to the USA. They form a protective zone against Soviet expansion to the west.
- March 12: US President Harry S. Truman proclaims the doctrine in front of the American Congress . It marked the end of the American war coalition with the Soviet Union and marked the beginning of the Cold War with the Iron Curtain in Europe.
Asia and the Pacific
- July 1945 - December 1946: Iran crisis (continuation of the occupation of northern Iran by Soviet forces, negotiations in the UN Security Council )
- January 1, 1946 :
- the last US occupation troops from Iran withdrawn
- Signing of the peace treaty with India , Great Britain and Thailand in Bangkok
- May 3, 1947 : the new Japanese constitution comes into force
- January 4th: Myanmar (Burma, Burma) gains independence from Great Britain
- February 4th: Sri Lanka (then Ceylon) becomes independent
- May 14: Establishment of the State of Israel . Egypt , Saudi Arabia , Jordan , Lebanon , Iraq and Syria declare war on Israel ( 1st Palestinian War )
- September 8: The San Francisco Peace Treaty between Japan and the United States is signed, along with the Treaty on Mutual Security .
- Both treaties come into force in April 1952.
- The Republic of China (Taiwan), the People's Republic of China, the Soviet Union and India were missing from the 50 countries that signed them. A separate peace treaty (Treaty of Taipei) was signed in 1952 with representatives of the Republic of China who had fled to the island of Taiwan. A peace treaty was concluded with the People's Republic of China in 1978. Peace negotiations with the Soviet Union (and from 1992 with the Russian Federation) have repeatedly failed.
- Lieutenant Onoda Hirō (1922-2014) was a Japanese officer who, after the end of the World War, waited until 1974 on the Philippine island of Lubang , which was captured by American troops in February 1945, in a small group of holdouts for orders to fight and only many years later could be convinced by his former superior of the end of the war. He had killed around 30 people and wounded around 100 others and was pardoned by Philippine President Marcos . Compare with Nakamura Teruo (discovered December 1974 in Indonesia ; 1919–1979).
- 1978 : Conclusion of the peace treaty between the People's Republic of China and Japan
Overview of important conferences
Data from conferences on / during the war in the period 1936–1945
- See also Article League of Nations
- 1936: Anti-Comintern Pact
- 1938: Munich Agreement of September 29th
- 1940: Three-Power Pact between the German Empire, Italy and the Japanese Empire (September 27)
- 1941/42:
- British-American Secret Atlantic Conference (August 9-12); Location: Placentia Bay, Newfoundland. There Franklin D. Roosevelt and Winston S. Churchill decided on the Atlantic Charter on the 14th, which other countries joined in September.
- Allied Arcadia Conference in Washington, DC (December 22, 1941 to January 14, 1942, also UN declaration)
- Moscow Conference 1942 (August 12-17), Stalin, Churchill and Harriman
- 1943:
- Allied Casablanca Conference (January 12-24, Morocco)
- Cairo Conference : Allied Politicians, Roosevelt, Churchill, Chiang Kai-shek, and Military Advisers
- Allied Conference of Moscow ( Conference of Foreign Ministers, October 19 to November 1, European Advisory Commission established)
- Allied Conference of Tehran (November 28 to December 1, Iran)
- 1944:
- European Advisory Commission (EAC, London) developed the plan for the creation of 3 zones of occupation in Germany in the London Protocol (September 12)
- 1945:
- Allied Yalta Conference (February 4-11, Crimea , Ukraine )
- The Arab League is founded in Cairo (March 22)
- Tripartite Conference in Berlin - Potsdam Conference (July 17th to August 2nd)
See also
- Equipment and military technology items
- War dead of the Second World War - prisoners of war of the Second World War
- Theater of war Mediterranean
- List of code names / designations of military operations , German aliases for such operations
-
Air War in World War II
- Category of WP articles on air war operations in World War II
- Espionage, secret / intelligence services, decryption, (category)
- Uranium project - the entirety of the work in the German Reich to make the nuclear fission discovered in 1938 technically and possibly militarily usable. There is no evidence that small nuclear weapons tests were undertaken on the German side towards the end of the war. Eight scientists involved in the uranium project were caught by the US Alsos mission on April 24, 1944 and initially interned in Farm Hall (England).
- World War Museum (WW2) , World War II collections
- Timeline Switzerland in World War II
- before and after:
- World War I (main article) - Chronology of the First World War
- The Cold War and proxy wars
literature
- Gerhard Schreiber : The Second World War . Beck, Munich 2002, ISBN 3-406-44764-3 .
- further literature in the main article: Second World War
Web links
- Second World War at the LeMO ( German Historical Museum - virtual museum)
- Timeline of the Shoah and the genocides of the Nazi state (1933–1945)
- Chronology of the Holocaust (Knut Mellenthin, 2005, long version)
Individual evidence
- ↑ Wolfgang Michalka , Documents, 1999, p. 112.
- ^ Hermann Graml: Europe's way to war . Munich 1990, p. 105.
- ↑ Jutta Sywottek: Mobilization for total war. The propaganda preparation of the German population for the Second World War . Opladen 1976, p. 166.
- ^ Text of the agreement printed by: Walther Hofer : The Entfesselung des Second World War. A study of international relations in the summer of 1939 . Frankfurt a. M. 1960, p. 172 f.
- ↑ Klaus Larres: Churchill's Cold War. The Politics of Personal Diplomacy. New Haven 2002, p. 31 f.
- ↑ Hubert Fischer: Der deutsche Sanitätsdienst 1921–1945, Vol. 1; Osnabrück 1982; P. 236.
- ↑ Alexander Kranz (Military History Research Office, ed.): Reichsstatthalter Arthur Grieser and the "civil administration" in Wartheland 1939/40. Population policy in the first phase of German occupation in Poland. ISBN 3-941571-05-2 , p. 19 .
- ↑ OKŚZpNP w Lublinie poszukuje osób mających wiedzę dot. zbrodni popełnionych we wrześniu 1939 przez żołnierzy 29 Dywizji Wehrmachtu na terenie Lipska, Ciepielowa i okolic . Instytut Pamięci Narodowej . Retrieved February 24, 2019.
- ^ Tanner, 2015
- ↑ Gerhard Schreiber, 2007, p. 36; July 3: Jürgen Förster, 1983, p. 9 f.
- ↑ The exact delivery date for him, not before December 7, 1941 1:00 p.m. Eastern Standard Time, of the last part of a note to the USA already prepared for the embassy as a telegram had been deciphered by the US secret services on December 6, 1941 - Joint Committee on the Investigation of the Pearl Harbor Attack (Final report issued: Jun 20, 1946)
- ↑ Quoting from Götz Aly : He reported: “It was written on Monday, April 23, 1945. When it was 3 pm, the first Soviet soldier passed through the gate of our cemetery! His walk was upright and straight. I had the feeling that every step of the way he stepped on a piece of the wicked swastika. We hugged this messenger of freedom, we kissed him - and we cried! "