1952
Portal History | Portal Biographies | Current Events | Annual Calendar | Article of the day
◄ |
19th Century |
20th Century
| 21st Century
◄ |
1920s |
1930s |
1940s |
1950s
| 1960s
| 1970s
| 1980s
| ►
◄◄ |
◄ |
1948 |
1949 |
1950 |
1951 |
1952
| 1953
| 1954
| 1955
| 1956
| ►
| ►►
| 1952 | |
|---|---|
| Explosion of Ivy Mike , the first hydrogen bomb | |
| Fulgencio Batista 's coup in Cuba | The accident-plagued De Havilland Comet is the first jet airliner |
| The "July 23rd Revolution" leads to the overthrow of King Faruq in the Kingdom of Egypt and changes the power structure of the entire region | |
| 1952 in other calendars | |
|---|---|
| Ab urbe condita | 2705 |
| Armenian calendar | 1400-1401 |
| Ethiopian calendar | 1944-1945 |
| Badi calendar | 108-109 |
| Bengali calendar | 1358-1359 |
| Berber calendar | 2902 |
| Buddhist calendar | 2496 |
| Burmese calendar | 1314 |
| Byzantine calendar | 7460-7461 |
| Chinese calendar | |
| - era | 4648-4649 or 4588-4589 |
| – 60-year cycle |
Metal Rabbit (辛卯, 28)– |
|
French Revolutionary Calendar |
CLX - CLXI 160-161 |
| Hindu calendar | |
| – Vikram Sambat | 2008-2009 |
| – Shaka Samvat | 1874-1875 |
| Iranian calendar | 1330-1331 |
| Islamic calendar | 1371-1372 |
| Japanese calendar | |
| – Nengō (era): | Showa 27 |
| - Koki | 2612 |
| Jewish calendar | 5712-5713 |
| Coptic calendar | 1668-1669 |
| Korean calendar | |
| – Dangun era | 4285 |
| – Juche era | 41 |
| Minguo calendar | 41 |
| Modern Olympics | XV |
| Seleucid calendar | 2263-2264 |
| Thai solar calendar | 2495 |
The year 1952 was marked by the ongoing Korean War . In Europe, the Montanunion laid the foundation for what would later become the European Community, and the Federal Republic was thus further integrated into Western Europe.
overview
East Asia/Korean War

The ongoing Korean War developed into a trench warfare along the 38th parallel; Even massive bombing of North Korea's infrastructure did little to change that. The USA was interested in strengthening its position in the Far East and played a key role in the conclusion of a peace treaty with Japan that officially ended the occupation regime. At the same time, the USA demonstrated their military strength against the Eastern bloc by detonating their first hydrogen bomb ; The election of Republican Dwight D. Eisenhower as US President, who replaced Democrat Harry S. Truman , did not change this firm position .
Federal Republic of Germany
On the German question, Adenauer 's CDU government consistently backed integration with the West against the opposition of the SPD. The Soviet Union tried to counteract this development by making the offer of a reunited but neutral Germany with the Stalin note . However, Stalin was not able to prevent the Bonn government from deciding to join the European Defense Community .
The European Coal and Steel Community (= “Montanunion”: Federal Republic of Germany, Benelux countries, France and Italy), founded by the Treaty of Paris on April 18, 1951 , came into force on July 23, 1952.
GDR
On July 24, 1952, the district reforms in the GDR were implemented. This meant a redistribution through local government reforms into districts and districts . The second party conference of the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED) also took place in July 1952 in the Werner-Seelenbinder-Halle in East Berlin . Under the formula of the "planned construction of socialism " coined by Walter Ulbricht , a "Sovietization" of society and a strengthening of state power based on the Soviet model were introduced.
middle East
The Middle East was particularly shaken by two coups d'etat: In July, King Faruq was overthrown by the military in Egypt and his underage son Fu'ad II was formally crowned king; A little later, the military deposed King Talal in Jordan , who was replaced by King Hussein I. In the meantime, Israel has agreed a reparations agreement with the Federal Republic of Germany , which has met with criticism, especially from the Holocaust survivors.
Latin America
In the Latin American countries, Fulgencio Batista 's coup in Cuba and Víctor Paz Estenssoro 's seizure of power in Bolivia are particularly noteworthy; The latter aroused the suspicion of conservative circles in America with his socialization policy.
Africa
In Africa, colonial rule, especially that of the British and French, continued; With the Mau Mau uprising in Kenya , however, the first powerful independence movement made itself heard, which the British opposed by imposing martial law.
technology
In the field of technology, progress was evident, among other things, in the presentation of new supercomputers such as the UNIVAC . The use of jet aircraft ( De Havilland DH.106 Comet ) also became increasingly common in the civil sector, making it possible to fly from England to South Africa or make a return trip across the Atlantic on the same day. Meanwhile, television was introduced in the two German states at the end of the year.
Sports
In sports, the focus was on the Olympic Games. The Winter Games took place in Oslo, the Summer Games , dominated by the achievements of Emil Zátopek , in Helsinki. It was the first Olympic Games after the Second World War in which German athletes were again allowed to take part.
- 28 July Pakistan becomes a full member of the Imperial Cricket Conference (now the International Cricket Council, ICC).
events
politics and world affairs
- January 1: Karl Kobelt becomes President of Switzerland again .
- January 1: Greece 's new constitution comes into force and regulates the distribution of land ownership.
- January 2: The GDR refuses entry to a UN commission. It should clarify the prerequisites for possible pan-German elections.
- January 2: Gustav Heinemann and Helene Wessel found the Notgemeinschaft für den Frieden Europa .
- January 2: The evangelical church president Martin Niemöller travels to the Soviet Union to talk to the leadership there about the release of German prisoners of war.
- January 10: The freighter Flying Enterprise sinks off the coast of England . The captain, Kurt Carlson, was rescued only just before sinking after staying on the list-driving wreck for two weeks.
- January 11: The Bundestag ratifies the treaty establishing the Montanunion against the votes of the SPD .
- January 20: Edgar Faure becomes the new Prime Minister of France, succeeding René Pleven , who resigned on January 7 .
- January 26: In Cairo , after British occupation forces in the Canal Zone besieged and shelled an Egyptian government building in Ismailia , the events of “Black Saturday” ensued. Western facilities such as hotels and cinemas go up in flames during the riots, and offices of the Muslim Brotherhood are also attacked.
- February 5: Otto Grotewohl lays the foundation stone for the new residential building on East Berlin's Stalinallee , one of the most important prestige projects in the GDR.
- February 6: Elizabeth II becomes after the death of her father George VI. Queen and Head of State of the United Kingdom and various other Commonwealth countries . She finds out about it after spending the night at the Treetops Hotel in Kenya .
- February 8: According to the Federal Statistical Office , 9.6 million refugees live in Germany.
- February 8: In the major defense debate, the Bundestag decides with 204:156 votes that the Federal Republic should make a military contribution alongside the western powers.
- February 18: Greece and Turkey join NATO .
- February 20: The member of the Bundestag “Dr. Franz Richter” ( SRP ) is arrested in the Federal Palace on the accusation that he is in fact the former NSDAP head of the Gau head office in Saxony , Fritz Rößler .
- February 21: Bengali Language Movement : The Pakistani government 's decision to use Urdu as the sole official language causes resistance in East Pakistan , where Bengali is spoken almost exclusively . Several demonstrators are killed in clashes with police during student demonstrations in Dhaka .
- February 22: Nicaragua becomes a member of UNESCO .
- February 29 Edgar Faure resigns as Prime Minister of France after just six weeks ; his successor will be Antoine Pinay .
- March 1st: The British give Heligoland back to Germany.
- March 10: Fulgencio Batista's coup d'état in Cuba . Former President Carlos Prío flees to the United States.
- March 10: The Soviet Union submits the Stalin Note to the Western powers .
- March 27: A demolition expert dies in the explosion of a package filled with explosives that was addressed to Chancellor Konrad Adenauer .
- March 29: US President Harry S. Truman , who has been in office since 1945, announces that he will not stand for another full term in the upcoming November elections .
- 15 April: Víctor Paz Estenssoro's coup in Bolivia ; he had the mining industry nationalized and pushed through an agrarian reform.
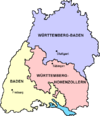
- April 25: The federal state of Baden-Württemberg is formed by the unification of the states of Baden , Württemberg-Baden and Württemberg-Hohenzollern . The FDP politician Reinhold Maier becomes the country's first prime minister at the head of a social-liberal government; the CDU loses its majority in the Bundesrat.
- April 27: Vienna 's St. Stephen's Cathedral , which was destroyed in World War II, is reopened.
- April 28: The peace treaty between Japan and the Republic of China (Taiwan) is signed in Taipei . On the same day, the San Francisco Peace Treaty between the Allies (though excluding the People's Republic of China and the Soviet Union) and Japan comes into force, thereby regaining its sovereignty.
- May 6: Federal President Theodor Heuss advocates using the 3rd stanza of the Deutschlandlied as the German national anthem.
- May 11: On the "Bloody Sunday in Essen" the communist Philipp Müller is shot dead by the police during a demonstration.
- May 13: Jawaharlal Nehru begins his second term as Prime Minister after India's Congress Party is confirmed in India's first general election since independence .
- 26./27. May : In the GDR , a five-kilometer-wide exclusion zone begins to be set up along the demarcation line with the Federal Republic of Germany. This marks the start of the forced resettlement of over 12,000 residents. By order of the SED, the telephone lines between West Berlin and the GDR are cut on May 27.
- May 27: Signature of the treaty establishing the European Defense Community (EDC) .
- June 1: West Berliners are only allowed to enter the GDR with permission.
- June 13: Soviet fighter planes shoot down a Swedish military aircraft over the Baltic Sea.
- June 23: US bombing of North Korea .
- June 30: End of Marshall Plan aid.
- July 8: The first zebra crossings in Germany are laid out for pedestrians in Munich.
- July 9: SED General Secretary Walter Ulbricht announces the decision of the Second Party Conference that “socialism will be built up according to plan” in the GDR, thereby beginning the Sovietization of the GDR.
- July 16: GDR President Wilhelm Pieck inaugurates the Pioneer Camp of the Wilhelm Pieck Pioneer Republic on Lake Werbellinsee .
- July 23: The European Coal and Steel Community comes into force.
- July 23: Coup d'etat in Egypt : Imprisonment of King Faruq by General Muhammad Nagib .
- July 23: The People's Chamber of the GDR decides to dissolve the five central German states in favor of 14 districts .
- July 26: Abdication of Faruq. Proclamation of Fu'ad II as the last Egyptian-Sudanese king.
- August 11: King Talal of Jordan is deposed by the military; his successor is Hussein I.
- August 12: About 30 Russian-Yiddish writers, artists and intellectuals are executed in Moscow's Lubyanka on the “ Night of the Murdered Poets ”; the exact number of victims is uncertain. Many of them were associated with the Jewish Anti-Fascist Committee , including Itzik Feffer , Leib Kvitko , Solomon Abramovich Lozovsky and Perez Markish .
- August 14: The Federal Republic of Germany becomes a member of the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
- August 14: In an article appearing in L'Observateur under the heading Trois mondes, une planète (“Three worlds, one planet”), the French demographer and historian Alfred Sauvy formulates the term “ Third World ” for the first time.
- August 24: British troops evacuate the Suez Canal .
- September 10: In the Luxembourg Agreement , the Federal Republic of Germany undertakes to pay compensation to Jewish victims of National Socialism in the amount of DM 3.5 billion.
- 28 September: Erich Ollenhauer succeeds the late Kurt Schumacher as SPD leader .
- October 3: First British atomic bomb detonated off Australia 's Montebello Islands .
- 5 to 14 October : XIX. Party Congress of the CPSU
- October 17: Walter Freitag becomes the new DGB chairman, succeeding Christian Fette .
- 20 October: British Governor Evelyn Baring, 1st Baron Howick of Glendale declares a state of emergency in Kenya , citing the Mau Mau Uprising .
- October 23: The SRP is banned in the Federal Republic of Germany.
- November 4: Republican Dwight D. Eisenhower is elected 34th President of the United States . He wins over his Democratic challenger Adlai Stevenson .
- 10 November: United Nations Secretary-General Trygve Lie resigns from office.
- November 18: Later Kenyan President Jomo Kenyatta is imprisoned by the British colonial authorities for taking part in the Mau Mau uprising .
- November 21: In Czechoslovakia , there are show trials against opponents of Prime Minister Gottwald within the party. Eleven death sentences are imposed in the Slánský trial .
- November 29: Foundation of the All- German People's Party (GVP) by the Bundestag deputies Thea Arnold , Helene Wessel (both German Center Party ), Hans Bodensteiner ( CSU ) and Hermann Etzel ( Bavarian Party ) as well as the later Federal Presidents Gustav Heinemann and Johannes Rau .
- November 29: Newly elected US President Eisenhower visits Korea to explore a solution to the Korean War .
- December 10: Nagib's military government repealed the 1923 constitution of the Kingdom of Egypt .
- December 25: During a border incident in Berlin-Frohnau, a West Berlin constable is shot dead by Soviet soldiers.
- Signing of the European Defense Community Treaty by France, the Federal Republic of Germany, Italy and the three Benelux countries
business
- 2 May: British airline BOAC becomes the first company to use a jet airliner on scheduled services. A De Havilland DH.106 Comet flies the London– Johannesburg route .
- May 21: Queen Juliana in the Netherlands hands over the Amsterdam-Rhine Canal to its intended use.
- 12 June: In the Wedel district of Schulau on the Lower Elbe, the Willkomm-Höft ship greeting system goes into operation. Ships calling at the Port of Hamburg are greeted or said goodbye with it.
- 24 June: first publication of the Bild (newspaper)
- Founding of the first German airline after the Second World War ( Südflug International ) by Rul Bückle
science and technology
- January 2nd: The first cars are produced at the Ford company in Cologne .
- July 18: The German Fulbright Commission is established. With the Fulbright program , it enables students and academics to study in the USA and vice versa in Germany via scholarships .
- August 26: For the first time, a British jet plane makes a return flight across the Atlantic in one day.
- September 11: The American doctor Charles A. Hufnagel puts the first patient in an artificial heart valve that he developed himself.
- September 17: EJ Smith flies 1,958.2 km in his Bell 47D helicopter: world record.
- October 14: The Cité radieuse is opened in Marseille. The building is the first of five modern residential units designed by the architect Le Corbusier .

- November 1 (local time) : US nuclear physicists detonate the first hydrogen bomb on Eniwetok Atoll in the Pacific Ocean . The test, codenamed Ivy Mike , incidentally leads to the discovery of the chemical elements fermium and einsteinium .
- December 21: In the GDR , television begins as a "public test program" from Berlin-Adlershof with two hours of daily transmission time.
- December 25: From Christmas on there are regular official television programs in the Federal Republic of Germany, which are broadcast by the Northwest German Broadcasting Corporation . Only 1,000 connections are registered.
Culture
- January 13: World premiere of the comic opera Die Schlaue Susanne by Franz Xaver Lehner in Nuremberg
- January 17: At the premiere of the film Hanna Amon with Veit Harlan , there are protests because of its Nazi past.
- February 7: Wolfgang Koeppen 's novel Tauben im Gras is published.
- February 17: First performance of the lyrical drama Boulevard Solitude by Hans Werner Henze at the Staatstheater in Hannover .
- March 26: Premiere of the opera Leonore 40/45 by Rolf Liebermann in Basel .
- March 29: Doctor Eisenbart , a powerful spectacle in seven scenes by Nico Dostal (music) and Hermann Hermecke (libretto) has its world premiere in Nuremberg .
- April 19: The rediscovery of Emil Nolde 's work begins with an exhibition in Mannheim .
- May 16: Premiere of Oscar Straus ' operetta Bozena in Munich
- June 10: The 1952 Goethe Prize is awarded to the playwright Carl Zuckmayer .
- June 12: Premiere of the opera Trouble in Tahiti by Leonard Bernstein at Brandeis University in Waltham , Massachusetts .
- June 16: At the Hugo Gallery in New York City , Andy Warhol presents Fifteen Drawings Based on the Writings of Truman Capote , his first solo show.
- 23 June: The new version of Paul Hindemith 's opera Cardillac – extended from three to four acts and newly arranged by the composer – is premiered at the Stadttheater in Zurich .
- September: Beyond Eden by John Steinbeck is published.
- August 16: Pig or Not Pig , another novel by PG Wodehouse and starring the absent -minded Lord Emsworth as the protagonist, first appears as a serial in Collier's Weekly , US magazine .
- September 4: Ernest Hemingway 's novel The Old Man and the Sea is published.
- September 23: Premiere of the ballet opera Prussian Fairy Tale by Boris Blacher in the German State Opera .
- 25 September: World premiere of Agatha Christie 's play The Mousetrap at the Ambassadors Theatre, London .
- September 30: The New York Broadway Theater premieres the first cinerama-screened film , This is Cinerama .
- 31 December: World premiere of Siegfried Koehler 's operetta Alles Kapriolen in Koblenz
- Samuel Beckett 's play Waiting for Godot is published; it premieres in 1953.
Sports
- 2 February: The Westfalenhalle , with 13,500 seats the largest sports hall in Europe at the time, is inaugurated in Dortmund .
- The VI Winter Olympics will be held February 14–25 in Oslo , Norway .
- May 18th to September 7th: Hosting of the 3rd Formula 1 World Championship
- The XV Summer Olympics will be held in Helsinki , Finland , from July 19 to August 3 .
- June 8: In Cologne , middleweight Peter Müller , nicknamed de Aap , knocks out the referee during a boxing match
- 4 July: Frank Sedgman ( USA) defeats Jaroslav Drobný (Egypt) in the Wimbledon tennis final .
- July 20: Fausto Coppi wins the Tour de France .
- September 7: Italian Alberto Ascari wins the Formula One World Championship .
- September 14: German altitude record of 13,015 m in a glider by Joachim P. Kuettner as part of the "Jetstream Project"
- October 16: KFC Phönix and VfB Mühlburg merge to form Karlsruher SC .
disasters
- April 27: The fast minesweeper USS Hobson sinks during maneuvers in the Atlantic after colliding with the aircraft carrier Wasp (both USA). 176 dead and many injured.
- October 8: One of the worst rail disasters in British Rail history occurs at Harrow & Wealdstone station , north-west of London . 112 people die and 340 are injured when an express train rams the rear of a commuter train and another express train goes in the opposite direction into the accident site.
- November 5: A tsunami destroys the city of Severo-Kurilsk in the Kuril Islands, killing 2,336 people.
- 5th-9th December: London : A smog catastrophe claims several thousand lives.
Minor accidents are listed in the sub-articles of Disaster .
Born
January
- January 1 Ahn Sung-ki , South Korean actor
- January 1: François Chatriot , French rally driver
- January 1: Steve Earle , American racing driver
- January 1: Ítalo Estupiñán , Ecuadorian-Mexican soccer player († 2016)
- January 1: Knut Folkerts , former RAF terrorist
- January 1: Urs Leimgruber , Swiss saxophonist
- January 2: Indulis Emsis , Latvian biologist, politician and former Prime Minister
- January 2: Hartmut Büttner , German politician
- January 2: Konrad Steffen , Swiss glaciologist († 2020)
- January 3: Adelheid Arndt , German actress
- January 3: Gianfranco Fini , Italian politician
- January 4: Rudolf Borchert , German politician (died 2019)
- January 4: Josef Cap , Austrian politician
- January 4: Michael Hoenig , German musician
- January 5: Uli Hoeneß , German soccer player and manager
- January 5: Leif Øgaard , Norwegian chess player
- January 6: Wolfgang Merkel , German political scientist
- January 7 Sammo Hung , Chinese martial artist
- January 7: Hans-Josef Fell , German politician
- January 8: Klaus-Peter Flosbach , German politician
- January 9: Marek Belka , Prime Minister of Poland
- January 9: Hans-Martin Leili , German footballer
- January 10 William Parker , American jazz bassist
- January 10: Oleh Romanyshyn , Ukrainian chess grandmaster
- January 10 Monika Schnaitmann , German politician
- January 10: Gerhard Schöne , German singer-songwriter
- January 11: Bille Brown , Australian actor († 2013)
- January 11 Lucas da Costa , East Timorese politician, independence activist (died 2019)
- January 11: Jens Goebel , German politician
- January 11 Diana Gabaldon , American contemporary author
- January 11 Lee Ritenour , American musician and producer
- January 12: John Walker , New Zealand track and field athlete
- January 12: Florian Havemann , German writer, painter and composer
- January 12 Ricky Van Shelton , American country music singer
- January 12 Walter Mosley , American crime writer
- January 13: Max Beck , Liechtenstein luger (died 2019)
- January 13: Klaus Rapp , German politician
- January 13: Pekka Pohjola , Finnish musician († 2008)
- January 14 Gaby Berger , German pop singer
- January 14 Michele Castoro , Italian theologian, Archbishop of Manfredonia (died 2018)
- January 14: Călin Popescu-Tăriceanu , Romanian politician and head of government
- January 14: Klaus Jensen , German politician; Secretary of State
- January 15: Juan Antonio Ahuntchain Alles , Uruguayan soccer coach and soccer player
- January 15: Boris Blank , Swiss musician
- January 15 C. George Boeree , American psychologist (died 2021)
- January 16: Piercarlo Ghinzani , Italian racing driver
- January 17: Saulius Arlauskas , Lithuanian jurist, legal philosopher
- January 17: Michael Sommer , Federal Chairman of the German Trade Union Confederation (DGB)
- January 17: Lothar Vogt , German chess grandmaster
- January 18 Michael Jüllich , German percussionist and composer
- January 18: Wim Rijsbergen , Dutch footballer and coach
- January 18: KM Veerappan , Indian gang boss (d. 2004)
- January 19: Erwin Kaipel , Austrian politician (SPÖ)
- January 19: Christiane Kuby , German translator
- January 20: Ute Hommola , German athlete
- January 20: Thomas Reuter , German composer, choir director and pianist
- January 20: Ann Savoy , American Cajun musician (vocals and guitar)
- January 20 Hans-Joachim Schabedoth , German trade unionist and politician († 2020)
- January 20 Paul Stanley , American guitarist and singer
- January 21 Karl Timmermann , German singer, lyricist, composer and producer
- January 21 Werner Grissmann , Austrian alpine skier
- January 21: Mikhail Umansky , Russian-German chess champion (died 2010)
- January 22: Stefano Bartolini , Italian political scientist
- January 22 Aloys Wobben , German electrical engineer and entrepreneur (died 2021)
- January 23: Dorothee Eberhardt , German composer
- January 23: Henrique da Costa Mecking , Brazilian chess champion and clergyman
- January 23: Jaroslav Pouzar , Czechoslovak ice hockey player
- January 23: Reinhard Saftig , German football coach
- January 24: Siegmund Ehrmann , German politician
- January 24 Fausto Gaibor García , Ecuadorian Catholic bishop (died 2021)
- January 25: Malan Marnersdóttir , Faroese literary scholar
- January 26: Frédéric Lodéon , French cellist and conductor
- January 26 Konrad Samwer , German physicist and materials scientist
- January 27: Asma Jilani Jahangir , Pakistani lawyer (died 2018)
- January 27 Billy Johnson , American football player
- January 28: Richard Glatzer , American director and film producer († 2015)
- January 28: Michael Jones , French singer and guitarist
- January 29: Jakob Brechbühl , former Swiss soccer player
- January 29: Klaus-Uwe Nommensen , German Protestant theologian and author
- January 30: Valery Mikhailovich Khalilov , Russian general and composer (died 2016)
- January 30 Christa Moog , German writer
- January 30: Lorenz-Günther Köstner , German football coach
- January 31: Ulrike Apel-Haefs , German politician (died 2009)
- January 31: Rodolfo Daluisio , Argentine composer and music educator
- January 31 Leslie Lemke , American musician and composer
February
- February 1: Norbert Barthle , German politician, MP
- February 2: Jeffrey Archibald , New Zealand hockey player
- February 2: Yuri Boidman , Ukrainian-German chess champion
- February 2 Agenor Girardi , Brazilian Catholic Bishop of União da Vitória (died 2018)
- February 2: Reinhard Häfner , German soccer player (died 2016)
- February 2: Ralph Merkle , pioneer of asymmetric cryptosystems
- February 2 Park Geun-hye , South Korean politician
- February 2: Carol Ann Susi , American actress (died 2014)
- February 2: Michael Wickmann , German local politician
- February 3 Cellou Dalein Diallo , Prime Minister of Guinea
- February 3 Andrei Makeyev , Soviet basketball player (died 2021)
- February 4: Kudsi Erguner , Turkish nay player and composer
- February 4 Kurt Klühspies , German handball player
- February 4: Dominique Lacaud , French racing driver
- February 5: Daniel Balavoine , French singer (died 1986)
- February 6: Viktor Giacobbo , Swiss author, cabaret artist, presenter and actor
- February 6: Ricardo Antonio La Volpe , Mexican soccer player and coach
- February 6: Christian Mähr , Austrian editor and writer
- February 7: Hans-Jürgen Appelrath , German computer scientist († 2016)
- February 7 Antonio Catricalà , Italian lawyer, university lecturer and manager († 2021)
- February 7: Wolfgang U. Eckart , German medical historian († 2021)
- February 7: Vasco Rossi , Italian singer, songwriter and radio host
- February 7: Didi Senft , German artist and inventor, "Tourteufel"
- February 8 Francisco Marinho , Brazilian soccer player (died 2014)
- February 9 Tony Attwood , British psychologist
- February 9 Zhang Jilong , Chinese football official
- February 10: Frank Bsirske , German union official, chairman of the ver.di union
- February 10: Lee Hsien Loong , Prime Minister of Singapore
- February 12: Patrick Gaillard , French Formula One racing driver
- February 12: Anton Himstedt , German sculptor
- February 12: Heinz-Josef Koitka , German footballer
- February 12: Simon MacCorkindale , British actor and filmmaker (died 2010)
- February 12 Michael McDonald , American rock singer and keyboardist
- February 12: Angelika Speitel , German RAF terrorist
- February 13: Freddy Maertens , Belgian cyclist
- February 13: Hans-Joachim Fuchtel , German politician
- February 13 Irene Dische , German-American writer
- February 14 Marlies Ameling , German designer and industrial designer
- February 14: Peter-Michael Diestel , Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of the Interior of the GDR
- February 14 Sushma Swaraj , Indian politician (died 2019)
- February 14: Leslie Wilson , New Zealand field hockey player
- February 15: George Antonysamy , Archbishop of India
- February 15: Bill T. Jones , American dancer and choreographer
- February 15: Hans Kruppa , German writer
- February 15: Tomislav Nikolić , Serbian politician
- February 15 Arthur Parkin , New Zealand field hockey player
- February 15 Nikolai Yevgenievich Sorokin , Russian actor and director (died 2013)
- February 15 Rosemarie Tüpker , German music therapist and musicologist
- February 16: James Ingram , American soul musician, songwriter and record producer († 2019)
- February 16 – Jan Kerouac , American author (died 1996)
- February 16: Wolfgang Lippert , German singer, presenter and entertainer
- February 17: Anders Åslund , Swedish economist
- February 17 Karin Büttner-Janz , German artistic gymnast and clinic director
- February 17: Ludger Volmer , German politician
- February 17: Peter Freund , German writer
- February 18: Efva Katarina Attling , Swedish actress and model
- February 18: Hansjörg Aemisegger , Swiss cyclist
- February 18: Johann Schneider-Ammann , Swiss entrepreneur and politician
- February 19 Amy Tan , Chinese-US writer
- February 19: Ryū Murakami , Japanese author
- February 19: Matthias Kurth , President of the Federal Network Agency (regulatory authority)
- February 19: Danilo Türk , Slovenian politician
- February 20 Udo Böbel , German handball player and handball coach
- February 20 Abdalá Bucaram , Ecuadorian lawyer and politician
- February 20: Hans-Jürgen Irmer , German politician
- February 21 Vitaly Churkin , Russian UN diplomat (died 2017)
- February 21: Jean-Jacques Burnel , Anglo-French musician
- February 22: Bernd August , German boxer (died 1988)
- February 22: Thomas Wessinghage , German athlete
- February 23: Sören Åkeby , Swedish football coach
- February 23: Peter Ammon , German diplomat
- February 23 Pedro Pérez , Cuban track and field athlete, triple jumper († 2018)
- February 23: Stefan Winghart , German prehistoric archaeologist, monument conservator and state conservator
- February 23: Knud Wollenberger , German poet (died 2012)
- February 24 – Fred Dean , American football player († 2020)
- February 24: Jadwiga Rappé , Polish singer
- February 24: Bruno Zuppiger , Swiss politician of the SVP († 2016)
- February 25: Kristin Heyne , German politician (died 2002)
- February 25: Joey Dunlop , British motorcycle racer (d. 2000)
- February 25: Christian Kolonovits , Austrian composer and conductor
- February 26: John Giblin , British bassist
- February 28 Rudolf Bastiaan Andeweg , Dutch political scientist
- February 28 Arthur Barrow , American musician
- February 28: Michel Bury , French sports shooter
- February 29: Raúl González , Mexican walker and Olympic gold medalist
- February 29 Holger Oertel , German handball goalkeeper and handball coach
- February 29 Gérard Pansanel , French jazz guitarist
- February 29: Hermann Schützenhöfer , Austrian politician
March
- March 1: Matthäus Strebl , German politician and MP
- March 2 Nugsar Ashuba , Abkhazian politician
- March 2: Sergei Vadimovich Stepashin , Prime Minister of Russia
- March 3: Wolfgang Kubicki , German politician
- March 3: Günter Assenmacher , Official of the Archdiocese of Cologne
- March 4 Claudia Guderian , German author and journalist
- March 4: Terje Andersen , Norwegian speed skater
- March 4 Umberto Tozzi , Italian musician
- March 5: Rodrigo Aguilar Martínez , Mexican bishop
- March 5: Alan Clark , British keyboardist
- March 5: Hartmut Heinrich , discoverer of the so-called. Heinrich events
- March 5: Yuri Mikhailovich Kutsenko , Soviet track and field athlete, decathlete († 2018)
- March 5: Fernando da Piedade Dias dos Santos , Prime Minister of Angola
- March 5 Isatou Njie Saidy , Vice President of The Gambia
- March 6: Marielle Labèque , French pianist (Duo Katia and Marielle Labèque )
- March 7 Stelian Anghel , Romanian football player and sports official (died 2009)
- March 7: William Boyd , Scottish novelist, screenwriter and director
- March 7: Dominique Mamberti , French Curia cardinal
- March 7: Wolf Rauch , Austrian information scientist
- March 8: Pius Segmüller , Commander of the Pontifical Swiss Guard, National Council
- March 9 Bill Beaumont , English rugby player
- March 9: Reto Parolari , Swiss conductor († 2019)
- March 9: Amir Peretz , Israeli politician and trade unionist
- March 10: Morgan Tsvangirai , Zimbabwean politician (died 2018)
- March 11: Douglas Adams , English novelist (died 2001)
- March 11: Pier Paolo Bianchi , Italian motorcycle racer
- March 11: Ricardo Martinelli , Panamanian politician and entrepreneur
- March 12: Yasuhiko Okudera , Japanese soccer player
- March 12 Randy Stonehill , American singer and composer
- March 13: Wolfgang Rihm , German composer, musicologist and essayist
- March 14: Jaime Caruana , Spanish banker
- March 14: Martin E. Dempsey , US Army General
- March 16 Alice Hoffman , American author
- March 16: Jan Jóźwik , Polish speed skater (died 2021)
- March 17 Susie Allanson , American country music singer
- March 17: Manolo Badrena , Puerto Rican percussionist
- March 18: Pat Eddery , Irish jockey (died 2015)
- March 18 Dennis Chun , American actor
- March 18: Michaela May , German actress
- March 18: Peter Prager , German actor
- March 18: Salome Zurabishvili , Georgian Foreign Minister
- March 19 Wolfgang Ambros , Austrian musician, songwriter
- March 19: Joseph Borġ , Maltese politician and EU Commissioner
- March 19: Jörg Pfeifer , German track and field athlete
- March 19: Ulrich Schröder , German lawyer and bank manager († 2018)
- March 19: Joseph J. Urusemal , President of the Federated States of Micronesia
- March 19 Harvey Weinstein , American film producer
- March 20: Geoff Brabham , Australian motor racing driver
- March 21: John Fergus , American racing driver
- March 21: John Holmes , British rugby player (died 2009)
- March 23: Peter Louis Caku , Myanmar Bishop of Kengtung († 2020)
- March 23: Bodo Dieckmann , German archaeologist
- March 23: Jan Hadermann , Belgian composer
- March 23: Pola Kinski , German actress
- March 23 Kim Stanley Robinson , American science fiction writer
- March 23: Rex Tillerson , American manager and politician
- March 23: Franziska Walser , German actress
- March 24: Dioni Fernández , Dominican merengue musician
- March 24 Reinhard Genzel , German astrophysicist
- March 24: Allan Guggenbühl , Swiss psychologist and expert on youth violence
- March 25 Jung Chang , Chinese-born British writer
- March 25: Antanas Mockus , Colombian philosopher, mathematician and politician
- March 26: Yoshitaka Amano , Japanese artist
- March 26: David Amess , British politician (died 2021)
- March 26: Peter Augar , German football referee
- March 26: Bodo Henkel , German presenter and voice actor
- March 26: Wolfgang Hegewald , German writer
- March 26: Didier Pironi , French Formula 1 racing driver (d. 1987)
- March 26: Pavol Szikora , Czechoslovak walker (died 2021)
- March 26: Wang Jun , Chinese politician
- March 27: Felix Haug , Swiss pop musician († 2004)
- March 27 Pamela Roylance , American actress
- March 27: Maria Schneider , French actress († 2011)
- March 28: Keith Ashfield , Canadian politician (died 2018)
- March 28: Tony Brise , British Formula One racing driver (d. 1975)
- March 29: Rainer Bonhof , German footballer and coach
- March 29: Teófilo Stevenson , Cuban amateur boxer (died 2012)
- March 30: Jose F. Advincula , Philippine Archbishop of Manila and Cardinal
- March 30 Wallace Arthur , British zoologist
- March 31 Horst Bredemeier , German handball coach and official
- March 31: Nelly Miricioiu , Romanian opera singer, soprano
- March 31: Paul-Heinz Wellmann , German track and field athlete
- March 31 Vanessa del Rio , American model, pornographic actress and entrepreneur
- March: Chen Zhenggao , Chinese politician
- March: Yuan Chunqing , Chinese politician
April
- April 1 Angelika Bahmann , German canoeist
- April 1: Uwe Behrendt , German right-wing extremist (died 1981)
- April 1: Hans-Georg Bürger , German racing driver (died 1980)
- April 1: Abdel Basset Ali al-Megrahi , Libyan assassin (died 2012)
- April 2: Thomas Bscher , German racing driver, banker and manager
- April 2 Alex Conti , German guitarist
- April 2: Richard Spénard , Canadian racing driver
- April 3: Beat Fäh , Swiss director, actor and author
- April 3 Dieter Krause , German handball player
- April 3: Franz XA Zipperer , German music journalist (died 2015)
- April 4 Rosemarie Ackermann , German track and field athlete
- April 4 Pat Burns , Canadian ice hockey player and coach (died 2010)
- April 4: Klaus Franz , German union official
- April 4: María Mendiola , Spanish crooner († 2021)
- April 4 – Gary Moore , Northern Irish blues and rock musician († 2011)
- April 4: Villy Søvndal , Danish politician
- April 4: Pius Walder , Austrian lumberjack and poacher (died 1982)
- April 5 Mitch Pileggi , American actor
- April 6: Michael Vesper , German politician
- April 7 Rubén Galván , Argentine soccer player (died 2018)
- April 7: Hans-Ulrich Krüger , German politician, MP
- April 7: Vladimir Alexandrovich Sharov , Russian writer (died 2018)
- April 8: Arcadi Gaydamak , Israeli billionaire
- April 8 Kim Warwick , Australian tennis player
- April 9: Jerzy Szmajdziński , Polish politician (died 2010)
- April 10: Grigory Alexeyevich Yavlinsky , Russian politician from the Yabloko party
- April 10 Steven Seagal , American actor
 Steven Seagal , 2007
Steven Seagal , 2007 - April 10: Richard Wagner , German writer
- 11 April: Karl-Heinz Dellwo , German publisher, former RAF terrorist
- April 12 Hellmut Hattler , German jazz and rock bassist
- April 12: Hermann Strampfer , German lawyer and civil servant († 2015)
- April 12 Christof Wetterich , German theoretical physicist
- April 13 Nari Erick Avari , Indian actor
- April 13 Thomas Milani , Canadian-Italian ice hockey player (d. 2021)
- April 14 Udo Voigt , German political scientist and politician
- April 15: Glenn Shadix , American actor (died 2010)
- April 16: Yochanan Afek , Israeli-Dutch chess composer and player
- April 16: Peter Arnold , German horn player
- April 16: Ulrich Deuschle , German politician
- April 16 Rico Saccani , American conductor
- April 16: Alexander Tschäppät , Swiss politician (died 2018)
- April 16 Billy West , American animated series and film voice talent
- April 16 Peter Westbrook , American fencer
- April 17: Helge Achenbach , German art consultant
- April 17: Joe Alaskey , American actor and voice actor († 2016)
- April 17: Ernest Wichner , German writer
- April 18: Enzo Calderari , Swiss entrepreneur and racing driver
- April 18 Andreas Hellmann , German doctor and medical official
- April 18 Bo Katzman , Swiss musician, singer
- April 18: Hans-Ulrich Seidt , German diplomat
- April 19: Alexis Argüello , Nicaraguan boxer and politician (died 2009)
- April 20: Peep Aru , Estonian politician
- April 20: Karl Friedrich von Hohenzollern , German entrepreneur
- April 21: Soslan Petrovich Andiyev , Soviet wrestler (died 2018)
- April 21 Pascal Auberson , Swiss singer, percussionist and pianist
- April 22: François Berléand , French actor
- April 22 Marilyn Chambers , American pornographic actress († 2009)
- April 22 Dave Mancini , American percussionist, music educator and composer
- April 22: Alfons Karl Zwicker , Swiss composer and pianist
- April 23: Esther Dischereit , German writer
- April 23 Narada Michael Walden , American producer and singer
- April 24 Jean-Paul Gaultier , French fashion designer
- April 25 Vladislav Alexandrovich Tretyak , Russian ice hockey player
- April 25: Claus Bernhard Auer , German diplomat
- April 25: Michael Aufhauser , German animal rights activist
- April 25: Jacques Santini , French football coach and football player
- April 26 Renate Ackermann , German politician
- April 27: Ari Vatanen , Finnish rally driver and politician
- April 28 Mary McDonnell , American actress
- April 29: Barbara Hendricks , German politician
- April 29 David Icke , British publicist and footballer
- April 29: Anatoly Nogovitsyn , Russian colonel general (died 2019)
- April 29: Karl Rauber , German politician
- April 29 Dietmar Schmidt , German handball player and handball coach
- April 29: Dave Valentin , American jazz flutist († 2017)
- April 30: Jacques Audiard , French film director and screenwriter
- April 30: Martin Gutzeit , founder of the Social Democratic Party of the GDR
May
- May 2 Christopher Doyle , Australian cinematographer, photographer, director, screenwriter
- May 2nd: Gotthold Schwarz , Thomaskantor and director of the Thomanerchor Leipzig
- May 3: Robert Donatucci , American politician (died 2010)
- May 3: Ruth W. Lingenfelser , German poet
- May 3 Christine Prinsloo , Zimbabwean field hockey player
- May 3: Christian Schramm , former mayor of Bautzen
- May 3: Joseph William Tobin , American cardinal, Archbishop of Newark
- May 3 Allan Wells , British athlete
- May 4: Hans Affenzeller , Austrian politician
- May 4: Günter Aumann , German mathematician
- May 4: Antony Hamilton , British film actor (died 1995)
- May 4: This Jenny , Swiss entrepreneur and politician (died 2014)
- May 4 Vera Lengsfeld , German politician
- May 4 Bärbel Höhn , German politician
- May 5: Maia Ciobanu , Romanian composer
- May 5: Edwin M. Lee , US Mayor (died 2017)
- May 5: Jorge Llopart , Spanish walker († 2020)
- May 5 Ryszard Szeremeta , Polish composer, conductor and jazz singer
- May 6: Claudius Armbruster , German Romanist
- May 6 Christian Clavier , French actor
- May 6: Andrea Čunderlíková , Czech actress
- May 6: Michael O'Hare , American actor (died 2012)
- May 6: Alexander Radszun , German actor
- May 6: Herbert Rusche , German politician and gay activist
- May 7: Stanley Dickens , Swedish racing car driver
- May 8: Matti Geschonneck , German director
- May 8 Charles J. Camarda , American astronaut
- May 8 Vittorio Sgarbi , Italian art critic and politician
- May 9 Dick Annegarn , Dutch singer, songwriter and guitarist
- May 10 - Kikki Danielsson , Swedish singer and accordionist
- May 10: Vanderlei Luxemburgo , Brazilian soccer coach
- May 10 Mario Capezzuto , German politician and MdL
- May 10: Ulrich Hahnen , German politician (died 2016)
- May 10: Roland Kaiser , German crooner
- May 10 Sly Dunbar , Jamaican drummer and producer
- May 11 Frances Fisher , British-American theater and film actress
- 11 May: Hallur Ellingsgaard , Faroese Republican Party leader
- May 11 Renaud , French musician
- May 11 Shohreh Aghdashloo , Iranian actress
- May 12 Carlos Burga , Peruvian boxer (died 2021)
- May 12: André Greiner-Pol , German rock musician († 2008)
- May 12: Patrick Hooper , Irish marathon runner (died 2020)
- May 12 Margie Mahoney , American cross-country skier
- May 13: Olaf Bernstengel , German puppeteer (died 2020)
- May 13: Mary Cleere Haran , American singer and author († 2011)
- May 14 Bolat Atabaev , Kazakh theater director and human rights campaigner (died 2021)
- May 14 David Byrne , British musician
- May 14 Robert Zemeckis , American director and film producer
- May 15 Christine Goetz , German art historian († 2020)
- May 15 Herbert Marxer , Liechtenstein ski racer
- May 15: Peter Strieder , German politician
- May 16 James Herndon , American media psychologist
- May 16 Erich Weishaupt , German ice hockey player
- May 17 Bernhard Brink , German schlager singer and TV presenter
- May 17: Eva Schmidt , Austrian writer
- May 17: Klaus Zapf , German entrepreneur (died 2014)
- May 18 Jeana Yeager , US test pilot
- May 18 George Strait , American country musician
- May 19: Gustav Deutsch , Austrian film artist († 2019)
- May 19 Guri Ingebrigtsen , Norwegian doctor and politician (died 2020)
- May 19: Lambertus van Marwijk , Dutch footballer and coach
- May 19: Cristóbal López Romero , Spanish priest, Archbishop of Rabat, cardinal
- May 19: Heiko Wildberg , German politician
- May 20: Christian Klar , German terrorist (RAF)
- May 20: Roger Milla , Cameroonian footballer
- May 20 Rick Upchurch , American football player
- May 21 Mr. T , American actor
- May 22: Bernhard Brinkmann , German politician
- May 22: Peter Jaskola , Polish Catholic priest and professor of theology
- May 23 Deborah Adair , American actress
- May 23 Christina Vanja , German historian and archivist
- May 24 Ranieri Randaccio , Italian racing driver
- May 25: Vera Vasilyevna Anissimova , Soviet sprinter
- May 25: Philipp Graf Lerchenfeld , German politician (died 2017)
- May 26 Ursula Arnold-Cramer , German politician
- May 27: Hans Peter Stauch , German industrial foreman and politician
- May 28 Mahmoud Jibril , Libyan politician (died 2020)
- May 28: Heino Wiese , German politician
- May 29: Walter Landin , German writer (died 2021)
- May 29: Ekkehard Wenger , German economist
- May 30: Zoltán Kocsis , Hungarian pianist and conductor (died 2016)
- May 30 Younus Shaikh , Pakistani doctor, human rights activist, rationalist and freethinker
- May 31: Frank Ulrich Montgomery , German physician and association official
June
- June 1: Johannes Lerle , German anti-abortion advocate and theologian
- June 1: Peter Thiesen , German educator and writer
- June 1: Mindaugas Urbaitis , Lithuanian composer
- June 2 – Pete Farndon , British rock musician (d. 1983)
- June 2: Hildegard Krekel , German actress († 2013)
- 3 June: David Richards , British motorsport official
- June 3: Dominique Laffin , French actress (died 1985)
- June 4 Bronisław Komorowski , Polish politician, President of the State
- June 4 Karl-Heinz Lambertz , Belgian politician
- June 5: Helmuth Markov , German politician
- June 5 Nicko McBrain , English musician and drummer for the group Iron Maiden
- June 5: Bernd Busemann , German politician
- June 6: Bernd Wehmeyer , German football player and manager
- June 6: Thomas Arndt , German ornithologist
- June 7 Hubert Auriol , French motocross and enduro racer († 2021)
- June 7 Liam Neeson , Irish actor
- June 7 Orhan Pamuk , Turkish journalist and writer

- June 8: Peter Fischli , Swiss artist
- June 8: Paul Hildgartner , Italian luger
- June 8 Janusz Kowalski , Polish cyclist
- June 9: Elia Andrioletti , Italian enduro athlete
- June 9 Günter Hujara , German skiing official and coach
- June 9: Carlos Perón , Swiss musician
- June 10 Bernd Stegmann , German church musician
- June 11: Doris Maletzki , German track and field athlete
- June 11: Wolfgang Bosbach , German politician
- June 11: Bronisław Wildstein , Polish journalist and writer
- June 12 Spencer Abraham , American politician
- June 12: Jean-Pierre Audy , French politician
- June 12: Wolfgang Bierstedt , German politician and MP
- June 12: Cornelia Hanisch , German fencer
- June 13 Jonathan Feldman , American pianist and music teacher
- June 13: Wilfried Kowarik , Austrian Benedictine monk and historian (died 2018)
- June 13 Angelo Moreschi , Italian bishop in Ethiopia († 2020)
- June 15 Aina Kemanis , American singer and flutist
- June 16: Giorgos Andrea Papandreou , Greek politician
- June 16 – Alexander Gennadievich Zaitsev , Russian figure skater
- June 16: Jerry Hadley , American opera singer (died 2007)
- June 17: Miguel Ángel Ayuso Guixot , Spanish Curial Bishop, cardinal
- June 17: Franz Böni , Swiss writer
- June 17: Sergio Marchionne , Italian-Canadian manager († 2018)
- June 17: Nikolaus Piper , German journalist
- June 17 Matteo Thun , Italian architect and designer
- June 18 Tiiu Aro , Estonian politician
- June 18 Marcella Bella , Italian singer
- June 18 Idriss Déby , President of Chad (died 2021)
- June 18 Isabella Rossellini , Italian actress
- June 18: John Carl Buechler , American film director and actor (died 2019)
- June 19: Robert William Ainsworth , British politician
- June 19: Philippe Manoury , French composer
- June 20 John Goodman , American actor and comedian
- June 20 Mabel Rivera , Spanish actress
- June 21: Luis Días , Dominican rock and jazz musician († 2009)
- June 21 Kadir Özcan , Turkish soccer player and coach (died 2013)
- June 22 Graham Greene , Canadian actor
- June 23: Jürgen Schmieder , German politician
- June 23: Rita Maiburg , German pilot, world's first female airline captain (d. 1977)
- June 23: Peter Whiteside , British modern pentathlete (d. 2020)
- June 25 Marieluise Beck , German politician
- June 25 Hans-Joachim Abel , German footballer
- June 25: Péter Erdő , Archbishop of Budapest and Cardinal
- June 26: Enrico Ghezzi , Italian film critic, author and television presenter
- June 26 Hansi Kraus , German actor
- June 26 Gordon McQueen , Scotland footballer
- June 27 Verena Plangger , Italian actress and director
- June 27 Rita Russek , German actress and director
- June 27 Paul Wellens , Belgian cyclist
- June 28: Abdo Arbach , Syrian cleric and Exarch of Argentina
- June 28: Pietro Mennea , Italian athlete (died 2013)
- June 28 Alan Pasqua , American jazz and rock pianist
- June 29: Frank Magnitz , German politician
- June 29 Klaus Ohlmann , German dentist and glider pilot
- June 29 Hans-Werner Rhein , German insurance lawyer
- June 30 Stefan Zauner , German musician
July

- July 1 David Arkenstone , American musician and composer
- July 1 Dan Aykroyd , Canadian film actor
- July 1 Philippe Barakat , Syrian Catholic priest, Archbishop of Homs (died 2020)
- July 1 Leon Ndugu Chancler , American drummer, music producer († 2018)
- July 1: Peter Graham , Czech composer and music educator
- July 2 Ian Affleck , Canadian theoretical physicist
- July 2 Ahmed Ouyahia , Algerian politician
- July 2: Norbert Hansen , German trade unionist
- July 2 Jamey George Haddad , American drummer and percussionist
- July 2: Joseph Vu Duy Thông , Vietnamese Catholic bishop (died 2017)
- July 3 Lena Andersson , Swedish table tennis player and coach
- July 3 Laura Branigan , American pop singer († 2004)
- July 3: Andy Fraser , British musician (died 2015)
- July 3: Hugo Moraga , Chilean cant author
- July 3 Klaus-Peter Wiedmann , German economist
- July 4: Álvaro Uribe Vélez , Colombian politician and President
- July 5 Albert Fortell , Austrian actor and author
- July 5: Nicky Gebhard , German drummer and music teacher († 2021)
- July 5: Adolphe Lechtenberg , German painter and draftsman
- July 5 Kitamura Sō , Japanese playwright and essayist
- July 6 Hilary Mantel , British novelist
- July 6: Dimitris Reppas , Greek politician
- July 6 Ralph Richeson , American painter and actor (died 2015)
- July 6: Adi Shamir , Israeli mathematician and cryptologist
- July 7: Ulrich Potofski , German sports presenter
- July 7 Christina Voß , German handball player
- July 8: Ahmad Nazif , Prime Minister of Egypt
- July 8 Ulrich Wehling , German skier
- July 8 Alan Whitney Brown , American comedian
- July 9: Rodney Boll , Canadian marksman (died 2021)
- July 9: François Diederich , Luxembourgish chemist († 2020)
- July 9: David Macdonald , Canadian organist († 2003)
- July 9: Hans Jürgen Fahn , Bavarian politician (Free Voters)
- July 10 Michael Schottenberg , Austrian actor and director
- July 10 Scott Adams , American programmer, computer game developer
- July 10: Lee Hae-chan , South Korean politician and prime minister
- July 11 Bill Barber , Canadian ice hockey player
- July 11 Otto Hauser , German politician and MP
- July 11 Raymond Voß , German musician
- July 12 Liz Mitchell , Jamaican singer
- July 12 Tomy Wigand , German director
- July 14: José Aristeu Vieira , Brazilian bishop
- July 14 Joel Silver , American film producer
- July 15 Włodzimierz Kiniorski , Polish composer, jazz saxophonist and multi-instrumentalist
- July 15 Terry O'Quinn , American actor
- July 15 Pierluigi Pairetto , Italian football referee
- July 15 Marky Ramone , American drummer with the Ramones
- July 15: Johnny Thunders , New York punk musician (d. 1991)
- July 16 Stewart Copeland , American pop star
- July 16 Brigitte Fronzek , German politician and mayor of Elmshorn (died 2021)
- July 16: Juliane Plambeck , German terrorist (died 1980)
- July 16: Gabriela Schimmer-Göresz , German politician (ÖDP)

- July 17: Thomas Ahlström , Swedish footballer
- July 17 Donal Fox , American pianist and composer
- July 17 David Hasselhoff , American singer and actor
- July 17: Renate Köcher , German pollster
- July 18 James Forbes , American basketball player and coach (d. 2022)
- July 18 Klaus Moegling , German teacher, political didactic and sports scientist
- July 19: Harald Aumeier , German footballer
- July 19 Allen Larkin Collins , American musician (d. 1990)
- July 19: Winfried Hermann , German politician (Bündnis 90/Die Grünen), state minister
- July 19 Bonnie Johansen-Werner , American composer and music teacher
- July 19 Hans-Georg Panczak , German actor and voice actor
- July 20: Frederik Kristensen , Greenlandic painter, sculptor, musician and poet († 2021)
- July 21 Hannele Lauri , Finnish actress
- July 21 – Peter Schoenen , German teacher, novelist and non-fiction author († 2014)
- July 21: Nina Serbina , Ukrainian high jumper
- July 23: Leopoldo Billings , Venezuelan composer
- July 23 Peter Bleser , German politician and MP
- July 23: Mark Weiser , American computer scientist (died 1999)
- July 24 Mario Mettbach , German politician
- July 24 Gus Van Sant , American film director and film producer
- July 25: Hans-Robert Metelmann , Minister of Education of Mecklenburg-West Pomerania
- July 26 Heiner Brand , German handball player and coach
- July 26 Stellan Bengtsson , Swedish table tennis player
- July 26: Mathias Schubert , German politician (died 2004)
- July 27 Roxanne Hart , American actress
- July 27: Ellen Streidt , German track and field athlete and Olympian
- July 28: Maha Vajiralongkorn , Rama X, King of Thailand
- July 28: Cordt Schnibben , German journalist
- July 28: Eva Wilms , German track and field athlete
- July 29 Susanne Amatosero , German painter, playwright and radio playwright and director
- July 29: Wendy Hughes , Australian actress († 2014)
- July 29 Joe Johnson , English snooker player
- July 29 Christa Nickels , German politician
- July 29 Harold Robinson , American double bass player and music educator
- July 30 Renata Al-Ghoul , German business lawyer, artist and oil painter
- July 30 Ilan Chester , Venezuelan musician and singer
- July 31 Marlies Amann-Marxer , Liechtenstein politician
- July 31 Alejandro Víctor Washington Atchugarry Bonomi , Uruguayan politician (died 2017)
- July 31: Reinhard Goebel , German baroque violinist
- July 31: Helmuts Balderis , Latvian ice hockey player
- July: Anne Anderson , Irish diplomat
August
- August 1: Zoran Đinđić , Serbian politician and writer († 2003)
- August 2: Alain Giresse , French footballer
- August 2 Sebastiano Tusa , Italian archaeologist and politician (died 2019)
- August 3 Osvaldo Ardiles , Argentine footballer
- August 3: Axel Schäfer , German politician
- August 3: Thomas Munkelt , German athlete
- August 3 Frank Schaeffer , American author, director, and painter
- 3 August: Ihor Vosnyak , Ukrainian clergyman, Archbishop of Lviv
- August 4 Moya Brennan , Irish singer
- August 4: Daniel Bautista , Mexican track and field athlete
- August 4: Gábor Demszky , Hungarian politician
- August 4 Franco Saudelli , Italian comic artist
- August 4: Tadeusz Wojciechowski , conductor and cellist
- August 5: Hun Sen , Cambodian politician
- August 6: Vito Angiuli , Italian bishop
- August 6: Hans-Jörn Arp , German politician
- August 6: Christoph Biemann , German author, director and television presenter
- August 6: Wojciech Fortuna , Polish ski jumper and Olympic champion
- August 6: David McLetchie , British politician (died 2013)
- August 6 Vinnie Vincent , American guitarist
- August 7 Caroline Aaron , American actress
- August 7 Helga Lopez , German politician and MP
- August 7: Karl Schweitzer , Austrian politician
- August 8: Brigitte Ahrenholz , German rower (died 2018)
- August 8 Anton Fig , American rock and jazz drummer
- August 8: Norbert Glante , German politician
- August 8: Jostein Gaarder , Norwegian writer
- August 8: Jean-Claude Mermoud , Swiss politician (died 2011)
- August 8 – Carsten Peter Thiede , German historian and papyrologist (died 2004)
- August 9: Jürgen Gehb , German politician
- August 9: Hubert Haensel , German writer
- August 9: Rui Jordão , Portuguese footballer († 2019)
- August 10 Dietmar Käbisch , German cyclist
- August 10: Jerzy Pilch , Polish writer (died 2020)
- August 10 Diane Venora , American actress
- August 11 Tabea Blumenschein , German actress and author († 2020)
- August 11: Curt Cress , German drummer
- August 12 Gerardo Amato , Italian actor
- August 12: Ingela Bruner , Swedish-Austrian scientist (died 2014)
- August 12: Chen Kaige , Chinese director and writer
- August 12: Hans-Ulrich Treichel , German writer
- August 12: Charlie Whiting , British motorsport official (d. 2019)
- August 13: Herb Ritts , American photographer (died 2002)
- August 14: Joseph Atanga , Archbishop of Cameroon
- August 14 Christina Rost , German handball player
- August 14: Alex van Warmerdam , Dutch director
- August 15: Jirō Atsumi , Japanese enka singer
- August 15 Barbara Imhof , German politician
- August 15 Rudi Kargus , German footballer
- August 15 Bernard Lacombe , French footballer
- August 15 Heinzpeter Moecke , German doctor, manager and publicist (died 2015)
- August 16: Isa Jank , German actress
- August 16: Walter Olivera , Uruguayan footballer
- August 16: Sonia Silvestre , Dominican singer († 2014)
- August 16 Reginald VelJohnson , American actor
- August 17 Gary Armagnac , American actor
- August 17: Nelson Piquet , Brazilian Formula One racing driver
- August 17: Heiner Goebbels , German composer, director and radio play maker
- August 17: Walter Knofel , Austrian director († 2018)
- August 17 Guillermo Vilas , Argentine tennis player
- August 17: Werner Stepanek , German educator
- August 18: Lowell Lyttleton Lewis , German politician
- August 18: Markus Meckel , German politician and East German foreign minister
- August 18: Wolfgang Niess , German historian, author and moderator
- August 18: Patrick Swayze , American actor (died 2009)
- August 18 Ricardo Julio "Ricky" Villa , Argentine soccer player
- August 19 Jonathan Frakes , American actor and director
- August 19 Gabriela Grillo , German entrepreneur and dressage rider
- August 19: Bodo Hombach , German politician
- August 19 David Munyon , American singer-songwriter and guitarist
- August 19: Alexei Nikolayevich Rudoi , Russian geographer (died 2018)
- August 20 John Hiatt , American country music singer-songwriter
- August 21: Joe Strummer , English punk musician (died 2002)
- August 21: Jiří Paroubek , Czech politician
- August 22 Hans Otfried Dittmer , German writer and publisher (died 2018)
- August 22: George Ferguson , Canadian ice hockey player (died 2019)
- August 22 Klaus Gruner , German handball player
- August 22: Valery Pidlushnyj , Soviet long jumper († 2021)
- August 22: Santiago Santamaría , Argentine soccer player († 2013)
- August 22: Michael Sziedat , German footballer
- August 23: Stephan Articus , German sociologist
- August 23 Terry Austin , American comic artist
- August 23: Kirby Dick , American film director, film producer and screenwriter
- August 23: Bernd Protzner , German politician, General Secretary of the CSU († 2018)
- August 23: Santillana , Spanish footballer
- August 23 Vicky Leandros , Greek crooner
- August 23: Klaus-Dietrich Flade , German astronaut
- August 24: Raymond Asquith , British diplomat and politician
- August 24: Ian Grob , British motor racing driver
- August 24 Linton Kwesi Johnson , English poet and reggae musician
- August 24: Udo Pastors , German politician
- August 24 Rubén Tierrablanca González , Mexican religious priest and bishop (d. 2020)
- August 24 Billy Ward , American jazz drummer
- August 25 Geoff Downes , British rock musician
- August 26: Michael Jeter , American actor (d. 2003)
- August 26 Peter Wolf , Austro-American producer and composer
- August 27 Karl Adamek , German music sociologist
- August 27 Daniel Astegiano , Argentine footballer
- August 27: Karel De Wolf , Belgian composer and conductor († 2011)
- August 27: Undine Gruenter , German writer (died 2002)
- August 27: Matthias Raue , German composer and musician
- August 28 Rita Dove , American poet and writer
- August 28: Eduardo Fernández , Uruguayan guitarist
- August 28: Wendelin Wiedeking , CEO of Volkswagen AG and Porsche AG
- August 29: Sanny Åslund , Swedish football player, coach and manager
- August 29: Michael Wessing , German athlete (died 2019)
- August 30: Hans-Werner Ehrenberg , German teacher and politician
- August 30 Wojciech Fibak , Polish tennis player
- August 31: Herbert Reul , German MEP
- August 31 Kim Kashkashian , American violist
- August 31: Lee Hyla , American composer († 2014)
September
- September 1 Ed Neumeister , American jazz trombonist
- September 1: Clemente Rojas , Colombian boxer
- September 2 Jimmy Connors , American tennis player
- September 3: François Emmanuel , Belgian writer, psychiatrist and psychoanalyst
- September 3 Kurt Gartlehner , Austrian politician
- September 4: Rishi Kapoor , Indian actor († 2020)
- September 4 Evelyn Roll , German journalist and publicist
- September 5: Ricky Fataar , South African drummer
- September 6 Dominik Graf , German film and television director
- 6 September: Alfred Klink , German chef
- September 6: Bernd Römer , German guitarist, Band Karat

- September 7: Ricardo Tormo , Spanish motorcycle racer (d. 1998)
- September 8: Ioanna Karystiani , Greek writer
- September 8: Udo Schnell , German Protestant theologian
- September 9 Phil Palmer , English session guitarist
- September 9: Bi Skaarup , Danish historian (died 2014)
- September 9: Luzi Stamm , Swiss politician
- September 9: José María de la Torre Martín , Mexican Roman Catholic Bishop (d. 2020)
- September 10: Wolfgang Aßbrock , German politician (died 2007)
- September 10: Gregor Eichele , Swiss chemist and molecular biologist
- September 10 Bruno Giacomelli , Italian Formula One racing driver
- September 10: Werner Hug , Swiss chess champion
- September 10: Margitta Pufe , German track and field athlete
- September 11 Klaus-Peter Hildenbrand , German track and field athlete
- September 12: Neil Peart , lyricist and drummer for rock band Rush († 2020)
- September 12 Selimkhan Abdumuslimovich Yandarbiev , Chechen poet and separatist leader (died 2004)
- September 13: Johanna Schaller , later Johanna Klier, German track and field athlete and Olympic champion
- September 13 Don Was , American musician and record producer
- September 14 Martyn Burke , Canadian novelist, screenwriter and director
- September 14: Margit Schumann , German luger (died 2017)
- September 14: William Taylor , British boxer (died 2022)
- September 16: Fatos Nano , Prime Minister of Albania
- September 16: Gernot Grumbach , German politician
- September 16 Mickey Rourke , American actor
- September 17: Barbara Engel , German reality TV actress
- September 17 Milan Šašik , Ukrainian bishop (died 2020)
- September 17 Harold Solomon , American tennis player
- September 17: Norbert Walter-Borjans , German politician
- September 18 John Ruocco , American jazz clarinetist and saxophonist
- September 18: Heinz Seiffert , German politician, MP
- September 19: Holger Biege , German composer, singer, pianist, arranger and lyricist († 2018)
- September 19: Bernard de Dryver , Belgian racing driver
- September 19 Nile Rodgers , American musician and record producer
- September 19: Marina Ruperti , German television journalist
- September 19 Elfi Scho-Antwerpes , German politician
- September 20 Gabriele Badorek , German handball player
- September 20: Grażyna Rabsztyn , Polish track and field athlete and multiple world record holder
- September 21 Claus Dittbrenner , German politician (died 2013)
- September 21: Anneliese Michel , German Catholic, died after exorcism († 1976)
- September 22: Jürgen Jürgens , German radio host (died 2018)
- September 22 Lutz Rathenow , German poet and prose writer
- September 24: Annegret Kroniger , German track and field athlete
- September 24: Sepp Zeilbauer , Austrian track and field athlete, decathlete
- September 25 Colin Friels , Australian actor
- September 25 Christopher Reeve , American actor and director († 2004)

- September 28: Sylvia Kristel , Dutch actress († 2012)
- September 28: Lenny Solomon , Canadian jazz violinist, arranger and composer
- September 29: Lonzo , German musician (died 2001)
- September 29: Ross Daly , world musician and multi-instrumentalist of Irish descent
- September 29: Monika Zehrt , GDR track and field athlete
- September 30 Glenn Leslie Aitken , English footballer
- September 30 Margit Conrad , German politician
- September 30: Jürgen Glowacz , German footballer
- September 30: Philippe Laguérie , French Catholic priest
- September 30 Al Leong , American actor and stuntman
October
- October 1 Olga Mineyeva , Russian track and field athlete and Olympian
- October 2 Matthias Brand , German writer
- October 3: Wolfgang Burger , German crime writer
- October 3 Neil Gehrels , American astronomer (died 2017)
- October 3 Randy Tate , American baseball player (died 2021)
- October 5 Regine Aeppli Wartmann , Swiss politician
- October 5: Clive Barker , British writer and director
- October 5: Imran Khan , Pakistani cricketer and politician
- October 5: David Lebón , Argentine rock musician
- 5 October: Vladimir Nezorov , Soviet-Russian judoka and Olympic champion
- October 5: Hermes Phettberg , Austrian artist, actor, author and talk show host
- 5 October: Emomalij Rahmon , President of Tajikistan
- October 6: Matthew Sweeney , Irish writer (died 2018)
- October 7 Mary Badham , American actress
- October 7 Don Edward Machholz , American amateur astronomer
- October 7: Vladimir Putin , President of Russia
- October 7 Neithardt Riedel , German actor and screenwriter
- October 9 Philipp Meikl , Austrian singer and musician
- October 9 Dennis Stratton , British musician
- October 10: Siegfried Stohr , Italian racing driver
- October 11 Jim Kahr , American guitarist and singer
- October 11 Angelika Mertens , German politician (died 2019)
- October 11 Hartmut Schreier , German actor
- October 12 Danielle Proulx , Canadian actress
- October 13: Michael R. Clifford , American astronaut (died 2021)
- October 13: Helmut F. Kaplan , Austrian writer, philosopher, ethicist
- October 13: John Lone , Chinese-American actor
- October 13 Elisabeth Motschmann , German politician
- October 13: Henry Padovani , French guitarist
- October 14: Harry Anderson , American actor (died 2018)
- October 14: Nikolai Andrianov , Soviet artistic gymnast (died 2011)
- October 14: Rick Aviles , American stand-up comedian and actor (d. 1995)
- October 14: Margriet Eshuys , Dutch pop singer
- October 14: Kaija Saariaho , Finnish composer
- October 14 Peach Weber , Swiss cabaret artist and comedian
- October 15: Manuel Jiménez , Dominican singer and composer
- October 16 Ray Anderson , American jazz trombonist
- 18 October Haya Raschid Al Khalifa , Bahraini lawyer and diplomat
- October 19: Marie-Christine Arnautu , French politician
- October 19 Perico Fernández , Spanish boxer (died 2016)
- October 19: Virginio Ferrari , Italian motorcycle racer
- October 19 Heike Wilms-Kegel , German politician
- October 19: Edo Zanki , German musician and producer († 2019)
- October 20: Linus Okok Okwach , Kenyan Bishop (d. 2020)
- October 20 Ed Fagan , US attorney
- October 21: Mehdi Charef , Algerian writer, film director and playwright
- October 21: Brent Mydland , keyboardist on Grateful Dead († 1990)
- October 22 Jeff Goldblum , American actor
- October 22: Yoshiki Tanaka , Japanese writer
- October 23: Pierre Moerlen , French drummer and composer († 2005)
- October 23 Bengt Nilsson (cyclist) , Swedish cyclist
- October 23 Heimo Schwilk , German journalist and author
- October 24: Tania Libertad , Peruvian-Mexican singer
- October 24 David Weber , American science fiction and fantasy author
- October 25: Martin Heller , Swiss cultural entrepreneur, curator and author († 2021)
- October 26: Solveig Fiske , Norwegian bishop
- October 26 William Wright , Australian Roman Catholic Bishop (d. 2021)
- October 27 – Anthony Arndt , German actor, presenter and cyclist
- October 27 Roberto Benigni , Italian director and actor
- October 27: Francis Fukuyama , American political scientist
- October 27 Serge Saulnier , French racing driver, racing team owner and motorsport official
- October 28 Tuck Andress , American jazz guitarist
- October 28: Jörgen Augustsson , Swedish footballer
- October 29: Peter Bond , German actor and TV presenter of Polish origin
- October 29 Marcia Fudge , US politician
- October 29 Ida Kavafian , American violinist, violist, and music teacher
- October 30 Arnold Karibone Amet , Papua New Guinean jurist and politician
- October 30 Patrick Pugliese , Canadian water polo player (died 2020)
- October 30: Hans-Joachim Otto , German politician
- October 31: Andrea Breth , German theater director
- October 31: Franz-Josef Tenhagen , German football player and coach
November
- November 1 Ali-Reza Asgari , Iranian politician and military officer
- November 2: Hanery Amman , Swiss musician († 2017)
- November 2 David Andrews , American actor
- November 2 Larry Fink , American entrepreneur
- November 2 Maxine Nightingale , British disco and soul singer
- November 2: Jean-Remy von Matt , Swiss entrepreneur and copywriter
- November 3 Roseanne Barr , American actress
- November 3: Jim Cummings , American voice actor
- November 4: Robin Lautenbach , German television journalist
- 4 November: Tawadros II , Patriarch of Alexandria and Pope of the Copts
- November 5: Oleg Blokhin , Ukrainian footballer
- November 5: Vandana Shiva , Indian philosopher, ecologist, civil rights activist and feminist
- November 6 Michael Cunningham , American novelist
- November 7: Modibo Sidibé , Malay politician
- November 8 John Denny , American baseball player
- November 8 Christie Hefner , American entrepreneur
- November 8: Jan Raas , Dutch racing cyclist
- November 9: Andreas Aigmüller , German-Austrian musician and composer
- November 9: Peter Hahne , German TV presenter
- November 10: Vesna Acevska , Macedonian poet, author and translator
- November 10: Fernando Allende , Mexican actor and singer
- November 10: Marco Arnolfo , Italian archbishop
- November 11 Lothar Angermund , German footballer
- November 11: Christopher Loeak , President of the Marshall Islands
- November 11: Mohan Patel , New Zealand hockey player
- November 11 Gertrude Tumpel-Gugerell , Austrian bank director
- November 12: Dietrich Grönemeyer , German physician and co-founder of microtherapy
- 12 November: Mary Honeyball , German MEP
- November 12: Ernie Fletcher , Governor of Kentucky
- 12 November: Ján Kubiš , Slovak diplomat and OSCE Secretary General
- November 12: Thomas Lengauer , German computer scientist
- November 13: Stuart Cornfeld , American film producer († 2020)
- November 13: Hans Heiss , Italian historian and archivist and South Tyrolean politician
- November 13: Bjambasürengiin Scharaw , Mongolian composer († 2019)
- 14 November: Metin Kaplan , self-proclaimed "Caliph of Cologne"
- November 14: Maria Kliegel , German cellist
- November 14: Pascal Pessiot , French racing driver and entrepreneur
- November 15: Rolf Arnold , German educator
- November 15 Dieter R. Fuchs , German scientist and writer
- November 15: Antonella Ruggiero , Italian singer
- November 15: Randy Savage , American professional wrestler (died 2011)
- November 16 Karl-Heinz Ach , German soccer player and coach
- November 16 Lawrence Rush Atkinson IV , American journalist, military historian and non-fiction author
- November 16 Diepreye Alamieyeseigha , Nigerian politician (died 2015)
- November 16 Lauren Newton , American singer and composer
- November 16: Jean Salem , French philosopher (died 2018)
- November 16: Klaus Zeh , German politician
- November 16: Shigeru Miyamoto , main manager of Japanese video game company Nintendo
- November 17: Ernst-Michael von Abercron , German politician
- November 17 Christopher Butterfield , Canadian composer, music educator, performance artist and rock guitarist
- November 17: Hubert von Goisern , Austrian musician
- November 17: Ties Kruize , Dutch hockey player
- November 17; Miroslava Němcová , Czech politician
- November 17: Cyril Ramaphosa , South African politician
- November 17 Marion Tietz , German handball player
- November 18: Frank Köllges , German jazz percussionist, composer and performance artist († 2012)
- November 18: Harald Konopka , German footballer
- November 18 Willi Frommelt , Liechtenstein skier
- November 18: Karl-Georg Wellmann , German politician (CDU) and MP
- November 18: Paul Wengert , Lord Mayor of the City of Augsburg
- November 20: Hans Jürgen Noss , German politician
- November 20: Wolfgang Kneib , German footballer
- November 20: Elfi Graf , Austrian pop singer
- November 21: Pietro Ghedin , Italian football player and coach
- November 21: Cornelius Littmann , German LGBT activist
- November 21: Eimuntas Nekrošius , Lithuanian director († 2018)
- November 23: Josip Turčik , Yugoslav footballer
- November 23 Corinna Werwigk-Hertneck , German politician
- November 24: Norbert Haug , German journalist and head of motorsport for Daimler-Chrysler
- November 24: Ilja Richter , German actor and TV presenter
- November 24 Rachel Chagall , American actress
- 25 November: Daniel Marco Kur Adwok , Sudanese Auxiliary Bishop
- November 25: Stanisław Krupowicz , Polish composer and music educator
- November 25: Gabriele Oriali , Italian footballer
- November 26: Eva Brunner , Swiss author and translator
- November 26: Richard Carrión , Puerto Rican financial manager and sports official
- November 26 Jan Philipp Reemtsma , German literary scholar, essayist
- November 26 Wendy Turnbull , Australian tennis player
- November 27: Wilhelm-Albrecht Achilles , German jurist and judge at the Federal Court of Justice
- November 27: Michele Barra , Swiss politician (died 2013)
- November 27 Daryl Stuermer , American rock musician
- 27 November: Axel Viehweger , Minister for Building and Urban Development of the GDR
- November 28: Rolf Oesterreich , German figure skater
- November 28: Pat Cox , President of the European Parliament
- November 29: John D. Barrow , British physicist and mathematician (d. 2020)
- November 29: Erzsébet Wolf , Hungarian badminton player
- November 29 Tom Wright , American actor and stuntman
- November 30 Chris Joris , Belgian jazz musician (percussion, piano) and composer
- November 30 Christine Price , British former middle and long-distance runner
December
- December 1: Franz Wiese , German entrepreneur and politician († 2021)
- December 2 Andreas Mölzer , Austrian politician and publicist
- December 2: Klaus F. Zimmermann , German economist
- December 3 Bruno Jonas , German cabaret artist
- December 4: Heinz Strobl , Austrian composer and musician
- December 5: Günther Förg , German artist († 2013)
- December 5 Michaela Pilters , German journalist
- December 5 Walter Sittler , German actor
- December 5: Georg Schuchter , Austrian actor (died 2001)
- December 6: Christian Kulik , German footballer
- December 7: Paco Romero , Spanish racing car driver
- December 8 Heinz Prokop , German handball coach and handball player
- December 9 Michael Dorn , American actor
- December 10 Julianne Baird , American soprano and specialist author
- December 10: Herbert Bastian , German chess teacher, International Master
- December 10: Bernd Jakubowski , German soccer goalkeeper (died 2007)
- December 11: Josef Bläser , German footballer
- December 11 Andrea De Carlo , Italian writer
- December 11: Thomas Gumpert , German actor (died 2021)
- December 11 Susan Seidelman , American film director
- December 12: Päivi Aulikki Aaltonen , Finnish archer
- December 12 Sarah Douglas , British actress
- December 12: Helen Dunmore , British novelist (died 2017)
- December 12: Pankraz Friday , Swiss politician (died 2013)
- December 12: Frank Schwalba-Hoth , German politician
- December 13: Jean Rouaud , French writer
- December 14: Tamara Danz , German singer (died 1996)
- December 14 John Lurie , American composer, musician, actor
- December 15 Lee Aronsohn , American television producer and screenwriter
- December 15 Robert Jarowoy , German author and politician (died 2020)
- December 15: Allan Simonsen , Danish footballer
- December 16: Manuel Barrueco , Cuban guitarist
- December 16: Alex Fergusson , Scottish guitarist and record producer
- December 16 Francesco Graziani , Italian footballer
- December 16: Jon Laukvik , Norwegian organist and music professor
- December 17 Ed Starink , Dutch studio musician, composer, arranger and music producer
- 18 December: Irja Askola , Finnish bishop
- December 18: Hans Hurch , Austrian film journalist and culture manager († 2017)
- December 18 Phil Shoenfelt , British singer-songwriter
- December 18 Bettina Rheims , French photographer
- December 18: Krystyna Janda , Polish actress
- 19 December: Paul-Siméon Ahouanan Djro , Ivorian priest and archbishop
- December 19 Peter Stephan Jungk , American German-language writer
- December 20: Jenny Agutter , British actress
- December 20 Lena Strothmann , German politician
- December 20: Ray Bumatai , American actor, comedian and musician († 2005)
- December 20: Frederick Schipizky , Canadian double bass player and composer
- December 21: Hani Shaker , Egyptian actor and singer
- December 22: Uri Yehuda Ariel , Israeli politician
- December 22: Jochen Wiedemann , German scientist
- 22 December: Sandra Kalniete , Latvian EU Commissioner
- December 23: William Kristol , American political commentator and columnist
- December 23: Andreas Martin , German crooner
- December 24: Lorne Calvert , Canadian politician
- December 24: Helmut Schüller , Austrian Catholic priest
- December 25 Christine Lehder , German politician
- December 25: Desireless , French singer
- December 25: Youssouf Ouédraogo , Prime Minister of Burkina Faso († 2017)
- 26 December: Alexander Ankvab , Prime Minister of Abkhazia
- December 26 André-Michel Schub , American pianist and music teacher
- December 26: Riki Sorsa , Finnish pop and rock singer († 2016)
- December 27: Ainsley Edward Armstrong , sprinter from Trinidad and Tobago
- December 27: Bob Flanagan , American writer and artist (died 1996)
- December 27: Herman Jeurissen , Dutch bugler
- December 27: Gerlinde Kaupa , German politician
- December 27: David Knopfler , Scottish musician (Dire Straits)
- December 27: Raimund Krauth , German soccer player (died 2012)
- December 28: Arun Jaitley , Indian politician (died 2019)
- December 29: Joe Lovano , American jazz musician
- December 30 June Anderson , American opera singer
- December 30 Hans-Lothar Bock , German handball player
- December 30: Woody Mann , American guitarist († 2022)
- December 30 – Gerd Schädlich , German football coach and football player († 2022)
- December 31: Thomas Bopp , Baden-Württemberg politician
- December 31: Lawrence Fritts , American composer and music educator
- December 31: Vaughan FR Jones , New Zealand mathematician (d. 2020)
- December 31: Jean-Pierre Rives , French rugby union player and sculptor
- December 31: Wolfgang Welt , German writer (died 2016)
day unknown
- Youssouf Saleh Abbas , Chadian politician
- Mustafa Muhammad Abd al-Jalil , Libyan politician
- Fulvio Accialini , Italian film actor
- Bernd Ahlert , German guitarist, university lecturer and luthier
- Ahn Sang-soo , South Korean graphic designer and typographer
- Wolfgang Aichinger , Austrian cellist
- Hamad bin Khalifa bin Hamad bin Abdullah bin Jassim bin Muhammed Al Thani , Emir of Qatar
- Mohammed Al-Fassi , Saudi Arabian-Moroccan businessman (died 2002)
- Dan Allender , American psychologist, therapist, author, and speaker
- Christine Amor , Australian actress
- Craig A. Anderson , American psychologist
- Walt Anderson , American dentist and American football umpire
- Dörte Andres , German interpreting scholar
- Kurt App , German object artist
- Malcolm Archer , British organist, choirmaster and composer
- Atsuo Asami , Japanese amateur astronomer and asteroid discoverer
- William Aspray , American historian of science
- Carlos Atilano , Venezuelan composer and guitarist
- Caroline Atkinson , American economist and journalist
- Scott Atran , American anthropologist
- Pascal Attinger , Swiss ancient orientalist
- Dimos Avdeliodis , Greek director and actor
- Vishwa Mohan Bhatt , Indian guitarist
- Karl Braun , German ethnologist
- Michael Brook , Canadian musician, guitarist and record producer
- Klaus vom Bruch , German media artist
- Philip Carr-Gomm , English psychologist and druid
- Maria Berica Dalla Vecchia , Italian dancer, choreographer and music teacher
- Fernando José de França Dias Van Dúnem , Angolan politician and ambassador
- Susanne Fischer-Rizzi , German naturopath, phytotherapist and author
- Benedict Freitag , Swiss theater and film actor
- Perry Goldstein , American composer and music educator
- Ali Gomaa , Egyptian Grand Mufti
- Thomas Goritzki , German actor and director
- Henry Gwiazda , American composer
- Werner Hagen , German musician
- Michel Jarraud , French meteorologist
- Scott Johnson , American composer
- Gernot Krää , German film director and freelance writer.
- Frank Lloyd , British horn player
- Michael Loceff , American computer scientist, producer and screenwriter
- Thomas Lubowski , German journalist
- Hugh Lupton , English storyteller and author
- Luo Baoming , Chinese politician
- Samuel Magrill , American composer and music educator
- Nele Moost , German author
- Linsey Pollak , Australian musician and instrument maker
- Gabriele Quandt-Langenscheidt , German entrepreneur
- James Signorile , American composer
- Stephanie Sloan , Canadian freestyle skier
- Katerina Vatsella , art historian and curator
- Wang Sanyun , Chinese politician
- Wolfgang Schröder (cyclist) , German cyclist
- Serhiy Svyachenko Ukrainian artist
- Udo Witte , German director
- Manfredo Zimmermann , Argentine flutist and university teacher
- Paula Zsidi , Hungarian archaeologist and museologist
Died
January
- January 3: Luigi Stefano Giarda , Italian composer, cellist and music teacher (b. 1868)
- January 6: Alfred Meebold , German botanist, writer and anthroposophist (b. 1863)
- January 6: Hermann Stopperich , German politician (b. 1895)
- January 8: Antonia Maury , astronomer (b. 1866)
- January 9: Paul Ausserleitner , Austrian ski jumper (born 1925)
- January 9: Antonie Straßmann , German sports and zeppelin aviator (b. 1901)
- January 10: Honoré Jackson , Canadian journalist (b. 1861)
- January 11: Jean de Lattre de Tassigny , French general (b. 1889)
- January 14: Artur Kapp , Estonian composer (b. 1878)
- January 15: Samuel M. Shortridge , American politician (b. 1861)
- January 17: Paul Langhans , German geographer and cartographer (born 1867)
- January 18: Curly Howard , American comedian (b. 1903)
- January 19: Wilhelm Schäfer , German writer (b. 1868)
- January 20: Arthur Farwell , American composer (b. 1872)
- January 20: Pat Morris Neff , American politician (b. 1871)
- January 22: Alexander Behm , German physicist (b. 1880)
- January 22: Karl Glässing , Lord Mayor of Wiesbaden, Chief Finance President in Darmstadt (b. 1866)
- January 22: Robert Porter Patterson , American politician (b. 1891)
- January 22: Roger Vitrac , French playwright and surrealist (b. 1899)
- January 25: Sveinn Björnsson , first President of Iceland (b. 1881)
- January 26: Chorloogiin Choibalsan , Mongolian communist politician (b. 1895)
- January 28: Thomas Hicks , American marathon runner, Olympic gold medalist (b. 1876)
- January 30: Alfred Thon , German painter, draftsman and art teacher (b. 1886)
- January 31: Georg Kohl , German politician (b. 1881)
- January 31: Pedro Prado , Chilean writer (b. 1886)
February
- February 3: Kambara Ariake , Japanese writer (b. 1876)
- February 5: Elisabeth von Plotho , model for Theodor Fontane's Effi Briest (b. 1853)
- February 5: Adela Verne , English composer, pianist and music teacher (b. 1877)
- February 6: Lipót Aschner , Hungarian industrialist (b. 1872)
- February 6: George VI , King of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (b. 1895)
- February 7: Rudolf Hans Bartsch , Austrian writer (b. 1873)
- February 7 Pete Henry , American football player and coach (b. 1897)
- February 9: Peter Nonnenmühlen , local politician and mayor in Mönchengladbach (b. 1868)
- February 10: Macedonio Fernández , Argentine writer (b. 1874)
- February 11: Alfred Liebig , German architect (b. 1878)
- February 12: Ernst Zahn , Swiss writer (b. 1867)
- February 13: Alfred Einstein , German musicologist and music critic (born 1880)
- February 14: Maurice Dewaele , Belgian racing cyclist (b. 1896)
- February 14: William Joseph Elford , British chemist and microbiologist (born 1900)
- February 15: Gustaf Nagel , German eccentric and itinerant preacher (b. 1874)
- February 17: Lotte Pritzel , German doll maker, costume designer and draftsman (b. 1887)
- February 18: Cliff Eros , German circus entrepreneur, sensational actor, artiste and tamer (b. 1889)
- February 18: Johannes Antonius James Barge , Dutch anatomist (born 1884)
- February 19: Lawrence Grant , British actor (b. 1870)
- February 19: Knut Hamsun , Norwegian writer (b. 1859)
- February 20: Carlos Julio Arosemena Tola , Ecuadorian banker and president (b. 1888)
- February 20: Wilhelm Knothe , German politician (b. 1888)
- February 25: Erwein von Aretin , Bavarian journalist and homeland politician (b. 1887)
- February 25: Saitō Mokichi , Japanese poet and essayist (b. 1882)
- February 25: Carl Schröter , German politician (b. 1887)
- February 26: Theodoros Pangalos , general and politician in Greece (b. 1878)
- February 28: Albert Forster , Gauleiter of the NSDAP and Reich Governor in Danzig (b. 1902)
March
- March 1: Kume Masao , Japanese writer (b. 1891)
- March 1: Gregory La Cava , American film director and cartoonist (born 1892)
- March 1: Theodor Mollison , German anthropologist (b. 1874)
- March 2: Bernhard Lohmüller , German politician (born 1891)
- March 3 Howard Chandler Christy , American painter (b. 1872)
- March 4: Charles Scott Sherrington , British neurophysiologist (born 1857)
- March 5: Georg Arends , German plant breeder and gardener (b. 1863)
- March 5: Vladimir Vladimirovich Shcherbachev , Russian composer (b. 1889)
- March 6: Giacomo Rimini , American opera singer and music teacher of Italian descent (b. 1887)
- March 6: Jürgen Stroop , SS-Gruppenführer, leader of the Warsaw Ghetto mass murder (b. 1895)
- March 7: Yogananda , yogi and guru (b. 1893)
- March 9: Alexandra Kollontai , Russian revolutionary, diplomat and writer (b. 1872)
- March 9: Eberhard Wildermuth , German politician (b. 1890)
- March 10: Ben Fuller , Australian theater entrepreneur (b. 1875)
- March 13: Giovanni Battista Nasalli Rocca di Corneliano , Cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church (b. 1872)
- March 13: Johan Nygaardsvold , Norwegian social democratic politician (b. 1879)
- March 15: Wilhelm Burger , German auxiliary bishop (b. 1880)
- March 16: Stephan Weickert , German politician (b. 1892)
- March 17 Nándor Láng , Hungarian archaeologist, historian and classical philologist (b. 1871)
- March 19: John H. Bartlett , American politician (b. 1869)
- March 19: Hans Wittwer , Swiss architect (b. 1894)
- March 20: Mario Ajmone Cat , Italian general (b. 1894)
- March 21: Peter Petersen , German reform educator (b. 1884)
- March 22: Uncle Dave Macon , American country musician (b. 1870)
- March 24: Wilhelm Jelinek , German works council chairman and anarcho-syndicalist (born 1889)
- March 25: William Sutherland Maxwell , Canadian Baha'i (b. 1874)
- March 25: Egon von Tresckow , German illustrator, comic artist and caricaturist (b. 1907)
- March 26: John Ponsonby , British general and divisional commander in World War I (b. 1866)
- March 29 Katherine Sophie Dreier , American painter and art patron (b. 1877)
- March 30: Jigme Wangchuck , second king of Bhutan (b. 1905)
- March 31: John George Clark Anderson , British ancient historian and epigraphist (b. 1870)
- March 31: Walter Schellenberg , chief of military intelligence in the Third Reich (b. 1910)
- March 31: Wallace H. White , American politician (b. 1877)
April
- April 1: Ferenc Molnár , Hungarian writer and journalist (b. 1878)
- April 2: Antonio Cortis , Spanish opera singer (b. 1891)
- April 2: Bernard Ferdinand Lyot , French astronomer (born 1897)
- April 9: Carl Friedemann , Swiss composer and conductor (b. 1862)
- April 10: Frederic Austin , English opera singer and composer (b. 1872)
- April 10: Anna Mollwo , German painter (b. 1874)
- April 15: Bruno Barilli , Italian composer, journalist and writer (born 1880)
- April 15: Ludwig Kaas , Center politician during the Weimar Republic (b. 1881)
- April 15: Viktor Chernov , Russian politician (b. 1873)
- April 17: Rudolf Dix , German lawyer and notary (b. 1884)
- April 18: Agnes Smidt , German-Danish painter (born 1874)
- April 18: Leo Smith , Canadian composer, cellist and music educator (b. 1881)
- April 19 Carl August Graf von Attems-Petzenstein , Austrian zoologist (b. 1868)
- April 19: Jean-Marie Musy , Swiss politician (b. 1876)
- April 21: Alfred Andersen-Wingar , Norwegian composer (b. 1869)
- April 23: Richard Stafford Cripps , British jurist and politician (b. 1889)
- April 23: Wilhelm Paschek , German politician (born 1897)
- April 23: Elisabeth Schumann , German-American soprano (b. 1888)
- April 24: Hendrik Anthony Kramers , Dutch physicist (born 1894)
- April 26: Jan van der Hoeve , Dutch ophthalmologist (born 1878)
May
- May 2: Leopold van Itallie , Dutch pharmacologist and toxicologist (born 1866)
- May 3: Georges Cordey , Swiss motorcycle racer (*unknown)
- May 5: Hans Adolf von Arenstorff , German major general and manor owner (b. 1895)
- May 6: Maria Montessori , Italian physician, reform educator, philosopher and philanthropist (b. 1870)
- May 7: Alfred La Liberté , Canadian composer, pianist and music educator (b. 1882)
- May 9: Kurt Beyer , German engineer (born 1881)
- May 10: Paul Greifzu , German automobile and motorcycle racer (b. 1902)
- May 11: Alessio Ascalesi , Archbishop of Naples and Cardinal (b. 1872)
- May 11: Philipp Müller , German laborer (b. 1931)
- May 11: Giovanni Tebaldini , Italian composer, musicologist and organist (born 1864)
- May 15: Albert Bassermann , German actor (b. 1867)
- May 18: Rosetter Gleason Cole , American composer (b. 1866)
- May 21: John Garfield , American actor (b. 1913)
- May 23: Georg Schumann , German composer (b. 1866)
- May 25: Ibrahim Dalliu , Albanian clergyman and publicist (b. 1878)
- May 25: Ettore Tolomei , Italian nationalist (b. 1865)
- May 26: Emilie Flöge , Austrian designer, fashion designer, entrepreneur and partner of Gustav Klimt (b. 1874)
- May 27 Arthur Illies , German painter and printmaker (b. 1870)
June
- June 1: John Dewey , American philosopher and educator (born 1859)
- June 6: Josef Moser , Austrian politician (b. 1870)
- June 8: Johnny McDowell , American racing driver (b. 1915)
- June 9: Alice Austen , American photographer (b. 1866)
- June 9: Adolf Busch , German violinist and composer (b. 1891)
- June 12: Michael von Faulhaber , Cardinal and Archbishop of Munich and Freising (b. 1869)
- June 13 Emma Eames , American opera singer and singing teacher (b. 1865)
- June 13: Max Pulver , Swiss psychologist, graphologist, poet, playwright and storyteller (b. 1889)
- June 14: Felix Calonder , Swiss politician (b. 1863)
- June 15: Krystyna Skarbek , Polish agent of the British Special Operations Executive Intelligence Unit (b. 1908)
- June 16: Theodor Geiger , German sociologist (b. 1891)
- June 17: Heinrich Germer , SED politician and city councilor for popular education and culture in Magdeburg (b. 1900)
- June 17: Alberto Williams , Argentine composer and conductor (b. 1862)
- June 18: Efim Bogolyubov , Russian-German chess grandmaster (b. 1889)
- June 18: Heinrich Schlusnus , German opera and concert singer (baritone) (b. 1888)
- June 20: Luigi Fagioli , Italian racing driver (b. 1898)
- June 22: Eugen Abresch , German entrepreneur, inventor, art collector and politician (b. 1867)
- June 23: Peter Georg Cohrs , German politician (born 1894)
- June 23: Arthur Lisowsky , professor at the Commercial College of St. Gallen (b. 1895)
- June 24: Botho Henning Elster , German major general (b. 1894)
- June 25: Luke Jordan , American blues guitarist and singer (b. 1892)
- June 28 Ludwig Radermacher , German classical scholar (b. 1867)
- June: Charles Montier , French automobile racer and vehicle designer (b. 1879)
July
- July 1: Johann Paul Arnold , German aquarist (b. 1869)
- July 2: Frank Welsman , Canadian conductor, music educator and pianist (b. 1873)
- July 3: Wilhelm Schmidtbonn , German writer (b. 1876)
- July 3: Daniel Zamudio Guerrero , Colombian composer and musicologist (born 1887)
- July 6: Felix Huch , German physician and writer (b. 1880)
- July 7: André Pisart , Belgian racing driver (b. 1898)
- July 8: Karl Jakob Hirsch , German artist and writer (b. 1892)
- July 9: Max Clarenbach , German painter of the Düsseldorf school of painting (b. 1880)
- July 10: Rued Langgaard , Danish composer and organist (b. 1893)
- July 19: Elly Heuss-Knapp , German politician, founder of the Mothers' Convalescent Works (b. 1881)
- July 20: Ferdinand Lot , French historian (b. 1866)
- July 21 Edwin Hoernle , German writer, functionary of the KPD (b. 1883)
- July 21: Ben Olcott , American politician (b. 1872)
- July 22: Antonio María Valencia , Colombian composer (b. 1902)
- July 23: Carl Severing , German politician and minister (b. 1875)
- July 26: Eva Perón , First Lady of Argentina and second wife of Juan Perón (b. 1919)
- July 29: Georg Michael Martin Hubert von Arnswaldt , German forester and conservationist (born 1866)
- July 31: Clara Viebig , German storyteller (b. 1860)
- July 31: Waldemar Bonsels , German writer (born 1880)
August
- August 2: Johann Lemmerz , German designer and entrepreneur (b. 1878)
- August 2: Joseph Schnetz , Austrian philologist (b. 1873)
- August 6: Richard Charles Mills , Australian economist (b. 1886)
- August 9: Bartholomäus Koßmann , German politician (born 1883)
- August 13: Wilm Hosenfeld , Wehrmacht officer in World War II (b. 1895)
- August 15: Richard Adamík , Czech physician and moral idealist (b. 1867)
- August 15: Armida Barelli , Italian women's movement activist (b. 1882)
- August 15: Jesse Thoor , German writer (b. 1905)
- August 16: Philipp Auerbach , German politician and State Commissioner for Racially, Religiously and Politically Persecuted Persons (b. 1906)

- August 20: Kurt Schumacher , German politician (b. 1895)
- August 27: Armand Gagnier , Canadian clarinetist and conductor (b. 1895)
- August 31: Ernst Busse , head of the International Inmates Committee at Buchenwald concentration camp (b. 1897)
- August 31: Jim Rigsby , American racing driver (b. 1923)
September
- September 1: Kosugi Tengai , Japanese writer (b. 1865)
- September 4 Carlo Sforza , Italian politician, anti-fascist (b. 1872)
- September 6 William Ewart Napier , English-born American chess player (b. 1881)
- September 11: Robert Lauterborn , German hydrobiologist, zoologist, botanist and historian of science (born 1869)
- September 13: Friedrich Bothe , German teacher and historian (b. 1869)
- September 13: Hermann Hummel , German politician (b. 1876)
- September 17: Fred Sauer , Austrian actor, director and screenwriter (b. 1886)
- September 20: Bill Schindler , American racing driver (b. 1909)
- September 21: Roland H. Hartley , American politician (b. 1864)
- 22 September: Kaarlo Juho Ståhlberg , first President of Finland (b. 1865)
- September 23: Karel Hoffmeister , Czech pianist and musicologist (born 1868)
- September 26: George Santayana , American philosopher and writer (b. 1863)
- September 29: Clifford Hugh Douglas , British economic theorist, engineer (b. 1879)
- September 30: Waldorf Astor , British politician and newspaper publisher (b. 1879)
- September: Alexander Popovich , Austrian football player and coach (b. 1891)
October
- October 3 Alfred Neumann , German writer (b. 1895)
- 5 October: Vincentius Eugenio Bossilkoff , Blessed, Bulgarian Bishop (b. 1900)
- October 5: Jola Jobst , German actress (b. 1913)
- October 6: Felix Daniel Ascher , German architect (b. 1883)
- October 10: Franz Johann Ludwig August Adenauer , German jurist (b. 1872)
- October 11: Jack Conway , American director, actor and producer (b. 1887)
- October 13: Gaston Baty , French director, playwright and theater manager (b. 1885)
- October 14: Paul Hey , German illustrator and printmaker (b. 1867)
- October 18: Francis P. Matthews , American politician (b. 1887)
- October 19: Doi Bansui , Japanese poet and translator (b. 1871)
- October 19 Ernst Streeruwitz , Austrian officer, industrial manager and politician (b. 1874)
- October 19: Jan van der Sluis , Dutch footballer (b. 1889)
- October 19: Aleksander Wielhorski , Polish pianist and composer (born 1890)
- October 20: Michael Rostovtzeff , Russian-American ancient historian (b. 1870)
- October 21: Bernard Povel , German politician (b. 1897)
- October 22: Ernst Rüdin , Swiss physician, psychiatrist and racial hygienist (b. 1874)
- October 24: Frederick Jacobi , American composer (born 1891)
- October 25: Sergei Bortkiewicz , Russian composer (b. 1877)
- October 27: Ludwig Fahrenkrog , German poet and painter (born 1867)
- October 29: Sepp Straffner , Austrian politician (b. 1875)
- October 31: Alexander Alexandrovich Andronov , Soviet physicist (b. 1901)
- October 31: Adolf Chybiński , Polish musicologist and educator (born 1880)
November

- November 5: Joseph James , American racing driver (b. 1925)
- November 9: Chaim Weizmann , first President of Israel (b. 1874)
- November 10: Otto Appel , German herbalist (b. 1867)
- November 15 – Vasyl Krychevskyj , Ukrainian art historian, painter, architect, graphic artist and stage designer (b. 1873)
- November 16: Charles Maurras , French writer and political publicist (b. 1868)
- November 17: Franz John , German football official and photographer (b. 1872)
- November 18: Paul Éluard , French poet (b. 1895)
- November 18: A. Harry Moore , American politician (b. 1879)
- November 18 Dutch Speck , American football player (b. 1886)
- November 20: Benedetto Croce , Italian philosopher, humanist, historian, politician and critic (born 1866)
- November 20: Jock Porter , British motorcycle racer, entrepreneur and motorcycle designer (b. 1894)
- November 25: Julien-Fernand Vaubourgoin , French organist, composer and music teacher (born 1880)
- November 26: Sven Hedin , Swedish geographer, topographer, explorer (born 1865)
- 28 November: Ota Wićaz , Sorbian literary and cultural historian and writer (b. 1874)
- November 28: Elena of Montenegro , Queen of Italy (b. 1873)
December
- December 1: Edward James Gay , American politician (b. 1878)
- December 1: Wilhelm Speyer , German writer (b. 1887)
- December 3: Vladimír Clementis , Slovak politician, jurist, writer and translator (b. 1902)
- December 3: Otto Fischl , Czechoslovakian politician (b. 1902)
- 3 December: Josef Frank , Czechoslovak trade unionist (b. 1909)
- December 3: Ludvík Frejka , Czech politician and publicist (b. 1904)
- 3 December: Otto Katz , Czechoslovak author and Soviet Union agent (b. 1895)
- 3 December: Rudolf Margolius , Czechoslovak Minister of Foreign Trade (b. 1913)
- December 3: Rudolf Slánský , General Secretary of the Communist Party of Czechoslovakia (b. 1901)
- December 3: Otto Šling , Czechoslovak politician (b. 1912)
- December 4: Giuseppe Antonio Borgese , Italian critic and writer (born 1882)
- December 4 Karen Horney , German-American psychologist (b. 1885)
- December 5: Imre Waldbauer , Hungarian violinist and music teacher (b. 1892)
- 6 December: Karl Lautenschlager , Lord Mayor (b. 1868)
- December 7: Helmut Hugo Alfred Augustin , German pastor (b. 1912)
- December 8: Pedro Sinzig , Franciscan, Brazilian writer, journalist and composer (b. 1876)
- December 12: Lawrence Henry Aurie , Canadian ice hockey player and coach (b. 1905)
- December 12: Bedřich Hrozný , Czech linguist and orientalist (b. 1879)
- December 12: Max Laeuger , German artist (b. 1864)
- December 14: Fartein Valen , Norwegian composer (b. 1887)
- December 17 Wilhelm Bruckner , Swiss Germanist and linguist (b. 1870)
- December 18: Ernst Mayer , German politician (b. 1901)
- December 18: Ernst Stromer von Reichenbach , German paleontologist (born 1871)
- December 20: Heinrich Lilienfein , German writer and General Secretary of the German Schiller Foundation (b. 1879)
- December 20: Ivan Olbracht , Czech writer, publicist, journalist and translator (b. 1882)
- December 22: Vincas Bacevičius , Lithuanian music educator, pianist, conductor and composer (b. 1875)
- December 23: Eli Filip Heckscher , Swedish economic historian (b. 1879)
- 24 December: Ivo indicator , papal diplomat (b. 1898)
- December 25: Herman Sörgel , German architect (b. 1885)
- December 27: Henri Winkelman , Dutch general (b. 1876)
- December 28: Carlo Agostini , Archbishop and Patriarch of Venice and Cardinal (b. 1888)
- December 28: Alexander G. Barry , American politician (b. 1892)
- December 28: Fletcher Henderson , American jazz pianist, bandleader and composer (b. 1897)
- December 30: Willie Brown , American blues musician (born 1900)
day unknown
- Alessandro Abate , Italian painter (born 1867)
- Edith Andreae , German salonnière (born 1883)
- Red Newman , Canadian comedian and singer (born 1887)
Nobel prizes
- Physics : Felix Bloch and Edward Mills Purcell
- Chemistry : Archer John Porter Martin and Richard LM Synge
- Medicine : Selman Abraham Waksman
- Literature : Francois Mauriac
- Nobel Peace Prize : Albert Schweitzer
web links
- Annual review from tagesschau.de
- Annual chronicle from the house of the history of the FRG
- The cabinet minutes of the Federal Government (1952) in the Federal Archives
- Files on the Foreign Policy of the Federal Republic of Germany, Vol. 2, Adenauer and the High Commissioners 1952. ISBN 978-3-486-55201-0 (1st edition 1952)